Unlock Efficiency: The Ultimate Cold Forged Guide (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cold forged
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing high-quality cold forged components can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Cold forging, a process that enhances the strength and durability of metal parts at room temperature, offers numerous advantages, including reduced material waste and faster production times. However, navigating the diverse options and suppliers in the global market can be overwhelming, especially when considering factors like material specifications, production methods, and cost efficiency.
This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the cold forging market, providing insights into the various types of cold forged products, their applications across different industries, and effective strategies for supplier vetting. Buyers will learn about the intricacies of open and closed die forging, the benefits of using materials such as stainless steel and aluminum, and how to calculate the total cost of ownership for their purchases.
By equipping B2B buyers with actionable insights and best practices, this guide empowers them to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their specific needs and operational goals. Whether you are a procurement manager in Nigeria, an engineer in Brazil, or a business owner in Egypt, understanding the nuances of cold forging will enhance your ability to source high-quality components that drive your business forward.
Understanding cold forged Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Open-Dye Forging | Utilizes flat dies; allows for simpler shapes and designs. | Automotive components, brackets, and fixtures. | Pros: Lower tooling costs; Cons: Limited to simpler shapes. |
| Closed-Dye Forging | Uses custom-shaped dies; creates complex geometries. | Precision parts for machinery and aerospace. | Pros: High precision; Cons: Higher tooling costs. |
| Rolled Ring Forging | Involves creating a donut shape and reforming into rings. | Aerospace components, automotive parts. | Pros: High strength; Cons: Requires specific tooling. |
| Aluminum Forging | Focused on aluminum alloys; lightweight and corrosion-resistant. | Electrical components, automotive parts. | Pros: Lightweight; Cons: Limited to aluminum materials. |
| Copper & Brass Forging | Tailored for intricate shapes; precision control over temperature. | Plumbing fittings, electrical connectors. | Pros: Excellent conductivity; Cons: More expensive materials. |
What Are the Characteristics of Open-Dye Forging?
Open-dye forging is characterized by the use of flat dies that do not enclose the workpiece. This method allows for simpler shapes and designs, making it ideal for components that do not require complex geometries. It is particularly suited for high-volume production of automotive components, brackets, and fixtures. When considering purchasing open-dye forged parts, B2B buyers should evaluate the simplicity of design and the associated lower tooling costs, though they should also note the limitations in shape complexity.
How Does Closed-Dye Forging Differ in Precision?
Closed-dye forging employs custom-shaped dies that enclose the workpiece, allowing for the creation of intricate and precise geometries. This process is essential for industries requiring high precision, such as aerospace and machinery manufacturing. B2B buyers should consider the higher tooling costs associated with closed-dye forging but can benefit from the superior accuracy and reduced need for additional machining processes. This makes it a preferred choice for critical components where tolerances are crucial.
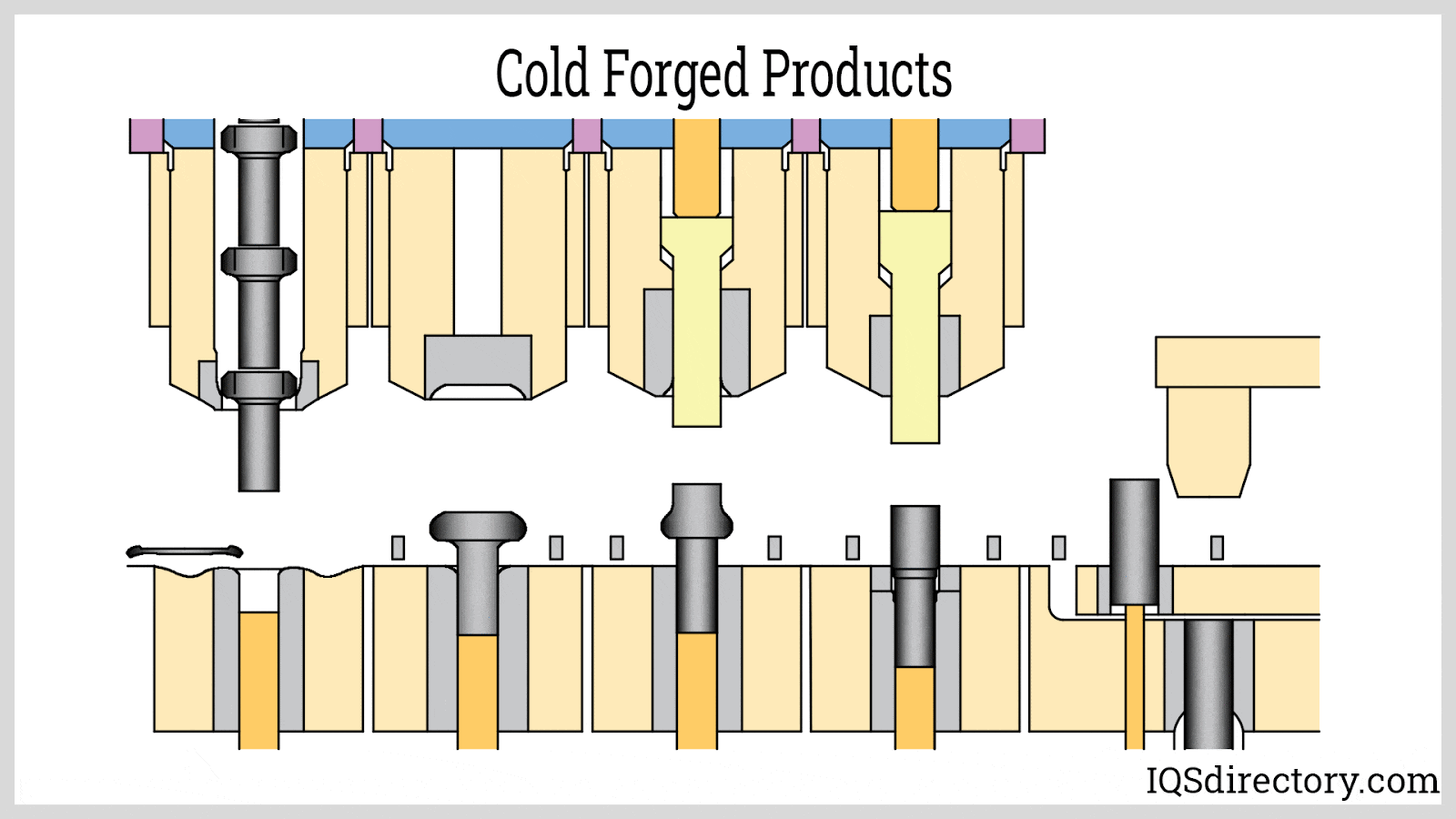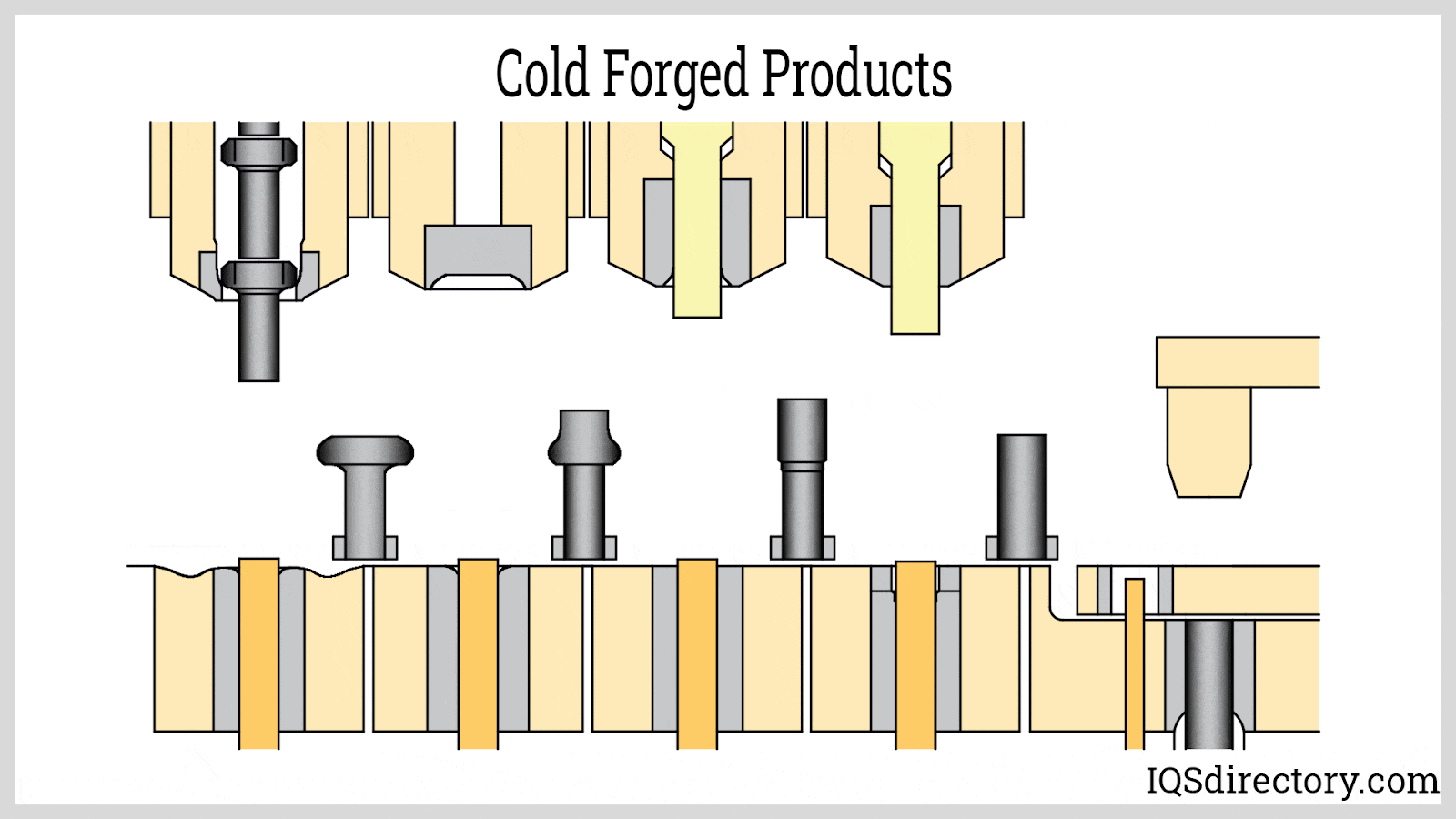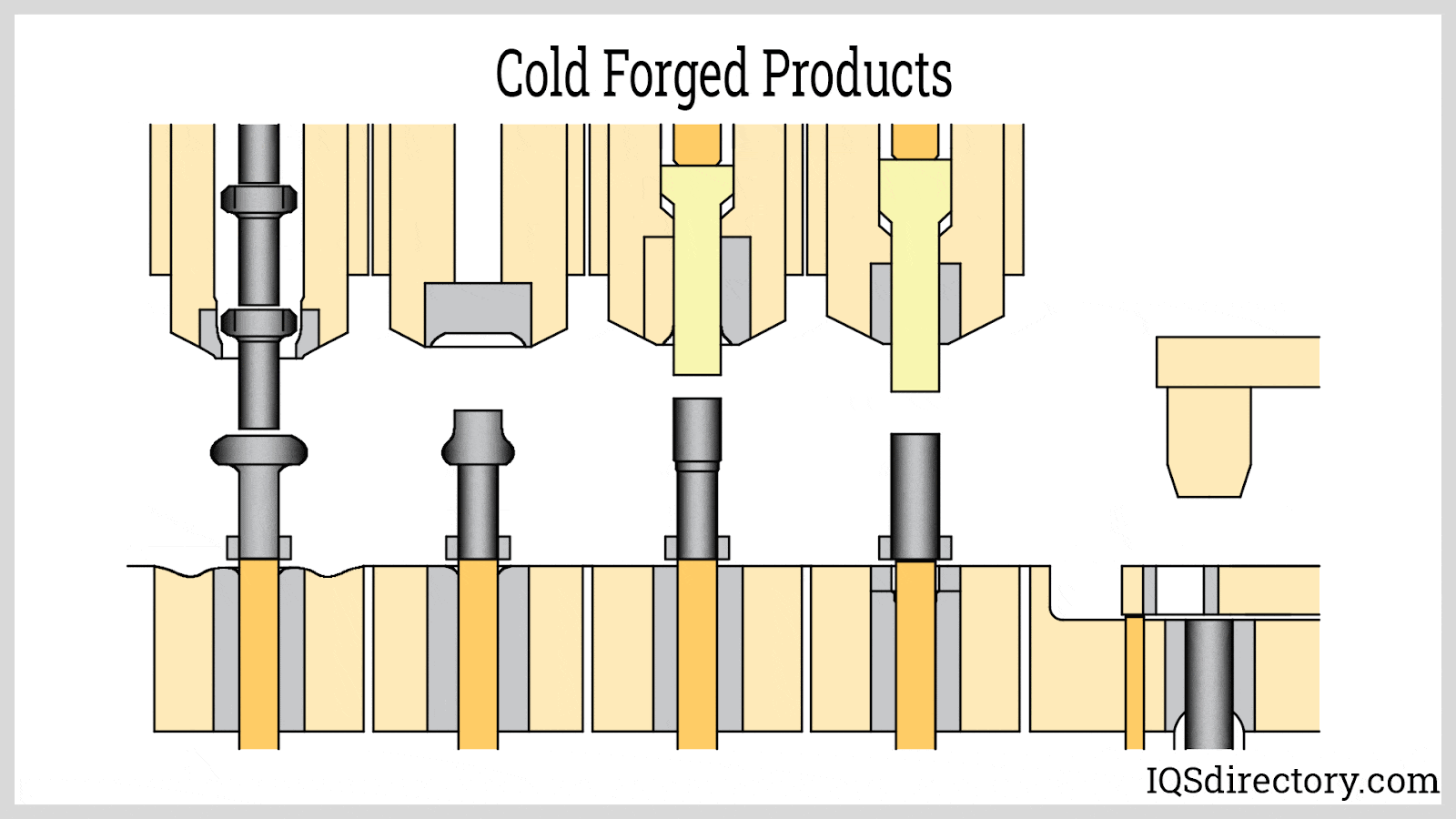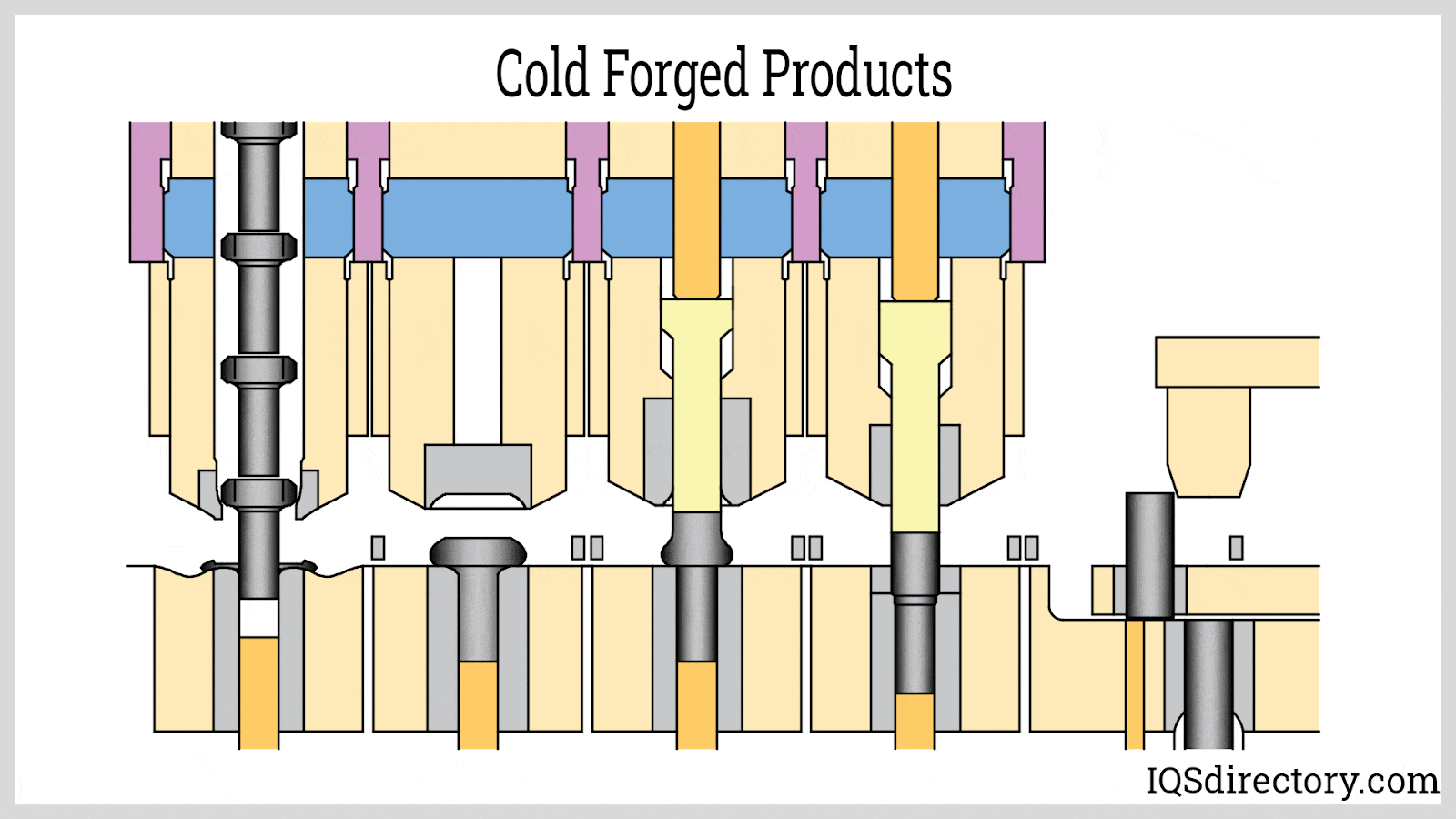
A stock image related to cold forged.
Why Choose Rolled Ring Forging for Your Components?
Rolled ring forging is a unique process that involves creating a donut-shaped workpiece which is then transformed into a thin ring. This method is particularly advantageous for producing high-strength components often used in aerospace and automotive applications. B2B buyers should consider this option for its strength and durability; however, the need for specialized tooling may increase initial costs. Evaluating the long-term benefits of strength and performance can justify the investment.
What Are the Benefits of Aluminum Forging?
Aluminum forging focuses on the manipulation of aluminum alloys, yielding lightweight yet durable components. This process is especially beneficial in industries such as automotive and electrical manufacturing, where weight reduction is critical. B2B buyers should weigh the advantages of aluminum’s corrosion resistance and lightweight properties against the limitation of material choices. Understanding the specific application requirements can help in making an informed decision.
How Do Copper and Brass Forging Techniques Stand Out?

A stock image related to cold forged.
Copper and brass forging is designed for producing intricate shapes and components, with precise control over temperature during the process. This method is commonly used in manufacturing plumbing fittings and electrical connectors due to the excellent conductivity of these metals. B2B buyers should consider the higher material costs associated with copper and brass, balanced against the benefits of their superior electrical and thermal properties. Evaluating the end-use requirements will be essential in deciding whether to invest in these types of forged products.
Key Industrial Applications of cold forged
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Cold Forged | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Production of spline shafts and gears | High strength and durability for critical components | Supplier reliability, material certification, and production capacity |
| Aerospace | Manufacturing of flanged bushings and pulleys | Lightweight and strong parts for fuel efficiency | Compliance with aerospace standards, traceability, and lead times |
| Oil & Gas | Fabrication of heat exchanger tubes | Enhanced performance in extreme conditions | Material sourcing, corrosion resistance, and custom design options |
| Construction & Heavy Machinery | Components for structural applications | Improved load-bearing capacity and longevity | Customization capabilities, volume production, and shipping logistics |
| Electronics & Electrical | Production of precision connectors and terminals | High precision and reliability for electronic devices | Quality control processes, material specifications, and cost efficiency |
How is Cold Forged Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, cold forging is utilized to produce critical components such as spline shafts and gears. These parts require high strength and durability to withstand rigorous operational conditions. Cold forging offers a cost-effective manufacturing solution, minimizing waste while enhancing mechanical properties. For international buyers, especially in Africa and South America, it’s crucial to consider supplier reliability and ensure that materials meet stringent automotive standards to maintain safety and performance.
What Role Does Cold Forging Play in Aerospace Manufacturing?
Cold forging finds significant application in aerospace, particularly for creating flanged bushings and pulleys. These components must be lightweight yet exceptionally strong to optimize fuel efficiency and performance during flight. Aerospace buyers must prioritize suppliers that comply with industry standards, ensuring traceability and adherence to rigorous quality control measures. Given the global nature of the aerospace supply chain, understanding lead times and logistics is also vital for timely project execution.
How is Cold Forging Beneficial in the Oil & Gas Sector?
In the oil and gas industry, cold forged heat exchanger tubes are crucial for maintaining operational efficiency under extreme temperatures and pressures. The process enhances the structural integrity and performance of these components, which are often subjected to harsh environments. Buyers from the Middle East, where oil and gas operations are prevalent, should focus on sourcing materials that offer corrosion resistance and durability. Custom design capabilities can also be a key factor in meeting specific project requirements.
A stock image related to cold forged.
What Advantages Does Cold Forging Provide in Construction and Heavy Machinery?
Cold forging is widely used in the construction and heavy machinery sectors for producing components that require enhanced load-bearing capacity. This process ensures that parts have a longer lifespan and can withstand significant stress, making them ideal for structural applications. For international buyers, especially in developing markets, the ability to customize components and ensure high-volume production can significantly impact project timelines and costs. Additionally, understanding shipping logistics is essential for timely delivery.
How is Cold Forging Utilized in Electronics and Electrical Applications?
In the electronics sector, cold forging is employed to manufacture precision connectors and terminals. These components are critical for ensuring reliable connections in electronic devices. The cold forging process allows for high precision and repeatability, essential for maintaining the integrity of electronic assemblies. Buyers in Europe should focus on suppliers with robust quality control processes and material specifications to ensure compliance with industry standards, as well as cost efficiency to remain competitive.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cold forged’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Challenges in Consistent Quality of Cold Forged Parts
The Problem: B2B buyers often face inconsistencies in the quality of cold forged components, especially when sourcing from multiple suppliers. Variations in material quality, production processes, and handling can lead to discrepancies in dimensions, surface finish, and mechanical properties. These inconsistencies can cause delays in production lines, increase rejection rates, and ultimately affect product reliability. For buyers in regions such as Africa and South America, where manufacturing capabilities can vary significantly, maintaining consistent quality becomes even more challenging.
The Solution: To ensure consistent quality in cold forged parts, buyers should establish clear specifications and quality assurance protocols with their suppliers. Start by defining stringent material standards, including specific grades of steel or aluminum, and request certifications that validate these standards. Implement a thorough vetting process for suppliers, focusing on their manufacturing capabilities, quality control measures, and past performance records. Additionally, consider conducting periodic audits of suppliers to verify compliance with your quality standards. Utilizing third-party testing services can also provide an added layer of assurance that the forged components meet your specifications consistently.
Scenario 2: High Production Costs Due to Inefficient Processes
The Problem: Buyers often struggle with high production costs related to cold forging, particularly when facing complex designs that require multiple operations. Inefficiencies in the forging process, such as excessive tooling changes, prolonged cycle times, and material waste, can significantly inflate overall costs. This issue is especially pertinent for buyers in the Middle East and Europe, where competitive pricing is essential to maintain market position.
The Solution: To mitigate high production costs, buyers should collaborate closely with manufacturers to optimize the cold forging process. Engage in early-stage design reviews to ensure that parts are designed for manufacturability. Simplifying designs can reduce the number of necessary operations and minimize tooling changes. Additionally, leveraging advanced manufacturing technologies, such as simulation software, can help identify potential inefficiencies before production begins. By working together to refine processes and implement lean manufacturing principles, buyers can achieve significant cost savings and improve overall efficiency.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Meeting Customization Requirements
The Problem: Many B2B buyers require customized cold forged components tailored to specific applications. However, not all suppliers have the capacity or expertise to meet these unique demands. Buyers may find themselves limited by the standard offerings of suppliers, which can stifle innovation and hinder the development of specialized products. This scenario is particularly critical for companies in diverse industries, such as automotive or aerospace, where precision and customization are paramount.
The Solution: To effectively address customization challenges, buyers should seek out suppliers with proven capabilities in custom cold forging. When approaching potential partners, clearly communicate your specific requirements, including dimensions, tolerances, and any unique features needed for your applications. Collaborate with suppliers during the early design stages to ensure that they can accommodate your needs. Additionally, consider establishing long-term partnerships with specialized manufacturers that can offer flexibility and innovation. By fostering open communication and collaboration, you can streamline the development of customized components and drive successful project outcomes.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cold forged
What Materials Are Commonly Used for Cold Forging?
When selecting materials for cold forging, international B2B buyers must consider various factors, including the mechanical properties, cost, and application suitability of each material. Below, we analyze four common materials used in cold forging: steel, aluminum, brass, and copper.
What Are the Key Properties of Steel for Cold Forging?
Steel is one of the most widely used materials in cold forging due to its excellent strength and durability. It can withstand high pressure and temperature ratings, making it suitable for demanding applications. Cold-forged steel components exhibit high tensile strength and fatigue resistance, which are critical for automotive and industrial applications.
Pros: Steel is cost-effective and offers high durability. It can be easily sourced globally, and its versatility allows for various applications, from automotive parts to machinery components.
Cons: The main limitation of steel is its susceptibility to corrosion, which may require additional surface treatments. Moreover, the complexity of manufacturing processes can increase costs if specialized tooling is needed.
Impact on Application: Steel’s compatibility with various media, including oil and gas, makes it a preferred choice for industries requiring robust components.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN is crucial for steel products. Buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East should ensure that suppliers adhere to these standards to guarantee quality and performance.
How Does Aluminum Perform in Cold Forging Applications?
Aluminum is another popular material for cold forging, particularly in industries where weight reduction is essential. It offers a favorable strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for aerospace and automotive applications.
Pros: Aluminum is lightweight, which contributes to energy efficiency in transportation. It also has good machinability and can be easily formed into complex shapes.
Cons: While aluminum is resistant to corrosion, it may not withstand high-temperature applications as effectively as steel. Additionally, its cost can be higher than that of steel, depending on the alloy used.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s compatibility with various environmental conditions makes it ideal for applications exposed to moisture and corrosive substances.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify the specific aluminum alloy and its compliance with international standards such as JIS. This is particularly important for industries in Europe and South America, where quality standards are stringent.
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of Brass in Cold Forging?
Brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, is often used in cold forging for applications requiring good corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity. It is commonly found in plumbing fixtures, electrical components, and decorative items.
Pros: Brass is highly resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for marine applications. Its excellent machinability allows for intricate designs and high-quality finishes.
Cons: The primary limitation of brass is its relatively lower strength compared to steel and aluminum. Additionally, brass can be more expensive, especially for high-quality alloys.
Impact on Application: Brass components are often used in environments where exposure to moisture is common, such as plumbing systems.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that brass components meet standards such as ASTM B16 for fittings and flanges, which is essential for compliance in regions like Africa and Europe.
Why Is Copper Considered for Cold Forging?
Copper is known for its exceptional electrical and thermal conductivity, making it a preferred choice for electrical components and heat exchangers. Cold forging copper allows for the creation of complex shapes while maintaining its conductive properties.
Pros: Copper’s high conductivity makes it ideal for electrical applications. It also exhibits good corrosion resistance and can be easily recycled.
Cons: Copper is generally more expensive than other metals, and its softness can limit its use in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: Copper is particularly suitable for applications involving electrical wiring and heat transfer systems.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM B75 for copper tubes is essential for buyers in the Middle East and Europe to ensure product reliability.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Cold Forging
| Material | Typical Use Case for Cold Forged | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Automotive parts, machinery components | High strength and durability | Susceptible to corrosion | Low |
| Aluminum | Aerospace, automotive applications | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Limited high-temperature performance | Medium |
| Brass | Plumbing fixtures, electrical components | Excellent corrosion resistance | Lower strength compared to steel | High |
| Copper | Electrical components, heat exchangers | Exceptional conductivity | Higher cost and softness | High |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the materials commonly used in cold forging, along with their properties, advantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers. Understanding these factors will aid in making informed purchasing decisions that align with specific application needs and compliance standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cold forged
What Are the Main Stages of the Cold Forging Manufacturing Process?
The cold forging manufacturing process consists of several critical stages that ensure the production of high-quality forged components. Each stage plays a vital role in achieving the desired mechanical properties and dimensional accuracy of the final product.
1. Material Preparation: How Is Raw Material Selected and Processed?
The first step in cold forging involves selecting the appropriate raw material. Common materials used include carbon steel, stainless steel, brass, and aluminum alloys. The material is typically delivered in the form of rods or bars, which are then cut into slugs or blanks of the required size.
Before forging, the raw material is treated with a lubricant to reduce friction during the forming process and to prevent it from sticking to the dies. Proper selection and preparation of the material are crucial as they directly affect the mechanical properties of the final product, including strength and ductility.
2. Forming: What Techniques Are Used in Cold Forging?
Cold forging can be executed through two primary techniques: open-die forging and closed-die forging.
-
Open-die Forging: In this method, the raw material is placed between two flat dies that do not completely enclose the workpiece. The compressive force from the dies deforms the metal into the desired shape. This method is suitable for larger components or when multiple shapes are needed.
-
Closed-die Forging: This technique uses custom-shaped dies to enclose the workpiece entirely. The material flows into the die cavity, allowing for more complex shapes and tighter tolerances. After forming, excess material (flash) is trimmed off, resulting in a finished part that often requires little to no further machining.
Both techniques are highly efficient and can achieve a high production rate, with some operations capable of producing hundreds of pieces per hour.
3. Assembly: How Are Forged Parts Joined Together?
In cases where the final product consists of multiple components, assembly may be required. This stage involves joining forged parts through methods such as welding, riveting, or mechanical fastening. The choice of assembly technique depends on the application and the materials involved.
Proper alignment and fit are crucial to ensure the integrity and performance of the final product. Quality control measures during assembly help identify any misalignments or defects early in the process.
4. Finishing: What Additional Processes Are Needed Post-Forging?
After the forging and assembly stages, finishing processes may be necessary to enhance the surface finish and meet specific tolerances. Common finishing techniques include:
- Trimming: Removal of excess material from the forged parts.
- Machining: Precision cutting to achieve tighter tolerances or complex geometries.
- Surface Treatment: Processes like anodizing, plating, or painting to improve corrosion resistance or aesthetics.
Each finishing method contributes to the overall quality of the product and should be considered when evaluating suppliers.
What Quality Assurance Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in the cold forging industry to ensure that the final products meet international standards and customer specifications. For international B2B buyers, understanding these standards and QA practices can significantly affect procurement decisions.
1. What Are the Relevant International and Industry-Specific Standards?
-
ISO 9001: This is a widely recognized quality management standard that outlines requirements for a quality management system (QMS). It ensures that organizations consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
-
CE Marking: In Europe, products must comply with specific safety, health, and environmental protection legislation to obtain CE marking, indicating conformity.
-
API Standards: For buyers in the oil and gas sector, the American Petroleum Institute (API) standards ensure that products meet industry-specific requirements for performance and safety.
Understanding these standards helps buyers assess the credibility and reliability of potential suppliers.
2. What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Cold Forging?
Quality control checkpoints are critical in the cold forging process to ensure that defects are identified and rectified before the final product is shipped. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications before processing begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the forging process, operators monitor critical parameters such as temperature, pressure, and dimensions to ensure that the parts are being manufactured correctly.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After production, a thorough inspection of the finished products is conducted to verify that they meet all specified requirements.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Quality Control?
Various testing methods are employed to ensure the mechanical properties and integrity of cold-forged parts, including:
- Tensile Testing: Measures the strength and ductility of the material.
- Hardness Testing: Assesses the hardness of the forged parts to ensure they meet performance criteria.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic or magnetic particle inspection are used to detect internal flaws without damaging the part.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, verifying the quality control practices of potential suppliers is essential. Here are actionable steps:
-
Conduct Audits: Regularly audit suppliers to assess their manufacturing processes and quality control systems. This can be done in-person or through third-party services.
-
Request Quality Reports: Ask for detailed quality assurance reports that include results from testing methods and compliance with relevant standards.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilize independent inspection services to evaluate the quality of products before shipment. This adds an extra layer of assurance regarding the reliability of the supplier.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
When sourcing cold-forged products from different regions, B2B buyers must be aware of specific quality control nuances:
-
Regional Compliance: Understand the compliance requirements specific to the regions you are sourcing from, such as local regulations in Africa, South America, or the Middle East.
-
Cultural Differences: Be mindful of cultural differences in business practices and quality expectations. Building strong relationships with suppliers can help bridge these gaps.
-
Communication: Clear and consistent communication regarding quality expectations and standards is vital to prevent misunderstandings.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in cold forging, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and quality expectations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cold forged’
In the quest for high-quality cold-forged products, B2B buyers must navigate various aspects of sourcing effectively. This guide provides a structured checklist to assist international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe in procuring cold-forged components that meet their technical and commercial requirements.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is vital for ensuring the cold-forged components meet your requirements. Consider factors such as material type (e.g., stainless steel, aluminum), dimensions, tolerances, and mechanical properties. Documenting these specifications will serve as a reference for suppliers and help in evaluating their capabilities.
Step 2: Identify Reputable Suppliers
Finding reliable suppliers is crucial for successful procurement. Conduct thorough research to identify manufacturers with a strong reputation in cold forging. Look for suppliers that have experience in your specific industry and can demonstrate expertise in producing the required components.
- Check online directories and industry associations.
- Seek recommendations from industry peers and attend relevant trade shows.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications and Standards
Before engaging with a supplier, verify their certifications and adherence to industry standards. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality management. This step is essential to ensure the supplier employs consistent processes and can deliver high-quality products.
- Request documentation of certifications.
- Inquire about compliance with international standards relevant to your industry.
Step 4: Assess Manufacturing Capabilities
Understanding a supplier’s manufacturing capabilities will help you gauge whether they can meet your production needs. Evaluate their equipment, technology, and production processes. Suppliers should have advanced machinery capable of high-speed production with minimal waste, which is a hallmark of effective cold forging.
- Ask about their production capacity and lead times.
- Consider whether they offer custom solutions for unique specifications.
Step 5: Request Samples and Prototypes
Before finalizing your order, request samples or prototypes of the cold-forged components. This allows you to assess the quality and suitability of the product for your application. Testing samples can reveal potential issues and help you make an informed decision.
- Specify any testing requirements you have.
- Use the samples to evaluate the supplier’s attention to detail and adherence to specifications.
Step 6: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you are satisfied with a supplier’s capabilities and product quality, begin negotiating pricing and terms. Consider factors such as bulk discounts, payment terms, and shipping costs. Establishing a clear agreement will help avoid misunderstandings later in the procurement process.
- Compare pricing with multiple suppliers to ensure competitiveness.
- Discuss delivery timelines and any potential penalties for delays.
Step 7: Establish Communication Channels
Effective communication is critical throughout the sourcing process. Establish clear channels for ongoing dialogue with your supplier, ensuring you can address any issues that arise during production or delivery. Regular updates will help maintain a strong working relationship.
- Set expectations for response times and preferred communication methods.
- Schedule regular check-ins to discuss progress and address concerns.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline the procurement of cold-forged products, ensuring they receive high-quality components that meet their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cold forged Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Cold Forging?
When analyzing the cost structure of cold forged products, several components come into play. Understanding these can help international B2B buyers make informed decisions.
-
Materials: The type of metal used significantly impacts cost. Common materials for cold forging include stainless steel, carbon steel, brass, and aluminum. Prices fluctuate based on market conditions, availability, and quality. Buyers should consider sourcing materials from local suppliers to reduce costs associated with logistics.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential in the cold forging process, especially for tasks like setup and quality control. Labor costs can vary by region; for example, labor is generally more affordable in parts of Africa and South America compared to Europe. This aspect should be factored into the overall cost, especially for large-volume orders.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, maintenance of machinery, and facility expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes, such as automation, can help reduce overhead, thus lowering the overall cost of production.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs can be significant, especially for custom designs. The initial investment in dies and molds can be high, but they are amortized over the production volume. Buyers should inquire about tooling costs in relation to their order volume, as larger orders may lead to reduced per-unit tooling costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that products meet required specifications is crucial. Investing in robust QC processes may add to the upfront costs but can prevent costly defects and rework down the line. Certifications such as ISO can also influence pricing due to the associated compliance costs.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs vary widely, depending on the destination and shipping method. Buyers should consider Incoterms to clarify responsibilities regarding shipping and import duties, which can significantly affect total costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their costs and profit. This margin can be influenced by factors such as the supplier’s market position, reputation, and the complexity of the order.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Cold Forged Products?
Several factors can influence the pricing of cold forged products, making it essential for buyers to understand their implications.
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Bulk orders can lead to significant discounts. Suppliers often have a tiered pricing structure, so negotiating for larger quantities may yield cost savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized parts often incur higher costs due to the additional tooling and setup required. Buyers should clearly define their specifications to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Material Selection: The choice of material can drastically impact pricing. Premium materials may enhance product performance but can also elevate costs. Buyers should balance quality with budget constraints.
-
Quality and Certifications: Higher quality and certified products typically come with a premium price tag. Buyers in regulated industries may need to prioritize certified products, which can limit options but ensure compliance.
-
Supplier Factors: Relationships with suppliers can influence pricing. Long-term partnerships may lead to better pricing, while new suppliers might charge higher rates until a trust level is established.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for cost calculation. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) dictate who bears shipping costs and risks, which can impact overall pricing.
What Negotiation Tips Should International Buyers Consider?
For international buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation can lead to significant cost savings.
-
Research and Benchmarking: Understanding market prices and competitor offerings can provide leverage during negotiations. Buyers should gather quotes from multiple suppliers to establish a baseline.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Rather than just the upfront price, consider the total cost, including maintenance, logistics, and potential downtime. A slightly higher initial price may result in lower TCO if the product is more reliable.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing good relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Open communication fosters trust and can result in preferential treatment in future transactions.
-
Be Transparent: Sharing your production needs and challenges with suppliers can encourage them to offer tailored solutions that are cost-effective.
-
Flexible Terms: Be open to discussing payment terms, delivery schedules, and other contractual aspects that could yield savings for both parties.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for cold forged products can vary significantly based on market conditions, material availability, and supplier capabilities. Buyers should conduct thorough due diligence and request updated quotes to ensure accurate budgeting and financial planning.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cold forged With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Cold Forged Solutions
When evaluating metal forming processes, it’s essential for B2B buyers to understand the landscape of available solutions. Cold forging is a widely recognized method due to its efficiency and the strength of the resulting products. However, other alternatives such as hot forging, die casting, and aluminum forging may also meet specific needs based on factors like cost, performance, and application. This analysis will provide a comparative overview of cold forging against these alternatives, helping international buyers make informed decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | Cold Forged | Hot Forging | Die Casting | Aluminum Forging |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High strength, minimal waste | Excellent ductility, high yield strength | High dimensional accuracy, smooth finish | Good strength, complex shapes |
| Cost | Cost-effective for high volumes | Higher initial costs due to heating | Moderate to high, depending on complexity | Moderate, but less than casting |
| Ease of Implementation | Relatively straightforward | Requires specialized equipment | Complex setup, requires molds | Requires expertise in handling metals |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance | Moderate maintenance required | High maintenance due to molds | Low maintenance if processes are optimized |
| Best Use Case | High-volume production of strong parts | Large components needing ductility | Intricate designs, high-volume production | Lightweight components, automotive applications |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Hot Forging Compared to Cold Forging?
Hot forging involves shaping metal at high temperatures, which allows for greater ductility and less force required during the shaping process. This method is particularly beneficial for producing large components that require significant deformation. However, the energy costs associated with heating and the potential for scaling on the metal can increase overall production costs. B2B buyers might find hot forging advantageous for applications requiring high yield strength and low hardness, but it may not be as cost-effective for smaller, high-volume runs.
How Does Die Casting Compare to Cold Forging?
Die casting is a process that involves injecting molten metal into a mold to create complex shapes with high dimensional accuracy. This method excels in producing intricate designs at high volumes, resulting in a smooth finish that often requires little to no machining. However, the initial setup cost for molds can be high, making it less viable for low-volume production runs. For buyers requiring detailed components with consistent quality, die casting is an excellent alternative, but they must weigh the cost implications against their production needs.
Why Consider Aluminum Forging Over Cold Forging?
Aluminum forging, while similar to cold forging in terms of process, focuses specifically on aluminum alloys. This method is ideal for applications in the automotive and aerospace industries where lightweight yet strong components are necessary. Aluminum forging can create complex shapes that meet stringent weight requirements. However, while it can produce strong parts, it may not achieve the same level of strength as cold forging with high-carbon steel. Buyers should consider aluminum forging when weight is a critical factor, but they must assess whether the strength requirements align with their application’s demands.
How to Choose the Right Metal Forming Solution for Your Needs?
When selecting a metal forming solution, B2B buyers should evaluate their specific requirements, including performance criteria, production volume, and budget constraints. Understanding the unique advantages and limitations of each method—be it cold forging, hot forging, die casting, or aluminum forging—will enable buyers to make informed decisions. Consideration of factors such as material properties, design complexity, and long-term maintenance can further guide buyers in selecting the most suitable process for their manufacturing goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cold forged
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Cold Forged Parts?
Understanding the essential technical properties of cold forged components is crucial for B2B buyers looking to make informed purchasing decisions. Here are some of the critical specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific type of metal used in the cold forging process, which can significantly impact the performance and durability of the final product. Common materials include stainless steel, carbon steel, brass, and aluminum. Selecting the appropriate material grade ensures that the forged parts meet the required strength, corrosion resistance, and thermal stability for their intended application.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance defines the allowable variation in dimensions for a forged part. Precision in tolerance is vital in industries such as automotive and aerospace, where parts must fit together perfectly. A tighter tolerance often results in higher manufacturing costs but can lead to improved performance and longevity of the components.
3. Surface Finish
Surface finish refers to the texture and smoothness of a forged part. A high-quality surface finish reduces friction and wear, which is particularly important in moving parts. Cold forging typically produces parts with a better surface finish than other methods, minimizing the need for additional machining processes, thus saving time and costs.
4. Strength and Hardness
Cold forging increases the strength and hardness of metals by deforming them at room temperature. The mechanical properties of the finished product, such as yield strength and tensile strength, are critical for performance. Buyers should verify these properties against industry standards to ensure the parts will withstand operational stresses.
5. Production Rate
Production rate indicates the number of parts that can be produced in a specific timeframe. Cold forging offers high production rates, making it an attractive option for manufacturers who require large volumes of parts quickly. Understanding production rates can help buyers gauge lead times and plan inventory more effectively.
6. Formability
Formability measures how easily a material can be shaped without fracturing. Different metals have varying levels of formability, which can affect the design and complexity of the parts produced. Understanding this property helps buyers choose the right metal for their specific applications.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Cold Forging?
Familiarity with industry jargon can help B2B buyers navigate the complexities of cold forging. Here are some essential terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts that are used in another company’s end product. Understanding the role of OEMs is vital for buyers who need to ensure that the parts they purchase are compatible with existing systems or machinery.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is particularly important for international buyers, as it can influence inventory management and cost-effectiveness. Knowing the MOQ helps in negotiating terms and planning purchases accordingly.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a price quote for specific products or services. It is a crucial step in the procurement process, enabling buyers to compare costs and terms from different vendors. A well-prepared RFQ can streamline negotiations and lead to better pricing.
4. Incoterms
Incoterms, or International Commercial Terms, are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is essential for buyers to clarify shipping costs, risk, and delivery responsibilities, ensuring smoother transactions across borders.
5. Flash
In cold forging, flash is the excess material that flows out of the die during the forging process. While flash is often trimmed off, understanding its implications can assist buyers in assessing material efficiency and production costs.
6. Die Types
Cold forging can be performed using various die types, including open and closed dies. Each type offers distinct advantages for different applications. Familiarity with die types helps buyers understand the production process and the expected quality of the forged parts.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing cold forged components, ultimately leading to better outcomes for their operations.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cold forged Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Cold Forged Sector?
The cold forged sector is witnessing significant growth driven by increased demand for high-strength components across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. Globalization has opened new markets, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where industries are expanding rapidly. The rise of technology-driven manufacturing processes, such as automation and Industry 4.0, is reshaping sourcing strategies. These advancements enable manufacturers to optimize production efficiency, reduce lead times, and enhance product quality.
Emerging B2B technology trends include the adoption of additive manufacturing and digital twins, which allow for better simulation of the cold forging process and improved design accuracy. Additionally, the integration of data analytics and IoT solutions provides insights into production metrics, enabling suppliers to anticipate market needs and adapt quickly. For international buyers, particularly from regions like Nigeria and Egypt, this means access to more reliable and innovative sourcing options that align with their specific requirements.
Furthermore, the trend toward customization is growing, as businesses seek tailored solutions that meet unique specifications. This trend is particularly pronounced in sectors like construction and energy, where specific component designs are essential for operational efficiency. As a result, buyers are encouraged to engage with suppliers who offer flexibility in production capabilities and demonstrate a willingness to collaborate on custom projects.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Cold Forged Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming increasingly critical considerations for international B2B buyers in the cold forged sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including energy consumption and waste generation, is under scrutiny. Cold forging is inherently more sustainable compared to hot forging, as it operates at room temperature, reducing energy requirements and minimizing material waste. The ability to recycle excess material—such as flash generated during the forging process—further enhances its eco-friendly profile.
Moreover, ethical supply chains are gaining importance among consumers and businesses alike. Buyers are now looking for suppliers who prioritize transparency and accountability in their sourcing practices. This includes ensuring that raw materials are sourced responsibly, with a focus on reducing carbon footprints and promoting fair labor practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety) are increasingly sought after by buyers as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
In addition, the demand for “green” materials is rising, pushing suppliers to innovate and offer products that not only meet performance standards but also adhere to environmental regulations. For international buyers from regions like Europe and South America, aligning with suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability can enhance their corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives and improve their brand image.
What Is the Historical Context of Cold Forging and Its Relevance to Today’s Market?
Cold forging, a process that reshapes metal at room temperature, has its roots in the industrial revolution of the 19th century. Initially adopted for its efficiency and ability to produce high-strength components without the need for extensive finishing, cold forging has evolved significantly over time. The process gained popularity due to its cost-effectiveness and minimal material waste, making it an attractive option for manufacturers aiming to meet the growing demands of various industries.
As industries continue to evolve, the relevance of cold forging remains strong. Its ability to produce complex shapes and high-volume parts positions it as a vital manufacturing technique for modern applications. Today, international B2B buyers can benefit from the long-standing tradition of cold forging, leveraging its advantages to enhance their production capabilities and meet market demands effectively. As buyers seek reliable and sustainable sourcing options, understanding the historical context of cold forging can provide valuable insights into its continued importance in the global market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cold forged
-
How do I solve challenges related to sourcing cold forged components internationally?
To effectively source cold forged components internationally, start by identifying reliable suppliers through trade directories and industry associations. Engage in thorough due diligence by checking their certifications, client references, and production capabilities. Consider visiting their facilities if possible, as this can provide insight into their operational standards. Establish clear communication regarding quality expectations, delivery timelines, and compliance with international standards to mitigate risks associated with sourcing. -
What is the best cold forging method for producing high-strength components?
The best cold forging method for producing high-strength components typically involves closed-die forging. This method allows for precise shaping and enhances the mechanical properties of the metal by compressing it within custom-shaped dies. This process reduces material waste and often results in parts that require minimal finishing. For specific applications, consult with manufacturers to determine the most suitable method based on your component’s design and performance requirements. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for cold forged parts?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for cold forged parts can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the components. Generally, MOQs can range from a few hundred to several thousand pieces. It’s essential to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to understand their MOQ policies. Some manufacturers may offer flexibility for initial orders or prototypes, particularly for custom designs, which can be beneficial for businesses testing new products. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing cold forged products internationally?
Payment terms for international sourcing of cold forged products often include options such as advance payments, letters of credit, or net payment terms (e.g., 30, 60, or 90 days). Expect to negotiate these terms based on your relationship with the supplier and the size of the order. It’s advisable to establish clear payment schedules and methods to avoid any potential disputes. Always ensure that the payment terms align with your cash flow and financial policies. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) in cold forged products?
To ensure quality assurance in cold forged products, request detailed quality control processes from your suppliers. This may include certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality management systems. Discuss inspection protocols for raw materials and finished products, including dimensional checks and mechanical property testing. Establishing a clear QA agreement before production can help maintain high standards and avoid issues post-delivery. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing cold forged components?
When importing cold forged components, consider logistics aspects such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Choose between air freight for speed or sea freight for cost-effectiveness based on your delivery timelines. Ensure that your supplier provides proper documentation, including customs invoices and certificates of origin, to facilitate smooth customs clearance. Partnering with a reliable logistics provider familiar with international trade can streamline the process and minimize delays. -
Are there customization options available for cold forged parts?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for cold forged parts to meet specific application needs. Customization can include variations in size, shape, and material type. When discussing your requirements with potential suppliers, provide detailed specifications and any necessary drawings. Collaborating closely with the manufacturer during the design phase can help ensure that the final product meets your performance standards while optimizing production efficiency. -
What types of materials are commonly used in cold forging?
Common materials used in cold forging include various grades of steel (such as carbon steel and stainless steel), aluminum, brass, and copper. The choice of material depends on the application and the desired mechanical properties of the final product. It is crucial to communicate your specific requirements to suppliers, as they can recommend the most suitable material based on factors like strength, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness for your intended use.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cold forged
In conclusion, cold forging presents a highly efficient and cost-effective solution for international B2B buyers seeking reliable metal components. By utilizing cold forging, companies can achieve high production outputs while minimizing waste, making it an environmentally friendly option. The method’s ability to produce parts with enhanced mechanical properties at room temperature not only ensures durability but also reduces the need for secondary processing, ultimately lowering costs.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Cold Forging Procurement?
For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, strategic sourcing is crucial. It involves understanding market dynamics, supplier capabilities, and the specific needs of your operations. Engaging with trusted manufacturers can facilitate tailored solutions, ensuring the right materials and production techniques are employed to meet your unique specifications.
What’s Next for International B2B Buyers in Cold Forging?
As you navigate the cold forging landscape, consider forging partnerships with manufacturers that emphasize innovation and sustainability. The future of cold forging is bright, with advancements in technology promising even greater efficiencies. Take proactive steps now to secure your supply chain, optimize your sourcing strategies, and position your business for long-term success in this competitive market.