Maximize Efficiency: The Complete Guide to Automated Systems (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for automated systems
Navigating the complexities of sourcing automated systems can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers. With the rapid evolution of technology, businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including markets like Saudi Arabia and Vietnam) are increasingly looking to automation as a means to enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs. This guide delves into the myriad types of automated systems available—ranging from industrial robots and automated guided vehicles (AGVs) to advanced document management solutions. Each section is meticulously designed to provide insights into applications, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations, empowering you to make informed purchasing decisions.
As global markets become more interconnected, understanding the nuances of automation technology is critical. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, offering actionable insights tailored to the unique challenges faced by B2B buyers in diverse regions. Whether you’re aiming to streamline production lines or improve customer engagement, the information contained herein will help you identify suitable solutions that align with your business goals. By leveraging this guide, you will be equipped to navigate the global market of automated systems with confidence, ensuring that your investments contribute to sustainable growth and operational excellence.
Understanding automated systems Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Industrial Robots | Autonomous systems for repetitive tasks with sensors | Manufacturing, assembly lines, packaging | Pros: High efficiency, reduced labor costs. Cons: High initial investment and maintenance needs. |
| Collaborative Robots (Cobots) | Designed to work alongside human workers safely | Assembly, quality control, logistics | Pros: Flexibility and ease of integration. Cons: Limited payload capacity compared to industrial robots. |
| Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) | Self-operating vehicles for material transport | Warehousing, distribution centers | Pros: Improved efficiency and reduced labor costs. Cons: Requires infrastructure modifications. |
| Document Management Systems | Centralized digital storage and retrieval of documents | Banking, legal, corporate sectors | Pros: Enhanced security and compliance. Cons: Initial setup complexity and potential user resistance. |
| Cloud-Based Automation Systems | Scalable solutions hosted on cloud platforms | Various sectors including finance and retail | Pros: Cost-effective, scalable, and accessible. Cons: Dependency on internet connectivity and data security concerns. |
What are Industrial Robots and Their Key B2B Considerations?
Industrial robots are automated systems designed for repetitive tasks in manufacturing environments. Equipped with sensors and controllers, they execute specific functions such as welding, painting, or assembly with high precision. B2B buyers should consider the initial investment, which can be substantial, alongside ongoing maintenance costs. The efficiency gains and labor cost reductions make them a compelling choice, particularly for high-volume production settings.
How Do Collaborative Robots (Cobots) Enhance B2B Operations?
Collaborative robots, or cobots, are designed to work alongside human employees, enhancing productivity without replacing the workforce. They are particularly suitable for tasks that require human oversight, such as assembly and quality control. Buyers should assess the flexibility of cobots, as they can be reprogrammed for various tasks. However, their payload capacity is lower than traditional industrial robots, which may limit their applications in heavy-duty settings.
What Are Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) and Their Applications?
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) are self-operating robots used primarily for transporting materials within warehouses and distribution centers. They improve operational efficiency by automating the movement of goods, reducing labor costs, and minimizing human error. Buyers must consider the infrastructure changes required to implement AGVs, as they often necessitate the installation of guiding systems or pathways. Their ability to operate continuously makes them a valuable asset in high-demand environments.
How Can Document Management Systems Improve Efficiency in B2B?
Document Management Systems (DMS) centralize the storage and retrieval of documents, significantly enhancing security and compliance in sectors like banking and legal. These systems reduce reliance on paper, streamline workflows, and ensure that documents are easily accessible. However, B2B buyers should be prepared for the complexity of initial setup and potential resistance from employees accustomed to traditional methods. The long-term benefits of improved efficiency and compliance often outweigh these challenges.
What Are the Benefits of Cloud-Based Automation Systems for Businesses?
Cloud-Based Automation Systems provide scalable solutions that can adapt to a business’s changing needs without significant upfront costs. They are accessible from anywhere with an internet connection, making them ideal for businesses operating in multiple locations. However, buyers must consider the implications of relying on internet connectivity and the associated data security risks. The flexibility and cost-effectiveness of these systems make them an attractive option for many B2B applications.
Key Industrial Applications of automated systems
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Automated Systems | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Industrial Robotics for Assembly Lines | Increased production efficiency and reduced labor costs | Compatibility with existing systems and ease of integration |
| Logistics and Warehousing | Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) for Material Handling | Enhanced accuracy in inventory management and reduced operational costs | Robustness for diverse environments and maintenance support |
| Banking | Automated Document Management Systems | Improved compliance and reduced processing time | Scalability and security features to handle sensitive data |
| Agriculture | Automated Irrigation Systems | Water conservation and increased crop yield | Adaptability to various soil and climate conditions |
| Healthcare | Robotic Surgical Systems | Precision in surgeries leading to better patient outcomes | Regulatory compliance and training for medical staff |
How Are Automated Systems Transforming Manufacturing Processes?
In the manufacturing sector, industrial robotics are revolutionizing assembly lines by automating repetitive tasks such as welding, painting, and assembly. This technology not only increases production efficiency but also significantly reduces labor costs. For international buyers, particularly in Africa and South America, sourcing robotics requires careful consideration of compatibility with existing systems and the ease of integration into current workflows. Additionally, potential buyers must assess local support and maintenance services to ensure operational continuity.
What Are the Benefits of Automated Guided Vehicles in Logistics?
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) are increasingly utilized in logistics and warehousing for material handling tasks. These vehicles transport goods within warehouses with high accuracy, significantly reducing the risk of human error and improving inventory management. For B2B buyers in the Middle East and Europe, key considerations when sourcing AGVs include their robustness to operate in diverse environments and the availability of comprehensive maintenance support to minimize downtime.
How Do Automated Document Management Systems Enhance Banking Operations?
In the banking industry, automated document management systems streamline processes by digitizing paperwork, thereby improving compliance and significantly reducing processing times. This automation allows banks to focus on customer service rather than on administrative burdens. International buyers from Europe and Africa must prioritize scalability and security features when sourcing these systems to ensure they can handle sensitive data while adapting to regulatory changes in their regions.
What Role Do Automated Irrigation Systems Play in Agriculture?
Automated irrigation systems are essential in modern agriculture, allowing for precise water management that conserves resources while maximizing crop yield. These systems can be tailored to various soil types and climatic conditions, making them particularly beneficial for farmers in regions like South America and Africa. Buyers should consider the adaptability of these systems to local conditions and the availability of local technical support to ensure effective implementation.
How Are Robotic Surgical Systems Improving Healthcare Outcomes?
Robotic surgical systems are transforming healthcare by providing enhanced precision during surgeries, which leads to better patient outcomes and faster recovery times. Hospitals in Europe and the Middle East are increasingly investing in this technology. When sourcing robotic systems, healthcare providers must ensure compliance with local regulations and consider the necessary training for medical staff to operate these advanced systems effectively.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘automated systems’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Struggling with Integration of Automated Systems Across Diverse Operations
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, particularly in industries such as manufacturing and logistics, face the daunting challenge of integrating new automated systems with existing infrastructure. This can be particularly troublesome when businesses operate across multiple locations or regions, such as Africa and Europe, where technological standards and legacy systems may vary widely. The lack of compatibility can lead to data silos, operational inefficiencies, and a failure to leverage the full potential of automation. This not only frustrates management but also hampers overall productivity, resulting in lost revenue and dissatisfied customers.
The Solution: To overcome integration challenges, buyers should prioritize selecting automated systems that are built on open architecture. This allows for easier connections with existing technologies. When sourcing solutions, ask potential vendors about their integration capabilities and request case studies from similar industries or geographical areas. Additionally, consider investing in middleware solutions that can bridge gaps between different systems, enabling seamless data flow and operational coherence. Conducting a thorough needs analysis before implementation can help identify which systems require integration and the best approach to achieve this.
Scenario 2: Overwhelmed by Complexity and Usability of Automated Systems
The Problem: As automated systems become more sophisticated, their complexity can intimidate employees, especially in regions where workforce training in advanced technologies is limited. B2B buyers may find that the systems they invest in are not user-friendly, leading to poor adoption rates among staff. This situation is particularly prevalent in sectors like banking and healthcare, where the need for precise and efficient operations is critical. Employees may resist using these systems, fearing they lack the necessary skills, which ultimately affects overall operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
The Solution: To tackle usability issues, buyers should look for automated systems that prioritize user experience (UX) and offer intuitive interfaces. During the selection process, request demonstrations and user feedback from current clients. It’s also essential to provide comprehensive training and continuous support for employees. Consider establishing a mentorship program where tech-savvy employees can assist their peers. Furthermore, implement phased rollouts of new systems to allow users to acclimate gradually, ensuring that support and resources are readily available during this transition.
Scenario 3: Navigating Compliance and Regulatory Challenges with Automated Systems
The Problem: B2B buyers operating in heavily regulated industries, such as finance and healthcare, often struggle to ensure that their automated systems comply with local and international regulations. Non-compliance can lead to severe penalties, legal issues, and reputational damage. This challenge is exacerbated for buyers in diverse markets, such as the Middle East and South America, where regulatory landscapes can shift frequently and vary significantly. The complexity of managing compliance across different jurisdictions can overwhelm even the most diligent teams.
The Solution: To mitigate compliance risks, buyers should partner with vendors who have a strong understanding of the regulatory environment in their target markets. Request information on how automated systems can be tailored to meet specific compliance requirements. Additionally, consider implementing compliance management software that can automate the tracking of regulations and generate reports as needed. Regular training sessions on compliance for all employees involved in the automated processes can also be beneficial. Lastly, establishing a dedicated compliance team or appointing a compliance officer can ensure that there is ongoing oversight and that any changes in regulations are promptly addressed.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for automated systems
When selecting materials for automated systems, it is crucial to consider the specific requirements of your application, including environmental conditions, mechanical stresses, and regulatory compliance. Below, we analyze four common materials used in automated systems, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of Aluminum in Automated Systems?
Aluminum is a lightweight metal known for its excellent corrosion resistance and good thermal and electrical conductivity. Its temperature rating typically ranges from -200°C to 1200°C, making it suitable for various applications.
Pros & Cons:
Aluminum is durable and easy to fabricate, which simplifies manufacturing processes. However, it can be more expensive than other metals like steel, particularly in regions with high import tariffs. Its lower strength compared to steel may limit its use in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is compatible with a variety of media, including water and many chemicals, making it versatile for different automated systems.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM and ISO. In regions like the Middle East, where high temperatures are common, verifying the material’s performance under extreme conditions is essential.
How Does Stainless Steel Perform in Automated Systems?
Stainless steel is renowned for its exceptional strength and corrosion resistance, particularly in harsh environments. It typically withstands temperatures up to 800°C, making it suitable for high-temperature applications.
Pros & Cons:
The durability of stainless steel makes it ideal for long-term use, but it comes at a higher cost compared to aluminum. Its heavier weight can also complicate the design of automated systems, especially in mobile applications.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is highly compatible with various media, including aggressive chemicals, making it a preferred choice in food processing and pharmaceuticals.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with international standards like DIN and JIS is vital, especially for buyers from Europe and Asia. Additionally, understanding local sourcing options can help mitigate costs.
What Are the Advantages of Using Polycarbonate in Automated Systems?
Polycarbonate is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its excellent impact resistance and transparency. It can withstand temperatures ranging from -40°C to 120°C.
Pros & Cons:
While polycarbonate is lightweight and offers good insulation properties, it can be less durable than metals in high-stress applications. Its susceptibility to scratching may also limit its use in certain environments.
Impact on Application:
Polycarbonate is often used in protective covers and housings for automated systems, providing visibility while protecting sensitive components.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should consider local regulations regarding plastics, as some regions may have restrictions on specific types of materials. Understanding the environmental impact and recycling options is also crucial.
Why Choose Composite Materials for Automated Systems?
Composite materials, such as fiberglass and carbon fiber, are engineered for high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent durability. They can operate effectively within a temperature range of -50°C to 150°C.
Pros & Cons:
Composites are lightweight and resistant to corrosion, making them ideal for specialized applications. However, they can be more expensive and complex to manufacture, which may deter some buyers.
Impact on Application:
These materials are particularly useful in aerospace and automotive applications, where weight savings are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers:
International buyers should be aware of the specific certifications required for composites in their industry, as well as the availability of local suppliers to reduce lead times.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Automated Systems
| Material | Typical Use Case for automated systems | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Structural components in robotics | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower strength than steel | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing equipment | High strength and durability | Higher cost and weight | High |
| Polycarbonate | Protective covers for sensors | Impact resistance and transparency | Less durable in high-stress areas | Medium |
| Composite | Aerospace and automotive parts | High strength-to-weight ratio | Higher manufacturing complexity | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the materials commonly used in automated systems, along with actionable insights for international B2B buyers. By considering these factors, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for automated systems
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Automated Systems?
The manufacturing of automated systems involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the final product meets the required specifications and quality standards. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation: This initial stage involves selecting and preparing raw materials according to the specifications of the automated system. Suppliers must provide materials that meet industry standards, such as ASTM or ISO certifications. Buyers should verify the quality of materials through supplier certifications and testing reports.
-
Forming: In this stage, the prepared materials undergo various processes to shape them into components of the automated system. Techniques such as machining, casting, and molding are commonly used. Advanced technologies, including CNC machining and 3D printing, are increasingly adopted to enhance precision and reduce waste.
-
Assembly: During assembly, individual components are combined to create the automated system. This process may involve mechanical assembly, electrical wiring, and programming of control systems. Collaborative robots (cobots) are often utilized in this stage to enhance efficiency and ensure safety for workers.
-
Finishing: The final stage involves surface treatment, coating, and quality checks. Finishing techniques may include painting, anodizing, or applying protective coatings to enhance durability and aesthetics. This stage is crucial for ensuring the system’s functionality and longevity.
What Quality Control Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
Quality assurance is vital in the manufacturing of automated systems, ensuring that products meet international and industry-specific standards. Key standards include:
-
ISO 9001: This international standard outlines requirements for a quality management system (QMS). Compliance demonstrates a commitment to quality and continuous improvement, which is crucial for B2B buyers seeking reliable suppliers.
-
CE Marking: For products sold within the European Economic Area, CE marking indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers obtain this certification to facilitate market entry.
-
API Standards: For automated systems used in the oil and gas industry, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is essential. These standards ensure that products meet rigorous safety and performance criteria.
How Is Quality Control Implemented During Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) in the manufacturing of automated systems is typically structured around several key checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial inspection focuses on the materials and components received from suppliers. B2B buyers should insist on documentation that confirms compliance with specifications, including material test reports and certificates of conformity.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During production, ongoing inspections are conducted to ensure that processes are adhered to and that components are being manufactured correctly. This includes monitoring machinery, tooling, and operator performance.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once assembly is complete, a thorough final inspection is conducted. This includes functional testing, performance assessments, and safety evaluations. Buyers can request detailed FQC reports to understand how the final product has been validated.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Automated Systems Manufacturing?
Testing is crucial to ensure the functionality and reliability of automated systems. Common testing methods include:
-
Functional Testing: This method verifies that the automated system performs its intended functions under various conditions. It may include simulating real-world scenarios to assess performance.
-
Environmental Testing: Automated systems often need to operate in diverse environmental conditions. Environmental testing assesses performance under temperature extremes, humidity, vibration, and other factors.
-
Safety Testing: Safety is paramount in automated systems. Safety testing involves evaluating the system’s compliance with safety standards and protocols, such as electrical safety tests and emergency shut-off systems.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
Verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential for B2B buyers to ensure they receive reliable products. Here are actionable steps:
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits of suppliers’ manufacturing facilities can provide insights into their quality control processes. Buyers should assess compliance with international standards and the effectiveness of their QC systems.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed quality reports, including IQC, IPQC, and FQC results. This documentation helps buyers understand the quality assurance measures in place.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control practices. This can be particularly valuable for international buyers who may not have the capacity to conduct audits themselves.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, face unique challenges in quality control:
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions have varying regulatory requirements. Buyers must ensure that suppliers comply with local regulations and international standards, which may vary significantly across markets.
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding cultural attitudes towards quality can influence supplier relationships. Buyers should engage in open communication and establish clear expectations regarding quality standards and testing.
-
Supply Chain Integrity: The integrity of the supply chain can impact quality. Buyers should evaluate the entire supply chain, from raw material sourcing to final assembly, to ensure consistent quality throughout the process.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers for automated systems, ensuring they receive high-quality products that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘automated systems’
Introduction
Sourcing automated systems can significantly enhance operational efficiency and competitiveness in the global marketplace. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist designed for international B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By following these actionable insights, buyers can ensure they select the right automated systems that meet their specific needs and regulatory requirements.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding your specific requirements is essential before initiating the sourcing process. This includes identifying the types of automated systems you need, such as industrial robots, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), or document management systems. Clarifying these specifications helps in aligning solutions with your operational goals and budget.
Step 2: Conduct Market Research
Thorough market research allows buyers to identify the latest technologies and trends in automated systems. Investigate various suppliers and their offerings, paying close attention to their innovations and customer reviews. This step helps in understanding the competitive landscape and enables informed decision-making.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, it’s crucial to conduct a comprehensive evaluation. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from clients in similar industries or regions. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in your specific area of automation to ensure reliability and performance.
- Supplier Certifications: Verify that the suppliers possess necessary certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) to ensure compliance with international standards.
- Experience: Assess the supplier’s experience in your industry, as this can significantly impact the integration of their systems into your operations.
Step 4: Assess System Compatibility
Ensure that the automated systems you intend to procure are compatible with your existing infrastructure. This includes evaluating software integration, hardware requirements, and any necessary modifications to current processes. Compatibility is vital for seamless operation and minimizes potential disruptions during implementation.
Step 5: Request Demonstrations and Trials
Before finalizing your purchase, request product demonstrations or trial periods. This allows your team to assess the usability and effectiveness of the automated systems in a real-world setting. Observing the system in action can provide insights into its performance and user-friendliness, helping you make a more informed decision.
Step 6: Review Support and Maintenance Services
Understanding the level of support and maintenance offered by the supplier is critical. Evaluate their customer service response times, availability of technical support, and warranty terms. Reliable post-purchase support ensures that your automated systems continue to operate efficiently and any issues are addressed promptly.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Finalize Contracts
Once you have selected a supplier, it’s time to negotiate contract terms. Discuss pricing, delivery schedules, payment plans, and any additional services included in the agreement. Ensure all negotiated terms are documented clearly in the contract to avoid misunderstandings and ensure mutual accountability.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the procurement of automated systems, ensuring that their investments lead to enhanced efficiency and growth in their operations.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for automated systems Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Automated Systems Sourcing?
When sourcing automated systems, understanding the cost structure is essential for effective budgeting and negotiation. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The raw materials used in manufacturing automated systems significantly influence the overall cost. Quality and sourcing of these materials can vary widely, impacting price.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass both direct and indirect labor involved in the manufacturing process. This includes wages for skilled technicians and engineers who design and assemble the systems.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facilities, equipment maintenance, utilities, and other expenses that are not directly tied to production but are essential for the manufacturing process.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling may be required for specific automated systems, which adds to the initial investment. The complexity and specificity of the tooling can vary based on the project requirements.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures that the automated systems meet industry standards and client specifications. The costs associated with testing and certification should be factored into the overall pricing.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling can vary significantly depending on the origin of the materials and the destination. Costs may include freight, insurance, and customs duties, especially for international transactions.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a profit margin to the total cost of producing the automated systems. This margin can vary depending on market conditions, competition, and perceived value.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Automated Systems Costs?
Several factors influence pricing for automated systems, which can be particularly nuanced in international B2B transactions:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Bulk orders often lead to discounts, making it crucial to understand the supplier’s MOQ policies. Negotiating for a higher volume can significantly reduce per-unit costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Tailored solutions typically incur higher costs due to the additional design and engineering work involved. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the potential price increase.
-
Materials: The choice of materials affects both the durability and cost of the automated system. High-quality materials may lead to a higher upfront cost but can reduce maintenance expenses over time.
-
Quality and Certifications: Systems with industry certifications may come at a premium. However, they often provide assurance of reliability and compliance, which can be crucial in regulated markets.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and location of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while newer entrants might offer competitive pricing to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for international shipping costs and responsibilities. Different terms can affect the total landed cost of the systems, impacting overall pricing strategies.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Automated Systems?
International B2B buyers can leverage several strategies to enhance cost-efficiency when sourcing automated systems:
-
Negotiation: Engage in proactive negotiations with suppliers. Leverage volume discounts, longer-term contracts, or bundled services to achieve better pricing.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Assess the TCO rather than just the initial purchase price. Consider maintenance, training, and potential downtime costs in your analysis to make informed decisions.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and local regulations that may affect pricing. Establish relationships with local suppliers where possible to mitigate these costs.
-
Market Research: Conduct thorough market research to understand pricing trends and competitor offers. This knowledge can empower buyers during negotiations and help identify the best value options.
-
Supplier Audits: Regularly audit suppliers to ensure they meet quality and compliance standards. This can prevent costly issues later and help maintain a consistent supply chain.
By focusing on these cost components and pricing influencers, international B2B buyers can make more informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing automated systems With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Automated Systems in B2B Solutions
In the landscape of B2B operations, automation has emerged as a critical factor in enhancing efficiency and reducing costs. However, it’s essential for international buyers, especially those from diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, to evaluate alternatives that could also meet their operational needs. This analysis aims to compare automated systems with two alternative solutions: Manual Processes and Semi-Automated Systems. Each option presents unique advantages and challenges that can influence the decision-making process.
Comparison Table of Automated Systems vs Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Automated Systems | Manual Processes | Semi-Automated Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency, consistent output | Variable performance, prone to errors | Moderate efficiency, improved accuracy |
| Cost | Higher initial investment, long-term savings | Low upfront costs, high labor costs | Moderate costs, balanced investment |
| Ease of Implementation | Complex setup, requires training | Simple to implement | Moderate complexity, partial training |
| Maintenance | Requires regular updates and support | Minimal maintenance | Requires periodic maintenance |
| Best Use Case | High-volume, repetitive tasks | Low volume, custom tasks | Tasks needing flexibility and precision |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Manual Processes?
Manual Processes involve human intervention for every task, which can lead to variability in performance.
Pros:
– Cost-Effective: With low upfront costs, businesses can avoid significant investment in technology.
– Flexibility: Adaptable to changing needs without the constraints of a set system.
Cons:
– Inconsistency: Results can vary significantly based on human factors, leading to potential quality issues.
– Labor-Intensive: Higher labor costs over time can negate initial savings, particularly in high-demand environments.
Manual processes may be suitable for small businesses or those in industries where customization is key, but they can struggle to scale efficiently.
How Do Semi-Automated Systems Compare?
Semi-Automated Systems blend human input with technology, allowing for some level of automation while retaining manual oversight.
Pros:
– Improved Accuracy: Reduces the margin for error compared to fully manual processes while allowing for human judgment where necessary.
– Scalable: Provides a middle ground that can grow with business needs without the full investment of automated systems.
Cons:
– Moderate Costs: While less expensive than fully automated systems, initial costs can still be significant.
– Training Required: Employees need to be trained to operate and maintain the system effectively.
Semi-automated systems can be particularly beneficial in sectors where flexibility and human oversight are essential, but they may not achieve the efficiency of fully automated solutions.
How Can B2B Buyers Make the Right Choice?
When considering the right solution for their specific needs, B2B buyers should evaluate their operational requirements, budget constraints, and the scalability of the solution. Automated systems offer a robust solution for businesses with high-volume, repetitive tasks, but they come with higher initial costs and complexity. In contrast, manual processes might suffice for smaller operations but can incur higher long-term costs due to inefficiencies. Semi-automated systems represent a hybrid option that can provide flexibility and scalability.
Ultimately, the decision should align with the company’s strategic goals, operational demands, and long-term vision. Engaging with industry experts and conducting a thorough cost-benefit analysis can further aid in making an informed choice that enhances productivity and drives growth.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for automated systems
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Automated Systems?
When evaluating automated systems, understanding their technical properties is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some key specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
The material grade refers to the quality and type of materials used in the construction of automated systems, such as metals, plastics, or composites. High-grade materials enhance durability and resistance to wear and tear, which is particularly important in industries with harsh operating conditions. For B2B buyers, investing in systems made from superior materials can reduce long-term maintenance costs and improve operational reliability.
2. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance levels indicate the allowable deviation from specified dimensions in manufacturing components. This specification is critical in ensuring compatibility between different system parts, especially in automated assembly lines. B2B buyers must pay attention to tolerance levels to ensure smooth integration with existing equipment and to maintain product quality.
3. Throughput Capacity
Throughput capacity measures the volume of materials or products that can be processed within a specific timeframe. This property is vital for businesses looking to optimize production efficiency. B2B buyers should assess their operational needs and select systems that can meet or exceed their throughput requirements to avoid bottlenecks in production.
4. Power Consumption
Power consumption refers to the energy required for the automated system to operate effectively. Systems with lower energy demands can lead to significant cost savings over time, making them more sustainable options. Buyers should consider energy-efficient systems that align with their operational budget and sustainability goals.
5. Integration Capability
Integration capability is the system’s ability to connect and communicate with other existing technologies and systems. This property is crucial for ensuring seamless operations and data sharing across different platforms. B2B buyers should prioritize systems that offer easy integration to maximize their return on investment and enhance productivity.
What Are Common Trade Terminology and Jargon in Automated Systems?
Understanding industry terminology is equally important for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are several common terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help B2B buyers ensure they are sourcing reliable components that meet their specifications, which is critical for maintaining quality in automated systems.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is essential for B2B buyers to understand as it affects inventory management and cash flow. Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their purchases effectively and negotiate better terms with suppliers.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to request pricing and terms from suppliers for specific products or services. For B2B buyers, submitting RFQs is a critical step in obtaining competitive pricing and understanding supplier capabilities, which aids in making informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms helps B2B buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and delivery obligations, which is particularly important when sourcing automated systems from global suppliers.
5. Automation Architecture
This term refers to the design and structure of an automated system, including its hardware and software components. Understanding automation architecture is crucial for B2B buyers to evaluate how well a system will meet their operational needs and integrate with existing processes.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when investing in automated systems, leading to improved operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the automated systems Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Automated Systems Sector?
The automated systems sector is experiencing transformative changes driven by technological advancements, increasing demand for efficiency, and globalization. Key trends include the adoption of collaborative robots (cobots) that work alongside human operators, which enhances productivity while ensuring workplace safety. Moreover, the rise of autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) is reshaping logistics and warehousing, allowing for real-time inventory management and reduced labor costs. For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial for making informed sourcing decisions.
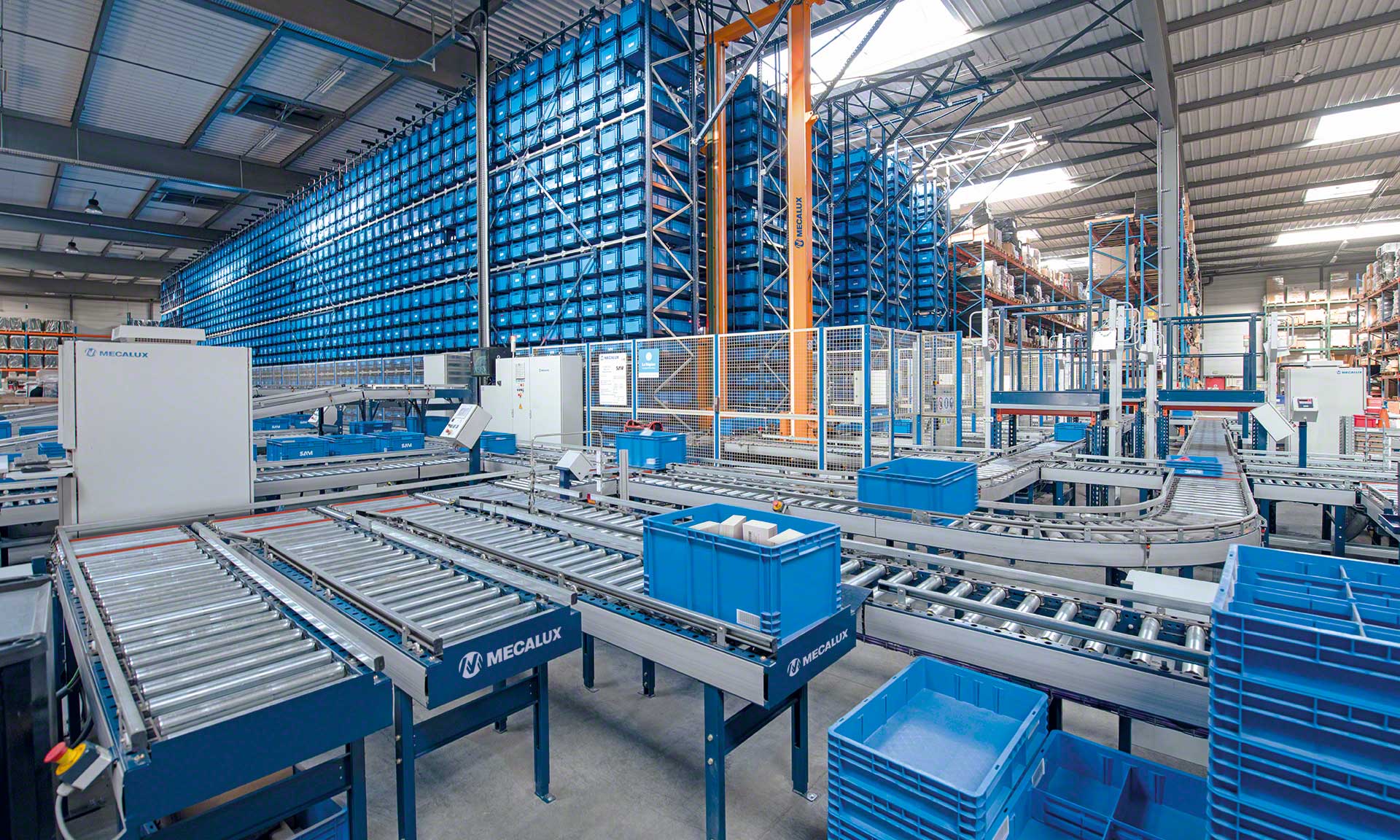

A stock image related to automated systems.
One significant market driver is the growing emphasis on digital transformation across industries. Companies are increasingly seeking integrated solutions that offer scalability and flexibility to adapt to changing market conditions. Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the shift towards automation as businesses sought to minimize human interaction and maintain operational continuity. Buyers should also note the rising importance of data analytics in optimizing automated systems, enabling real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance.
Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) are further enhancing the capabilities of automated systems, allowing for smarter decision-making processes. This evolution presents opportunities for international buyers to source innovative solutions that can drive operational efficiencies and competitive advantages in their respective markets.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact B2B Buyers in the Automated Systems Sector?
A stock image related to automated systems.
Sustainability is becoming a non-negotiable aspect of sourcing decisions in the automated systems sector. Buyers must consider the environmental impact of the systems they procure, including energy consumption, waste generation, and the carbon footprint of manufacturing processes. The demand for sustainable practices is driving manufacturers to invest in greener technologies and materials, which can lead to cost savings and improved brand reputation.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as buyers are increasingly held accountable for their supply chain practices. This includes ensuring fair labor practices, compliance with local regulations, and transparency in sourcing materials. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems or LEED for green building practices.
Incorporating ‘green’ certifications and materials not only aligns with corporate social responsibility goals but can also enhance competitiveness in the marketplace. Companies that adopt sustainable practices are more likely to attract environmentally conscious customers and partners, thereby expanding their business opportunities.
What Is the Brief Evolution of Automated Systems and Its Importance for B2B Buyers?
The evolution of automated systems can be traced back to the early 20th century with the introduction of mechanized production lines. Over the decades, advancements in technology have led to the integration of sophisticated control systems and robotics, revolutionizing manufacturing and service industries. The introduction of programmable logic controllers (PLCs) in the 1960s marked a significant milestone, allowing for greater flexibility and automation of complex processes.
In recent years, the convergence of AI, machine learning, and IoT has further transformed automated systems, enabling real-time data processing and enhanced operational efficiency. For B2B buyers, understanding this historical context is crucial as it highlights the trajectory of innovation and the potential for future advancements. Companies that stay informed about technological developments are better positioned to leverage automation strategically, ensuring they remain competitive in an increasingly automated world.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of automated systems
-
How do I solve the challenge of integrating automated systems into my existing operations?
Integrating automated systems requires a comprehensive analysis of your current operations. Begin by mapping out your workflows to identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement. Collaborate with suppliers who offer robust integration support and customization options. Ensure that the automated systems are compatible with your existing infrastructure, and consider phased implementation to minimize disruption. Additionally, invest in employee training to facilitate a smooth transition and to maximize the benefits of automation. -
What is the best automated system for enhancing efficiency in manufacturing processes?
The best automated system for your manufacturing needs will depend on specific operational requirements, such as production volume, product type, and flexibility. For high-volume production, consider robotic arms or automated conveyor systems that can streamline assembly lines. If your processes require flexibility, collaborative robots (cobots) may be ideal, as they can work alongside human operators. Evaluate potential systems based on scalability, ease of integration, and vendor support to ensure they align with your long-term goals. -
How can I assess the reliability of suppliers for automated systems?
To assess supplier reliability, start by reviewing their track record in the industry, including client testimonials and case studies. Request references and connect with previous clients to gauge their satisfaction with the supplier’s products and support. Additionally, evaluate the supplier’s certifications and compliance with international standards, which can indicate a commitment to quality. Consider conducting site visits to their facilities to observe their manufacturing processes firsthand. -
What customization options are available for automated systems?
Customization options for automated systems can vary significantly among suppliers. Most vendors offer modular systems that allow you to select specific components based on your operational needs. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to explore available configurations, software integrations, and hardware modifications. Additionally, inquire about their capacity for future upgrades, ensuring that the system can evolve with your business demands. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for automated systems?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for automated systems often depend on the supplier and the type of system being ordered. Some manufacturers may have stringent MOQs to justify production costs, while others may be flexible, especially for customized solutions. It’s advisable to communicate your needs upfront and negotiate terms that align with your purchasing capacity. Additionally, consider the potential for bulk purchasing discounts if you’re planning to scale operations in the future. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing automated systems?
Payment terms for automated systems can vary widely among suppliers. Common practices include upfront payments, partial payments during production, and final payments upon delivery. International buyers should also be aware of currency exchange rates and potential tariffs. It’s essential to negotiate payment terms that provide adequate cash flow while ensuring the supplier’s commitment to timely delivery and quality. Establishing clear terms in the contract will protect both parties. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for automated systems?
To ensure quality assurance, establish a rigorous QA process that includes pre-production samples and testing. Collaborate with suppliers who adhere to international quality standards, such as ISO certifications, and who provide detailed documentation of their QA protocols. Request regular updates and reports during the manufacturing process to monitor compliance with specifications. Additionally, consider post-installation support and maintenance agreements to maintain system performance over time. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing automated systems internationally?
When sourcing automated systems internationally, logistics considerations include shipping methods, customs regulations, and delivery timelines. Choose a reliable freight forwarder familiar with international trade to facilitate smooth transportation. Be aware of import duties and taxes, as well as compliance with local regulations in your country. Effective communication with your supplier regarding packaging and labeling can prevent delays. Lastly, plan for potential contingencies, such as supply chain disruptions, to minimize risks.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.

A stock image related to automated systems.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for automated systems
As international B2B buyers navigate the complexities of sourcing automated systems, it is crucial to understand the significant advantages these technologies offer. By leveraging strategic sourcing, businesses can enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs, and meet the rising expectations of customers across diverse markets. Key takeaways include the importance of selecting integrated solutions that align with organizational goals and the need to stay abreast of the latest innovations in automation, such as collaborative robots and advanced material handling systems.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Business Operations?
Strategic sourcing not only streamlines procurement processes but also fosters long-term partnerships with suppliers who can adapt to evolving needs. For businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, this approach is essential for gaining a competitive edge in an increasingly automated world.
What is the Future of Automated Systems in Global Markets?
Looking ahead, the demand for automated systems will continue to grow, driven by technological advancements and globalization. Now is the time for international buyers to embrace these innovations, ensuring they are well-positioned to capitalize on future opportunities. Engage with trusted suppliers who understand local market dynamics and can provide tailored solutions that drive growth and efficiency. The future of automation is bright—make strategic sourcing a cornerstone of your business strategy today.