Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Four Axis Cnc Machine
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for four axis cnc machine
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, the four-axis CNC machine stands out as a pivotal technology that enhances precision, efficiency, and versatility. As industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe strive for innovation, understanding the significance of four-axis capabilities can empower businesses to elevate their production processes. These machines enable complex machining operations, allowing for intricate designs that would be nearly impossible with traditional equipment.
This comprehensive guide delves into the essential aspects of sourcing four-axis CNC machines. It covers various types of machines available in the market, the materials they can work with, and the critical aspects of manufacturing and quality control. Furthermore, it offers insights into reputable suppliers and a thorough analysis of cost considerations, ensuring that buyers can make informed financial decisions. The guide also explores current market trends and addresses common FAQs that international buyers might encounter.
By equipping B2B buyers with detailed information and actionable insights, this guide serves as a vital resource for making informed sourcing decisions. Whether you are a manufacturer seeking to upgrade your capabilities or a procurement specialist looking to streamline operations, understanding the four-axis CNC machine market is essential for gaining a competitive edge in the global arena. Embrace the opportunity to leverage advanced technology and transform your manufacturing operations today.
Understanding four axis cnc machine Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rotary Axis CNC Machine | Incorporates a rotating axis for enhanced machining capabilities | Aerospace, automotive, medical | Pros: High precision, versatile; Cons: Higher cost, complexity in operation |
| Horizontal CNC Machine | Features a horizontal spindle and multiple axes for efficient machining | Heavy machinery, energy sector | Pros: Efficient for large parts; Cons: Requires more floor space, higher energy consumption |
| Vertical CNC Machine | Vertical orientation allows for easy loading/unloading and visibility | Electronics, metal fabrication | Pros: Space-saving, user-friendly; Cons: Limited to certain shapes, less versatile |
| 5-Axis CNC Machine | Adds two additional axes for intricate designs and complex geometries | Mold making, intricate parts manufacturing | Pros: Exceptional precision, complex shapes; Cons: High initial investment, requires skilled operators |
| Multitasking CNC Machine | Combines turning and milling capabilities in one machine | Oil & gas, automotive components | Pros: Reduced cycle time, versatile; Cons: Higher maintenance, operational complexity |
Rotary Axis CNC Machine
The Rotary Axis CNC Machine is designed to incorporate a rotating axis, allowing for complex machining operations. This type is particularly suitable for industries like aerospace and automotive, where precision and the ability to create intricate components are critical. When considering a purchase, B2B buyers should evaluate the machine’s capability to handle specific materials and the availability of skilled operators to maximize its potential.
Horizontal CNC Machine
Horizontal CNC Machines are characterized by their horizontal spindle orientation, which facilitates efficient machining of larger workpieces. Commonly used in the heavy machinery and energy sectors, these machines excel in high-volume production settings. Buyers should assess the space requirements and energy consumption associated with these machines, as they typically require more floor space and can be less energy-efficient compared to vertical options.
Vertical CNC Machine
Vertical CNC Machines are designed with a vertical spindle, making them ideal for easy loading and unloading of materials. They are widely used in electronics and metal fabrication due to their user-friendly nature and space-saving design. However, buyers must consider the limitations in machining certain shapes and the machine’s overall versatility, especially for projects requiring complex geometries.
5-Axis CNC Machine
The 5-Axis CNC Machine is a sophisticated option that adds two additional axes to the standard four, allowing for the machining of complex shapes and intricate designs. This type of machine is particularly valuable in mold making and parts manufacturing where precision is paramount. While the investment can be substantial, B2B buyers should consider the long-term benefits, including reduced setup times and enhanced design capabilities, as well as the need for skilled personnel to operate these advanced systems.
Multitasking CNC Machine
Multitasking CNC Machines combine both turning and milling functionalities, making them incredibly versatile for industries like oil and gas and automotive components. These machines can significantly reduce cycle times and improve efficiency in production lines. However, buyers need to be aware of the higher maintenance requirements and operational complexity that come with these machines. Evaluating the total cost of ownership and the potential for increased productivity is crucial for making an informed purchasing decision.
Key Industrial Applications of four axis cnc machine
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of four axis cnc machine | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Precision component manufacturing | High accuracy in producing lightweight parts, reducing material waste | Certification compliance, advanced material handling capabilities |
| Automotive | Complex part fabrication | Streamlined production processes, enhanced design flexibility | Supplier reputation, after-sales support, and maintenance services |
| Medical Devices | Custom surgical instruments and implants | Tailored solutions that meet specific patient needs, improved patient outcomes | Regulatory certifications, biocompatibility of materials, lead times |
| Electronics | PCB prototyping and housing fabrication | Faster time-to-market for new products, high precision in small components | Material sourcing, technology compatibility, scalability options |
| Furniture and Interior Design | Custom furniture and intricate designs | Unique offerings that attract high-end clients, increased market differentiation | Design capabilities, finishing options, delivery timelines |
Aerospace Industry
In the aerospace sector, four-axis CNC machines are utilized for the production of precision components such as brackets, housings, and structural parts. These machines offer the ability to work with lightweight materials like aluminum and titanium, which are essential for reducing overall aircraft weight and improving fuel efficiency. For international buyers, it is crucial to consider suppliers that comply with aerospace standards and certifications, as well as those that possess advanced material handling capabilities to ensure quality and safety.
Automotive Industry
The automotive industry employs four-axis CNC machines for fabricating complex parts, including engine components, transmission housings, and chassis elements. The flexibility of these machines allows for rapid prototyping and small batch production, which can significantly streamline manufacturing processes. B2B buyers should focus on sourcing from reputable suppliers who offer robust after-sales support and maintenance services to minimize downtime and ensure operational efficiency.
Medical Devices
In the medical device industry, four-axis CNC machines are instrumental in producing custom surgical instruments and implants tailored to individual patient needs. This precision machining not only enhances patient outcomes but also allows manufacturers to adhere to stringent regulatory requirements. Buyers in this sector must prioritize sourcing from manufacturers with relevant regulatory certifications and a proven track record of using biocompatible materials, as well as understanding lead times for custom orders.
Electronics
Four-axis CNC machines are increasingly used in the electronics sector for tasks such as PCB prototyping and the fabrication of housing for electronic devices. The ability to achieve high precision in small components accelerates the time-to-market for new products, which is vital in the fast-paced electronics industry. When sourcing, companies should consider the supplier’s material sourcing capabilities, technology compatibility, and options for scalability to meet fluctuating demand.
Furniture and Interior Design
In furniture and interior design, four-axis CNC machines allow for the creation of custom furniture pieces and intricate designs that cater to niche markets. This capability not only meets the growing demand for personalized products but also enhances market differentiation. Buyers should evaluate suppliers based on their design capabilities, finishing options, and delivery timelines to ensure that they can meet customer expectations effectively.
Related Video: How milling on a 4-axis CNC machine works
Strategic Material Selection Guide for four axis cnc machine
When selecting materials for four-axis CNC machining, international B2B buyers must consider various factors, including the material’s properties, suitability for specific applications, and compliance with regional standards. Below is an analysis of three common materials used in four-axis CNC machining, along with insights tailored for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, has excellent corrosion resistance, and offers good thermal conductivity. It typically withstands temperatures up to 150°C and is suitable for applications requiring precision and lightweight components.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantages of aluminum include its ease of machining and relatively low cost compared to other metals. However, it has lower strength compared to steel and can be less durable in high-stress applications. Additionally, the manufacturing complexity can increase if intricate designs are required.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is ideal for applications in aerospace, automotive, and consumer electronics, where weight reduction is critical. Its compatibility with various media makes it suitable for diverse industries.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify compliance with standards such as ASTM and EN for quality assurance. In regions like Africa and South America, sourcing aluminum may involve navigating import tariffs, so understanding local regulations is crucial.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel is known for its high strength, excellent corrosion resistance, and ability to withstand high temperatures (up to 800°C). It is often used in environments where hygiene is paramount due to its non-reactive nature.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of stainless steel is its durability and resistance to wear and tear. However, it is more expensive than aluminum and can be more challenging to machine, requiring specialized tools and techniques.
Impact on Application: This material is commonly used in the food processing, medical, and chemical industries due to its ability to resist corrosion and contamination. Its robustness makes it suitable for high-stress applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM A240 for stainless steel grades. Additionally, understanding local market preferences and availability can influence sourcing decisions, particularly in the Middle East and Europe.
Plastic (e.g., POM, Nylon)
Key Properties: Plastics like Polyoxymethylene (POM) and Nylon offer good mechanical strength, low friction, and excellent chemical resistance. They typically operate effectively in temperatures ranging from -40°C to 100°C.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of plastics is their lightweight nature and lower cost compared to metals. They are also easier to machine and can be produced in complex shapes. However, they may not be suitable for high-temperature applications and can be less durable than metals.
Impact on Application: Plastics are widely used in automotive components, consumer goods, and electronic housings due to their versatility and cost-effectiveness. Their compatibility with various chemicals makes them suitable for diverse applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should look for compliance with standards like ASTM D638 for tensile properties. In regions such as South America and Africa, understanding the availability of specific plastic grades can impact production timelines.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for four axis cnc machine | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Aerospace components, automotive parts | Lightweight and easy to machine | Lower strength than steel | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing equipment, medical devices | High durability and corrosion resistance | Higher cost and machining complexity | High |
| Plastic (POM, Nylon) | Automotive components, consumer goods | Lightweight and cost-effective | Limited high-temperature use | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides international B2B buyers with essential insights to make informed decisions when sourcing materials for four-axis CNC machining. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material, along with regional considerations, can significantly enhance procurement strategies and product performance.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for four axis cnc machine
Manufacturing Processes for Four Axis CNC Machines
The manufacturing process for four-axis CNC machines is a complex interplay of precision engineering, advanced technology, and meticulous quality assurance. Understanding these processes is essential for international B2B buyers to ensure they are sourcing high-quality machines that meet their operational needs.
Main Stages of Manufacturing
-
Material Preparation
– Selection of Raw Materials: High-quality metals like aluminum, steel, and titanium are commonly used. The choice depends on the end-use application and desired machine characteristics.
– Cutting and Shaping: Raw materials are cut into manageable sizes using techniques such as laser cutting or water jet cutting. This step ensures that the materials are ready for the subsequent forming process. -
Forming
– CNC Machining: This is where the heart of the four-axis technology comes into play. The machine uses computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software to guide the machining process, allowing for intricate designs and precision shaping.
– Drilling and Milling: These processes create the necessary holes and shapes in the workpiece. The four-axis capability allows for more complex geometries that are not achievable with three-axis machines.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Assembly
– Component Assembly: After individual components are machined, they are assembled. This includes integrating the motor systems, control units, and other critical components.
– Alignment and Calibration: Proper alignment and calibration are crucial to ensure that the machine operates as intended. This process involves adjusting the machine’s axes and verifying that all components function harmoniously. -
Finishing
– Surface Treatment: Various finishing techniques such as anodizing, powder coating, or painting are applied to enhance aesthetics and protect against corrosion.
– Final Inspection: Before the machine is shipped, it undergoes a thorough inspection to ensure that all specifications and quality standards are met.
Quality Assurance Measures
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing of four-axis CNC machines. It ensures that the final product meets both international and industry-specific standards.
International Standards
- ISO 9001: This is a widely recognized quality management standard that outlines criteria for an effective quality management system (QMS). Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that the manufacturer consistently provides products that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- CE Marking: For machines sold in the European Economic Area, CE marking is essential. It indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
Industry-Specific Standards
- API (American Petroleum Institute): For CNC machines used in the oil and gas industry, compliance with API standards is critical for ensuring operational safety and reliability.
- AS9100: This standard is vital for manufacturers serving the aerospace sector, focusing on quality management systems in the production of aerospace products.
Quality Control Checkpoints
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
– Inspection of raw materials upon receipt to verify compliance with specified standards. This includes checking material certifications and conducting initial tests. -
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
– Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process to ensure that machining processes are within specified tolerances. This involves real-time inspections at various stages. -
Final Quality Control (FQC)
– A comprehensive evaluation of the finished product before shipping. This includes functionality tests, dimensional checks, and visual inspections to ensure the machine meets all specifications.
Common Testing Methods
- Functional Testing: Ensures that all machine features operate as intended. This includes running the machine through its operational cycles.
- Dimensional Inspection: Utilizing tools like calipers and gauges to measure critical dimensions against specifications.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing or dye penetrant testing to identify any internal defects without damaging the components.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying the quality control measures of potential suppliers is crucial. Here are actionable strategies:
- Supplier Audits: Conduct regular audits of suppliers to assess their manufacturing processes and quality control systems. This provides insight into their adherence to international standards.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Ask suppliers for detailed quality reports that outline their quality assurance processes and results from various inspections and tests.
- Engaging Third-Party Inspectors: Consider hiring independent inspection agencies to conduct audits and verify compliance with quality standards. This adds an extra layer of assurance.
Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
When sourcing four-axis CNC machines from international suppliers, buyers must navigate various certification and quality control nuances:
- Understanding Local Regulations: Different regions may have specific regulations and standards that manufacturers must adhere to. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these requirements to ensure compliance.
- Language Barriers: Documentation and communication may be in different languages. Ensure that all technical documents, certifications, and quality reports are available in a language that can be easily understood.
- Cultural Differences: Be aware of cultural differences that may affect business negotiations and expectations regarding quality and compliance. Establishing clear communication channels can mitigate misunderstandings.
By thoroughly understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures associated with four-axis CNC machines, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and quality expectations.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for four axis cnc machine Sourcing
In the sourcing of four-axis CNC machines, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers. This analysis outlines the primary cost components, price influencers, and actionable insights tailored for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the cost of a four-axis CNC machine. Common materials include steel, aluminum, and various alloys. Prices fluctuate based on global market trends, availability, and quality specifications.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary widely depending on the manufacturing location. Regions with lower labor costs may offer attractive pricing, but it’s essential to consider the skill level and expertise required for precision machining.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses fixed and variable costs associated with the production process, including utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient operations can lead to lower overhead costs, which can be passed on to buyers.
-
Tooling: Specialized tooling is often required for four-axis CNC machines, impacting initial costs. Tooling costs should be factored into the overall budget, especially if custom tools are needed for specific machining tasks.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the machines meet specified quality standards involves additional costs for inspections and testing. Buyers should verify that suppliers adhere to international standards and certifications, which can influence pricing.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs are significant, especially for bulky machinery. These costs can vary based on the shipping method, distance, and whether any tariffs or duties apply. Understanding Incoterms is vital for managing these expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. This margin can vary based on competition, market demand, and the supplier’s positioning in the market.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk orders often lead to discounts. Buyers should assess their needs carefully and consider negotiating minimum order quantities (MOQs) to optimize costs.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom features or high precision specifications can increase costs. Clearly defining requirements upfront can prevent unexpected expenses later in the process.
-
Materials and Quality/Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (like ISO) usually come at a premium. However, investing in quality can reduce long-term operational costs and maintenance.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but can provide assurance of quality and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international transactions. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly affect the total cost.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Always negotiate pricing, especially when ordering in bulk. Suppliers are often willing to offer discounts to secure larger orders.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes purchase price, maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime. A lower upfront cost may not always translate to savings over time.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing variations. For instance, suppliers in Europe may have different cost structures compared to those in Africa or South America due to labor and material costs.
-
Research and Compare: Conduct thorough market research to compare prices and specifications from multiple suppliers. This will help in understanding the market standard and identifying reasonable pricing.
-
Long-Term Relationships: Building a long-term relationship with suppliers can lead to better pricing, improved service, and priority in production schedules.
Disclaimer
The prices indicated in this analysis are indicative and may vary based on market conditions, exchange rates, and specific negotiations. Always conduct due diligence and obtain multiple quotes before making purchasing decisions.
Spotlight on Potential four axis cnc machine Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘four axis cnc machine’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for four axis cnc machine
When considering the acquisition of a four-axis CNC machine, understanding its technical specifications and trade terminology is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Below is a detailed overview of essential properties and industry terms that can significantly impact your buying process.
Key Technical Properties
-
Material Grade
– Definition: Refers to the type of materials the machine can process, such as aluminum, steel, or plastics.
– B2B Importance: Choosing a machine that can handle the specific materials relevant to your business ensures compatibility with your production needs. It impacts the durability and quality of the finished products. -
Tolerance
– Definition: The allowable limit of variation in a physical dimension, often expressed in millimeters or micrometers.
– B2B Importance: High precision is essential for industries such as aerospace and medical devices. Understanding tolerance levels helps buyers ensure that the CNC machine meets the required standards for their products, minimizing the risk of defects. -
Spindle Speed
– Definition: The maximum speed at which the spindle can rotate, typically measured in revolutions per minute (RPM).
– B2B Importance: A higher spindle speed allows for faster machining operations, which can lead to increased productivity. Buyers should assess spindle speed based on the materials they intend to work with and the desired finish quality. -
Axis Movement Range
– Definition: The extent to which the machine can move along each axis, often specified as X, Y, Z, and A (the fourth axis).
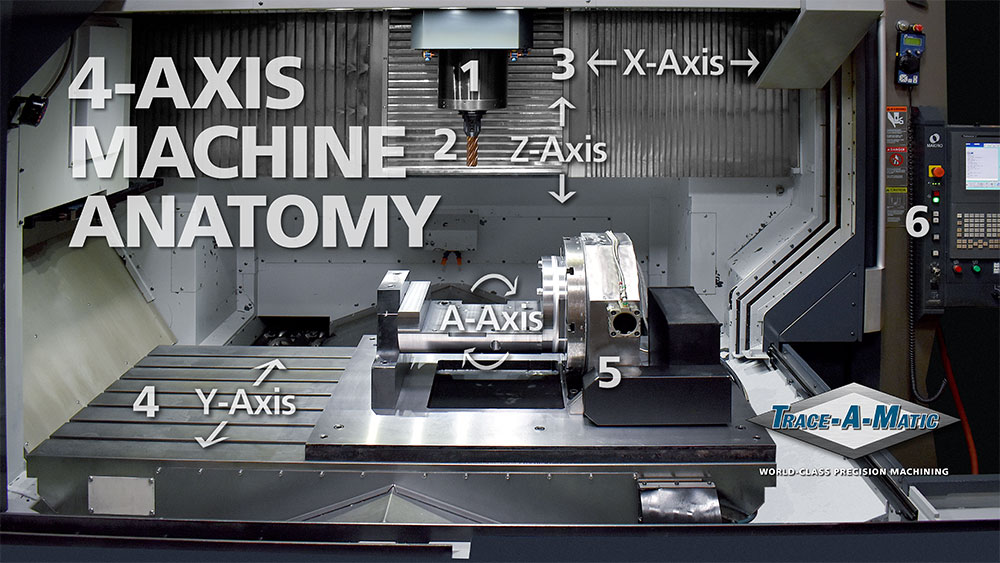
– B2B Importance: The movement range determines the size of the components that can be machined. Buyers need to evaluate whether the machine can accommodate the dimensions of their products. -
Control System
– Definition: The software and hardware that manage the machine’s operations, including programming languages like G-code.
– B2B Importance: A user-friendly control system can significantly reduce training time and operational errors. Buyers should consider compatibility with their existing systems and the learning curve for operators.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Significance: Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reputable suppliers and ensure they are sourcing quality components for their CNC machines. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Significance: This term is critical for budgeting and inventory management. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their production volumes to avoid excess inventory costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services.
– Significance: An RFQ process allows buyers to compare pricing and terms from multiple suppliers, ensuring they secure the best deal for their CNC machinery needs. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions.
– Significance: Understanding Incoterms is vital for clarifying shipping responsibilities, costs, and risks associated with the delivery of CNC machines, which can affect total purchase costs. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time taken from the placement of an order until the product is delivered.
– Significance: Knowing the lead time is essential for planning production schedules. Buyers should communicate expected timelines with suppliers to align delivery with operational needs.
By familiarizing yourself with these technical properties and trade terms, you can navigate the complexities of purchasing a four-axis CNC machine more effectively, ensuring that your investment aligns with your operational goals and market demands.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the four axis cnc machine Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The four-axis CNC machine sector is experiencing robust growth driven by advancements in automation and the increasing demand for precision engineering across various industries. Key global drivers include the rapid expansion of manufacturing capabilities in emerging markets, particularly in Africa and South America, where infrastructure development is a priority. Additionally, the rising trend of Industry 4.0, characterized by smart factories and interconnected systems, is pushing B2B buyers towards investing in sophisticated CNC technologies that enhance productivity and operational efficiency.
Current sourcing trends highlight a shift towards digital procurement processes, allowing buyers to streamline their supply chain management. This evolution is especially pertinent for international buyers in regions like the Middle East and Europe, where procurement efficiency can lead to significant cost savings. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on customization capabilities of four-axis CNC machines, enabling businesses to cater to niche markets and specific customer requirements.
Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning are also influencing market dynamics. These technologies improve predictive maintenance, reduce downtime, and optimize production processes. For B2B buyers, understanding these trends is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions and staying competitive in a rapidly changing landscape.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability has become a pivotal concern in the four-axis CNC machine sector, with an increasing focus on minimizing environmental impact. B2B buyers are urged to prioritize suppliers that adopt sustainable practices, such as reducing energy consumption and waste production during manufacturing processes. Implementing energy-efficient technologies not only aligns with global sustainability goals but also often results in reduced operational costs.
Moreover, the importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers should consider the sourcing of materials, ensuring that they come from suppliers who adhere to fair labor practices and environmental regulations. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety are indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Utilizing ‘green’ materials and technologies in the production of four-axis CNC machines can enhance a company’s reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious clients. Buyers should actively seek out suppliers who can provide documentation on the sustainability of their materials and processes, fostering a transparent and responsible supply chain.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of four-axis CNC machines can be traced back to the early days of CNC technology in the 1950s. Initially, CNC machines were limited to two-dimensional operations, but the introduction of the third axis enabled more complex shapes and designs. The addition of a fourth axis in the 1990s allowed for enhanced machining capabilities, enabling manufacturers to produce intricate components with higher precision.
As global manufacturing demands have evolved, so too has the technology behind four-axis CNC machines. The rise of digital technologies and automation has transformed the landscape, making these machines not only essential for efficiency but also for meeting the increasing customization needs of diverse markets. This historical context underscores the continuous innovation within the sector, which is vital for B2B buyers aiming to leverage cutting-edge technology in their operations.
Related Video: Chapter 9: International Trade
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of four axis cnc machine
-
What should I consider when vetting suppliers of four axis CNC machines?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their industry experience and reputation. Look for manufacturers with a proven track record in producing four axis CNC machines, ideally with international clientele. Request references and check customer reviews or testimonials. Assess their production capabilities, including technology and machinery used. It’s also beneficial to visit their facilities or request a virtual tour to evaluate quality control processes and workforce expertise. -
Can four axis CNC machines be customized to meet specific project requirements?
Yes, most suppliers offer customization options for four axis CNC machines. It is important to communicate your specific needs, such as size, software compatibility, and additional features. Discuss the feasibility of these customizations early in the sourcing process to avoid delays. Ensure that the supplier provides a detailed proposal outlining the modifications, associated costs, and any potential impacts on lead times. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for four axis CNC machines?
MOQs can vary significantly among suppliers, often depending on the complexity of the machine and the level of customization required. Generally, expect MOQs to range from one unit for standard models to several units for customized machines. Lead times can also vary, typically ranging from 6 to 12 weeks. Always clarify these terms upfront to align production schedules with your project timelines. -
What payment terms are standard for purchasing four axis CNC machines internationally?
Payment terms can differ based on the supplier’s policies and your negotiation. Common arrangements include a deposit (often 30-50%) upfront, with the balance due upon delivery or installation. Consider using secure payment methods, such as letters of credit, to protect your investment. Discuss any financing options available, as some suppliers may offer installment plans for large purchases. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and certifications for four axis CNC machines?
Request copies of relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001 or CE marking, which indicate compliance with international quality standards. Inquire about the supplier’s quality control processes, including testing and inspection procedures. It may also be beneficial to conduct third-party quality audits or inspections prior to shipment to ensure that the machines meet your specifications and industry standards. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing four axis CNC machines?
When importing, consider shipping costs, customs duties, and any additional fees that may arise. Work with logistics providers experienced in handling heavy machinery to ensure safe and timely delivery. Understand the import regulations of your country and ensure all necessary documentation is prepared, such as bills of lading and customs declarations, to avoid delays at customs. -
What steps should I take if a dispute arises with a supplier?
First, maintain open communication to resolve the issue amicably. Document all correspondence related to the dispute and keep records of agreements. If direct negotiation fails, refer to the terms outlined in your contract regarding dispute resolution. Consider mediation or arbitration as alternatives to litigation, as they can be more cost-effective and quicker. Always consult legal counsel familiar with international trade laws for guidance. -
How can I evaluate the after-sales support offered by suppliers of four axis CNC machines?
Assess the supplier’s commitment to after-sales support by inquiring about their warranty terms, parts availability, and technical assistance. Determine if they provide training for operators and maintenance staff. A reliable supplier should also offer a clear process for reporting issues and obtaining support. Reading reviews from other customers can provide insights into the supplier’s responsiveness and effectiveness in handling after-sales service.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for four axis cnc machine
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of four-axis CNC machines presents significant opportunities for international B2B buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By leveraging advanced manufacturing capabilities, businesses can enhance production efficiency and precision, ultimately leading to improved product quality and reduced operational costs.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Key takeaways include the importance of conducting thorough supplier evaluations, understanding the regional market dynamics, and fostering strong relationships with manufacturers to ensure a reliable supply chain. Additionally, staying informed about technological advancements and industry trends is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions.
As the global demand for customized and intricate machining solutions continues to grow, now is the opportune time for buyers to engage with reputable suppliers and explore potential partnerships. Emphasizing strategic sourcing not only mitigates risks but also positions businesses to remain competitive in an evolving market landscape.
Take action today: Assess your current sourcing strategies, identify potential suppliers, and invest in the right four-axis CNC machines to drive your business forward in this dynamic environment. The future of manufacturing is here—embrace it!