Unlock Cost Savings: The Ultimate Compressed Spring Guide (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for compressed spring
Navigating the complexities of sourcing compressed springs can be a daunting task for international B2B buyers, especially when considering the diverse requirements across industries and geographical markets. From Africa to South America, the Middle East, and Europe, businesses face the challenge of finding reliable suppliers who can provide high-quality springs tailored to specific applications. This guide aims to demystify the global market for compressed springs by covering various types, applications, and the essential criteria for vetting suppliers.
Understanding the nuances of compression spring design is crucial for optimizing performance and ensuring safety in applications ranging from automotive to electronics. Buyers will gain insights into the different variations of compressed springs, including conical, barrel, and variable pitch designs, each serving unique functional purposes. Moreover, this guide will delve into cost considerations, helping businesses establish budgets and make informed financial decisions when purchasing springs in bulk or for custom projects.
Equipped with this comprehensive knowledge, international B2B buyers will be empowered to navigate the global market confidently, ensuring they select the right suppliers and products that meet their operational needs. By focusing on quality, compliance, and supplier reliability, businesses can enhance their production capabilities and achieve their strategic objectives more effectively.
Understanding compressed spring Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compression Spring | Open-coil helical design; resists compressive forces | Automotive, electronics, medical devices | Pros: Versatile; Cons: May require precise specifications |
| Conical Spring | Tapered design; low solid height; compact storage | Precision instruments, small appliances | Pros: Space-saving; Cons: Limited load capacity |
| Barrel Spring | Uniform coil diameter; stable force distribution | Heavy machinery, industrial applications | Pros: Consistent performance; Cons: Limited flexibility |
| Variable Pitch Spring | Coils spaced variably; adjustable stiffness | Specialized machinery, aerospace applications | Pros: Customizable; Cons: Complex design considerations |
| Tapered Compression Spring | Gradual reduction in diameter; reduced surging | Automotive suspensions, vibration dampening systems | Pros: Enhanced control; Cons: More complex to manufacture |
What Are Compression Springs and Their Characteristics?
Compression springs are the most common type of spring configuration, designed to resist compressive forces along their axis. These springs are vital in various applications, such as automotive systems, electronics, and medical devices. When selecting compression springs, buyers should consider factors like material properties, wire diameter, and coil count, as these directly impact the spring’s stiffness and energy storage capacity. Buyers must ensure they specify the correct dimensions and load requirements to achieve optimal performance in their applications.
How Do Conical Springs Differ From Other Types?
Conical springs, with their tapered design, are specifically engineered for applications requiring low solid height and compact storage. This unique shape allows for efficient use of space, making them ideal for precision instruments and small appliances. However, it’s crucial for buyers to understand that while conical springs save space, they may have limitations in load capacity. When sourcing these springs, consider the specific application requirements to ensure they can handle the necessary force without compromising functionality.
What Are the Advantages of Barrel Springs?
Barrel springs feature a uniform coil diameter, providing stable force distribution during operation. They are commonly used in heavy machinery and industrial applications, where consistent performance is critical. Buyers should appreciate the reliability of barrel springs, but must also recognize their limitations in flexibility compared to other spring types. When procuring barrel springs, it’s essential to assess the specific load and application needs to select the right variant for optimal performance.
Why Choose Variable Pitch Springs for Specialized Applications?
Variable pitch springs are designed with coils spaced variably, allowing for adjustable stiffness tailored to specific applications. This feature is particularly beneficial in specialized machinery and aerospace applications, where precise force control is paramount. However, the complexity of their design may pose challenges during manufacturing. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against potential production difficulties, ensuring they collaborate closely with manufacturers to meet their unique specifications.
What Makes Tapered Compression Springs Unique?
Tapered compression springs gradually reduce in diameter, which helps reduce surging and enhances control in applications such as automotive suspensions and vibration dampening systems. These springs are effective in managing dynamic loads, providing a balance between strength and flexibility. Buyers interested in tapered compression springs should consider the specific dynamics of their applications and the potential need for custom manufacturing to accommodate unique requirements.
Key Industrial Applications of compressed spring
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Compressed Spring | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Suspension systems | Enhances vehicle stability and ride comfort | Material quality, load specifications, and delivery time |
| Electronics | Button mechanisms in devices | Provides reliable user interaction and durability | Precision manufacturing, size variations, and lead times |
| Medical Devices | Patient monitoring equipment | Ensures accurate readings and patient safety | Compliance with health regulations, material biocompatibility |
| Industrial Machinery | Stamping and assembly line equipment | Improves efficiency and reduces downtime | Customization capabilities, strength requirements, and volume needs |
| Consumer Products | Toys and household appliances | Enhances product functionality and user experience | Safety standards, design specifications, and cost-effectiveness |
How Are Compressed Springs Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, compressed springs are integral to suspension systems. They absorb shocks and maintain vehicle stability, which is crucial for safety and comfort. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing high-quality springs that can withstand varying road conditions is essential. Buyers should consider the spring’s load specifications and the material used to ensure durability and performance.
What Role Do Compressed Springs Play in Electronics?
In electronics, compressed springs are often utilized in button mechanisms within devices such as remote controls and smartphones. They provide tactile feedback and ensure the longevity of the button function. For B2B buyers from Europe and the Middle East, precision in manufacturing is critical. Ensuring the springs meet specific size and strength requirements will enhance the user experience and product reliability.
How Are Compressed Springs Essential in Medical Devices?
Compressed springs are vital in patient monitoring equipment, where they help ensure accurate readings and functionality. These springs must comply with strict health regulations, necessitating careful selection of materials that are biocompatible. For international buyers in regions like Africa, understanding the compliance standards is crucial when sourcing these components to ensure patient safety and device efficacy.
What Benefits Do Compressed Springs Provide in Industrial Machinery?
In industrial machinery, compressed springs are used in stamping and assembly lines to enhance operational efficiency. They provide the necessary force to facilitate movement and ensure that machinery operates smoothly, reducing downtime. Buyers from South America and Europe should focus on sourcing customized springs that meet specific strength requirements, as well as considering the volume needs for their production processes.
How Do Compressed Springs Enhance Consumer Products?
In consumer products such as toys and household appliances, compressed springs enhance functionality and user experience. They are often used in mechanisms that require push-button functionality or spring-loaded actions. For international B2B buyers, understanding safety standards and design specifications is critical to ensure that the springs not only perform well but also comply with regional regulations and consumer expectations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘compressed spring’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Challenges in Sourcing the Right Compressed Spring for Unique Applications
The Problem: International B2B buyers often face difficulties in sourcing the right compressed spring that meets specific application requirements. For example, a manufacturer in Brazil might need a custom spring for a specialized machinery component but struggles to find suppliers who understand the nuances of their design specifications. This can lead to delays in production and increased costs, as the wrong spring can result in operational inefficiencies or even equipment failure.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, buyers should start by thoroughly defining their spring requirements, including load capacity, dimensions, material, and environmental factors. Utilizing a compression spring calculator can help determine the necessary specifications for the spring, ensuring it can handle the intended load without compromising safety. After defining the requirements, engage with suppliers who specialize in custom solutions, like Acxess Spring. It’s essential to communicate clearly and provide detailed drawings or prototypes. Additionally, consider suppliers who offer quick prototyping services, allowing for rapid iteration and testing before finalizing orders. This approach not only saves time but also ensures that the springs will perform as needed in the final application.
Scenario 2: Issues with Delivery Timelines and Lead Times
The Problem: A common pain point for B2B buyers in regions like Africa and the Middle East is managing the lead times associated with ordering compressed springs. Companies often rely on these components for critical machinery or products, and any delay can have a cascading effect on production schedules. Buyers may find themselves in a situation where they need springs urgently but face extended lead times due to supplier inefficiencies or shipping delays.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, it’s crucial to establish relationships with suppliers who have a proven track record of meeting delivery deadlines. Look for suppliers with extensive stock catalogs, such as those offering over 42,000 unique designs. This allows for immediate access to ready-to-ship products, reducing lead times significantly. Additionally, consider suppliers that provide real-time inventory updates and offer expedited shipping options. Buyers should also maintain a buffer stock of critical components to avoid production downtime. Implementing a just-in-time inventory system can help manage stock levels while ensuring that necessary components are always available when needed.
Scenario 3: Understanding Compression Spring Specifications and Technical Details
The Problem: Many B2B buyers lack the technical knowledge required to specify the right compression springs for their applications, leading to suboptimal performance or component failure. For instance, a European automotive parts manufacturer might not fully understand how wire diameter and the number of coils affect the spring’s stiffness and energy storage capacity. This gap in understanding can result in choosing springs that do not meet the necessary performance criteria.
The Solution: To address this knowledge gap, buyers should invest time in understanding the fundamental principles of compression spring design. Resources such as technical guides and webinars provided by reputable spring manufacturers can be invaluable. Buyers should also utilize online tools like compression spring calculators to experiment with different specifications and understand how changes impact performance. Engaging with engineering teams or consultants familiar with spring mechanics can provide additional insights. When communicating with suppliers, don’t hesitate to ask for assistance in understanding product specifications. Most reputable suppliers will be happy to provide technical support and help ensure that you select the right spring for your application. This proactive approach can lead to better product performance and increased reliability in operations.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for compressed spring
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials for Compressed Springs?
When selecting materials for compressed springs, it is crucial to consider their mechanical properties, which significantly influence performance in various applications. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the manufacturing of compressed springs, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Music Wire: The Standard Choice for Compression Springs
Key Properties:
Music wire is known for its high tensile strength and excellent fatigue resistance. It typically operates effectively in temperatures up to 250°F (121°C) and has a good yield strength, making it suitable for most general applications.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of music wire is its cost-effectiveness and availability. However, it is susceptible to corrosion unless properly coated or treated, which can limit its use in harsh environments.
Impact on Application:
Music wire is ideal for applications requiring high strength and durability, such as automotive and industrial machinery. However, its susceptibility to corrosion may limit its use in wet or corrosive environments.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards (e.g., ASTM A228) and consider the availability of protective coatings to enhance corrosion resistance.
2. Stainless Steel: The Corrosion-Resistant Alternative
Key Properties:
Stainless steel springs, particularly those made from 302 or 316 grades, offer excellent corrosion resistance and can withstand higher temperatures (up to 800°F or 427°C) without losing strength.
Pros & Cons:
The key advantage of stainless steel is its durability and resistance to environmental factors. However, it is more expensive than music wire and may require more complex manufacturing processes, which can increase lead times.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is suitable for applications in medical devices, food processing, and marine environments where corrosion resistance is critical.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with standards such as ASTM A313 is important for buyers in Europe and the Middle East. Additionally, understanding the specific grade requirements for their applications can help in material selection.
3. Oil-Tempered Steel: The Cost-Effective Solution for Heavy-Duty Applications
Key Properties:
Oil-tempered steel springs exhibit enhanced fatigue resistance and can operate in temperatures up to 400°F (204°C). This material is typically treated to improve its mechanical properties.
Pros & Cons:
The main advantage of oil-tempered steel is its balance of performance and cost, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. However, it may not be as corrosion-resistant as stainless steel, which could limit its use in certain environments.
Impact on Application:
This material is often used in automotive and industrial applications where high strength and fatigue resistance are required.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the necessary heat treatment processes and ensure compliance with relevant standards such as ASTM A313. Understanding local manufacturing capabilities can also help in sourcing.
4. Inconel: The High-Performance Material for Extreme Conditions
Key Properties:
Inconel is a nickel-chromium alloy known for its exceptional heat and corrosion resistance, functioning effectively in extreme temperatures (up to 2000°F or 1093°C).
Pros & Cons:
Inconel’s primary advantage is its ability to perform in harsh environments, making it ideal for aerospace and chemical processing applications. However, it is significantly more expensive and may require specialized manufacturing techniques.
Impact on Application:
Inconel springs are suited for applications where both high strength and resistance to oxidation are essential, such as in gas turbines and nuclear reactors.
Considerations for International Buyers:
International buyers must consider the high cost and availability of Inconel, as well as compliance with specific standards (e.g., ASTM B168) relevant to their industry.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Compressed Springs
| Material | Typical Use Case for Compressed Spring | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Music Wire | General industrial applications | Cost-effective and widely available | Susceptible to corrosion | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Medical devices, food processing | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Oil-Tempered Steel | Automotive and industrial machinery | Good fatigue resistance and cost-effective | Limited corrosion resistance | Medium |
| Inconel | Aerospace and chemical processing | Exceptional heat and corrosion resistance | Very high cost and specialized manufacturing | High |
This comprehensive material selection guide provides B2B buyers with actionable insights to make informed decisions regarding compressed springs, ensuring optimal performance for their specific applications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for compressed spring
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Compressed Springs?
The manufacturing process of compressed springs is a multi-stage procedure that requires precision and adherence to strict quality standards. Understanding these stages is crucial for international B2B buyers, as it impacts product reliability and performance.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing of compressed springs involves selecting the right materials. Common materials include high-carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloys, each chosen based on the specific application requirements. The material is then cut into wire, with diameters ranging from 0.006 inches to 1.250 inches, depending on the spring’s design specifications.
During this stage, suppliers may also perform heat treatment processes to enhance the material’s strength and elasticity. This pre-conditioning is essential, as it affects the spring’s overall performance and longevity.
A stock image related to compressed spring.
2. Forming the Spring
Once the material is prepared, the next step is forming the spring. This involves coiling the wire into the desired shape using specialized machinery. Key techniques in this stage include:
- Cold Coiling: This method is commonly used for standard compression springs, where the wire is coiled at room temperature to maintain its properties.
- Hot Coiling: Suitable for thicker wire diameters, this technique involves heating the wire before coiling, which can lead to improved resilience.
The accuracy of this process is critical, as the dimensions of the spring directly influence its functional characteristics. Advanced CNC machines ensure that the coils are uniform and within specified tolerances.
3. Assembly and Finishing
Following the forming process, the springs may undergo assembly if they are part of a more complex mechanism. This could involve integrating additional components, such as end fittings or guides, to enhance functionality.
Finishing processes include surface treatments like plating, coating, and passivation. These treatments not only improve aesthetic appeal but also enhance corrosion resistance, which is particularly important for applications in harsh environments.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Compressed Spring Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a fundamental aspect of the manufacturing process, ensuring that each spring meets international standards and client specifications. For B2B buyers, understanding these QA measures can significantly mitigate risks associated with product reliability.
International Standards and Certifications
Manufacturers often adhere to international quality standards such as ISO 9001, which focuses on consistent quality management systems. For specific industries, additional certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) for European markets and API (American Petroleum Institute) for oil and gas applications may be required.
These certifications signify that the manufacturer has implemented rigorous quality controls and is committed to continuous improvement.
Key Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control is integrated at various checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process, including:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial inspection checks raw materials for compliance with specifications before they are used in production.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing stages, random samples are tested for dimensional accuracy, tensile strength, and other critical parameters.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): At the end of the production line, finished products undergo thorough testing to ensure they meet all design specifications and performance criteria.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Compressed Springs?
Various testing methods are employed to assess the quality and performance of compressed springs. These methods ensure that the springs can withstand the stresses they will encounter in real-world applications.
Common Testing Methods
-
Load Testing: Measures the spring’s ability to withstand loads without permanent deformation. This is crucial for applications where springs are subjected to varying forces.
-
Fatigue Testing: Evaluates the spring’s durability over time, simulating long-term usage conditions to identify potential failure points.
-
Dimensional Inspection: Uses precision measuring tools to ensure that each spring adheres to specified dimensions and tolerances.
-
Surface Roughness Testing: Assesses the surface finish of the spring, as rough surfaces can lead to premature wear and failure.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, ensuring the quality of compressed springs is paramount. Here are actionable steps to verify a supplier’s quality control processes:
Conducting Supplier Audits
Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing and quality control processes. Buyers should request access to quality management system documentation, including certifications and audit reports.
Requesting Quality Reports
Buyers can ask suppliers for quality reports detailing test results, including data from IQC, IPQC, and FQC. These reports should provide transparency regarding any defects or non-conformities encountered during production.
Engaging Third-Party Inspectors
For added assurance, engaging third-party inspection services can help verify that the springs meet specified standards. These independent inspectors can conduct on-site evaluations and testing, providing an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s capabilities.
What Are the Unique Quality Control Considerations for International B2B Buyers?
When sourcing compressed springs internationally, buyers must navigate various quality control nuances, particularly concerning shipping, cultural differences, and regional regulations.
Understanding Regional Standards
Each region may have specific standards that affect spring design and performance. For example, European buyers must consider CE marking regulations, while those in the Middle East might need to comply with local manufacturing standards.
Cultural Factors in Quality Assurance
Cultural attitudes towards quality and customer service can vary significantly by region. Buyers should foster strong relationships with suppliers to ensure open communication regarding quality expectations and issues.
Conclusion
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for compressed springs are complex yet vital for ensuring product reliability. By understanding these processes, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ultimately leading to successful procurement and application of compressed springs in their projects. Adopting a thorough approach to supplier evaluation and quality verification can mitigate risks and enhance overall supply chain effectiveness.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘compressed spring’
In the competitive landscape of sourcing compressed springs, international B2B buyers must navigate various challenges to ensure they procure high-quality components that meet their specific requirements. This guide provides a practical checklist to streamline the sourcing process, ensuring that buyers can make informed decisions.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements of your compressed springs, including dimensions, material type, and load capacity. Knowing the specifics helps suppliers provide precise solutions tailored to your needs. Consider factors such as wire diameter, outer diameter, and free length, as these will directly impact the performance of the spring in your application.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers with a solid reputation in the industry. Look for companies that specialize in compressed springs and have extensive catalogs or custom manufacturing capabilities. Pay attention to their experience in serving international clients, especially from your target regions—Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before engaging with a supplier, verify their certifications, such as ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality management. Certifications can provide assurance of consistent product quality and adherence to industry standards. Additionally, check for compliance with relevant regulations, such as RoHS, especially if you are sourcing for industries like electronics or automotive.
Step 4: Request Samples and Prototypes
Ask for samples or prototypes of the compressed springs that meet your specifications. Testing these samples can help you assess the quality and performance before placing a larger order. This step is crucial to ensure that the springs will function correctly in your application and will help you avoid costly mistakes down the line.
Step 5: Understand Lead Times and Shipping Options
Discuss lead times and shipping options with potential suppliers. Understanding their production capacity and delivery timelines is vital, especially if you have urgent project deadlines. Ensure that the supplier can accommodate your timeline and offers reliable shipping methods to your location, whether you are in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe.
Step 6: Compare Pricing and Payment Terms
Gather quotes from multiple suppliers to compare pricing structures. Consider not only the cost per unit but also the total cost of ownership, which includes shipping, taxes, and potential import duties. Additionally, discuss payment terms to ensure they align with your financial planning and cash flow management.
Step 7: Review Customer Feedback and Case Studies
Seek out customer testimonials and case studies to gauge the reliability and service quality of potential suppliers. Positive feedback from other businesses, especially those within your industry or region, can provide valuable insights into the supplier’s performance and support capabilities. Look for specific examples of how they addressed challenges similar to yours.
By following this checklist, international B2B buyers can effectively navigate the sourcing process for compressed springs, ensuring they select the best suppliers to meet their specific needs while minimizing risks associated with procurement.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for compressed spring Sourcing
What are the Key Cost Components in Compressed Spring Sourcing?
When sourcing compressed springs, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The type of steel or alloy used significantly affects costs. Stainless steel, for example, is generally more expensive than carbon steel. Buyers should consider the long-term benefits of investing in higher-quality materials that offer better corrosion resistance and durability.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on the region and the complexity of the spring design. Skilled labor is essential for custom spring manufacturing, and regions with higher labor costs might reflect that in their pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead costs, potentially leading to lower prices for buyers.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be substantial, especially for custom springs. These costs are often amortized over the production run, so larger orders can result in lower per-unit tooling expenses.
-
Quality Control (QC): High-quality springs undergo rigorous testing and inspection, which adds to the cost. Certifications such as ISO 9001 can also influence pricing, as they require compliance with stringent quality standards.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary based on distance, shipping method, and the chosen Incoterms. Buyers should factor in the total cost of delivery when assessing spring prices.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin based on the above costs, which can vary widely depending on the supplier’s market position and operational efficiency.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Compressed Spring Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of compressed springs, particularly for international buyers:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often qualify for bulk pricing discounts. Understanding MOQ requirements can help buyers negotiate better deals.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom springs tailored to specific applications will generally cost more than off-the-shelf options. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected costs.
-
Materials: The choice of materials not only impacts initial costs but also long-term performance and replacement frequency. Buyers should evaluate the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and replacement costs.
-
Quality and Certifications: Springs that meet specific industry standards or certifications may be priced higher. However, investing in quality can reduce failure rates and enhance overall project reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their experience and service quality, but they often provide better support and reliability.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is vital. Different Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) can lead to varied responsibilities and costs for buyers, impacting the overall price.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Costs When Sourcing Compressed Springs?
To maximize value when sourcing compressed springs, buyers should consider the following tips:
-
Negotiate Wisely: Leverage your purchasing power by negotiating prices, especially for larger orders. Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can also lead to better pricing over time.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate suppliers based on their total cost of ownership rather than just the initial purchase price. This includes considering the lifespan, failure rates, and maintenance costs of the springs.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and import duties that can affect overall costs. Being informed can help in budget planning and negotiations.
-
Request Detailed Quotes: Always ask for itemized quotes that break down costs. This transparency helps identify areas where you can negotiate better prices or explore alternative options.
-
Explore Local Suppliers: Depending on your region, sourcing from local suppliers may reduce shipping costs and lead times, enhancing overall efficiency.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of compressed spring sourcing requires a thorough understanding of cost components and pricing influencers. By applying these insights and strategies, international B2B buyers can optimize their procurement processes and achieve better value in their spring sourcing endeavors. Always remember to evaluate the total cost of ownership and maintain open lines of communication with your suppliers to ensure a successful partnership.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing compressed spring With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives to Compressed Springs
When considering the best solutions for energy storage and force generation in mechanical applications, it’s essential to evaluate various alternatives to compressed springs. While compressed springs are widely recognized for their efficiency and versatility, other options may offer benefits depending on specific use cases, budget constraints, and operational requirements. This analysis will compare compressed springs against two viable alternatives: pneumatic actuators and hydraulic cylinders, providing B2B buyers with a comprehensive understanding of each option.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Compressed Spring | Pneumatic Actuator | Hydraulic Cylinder |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High linear force, compact design | Quick response, adjustable force | High power output, continuous force |
| Cost | Generally low-cost for mass production | Moderate initial investment | Higher costs due to complexity |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple integration and installation | Requires air supply infrastructure | Complex installation and setup |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, durable materials | Moderate, requires regular checks | High, involves fluid management |
| Best Use Case | Small devices, consumer products | Robotics, automation applications | Heavy machinery, industrial equipment |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What Are Pneumatic Actuators and Their Advantages?
Pneumatic actuators utilize compressed air to produce mechanical motion. They are particularly advantageous in applications requiring rapid actuation, such as robotics and automated assembly lines. The ability to adjust force output easily makes them suitable for tasks with varying load requirements. However, pneumatic systems necessitate a reliable air supply and regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance, which may increase operational costs over time.
How Do Hydraulic Cylinders Compare to Compressed Springs?
A stock image related to compressed spring.
Hydraulic cylinders operate using pressurized fluid to generate linear motion, providing significant power output, making them ideal for heavy machinery and industrial applications. They excel in scenarios requiring sustained force over extended periods. However, the complexity of installation and the need for hydraulic fluid management can lead to higher initial costs and maintenance demands compared to compressed springs. Additionally, hydraulic systems can be less compact, limiting their use in smaller applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the best solution for energy storage and force generation, international B2B buyers must consider their specific application requirements, budget constraints, and operational capabilities. Compressed springs offer a cost-effective and efficient option for smaller devices and consumer products, while pneumatic actuators and hydraulic cylinders provide powerful alternatives for more demanding applications. By thoroughly evaluating the performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases of each solution, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and project specifications.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for compressed spring
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Compressed Springs?
Understanding the essential technical properties of compressed springs is crucial for B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. Below are some critical specifications that every buyer should consider:
1. Material Grade: How Does Material Affect Spring Performance?
Compressed springs are typically made from various materials, including stainless steel, carbon steel, and alloy steel. The choice of material affects not only the spring’s strength and durability but also its resistance to corrosion and fatigue. For example, stainless steel springs are ideal for applications in moist or corrosive environments, while carbon steel springs may be sufficient for less demanding conditions. Selecting the right material grade ensures that the spring meets the specific requirements of your application, thereby reducing the likelihood of premature failure.
2. Tolerance: Why Is Tolerance Important in Spring Manufacturing?
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from a specified dimension or performance characteristic. In the context of compressed springs, tighter tolerances can lead to more predictable performance and better fit within assemblies. For B2B buyers, understanding the tolerance levels offered by suppliers can be crucial, especially for applications requiring precise force generation and displacement. Poor tolerance can result in misalignment or malfunctioning components, which may lead to costly downtime.
3. Spring Rate: What Is Spring Rate and How Does It Impact Performance?
The spring rate, measured in pounds per inch (lb/in) or newtons per millimeter (N/mm), indicates the amount of force required to compress the spring by a certain distance. A higher spring rate means that the spring will provide greater resistance to compression, while a lower rate allows for easier compression. Buyers must carefully consider the spring rate to ensure it aligns with their application requirements, balancing the need for force against the physical constraints of their designs.
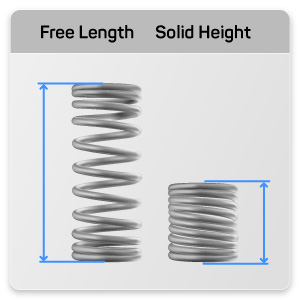
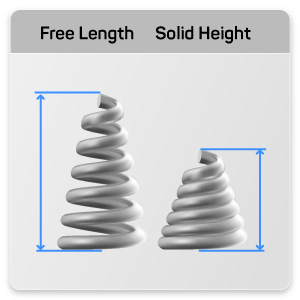
4. Free Length: What Is Free Length and Why Is It Significant?
Free length is the total length of a spring when it is not under any load. This specification is essential for determining how much compression is possible in a given application. Understanding free length helps buyers design their products effectively, ensuring that the spring can operate within the required parameters. If the free length is too short, the spring may not provide adequate force; if it’s too long, it may not fit into the designated space.
5. Solid Height: How Does Solid Height Influence Design?
Solid height refers to the height of the spring when all coils are in contact and no further compression is possible. Knowing the solid height is crucial for applications where the spring must be compressed fully without exceeding its limits. This property directly influences the design and functionality of the assembly, making it vital for buyers to specify solid height requirements when ordering springs.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Compressed Springs?
Familiarity with industry-specific terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some commonly used terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): What Does OEM Mean in Spring Supply?
OEM refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of springs, an OEM may require custom spring solutions tailored for their specific applications. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify suppliers who can meet their unique needs efficiently.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Why Is MOQ Important for Buyers?
MOQ is the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to sell in a single order. This term is crucial for buyers, especially those with limited budgets or smaller projects. Knowing the MOQ can help businesses plan their purchasing strategies and manage inventory effectively.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation): How to Use RFQ for Competitive Pricing?
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and other essential details for a specific quantity of goods. By issuing an RFQ, buyers can compare offers from multiple suppliers, ensuring they receive the best price and terms for their compressed spring needs.
4. Incoterms: What Are Incoterms and How Do They Affect Shipping?
Incoterms are international commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade, including shipping and risk. Understanding these terms can help B2B buyers negotiate better contracts, clarify delivery responsibilities, and mitigate potential disputes.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing compressed springs, ultimately leading to successful project outcomes and enhanced operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the compressed spring Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Compressed Spring Sector?

A stock image related to compressed spring.
The compressed spring sector is witnessing significant growth driven by various global factors, including the expanding automotive and aerospace industries, which require high-performance components. Innovations in manufacturing technologies, such as automation and advanced materials, are reshaping how compression springs are produced. For international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial for informed sourcing decisions.
Emerging trends include the increasing demand for custom springs tailored to specific applications, particularly in specialized industries such as medical devices and electronics. The rise of e-commerce platforms has simplified access to a wide range of stock and custom springs, allowing buyers to quickly find and order the required components. Additionally, the integration of data analytics and IoT technologies is enhancing inventory management and supply chain transparency, which are essential for maintaining competitive advantage.
Buyers should also be aware of the fluctuations in raw material prices, particularly steel, which can affect the cost of compression springs. Establishing strong relationships with suppliers who can provide real-time updates on market conditions will be beneficial. Overall, staying abreast of these trends can help B2B buyers navigate the complexities of the compressed spring market effectively.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact Your Compressed Spring Purchases?
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal factor in B2B procurement processes, including the sourcing of compressed springs. The environmental impact of manufacturing practices has led to a growing emphasis on ethical supply chains. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to reducing their carbon footprint through sustainable manufacturing processes and the use of recyclable materials.
Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and RoHS compliance for hazardous substances are indicators of a supplier’s dedication to sustainability. Buyers from regions such as Africa and South America, where regulatory frameworks may be evolving, should prioritize partners who can provide these certifications, ensuring that their sourcing practices align with global sustainability standards.
Furthermore, the use of green materials—such as stainless steel and other alloys that are easier to recycle—can significantly reduce the environmental impact of compressed springs. By choosing suppliers that focus on sustainable practices, international buyers not only enhance their corporate social responsibility (CSR) profile but also cater to an increasingly eco-conscious market, creating a competitive edge.
What Is the Brief Evolution of the Compressed Spring Industry?
The evolution of the compressed spring industry traces back to the industrial revolution when the demand for mechanical components surged. Initially crafted from basic metals, early compression springs were limited in design and functionality. Over the decades, advancements in metallurgy and manufacturing techniques have allowed for the production of more complex and durable springs.
The introduction of computer-aided design (CAD) in the late 20th century revolutionized the way springs were engineered, enabling precise calculations of spring constants and load capacities. This technological leap has paved the way for custom solutions that meet specific application needs, particularly in high-tech industries.
Today, the compressed spring sector continues to evolve with innovations in materials science and manufacturing processes, driving efficiency and performance. As the market grows, international B2B buyers must recognize the importance of these advancements to ensure they are sourcing the most effective and sustainable solutions for their needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of compressed spring
-
How do I determine the right specifications for a compressed spring?
To select the appropriate specifications for a compressed spring, first identify the application’s requirements, including load capacity, space constraints, and movement range. Consider factors such as wire diameter, coil count, and material type, as these will affect the spring’s strength and flexibility. Utilize tools like compression spring calculators available on supplier websites to ensure your design achieves the desired force and travel characteristics. Collaborating with an experienced supplier can also provide insights into optimizing your design for performance and cost-effectiveness. -
What is the best material for a compressed spring in industrial applications?
The best material for a compressed spring largely depends on the specific application and environmental conditions. Common materials include music wire for general use, stainless steel for corrosion resistance, and high-carbon steel for enhanced strength. Each material offers distinct benefits, such as fatigue resistance or temperature tolerance, which are crucial for applications in industries like automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. Assess your application’s requirements to select a material that balances performance, durability, and cost. -
How can I customize a compressed spring for my specific needs?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for compressed springs, allowing you to tailor dimensions, material, and design features to meet your requirements. When requesting a custom spring, provide detailed specifications, including wire diameter, outer diameter, free length, and required load capacity. Including a sample or detailed drawings can facilitate the design process. It’s advisable to work closely with your supplier to ensure that the custom spring aligns with your application’s performance needs and production capabilities. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) for compressed springs?
Minimum order quantities for compressed springs can vary significantly between suppliers. Generally, stock springs may have lower MOQs, while custom springs often require larger orders due to setup costs. International buyers should inquire about MOQs specific to their requirements, as some manufacturers may offer flexibility based on order size or ongoing contracts. Understanding MOQ policies can help you manage inventory levels and production schedules effectively. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing compressed springs internationally?
Payment terms can differ based on the supplier’s policies, your relationship with them, and the nature of the order. Common terms include upfront payments, partial payments upon order confirmation, or net payment options within a specified period after delivery. For international transactions, consider payment methods that offer security and traceability, such as letters of credit or escrow services. Clear communication regarding payment terms can help avoid misunderstandings and ensure a smooth transaction process. -
How do I ensure quality assurance when sourcing compressed springs?
To ensure quality assurance when sourcing compressed springs, choose suppliers with recognized certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates adherence to quality management standards. Request documentation such as material certificates, test reports, and compliance with industry standards. Additionally, consider conducting audits or quality checks during production and before shipment. Building a strong relationship with your supplier can also facilitate transparency and ongoing quality improvements. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing compressed springs?
Logistics plays a crucial role in the successful importation of compressed springs. Consider factors such as shipping costs, lead times, and customs regulations in your country. Collaborate with your supplier to choose the most efficient shipping method, whether by air or sea, based on your urgency and budget. It’s also essential to understand import duties and taxes that may apply. Establishing a reliable logistics partner can streamline the import process and minimize delays. -
How can I evaluate potential suppliers of compressed springs?
Evaluating potential suppliers involves assessing their experience, product range, and industry reputation. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in your specific application area and positive customer testimonials. Verify their manufacturing capabilities, quality control processes, and compliance with international standards. Additionally, consider engaging in initial discussions to gauge their responsiveness and willingness to collaborate on your needs. A thorough vetting process can lead to long-term partnerships and successful sourcing outcomes.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for compressed spring
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers of Compressed Springs?
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of compressed springs is essential for international B2B buyers looking to optimize their supply chain and enhance product performance. Understanding the various types of compression springs—such as conical, variable pitch, and barrel designs—enables buyers to select the most suitable solutions for their specific applications. Prioritizing quality, as evidenced by ISO certifications and customer testimonials, ensures reliability and longevity in product performance.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Drive Efficiency and Cost Savings?
Engaging with reputable manufacturers who offer ready-to-ship stock and custom solutions can significantly reduce lead times and costs. Utilizing tools like compression spring calculators can assist in achieving the desired force output while minimizing material waste. This not only aligns with sustainability goals but also enhances the overall efficiency of your operations.
What’s Next for B2B Buyers in Diverse Regions?
As the global market continues to evolve, B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should proactively explore partnerships with leading spring manufacturers. By leveraging advancements in technology and engineering capabilities, businesses can stay ahead of market demands. Seize the opportunity to innovate and secure a competitive edge by reaching out to suppliers today for your custom spring solutions. The future of your projects depends on the strategic choices you make now.