The Ultimate Guide to Us Electrical Plug Types (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for us electrical plug types
In the global marketplace, understanding the complexities of US electrical plug types is crucial for businesses looking to ensure compatibility and safety in their operations. International B2B buyers face the challenge of sourcing the right electrical components that not only meet their operational needs but also comply with local standards and regulations. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, detailing the various types of electrical plugs and sockets used in the United States, including Type A and Type B, along with their specific applications, voltage requirements, and safety features.
Navigating the nuances of US electrical plug types can be daunting, particularly for buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where plug standards may differ significantly. This guide is designed to empower these buyers by providing actionable insights on sourcing, supplier vetting, and cost considerations. By understanding the electrical infrastructure of the US, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their procurement processes.
Furthermore, this guide addresses common concerns, such as the necessity of travel adapters and voltage converters, ensuring that international companies can seamlessly integrate their operations within the US market. With a focus on practicality and expertise, we aim to facilitate a smoother transition for businesses looking to expand their reach into the American landscape.
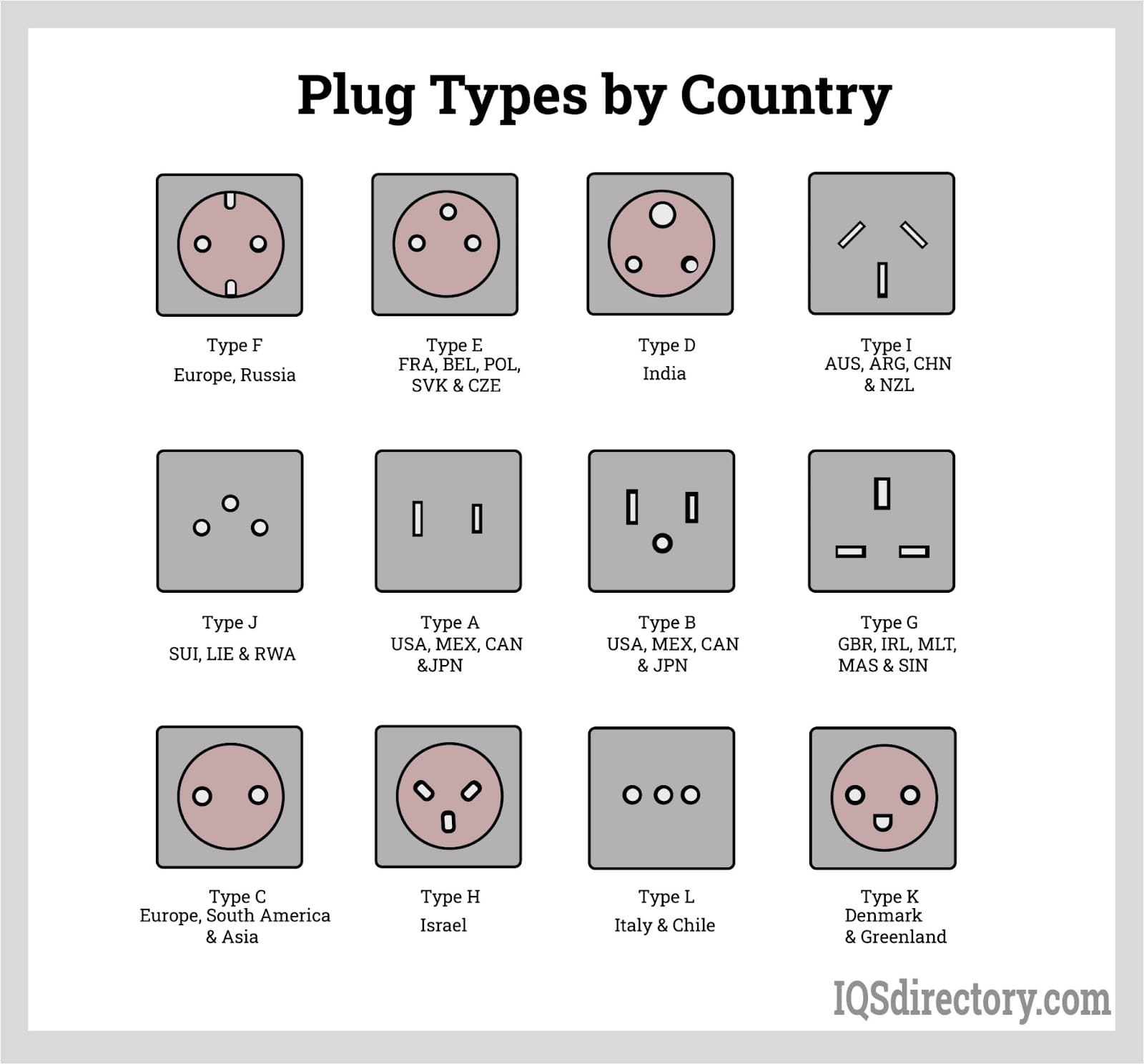
Understanding us electrical plug types Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type A | Two flat parallel pins | General appliances, small electronics | Pros: Widely used; easy to find adapters. Cons: Limited grounding; not suitable for high-power devices. |
| Type B | Two flat parallel pins and one round pin | Commercial appliances, heavy-duty electronics | Pros: Grounded for safety; supports higher power loads. Cons: Less common in some regions; may require adapters. |
| Type C | Two round pins | International equipment, travel adapters | Pros: Common in many countries; versatile. Cons: Requires adapter for use in the US; not suitable for high-power devices. |
| Type D | Three round pins in a triangular configuration | Industrial machinery, specialized equipment | Pros: High power capacity; stable connection. Cons: Limited availability in the US; requires specialized outlets. |
| Type I | Two flat pins in a V-shape and one grounding pin | Electrical appliances, power tools | Pros: High safety standards; supports high current. Cons: Not compatible with US plugs; requires adapters. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of Type A Plugs?
Type A plugs feature two flat parallel pins and are primarily used for small appliances and electronics. They are commonly found in North America and parts of Japan. For B2B buyers, it’s crucial to consider the limited grounding capability of Type A plugs, which may pose safety risks when connecting high-power devices. While they are easy to find and adapt to, their suitability is primarily for low-wattage applications.
Why Choose Type B Plugs for Heavy-Duty Applications?
Type B plugs include two flat parallel pins and a round grounding pin, making them suitable for commercial and heavy-duty applications. Their grounding feature enhances safety when using high-power devices such as industrial machinery. B2B buyers should note that while Type B plugs are more robust, they may not be as readily available in certain regions, necessitating the purchase of adapters or converters.
How Does Type C Plug Adaptability Benefit International Buyers?
Type C plugs, characterized by two round pins, are widely used in many countries outside the US, making them ideal for international equipment and travel adapters. They are versatile and can be adapted easily for various devices. However, B2B buyers should be aware that Type C plugs are not suitable for high-power applications, and an adapter is needed for compatibility in the US market.
What are the Advantages of Using Type D Plugs in Industrial Settings?
Type D plugs are distinguished by their three round pins arranged in a triangular configuration. They are designed for industrial machinery and specialized equipment, providing a stable connection and high power capacity. B2B buyers must consider that Type D plugs are not commonly found in the US and may require specialized outlets, making them less convenient for general use but essential for specific industrial applications.
Why Consider Type I Plugs for Electrical Appliances?
Type I plugs feature two flat pins in a V-shape along with a grounding pin, making them suitable for various electrical appliances and power tools. Their design adheres to high safety standards, allowing for a higher current capacity. However, B2B buyers should note that Type I plugs are not compatible with US sockets, requiring adapters for use in the US market. This factor should be considered when planning for equipment compatibility.
Key Industrial Applications of us electrical plug types
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of US Electrical Plug Types | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Powering industrial machinery using Type B plugs | Ensures reliable operation of machinery, reducing downtime | Compatibility with local voltage and frequency standards |
| Healthcare | Medical equipment that requires Type A/B plugs | Facilitates safe and efficient operation of critical devices | Compliance with medical safety regulations |
| Hospitality | Use of appliances like coffee machines and chargers | Enhances guest experience through reliable amenities | Need for multiple plug types to accommodate diverse guests |
| Construction | Tools and equipment using Type B plugs | Improves efficiency on-site with reliable power supply | Durability and weather resistance of plugs and sockets |
| Retail | Point of Sale (POS) systems using Type A plugs | Ensures seamless transactions and customer satisfaction | Need for robust power solutions to handle peak hours |
How Are US Electrical Plug Types Utilized in Manufacturing?
In the manufacturing sector, Type B plugs are commonly used to power industrial machinery. These plugs provide a secure connection for heavy equipment that requires a reliable power supply. International buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure that their machinery is compatible with the 120V, 60Hz standard in the U.S. This helps prevent operational disruptions and reduces the risk of equipment damage due to improper voltage.
What Are the Applications of US Electrical Plug Types in Healthcare?
Healthcare facilities frequently utilize medical equipment that requires Type A and B plugs for operation. This includes devices such as patient monitors, infusion pumps, and diagnostic machines. For buyers in the Middle East and Europe, understanding the voltage and safety compliance is crucial, as these devices must meet strict health regulations. Ensuring compatibility with U.S. standards can facilitate smoother operations and enhance patient care.
How Do US Electrical Plug Types Enhance Hospitality Services?
In the hospitality industry, Type A and B plugs are essential for powering guest amenities like coffee machines, hairdryers, and charging stations. This enhances the overall guest experience by providing reliable access to essential services. For international buyers, especially from Europe and Africa, it is critical to source equipment that can seamlessly integrate with U.S. electrical systems to avoid inconveniences for guests.
What Role Do US Electrical Plug Types Play in Construction?
Construction sites often rely on tools and equipment that utilize Type B plugs for power. These plugs are designed to handle the demands of heavy-duty tools, ensuring efficient operation in various conditions. Buyers from regions with different electrical standards should consider the durability and weather resistance of the plugs and sockets used on-site, which can significantly impact project timelines and safety.
How Are US Electrical Plug Types Critical for Retail Operations?
In the retail sector, Point of Sale (POS) systems commonly use Type A plugs. These systems must operate reliably to ensure seamless transactions and enhance customer satisfaction. International B2B buyers should focus on sourcing robust power solutions that can withstand high traffic periods, ensuring that their retail operations remain uninterrupted during peak hours. Compatibility with U.S. electrical standards is essential for maintaining operational efficiency.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘us electrical plug types’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Voltage Compatibility Issues in Equipment Sourcing
The Problem:
Many B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East often encounter difficulties when sourcing electrical equipment that operates on different voltage standards. The standard voltage in the United States is 120V at 60Hz, which can be incompatible with devices designed for higher voltages commonly found in other parts of the world, such as 220V in Europe or Africa. This discrepancy can lead to costly equipment failures, operational delays, and the need for additional voltage converters, complicating logistics and increasing project timelines.
The Solution:
To mitigate voltage compatibility issues, B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing devices that are designed to accommodate a wide voltage range, specifically those labeled with “INPUT: 100-240V, 50/60 Hz.” This versatility ensures that the equipment can operate seamlessly in various electrical environments, including the U.S. market. Additionally, it’s advisable to work closely with suppliers who are knowledgeable about international standards and can provide detailed specifications on voltage compatibility. When procuring equipment, always verify the voltage requirements and consider purchasing a few voltage converters as backups, especially for critical machinery. This proactive approach not only prevents operational disruptions but also enhances long-term reliability in international operations.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Finding Suitable Plug Adapters
The Problem:
For B2B buyers planning to send staff or equipment to the U.S., a common pain point is the challenge of finding suitable plug adapters for type A and type B sockets. Many devices are shipped without the appropriate adapters, causing delays in setup and operations. This issue is particularly prevalent for companies that import machinery or electronic devices, as the wrong adapter can render equipment unusable until a solution is found.
The Solution:
To address this challenge, B2B buyers should invest in universal travel adapters that accommodate multiple plug types, including type A and type B. These adapters are widely available from reputable electronics suppliers and can serve as a long-term solution for various devices. Additionally, companies can create a checklist of all devices being sent to the U.S. and pre-order the necessary adapters to ensure that everything is operational upon arrival. Establishing relationships with local suppliers in the U.S. can also facilitate quick access to adapters, reducing downtime. By preparing in advance, businesses can streamline their operations and avoid costly delays.
Scenario 3: Compliance with U.S. Electrical Standards
The Problem:
International B2B buyers often face compliance challenges when dealing with U.S. electrical standards. Understanding the various types of outlets, such as GFCI and AFCI, and ensuring that imported equipment meets safety regulations can be daunting. Non-compliance not only poses safety risks but can also lead to legal issues and financial penalties.
The Solution:
To navigate compliance effectively, B2B buyers should familiarize themselves with the National Electrical Code (NEC) requirements and the types of outlets commonly used in the U.S. Engaging with local electrical engineers or consultants can provide invaluable insights into compliance standards. When purchasing equipment, buyers should insist on detailed documentation proving that devices meet U.S. safety regulations, including certifications from recognized testing laboratories. Additionally, consider investing in training for staff on U.S. electrical standards to ensure that all installations and operations adhere to safety protocols. By prioritizing compliance, businesses can minimize risks and enhance their operational integrity in the U.S. market.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for us electrical plug types
When selecting materials for U.S. electrical plug types, it’s essential to consider various properties and how they align with the specific requirements of international B2B buyers. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the manufacturing of electrical plugs: thermoplastics, thermosetting plastics, metals, and rubber. Each material has unique characteristics that influence performance, cost, and suitability for different applications.
What Are the Key Properties of Thermoplastics for U.S. Electrical Plugs?
Thermoplastics, such as polycarbonate and nylon, are widely used in the production of electrical plugs due to their excellent electrical insulation properties and durability. They can withstand high temperatures (up to 120°C) and are resistant to impact and chemicals, making them suitable for various environments.
Pros: Thermoplastics are lightweight, easy to mold, and can be produced in various colors. They also offer good resistance to UV light and moisture, which is crucial for outdoor applications.
Cons: While thermoplastics are generally durable, they can become brittle over time if exposed to extreme temperatures. Additionally, their cost can vary based on the grade and supplier, impacting overall manufacturing expenses.
Impact on Application: Thermoplastics are ideal for consumer electronics and household appliances. However, buyers must ensure compliance with international standards like ASTM and IEC to guarantee safety and performance.
How Do Thermosetting Plastics Compare in Performance?
Thermosetting plastics, such as epoxy resin, are known for their high thermal stability and resistance to deformation under heat. They typically have a higher temperature rating than thermoplastics, making them suitable for applications where plugs may encounter high heat.
Pros: These materials provide excellent electrical insulation and are resistant to chemicals and moisture. They also have a longer lifespan compared to thermoplastics.
Cons: Thermosetting plastics are more challenging to manufacture as they cannot be remolded once set, leading to higher production costs. They are also heavier, which may not be ideal for portable applications.
Impact on Application: Thermosetting plastics are often used in heavy-duty electrical applications, such as industrial machinery and automotive components. International buyers should verify compliance with local regulations to avoid issues during importation.
What Are the Advantages of Using Metals in Electrical Plugs?
Metals, particularly brass and copper, are commonly used for the conductive parts of electrical plugs due to their excellent electrical conductivity and strength.
Pros: Metal components enhance the durability and reliability of electrical connections. They are also resistant to corrosion when properly coated.
Cons: Metals can be susceptible to oxidation if not adequately protected, leading to increased resistance and potential failure. Additionally, they are heavier and can increase the overall cost of the plug.
Impact on Application: Metal parts are essential for plugs used in high-power applications. Buyers from regions with high humidity, such as parts of Africa and South America, should consider corrosion-resistant coatings.
Why Is Rubber Important for Electrical Plug Design?
Rubber is often used in the insulation and protective components of electrical plugs due to its flexibility and excellent dielectric properties.
Pros: Rubber provides superior shock resistance and can withstand a wide range of temperatures. It is also highly resistant to moisture and environmental factors.
Cons: Over time, rubber can degrade due to exposure to UV light and extreme temperatures, which may limit its lifespan. Additionally, rubber components can be more expensive to produce.
Impact on Application: Rubber is particularly beneficial in outdoor and industrial applications where plugs may be exposed to harsh conditions. Buyers should ensure that the rubber used meets relevant international standards for safety and performance.
Summary Table of Material Selection for U.S. Electrical Plug Types
| Material | Typical Use Case for U.S. Electrical Plug Types | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermoplastics | Consumer electronics, household appliances | Lightweight and easy to mold | Can become brittle over time | Medium |
| Thermosetting Plastics | Heavy-duty electrical applications | High thermal stability | More challenging to manufacture | High |
| Metals | High-power applications | Excellent electrical conductivity | Susceptible to oxidation | Medium |
| Rubber | Outdoor and industrial applications | Superior shock resistance | Degrades with UV exposure | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides international B2B buyers with insights into the properties, advantages, and limitations of materials used in U.S. electrical plugs. Understanding these factors can help in making informed purchasing decisions that align with local regulations and market demands.
A stock image related to us electrical plug types.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for us electrical plug types
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing US Electrical Plug Types?
The manufacturing of US electrical plug types, specifically Type A and Type B, involves several critical stages that ensure the production of high-quality, reliable electrical components. Understanding these processes is vital for international B2B buyers looking to source electrical plugs for their markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used?
The first step in the manufacturing process involves the selection and preparation of raw materials. Common materials for electrical plugs include:
- Thermoplastics: Used for the plug casing, these materials provide durability and insulation.
- Copper: Used for the conductive pins, copper is chosen for its excellent conductivity properties.
- Nickel or Tin Plating: Often applied to copper to enhance corrosion resistance and reduce wear.
Once the materials are selected, they undergo quality checks to ensure they meet industry standards. This step is crucial as it lays the foundation for the plug’s overall performance and safety.
How Are Electrical Plugs Formed?
The forming stage involves several techniques to shape the raw materials into the desired plug configuration. Key processes include:
- Injection Molding: This is the most common technique used for creating the plastic casing of the plugs. Molten thermoplastic is injected into a mold to form the desired shape.
- Metal Stamping: Copper is often shaped into pins through stamping processes that ensure precise dimensions and strength.
- Die Casting: This method may be used for producing more complex metal parts, ensuring high dimensional accuracy.
These techniques require specialized machinery and skilled operators to achieve the necessary precision and quality.
What Does the Assembly Process Entail?
After forming, the next stage is assembly, where various components are brought together to create the final product. This process typically includes:
- Pin Insertion: The copper pins are inserted into the molded plastic casing.
- Soldering: In some designs, soldering is used to secure electrical connections.
- Final Assembly: The assembled components are fitted together, ensuring proper alignment and securing with screws or clips.
Quality control measures are implemented throughout this stage to ensure that each plug meets the required specifications before moving on to the finishing phase.
How Are Electrical Plugs Finished?
The finishing stage enhances the aesthetic appeal and functional performance of the plugs. Key activities in this stage include:
- Surface Treatment: This may involve polishing or coating the plugs to improve appearance and resistance to environmental factors.
- Labeling: Proper labeling is crucial for compliance with international standards and regulations.
- Final Inspection: A thorough inspection is conducted to check for defects and ensure that the plugs meet all specifications.
What Quality Assurance Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?

A stock image related to us electrical plug types.
For international buyers, understanding the quality assurance processes in place is essential. Manufacturers of US electrical plug types typically adhere to several international and industry-specific standards, including:
- ISO 9001: This standard ensures that manufacturers maintain a quality management system (QMS) that is effective and continually improving.
- CE Marking: This certification indicates compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards, which is particularly relevant for buyers in Europe.
- UL Certification: Underwriters Laboratories (UL) certification is critical for electrical safety and is recognized internationally.
These standards help ensure that electrical plugs are safe, reliable, and of high quality.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is integral to the manufacturing process, ensuring that each product meets stringent safety and performance standards. Key QC checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint verifies the quality of raw materials before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing checks during the manufacturing process help identify defects early, reducing waste and ensuring consistency.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive inspection of the finished product ensures it meets all specifications and regulatory requirements before packaging and shipping.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control is crucial for ensuring product reliability. Here are actionable steps to consider:
-
Supplier Audits: Conduct on-site audits to evaluate the manufacturing processes and QC systems in place. This firsthand observation provides insights into the supplier’s operations.
-
Request QC Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation of their QC processes, including test results and compliance certifications. This documentation serves as evidence of adherence to industry standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engage third-party inspection services to conduct independent evaluations of the manufacturing process and product quality. This adds an additional layer of assurance.
-
Certifications: Verify that suppliers hold relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001 or UL, and ensure they are up to date. This demonstrates a commitment to quality management.
What Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
When sourcing electrical plugs from manufacturers, international B2B buyers should consider specific nuances that can affect their purchasing decisions:
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions have distinct regulatory requirements for electrical products. Familiarize yourself with local standards in your target market to ensure compliance.
-
Import Tariffs and Duties: Be aware of any tariffs or duties that may apply to importing electrical plugs into your country, as these can significantly impact overall costs.
-
Cultural and Communication Differences: Understanding cultural nuances and establishing clear communication channels with suppliers can facilitate smoother transactions and foster long-term partnerships.
By comprehensively understanding the manufacturing processes, quality assurance standards, and verification methods, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing US electrical plug types for their specific markets.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘us electrical plug types’
To effectively procure US electrical plug types, international B2B buyers must navigate specific technical requirements and supplier capabilities. This guide provides a detailed checklist to streamline the sourcing process, ensuring that you obtain the right electrical components for your needs.
Step 1: Identify Your Voltage and Frequency Needs
Understanding the electrical specifications is crucial for compatibility. The standard voltage in the United States is 120V at a frequency of 60Hz. Ensure that your devices can operate within these parameters to avoid malfunction or damage.
Step 2: Determine the Type of Plugs Required
The US uses two primary plug types: Type A and Type B. Type A features two flat parallel pins, while Type B has an additional round grounding pin. Assess the plugs used in your equipment to ensure you source the correct type for seamless integration.
Step 3: Research Local Regulations and Standards
Before purchasing, familiarize yourself with local regulations regarding electrical devices. Compliance with the National Electrical Code (NEC) is essential in the US. This step can prevent legal issues and ensure safety in installations, especially in industrial environments.
Step 4: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Choosing the right supplier is critical to ensuring quality and reliability. Request detailed company profiles, certifications, and case studies from potential suppliers. Look for those with a proven track record in supplying electrical components to your region, as this can facilitate smoother transactions and support.
- Supplier Certifications: Verify that suppliers hold relevant certifications, such as UL or CE, which indicate compliance with safety and quality standards.
- References: Ask for references from other B2B clients who have sourced similar products to gauge the supplier’s reliability.
Step 5: Request Samples for Testing
Before making a bulk order, it’s advisable to request samples. Testing samples ensures that the plugs meet your specifications in terms of quality and functionality. Evaluate their performance under actual operating conditions to confirm compatibility with your devices.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you’ve identified suitable suppliers and tested samples, negotiate favorable terms. Discuss pricing, delivery timelines, warranty conditions, and after-sales support. Clear agreements can prevent misunderstandings and ensure a smoother procurement process.
Step 7: Plan for Logistics and Distribution
Consider how the sourced plugs will be delivered and distributed within your organization. Evaluate shipping options, customs regulations, and potential tariffs, especially if you are importing into regions like Africa or South America. A well-planned logistics strategy can save time and costs.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of procuring US electrical plug types with confidence, ensuring that their operations run smoothly and efficiently.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for us electrical plug types Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing US Electrical Plug Types?
When sourcing US electrical plug types, a comprehensive understanding of the cost structure is essential. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly affects the cost. Common materials used in electrical plugs include thermoplastics for housing and copper for conductors. Higher-quality materials, while more expensive, can enhance durability and safety, making them preferable for B2B buyers focused on long-term use.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on the manufacturing location. For example, manufacturers in regions with higher labor costs, such as parts of Europe, may charge more than those in lower-cost countries in Asia or South America. Understanding local labor rates can help buyers gauge potential costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to facilities, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can lower overhead, which can be an essential factor when negotiating prices.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific plug designs can be a significant initial investment. However, the cost can be amortized over larger production volumes, making it crucial for buyers to consider minimum order quantities (MOQs) when evaluating the total cost.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring compliance with safety and quality standards can add to the cost. Buyers should look for suppliers with robust QC processes, as this can prevent costly returns or safety issues down the line.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary greatly depending on the origin of the products and destination. Factors such as freight costs, customs duties, and insurance should be factored into the total cost of ownership.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a profit margin to their costs, which can vary widely based on market conditions and competition. Understanding the typical margins in the electrical plug market can assist buyers in negotiating better prices.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Sourcing Decisions for US Electrical Plug Types?
Several factors can influence the pricing of US electrical plug types, particularly for international B2B buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ: Higher order volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should consider their anticipated needs to negotiate favorable terms.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specific certifications can significantly increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Plugs that meet specific safety certifications (e.g., UL, CE) may come at a premium. It’s crucial for buyers to balance cost with the necessary compliance for their markets.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while newer companies might offer lower prices to attract customers.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for international transactions. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping and logistics, which can affect overall costs.
What Are the Best Negotiation Strategies for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation can significantly impact costs:
-
Research and Prepare: Understand the market rates for electrical plugs in your region and compare them with quotes from suppliers. This information will empower you during negotiations.
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: If you plan to order in bulk, use this as a negotiation point. Suppliers are often willing to offer better rates for larger orders.
-
Be Clear About Requirements: Clearly communicate your specifications and quality requirements upfront. This clarity can help avoid misunderstandings and potential additional costs.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership: Evaluate not just the purchase price but the entire lifecycle cost of the plugs, including maintenance, compliance, and potential downtimes. This perspective can guide you toward better long-term decisions.
-
Establish Relationships: Building a strong relationship with suppliers can lead to better terms and pricing over time. Long-term partnerships often yield more favorable conditions.
Conclusion: Why Understanding Costs and Pricing Is Crucial for B2B Buyers
Understanding the cost structure and pricing influences for US electrical plug types is crucial for international B2B buyers. By focusing on the key components and employing effective negotiation strategies, buyers can make informed decisions that lead to cost-effective sourcing solutions. Always keep in mind that prices can vary, and it is advisable to obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitiveness.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing us electrical plug types With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to US Electrical Plug Types: A Comparative Analysis
When considering the use of US electrical plug types, international B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, may seek alternative solutions that better align with their operational needs. This analysis evaluates the traditional US plug types (Type A and Type B) against alternative solutions like universal plug adapters and regional plug types, providing insights into their performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases.
| Comparison Aspect | US Electrical Plug Types | Universal Plug Adapters | Regional Plug Types |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Standardized for 120V, 60Hz | Versatile for multiple plug types | Varies by region, may not support all devices |
| Cost | Low initial costs | Moderate; varies based on brand | Varies; some regions have low-cost options |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy for US devices | Simple to use; plug and play | Requires knowledge of local standards |
| Maintenance | Minimal maintenance | Low; occasional replacement needed | Varies; may require local electrician |
| Best Use Case | Domestic and specific commercial use | Traveling and multi-device environments | Local compliance and specific device requirements |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Universal Plug Adapters?
Universal plug adapters offer a flexible solution for international travelers and businesses needing to connect devices with various plug types. The primary advantage of these adapters is their versatility; they can accommodate multiple plug styles, making them ideal for businesses that operate in different regions. Additionally, they are generally lightweight and easy to carry. However, the downside is that they may not support high-power devices effectively, and some adapters may not be compatible with all socket types, leading to potential connectivity issues.
How Do Regional Plug Types Compare?
Regional plug types, such as those used in Europe (Type C, Type E, and Type F) or South America (Type C and Type N), are designed to meet the specific electrical standards of their respective areas. The primary advantage of using regional plugs is that they ensure compliance with local electrical codes, which can enhance safety and reliability. However, the challenge for international businesses is the need to invest in different devices or adapters for each region, which can complicate logistics and increase costs.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
For international B2B buyers, the choice between US electrical plug types, universal plug adapters, and regional plug types should be guided by the specific operational context. Businesses focusing on the US market might find the standard Type A and B plugs most suitable due to their compatibility with local devices. In contrast, companies with a global presence may benefit from universal plug adapters for their flexibility, while those operating exclusively in specific regions should consider regional plug types for compliance and efficiency. Ultimately, evaluating the performance, cost implications, and ease of implementation will help buyers make informed decisions that align with their operational needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for us electrical plug types
What Are the Key Technical Properties of US Electrical Plug Types?
Understanding the technical specifications of US electrical plug types is crucial for international B2B buyers, particularly when sourcing equipment or products that need to be compatible with US standards. Here are some critical specifications:
1. Voltage Rating
The standard voltage in the United States is 120 V, operating at a frequency of 60 Hz. This is essential for ensuring that electrical devices function correctly and safely. B2B buyers must ensure that any imported equipment or appliances are rated for this voltage to avoid damage or malfunction.
2. Current Rating
US plugs and sockets are typically rated for 15 amps (Type A) or 20 amps (Type B). The current rating determines the maximum amount of electrical current that can safely pass through the plug without overheating. Understanding this rating is vital for selecting the right equipment for specific applications, especially in sectors like manufacturing or construction.
3. Material Composition
The materials used in electrical plugs, such as thermoplastic or rubber, can significantly affect durability and safety. High-quality materials resist wear and tear, reducing the risk of electrical failures. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who use reliable materials to enhance the longevity of their products.
4. Pin Configuration
Type A plugs feature two flat parallel pins, while Type B plugs include an additional round grounding pin. This pin configuration not only influences compatibility with sockets but also impacts safety by providing grounding for devices. Buyers should consider the pin type when evaluating products from different manufacturers.
5. Temperature Tolerance
Electrical plugs must withstand a range of temperatures to ensure safe operation. Most US plugs are designed to operate efficiently between -10°C to 40°C (14°F to 104°F). Understanding temperature tolerance is critical for applications in extreme environments, ensuring that devices perform reliably.
6. Safety Standards Compliance
US plugs must comply with safety standards set by organizations such as Underwriters Laboratories (UL) and the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA). Compliance ensures that products meet safety and performance criteria, which is essential for B2B buyers to mitigate liability and ensure customer satisfaction.
What Common Trade Terms Should International Buyers Understand?
Familiarity with industry jargon is vital for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B landscape. Here are some essential trade terms related to US electrical plugs:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that manufacture products or components that are sold under another company’s brand. For buyers, partnering with OEMs can provide access to high-quality components tailored to specific needs.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for B2B buyers to manage inventory costs and ensure that they order sufficient quantities to meet their needs without overstocking.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used by buyers to solicit price offers from suppliers for specific products. This is a crucial step in the procurement process, enabling buyers to compare prices and terms effectively.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce, defining the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms is critical for understanding shipping costs, risk, and logistics.
5. Certification
Certification involves verifying that products meet specific standards or regulations. For electrical plugs, certification from recognized bodies ensures compliance with safety and performance standards, which is vital for market acceptance.
6. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the products. Understanding lead times helps B2B buyers plan their procurement and inventory management effectively, ensuring timely delivery for projects.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing US electrical plug types, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and product safety.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the us electrical plug types Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics Affecting the US Electrical Plug Types Sector?
The US electrical plug types market is heavily influenced by globalization and the increasing demand for interoperability among electrical devices. As international trade expands, B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must navigate varying voltage standards and plug types. Currently, the predominant plug types in the US are Type A and Type B, which are characterized by their unique pin configurations and voltage ratings of 120V at 60Hz.
Emerging trends include the rise of smart technology and the Internet of Things (IoT), leading to an increased demand for specialized electrical sockets that accommodate various smart devices. Furthermore, the integration of renewable energy sources is pushing manufacturers to design plugs and sockets that are compatible with solar and other alternative energy systems. B2B buyers should also be aware of the growing emphasis on safety standards, such as GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) outlets, which are becoming more common in residential and commercial spaces.
Understanding these market dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers, as they must ensure that the electrical products they source meet both regulatory requirements and customer expectations in their home markets. This could involve investing in adapters, converters, or even sourcing locally compliant products to avoid complications.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact B2B Decisions in the US Electrical Plug Types Market?
Sustainability is becoming a non-negotiable element in B2B sourcing strategies, particularly in the electrical sector. As environmental concerns gain traction, international buyers must consider the ecological impact of the electrical plug types they source. Manufacturers are increasingly held accountable for their carbon footprint, prompting many to adopt sustainable practices in their supply chains.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, with buyers looking for suppliers who maintain transparency and adhere to fair labor practices. Certifications such as Energy Star and RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) are becoming critical indicators of a product’s environmental compliance. For B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, aligning with suppliers who prioritize sustainability can enhance brand reputation and appeal to environmentally-conscious consumers.
Additionally, the use of recycled materials in the production of electrical plugs and sockets is on the rise, providing a dual benefit of reducing waste while also potentially lowering costs. Buyers should assess their suppliers’ sustainability credentials and opt for those who can demonstrate a commitment to ethical and environmentally-friendly practices.
What Is the Historical Context of US Electrical Plug Types Relevant for B2B Buyers?
The evolution of electrical plugs in the US is rooted in the early 20th century, when the need for standardized electrical connections became apparent with the proliferation of electrical appliances. The introduction of Type A and Type B plugs represented significant advancements in safety and usability. Type A, featuring two flat parallel pins, was widely adopted for low-power devices, while Type B, which includes a grounding pin, was developed for higher-powered appliances.
Over time, safety regulations and electrical standards have evolved, leading to the introduction of GFCI and AFCI outlets, which protect against electrical hazards. For B2B buyers, understanding this historical context is essential, as it highlights the ongoing advancements in technology and safety standards that influence current sourcing decisions. Recognizing the evolution of these products can also inform future purchasing strategies, ensuring compliance with both local and international regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of us electrical plug types
-
How do I solve compatibility issues with US electrical plug types?
To address compatibility issues, it’s essential to identify the plug types used in your country and compare them with US types A and B. If your devices use different plug shapes, you will need a travel adapter. For bulk purchasing, consider sourcing adapters that accommodate multiple plug types to cater to diverse needs. Additionally, ensure that the voltage and frequency of your devices align with US standards (120V, 60Hz) to avoid operational issues. -
What is the best approach to source US electrical plugs for my business?
When sourcing US electrical plugs, prioritize suppliers with proven reliability and experience in the electrical components market. Look for manufacturers who can provide certifications such as UL or CE, ensuring product safety and compliance. Request samples to assess product quality before placing large orders. Additionally, consider suppliers who offer customization options to meet specific business requirements, such as branding or unique specifications. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for US electrical plugs?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly among suppliers, typically ranging from 100 to 1,000 units for bulk orders. It’s essential to negotiate MOQs based on your business needs and the supplier’s capabilities. Some manufacturers may offer lower MOQs for customized products, while others may have higher MOQs for standard items. Always clarify MOQ terms before finalizing contracts to ensure they align with your budget and inventory strategy. -
How do I vet suppliers for US electrical plugs?
To vet suppliers effectively, start by checking their business credentials, including registration and industry certifications. Review their track record by seeking references from other clients and examining online reviews. Conduct factory visits if possible, or utilize third-party inspection services to evaluate their manufacturing practices. Ensure that the supplier can provide documentation for product compliance with international safety standards relevant to your market. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing US electrical plugs?
Payment terms can vary, but common practices include a 30% deposit upon order confirmation and the remaining 70% before shipment. Some suppliers may offer favorable terms such as letters of credit or extended payment periods for larger orders. Discuss payment methods such as bank transfers, PayPal, or escrow services to ensure secure transactions. Always clarify terms in the contract to avoid misunderstandings. -
How can I ensure the quality of US electrical plugs before shipping?
To ensure quality, request a comprehensive quality assurance (QA) plan from your supplier. This plan should include details on inspection processes, testing methods, and compliance with safety standards. Conduct pre-shipment inspections to verify that the products meet your specifications and quality expectations. Consider hiring third-party QA services for an unbiased assessment of the products before they leave the factory. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing US electrical plugs?
When importing, consider shipping methods (air vs. sea), as they can significantly affect delivery times and costs. Ensure you have a clear understanding of customs regulations and tariffs in your country, as these can impact your total cost. Work with a freight forwarder who can assist with documentation and logistics management to streamline the import process. Additionally, plan for potential delays by allowing ample time for customs clearance and transportation. -
Are there any customization options available for US electrical plugs?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for US electrical plugs, including color, branding, and specific technical specifications. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to understand their capabilities and any additional costs involved. Customization can enhance your brand visibility and ensure that the products meet specific market needs, making them more appealing to your target audience. Always request samples of customized products to evaluate quality before mass production.
A stock image related to us electrical plug types.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for us electrical plug types
In summary, understanding the nuances of U.S. electrical plug types—primarily Type A and Type B—is critical for international B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The standard voltage of 120V at 60Hz means that many devices will function seamlessly, provided the correct plug adapter is used. Buyers should prioritize sourcing high-quality travel adapters to ensure compatibility with U.S. sockets, thereby avoiding potential operational disruptions.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Business Operations?
Strategic sourcing not only mitigates the risks associated with incompatible electrical systems but also optimizes supply chains by ensuring that the right components are procured efficiently. By establishing reliable supplier relationships and understanding local electrical standards, businesses can enhance operational reliability and customer satisfaction.
What’s Next for International Buyers?
As global commerce continues to evolve, staying informed about electrical requirements will be crucial. Buyers are encouraged to proactively engage with suppliers who can provide insights into the latest trends and technologies in electrical components. By doing so, they can ensure compliance and leverage opportunities in the diverse markets they serve. Embrace this knowledge to empower your business and navigate the complexities of international trade confidently.