Improve Efficiency: The Ultimate Toroidal Transformer Guide (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for toroidal transformer
Navigating the global market for toroidal transformers can be a daunting task for international B2B buyers, particularly given the diverse applications and varying efficiency standards across regions. These innovative power transformers, known for their compact design and exceptional efficiency, are essential components in numerous industries, from electronics to medical devices. However, sourcing the right toroidal transformer involves more than just identifying specifications; it requires an understanding of market dynamics, supplier capabilities, and cost considerations.
This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the process of procuring toroidal transformers by exploring various types, applications, and the nuances of supplier vetting. We’ll provide actionable insights on how to assess product quality, understand pricing structures, and navigate shipping logistics, particularly for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key markets like Poland and Italy. By equipping you with the knowledge to make informed purchasing decisions, this guide empowers you to select the most suitable toroidal transformers that meet your operational needs while optimizing cost-efficiency.
Whether you’re a seasoned procurement professional or new to the world of electrical components, understanding the intricacies of toroidal transformers will enhance your ability to drive value and ensure the reliability of your electronic systems.
Understanding toroidal transformer Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power Toroidal Transformer | High efficiency, low weight, compact design | Medical devices, audio equipment | Pros: Efficient power transfer, low heat generation. Cons: Higher initial cost compared to traditional transformers. |
| Isolation Toroidal Transformer | Provides electrical isolation between circuits | Industrial machinery, sensitive electronics | Pros: Protects equipment from voltage spikes. Cons: May require more space than standard transformers. |
| Three-Phase Toroidal Transformer | Designed for three-phase systems, balanced load | Large industrial operations, data centers | Pros: Efficient for high-power applications. Cons: Complexity in installation and higher costs. |
| Audio Toroidal Transformer | Low noise operation, optimized for audio applications | Home audio systems, professional sound equipment | Pros: Minimal electromagnetic interference, compact size. Cons: Limited to specific applications. |
| Custom Toroidal Transformer | Tailored specifications for unique requirements | Specialized machinery, custom electronics | Pros: Perfect fit for specific applications. Cons: Longer lead times and potential for higher costs. |
What Are the Characteristics of Power Toroidal Transformers?
Power toroidal transformers are known for their high efficiency and compact design. They utilize a toroidal core that allows for shorter coils, resulting in reduced resistive losses. This makes them ideal for applications in medical devices and audio equipment where efficiency and low heat generation are critical. When purchasing, consider the specific voltage and current requirements, as well as the importance of low electromagnetic interference in your application.
How Do Isolation Toroidal Transformers Work?
Isolation toroidal transformers are designed to provide electrical isolation between circuits, making them essential in industrial machinery and sensitive electronic devices. These transformers help protect equipment from voltage spikes and reduce noise. Buyers should evaluate the isolation voltage ratings and the physical space available for installation, as these transformers may require more room than standard options.
What Are the Benefits of Three-Phase Toroidal Transformers?
Three-phase toroidal transformers are specifically engineered for three-phase systems, ensuring a balanced load across phases. They are commonly used in large industrial operations and data centers, where efficiency in high-power applications is crucial. When considering a purchase, assess the total power requirements and the complexity of installation, as these transformers can be more intricate to set up and come at a higher cost.
Why Choose Audio Toroidal Transformers?
Audio toroidal transformers are optimized for low noise operation, making them ideal for home audio systems and professional sound equipment. Their design minimizes electromagnetic interference, which is vital for preserving sound quality. Buyers should focus on the specifications related to power handling and noise levels to ensure compatibility with their audio setups.
What Are the Advantages of Custom Toroidal Transformers?
Custom toroidal transformers are tailored to meet specific requirements, making them suitable for specialized machinery and custom electronic applications. They provide a perfect fit for unique needs but may have longer lead times and higher costs. B2B buyers should clearly define their specifications and consider their timelines when opting for custom solutions, ensuring that the investment aligns with their operational needs.
Key Industrial Applications of toroidal transformer
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Toroidal Transformer | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medical Equipment | Power supply for diagnostic and imaging devices | Low leakage currents and noise reduction | Compliance with medical safety standards, compact design |
| Consumer Electronics | Audio amplification systems | Enhanced sound quality with minimal electromagnetic interference | Size constraints, efficiency ratings, and durability |
| Renewable Energy | Inverters for solar power systems | High efficiency and reduced heat generation | Adaptability to various voltage levels and environmental durability |
| Industrial Automation | Control systems for manufacturing machinery | Improved reliability and reduced maintenance costs | Customization options for specific voltage and current needs |
| Telecommunications | Signal processing equipment | Enhanced signal integrity and reduced noise | Compatibility with existing systems and international standards |
How Are Toroidal Transformers Used in Medical Equipment?
In the medical industry, toroidal transformers are essential for powering diagnostic and imaging devices such as MRI machines and ultrasound equipment. Their design minimizes leakage currents, which is critical for patient safety, while also ensuring noiseless operation, which is vital for sensitive environments. International buyers, especially from regions like Africa and the Middle East, must ensure that these transformers comply with strict medical safety standards and are compact enough to fit into space-constrained devices.
What Role Do Toroidal Transformers Play in Consumer Electronics?
Toroidal transformers are commonly utilized in audio amplification systems within consumer electronics, providing superior sound quality by minimizing electromagnetic interference. This is particularly important for high-fidelity audio applications where clarity is paramount. Buyers from Europe, including countries like Poland and Italy, should consider the size constraints and efficiency ratings of these transformers, as well as their durability to withstand continuous use in demanding environments.
How Are Toroidal Transformers Beneficial in Renewable Energy?
In the renewable energy sector, toroidal transformers are used in inverters for solar power systems, where their high efficiency and reduced heat generation are significant advantages. This efficiency not only enhances the overall performance of solar installations but also contributes to lower operational costs. Buyers from South America, where solar energy is rapidly growing, need to ensure that these transformers can adapt to various voltage levels and are robust enough to handle environmental challenges.
Why Are Toroidal Transformers Important for Industrial Automation?
In industrial automation, toroidal transformers provide reliable power to control systems in manufacturing machinery. Their compact design and high efficiency lead to improved reliability and lower maintenance costs, essential for maximizing productivity. B2B buyers in Africa and the Middle East should focus on customization options that meet specific voltage and current needs, ensuring compatibility with existing systems.
How Do Toroidal Transformers Enhance Telecommunications Equipment?
Telecommunications equipment benefits from toroidal transformers by enhancing signal integrity and reducing noise, which is crucial for effective communication. These transformers are used in signal processing equipment to ensure high-quality transmission. Buyers from various regions should prioritize compatibility with existing systems and adherence to international standards, as this will facilitate smoother integration and operation.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘toroidal transformer’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Sizing Toroidal Transformers for Specific Applications
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face challenges when selecting the appropriate size of toroidal transformers for their specific applications. An incorrect size can lead to inefficiencies, overheating, or even equipment failure. For instance, a company manufacturing medical devices in Europe may require transformers that not only meet electrical specifications but also conform to strict safety regulations. Misestimating the power requirements can result in delays in product launches and increased costs due to the need for redesigns.
The Solution:
To overcome sizing challenges, B2B buyers should begin by accurately calculating the total power requirements of their systems. This includes not only the voltage and current but also considering the peak load conditions. Engaging with manufacturers who provide detailed datasheets and specifications is crucial. Buyers should ask for support in application engineering to ensure that the transformer is tailored to their needs. Additionally, conducting thermal analysis can help assess how the transformer will perform under operational conditions, ensuring compliance with safety standards.
Scenario 2: Managing Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) in Sensitive Applications
The Problem:
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) can significantly impact the performance of sensitive electronic devices, particularly in sectors such as telecommunications and medical equipment. For example, a B2B buyer in South America might find that their toroidal transformers are affecting the signal integrity of critical communication systems, leading to data loss and reliability issues. This not only hampers operational efficiency but can also damage the reputation of the products involved.
The Solution:
To mitigate EMI issues, buyers should prioritize sourcing toroidal transformers that feature shielding options. Effective shielding can reduce stray magnetic fields and minimize interference. It’s advisable to engage with suppliers who offer customizable solutions, allowing for tailored designs that meet specific EMI requirements. Additionally, implementing good grounding practices and ensuring proper layout in circuit designs can further help reduce EMI impact. Regular testing of the system for EMI compliance can also ensure that any potential issues are identified and addressed proactively.
Scenario 3: Cost and Supply Chain Challenges in Procurement
The Problem:
International B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and the Middle East, may encounter significant challenges related to the cost and reliability of sourcing toroidal transformers. Fluctuations in raw material prices, shipping delays, and varying import tariffs can lead to unpredictability in project budgets and timelines. This uncertainty can strain relationships with clients who expect timely delivery and adherence to financial estimates.
The Solution:
To navigate these procurement challenges, it is essential for buyers to build strong relationships with multiple suppliers, thus diversifying their sourcing strategy. Establishing long-term contracts with manufacturers can help lock in prices and ensure availability. Furthermore, buyers should explore regional manufacturers that may offer more competitive pricing and reduced shipping costs. Implementing a just-in-time inventory system can also help manage cash flow while reducing the risk of overstocking. Regular communication with suppliers about market trends and potential disruptions can help buyers stay informed and prepared for changes in the supply chain.
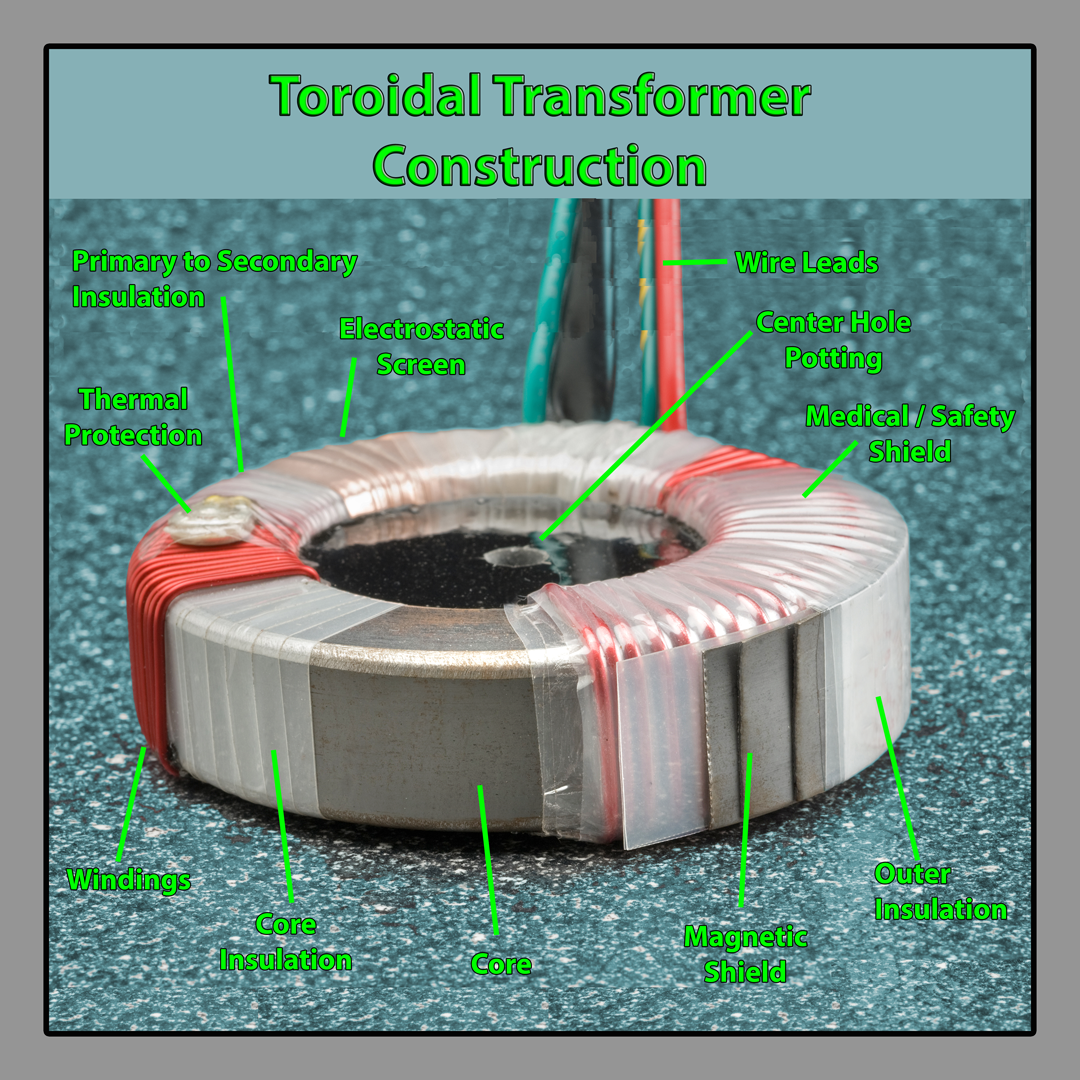
Strategic Material Selection Guide for toroidal transformer
What Are the Best Materials for Manufacturing Toroidal Transformers?
When selecting materials for toroidal transformers, it is crucial to consider their properties and how they align with the performance requirements of specific applications. Below are analyses of four common materials used in the production of toroidal transformers, focusing on their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
A stock image related to toroidal transformer.
1. Silicon Steel
Key Properties: Silicon steel is characterized by its high magnetic permeability and low core loss, making it an excellent choice for toroidal transformers. It can operate effectively at elevated temperatures, typically rated up to 150°C, and offers good corrosion resistance.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of silicon steel is its efficiency in reducing energy losses during operation, which translates to lower operational costs. However, it can be more expensive than other materials, and its manufacturing process is complex due to the need for precise lamination to optimize performance.
Impact on Application: Silicon steel is particularly well-suited for applications requiring high efficiency, such as audio equipment and medical devices. Its compatibility with high-frequency operations makes it ideal for these sectors.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with relevant standards, such as DIN and IEC, which govern the quality and performance of electrical components.
2. Ferrite Core
Key Properties: Ferrite cores are made from ceramic compounds of iron oxide mixed with other metals. They exhibit high electrical resistance and low eddy current losses, making them suitable for high-frequency applications.
Pros & Cons: Ferrite cores are lightweight and compact, which is advantageous for space-constrained designs. However, they can be brittle and susceptible to cracking under mechanical stress, which may limit their application in rugged environments.
Impact on Application: Ferrite cores are ideal for applications in telecommunications and high-frequency power supplies. Their ability to operate efficiently at high frequencies makes them a preferred choice in these areas.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the specific frequency requirements of their applications and ensure that the ferrite material meets international standards like JIS for quality assurance.
3. Amorphous Steel
Key Properties: Amorphous steel is known for its unique non-crystalline structure, which significantly reduces core losses. It operates effectively at temperatures up to 130°C and exhibits excellent magnetic properties.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of amorphous steel is its superior energy efficiency, which can lead to reduced operational costs over time. However, it is generally more expensive than traditional silicon steel and may require specialized manufacturing techniques.
Impact on Application: This material is especially beneficial for applications in renewable energy systems and high-efficiency transformers, where energy conservation is paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like South America and Africa should be aware of the cost implications and ensure that their suppliers can meet local compliance standards.
4. Copper Winding
Key Properties: Copper is widely used for winding in toroidal transformers due to its excellent electrical conductivity and thermal properties. It can handle high currents and has a melting point of approximately 1,085°C.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of copper is its superior conductivity, which enhances the efficiency of the transformer. However, it is heavier and more expensive than aluminum, and its susceptibility to corrosion can be a concern in certain environments.
Impact on Application: Copper windings are ideal for applications requiring high current capacity, such as industrial power supplies and audio amplifiers.
Considerations for International Buyers: International buyers should consider the local availability of copper and its pricing fluctuations, as well as compliance with standards like ASTM for material quality.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Toroidal Transformers
| Material | Typical Use Case for toroidal transformer | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silicon Steel | Audio equipment, medical devices | High efficiency, low operational costs | Complex manufacturing process | High |
| Ferrite Core | Telecommunications, high-frequency power | Lightweight, compact | Brittle, prone to cracking | Medium |
| Amorphous Steel | Renewable energy systems | Superior energy efficiency | Higher cost, specialized manufacturing | High |
| Copper Winding | Industrial power supplies, audio amplifiers | Excellent conductivity | Heavier, corrosion susceptibility | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, helping them make informed decisions when sourcing toroidal transformers.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for toroidal transformer
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Toroidal Transformers?
Manufacturing toroidal transformers involves a series of well-defined stages, each critical to ensuring product quality and performance. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
1. Material Preparation
The manufacturing process begins with the selection of high-quality materials. The core is typically made from silicon steel or ferrite, chosen for its magnetic properties. Wire for the windings is often copper, known for its excellent conductivity. This stage includes cutting the core material to size and preparing the winding wire, which may involve insulating the wire to prevent short circuits.
2. Forming the Core
In the forming stage, the core is shaped into a toroidal form, usually done through precision machining or die-cutting processes. This step is crucial, as the geometry of the core directly impacts the efficiency and performance of the transformer. The toroidal shape minimizes stray magnetic fields and allows for a more compact design, which is beneficial in applications requiring space efficiency.
3. Assembly of Windings
Once the core is formed, the next step involves winding the copper wire around the core. This process can be performed manually or through automated winding machines, ensuring that the number of turns and winding technique meets the specifications for the transformer’s intended application. The winding process is critical, as it affects the inductance and voltage transformation ratios.
4. Finishing Processes
After the assembly of windings, the toroidal transformer undergoes several finishing processes. This may include insulation application, where the transformer is coated with materials that enhance electrical insulation and protect against environmental factors. Final assembly also involves connecting the leads and installing any necessary terminals or connectors. The transformer is then subjected to a visual inspection to ensure that there are no visible defects.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Toroidal Transformer Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing process, ensuring that the final product meets both international standards and customer expectations. The QA framework typically includes adherence to international standards such as ISO 9001, as well as industry-specific certifications like CE and API.
Key Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control in toroidal transformer manufacturing involves multiple checkpoints throughout the production process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint assesses the quality of raw materials and components before they enter the production line. Rigorous testing ensures that only materials meeting specified standards are used.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, IPQC monitors the processes at various stages, particularly during winding and assembly. This includes checks for correct winding techniques and dimensional accuracy of the core and windings.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, FQC includes comprehensive testing of the completed transformers to verify performance parameters such as voltage, current, and efficiency. This stage often involves both electrical testing and environmental stress testing to simulate real-world operating conditions.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Look for?
For B2B buyers sourcing toroidal transformers, it is crucial to verify that suppliers adhere to relevant international standards. ISO 9001, which outlines quality management systems, is a fundamental certification that indicates a commitment to quality and continuous improvement. Other industry-specific certifications may include:
-
CE Marking: This certification indicates compliance with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards, essential for buyers in Europe.
-
API Certification: For transformers used in oil and gas applications, API certification ensures adherence to industry standards for safety and reliability.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Toroidal Transformer Quality Control?
Various testing methods are employed to ensure the reliability and performance of toroidal transformers:
-
Electrical Testing: This includes measuring parameters such as insulation resistance, winding resistance, and voltage regulation. These tests verify that the transformer operates efficiently under specified conditions.
-
Thermal Testing: Since toroidal transformers are often used in applications sensitive to temperature, thermal testing assesses the heat generated during operation to ensure it remains within safe limits.
-
Load Testing: By simulating real-world operational conditions, load testing evaluates the transformer’s performance under different loads, ensuring it can handle expected demands.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying the quality control practices of suppliers is essential. Here are some actionable steps:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures. Buyers should consider both on-site audits and remote assessments, especially for suppliers in regions with logistical challenges.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should be willing to provide detailed quality reports, including data from IQC, IPQC, and FQC stages. This documentation offers transparency regarding the quality measures implemented throughout the manufacturing process.
-
Engage Third-party Inspectors: Hiring independent third-party inspection services can add an extra layer of assurance. These inspectors can evaluate the manufacturing facility and processes, providing unbiased assessments of compliance with standards and specifications.
What Are the QC/Cert Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
When sourcing toroidal transformers globally, buyers must navigate various certifications and quality control practices that may differ by region.
-
Understanding Regional Standards: Buyers from Europe should be particularly aware of CE marking requirements, while those in the Middle East may need to consider local regulations that govern electrical components.
-
Cultural Considerations in Quality Practices: Quality control practices may vary significantly across different regions. Understanding the cultural context can aid in establishing effective communication with suppliers and ensuring mutual understanding of quality expectations.
By focusing on these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing toroidal transformers, ultimately enhancing their supply chain reliability and product performance.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘toroidal transformer’
In this sourcing guide, we provide a structured checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure toroidal transformers. Whether you’re in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe, following these steps will help you make informed decisions and secure high-quality products tailored to your specific needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging with suppliers, clearly outline the technical requirements for your toroidal transformer. Consider factors such as power rating, voltage levels, and application context.
– Key Considerations: Identify whether you need a transformer for audio applications, medical devices, or industrial use, as this will impact design and performance specifications.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify reputable manufacturers and distributors of toroidal transformers. Utilize online directories, industry forums, and trade shows to gather a list of potential suppliers.
– Where to Look: Platforms like Alibaba, ThomasNet, and local trade associations are excellent starting points. Pay attention to suppliers with positive reviews and a robust online presence.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before making a purchase, verify that your chosen suppliers hold relevant certifications and comply with international standards. This can include ISO certifications, CE marking, or UL listing, depending on your region.
– Why It Matters: Certifications ensure that the products meet safety and performance standards, which is crucial for minimizing risks in sensitive applications, especially in industries such as healthcare or aerospace.
Step 4: Request Detailed Product Information
Once you’ve shortlisted suppliers, request comprehensive product data sheets that include specifications, performance metrics, and warranty information for the toroidal transformers.
– What to Look For: Ensure the transformers meet your defined technical specifications and inquire about the efficiency ratings, temperature rise, and noise levels, particularly if the application is sensitive to these factors.
Step 5: Assess Lead Times and Availability
Understand the lead times and inventory availability for the toroidal transformers you wish to purchase. This is essential for planning your project timelines and ensuring timely delivery.
– Key Questions: Ask suppliers about their production capabilities and whether they can handle urgent requests. This is particularly important in regions with supply chain challenges.
Step 6: Compare Pricing and Payment Terms
Request quotes from multiple suppliers and compare prices, but don’t just focus on the lowest bid. Evaluate payment terms, shipping costs, and potential discounts for bulk purchases.
– Consider Total Cost of Ownership: Factor in long-term operational costs, such as energy efficiency and maintenance, which can significantly impact your overall investment.
Step 7: Conduct a Final Supplier Review
Before making a final decision, perform a thorough review of the selected supplier’s reputation and customer service. Reach out for references or testimonials from other businesses in your industry.
– Why This Step is Critical: A reliable supplier will not only provide quality products but also support you with after-sales service and technical assistance, ensuring a smoother procurement process and ongoing partnership.
By following this checklist, you can navigate the complexities of sourcing toroidal transformers with confidence, ensuring that your procurement aligns with both your technical needs and business objectives.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for toroidal transformer Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Toroidal Transformer Production?
When sourcing toroidal transformers, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The core material, typically high-grade silicon steel or ferrite, significantly influences the transformer’s performance and cost. Additionally, copper wire for windings adds to material costs. The choice of materials directly impacts efficiency and durability.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for the precise winding and assembly of toroidal transformers. Labor costs can vary by region; for instance, manufacturers in Europe may have higher labor costs compared to those in Africa or South America.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate these costs.
-
Tooling: Specialized tools for winding and assembling toroidal transformers can represent a significant upfront investment. Custom tooling may be necessary for bespoke designs, further increasing costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that transformers meet industry standards requires rigorous testing and inspection, adding to the overall cost. Certifications such as ISO or CE can also influence pricing.
-
Logistics: Transportation and warehousing costs are critical, especially for international shipments. Incoterms selected can affect the total landed cost, influencing pricing negotiations.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. This margin can vary based on competition, demand, and the supplier’s market position.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Toroidal Transformer Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of toroidal transformers:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) can significantly impact pricing. Larger orders often lead to discounts, making it essential for buyers to assess their needs versus potential savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs tailored to specific applications can drive up costs. Understanding the balance between required specifications and budget constraints is vital.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications often correlate with increased costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of enhanced performance against budget limitations.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and location of the supplier can influence pricing. Suppliers with a strong track record may command higher prices but can offer better assurance of quality and service.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms affects shipping responsibilities and costs. Understanding these terms can help buyers avoid unexpected charges and manage their total cost effectively.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficient Toroidal Transformer Sourcing?
B2B buyers should consider the following strategies to optimize their sourcing of toroidal transformers:
-
Negotiate for Better Pricing: Engage in discussions with suppliers to negotiate better terms, especially for larger orders. Leverage competitive quotes from multiple suppliers to strengthen your position.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the long-term costs associated with the transformer, including installation, maintenance, and operational efficiency. Sometimes, higher initial costs can lead to lower operational expenses.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Different regions have varying pricing structures influenced by local economies, labor costs, and material availability. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should account for these differences in their procurement strategies.
-
Stay Informed About Market Trends: Regularly monitor market conditions, material prices, and technological advancements that can affect transformer pricing. This knowledge can empower buyers to make informed decisions and anticipate price fluctuations.
-
Request Samples: Before placing bulk orders, request samples to assess quality and ensure that the transformer meets your specifications. This step can prevent costly mistakes in large orders.
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices
Pricing for toroidal transformers can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors. It is advisable for buyers to request detailed quotes from multiple suppliers to obtain accurate and current pricing tailored to their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing toroidal transformer With Other Solutions
When evaluating power transformation solutions, it is essential for B2B buyers to consider various alternatives to the toroidal transformer. This analysis will compare toroidal transformers with two viable alternatives: conventional laminated transformers and ferrite core transformers. Understanding these options will help international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe make informed decisions based on their specific application needs.
Comparison Table of Toroidal Transformer and Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Toroidal Transformer | Conventional Laminated Transformer | Ferrite Core Transformer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency, low losses, compact size | Moderate efficiency, larger size, higher losses | High frequency performance, low size |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost | Moderate cost |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized design | Widely available, easy to implement | Requires careful design for high frequencies |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance due to fewer components | Moderate maintenance, more parts to check | Low maintenance, but sensitive to heat |
| Best Use Case | Medical devices, audio equipment | General industrial applications, power distribution | High-frequency applications like switch-mode power supplies |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Conventional Laminated Transformers?
Conventional laminated transformers are among the most common types of transformers. They consist of stacked sheets of silicon steel, which help to reduce eddy current losses. The advantages of laminated transformers include lower initial costs and ease of sourcing. They are suitable for general industrial applications, including power distribution. However, they are less efficient than toroidal transformers, leading to higher energy losses and heat generation. Additionally, their larger size can be a drawback in applications with space constraints.
How Do Ferrite Core Transformers Compare?
Ferrite core transformers are known for their excellent performance in high-frequency applications. They are compact and lightweight, making them ideal for devices like switch-mode power supplies. The advantages of ferrite transformers include high efficiency and lower losses at high frequencies. However, they are more sensitive to temperature variations and require careful design to ensure optimal performance. The initial cost can be moderate, but the need for precise design may increase overall project costs, making them less favorable for standard applications compared to toroidal transformers.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When selecting the appropriate transformer solution, B2B buyers should assess their specific application requirements, including efficiency, space constraints, and budget. For instance, if the application demands high efficiency and minimal heat generation, such as in medical or audio equipment, a toroidal transformer may be the best choice despite its higher initial cost. Conversely, for general industrial uses where budget constraints are a priority, conventional laminated transformers could be more suitable. Lastly, for high-frequency applications, ferrite core transformers may offer the best performance but require careful consideration of design and thermal management.
In conclusion, understanding the pros and cons of toroidal transformers and their alternatives enables buyers to make well-informed decisions that align with their operational needs and financial parameters.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for toroidal transformer
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of a Toroidal Transformer?
When evaluating toroidal transformers for your business needs, understanding the critical technical properties is vital. Here are some key specifications that can impact performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
What Material Grade Should You Consider for Toroidal Transformers?
The material grade of the core, typically silicon steel or ferrite, significantly influences the transformer’s efficiency and performance. High-quality materials reduce core losses, which can lead to better energy efficiency. For B2B buyers, selecting the right material grade can optimize energy costs and enhance the longevity of the transformer, thus reducing overall operational expenses.
How Does Winding Tolerance Affect Performance?
Winding tolerance refers to the acceptable variations in the coil’s dimensions and resistance. A tighter tolerance can result in improved performance and efficiency, as it minimizes losses due to heat and electrical resistance. For businesses operating in sectors where reliability and efficiency are paramount—such as medical equipment or high-end audio systems—choosing transformers with strict winding tolerances can prevent costly downtime and enhance product quality.
Why Is Temperature Rise Important in Toroidal Transformers?
A stock image related to toroidal transformer.
Temperature rise indicates how much the transformer’s temperature increases above ambient conditions during operation. A well-designed toroidal transformer should maintain a temperature rise within 25 ºC (77 ºF) to 55 ºC (131 ºF). For B2B buyers, understanding this specification is crucial, especially for applications in compact spaces where overheating could damage surrounding components or lead to safety hazards.
What Is the Significance of Regulation in Toroidal Transformers?
Regulation refers to the ability of a transformer to maintain a constant output voltage despite variations in load. This is usually expressed as a percentage. For instance, a regulation of 0.7% to 12.3% signifies how much the output voltage can fluctuate under varying loads. In critical applications, such as telecommunications or data centers, tight regulation ensures that equipment operates reliably, safeguarding against voltage spikes that could cause equipment failure.
What Are the Key Trade Terminology and Concepts in Toroidal Transformer Procurement?
Understanding trade terminology is essential for smooth transactions and negotiations. Here are some common terms that B2B buyers should be familiar with:
What Does OEM Mean in the Context of Toroidal Transformers?
OEM stands for Original Equipment Manufacturer. In the context of toroidal transformers, it refers to companies that produce these transformers to be integrated into another manufacturer’s end products. Buyers should consider OEM partnerships to ensure they receive high-quality, compatible components tailored to their specific applications.
Why Is MOQ Important for B2B Buyers?
MOQ, or Minimum Order Quantity, is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for B2B buyers as it affects inventory management and cash flow. Some suppliers may offer lower MOQs for custom transformers, making it easier for smaller businesses to procure specialized products without overcommitting financially.
What Is RFQ and How Does It Work?
RFQ stands for Request for Quotation. It is a standard business process where a buyer solicits price proposals from suppliers. For B2B buyers, issuing an RFQ for toroidal transformers allows for competitive pricing and helps evaluate multiple suppliers based on quality, delivery time, and terms of service.
What Are Incoterms and Why Are They Relevant?
Incoterms, or International Commercial Terms, are standardized trade terms used in international sales contracts. These terms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for international B2B buyers to ensure clarity in logistics and cost responsibilities, especially when sourcing toroidal transformers from global suppliers.
By understanding these essential technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring that they select the right toroidal transformers for their specific applications while navigating the complexities of international trade.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the toroidal transformer Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Toroidal Transformer Sector?
The toroidal transformer market is experiencing significant growth driven by increasing demand for energy-efficient solutions across various industries. As businesses worldwide prioritize efficiency and sustainability, the compact design and superior performance of toroidal transformers make them an attractive option for applications in electronics, telecommunications, and medical devices. For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial.
Key trends include the rising adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies, such as automation and IoT integration, which streamline production and enhance quality control. Additionally, the shift towards renewable energy sources is propelling demand for specialized transformers that can handle variable power inputs efficiently. Buyers should be aware of the growing emphasis on customization, as manufacturers increasingly offer tailored solutions to meet specific application requirements.
Moreover, the global supply chain landscape is evolving, with companies seeking to diversify their sourcing strategies to mitigate risks associated with geopolitical tensions and economic fluctuations. Engaging with suppliers who demonstrate agility and reliability can provide a competitive edge. Buyers should also consider the importance of local partnerships and collaborations to facilitate smoother logistics and compliance with regional regulations.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Toroidal Transformer Supply Chain?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming paramount in the procurement strategies of B2B buyers. As environmental concerns grow, the impact of manufacturing processes on the ecosystem is under scrutiny. In the toroidal transformer sector, buyers should prioritize suppliers that adopt sustainable practices, such as using recyclable materials and minimizing waste during production.
Investing in ‘green’ certifications can enhance a company’s reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious customers. Certifications such as ISO 14001 demonstrate a commitment to effective environmental management systems, while products made from eco-friendly materials can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of electrical devices.
Additionally, ethical sourcing ensures that suppliers adhere to labor rights and fair trade practices. This is particularly relevant for international buyers who may operate in regions with varying regulatory standards. By establishing strong relationships with suppliers who prioritize ethical practices, companies can build resilient supply chains that not only meet compliance requirements but also foster goodwill in the marketplace.
What Is the Brief Evolution of the Toroidal Transformer Sector?
The evolution of the toroidal transformer sector is marked by significant technological advancements and a growing understanding of electromagnetic principles. Initially developed in the mid-20th century, toroidal transformers gained popularity due to their compact size and efficiency compared to traditional laminated transformers.
Over the years, innovations in materials science have led to the development of high-performance magnetic materials that enhance the efficiency and reduce losses in toroidal transformers. The introduction of precision winding techniques has further improved the manufacturing process, allowing for greater customization and scalability.
As the demand for energy-efficient solutions escalates in the 21st century, the toroidal transformer continues to adapt, integrating advanced technologies and responding to the evolving needs of various industries. For international B2B buyers, this evolution signifies a robust market with opportunities for investment in cutting-edge solutions that promise efficiency and reliability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of toroidal transformer
-
How do I choose the right toroidal transformer for my application?
Selecting the right toroidal transformer involves assessing your specific power requirements, including voltage, current, and frequency. Consider the application environment—whether it’s for medical devices, audio systems, or industrial applications. Evaluate the transformer’s efficiency ratings and compactness to ensure optimal performance. Additionally, consult with suppliers about customization options to meet unique specifications, ensuring that the transformer will integrate seamlessly into your existing systems. -
What are the key advantages of using toroidal transformers in my projects?
Toroidal transformers offer several benefits, including higher efficiency, reduced electromagnetic interference, and compact size. Their design minimizes resistive losses, which leads to lower operational temperatures and energy consumption. They are quieter than traditional transformers, making them ideal for sensitive applications like audio equipment and medical devices. The circular core design also provides a more uniform magnetic field, enhancing reliability and performance in various applications. -
What customization options are available for toroidal transformers?
Many manufacturers offer customization for toroidal transformers to suit specific project needs. Customization can include adjustments in voltage ratings, winding configurations, and core materials. Buyers can also request specific dimensions to fit into compact designs or unique applications. It’s advisable to discuss your requirements with the supplier to explore available options and ensure the transformer meets your operational needs. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for toroidal transformers?
The MOQ for toroidal transformers can vary significantly among suppliers. Typically, manufacturers may require a minimum order of 10 to 50 units, but this can depend on the complexity of the transformer and customization level. For international buyers, it’s essential to negotiate with suppliers to find a flexible MOQ that aligns with your project scale, especially if you’re entering a new market or testing a prototype. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing toroidal transformers internationally?
Payment terms can vary based on the supplier and your negotiation power. Common terms include upfront payments, deposits, or payment upon delivery. International buyers may also encounter options like letter of credit or PayPal for added security. Ensure to clarify payment terms upfront and consider the implications of currency exchange rates, especially when dealing with suppliers in different regions. -
How can I ensure quality assurance when sourcing toroidal transformers?
Quality assurance is critical in ensuring the reliability of toroidal transformers. Request certifications such as ISO 9001 or relevant compliance with international standards. Conducting factory audits or requiring samples for testing can further ensure quality. Establish clear communication with suppliers about your quality expectations and consider third-party inspection services to validate product quality before shipment. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing toroidal transformers?
Logistics play a vital role in the successful import of toroidal transformers. Consider shipping methods that balance cost and delivery time, such as air freight for urgent needs versus sea freight for larger orders. Understand customs regulations in your country to avoid delays and additional charges. Partnering with a reliable logistics provider can help streamline the process and ensure timely delivery. -
How do I vet suppliers for toroidal transformers in different regions?
Vetting suppliers involves thorough research and due diligence. Start by checking the supplier’s reputation through online reviews and industry recommendations. Request references from other clients, especially those within your industry. Analyze their manufacturing capabilities and certifications to ensure compliance with international standards. Engaging in direct communication to assess responsiveness and professionalism can also provide insights into their operational reliability.

A stock image related to toroidal transformer.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for toroidal transformer
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers of Toroidal Transformers?
Strategic sourcing of toroidal transformers offers significant advantages for international B2B buyers, particularly in markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. These transformers are not only compact and efficient but also provide lower electromagnetic interference, making them ideal for sensitive applications in electronics and medical devices. By focusing on suppliers that offer customized solutions, businesses can ensure that their unique operational needs are met, ultimately enhancing product performance and reliability.
How Can Buyers Leverage the Advantages of Toroidal Transformers?
Buyers should prioritize suppliers with a proven track record of innovation and customer service. Understanding the specific operational requirements—such as voltage ratings, space constraints, and efficiency levels—will enable businesses to make informed decisions. Additionally, engaging with manufacturers who provide comprehensive support and rapid shipping options can significantly reduce lead times and enhance supply chain efficiency.
What Does the Future Hold for Toroidal Transformers in Global Markets?
As the demand for energy-efficient solutions continues to rise, the outlook for toroidal transformers remains positive. With advancements in manufacturing processes and materials, these transformers are likely to become even more efficient and versatile. International B2B buyers are encouraged to explore partnerships with leading suppliers who can adapt to evolving market needs. Now is the time to act—investing in toroidal transformers can provide a competitive edge in your industry.