Maximize Efficiency: The Ultimate Stranded Wire Guide (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for stranded wire
Navigating the global market for stranded wire can be a daunting task for international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With a variety of types, applications, and specifications to consider, sourcing stranded wire tailored to specific project needs often leads to confusion. This guide aims to demystify the process, offering insights into the different types of stranded wire, their applications across various industries, and key considerations for supplier vetting.
Understanding the nuances of stranded wire is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. This comprehensive resource will explore critical factors such as wire gauge, material types, and cost implications, equipping buyers with the knowledge necessary to evaluate options effectively. Additionally, we will delve into the importance of selecting reputable suppliers and provide actionable tips on how to negotiate favorable terms and ensure quality.
By leveraging this guide, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of the stranded wire market with confidence, ultimately leading to improved procurement strategies and enhanced project outcomes. Whether you’re looking to source stranded wire for electrical applications, construction, or industrial purposes, this guide serves as a valuable tool in your decision-making process.
Understanding stranded wire Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multistranded Wire | Composed of multiple small wires for flexibility and durability. | Electronics, automotive, and telecommunications. | Pros: Highly flexible; ideal for tight spaces. Cons: Slightly higher cost than solid wire. |
| Stranded Hookup Wire | Typically lighter gauge, designed for low-voltage applications. | Wiring for circuit boards and small devices. | Pros: Easy to work with; good for prototyping. Cons: Limited to lower amperage applications. |
| Flexible Stranded Wire | Enhanced flexibility and movement; often rubber or silicone insulated. | Robotics, automation, and portable devices. | Pros: Excellent for dynamic applications. Cons: Can be more expensive due to specialized insulation. |
| Tinsel Wire | Features a flat, thin construction with a high number of strands. | Audio cables and high-flex applications. | Pros: Superior flexibility; ideal for tight bends. Cons: Not suitable for high current applications. |
| Stranded Power Cable | Designed for high current applications with thicker strands. | Power distribution and industrial machinery. | Pros: Handles high amperage; robust construction. Cons: Bulkier and less flexible than lighter options. |
What are the characteristics of Multistranded Wire?
Multistranded wire is characterized by its construction of many small wires twisted together, which enhances its flexibility and conductivity. This type of wire is suitable for applications where movement and bending are required, such as in electronics and automotive wiring. When purchasing, consider the wire gauge and the specific environmental conditions it will face, as these factors can affect performance and longevity.
How does Stranded Hookup Wire differ from other types?
Stranded hookup wire is typically used in low-voltage environments and consists of thinner strands that provide good flexibility. It’s often employed in circuit boards and small electronic devices. B2B buyers should focus on the wire’s insulation type and gauge to ensure compatibility with their specific applications, especially in terms of current capacity and voltage ratings.
Why is Flexible Stranded Wire essential for dynamic applications?
Flexible stranded wire is specifically designed for applications that require constant movement, such as robotics and automation systems. Its unique insulation, often made from rubber or silicone, allows for extreme flexibility without compromising durability. Buyers should assess the wire’s flexibility rating and ensure it meets their operational demands to avoid premature wear.
What advantages does Tinsel Wire offer for audio applications?
Tinsel wire is known for its thin, flat construction, which allows for exceptional flexibility and is ideal for audio cables and applications requiring tight bends. While it excels in flexibility, it is not suitable for high-current applications. Buyers should consider the wire’s resistance and flexibility to ensure it meets the demands of their specific audio setup.
How does Stranded Power Cable support high current applications?
Stranded power cable is designed to handle high amperage, making it suitable for power distribution and industrial machinery. This type of wire consists of thicker strands that provide robust conductivity and durability. When purchasing, B2B buyers should evaluate the wire’s gauge, insulation type, and environmental resistance to ensure it aligns with their operational requirements.
Key Industrial Applications of stranded wire
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Stranded Wire | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Telecommunications | Cable assemblies for communication networks | Enhanced signal integrity and flexibility | Compliance with international standards and certifications |
| Renewable Energy | Solar panel connections and wind turbine wiring | Improved energy efficiency and durability | Sourcing from certified suppliers with quality assurance |
| Automotive | Wiring harnesses for vehicle electronics | Enhanced reliability and performance in vehicles | Compatibility with local regulations and environmental standards |
| Construction & Infrastructure | Electrical installations in buildings and infrastructure | Reliable power distribution and safety | Local sourcing to reduce lead times and shipping costs |
| Consumer Electronics | Internal wiring for devices like speakers and appliances | Greater flexibility in design and assembly | Availability of various gauges and insulation types |
How is Stranded Wire Used in Telecommunications?
In the telecommunications industry, stranded wire is crucial for creating cable assemblies that connect various components within communication networks. Its flexibility allows for easy routing in tight spaces, ensuring minimal signal loss and maintaining high performance. For international buyers, especially in Africa and South America, sourcing stranded wire that meets international standards is vital for ensuring reliability and compliance with local regulations.
What Role Does Stranded Wire Play in Renewable Energy?
Stranded wire is extensively used in renewable energy applications, such as connecting solar panels and wind turbines. The wire’s flexibility and resistance to fatigue make it suitable for outdoor environments, where it can withstand harsh weather conditions. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should prioritize sourcing from suppliers that offer certified stranded wire, ensuring durability and compliance with environmental standards.
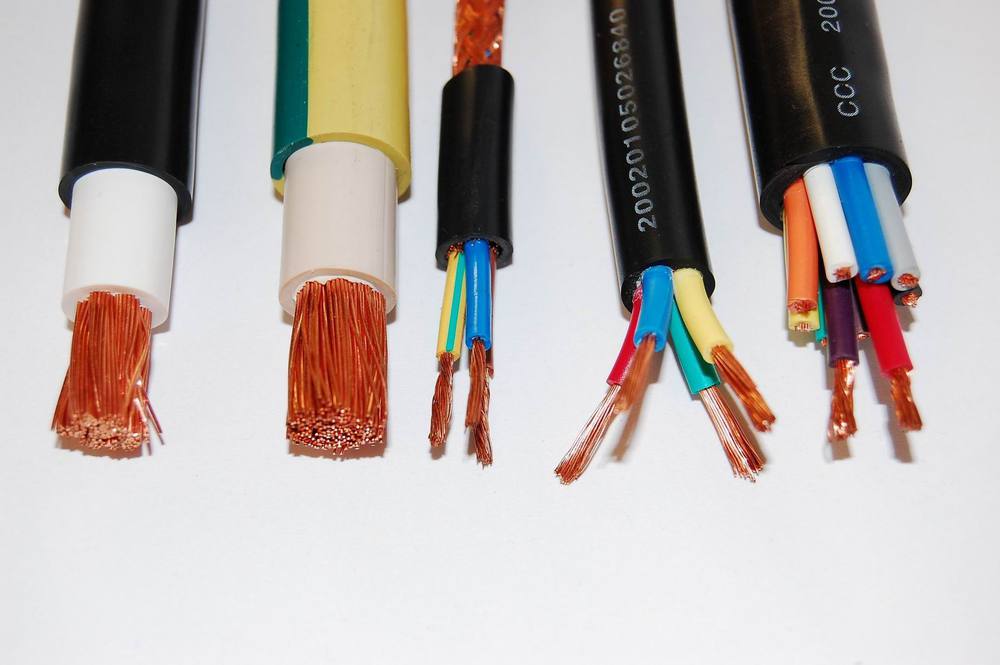
A stock image related to stranded wire.
Why is Stranded Wire Important in the Automotive Sector?
In the automotive industry, stranded wire is used for wiring harnesses that power electronic systems within vehicles. Its flexibility allows for intricate designs that accommodate the complex layouts of modern vehicles, enhancing reliability and performance. International B2B buyers must consider local regulations when sourcing stranded wire, ensuring compatibility with automotive standards in their respective regions.
How is Stranded Wire Utilized in Construction and Infrastructure?
Stranded wire plays a critical role in electrical installations within buildings and infrastructure. It provides reliable power distribution while ensuring safety through its insulation properties. For buyers in Africa and South America, sourcing stranded wire locally can help mitigate shipping costs and lead times, facilitating timely project completions.
What Benefits Does Stranded Wire Offer in Consumer Electronics?
In the consumer electronics sector, stranded wire is commonly used for internal wiring in devices such as speakers and appliances. Its flexibility allows for easier assembly and design, leading to more compact and efficient products. Buyers should seek suppliers that offer a variety of stranded wire gauges and insulation types to meet specific product requirements, ensuring optimal performance and safety.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘stranded wire’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Sourcing the Right Gauge for Specific Applications
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter challenges in selecting the appropriate gauge of stranded wire for their projects. For instance, a manufacturer in South America might need to wire a new assembly line but is unsure whether to use 12 gauge or 10 gauge wire. Using the wrong gauge can lead to overheating, increased resistance, and ultimately equipment failure, which can be costly and disrupt production schedules.
The Solution: To effectively source the right gauge stranded wire, buyers should start by assessing the specific amperage requirements of their applications. Consulting with the manufacturer’s specifications for equipment can provide critical insights into the necessary wire gauge. Additionally, it is advisable to leverage digital tools such as wire gauge calculators or consult industry standards (e.g., NEC in the U.S.) to ensure compliance and safety. When ordering, buyers should also consider bulk purchasing options from reputable suppliers to reduce costs and ensure a consistent supply. Establishing relationships with multiple suppliers across different regions can further mitigate risks associated with sourcing, especially in regions like Africa and the Middle East where availability may vary.
Scenario 2: Handling Stranded Wire in Tight Spaces
The Problem: A common challenge faced by electrical engineers in Europe is the installation of stranded wire in confined spaces, such as in residential wiring or inside machinery. The flexibility of stranded wire is advantageous; however, the risk of kinking or improper bending can lead to connectivity issues, causing short circuits or signal loss.
The Solution: To overcome these installation challenges, it is essential to utilize proper handling techniques. Buyers should invest in high-quality stranded wire with enhanced flexibility features, such as those rated for high bending cycles. Additionally, using tools specifically designed for working with stranded wire—like wire strippers and crimping tools—can prevent damage during installation. Training installation teams on best practices for routing and securing wire in tight spaces can also minimize risks. For projects requiring extensive installations, consider modular wiring systems that incorporate stranded wire, allowing for easier adjustments and maintenance in compact environments.
Scenario 3: Cost Management for Large-Scale Projects
The Problem: In Africa, businesses engaged in large-scale construction or manufacturing projects often struggle with managing costs related to stranded wire. Fluctuating prices for raw materials, currency exchange rates, and shipping costs can create significant budgetary challenges. Buyers may find themselves facing unexpected expenses that can derail project timelines and profitability.
The Solution: To effectively manage costs, buyers should adopt a strategic procurement approach. This includes engaging in bulk purchasing agreements with suppliers, which can often lead to discounts and locked-in prices for extended periods. Conducting market research to identify the most reliable and cost-effective suppliers across different regions can also provide leverage in negotiations. Additionally, buyers should consider forecasting their wire needs based on project timelines to avoid last-minute purchases at inflated prices. Implementing inventory management systems can help track usage and optimize ordering schedules, ensuring that they have sufficient stock without overcommitting financial resources. Collaborating with local suppliers can also reduce shipping costs and times, enhancing overall project efficiency.
By addressing these common pain points with actionable solutions, B2B buyers can enhance their procurement processes, ensure project success, and ultimately contribute to their bottom line.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for stranded wire
What Are the Key Properties of Copper Stranded Wire?
Copper is the most widely used material for stranded wire due to its excellent electrical conductivity and thermal properties. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 90°C (194°F) and can handle high amperage loads, making it suitable for various applications, including residential and industrial electrical systems. Copper stranded wire also offers good corrosion resistance, especially when coated with tin or other protective materials.
Pros: The primary advantages of copper stranded wire include high conductivity, flexibility, and durability. Its malleability allows it to be easily bent and twisted, which is essential for intricate installations.
Cons: However, copper is relatively expensive compared to other materials like aluminum. Additionally, it can be prone to oxidation, which may require additional protective coatings for outdoor applications.
Impact on Application: Copper stranded wire is ideal for applications requiring reliable and efficient electrical connections, such as in power distribution and electronic devices. International buyers should consider compliance with standards such as ASTM B3 or B8, which govern the specifications for copper wire.
How Does Aluminum Stranded Wire Compare?
Aluminum is another common material for stranded wire, particularly in overhead power lines and large-scale electrical installations. It has a lower temperature rating than copper, typically around 75°C (167°F), but is lightweight and has good conductivity, albeit less than copper.
Pros: The key advantages of aluminum stranded wire include its low cost and lightweight nature, making it easier to transport and install. It is also resistant to corrosion when properly treated.
Cons: The main drawbacks include lower conductivity and a tendency to expand and contract with temperature changes, which can lead to connection issues over time.
Impact on Application: Aluminum stranded wire is often used in utility applications and large-scale projects where weight and cost are critical factors. Buyers from regions with stringent electrical codes should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM B230 and B231.
What Are the Benefits of Tinned Copper Stranded Wire?
Tinned copper stranded wire is copper wire that has been coated with a thin layer of tin. This coating enhances its corrosion resistance, making it suitable for marine and outdoor applications.
Pros: The primary benefits include improved resistance to oxidation and corrosion, which extends the wire’s lifespan in harsh environments. Tinned copper also maintains the excellent conductivity of copper.
Cons: The downside is that tinned copper stranded wire tends to be more expensive than standard copper wire due to the additional manufacturing process.
Impact on Application: This type of wire is particularly suitable for applications in coastal areas or environments with high humidity. International buyers should look for compliance with standards like ASTM B33 for tinned copper wire.
What Makes PVC Insulated Stranded Wire Unique?
PVC insulated stranded wire is designed for applications where insulation is critical. The PVC insulation provides good resistance to moisture, chemicals, and abrasion, making it suitable for various environments.
Pros: The key advantages of PVC insulated stranded wire include its durability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. It can withstand a range of environmental conditions, making it versatile for indoor and outdoor use.
Cons: However, PVC has a lower temperature rating (typically around 60°C or 140°F) compared to other insulation materials, which may limit its application in high-temperature environments.
Impact on Application: This wire is commonly used in residential wiring, appliances, and automotive applications. Buyers should ensure that the PVC insulation meets relevant standards such as UL 83 or IEC 60227.
Summary of Material Selection for Stranded Wire
| Material | Typical Use Case for stranded wire | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Power distribution, electronic devices | High conductivity and flexibility | Expensive, prone to oxidation | High |
| Aluminum | Overhead power lines, large-scale projects | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower conductivity, thermal expansion | Medium |
| Tinned Copper | Marine and outdoor applications | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost due to manufacturing | High |
| PVC Insulated | Residential wiring, appliances | Durable, flexible, cost-effective | Lower temperature rating | Low |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the materials commonly used in stranded wire applications. Buyers should carefully consider the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their specific needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for stranded wire
What Are the Main Stages of Stranded Wire Manufacturing?
The manufacturing process for stranded wire involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the desired specifications and quality standards. Understanding these stages can help international B2B buyers, especially from diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, to make informed purchasing decisions.
1. Material Preparation: What Raw Materials Are Used?
The first step in manufacturing stranded wire is material preparation, where raw materials such as copper or aluminum are sourced. Copper is often preferred due to its superior electrical conductivity, but aluminum is a lighter and more cost-effective alternative. The choice between these materials can influence the wire’s performance, cost, and application.
Once sourced, the metal undergoes processes such as drawing, which involves pulling the metal through a series of dies to achieve the desired gauge. This step ensures uniformity in wire diameter, critical for maintaining electrical performance.
2. Forming: How Are Stranded Wires Shaped?
After material preparation, the forming process begins. In this stage, multiple strands of wire are twisted together to create a flexible conductor. The twisting technique can vary, with the most common being concentric or helical twisting, which enhances flexibility and reduces the likelihood of wire breakage.
Key techniques employed during this stage include:
- Stranding Machines: These machines twist individual wire strands together, ensuring they are tightly bound to improve conductivity and flexibility.
- Insulation Application: Following stranding, the wire is typically coated with an insulating material, such as PVC or Teflon, to prevent electrical shorts and environmental damage.
What Are the Assembly and Finishing Processes in Stranded Wire Production?
3. Assembly: How Are Stranded Wires Constructed for Use?
The assembly process involves further enhancements to the stranded wire. This may include the addition of connectors, terminals, or other components necessary for specific applications. The assembly is critical for ensuring that the stranded wire can be easily integrated into larger systems, such as electrical panels or machinery.
4. Finishing: What Techniques Ensure Quality and Durability?
Finishing processes are essential for enhancing the stranded wire’s properties. Common finishing techniques include:
- Coating: Applying protective coatings to improve resistance to corrosion and environmental factors.
- Marking: Printing necessary information such as gauge, type, and standards on the wire for easy identification.
How Is Quality Assurance Managed in Stranded Wire Production?
Quality assurance (QA) is a crucial aspect of stranded wire manufacturing, ensuring that the final products meet international standards and customer specifications.
Relevant International Standards: What Should Buyers Look For?
International standards such as ISO 9001 play a significant role in quality assurance processes. These standards outline requirements for a quality management system, ensuring that manufacturers consistently produce high-quality products. Other industry-specific certifications, such as CE marking for the European market and API specifications for oil and gas applications, may also apply.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) is typically implemented at various checkpoints during the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards. For B2B buyers, verifying the supplier’s IQC processes can mitigate risks associated with subpar materials.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): As the manufacturing progresses, ongoing inspections are performed to monitor processes and identify potential issues early. This proactive approach reduces the likelihood of defects in the final product.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before packaging, the finished stranded wire undergoes rigorous testing to ensure it meets all specifications. Common tests include electrical conductivity tests, insulation resistance tests, and mechanical strength assessments.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers can take several steps to ensure the quality of stranded wire products from suppliers:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits of manufacturing facilities can provide insights into the supplier’s adherence to quality standards. Buyers should look for evidence of compliance with international standards and best practices.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide detailed quality reports, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC stages. These reports should clearly outline any deviations from expected standards and how they were addressed.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can add an additional layer of assurance. These independent entities can evaluate the manufacturing processes and final products against established standards.
What Are the Common Testing Methods for Stranded Wire Quality Assurance?
Stranded wire undergoes various testing methods to ensure its reliability and performance:
-
Electrical Testing: This includes measuring resistance, insulation resistance, and continuity to verify the wire’s electrical properties.
-
Mechanical Testing: Tests such as tensile strength and elongation help assess the wire’s durability under stress.
-
Environmental Testing: This involves exposing the wire to conditions such as temperature extremes, humidity, and corrosion to ensure its performance in various environments.
How Do Quality Control Nuances Affect International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must be aware of the nuances in quality control that may vary by region:
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different countries have varying regulations concerning wire manufacturing, which can affect product availability and compliance. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers comply with local regulations in their respective markets.
-
Cultural Differences: Cultural attitudes toward quality and manufacturing practices can differ. Understanding these differences can aid in establishing effective communication and expectations with suppliers.
By comprehensively understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols associated with stranded wire, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements. This knowledge not only supports the procurement of high-quality products but also fosters long-term partnerships with reliable suppliers.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘stranded wire’
Introduction
Navigating the procurement of stranded wire can be complex, especially for B2B buyers in diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This practical sourcing guide provides a step-by-step checklist to help streamline your purchasing process, ensuring you make informed decisions that align with your technical needs and business objectives.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before sourcing stranded wire, clearly outline your technical requirements. This includes determining the wire gauge, material (copper vs. aluminum), and insulation type needed for your specific applications. Understanding these specifications will guide your search and ensure compatibility with your projects.
- Wire Gauge: Choose based on the amperage load and application.
- Material Type: Consider the conductivity and cost implications of copper versus aluminum.
Step 2: Research and Compare Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers. Look for companies that specialize in stranded wire and have a proven track record in your region. Comparing different suppliers will help you identify the best options based on price, quality, and service.
- Supplier Reputation: Check online reviews and industry forums for feedback.
- Product Range: Ensure the supplier offers a variety of stranded wire products to meet diverse needs.
Step 3: Verify Supplier Certifications
It’s essential to verify that your suppliers hold relevant industry certifications. Certifications ensure that the wire meets international quality standards and safety regulations, which is crucial for compliance in your projects.
- ISO Certification: Look for ISO 9001 or similar certifications.
- Product Compliance: Confirm that the wire meets local and international electrical standards.
Step 4: Request Samples
Before making a bulk purchase, request samples of the stranded wire from shortlisted suppliers. Evaluating samples allows you to assess the wire’s quality and suitability for your specific applications.
- Test for Flexibility: Ensure the wire meets your bending and installation requirements.
- Conduct Electrical Tests: Check for conductivity and insulation performance.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you’ve selected a preferred supplier, engage in negotiations regarding pricing, delivery terms, and payment conditions. Effective negotiation can lead to better rates and more favorable terms, which is vital for optimizing your budget.
- Bulk Discounts: Inquire about pricing breaks for larger orders.
- Delivery Schedules: Confirm lead times to ensure timely project completion.
Step 6: Establish a Reliable Communication Channel
Maintaining open lines of communication with your supplier is crucial throughout the procurement process. Clear communication can help resolve any issues that arise and facilitate a smoother transaction.
- Designate a Point of Contact: Assign a dedicated representative for ongoing communication.
- Use Technology: Consider utilizing platforms for real-time updates and tracking.
Step 7: Plan for Logistics and Delivery
Finally, plan the logistics of receiving your stranded wire. Consider the best shipping options, customs requirements, and potential delays, particularly when sourcing internationally.
- Shipping Options: Compare air freight versus sea freight based on urgency and cost.
- Customs Regulations: Ensure you are aware of and compliant with local import regulations to avoid delays.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can enhance their sourcing process for stranded wire, ensuring they secure high-quality materials that meet their project needs while optimizing costs and delivery timelines.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for stranded wire Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Stranded Wire Sourcing?
When sourcing stranded wire, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of metals (copper vs. aluminum) significantly impacts the cost. Copper, being a premium material, often results in higher prices, while aluminum is more cost-effective but may not offer the same conductivity.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region, impacting the overall pricing. Countries with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but this could influence the quality of manufacturing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and salaries of non-production staff. These costs must be factored into the final pricing.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tools and machinery can be significant, especially for customized wire solutions. This cost is typically amortized over large production runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that stranded wire meets industry standards and certifications adds to the overall cost. Buyers should consider the implications of QC processes on pricing, especially when sourcing from international suppliers.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can fluctuate based on the distance, mode of transport, and Incoterms agreed upon. These factors are particularly important for buyers from Africa and South America, where logistics infrastructure may vary.
-
Margin: Suppliers often include a markup for profit, which can differ based on market competition and perceived value. Understanding the typical margins in different regions can aid in negotiations.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Stranded Wire Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of stranded wire, which B2B buyers should be aware of:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders typically lead to lower per-unit costs. Buyers should assess their needs against potential savings from bulk purchasing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can increase costs significantly. Buyers should evaluate whether standard products meet their needs or if customization is essential.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (like UL, CE) often come at a premium. Buyers should weigh the importance of these factors against their budget.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers with good track records may charge more, but they often provide better service and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: The agreed terms of shipment can affect costs and risks. Buyers should choose Incoterms that align with their logistical capabilities and risk tolerance.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Negotiating Stranded Wire Prices?
To maximize value and minimize costs when sourcing stranded wire, consider the following actionable tips:
-
Negotiate Wisely: Develop a clear understanding of market prices and leverage this knowledge during negotiations. Be prepared to walk away if the terms are not favorable.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Analyze the total cost of ownership (TCO) rather than just the initial purchase price. This includes considering durability, maintenance, and potential replacements.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware that international pricing can fluctuate due to currency exchange rates and geopolitical factors. Stay informed about market trends in your region.
-
Build Relationships with Suppliers: Establishing long-term relationships can lead to better pricing and terms. Suppliers are often more willing to negotiate with repeat customers.
-
Consider Local Regulations: Ensure compliance with local regulations and standards, as non-compliance can lead to additional costs and delays.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
It is important to note that the prices for stranded wire can vary widely based on the factors discussed above. Prices should be treated as indicative, and buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough market research and seek multiple quotations to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing stranded wire With Other Solutions

A stock image related to stranded wire.
When evaluating wiring solutions for electrical projects, it’s essential to consider the alternatives to stranded wire. Each option presents unique advantages and disadvantages that can significantly impact performance, cost, and usability in various applications. Below is a comparison of stranded wire against two viable alternatives: solid wire and flexible flat cable.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Stranded Wire | Solid Wire | Flexible Flat Cable |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High flexibility, ideal for tight spaces | Excellent for high current applications | Versatile in flat designs for tight spaces |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Generally lower cost | Higher due to specialized design |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple to install, bends easily | Requires more effort to install | Easy to install in flat spaces |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, durable | Low maintenance, but can break if bent repeatedly | Moderate maintenance, susceptible to wear in high-movement applications |
| Best Use Case | Electronics, circuit boards | Outdoor applications, building infrastructure | Consumer electronics, low-profile installations |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Solid Wire?
Solid wire consists of a single, solid metal core, which makes it more durable in outdoor applications and capable of handling higher currents. Its cost-effectiveness is a significant advantage, particularly in large-scale projects where budget constraints are critical. However, solid wire is less flexible than stranded wire, making it unsuitable for applications requiring intricate layouts or frequent movement.
How Does Flexible Flat Cable Compare?
Flexible flat cable is designed to be extremely versatile, allowing for compact installations in tight spaces. Its flat design can be ideal for consumer electronics and devices where space is at a premium. However, the cost of flexible flat cable can be higher compared to both stranded and solid wire due to its specialized construction. Additionally, while it is easy to install in flat configurations, it may be more prone to wear and tear in high-movement environments.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Wiring Solution?
For B2B buyers, selecting the appropriate wiring solution hinges on a clear understanding of the specific application requirements. Stranded wire is often the best choice for projects requiring flexibility and ease of installation, especially in electronic devices. Solid wire should be favored for outdoor applications where durability and high current capacity are paramount. Meanwhile, flexible flat cable is ideal for consumer electronics that necessitate a low-profile design. By thoroughly evaluating these factors, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their project needs and budget constraints.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for stranded wire
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Stranded Wire?
Understanding the technical specifications of stranded wire is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially when sourcing for various applications across diverse industries. Here are some essential properties to consider:
1. Material Grade: What Should You Look For?
Stranded wires are typically made from copper or aluminum. Copper is favored for its superior conductivity and resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for electrical applications. Aluminum, while less conductive, is lighter and more cost-effective, which can be advantageous in certain installations. When sourcing stranded wire, ensure the material grade meets the electrical and environmental requirements of your specific application.
2. Wire Gauge: How Does It Impact Performance?
Wire gauge, measured in American Wire Gauge (AWG), indicates the diameter of the wire. A lower gauge number means a thicker wire, which can carry more current. For instance, 10 AWG wire can handle significantly more amperage than 20 AWG wire. Understanding wire gauge is essential when determining the suitability of stranded wire for your projects, as it directly impacts both performance and safety.
3. Stranding Configuration: What Does It Mean for Flexibility?
The configuration of the strands—how many wires are bundled together and their arrangement—affects the wire’s flexibility and durability. Common configurations include Class K (very flexible), Class M (moderately flexible), and Class S (less flexible). For applications requiring bending or twisting, such as in robotics or complex machinery, a more flexible stranded wire is essential to ensure reliability and longevity.
4. Voltage Rating: Why Is It Critical?
The voltage rating of stranded wire indicates the maximum voltage the wire can safely carry. For example, wires rated for 300V or 600V are common in various electrical applications. Selecting a wire with the appropriate voltage rating is vital to prevent overheating and potential failures, particularly in high-demand environments.
5. Temperature Rating: How Does It Affect Your Application?
The temperature rating indicates the maximum operating temperature for stranded wire, which is crucial for ensuring safety and performance. Wires are typically rated for various environments, such as standard (60°C) or high-temperature (90°C) applications. Knowing the temperature rating helps in selecting the right wire for conditions that may involve heat exposure or thermal cycling.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Stranded Wire?
Familiarity with industry jargon is important for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B space. Here are several common terms you should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): What Does It Entail?
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of stranded wire, an OEM may provide customized wire solutions tailored to specific equipment needs. Understanding OEM relationships can help in sourcing high-quality products that meet your specific requirements.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Why Is It Important?
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management. Suppliers often set MOQs to ensure cost-effectiveness in production and shipping, which can impact your overall procurement strategy.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation): How to Use It Effectively?
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products. When dealing with stranded wire, submitting an RFQ can help clarify costs, lead times, and available specifications. This is particularly useful for large orders or complex projects where multiple suppliers may be considered.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms): How Do They Affect Shipping?
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is crucial for B2B buyers in ensuring that shipping, insurance, and risk management are clearly outlined in contracts, ultimately protecting your investment.
5. UL Certification: What Is Its Significance?
Underwriters Laboratories (UL) certification indicates that a product has been tested for safety and performance. For stranded wire, UL certification assures buyers that the wire meets specific safety standards, which is particularly important in electrical applications where safety is paramount.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring the selected stranded wire meets their operational needs while adhering to industry standards.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the stranded wire Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Stranded Wire Sector?
The global stranded wire market is witnessing robust growth driven by several key factors. The increasing demand for energy-efficient electrical systems, particularly in emerging economies in Africa and South America, is a significant driver. As urbanization accelerates and infrastructure projects ramp up, stranded wire is preferred for its flexibility and reliability in various applications, including renewable energy systems and smart grids.
In the Middle East and Europe, the rise of electric vehicles (EVs) and advancements in telecommunications are propelling the demand for high-performance stranded wires. These regions are also seeing a surge in automation and IoT applications, where stranded wire’s adaptability plays a crucial role. Additionally, the integration of Industry 4.0 technologies is influencing sourcing strategies, with B2B buyers increasingly turning to digital platforms for procurement, enhancing transparency, and streamlining supply chains.
Emerging trends include the shift toward customized wire solutions, where manufacturers provide tailored stranded wire products to meet specific industry needs. Moreover, the adoption of advanced manufacturing processes, such as automated wire assembly, is lowering production costs and improving quality, making it an attractive option for international buyers.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing the Stranded Wire Market?
Sustainability is becoming a core consideration for international B2B buyers in the stranded wire sector. The environmental impact of wire production, particularly concerning the sourcing of raw materials like copper and aluminum, has prompted a shift towards more sustainable practices. Companies are increasingly focused on reducing their carbon footprints and adhering to stricter environmental regulations.
Ethical supply chains are paramount, as buyers seek suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to responsible sourcing and fair labor practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and Responsible Business Alliance (RBA) membership are becoming essential criteria for supplier selection.
In addition, the introduction of ‘green’ stranded wire options—made from recycled materials or with reduced environmental impact—appeals to environmentally conscious buyers. By prioritizing suppliers who provide these sustainable materials, businesses can not only enhance their market position but also contribute to global efforts in promoting sustainable development.
What Is the Brief Evolution of Stranded Wire in the B2B Context?
The evolution of stranded wire dates back to the late 19th century when electrical systems began to proliferate. Initially, solid wire was the standard; however, the limitations in flexibility and durability for certain applications led to the development of stranded wire. Its unique structure, comprising multiple thin strands, allowed for greater flexibility and ease of installation, making it ideal for various electrical applications, especially in confined spaces.

A stock image related to stranded wire.
Over the decades, technological advancements have refined stranded wire production, improving conductivity and insulation properties. Today, stranded wire is indispensable in numerous sectors, from residential electrical systems to complex industrial machinery, reflecting its adaptability and essential role in the modern electrical landscape.
In summary, understanding the market dynamics, sustainability trends, and historical context of stranded wire is critical for international B2B buyers. This knowledge not only aids in informed purchasing decisions but also aligns with broader industry shifts towards sustainability and technological advancement.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of stranded wire
-
How do I choose the right stranded wire for my application?
Choosing the right stranded wire involves considering several factors, including the wire gauge, material (copper vs. aluminum), flexibility requirements, and the specific electrical load of your application. For flexible applications, such as connections in tight spaces or moving parts, stranded wire is ideal due to its malleability. If you are dealing with high amperage, ensure the wire gauge is appropriate to handle the load without overheating. Consulting with your electrical engineer or supplier can provide valuable insights tailored to your project needs. -
What is the best stranded wire for outdoor applications?
For outdoor applications, look for stranded wire that is specifically designed to be weather-resistant and UV-stabilized. THHN (Thermoplastic High Heat-resistant Nylon-coated) stranded wire is a popular choice for outdoor use due to its durability and resistance to moisture and heat. It’s important to ensure that the wire is rated for the specific environmental conditions it will face, including temperature extremes and exposure to chemicals. Always verify the wire’s compliance with local electrical codes to ensure safety and effectiveness. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for stranded wire?
Minimum order quantities for stranded wire can vary significantly between suppliers and regions. Generally, MOQs can range from 100 meters to several kilometers, depending on the manufacturer and the type of wire. For international B2B buyers, it’s advisable to discuss MOQs directly with suppliers, as they may offer flexibility based on your specific needs or the potential for future orders. Understanding the MOQ can help you plan your inventory and ensure you are not overcommitting financially. -
How can I ensure the quality of stranded wire from international suppliers?
To ensure quality, it’s crucial to vet potential suppliers thoroughly. Look for suppliers that provide certifications such as ISO 9001 or UL-listed products, which indicate adherence to quality management standards. Request samples to test the wire’s flexibility, conductivity, and insulation quality before placing a large order. Additionally, consider third-party inspections and audits to verify manufacturing practices and quality controls, particularly when sourcing from regions with less stringent regulations. -
What payment terms should I negotiate with stranded wire suppliers?
Payment terms can vary widely, but common practices include net 30 or net 60 days after delivery. For international transactions, consider options like letters of credit or escrow services to mitigate risks. Negotiating favorable terms can help manage cash flow, especially if you are placing a large order. Always clarify any upfront payments, such as deposits, and ensure you understand the implications of payment terms on delivery schedules and overall costs. -
How do logistics and shipping impact the cost of stranded wire?
Logistics and shipping can significantly influence the total cost of stranded wire, particularly for international buyers. Factors such as shipping method (air vs. sea), distance, and customs duties must be considered. To minimize costs, collaborate with suppliers who have established shipping agreements or can offer bulk shipping discounts. Additionally, be aware of import regulations in your country to avoid unexpected tariffs or delays that could affect your project timeline. -
What customization options are available for stranded wire?
Many suppliers offer customization options for stranded wire, including different gauges, lengths, insulation materials, and colors. Customization can be crucial for meeting specific application requirements or industry standards. When discussing options with suppliers, be clear about your technical specifications and intended use. This ensures that the customized wire will perform adequately in your applications and comply with any relevant regulations or standards. -
How can I handle potential disputes with stranded wire suppliers?
To handle disputes effectively, establish clear communication from the outset and document all agreements in writing, including specifications, timelines, and payment terms. In the event of a disagreement, refer to the contract to resolve issues. It may be beneficial to include a mediation or arbitration clause in the contract, which provides a structured approach to dispute resolution. Building strong relationships with suppliers can also facilitate smoother negotiations and conflict resolution in the future.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for stranded wire
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers of Stranded Wire?
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of stranded wire presents significant advantages for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the unique properties of stranded wire—its flexibility, durability, and adaptability to various applications—enables businesses to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs. For instance, stranded wire is ideal for intricate electronic applications, while solid wire may be better suited for high-load outdoor settings.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Supply Chain?
Engaging in strategic sourcing can optimize your supply chain by ensuring that you procure high-quality stranded wire at competitive prices, thus enhancing your product offerings and operational efficiency. By focusing on suppliers with robust quality assurance practices and reliable delivery schedules, you can mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions.
What’s Next for International Buyers of Stranded Wire?
As global demand for stranded wire continues to grow, international B2B buyers should remain proactive in exploring new supplier relationships and market trends. Investing time in understanding regional compliance standards and technological advancements will empower you to seize emerging opportunities. Now is the time to leverage strategic sourcing to elevate your procurement strategy and achieve long-term success in your projects.