Top 4 Pellet Fuel Manufacturers List and Guide: How To Solve Scen…
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for pellet fuel manufacturers
In today’s rapidly evolving energy landscape, sourcing high-quality pellet fuel can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers. With a growing emphasis on sustainable energy solutions, manufacturers face the task of navigating a complex marketplace filled with diverse suppliers and varying product standards. This guide aims to simplify that process by providing a comprehensive overview of the pellet fuel manufacturing sector, focusing on key elements such as types of pellets, their applications, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations.
By understanding the nuances of pellet fuel, buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including countries like Saudi Arabia and Brazil—can make informed purchasing decisions. This guide empowers you to evaluate suppliers effectively, ensuring that you select the right products to meet your energy needs while adhering to sustainability goals. With insights into market trends and best practices for procurement, you will be equipped to navigate the global market confidently, securing quality products that align with your operational requirements and environmental commitments.
In the pages that follow, we delve into the intricacies of pellet fuel manufacturing, offering actionable insights that will enhance your procurement strategy and drive your business forward.
Top 10 Pellet Fuel Manufacturers Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Energy Pellets America – Fuel & Animal Bedding Pellets
Domain: energypelletsamerica.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Fuel Pellets: 40lb Bag – $5.99; One Ton Pallet (50 bags) – $275.00; Animal Bedding Pellets: 40lb Bag – $5.99; One Ton Pallet (50 bags) – $275.00.
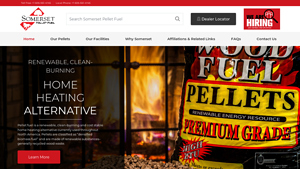
2. Somerset Pellets – Renewable Wood Fuel
Domain: somersetpellets.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Somerset Pellet Fuel is a renewable, clean-burning, and cost-stable home heating alternative made from 100% USA hardwoods. The pellets are classified as ‘densified biomass fuel’ and are produced from excess wood fiber and sawdust collected during the flooring and lumber manufacturing process at Merrick Hardwoods. Over 50,000 tons of wood fiber and sawdust are utilized annually to create this envir…
3. Greene Team Pellets – Hardwood
4. Hamers – Hot Ones
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: 1. Hamers Hot Ones: Best quality, hot, low ash, very clean burning.
2. Tractor Supply White Bag: Middle of the road, acceptable but not the best.
3. Maine Woods, Fireside Ultra, Green Team: Considered awful by some users.
4. Lignetics: Creates a lot of ash and soot, not recommended by some users.
5. Logik-e Softwood Pellets: Used by one user, not liked by their stove.
6. Clear Fire Softwood Pellet…
Understanding pellet fuel manufacturers Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wood Pellet Manufacturers | Focus on producing pellets from wood waste and biomass. | Residential heating, industrial energy generation. | Pros: Renewable, low emissions. Cons: Variability in quality. |
| Bedding Pellet Manufacturers | Specialize in creating pellets for animal bedding. | Livestock farming, equestrian facilities. | Pros: Absorbent, compostable. Cons: May require bulk storage. |
| Specialty Pellet Producers | Create niche products (e.g., BBQ, cooking pellets). | Restaurants, catering services, outdoor cooking. | Pros: Flavor enhancement, variety. Cons: Price variability. |
| Industrial Pellet Mills | Large-scale production for energy and manufacturing. | Power plants, manufacturing sectors. | Pros: Economies of scale, consistent supply. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Biomass Pellet Producers | Focus on sustainable biomass sources (agricultural residues). | Renewable energy projects, eco-friendly initiatives. | Pros: Sustainable, reduces waste. Cons: Supply chain complexities. |
What Are the Characteristics of Wood Pellet Manufacturers?
Wood pellet manufacturers primarily produce pellets from residual wood materials, such as sawdust and wood shavings. These pellets are commonly used for heating residential and commercial spaces, as well as for industrial energy generation. B2B buyers should consider the manufacturer’s adherence to quality standards, as the energy content and emissions can vary significantly. Additionally, buyers should evaluate the supply chain reliability, especially in regions where wood resources may be limited.
How Do Bedding Pellet Manufacturers Serve the Market?
Bedding pellet manufacturers focus on creating absorbent and compostable pellets specifically designed for animal bedding. These products are popular in livestock farming and equestrian facilities due to their high absorbency and ease of handling. B2B buyers must assess the bedding’s comfort and safety for animals, as well as the manufacturer’s production practices to ensure consistency and reliability. Bulk purchasing options can also provide cost advantages.
What Makes Specialty Pellet Producers Unique?
Specialty pellet producers create niche products, such as BBQ and cooking pellets, which enhance flavor and provide unique cooking experiences. These pellets cater to restaurants and catering services, making them an attractive option for businesses that prioritize quality and taste. Buyers should consider the variety of flavors available and the sourcing of raw materials, as these factors can influence the final product’s quality and price.
Why Choose Industrial Pellet Mills?
Industrial pellet mills focus on large-scale production, supplying pellets for energy and manufacturing sectors. These manufacturers benefit from economies of scale, ensuring a consistent supply of high-quality pellets. B2B buyers in power generation or large manufacturing should evaluate the mill’s capacity and reliability, as initial investments can be significant. Long-term contracts may also be beneficial for securing stable pricing and supply.
How Do Biomass Pellet Producers Contribute to Sustainability?
Biomass pellet producers utilize sustainable biomass sources, such as agricultural residues, to create pellets that support renewable energy initiatives. This approach not only reduces waste but also contributes to a circular economy. B2B buyers should consider the environmental impact of their purchases and the producer’s commitment to sustainable practices. However, supply chain complexities may arise, requiring careful planning and coordination.
Key Industrial Applications of pellet fuel manufacturers
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of pellet fuel manufacturers | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Production | Biomass Power Generation | Renewable energy source, reduces carbon footprint | Quality certifications, supply chain reliability, cost |
| Agriculture | Animal Bedding and Feed | Improved animal health and productivity | Material sourcing, sustainability practices, pricing |
| Residential Heating | Home Heating Solutions | Cost-effective, efficient heating alternative | Pellet quality standards, availability, local regulations |
| Food Industry | Cooking and BBQ Fuel | Enhanced flavor, sustainable cooking method | Sourcing from certified manufacturers, flavor profiles |
| Waste Management | Waste-to-Energy Conversion | Reduces landfill waste, generates energy | Compliance with regulations, feedstock consistency |
How Are Pellet Fuel Manufacturers Applied in Energy Production?
In the energy sector, pellet fuel manufacturers supply biomass pellets that serve as a renewable energy source for power generation. These pellets are burned in biomass power plants to produce electricity, offering a cleaner alternative to fossil fuels. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, it’s crucial to consider the quality certifications of the pellets to ensure they meet local environmental standards. Additionally, the reliability of the supply chain is essential to maintain continuous energy production.
What Role Do Pellet Fuel Manufacturers Play in Agriculture?
Pellet fuel manufacturers produce animal bedding and feed pellets that significantly benefit the agricultural sector. The use of these pellets can improve animal health, reduce bedding waste, and enhance overall productivity. For B2B buyers in the Middle East and Europe, sourcing pellets that are sustainably produced and free from harmful additives is vital. Price competitiveness and the availability of bulk purchasing options can also influence procurement decisions.
How Do Pellet Fuel Manufacturers Support Residential Heating Solutions?
In residential heating, pellet fuel manufacturers provide premium wood pellets for use in pellet stoves and boilers. These pellets offer an efficient and cost-effective heating solution, particularly in colder climates across Europe and North America. Buyers should pay attention to pellet quality standards, as this affects the efficiency and maintenance of heating appliances. Local regulations regarding emissions and energy efficiency can also impact sourcing decisions for international buyers.
In What Ways Do Pellet Fuel Manufacturers Enhance the Food Industry?
Pellet fuel manufacturers supply wood pellets specifically for cooking and BBQ applications, which enhance flavor and provide a sustainable cooking method. This application is particularly appealing to restaurants and catering businesses looking to differentiate their offerings. When sourcing, businesses should consider the flavor profiles of the pellets and ensure that they come from certified manufacturers to maintain food safety standards.
How Do Pellet Fuel Manufacturers Contribute to Waste Management Solutions?
Pellet fuel manufacturers play a crucial role in waste management through the production of pellets from organic waste materials for waste-to-energy conversion. This process not only reduces landfill waste but also generates energy, contributing to a circular economy. Buyers should focus on the compliance of manufacturers with local waste management regulations and the consistency of feedstock quality to ensure reliable energy production.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘pellet fuel manufacturers’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Quality of Pellet Fuels
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter issues with the inconsistent quality of pellet fuels from various manufacturers. This inconsistency can lead to inefficiencies in combustion, increased emissions, and even equipment damage. For instance, a buyer sourcing pellets for a biomass heating system may receive batches that vary significantly in moisture content, density, or ash content, affecting performance and increasing operational costs. This variability can disrupt supply chains and lead to frustration among end users who rely on stable heating solutions.
The Solution: To mitigate quality issues, buyers should prioritize sourcing from manufacturers who adhere to recognized quality standards, such as those established by the Pellet Fuels Institute (PFI) or similar organizations in their region. Establishing a robust supplier evaluation process is crucial; this includes checking for certifications, requesting sample batches for testing, and reviewing feedback from other clients. Additionally, implementing a consistent quality assurance protocol within their operations can help identify and rectify issues early, ensuring that only high-quality pellets are used in their systems. Buyers can also engage in direct communication with manufacturers to discuss specifications and quality expectations, fostering a partnership that prioritizes consistent delivery.
Scenario 2: Supply Chain Disruptions
The Problem: Global buyers face significant challenges in the logistics and supply chain of pellet fuels, especially in regions like Africa and South America where infrastructure may be lacking. Delays in shipping, unforeseen tariffs, or transportation issues can disrupt the timely delivery of pellet fuels, causing operational setbacks for businesses that depend on these fuels for heating or energy production. Such disruptions can lead to increased costs and lost revenue, as companies may have to scramble for alternative sources of fuel.
The Solution: To navigate supply chain issues effectively, buyers should diversify their supplier base to include multiple pellet fuel manufacturers. This strategy reduces dependency on a single source and provides alternatives in case of disruptions. Implementing just-in-time inventory practices can also help manage stock levels more efficiently, ensuring that companies are not over-reliant on any one shipment. Additionally, buyers should consider forming strategic partnerships with logistics providers who specialize in the transportation of bulk materials, as they can offer insights into the most reliable shipping routes and methods. Establishing clear communication channels with suppliers about delivery timelines and potential risks will also help in planning and mitigating disruptions.
Scenario 3: High Costs of Pellet Fuels
The Problem: As energy prices fluctuate, B2B buyers often face challenges in managing the costs associated with pellet fuels. This is particularly relevant in markets where alternative energy sources are rising in price, leading to increased demand and, consequently, higher prices for pellets. Buyers may find it difficult to justify these costs to stakeholders, especially if they are on a tight budget or if their clients are price-sensitive.
The Solution: To address high costs, buyers should conduct a thorough market analysis to understand pricing trends and negotiate better deals with manufacturers. Engaging in long-term contracts with suppliers can often secure lower prices compared to spot purchasing. Moreover, exploring the option of bulk purchasing can reduce per-unit costs significantly. Buyers should also evaluate their energy needs to ensure they are purchasing the right amount of pellets; over-purchasing can lead to unnecessary expenses. Additionally, considering the use of alternative biomass materials or blends can help reduce overall costs while maintaining energy output. Leveraging data analytics to forecast demand accurately can also assist buyers in making informed purchasing decisions, ultimately leading to more strategic financial planning.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for pellet fuel manufacturers
What Are the Key Materials Used in Pellet Fuel Manufacturing?
When selecting materials for pellet fuel production, manufacturers often consider wood, agricultural residues, and synthetic materials. Each of these materials has distinct properties, advantages, and limitations that can significantly influence production efficiency, cost, and end-product performance.
How Does Wood Perform as a Material for Pellet Fuel?
Wood is the most common material used in pellet fuel manufacturing, primarily due to its availability and high energy content. Key properties include a high calorific value (around 4,500 to 5,000 kcal/kg) and excellent combustion characteristics, which contribute to efficient energy production.
Pros: Wood pellets are generally durable, offer good storage stability, and have a lower ash content compared to other biomass materials. They are also widely accepted and recognized in international markets.
Cons: The primary limitations of wood include variability in moisture content, which can affect combustion efficiency, and the need for compliance with specific sustainability standards. Additionally, sourcing quality wood can sometimes be challenging, especially in regions where deforestation laws are stringent.
International Considerations: Buyers from regions such as Europe and North America may require compliance with standards like ENplus or DINplus for wood pellets, which ensure quality and sustainability. In contrast, buyers from Africa and South America may face different regulatory landscapes, necessitating a thorough understanding of local compliance requirements.
What Role Do Agricultural Residues Play in Pellet Fuel Production?
Agricultural residues, such as straw, corn stover, and rice husks, are increasingly being utilized in pellet fuel manufacturing. These materials are often abundant and inexpensive, providing an eco-friendly alternative to traditional wood pellets.
Pros: Agricultural residues are typically low-cost and can be sourced locally, reducing transportation costs. They also contribute to waste reduction, aligning with sustainability goals.
Cons: However, agricultural residues often have a lower energy density compared to wood, which can lead to higher transportation costs if not sourced locally. Additionally, the variability in composition can result in inconsistent pellet quality.
International Considerations: In regions like Brazil, where agricultural production is high, buyers may find a ready supply of residues. However, they should also consider local agricultural practices and regulations that may impact the availability and processing of these materials.
How Do Synthetic Materials Impact Pellet Fuel Quality?
Synthetic materials, including plastics and other non-biodegradable substances, are sometimes used to enhance pellet durability or improve combustion properties.
Pros: The use of synthetic materials can lead to increased pellet strength and reduced breakage during transportation. They can also enhance the combustion properties of the pellets, leading to higher efficiency.
Cons: The primary drawback is that synthetic materials can produce harmful emissions during combustion, which raises environmental concerns. Additionally, sourcing and processing synthetic materials can be more complex and costly compared to natural biomass.
International Considerations: Buyers in regions with stringent environmental regulations, such as the EU, may face significant challenges in using synthetic materials due to compliance with emissions standards. Understanding local regulations is crucial to avoid penalties.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Pellet Fuel Manufacturers
| Material | Typical Use Case for pellet fuel manufacturers | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wood | Primary feedstock for high-quality pellets | High calorific value and combustion efficiency | Variability in moisture content | Medium |
| Agricultural Residues | Alternative feedstock, often locally sourced | Low cost and sustainability benefits | Lower energy density and inconsistent quality | Low |
| Synthetic Materials | Enhancing pellet durability and combustion | Increased strength and reduced breakage | Potential harmful emissions during combustion | High |
This guide provides an overview of the strategic material selection considerations for pellet fuel manufacturers, emphasizing the importance of understanding both the properties of materials and the regulatory landscape in different international markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for pellet fuel manufacturers
What Are the Main Stages in Pellet Fuel Manufacturing?
The manufacturing process of pellet fuels involves several key stages, each crucial for ensuring the quality and efficiency of the final product. These stages include material preparation, forming, drying, cooling, and packaging.
How Is Material Prepared for Pellet Production?
Material preparation is the first stage and involves sourcing raw materials, which are typically wood residues such as sawdust, wood chips, and shavings. These materials must be clean, free from contaminants, and suitable for pelletizing.
The raw materials undergo size reduction through grinding to achieve a uniform particle size, which is essential for consistent pellet quality. Additionally, moisture content must be monitored and adjusted; optimal moisture levels range from 10% to 15%. This is crucial, as high moisture can lead to poor pellet formation, while too little moisture can cause the pellets to crumble.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Process?
The next stage is forming, where the prepared material is compressed into pellets using high-pressure pellet mills. This process typically involves the following techniques:
-
Pelletizing: The ground material is fed into a pellet mill where it is subjected to heat and pressure. The friction generated during compression softens the lignin in the wood, which acts as a natural binder.
-
Die and Roller Configuration: The configuration of the die and rollers plays a significant role in the formation of pellets. Different die designs can produce pellets of varying sizes and densities, tailored to meet specific market demands.
-
Quality Control During Forming: Continuous monitoring of parameters such as temperature, pressure, and feed rate during the pelletizing process ensures uniformity in pellet size and quality.
How Are Pellets Finished and Packaged?
After forming, the pellets undergo a cooling process to stabilize their structure. Cooling is critical as it helps reduce the risk of dust formation and enhances the durability of the pellets. Once cooled, the pellets are screened to remove fines and irregular particles.
The final step involves packaging, where pellets are typically bagged in 40lb bags or loaded onto pallets for bulk shipping. Proper packaging is essential for protecting the pellets from moisture and contamination during transport and storage.
What Are the Key Quality Assurance Standards for Pellet Fuel Manufacturers?
Quality assurance (QA) in pellet fuel manufacturing is vital to ensure product consistency, safety, and regulatory compliance. International standards such as ISO 9001 provide a framework for establishing effective quality management systems.
Which International and Industry-Specific Standards Should Buyers Be Aware Of?
-
ISO 9001: This standard outlines criteria for a quality management system and is applicable to any organization, regardless of size or industry. Adherence to ISO 9001 indicates a commitment to quality and customer satisfaction.
-
ENplus Certification: This is a specific certification for wood pellets, ensuring that pellets meet stringent quality criteria related to production, handling, and marketing. ENplus standards cover aspects such as pellet dimensions, ash content, and energy content.
-
Biomass Quality Assurance (BQA): This certification ensures that manufacturers adhere to best practices in sustainability and quality control throughout the production process.
-
API Standards: The American Petroleum Institute (API) provides standards for quality assurance in biofuels, which may also apply to pellet fuels.
How Are Quality Control Checkpoints Implemented in Pellet Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is integrated throughout the manufacturing process, with specific checkpoints established to monitor quality at various stages:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival. Key parameters include moisture content, particle size, and contamination levels.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During production, real-time monitoring of temperature, pressure, and pellet density is performed. This ensures that any deviations from the set parameters are immediately addressed.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After cooling and before packaging, a final inspection is conducted. This includes testing for pellet durability, energy content, and ash content to ensure compliance with relevant standards.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Pellet Fuel Quality Assurance?
Various testing methods are employed to ensure the quality of pellet fuels:
-
Durability Testing: This assesses how well the pellets hold together during handling and transportation. It typically involves subjecting pellets to mechanical stress and measuring the percentage of fines produced.
-
Moisture Content Testing: Accurate moisture content is crucial for combustion efficiency. This is often measured using a moisture meter or oven-drying methods.
-
Calorific Value Testing: This determines the energy content of the pellets, which is essential for evaluating performance in heating applications.
-
Ash Content Testing: Lower ash content is preferred for cleaner combustion. This is typically assessed through combustion tests.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers should conduct thorough due diligence when selecting pellet fuel suppliers to ensure their quality control processes align with industry standards. Here are some actionable steps:
-
Request Certification Documentation: Buyers should request copies of relevant certifications (ISO 9001, ENplus, etc.) and verify their validity.
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: On-site audits allow buyers to assess the supplier’s manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and adherence to standards directly.
-
Review Quality Assurance Reports: Regular quality assurance reports can provide insight into the supplier’s consistency in meeting quality standards.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing independent third-party inspectors can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality control processes.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly those from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control is essential.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have varying regulations regarding biomass fuels. It’s crucial for buyers to understand these regulations and ensure their suppliers are compliant.
-
Cultural Considerations: Cultural differences may affect communication and expectations regarding quality. Establishing clear communication channels and expectations is vital.
-
Logistical Challenges: Shipping and logistics can impact the quality of pellets. Buyers should ensure that suppliers have robust packaging and handling processes to mitigate any risks during transport.
By thoroughly understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in pellet fuel production, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and sustainability goals.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘pellet fuel manufacturers’
Introduction
Navigating the procurement of pellet fuel can be complex, especially for B2B buyers in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This step-by-step checklist serves as a practical guide to help you source reliable pellet fuel manufacturers effectively. By following these steps, you can ensure that your procurement process is efficient, cost-effective, and aligned with your specific needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to suppliers, clearly outline your technical requirements. This includes the type of pellets (e.g., wood, biomass), intended use (heating, animal bedding, etc.), and desired quality standards. Defining these specifications upfront will help you communicate your needs effectively and ensure that suppliers can meet your expectations.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential manufacturers. Utilize online directories, industry associations, and trade shows to compile a list of companies. Pay attention to their market presence, reputation, and product offerings to ensure they align with your requirements.
- Tip: Check online reviews and testimonials to gauge customer satisfaction.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verify that potential suppliers hold relevant certifications that validate their quality and sustainability practices. Look for certifications such as ISO, ENplus, or others that ensure adherence to industry standards. This step is crucial to ensure that the pellets meet safety and environmental regulations.
- Why it matters: Certifications can significantly impact the quality and reliability of the product you receive.
Step 4: Request Samples
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request samples of their pellets. Testing these samples allows you to assess their quality, moisture content, and combustion efficiency. This hands-on evaluation is essential for confirming that the product meets your specifications.
- Consideration: Be specific about what you want tested, such as ash content and energy output.
Step 5: Assess Pricing and Terms
After evaluating samples, compare pricing and payment terms among the shortlisted suppliers. Look for transparency in pricing structures and understand the terms of delivery and payment. This will help you make an informed decision that aligns with your budget and cash flow requirements.
- Important: Consider the total cost of ownership, including shipping and potential tariffs, especially for international transactions.
Step 6: Conduct Site Visits
If feasible, arrange visits to the suppliers’ manufacturing facilities. Site visits provide insight into their production processes, quality control measures, and overall operations. Engaging directly with the supplier can also foster a better working relationship.
- Benefit: Personal interactions can help build trust and facilitate smoother communication in future transactions.
Step 7: Finalize the Contract
Once you’ve selected a supplier, draft a comprehensive contract that outlines the agreed-upon terms. Include specifics about delivery schedules, quality expectations, and dispute resolution processes. A well-defined contract protects both parties and ensures accountability.
- Recommendation: Consult legal professionals to review the contract before signing, especially in cross-border agreements.
By following this checklist, you can streamline your sourcing process and establish a successful partnership with pellet fuel manufacturers that meet your operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for pellet fuel manufacturers Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Pellet Fuel Manufacturers?
Understanding the cost structure of pellet fuel manufacturing is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to optimize their sourcing strategies. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The price of raw materials, such as wood fiber or agricultural residues, varies significantly based on geographic availability and market conditions. For instance, sourcing from local suppliers can reduce costs compared to importing materials.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass wages, benefits, and training for staff involved in production. In regions with higher wage standards, manufacturers may experience increased operational costs, which can affect pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, maintenance, and facility costs. Efficient energy use and facility management can help lower overhead expenses, thus impacting the overall pricing strategy.
-
Tooling and Equipment: Initial investment in machinery and ongoing maintenance costs can be substantial. Advanced technology may lead to higher upfront costs but can improve efficiency and product quality in the long run.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality through rigorous QC processes adds to the cost. However, it is essential for maintaining certifications and meeting buyer specifications, which can justify higher prices.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs are a significant factor, particularly for international shipping. Factors such as distance, shipping methods, and fuel prices can greatly influence the final cost of pellet fuel.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically add a profit margin to their costs, which varies based on market competition, demand, and the unique value proposition of their products.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Pellet Fuel Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of pellet fuels, which B2B buyers should consider:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often attract discounts, making it essential for buyers to assess their needs accurately. Understanding the balance between inventory costs and order size can lead to significant savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom requirements may lead to higher prices due to additional processing or unique material sourcing. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against potential cost increases.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Premium materials and certifications (e.g., ENplus, DINplus) can enhance product value but also increase costs. Buyers should evaluate whether the added expense aligns with their operational goals.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record and quality assurance, while newer entrants might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms and responsibilities under Incoterms can affect total costs. Buyers should clarify who bears the costs and risks at various stages of transport to avoid unexpected expenses.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency?
To achieve cost-efficiency in sourcing pellet fuels, B2B buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers regarding pricing. Highlighting long-term purchasing commitments or bulk orders can leverage better rates.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond initial purchase price, consider logistics, storage, and maintenance costs. TCO provides a comprehensive view of expenses associated with a product over its lifecycle.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding local market dynamics, import duties, and currency fluctuations is vital. Engaging local experts can help navigate these complexities.
-
Market Research: Staying informed about market trends and competitor pricing can provide leverage in negotiations and help identify the best sourcing opportunities.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
It is important to note that prices for pellet fuels can fluctuate based on market conditions, raw material availability, and geopolitical factors. Always seek updated quotations from suppliers to ensure accurate budgeting and financial planning.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing pellet fuel manufacturers With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Pellet Fuel Manufacturers for Energy Solutions
In the pursuit of sustainable energy solutions, businesses often evaluate various options to meet their heating and energy needs. While pellet fuel manufacturers provide a reliable source of biomass energy, it is essential to consider other viable alternatives that may better suit specific operational requirements. This analysis explores two such alternatives: natural gas heating and electric heating solutions.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Pellet Fuel Manufacturers | Natural Gas Heating | Electric Heating |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency; consistent heat output | High efficiency; rapid heat delivery | Variable efficiency; dependent on source |
| Cost | Moderate initial cost; ongoing fuel costs | Lower initial costs; fluctuating fuel prices | Higher initial costs; stable electricity rates |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires storage and specialized equipment | Easier installation; existing infrastructure in many areas | Requires electrical upgrades; complex for large scale |
| Maintenance | Moderate maintenance; regular cleaning of stoves | Low maintenance; occasional inspections | Minimal maintenance; electrical checks |
| Best Use Case | Residential heating; agricultural applications | Industrial processes; residential heating | Urban residential; small businesses |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Natural Gas Heating: What Are Its Advantages and Disadvantages?
Natural gas heating systems offer high efficiency and rapid heat delivery, making them ideal for both residential and industrial applications. The initial installation costs are generally lower than those for pellet systems, especially in areas where gas infrastructure is already established. However, natural gas prices can be volatile, impacting long-term operational costs. Additionally, the reliance on fossil fuels raises concerns about sustainability and environmental impact, making it a less attractive option for environmentally conscious businesses.
Electric Heating: Is It a Sustainable Option?
Electric heating is increasingly popular due to its convenience and minimal maintenance requirements. This method allows for precise temperature control and can be powered by renewable energy sources, contributing to lower carbon footprints. However, the initial setup costs can be higher, particularly for large-scale applications. Moreover, the efficiency of electric heating systems can vary significantly based on the energy source, leading to potential cost fluctuations. This solution is best suited for urban environments and smaller businesses where infrastructure is readily available.
Conclusion: How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Energy Solution?
When evaluating energy solutions, B2B buyers should carefully consider their specific needs, including performance requirements, cost constraints, and maintenance capabilities. Pellet fuel manufacturers excel in providing a renewable energy source with moderate costs and efficiency, particularly for agricultural and residential applications. In contrast, natural gas heating offers rapid heat delivery with lower initial costs but poses sustainability challenges. Electric heating presents a clean, efficient option, albeit with higher upfront investments. Ultimately, the right choice will depend on the operational context, budget, and long-term sustainability goals of the business.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for pellet fuel manufacturers
What Are the Key Technical Properties for Pellet Fuel Manufacturers?
Understanding the technical specifications of pellet fuel is crucial for manufacturers and buyers alike. Here are some essential properties that impact the quality, performance, and marketability of pellet fuel:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the quality of the raw materials used in pellet production. High-grade materials, such as hardwood sawdust, result in denser and more energy-efficient pellets. For B2B buyers, selecting pellets made from premium materials ensures better combustion efficiency, lower ash content, and reduced emissions, making it vital for regulatory compliance and environmental standards.
2. Moisture Content
Moisture content is a critical specification that affects the energy output and combustion efficiency of pellets. Ideally, wood pellets should have a moisture content between 4% and 8%. Higher moisture levels can lead to lower heating values and increased production of smoke and ash. For manufacturers, maintaining optimal moisture levels is essential for product consistency and performance, while for buyers, it influences heating costs and efficiency.
3. Durability and Hardness
Durability measures how well pellets resist disintegration during handling and transportation. Hardness is often assessed through a durability test, where pellets are subjected to mechanical stress. High durability ratings reduce waste and ensure that pellets maintain their integrity during shipping. For buyers, this translates into better value and fewer logistical challenges.
4. Calorific Value
Calorific value indicates the amount of energy produced when the pellets are burned. It is typically measured in megajoules per kilogram (MJ/kg) or British thermal units (BTU). Higher calorific values mean more energy and heat generation, which is essential for heating applications. Buyers should prioritize pellets with high calorific values to maximize their heating efficiency and reduce fuel costs.
5. Ash Content
Ash content is the residual material left after combustion. Low ash content is preferable as it minimizes the need for frequent cleaning and maintenance of stoves or boilers. For manufacturers, achieving low ash levels often requires careful selection of feedstock and production processes. Buyers benefit from lower operational costs and enhanced efficiency.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Pellet Fuel Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon is vital for effective communication and negotiation between manufacturers and buyers. Here are some common trade terms that every stakeholder should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the pellet industry, OEMs might provide specialized equipment for pellet production. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and enhance product quality.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. In pellet manufacturing, MOQs can vary based on production capabilities and market demand. Buyers should be aware of MOQs to manage inventory effectively and negotiate favorable purchasing terms.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. In the pellet industry, issuing an RFQ helps buyers compare prices, quality, and delivery terms from multiple manufacturers, ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in the shipping process. They clarify who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and risk during transit. Understanding Incoterms helps both manufacturers and buyers avoid misunderstandings and disputes regarding shipping responsibilities.
5. Certification Standards
Certification standards, such as those from the Pellet Fuels Institute (PFI), ensure that pellet products meet specific quality and environmental criteria. Manufacturers seeking certification can improve their marketability, while buyers can use certification as a quality assurance measure to select reliable suppliers.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, optimize their purchasing processes, and foster successful partnerships within the pellet fuel industry.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the pellet fuel manufacturers Sector
What are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Pellet Fuel Sector?
The global pellet fuel market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing energy demands and a shift towards renewable energy sources. Countries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are recognizing the potential of wood pellets as a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. This trend is particularly pronounced in regions such as Saudi Arabia and Brazil, where energy diversification strategies are being implemented. The market is projected to expand due to rising investments in biomass energy and the ongoing transition to low-carbon economies.
Emerging technologies play a crucial role in shaping the sourcing landscape for international B2B buyers. Advanced manufacturing processes, such as automated pellet mills and quality control systems, enhance production efficiency and product consistency. Moreover, digital platforms are facilitating better supply chain management, allowing buyers to source materials directly from manufacturers. This trend is particularly beneficial for buyers in developing regions, providing them with access to global markets and competitive pricing.
Additionally, the rising importance of energy security is influencing sourcing strategies. Countries are increasingly looking to local suppliers to reduce reliance on imported fuels, thus fostering the growth of regional pellet manufacturing. Buyers should remain vigilant about market fluctuations, regulatory changes, and technological advancements that can impact sourcing dynamics.
How is Sustainability Shaping the Sourcing Strategies for Pellet Fuel Manufacturers?
Sustainability is at the forefront of the pellet fuel industry, compelling manufacturers to adopt environmentally responsible practices. The environmental impact of pellet production, particularly concerning deforestation and land use, has led to increased scrutiny from consumers and regulatory bodies alike. International B2B buyers are now prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable sourcing and production methods.
Ethical supply chains are becoming essential as buyers seek transparency regarding the origin of raw materials. Manufacturers are increasingly obtaining certifications such as the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) or Sustainable Forestry Initiative (SFI), which assure buyers that their products are sourced responsibly. These certifications not only enhance brand credibility but also align with the growing consumer demand for eco-friendly products.
Furthermore, incorporating ‘green’ materials into pellet production—such as agricultural residues and waste wood—can significantly reduce the environmental footprint of the manufacturing process. Buyers should evaluate their suppliers’ sustainability credentials and consider integrating sustainable sourcing practices into their procurement strategies to meet both regulatory requirements and consumer expectations.
What is the Historical Context of Pellet Fuel Manufacturing?
The pellet fuel industry has evolved significantly since its inception in the late 20th century. Initially, wood pellets were primarily used for residential heating in Europe and North America. However, as awareness of climate change and renewable energy sources grew, the industry began to expand its focus. The introduction of stringent regulations aimed at reducing carbon emissions spurred innovation in pellet manufacturing techniques, resulting in higher-quality products.
Over the past two decades, the market has diversified, with pellets now being utilized for various applications, including industrial heating and power generation. This evolution reflects a broader trend towards sustainable energy solutions, positioning the pellet fuel sector as a vital player in the global energy landscape. For B2B buyers, understanding this historical context can provide valuable insights into the sector’s growth trajectory and future potential.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of pellet fuel manufacturers
How do I solve supply chain disruptions when sourcing pellet fuel?
To address supply chain disruptions, establish strong relationships with multiple pellet fuel manufacturers across different regions. Diversifying your supplier base can mitigate risks associated with reliance on a single source. Regular communication with suppliers about their production capabilities and logistics can also help you anticipate potential issues. Implementing a robust inventory management system will enable you to maintain adequate stock levels and reduce the impact of any delays.
What is the best way to evaluate pellet fuel manufacturers for quality?
When evaluating pellet fuel manufacturers, consider their adherence to recognized quality standards such as the Pellet Fuels Institute (PFI) certification. Request samples for testing the pellets’ density, moisture content, and ash content, which are critical quality indicators. Additionally, review the manufacturer’s production processes and sustainability practices. Checking references and customer reviews can also provide insights into their reliability and product performance.
How can I negotiate favorable payment terms with pellet fuel suppliers?
To negotiate favorable payment terms, begin by researching industry standards and the financial health of potential suppliers. Propose terms that reflect your purchasing volume and frequency, which can justify requests for extended payment periods or discounts for upfront payments. Building a strong relationship with your supplier can also foster goodwill, making them more amenable to your terms. Always document any agreed-upon terms in a formal contract to avoid future disputes.
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for pellet fuel?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for pellet fuel can vary significantly depending on the manufacturer and region. Generally, MOQs can range from a few tons to several hundred tons. Larger manufacturers may offer more flexible MOQs, especially for regular customers. It is advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers and explore options for bulk purchasing to optimize costs and logistics.
How do I ensure compliance with international trade regulations when importing pellets?
Ensuring compliance with international trade regulations involves understanding both your home country’s import regulations and the exporting country’s export laws. Familiarize yourself with tariffs, customs documentation, and any specific health or safety standards applicable to pellet fuel. Working with a logistics partner experienced in international trade can simplify this process, as they can assist with documentation and ensure that shipments meet all regulatory requirements.
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing pellet fuel internationally?
When sourcing pellet fuel internationally, consider transportation modes, costs, and delivery times. Sea freight is often the most cost-effective for large shipments, but it may take longer than air freight. Evaluate the logistics capabilities of your suppliers, including their shipping partners and warehousing options. Ensure clear communication about delivery schedules and any potential customs delays to avoid disruptions in your supply chain.
How can I customize pellet fuel products to meet specific needs?
Customization of pellet fuel products may involve adjusting the pellet size, density, or blend of materials used. Engage directly with manufacturers to discuss your specific requirements and explore their capacity for customization. Many manufacturers are willing to accommodate specific formulations or packaging options, especially for larger orders. Be prepared to conduct trials to ensure that the customized pellets meet your performance expectations.
What quality assurance processes should I expect from pellet fuel manufacturers?
Expect pellet fuel manufacturers to implement rigorous quality assurance processes, including raw material inspections, in-process testing, and final product evaluations. They should provide documentation on their quality control measures and certifications. Inquire about their testing protocols for parameters such as moisture content, ash content, and calorific value. Regular audits and compliance checks can also provide assurance of their commitment to maintaining high standards.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for pellet fuel manufacturers
What Are the Key Insights for B2B Buyers in the Pellet Fuel Market?
As we conclude this guide, it is essential to recognize the growing significance of strategic sourcing in the pellet fuel industry. Buyers must prioritize partnerships with manufacturers that demonstrate commitment to quality, sustainability, and innovation. By choosing suppliers who adhere to industry standards, buyers can ensure a reliable supply chain that meets both regulatory requirements and customer expectations.
Furthermore, understanding market dynamics and regional preferences, especially in key markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, can enhance procurement strategies. This knowledge allows buyers to navigate fluctuations in pricing and availability while capitalizing on opportunities for growth in renewable energy sectors.
How Can International Buyers Prepare for Future Opportunities?
Looking ahead, the demand for pellet fuel is poised for growth, driven by increasing energy needs and a global shift towards sustainable practices. International buyers should actively seek out manufacturers that not only offer competitive pricing but also prioritize eco-friendly practices. Engaging with industry events and networks can provide valuable insights and foster connections with potential suppliers.
In summary, leveraging strategic sourcing in the pellet fuel market is critical for achieving long-term success. Take the initiative today to explore partnerships that align with your sustainability goals and operational needs. Embrace the future of energy with confidence.