Discover Cost-Saving Benefits of Thermoplastic Molding (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for thermoplastic molding
In today’s competitive landscape, international B2B buyers face the significant challenge of sourcing high-quality thermoplastic molding solutions that meet diverse industrial needs. From automotive components to consumer products, thermoplastic molding is a versatile manufacturing process essential for producing durable and functional plastic parts. However, navigating the global market requires a deep understanding of various molding techniques, material selections, and supplier capabilities to ensure optimal product performance and cost-effectiveness.
This comprehensive guide covers the intricacies of thermoplastic molding, including various types such as injection molding, blow molding, and overmolding, as well as their specific applications across different sectors. Additionally, it provides actionable insights into effective supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and emerging trends that impact the global supply chain. By equipping buyers with the necessary knowledge, this guide empowers them to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational goals and market demands.
For B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—particularly in key markets like Germany and the UK—understanding these nuances is crucial to successfully navigating the complexities of sourcing thermoplastic molding solutions. Whether you are exploring new suppliers or optimizing existing partnerships, this guide serves as a valuable resource for enhancing your procurement strategy and achieving sustainable growth.
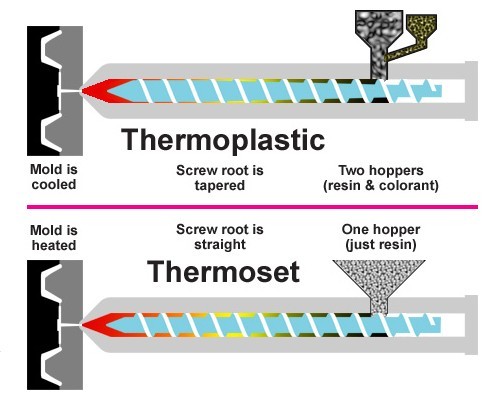
Understanding thermoplastic molding Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plastic Injection Molding | High precision, mass production, complex shapes | Automotive parts, consumer goods, electronics | Pros: High efficiency, scalability. Cons: Initial tooling costs can be high. |
| Blow Molding | Creates hollow parts, uses air pressure to form products | Bottles, containers, automotive fuel tanks | Pros: Cost-effective for large volumes. Cons: Limited to hollow shapes. |
| Rotational Molding | Produces seamless, hollow parts through rotation | Toys, storage tanks, large containers | Pros: Versatile for large and complex designs. Cons: Slower cycle times compared to injection molding. |
| Compression Molding | Utilizes heat and pressure to shape materials | Electrical housings, automotive components | Pros: Good for large parts, less waste. Cons: Longer cycle times. |
| Overmolding | Combines two materials for enhanced functionality | Grips, handles, multi-material components | Pros: Improved product performance. Cons: More complex design and production. |
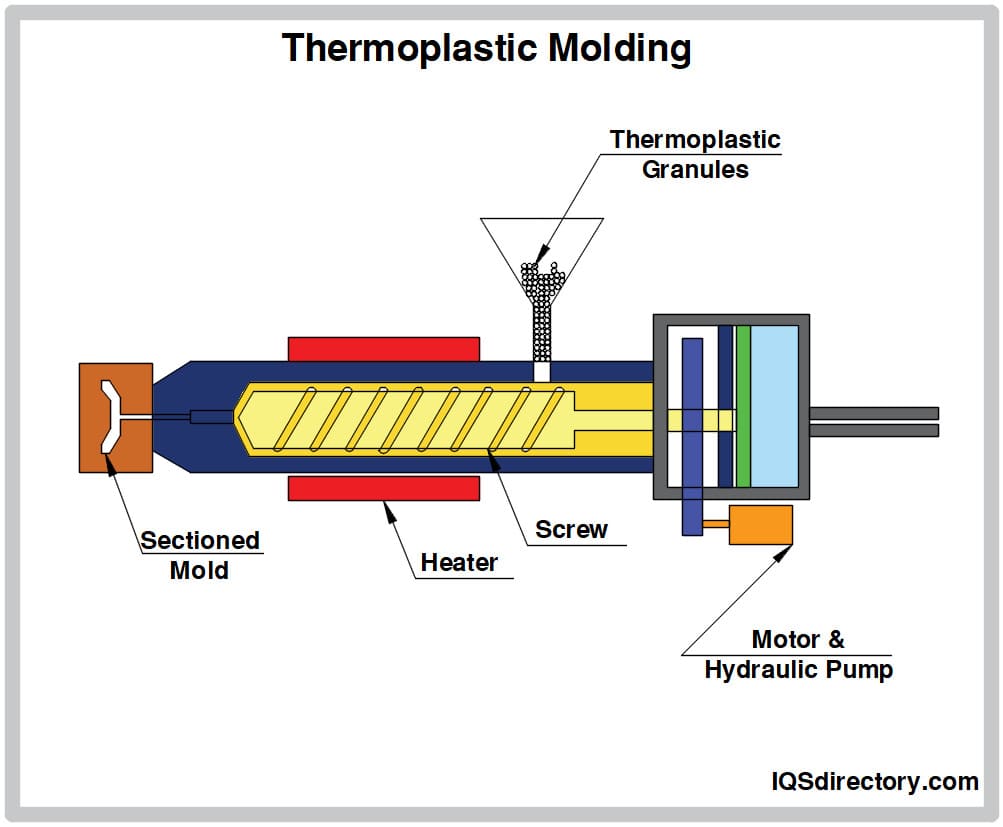
What Are the Characteristics of Plastic Injection Molding?
Plastic injection molding is a highly efficient method for producing a wide range of plastic parts. This technique is characterized by its ability to create intricate designs and high precision components in large quantities. B2B buyers should consider the initial investment in tooling, as this can be significant, but the benefits of scalability and reduced per-unit costs make it a compelling choice for mass production. Industries such as automotive, consumer goods, and electronics heavily rely on this process for its versatility and efficiency.
How Does Blow Molding Work and What Are Its Applications?
Blow molding is distinct for its ability to create hollow plastic products by inflating a heated plastic tube within a mold. This method is particularly suited for producing containers, such as bottles, and larger hollow items like automotive fuel tanks. Buyers should weigh the cost-effectiveness of blow molding for high-volume production against its limitations in terms of design complexity, as it is primarily suitable for simple, hollow shapes.
Why Choose Rotational Molding for Your Products?
Rotational molding stands out for its capability to produce seamless, hollow parts through a unique rotational technique. This process is ideal for larger products, including storage tanks and toys, where design complexity is essential. B2B buyers should note that while rotational molding allows for versatile shapes, the cycle times are generally slower than those of injection molding. Therefore, it is best suited for lower-volume production runs where quality and design are prioritized over speed.
What Advantages Does Compression Molding Offer?
Compression molding is a method that involves shaping materials using heat and pressure, making it suitable for producing large parts like automotive components and electrical housings. This process is advantageous for B2B buyers as it results in less waste compared to other molding techniques. However, the longer cycle times can be a drawback, especially for projects requiring quick turnaround. Buyers should assess their production needs against the capabilities of compression molding to determine its suitability.
How Can Overmolding Enhance Product Performance?
Overmolding is a specialized process that involves combining two different materials to create a single part, enhancing functionality and aesthetics. This technique is frequently used for grips and handles, as it allows for improved tactile surfaces and durability. B2B buyers should consider the complexity of the design and the potential for increased production costs, but the resultant product performance can justify the investment. Overmolding is particularly beneficial in applications where multi-material functionality is required.
Key Industrial Applications of thermoplastic molding
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Thermoplastic Molding | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Production of interior components | Lightweight, durable parts that enhance fuel efficiency | Material compatibility, precision manufacturing standards |
| Consumer Electronics | Manufacturing of housings and enclosures | Enhanced aesthetics and protection for electronic devices | Customization options, thermal resistance requirements |
| Medical Devices | Creation of surgical instruments and casings | High biocompatibility and precision for safety | Regulatory compliance, material certifications |
| Packaging | Production of containers and closures | Cost-effective, lightweight solutions for shipping | Sustainability of materials, sealing and barrier properties |
| Construction | Fabrication of piping and fittings | Durable, corrosion-resistant solutions for infrastructure | Compliance with local building codes, material strength |
How is Thermoplastic Molding Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, thermoplastic molding is pivotal for producing lightweight interior components, such as dashboards and door panels. These molded parts not only reduce vehicle weight, leading to improved fuel efficiency but also offer high durability and aesthetic appeal. International B2B buyers, particularly from Europe and South America, should consider sourcing materials that meet stringent automotive standards and ensure precise manufacturing to maintain quality and safety.
What Role Does Thermoplastic Molding Play in Consumer Electronics?
Thermoplastic molding is extensively used in the consumer electronics industry for creating housings and enclosures for devices such as smartphones and laptops. This application provides enhanced aesthetics, protection against environmental factors, and the ability to incorporate complex designs. Buyers from Africa and the Middle East should focus on suppliers who offer customizable options and ensure thermal resistance to protect sensitive electronic components.
Why is Thermoplastic Molding Important for Medical Devices?
In the medical field, thermoplastic molding is crucial for the production of surgical instruments and casings, where precision and biocompatibility are paramount. This process allows for the creation of complex geometries that are essential for functionality and safety. International buyers, especially from Europe, must prioritize sourcing materials that comply with healthcare regulations and certifications to ensure patient safety.
How is Thermoplastic Molding Used in Packaging Solutions?
Thermoplastic molding is a key process in the packaging industry, where it is utilized to manufacture containers and closures. This method offers cost-effective and lightweight solutions that are essential for shipping and storage. B2B buyers, particularly in Africa and South America, should consider the sustainability of materials and the sealing properties of molded products to meet the growing demand for eco-friendly packaging solutions.
What Applications Does Thermoplastic Molding Have in Construction?
In construction, thermoplastic molding is used for fabricating piping and fittings that are both durable and corrosion-resistant. These molded components are essential for maintaining the integrity of infrastructure projects. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should ensure compliance with local building codes and focus on sourcing materials that offer high strength and longevity to withstand environmental challenges.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘thermoplastic molding’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Material Selection for Thermoplastic Molding
The Problem:
International B2B buyers often face challenges in selecting the appropriate thermoplastic material for their specific applications. With a wide range of thermoplastics available—each with distinct mechanical properties, thermal stability, and cost implications—buyers may struggle to identify the best fit. This can lead to suboptimal product performance, increased costs due to material waste, or delays in production timelines.
The Solution:
To overcome material selection challenges, buyers should engage in a thorough material analysis process. Start by defining the application requirements, such as mechanical strength, temperature resistance, and environmental exposure. Utilize resources such as material data sheets and industry comparison tools to evaluate the properties of various thermoplastics like polycarbonate, polypropylene, or nylon. Collaborating with suppliers who offer material testing services can also provide insights into how different materials perform under specific conditions. Additionally, consider prototyping with different materials through small-scale production runs to assess performance before committing to large orders. This proactive approach not only reduces the risk of costly mistakes but also enhances product quality and reliability.
Scenario 2: Inconsistent Quality in Thermoplastic Parts
The Problem:
Quality inconsistencies in molded parts can severely impact a buyer’s operations, leading to increased rejection rates and customer dissatisfaction. Factors such as variations in mold temperature, injection speed, or cooling time can contribute to defects like warping, short shots, or surface imperfections. For buyers, this means facing potential losses and damage to their reputation in the market.
The Solution:
To ensure consistent quality in thermoplastic parts, buyers should implement a comprehensive quality control (QC) strategy throughout the molding process. Start by working closely with suppliers to establish standardized operating procedures that detail optimal temperature, pressure, and cycle times for each specific thermoplastic material. Additionally, investing in advanced molding machines equipped with real-time monitoring systems can help track critical parameters and ensure they remain within specified limits. Conducting regular audits and inspections during the production process can also identify deviations early, allowing for corrective actions before large quantities are produced. Furthermore, consider integrating automated quality assurance technologies, such as vision systems, to enhance the inspection process and ensure that only parts meeting quality standards reach the final customers.
Scenario 3: High Production Costs Due to Inefficient Processes
The Problem:
Many B2B buyers encounter high production costs associated with thermoplastic molding, stemming from inefficient processes, excessive waste, and extended cycle times. This issue is particularly pronounced in regions where operational costs are already high, such as Europe and parts of the Middle East, making it essential to find ways to optimize manufacturing without compromising quality.
The Solution:
To mitigate high production costs, buyers should focus on process optimization strategies that enhance efficiency. Start by conducting a thorough analysis of the current molding processes to identify bottlenecks or areas of waste. Implement lean manufacturing principles, such as reducing cycle times through improved cooling techniques and optimizing the injection process to minimize excess material use. Collaborating with suppliers who specialize in process engineering can provide valuable insights into best practices and advanced technologies that can streamline operations. Additionally, consider investing in energy-efficient machinery that reduces power consumption and lowers operational costs over time. Finally, fostering a culture of continuous improvement among the production team can lead to innovative solutions that further enhance productivity and reduce costs in the long run.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for thermoplastic molding
What Are the Key Properties of Common Thermoplastic Materials?
When selecting materials for thermoplastic molding, understanding the properties of various thermoplastics is essential for achieving optimal performance in applications. Below, we analyze four commonly used thermoplastic materials—Polyethylene (PE), Polypropylene (PP), Polycarbonate (PC), and Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)—focusing on their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
How Does Polyethylene (PE) Perform in Thermoplastic Molding?
Key Properties:
Polyethylene is known for its excellent chemical resistance, low-density characteristics, and good impact strength. It typically operates well at temperatures up to 80°C (176°F) and exhibits flexibility, making it suitable for a variety of applications.
Pros & Cons:
The durability of PE is commendable, particularly in applications requiring resistance to moisture and chemicals. However, its relatively low temperature resistance can limit its use in high-temperature environments. Additionally, while PE is cost-effective, it may not be suitable for applications requiring high structural integrity.
Impact on Application:
PE is often used in packaging, containers, and pipes, where its chemical resistance plays a crucial role. However, it may not be ideal for structural components exposed to high heat or stress.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with local regulations regarding food safety and environmental impact, especially in regions like Europe where stringent standards exist (e.g., EU regulations on plastic materials).
What Are the Advantages of Polypropylene (PP) in Molding?
Key Properties:
Polypropylene is characterized by its high melting point (around 160°C or 320°F), excellent fatigue resistance, and low density. It is also resistant to many chemical solvents, acids, and bases.
Pros & Cons:
PP offers a good balance of strength and flexibility, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, including automotive parts and consumer goods. However, its susceptibility to UV degradation can limit outdoor applications unless treated. While generally affordable, the cost can rise with specialty grades.
Impact on Application:
PP is ideal for applications requiring light weight and durability, such as automotive components and packaging. Its chemical resistance makes it suitable for containers holding various substances.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers from regions like South America and Africa should be aware of local standards regarding recycling and waste management, as PP is highly recyclable but can contribute to environmental concerns if not disposed of properly.
Why Choose Polycarbonate (PC) for High-Performance Applications?
Key Properties:
Polycarbonate is renowned for its high impact resistance and clarity. It can withstand temperatures up to 120°C (248°F) and has excellent dimensional stability.
Pros & Cons:
The durability and transparency of PC make it an excellent choice for applications like safety goggles and automotive lighting. However, it is more expensive than other thermoplastics and can be prone to scratching unless coated.
Impact on Application:
PC is often used in applications requiring transparency and toughness, such as electronic housings and optical lenses. Its ability to withstand high temperatures also makes it suitable for certain industrial applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with safety standards is critical, especially in Europe where regulations regarding optical clarity and impact resistance are stringent. Buyers should also consider the availability of protective coatings to enhance durability.
What Are the Limitations of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)?
Key Properties:
ABS is known for its toughness, impact resistance, and good thermal stability, operating effectively at temperatures up to 100°C (212°F). It also has excellent machinability.
Pros & Cons:
ABS is widely used due to its balance of strength, cost-effectiveness, and ease of processing. However, it is less resistant to UV light and may require additives for outdoor applications. Its manufacturing process can be complex, impacting production timelines.
Impact on Application:
Commonly used in consumer electronics, automotive parts, and toys, ABS is favored for applications requiring a good surface finish and strength.
Considerations for International Buyers:
B2B buyers should be aware of compliance with safety standards, especially in the toy industry, where regulations can vary significantly across regions like Europe and the Middle East.
Summary Table of Thermoplastic Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for thermoplastic molding | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene (PE) | Packaging, containers, pipes | Excellent chemical resistance | Limited high-temperature use | Low |
| Polypropylene (PP) | Automotive parts, consumer goods | Good strength and flexibility | UV degradation risk | Medium |
| Polycarbonate (PC) | Safety goggles, automotive lighting | High impact resistance | Higher cost, prone to scratching | High |
| Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Consumer electronics, toys | Good surface finish and strength | UV light sensitivity | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides international B2B buyers with essential insights into thermoplastic materials, enabling informed decisions that align with their specific application needs and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for thermoplastic molding
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Thermoplastic Molding?
The manufacturing process of thermoplastic molding involves several critical stages that ensure the creation of high-quality plastic components. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers assess suppliers’ capabilities effectively.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in the thermoplastic molding process is material preparation. This involves selecting the appropriate thermoplastic polymer based on the desired properties of the final product. Common materials include polyethylene, polypropylene, and polycarbonate, each chosen for specific mechanical and thermal characteristics. Prior to molding, the plastic pellets must be dried to remove moisture, which can adversely affect the melting process and the quality of the molded part.
2. Forming: How Is Thermoplastic Molding Conducted?
The forming stage consists of several sub-processes, primarily focusing on injection molding, which is the most prevalent technique for thermoplastic molding. The procedure begins with heating the plastic pellets in a barrel until they melt into a viscous state.
Once melted, the molten plastic is injected into a precisely designed mold under high pressure. The pressure and speed of injection are critical, as they determine the completeness and uniformity of the mold fill. After filling, the molten plastic is allowed to cool and solidify within the mold, during which time the part takes its final shape.
3. Assembly: What Happens After Molding?
After cooling, the molded part is ejected from the mold using ejector pins. The timing and force of this ejection process are crucial to prevent damage to the part. Following ejection, assembly may involve integrating various components if the final product consists of multiple parts. This could include the addition of fasteners, fittings, or other elements necessary for the product’s functionality.
4. Finishing: How Are Molded Parts Enhanced?
The finishing stage involves refining the molded parts to meet aesthetic and functional requirements. Common processes include trimming excess material, polishing surfaces, and applying coatings or paints as needed. Finishing ensures that the final product not only meets quality standards but also appeals to end-users.
What Are the Key Quality Control Measures in Thermoplastic Molding?
Quality assurance in thermoplastic molding is essential for ensuring that products meet international standards and customer expectations. Various quality control measures are implemented throughout the manufacturing process.
Relevant International Standards for Quality Assurance
International standards such as ISO 9001 are critical benchmarks for quality management systems. This standard emphasizes continuous improvement and customer satisfaction, making it a vital certification for suppliers in the thermoplastic molding industry. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE marking for safety compliance and API standards for oil and gas applications may also be relevant depending on the end-use of the molded products.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control checkpoints are systematically integrated into the manufacturing process to monitor and verify product quality:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified criteria. It helps prevent defective materials from entering the production line.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the molding process, regular checks are performed to monitor parameters such as temperature, pressure, and cycle time. These checks help identify deviations from optimal operating conditions that could affect product quality.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After the molding and finishing stages, a comprehensive inspection is conducted to assess the final products. This includes dimensional checks, visual inspections, and functional tests to ensure that the parts meet predefined specifications.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Thermoplastic Molding Quality Control?
Several testing methods are commonly employed to validate the quality of thermoplastic molded parts:
-
Mechanical Testing: This includes tensile tests, impact tests, and hardness tests to evaluate the mechanical properties of the molded parts. These tests determine how well the parts will perform under various conditions.
-
Thermal Testing: Thermal properties such as heat resistance and thermal expansion are assessed to ensure the material can withstand operational temperatures.
-
Visual Inspection: This involves a thorough examination of the molded parts for surface defects, color consistency, and overall appearance.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers must ensure that their suppliers adhere to rigorous quality control standards. Here are actionable steps to verify supplier QC:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of supplier facilities can provide insights into their quality management practices. These audits should focus on compliance with international standards and the effectiveness of their QC processes.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed quality reports that outline their testing methods, results, and any corrective actions taken in case of non-compliance. This transparency is vital for building trust.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality control practices. These inspectors can perform random checks and validate the quality of products before shipment.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, need to be aware of specific nuances in quality control and certification:
-
Regional Regulations: Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements for plastic products. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local standards and certifications required in their markets.
-
Cultural Considerations: Understanding the cultural attitudes towards quality and compliance in different regions can influence supplier relationships. For instance, European buyers may expect stringent adherence to regulations, whereas other regions may have more flexible approaches.
-
Communication: Clear communication about quality expectations and standards is essential. Buyers should establish comprehensive contracts that outline quality requirements, inspection protocols, and recourse in case of defects.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols in thermoplastic molding equips international B2B buyers with the knowledge to make informed decisions. By focusing on these elements, buyers can ensure they partner with reliable suppliers capable of delivering high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘thermoplastic molding’
The following guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers interested in procuring thermoplastic molding services and materials. It outlines essential steps to ensure informed decision-making, optimal sourcing, and successful partnerships.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging with suppliers, it is crucial to clearly outline your technical requirements. This includes specifying the types of thermoplastics needed, dimensions, tolerances, and any specific performance criteria relevant to your industry.
– Considerations: Identify the application of the molded parts and ensure that the materials selected align with these needs.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers specializing in thermoplastic molding. Utilize industry directories, trade shows, and online platforms to gather a list of candidates.
– Key Actions: Look for suppliers with a proven track record in your industry, and pay attention to their production capabilities, technology used, and customer reviews.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before making a commitment, verify that your shortlisted suppliers hold relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001 or industry-specific standards. Certifications indicate a commitment to quality and adherence to international best practices.
– Importance of Certifications: These credentials can help mitigate risks related to product quality and compliance with regulations, which is particularly important for buyers in regions with stringent import laws.
Step 4: Request Samples and Prototypes
Once you have narrowed down your options, request samples or prototypes of the thermoplastic parts you need. This step allows you to assess the quality, finish, and functionality of the products.
– What to Look For: Evaluate the samples for accuracy, surface quality, and structural integrity. This will provide insight into the supplier’s manufacturing capabilities and help you make a more informed decision.
Step 5: Assess Production Capabilities and Lead Times
Understand the supplier’s production capacity and lead times to ensure they can meet your demand. Inquire about their machinery, technology, and workforce qualifications to gauge their ability to handle your order size.
– Key Factors: Consider whether the supplier can scale production if your needs increase, and ensure their lead times align with your project timelines.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Engage in discussions about pricing, payment terms, delivery schedules, and warranties. This negotiation phase is crucial to establish a mutually beneficial agreement.
– Tips for Negotiation: Be clear about your budget constraints, but also consider the value of quality and reliability over the lowest price.
Step 7: Establish Communication and Support Channels
Once you’ve selected a supplier, set up clear communication channels for ongoing support. This includes defining points of contact for production updates, quality control, and addressing any potential issues that may arise.
– Importance of Communication: Effective communication can prevent misunderstandings and ensure that both parties are aligned throughout the production process.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline the sourcing process for thermoplastic molding, ensuring that they select reliable suppliers that meet their specific needs and quality standards.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for thermoplastic molding Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Thermoplastic Molding Sourcing?
Understanding the cost structure of thermoplastic molding is crucial for B2B buyers looking to optimize their sourcing strategies. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of thermoplastic materials significantly influences the overall cost. Common materials such as polyethylene, polypropylene, and polycarbonate vary in price based on market fluctuations and availability. Buyers should consider sourcing from suppliers that offer bulk pricing or long-term contracts to mitigate material cost volatility.
-
Labor: Labor costs are impacted by the complexity of the molding process and the location of the manufacturing facility. Regions with higher labor costs, such as Western Europe, may have higher overall pricing compared to emerging markets in Africa or South America. Understanding local labor rates can help buyers negotiate better terms.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with running the production facility, such as utilities, equipment maintenance, and administrative expenses. Buyers should inquire about overhead costs when evaluating supplier quotes, as these can significantly impact the final price.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs are a significant part of the initial investment in thermoplastic molding. High-quality molds are essential for producing accurate and durable parts. Buyers should consider the tooling life expectancy and whether the supplier offers maintenance services or replacements.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality through rigorous QC processes is essential, especially for industries with stringent standards. The costs associated with QC can vary depending on the level of certification required, such as ISO standards. Buyers should assess these costs to ensure they align with their quality requirements.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary widely depending on the shipping method, distance, and Incoterms chosen. Understanding these logistics costs is vital for calculating the total landed cost of products. Buyers should work with suppliers who have efficient logistics networks to minimize these expenses.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can vary based on their business model, market positioning, and competition. Understanding the supplier’s pricing strategy can provide insights into potential negotiation points.
What Factors Influence Pricing in Thermoplastic Molding?
Several factors can influence the pricing of thermoplastic molding, which are important for buyers to consider:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders typically result in lower per-unit costs. Buyers should assess their production needs to determine optimal order sizes that balance inventory costs and production schedules.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized parts may incur additional costs due to the need for unique molds and specialized production processes. Buyers should clearly communicate their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Material Selection: The specific thermoplastic material chosen can have a significant impact on pricing. Buyers should evaluate the performance characteristics of different materials against their application needs to make cost-effective choices.
-
Quality and Certifications: Parts that require higher quality standards or certifications (e.g., automotive or medical applications) may come at a premium. Buyers should factor these costs into their budgeting.
-
Supplier Factors: The reliability and reputation of the supplier can also affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, but they might also offer better quality and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the implications of Incoterms is essential for managing logistics costs and responsibilities. Buyers should negotiate terms that minimize their total cost of ownership while ensuring timely delivery.
What Are Effective Tips for Negotiating Thermoplastic Molding Prices?
To maximize cost-efficiency in thermoplastic molding sourcing, B2B buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Based on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial purchase price and consider long-term costs associated with quality, maintenance, and logistics. A lower upfront cost might lead to higher overall expenses if quality is compromised.
-
Leverage Market Research: Conduct thorough research on material prices, labor costs, and supplier capabilities. Having data on hand can strengthen your negotiation position.
-
Establish Long-Term Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, flexibility, and priority during high-demand periods. Consider entering into long-term contracts for better pricing stability.
-
Clarify Specifications Early: Ensure all product specifications are clearly defined from the outset to avoid costly changes later in the production process. This clarity can help suppliers provide more accurate quotes.
-
Explore Multiple Suppliers: Don’t settle for the first quote. Obtain multiple quotes from different suppliers to compare pricing and services, which can also provide leverage in negotiations.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for thermoplastic molding can fluctuate based on market conditions, material availability, and other factors. Buyers are encouraged to conduct their own due diligence and obtain updated quotes from suppliers to ensure accurate budgeting and planning.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing thermoplastic molding With Other Solutions
Introduction: What Are the Alternatives to Thermoplastic Molding?
In the dynamic landscape of manufacturing, selecting the right molding process is crucial for producing high-quality plastic components. Thermoplastic molding is a popular choice due to its versatility and efficiency. However, various alternative methods exist that may better suit specific applications or requirements. This analysis will compare thermoplastic molding with two viable alternatives: Compression Molding and Blow Molding. By examining critical factors such as performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Thermoplastic Molding | Compression Molding | Blow Molding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and repeatability; suitable for complex designs. | Good for large parts; less precision than thermoplastic molding. | Excellent for hollow parts; limited to certain shapes. |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; cost-effective for high volumes. | Lower initial setup costs; higher per-part costs for low volumes. | Moderate to high initial investment; economical for large quantities. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized machinery; longer setup time. | Simpler machinery; quicker setup for small runs. | Requires specific molds; longer cooling times can delay production. |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed for machinery; complex systems can lead to downtime. | Easier to maintain; fewer moving parts. | Maintenance can be complex due to machinery and mold requirements. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for high-volume production of intricate parts. | Best for larger, simpler parts and lower volume production. | Most effective for producing hollow products like bottles and containers. |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Compression Molding: What Are Its Advantages and Disadvantages?
Compression molding is a process that involves placing a pre-measured amount of plastic material into a heated mold cavity. The mold is then closed, and pressure is applied to shape the material.
Pros:
– Cost-Effective for Low Volumes: Compression molding has lower initial setup costs compared to thermoplastic molding, making it suitable for smaller production runs.
– Simplicity: The machinery is generally simpler, leading to easier operation and maintenance.
Cons:
– Lower Precision: This method is less precise than thermoplastic molding, which may affect the quality of intricate designs.
– Longer Cycle Times: While setup is quick, the overall production cycle can be longer due to the cooling time required.
Blow Molding: When Is It the Best Choice?
Blow molding is a specialized technique used primarily for creating hollow plastic products. The process involves inflating a heated plastic tube until it conforms to the shape of the mold.
Pros:
– Efficient for Hollow Shapes: Blow molding excels at producing lightweight, hollow products like bottles and containers, making it a preferred method for these applications.
– Cost-Effective for High Volumes: Once the initial setup is complete, the cost per unit can be very low for large production runs.
Cons:
– Limited Design Flexibility: Blow molding is not suitable for complex shapes or intricate designs, which may limit its applicability.
– Higher Initial Costs: The machinery and molds can require significant upfront investment, which may not be feasible for smaller operations.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Molding Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate molding process depends on various factors, including the specific requirements of your product, production volume, and budget. Thermoplastic molding offers high precision and versatility for complex designs, making it ideal for high-volume production. In contrast, compression molding may be more suitable for larger, simpler parts with lower production needs, while blow molding is the go-to method for hollow products. By assessing these factors, international B2B buyers can determine the most cost-effective and efficient solution tailored to their manufacturing needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for thermoplastic molding
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Thermoplastic Molding?
Understanding the critical technical properties of thermoplastic molding is essential for B2B buyers aiming to make informed decisions. Here are some key specifications to consider:
Material Grade: Why Is It Crucial for Product Quality?
Material grade refers to the specific classification of thermoplastic polymers based on their chemical composition and mechanical properties. Common grades include ABS, Polycarbonate, and Nylon, each tailored for different applications. For B2B buyers, selecting the right material grade is vital, as it directly impacts the performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness of the final product. For instance, choosing a higher-grade material may ensure better heat resistance for automotive parts, whereas a lower-grade might suffice for consumer goods.
Tolerance: How Does It Affect Manufacturing Precision?
Tolerance defines the allowable deviation in dimensions during the molding process. It is crucial for ensuring that parts fit together accurately in assemblies. A tighter tolerance often results in higher manufacturing costs, but it is essential for applications requiring precision, such as medical devices or automotive components. Buyers must understand the tolerance requirements for their products to avoid costly reworks or failures in functionality.
Cycle Time: What Is Its Impact on Production Efficiency?
Cycle time is the total time required to complete one full cycle of the injection molding process, including injection, cooling, and ejection. Shorter cycle times can lead to increased production efficiency and lower costs. For B2B buyers, understanding cycle time is important for scheduling and inventory management. Opting for advanced molding technologies can reduce cycle time and improve output, which is particularly beneficial in high-demand markets.
Impact Resistance: Why Is It Important for Product Longevity?
Impact resistance measures a material’s ability to withstand sudden forces without breaking. This property is particularly important for products subjected to wear and tear, such as automotive parts or consumer electronics. B2B buyers should prioritize materials with high impact resistance to enhance product durability and reduce returns or warranty claims, ultimately leading to greater customer satisfaction.
Surface Finish: How Does It Influence Aesthetics and Functionality?
Surface finish refers to the texture and appearance of the molded part. It can affect not only the aesthetic appeal but also the functionality, such as friction and wear characteristics. For example, a smooth surface finish may be critical for components that require low friction, while a textured finish might be necessary for better grip. Understanding the desired surface finish is essential for B2B buyers to meet both aesthetic and functional product specifications.
A stock image related to thermoplastic molding.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Thermoplastic Molding?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation. Here are some common trade terms related to thermoplastic molding:
OEM: What Does Original Equipment Manufacturer Mean?
An Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) produces components that are used in another company’s end products. For B2B buyers, partnering with an OEM can streamline sourcing and ensure high-quality components tailored to specific needs. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for maintaining supply chain efficiency.
MOQ: Why Is Minimum Order Quantity Important for Buyers?
Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to produce or sell. Understanding MOQ helps buyers manage inventory and costs effectively. For international buyers, negotiating MOQs can lead to better pricing but may require balancing order sizes with storage capabilities.
RFQ: How Does Request for Quotation Facilitate Procurement?
A Request for Quotation (RFQ) is a formal document sent to suppliers to solicit pricing and terms for specific products or services. For B2B buyers, issuing an RFQ can lead to competitive pricing and better supplier selection. It is an essential step in the procurement process, especially for bulk orders.
Incoterms: What Are International Commercial Terms and Why Do They Matter?
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade, particularly regarding shipping and delivery. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers, as they clarify who bears the risk and costs at each stage of the shipping process, helping to avoid disputes and ensure smooth transactions.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of thermoplastic molding more effectively, leading to better product outcomes and enhanced supplier relationships.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the thermoplastic molding Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in Thermoplastic Molding?
The thermoplastic molding sector is experiencing significant growth driven by advancements in manufacturing technology and increasing demand for lightweight, durable materials across various industries. Global players are focusing on automation and Industry 4.0 solutions, integrating smart manufacturing technologies that enhance production efficiency and reduce lead times. For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the rise of additive manufacturing and 3D printing in thermoplastic applications presents new sourcing opportunities and cost-effective production methods.
A stock image related to thermoplastic molding.
Moreover, the trend towards customization in product design is gaining traction, enabling manufacturers to offer tailored solutions that meet specific client requirements. As the automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods sectors continue to expand, the demand for thermoplastic components is expected to rise. Buyers should also be aware of regional market dynamics, as local supply chain capabilities and geopolitical factors can influence sourcing decisions. Collaborating with suppliers who demonstrate technological innovation and flexibility will be crucial for maintaining competitive advantages in this evolving landscape.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Thermoplastic Molding Industry?
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of strategic sourcing in the thermoplastic molding sector. As concerns about environmental impact escalate, B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that implement sustainable practices. The use of recycled thermoplastics and bio-based materials is gaining momentum, driven by both regulatory pressures and consumer preferences for eco-friendly products.
Ethical supply chains are critical in ensuring that materials are sourced responsibly, with transparency in the procurement process. Buyers should seek suppliers with certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and those that adhere to the principles of circular economy, which emphasize waste reduction and resource efficiency. Additionally, materials certified as “green” or compliant with standards like REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation, and Restriction of Chemicals) can significantly enhance a company’s sustainability profile. By aligning sourcing strategies with sustainability goals, businesses can not only mitigate risks but also tap into new market opportunities that appeal to environmentally-conscious consumers.
What Is the Brief Evolution of Thermoplastic Molding and Its Relevance for B2B Buyers?
The history of thermoplastic molding can be traced back to the early 20th century, with the introduction of Bakelite, the first synthetic plastic developed by Leo Baekeland. This innovation laid the groundwork for the development of various molding techniques, including injection molding, blow molding, and overmolding, which have since become essential in mass production.
As technology has advanced, so too have the materials and processes used in thermoplastic molding. The introduction of advanced thermoplastics, such as polycarbonate and nylon, has expanded the applications of molded products across industries, from automotive components to consumer electronics. For B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is crucial, as it informs material selection and production techniques that can enhance product performance and meet industry standards. Staying abreast of historical developments helps buyers appreciate the capabilities of modern suppliers and the potential for innovative solutions tailored to their specific needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of thermoplastic molding
-
How do I solve quality issues with thermoplastic molded parts?
To address quality issues in thermoplastic molded parts, start by conducting a thorough analysis of the manufacturing process. Evaluate the material selection, mold design, and machine settings. Ensuring precise temperature control during melting and injection is critical, as is monitoring cooling times to prevent warping. Collaborate closely with your supplier to implement quality assurance measures, including regular inspections and testing of the finished products. Utilizing advanced technologies such as automated quality control systems can also enhance consistency and reliability. -
What is the best thermoplastic material for automotive applications?
For automotive applications, materials such as polypropylene (PP), polycarbonate (PC), and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) are highly recommended due to their strength, durability, and impact resistance. Polypropylene is particularly favored for its lightweight properties and cost-effectiveness, while polycarbonate offers superior clarity and toughness for components requiring transparency. It’s essential to consult with your supplier to select the most suitable thermoplastic based on specific performance criteria, including heat resistance and chemical exposure. -
How can I find reliable suppliers for thermoplastic molding?
To find trustworthy suppliers for thermoplastic molding, begin by researching industry directories and trade platforms that feature verified manufacturers. Attend industry trade shows and exhibitions to connect directly with suppliers and assess their capabilities. Review customer testimonials and case studies to gauge the quality of their work. Additionally, consider conducting site visits to evaluate their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers who demonstrate transparency and responsiveness is crucial for successful sourcing. -
What minimum order quantities (MOQ) should I expect when sourcing thermoplastic molded parts?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for thermoplastic molded parts can vary significantly between suppliers and depend on factors such as complexity, material type, and production capabilities. Typically, MOQs range from 500 to 5,000 units. However, some suppliers may offer lower MOQs for custom or prototype orders. When negotiating terms, communicate your requirements clearly and explore the possibility of flexible arrangements if you are a smaller buyer. Establishing a collaborative relationship can lead to more favorable terms in future orders. -
What payment terms are commonly used in international B2B transactions for thermoplastic molding?
Payment terms in international B2B transactions for thermoplastic molding often include options such as advance payment, letter of credit, or net 30/60/90 days. Advance payment is common for new suppliers to mitigate risks, while letters of credit provide security for both parties. It’s essential to discuss and agree on payment terms upfront to avoid misunderstandings. Additionally, consider factors such as currency exchange rates and transaction fees, which can impact overall costs. Establishing a clear agreement will facilitate smoother transactions. -
How do I ensure compliance with international shipping regulations for thermoplastic products?
To ensure compliance with international shipping regulations for thermoplastic products, familiarize yourself with the specific laws and standards of both the exporting and importing countries. This includes understanding customs documentation, tariffs, and safety regulations relevant to thermoplastic materials. Work closely with your supplier to prepare the necessary paperwork, including certificates of origin and material safety data sheets (MSDS). Engaging a freight forwarder or customs broker can help navigate complex regulations and streamline the shipping process. -
What customization options are available for thermoplastic molded parts?
Customization options for thermoplastic molded parts include variations in material selection, color, surface finish, and design modifications. Suppliers often offer capabilities such as multi-material overmolding, where different materials are combined to enhance functionality. Additionally, you can request specific dimensions and tolerances to meet your project requirements. Discuss your needs with potential suppliers early in the design process to explore available customization options that align with your product specifications and market demands. -
How can I effectively manage logistics for thermoplastic molding imports?
To effectively manage logistics for importing thermoplastic molded parts, establish a comprehensive logistics plan that includes selecting reliable shipping partners and determining optimal shipping routes. Consider using a combination of air and sea freight to balance cost and delivery time. Implementing an inventory management system can help track shipments and manage stock levels efficiently. Additionally, maintain open communication with your suppliers to coordinate delivery schedules and address any potential delays proactively.

A stock image related to thermoplastic molding.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for thermoplastic molding
Why is Strategic Sourcing Essential for Thermoplastic Molding?
In the dynamic world of thermoplastic molding, strategic sourcing is crucial for optimizing supply chains and enhancing product quality. By carefully selecting suppliers who can meet specific material requirements and production standards, international B2B buyers can significantly improve operational efficiency and reduce costs. The versatility of thermoplastics allows for innovative applications across various industries, making it essential to align sourcing strategies with market demands and technological advancements.
What Key Takeaways Should B2B Buyers Consider?
As you navigate the procurement landscape, consider focusing on suppliers that offer advanced molding technologies and materials that suit your production needs. Emphasizing sustainability and recyclability in your sourcing decisions can also provide a competitive edge in markets increasingly concerned with environmental impact. Additionally, fostering strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better negotiation terms and access to cutting-edge materials.
How Can International Buyers Prepare for Future Trends?
Looking ahead, the thermoplastic molding industry is poised for growth, driven by advancements in materials science and manufacturing processes. International buyers, especially from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should remain vigilant about emerging trends and innovations. Engage with suppliers who are committed to research and development, and be proactive in adopting new technologies that enhance product performance and sustainability.
What Should Be Your Next Steps?
To leverage the full potential of thermoplastic molding, take actionable steps now: evaluate your current sourcing strategies, explore partnerships with innovative suppliers, and stay informed about industry developments. By doing so, you can position your business for success in a competitive global market.