The Ultimate Guide to Oxidant Oxidizing Agent (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for oxidant oxidizing agent
The global market for oxidant oxidizing agents presents a significant challenge for B2B buyers, especially when it comes to sourcing reliable and effective materials for various industrial applications. With the increasing demand for these agents across industries such as water treatment, chemical manufacturing, and pharmaceuticals, international buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including countries like Egypt and Brazil) must navigate a complex landscape of suppliers and products. This guide aims to demystify the intricacies of sourcing oxidizing agents, offering insights into the different types available, their specific applications, and best practices for supplier vetting.
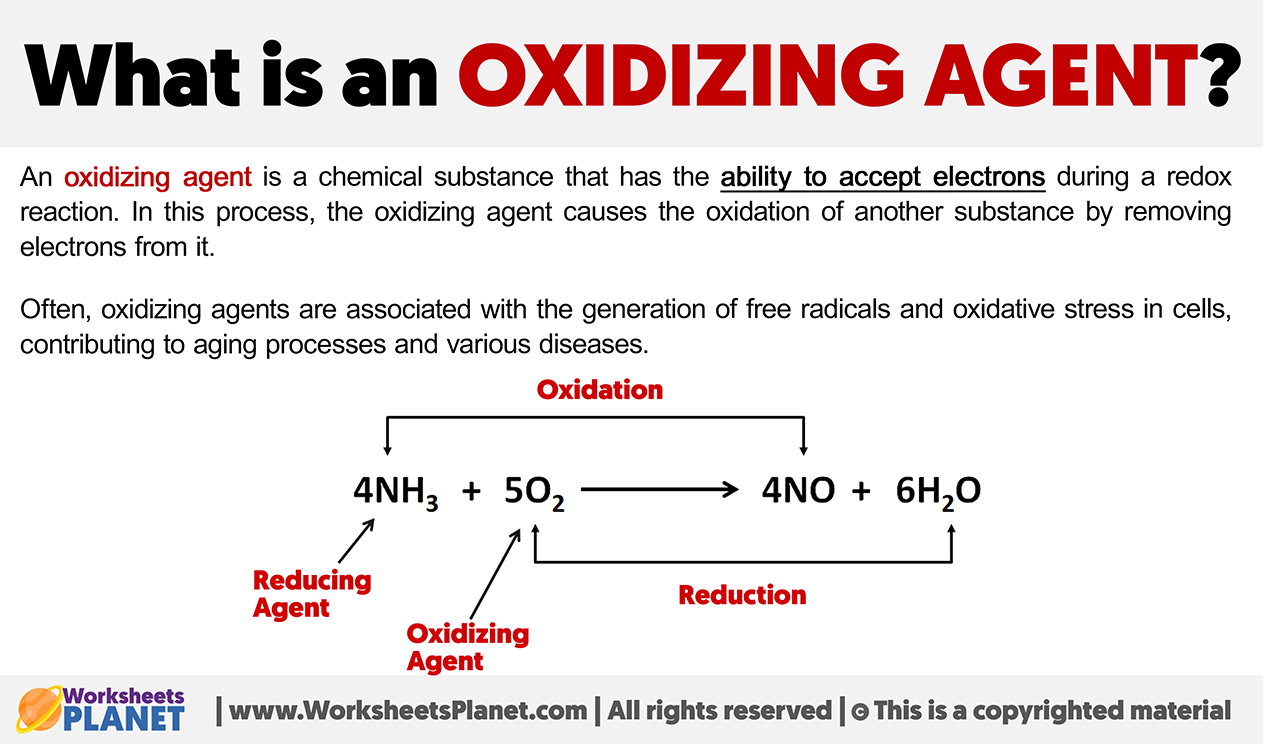
In this comprehensive resource, we will delve into the various categories of oxidizing agents, including halogens, peroxides, and nitrates, and highlight their roles in critical processes such as disinfection, bleaching, and combustion. Additionally, we will explore pricing structures and the factors influencing costs, equipping buyers with the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions. By understanding the market dynamics and the characteristics of reliable suppliers, international B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategies, ensuring they acquire high-quality oxidizing agents that meet their operational needs. This guide is designed to empower you with actionable insights that facilitate successful transactions in the global market for oxidants.
Understanding oxidant oxidizing agent Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Halogens | Highly electronegative, strong oxidizing agents | Water treatment, disinfection, bleaching | Pros: Effective and versatile; Cons: Highly reactive, safety concerns |
| Oxygen and Ozone | Essential for combustion, strong electron acceptor | Combustion processes, wastewater treatment | Pros: Readily available; Cons: Can be hazardous at high concentrations |
| Acids (e.g., H2SO4) | Strong acids that serve as oxidizers in various reactions | Metal processing, chemical synthesis | Pros: Highly effective; Cons: Corrosive, requires careful handling |
| Permanganates | Strong oxidizing properties, often used in redox reactions | Environmental remediation, analytical chemistry | Pros: High oxidizing power; Cons: Stability issues in storage |
| Hydrogen Peroxide | Versatile oxidizer, decomposes to water and oxygen | Sterilization, bleaching, food processing | Pros: Eco-friendly breakdown; Cons: Stability concerns, requires proper storage |
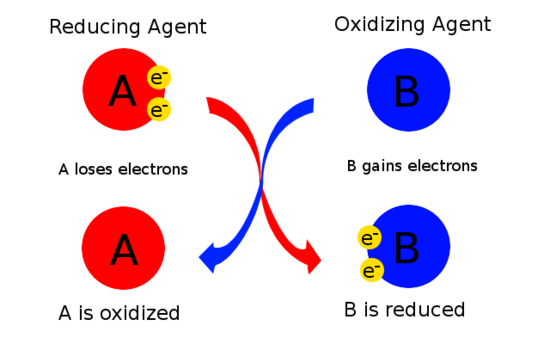
What Are Halogens and Their B2B Relevance?
Halogens, including chlorine and fluorine, are characterized by their high electronegativity and strong oxidizing capabilities. They are commonly used in water treatment processes to eliminate pathogens and in the bleaching industry for textiles. For B2B buyers, the effectiveness of halogens in various applications is a significant advantage; however, their reactivity poses safety challenges. Buyers must consider regulatory compliance and safe handling practices when purchasing halogen-based products.
How Do Oxygen and Ozone Function as Oxidizing Agents?
Oxygen and ozone are vital oxidizing agents in combustion processes and wastewater treatment. Their ability to facilitate oxidation reactions makes them essential in industries ranging from energy production to environmental management. B2B buyers should prioritize the availability and cost-effectiveness of these gases, while also being mindful of their potential hazards at high concentrations. Proper storage and handling protocols are crucial to mitigate risks associated with these oxidizers.
What Role Do Acids Play in Oxidation Processes?
Strong acids, such as sulfuric acid, are known for their oxidizing properties and are widely utilized in metal processing and chemical synthesis. Their effectiveness as oxidizing agents can enhance production efficiency in various industrial applications. However, buyers must weigh the benefits of high reactivity against the corrosive nature of these substances, necessitating stringent safety measures and proper handling during procurement and use.
Why Are Permanganates Important in B2B Applications?
Permanganates are recognized for their strong oxidizing power and are frequently employed in environmental remediation and analytical chemistry. Their ability to participate in redox reactions makes them valuable for treating wastewater and analyzing chemical substances. B2B buyers should consider the potency of permanganates while being aware of potential stability issues during storage. Ensuring proper storage conditions can help maintain their effectiveness and safety.
How Does Hydrogen Peroxide Serve as an Oxidizing Agent?
Hydrogen peroxide is a versatile oxidizing agent that decomposes into water and oxygen, making it an eco-friendly option for various applications, including sterilization, bleaching, and food processing. Its environmental benefits appeal to B2B buyers seeking sustainable solutions. However, stability concerns and the need for proper storage conditions should be taken into account to prevent degradation and ensure safety during use.
Key Industrial Applications of oxidant oxidizing agent
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of oxidant oxidizing agent | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water Treatment | Disinfection and purification | Ensures safe drinking water, reducing health risks | Regulatory compliance, availability of oxidants, transport logistics |
| Textile Manufacturing | Bleaching and dyeing processes | Enhances fabric quality and color consistency | Quality control, cost-effectiveness, and environmental impact considerations |
| Chemical Manufacturing | Synthesis of chemicals and intermediates | Enables production efficiency and product purity | Supplier reliability, consistency in oxidizing agent strength, and safety protocols |
| Energy Storage Solutions | Battery production and maintenance | Improves energy efficiency and longevity of batteries | Technical specifications, compatibility with existing systems, and sourcing of high-purity oxidants |
| Agriculture and Fertilizers | Soil sterilization and nutrient enhancement | Promotes plant growth and soil health | Environmental regulations, sourcing of organic oxidants, and effectiveness in local soil conditions |
How Are Oxidizing Agents Used in Water Treatment?
In the water treatment industry, oxidizing agents such as chlorine and ozone are critical for disinfection and purification processes. They effectively eliminate pathogens and harmful microorganisms, ensuring the safety of drinking water. For international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa and the Middle East, understanding local regulations regarding water treatment is essential. Buyers must also consider the availability and reliability of oxidizing agents, as well as logistics related to transport and storage.
What Role Do Oxidizing Agents Play in Textile Manufacturing?
In textile manufacturing, oxidizing agents are employed in bleaching and dyeing processes to enhance fabric quality and achieve desired color outcomes. Agents such as hydrogen peroxide and sodium hypochlorite are commonly used for their effectiveness in removing impurities and achieving uniform coloration. For B2B buyers in South America and Europe, it is crucial to evaluate the environmental impact of these chemicals and ensure compliance with local regulations regarding textile production.
How Are Oxidizing Agents Applied in Chemical Manufacturing?
Chemical manufacturing relies heavily on oxidizing agents for the synthesis of various chemicals and intermediates. These agents facilitate oxidation reactions, improving production efficiency and ensuring high purity of the final products. Buyers in this sector, particularly in Europe and Africa, should focus on sourcing oxidizing agents from reliable suppliers who can meet stringent quality standards and provide consistent product performance.
What Benefits Do Oxidizing Agents Offer in Energy Storage Solutions?
In the energy storage sector, oxidizing agents play a vital role in the production and maintenance of batteries. They enhance the efficiency and longevity of batteries by facilitating essential redox reactions. B2B buyers looking to source oxidizing agents for battery production must consider technical specifications, compatibility with existing systems, and the sourcing of high-purity oxidants to ensure optimal performance.
How Are Oxidizing Agents Utilized in Agriculture and Fertilizers?
Oxidizing agents are increasingly used in agriculture for soil sterilization and nutrient enhancement. They help promote plant growth by eliminating harmful pathogens and improving soil health. International B2B buyers, particularly in Africa and South America, should focus on sourcing environmentally friendly oxidizing agents that comply with local agricultural regulations and are effective in enhancing soil conditions.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘oxidant oxidizing agent’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Regulatory Compliance for Oxidizing Agents
The Problem: International B2B buyers often face the daunting task of ensuring that their procurement of oxidizing agents, such as chlorine or hydrogen peroxide, complies with local and international regulations. This challenge is compounded in regions like Africa and South America, where regulatory frameworks may vary widely and be subject to frequent changes. Failure to comply can lead to significant legal repercussions, fines, and disruption of supply chains.
The Solution: To navigate this complexity, buyers should invest in a robust compliance management system that tracks regulatory changes and provides updates on relevant laws and safety standards. Collaborating with local suppliers who have a deep understanding of the regulatory landscape can also be beneficial. Additionally, engaging legal consultants specializing in chemical procurement can help ensure that all purchased oxidizing agents meet safety and quality standards. Buyers should also consider obtaining certifications, such as ISO standards, which can enhance their credibility and compliance in the marketplace.
Scenario 2: Managing Supply Chain Disruptions for Oxidizing Agents
The Problem: Supply chain disruptions pose a significant risk for B2B buyers of oxidizing agents, especially in regions prone to political instability or natural disasters. For instance, buyers in the Middle East may experience delays in receiving critical oxidizing agents due to transport issues or geopolitical tensions. These disruptions can halt production processes, leading to financial losses and missed deadlines.
The Solution: To mitigate supply chain risks, buyers should diversify their supplier base by sourcing oxidizing agents from multiple regions. Establishing relationships with suppliers in stable countries can provide alternative options during crises. Additionally, buyers should implement a just-in-case inventory strategy rather than a just-in-time approach, allowing for a buffer stock of critical oxidizing agents. Investing in supply chain visibility tools can also help track shipments in real time and anticipate potential disruptions, enabling proactive responses.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Safe Handling and Storage of Oxidizing Agents
The Problem: The handling and storage of oxidizing agents present safety challenges that can lead to accidents, injuries, or even fatalities if not managed properly. For instance, buyers in Europe might struggle with the stringent safety standards required for storing chemicals like sodium hypochlorite or potassium nitrate. Inadequate training of staff or poor storage conditions can result in hazardous situations, raising liability concerns and impacting operational efficiency.
The Solution: To address these safety challenges, buyers should prioritize comprehensive training programs for all employees involved in the handling and storage of oxidizing agents. Regular safety drills and refresher courses can reinforce best practices. Implementing strict safety protocols, such as using appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and ensuring proper ventilation in storage areas, is essential. Additionally, utilizing advanced storage solutions, such as explosion-proof cabinets and automatic monitoring systems, can significantly reduce the risk of accidents. Collaborating with safety experts to conduct periodic audits of handling practices can also help identify potential hazards and ensure compliance with local safety regulations.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for oxidant oxidizing agent
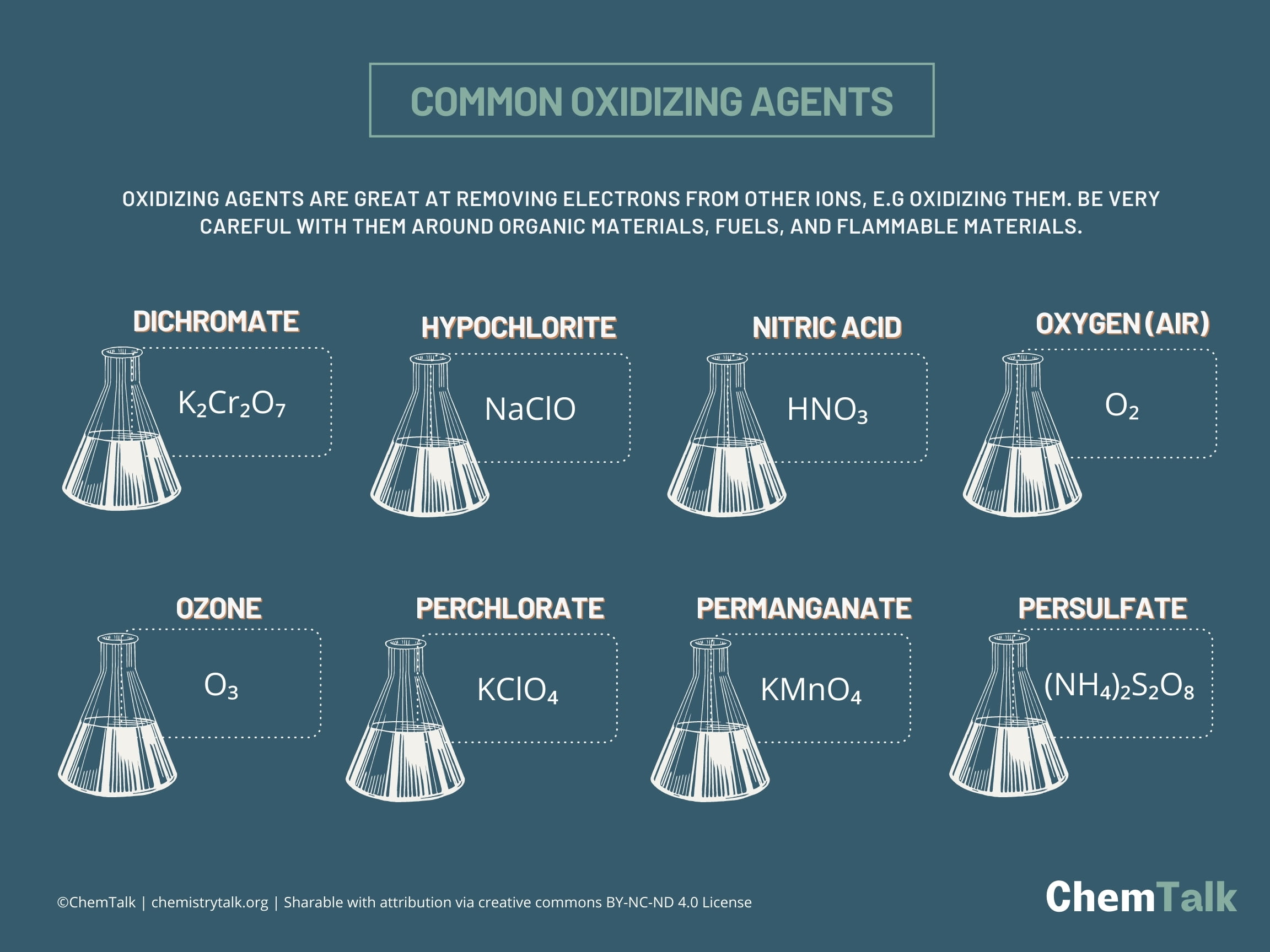
What Are the Key Properties of Common Oxidizing Agents?
When selecting oxidizing agents for industrial applications, it is essential to consider the specific properties that influence their performance. Here, we analyze four common materials used as oxidizing agents: hydrogen peroxide, potassium permanganate, nitric acid, and ozone. Each material has unique characteristics, advantages, and limitations that can significantly impact their application in various industries.
A stock image related to oxidant oxidizing agent.
How Does Hydrogen Peroxide Perform as an Oxidizing Agent?
Key Properties: Hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂) is known for its strong oxidizing properties and is often used in concentrations ranging from 3% to 90%. It decomposes exothermically, releasing oxygen, which can enhance its oxidizing capability. Its effectiveness is influenced by temperature and pH, making it versatile for various applications.
Pros & Cons: One of the primary advantages of hydrogen peroxide is its relatively low cost and availability. It is also less corrosive than other strong oxidizers, making it safer to handle. However, it has a limited shelf life and can decompose if not stored properly, which may lead to manufacturing complexities.
Impact on Application: Hydrogen peroxide is commonly used in water treatment, disinfection, and bleaching processes. Its compatibility with various media makes it suitable for diverse industrial applications, but users must ensure proper handling to prevent degradation.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with local regulations regarding the concentration and usage of hydrogen peroxide is critical. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should be aware of specific safety standards and certifications required for transportation and storage.
What Are the Advantages of Potassium Permanganate?
Key Properties: Potassium permanganate (KMnO₄) is a powerful oxidizing agent known for its high oxidation potential and stability in solid form. It is effective in both acidic and alkaline conditions, making it versatile for various applications.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of potassium permanganate is its strong oxidizing power, which makes it effective for water treatment and organic compound oxidation. However, it can be more expensive than other oxidizers, and its handling requires caution due to its staining properties and potential toxicity.
Impact on Application: In water treatment, potassium permanganate is used to remove iron and manganese, as well as to control taste and odor. Its effectiveness in various media is a significant advantage, but its cost may limit its use in some applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific regulations regarding the use of potassium permanganate in their regions. Compliance with standards such as ASTM or DIN is essential, especially in Europe, where environmental regulations are stringent.
Why Is Nitric Acid a Preferred Oxidizing Agent?
Key Properties: Nitric acid (HNO₃) is a strong oxidizing agent that can operate effectively at elevated temperatures and pressures. It is highly corrosive and can react violently with many organic materials.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of nitric acid is its strong oxidizing capabilities, making it suitable for various applications, including metal etching and nitrate production. However, its corrosive nature poses significant handling challenges, and it can be costly to store and transport safely.
Impact on Application: Nitric acid is widely used in the production of fertilizers and explosives, as well as in the metal finishing industry. Its compatibility with specific processes is beneficial, but safety concerns must be prioritized.
Considerations for International Buyers: International buyers must adhere to strict regulations regarding the transportation and storage of nitric acid. Knowledge of local compliance standards is crucial, particularly in regions like the Middle East, where safety regulations can be stringent.
How Does Ozone Compare as an Oxidizing Agent?
Key Properties: Ozone (O₃) is a powerful oxidizing agent with a high oxidation potential. It is unstable and must be generated on-site, which can complicate its use in industrial applications.
Pros & Cons: Ozone is highly effective for disinfection and water treatment due to its ability to oxidize organic and inorganic contaminants. However, its instability and the need for specialized equipment for generation can increase costs and complexity.
Impact on Application: Ozone is primarily used in water purification and food processing. Its effectiveness against pathogens makes it a preferred choice, but the infrastructure required for its generation can be a barrier for some businesses.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must consider the regulatory environment surrounding ozone use, particularly in Europe, where environmental regulations may dictate its application and monitoring.
Summary Table of Common Oxidizing Agents
| Material | Typical Use Case for oxidant oxidizing agent | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen Peroxide | Water treatment, disinfection, bleaching | Low cost, less corrosive | Limited shelf life, storage issues | Low |
| Potassium Permanganate | Water treatment, organic oxidation | Strong oxidizing power | Higher cost, potential toxicity | Med |
| Nitric Acid | Fertilizer production, metal etching | Strong oxidizing capabilities | Highly corrosive, costly handling | High |
| Ozone | Water purification, food processing | Highly effective against pathogens | Instability, requires on-site generation | Med |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for oxidant oxidizing agent
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Processes for Oxidant Oxidizing Agents?
The manufacturing of oxidant oxidizing agents involves several critical stages that ensure product quality and compliance with international standards. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation: What Raw Materials Are Used?
The first step in the manufacturing process is the selection and preparation of raw materials. Depending on the type of oxidizing agent being produced, common raw materials include halogens (like chlorine and fluorine), potassium nitrate, nitric acid, and hydrogen peroxide. Suppliers should ensure that these materials meet specific purity standards to avoid contamination, which could affect the final product’s efficacy.
Forming: How Are Oxidizing Agents Shaped?
During the forming stage, raw materials undergo chemical reactions to produce the desired oxidizing agents. For instance, the synthesis of hydrogen peroxide typically involves the anthraquinone process, where hydrogen is added to anthraquinone in the presence of a catalyst. This process requires precise temperature and pressure controls to optimize yield and minimize by-products.
Assembly: Are There Any Special Techniques Used?
In many cases, oxidizing agents are produced in bulk and may require additional steps for packaging and distribution. This assembly stage often involves blending, granulation, or crystallization, depending on the final form required (liquid, powder, or solid). Advanced techniques such as spray drying or vacuum distillation may be employed to ensure the purity and consistency of the end product.
Finishing: What Quality Controls Are Implemented?
The finishing stage involves refining the product and preparing it for shipping. This may include drying, milling, and sieving to achieve the desired particle size and moisture content. Quality control checks are critical at this stage to ensure that the oxidizing agent meets specific performance criteria, such as concentration and stability.
What Are the Key Quality Control Measures for Oxidant Oxidizing Agents?
Quality assurance is a vital aspect of the manufacturing process for oxidizing agents. B2B buyers should be aware of the relevant international standards and industry-specific regulations that govern the quality of these products.
What International Standards Should Buyers Be Aware Of?
One of the most recognized international standards for quality management is ISO 9001. Compliance with this standard ensures that manufacturers have established processes for maintaining quality throughout their operations. Additionally, for buyers in Europe, CE marking may be required, indicating that the product complies with EU safety and environmental regulations.
What Industry-Specific Certifications Are Relevant?
In sectors such as pharmaceuticals and food processing, oxidizing agents must comply with specific industry standards, such as the American Petroleum Institute (API) standards. These certifications often require rigorous testing and documentation, ensuring that products are safe for their intended use.
What Are the Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints are critical for maintaining the integrity of the manufacturing process. Common checkpoints include Incoming Quality Control (IQC), In-Process Quality Control (IPQC), and Final Quality Control (FQC).
How Is Incoming Quality Control (IQC) Conducted?
IQC involves the inspection of raw materials upon arrival at the manufacturing facility. Suppliers should verify that materials meet specified quality standards before they are allowed into the production process. This may involve visual inspections, chemical analyses, and reviewing certificates of analysis from suppliers.
What Is In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)?
IPQC focuses on monitoring the manufacturing process itself. This includes regular sampling and testing during production to ensure that parameters such as temperature, pressure, and reaction times are within acceptable limits. Any deviations from the process can be corrected in real-time to prevent defects.
How Is Final Quality Control (FQC) Implemented?
FQC occurs after the manufacturing process is complete. It typically involves comprehensive testing of the final product against established specifications. Common testing methods include titration, chromatography, and spectrophotometry to assess purity and concentration.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is crucial for ensuring product reliability and compliance.
What Steps Can Buyers Take to Conduct Supplier Audits?
A stock image related to oxidant oxidizing agent.
Buyers should conduct thorough supplier audits, which may involve site visits to inspect manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and overall compliance with industry standards. These audits provide insights into the supplier’s operational practices and highlight any areas of concern.
How Important Are Quality Control Reports?
Requesting quality control reports from suppliers is another essential step. These reports should detail the testing methods used, results obtained, and any corrective actions taken for non-conforming products. Regular updates on quality metrics can also help buyers gauge a supplier’s commitment to maintaining high standards.
What Role Do Third-Party Inspections Play?
Engaging third-party inspection services can add an additional layer of assurance. These independent entities can evaluate the supplier’s quality control processes and product quality, providing unbiased reports that can help buyers make informed decisions.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
Understanding the nuances of quality control and certification is particularly important for international buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
How Do Regional Regulations Affect Quality Standards?
Different regions may have varying regulations governing the production and sale of oxidizing agents. For example, the European Union has stringent regulations regarding chemical safety, which may not apply in other markets. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations and ensure that their suppliers comply with these requirements.
What Should Buyers Know About Import Regulations?
When importing oxidizing agents, buyers must be aware of customs regulations and safety compliance requirements in their respective countries. Proper documentation, including Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS), is often required to ensure safe handling and transportation of these chemicals.
Conclusion: Ensuring Quality and Compliance in the Purchase of Oxidant Oxidizing Agents
In conclusion, B2B buyers should prioritize understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures associated with oxidant oxidizing agents. By familiarizing themselves with manufacturing stages, quality control checkpoints, and international standards, buyers can make informed decisions that ensure product quality and compliance. Engaging in thorough supplier evaluations and understanding regional regulations will further enhance their procurement strategies, ultimately leading to successful business outcomes.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘oxidant oxidizing agent’
To effectively procure oxidizing agents for your business needs, it is essential to follow a structured approach. This guide serves as a practical checklist tailored for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The insights provided will help you navigate the complexities of sourcing oxidants while ensuring compliance and quality.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the specific types of oxidizing agents required for your applications. This includes determining the chemical composition, concentration, and physical state (solid, liquid, gas) that best fits your operational needs. Identifying these specifications early on can prevent costly mistakes later in the procurement process.
- Consider application requirements: Different industries may require specific oxidizers, such as hydrogen peroxide for bleaching or ozone for water treatment.
- Assess regulatory standards: Ensure that your specifications align with local and international regulations regarding the handling and use of these chemicals.
Step 2: Research and Identify Reliable Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers specializing in oxidizing agents. Utilize industry directories, trade shows, and online platforms to gather a list of candidates.
- Focus on reputation: Look for suppliers with positive reviews and established relationships within your industry.
- Check geographic proximity: Consider suppliers located closer to your operations to reduce shipping costs and lead times.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Before engaging with suppliers, verify their certifications and compliance with relevant safety and environmental standards. This step is crucial in ensuring that you are sourcing from reputable entities.
- Review certifications: Look for ISO certifications, REACH compliance, and other relevant industry standards.
- Request documentation: Ask for safety data sheets (SDS) and certificates of analysis (COA) to confirm the quality and safety of the products.
Step 4: Assess Quality Control Processes
Quality assurance is paramount when sourcing oxidizing agents. Investigate the quality control measures implemented by your potential suppliers.
- Ask about testing protocols: Inquire if they conduct regular testing for product consistency and purity.
- Evaluate their facilities: If possible, arrange a visit to their production facilities to assess their operational standards.
Step 5: Request Samples and Conduct Trials
Before finalizing any purchase, request samples of the oxidizing agents you intend to procure. Conduct trials to ensure that the products meet your performance expectations.
- Analyze performance: Test the samples in your specific applications to evaluate efficacy and compatibility.
- Document results: Keep detailed records of your findings to inform your final decision.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you’ve selected a suitable supplier, engage in negotiations regarding pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. This is a critical step to ensure that you receive the best value for your investment.
- Consider bulk discounts: If you plan to order large quantities, ask about potential discounts.
- Clarify delivery terms: Make sure to agree on logistics to avoid delays in your supply chain.
Step 7: Establish a Long-term Relationship
After successful procurement, focus on building a long-term relationship with your supplier. This can lead to better pricing, priority service, and access to new products or technologies.
- Provide feedback: Share your experiences regarding product performance and service quality.
- Stay engaged: Regular communication can help you stay informed about market trends and innovations that may benefit your business.
By following this checklist, international B2B buyers can streamline their sourcing process for oxidizing agents, ensuring they select the right products from reliable suppliers while minimizing risks.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for oxidant oxidizing agent Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Oxidant Oxidizing Agents?
When sourcing oxidant oxidizing agents, international B2B buyers must consider several cost components that contribute to the final pricing. The primary elements include:
-
Materials: The type and quality of the raw materials significantly impact costs. High-purity chemicals or specialized oxidizing agents, such as hydrogen peroxide or potassium permanganate, can command premium prices due to their application in sensitive industries like pharmaceuticals or food processing.
-
Labor: Labor costs include both direct production labor and indirect labor associated with research and development, quality assurance, and administrative tasks. Countries with lower wage rates may offer competitive advantages, but this must be balanced against quality and reliability.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses all operational costs not directly tied to production, such as utilities, maintenance, and facility costs. Efficient production facilities can lower overhead costs, which is crucial for maintaining competitive pricing.
-
Tooling and Equipment: Initial investments in specialized equipment and tooling can be significant, especially for custom formulations. Buyers should inquire about these costs, as they can be amortized over larger production runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC processes ensures product reliability and compliance with international standards. However, enhanced QC measures can increase costs. Buyers should assess the value of quality certifications in relation to their specific needs.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs are critical, particularly for hazardous materials. Shipping methods, distances, and local regulations in destination countries will influence logistics costs.
-
Margin: Supplier profit margins can vary widely based on market conditions, competition, and perceived value of the product. Understanding the supplier’s pricing strategy can aid in negotiations.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Oxidant Oxidizing Agents?
Several factors can influence the pricing of oxidant oxidizing agents, including:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Bulk purchases often lead to lower per-unit costs. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their consumption rates to maximize cost efficiency.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized formulations or specific purity levels can increase costs. Buyers should clearly outline their requirements to avoid unexpected price increases.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The source and quality of materials directly affect pricing. Certifications such as ISO or GMP can add to costs but may be necessary for compliance in certain industries.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, production capacity, and location can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer reliability and better service.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) affect the overall cost structure, including who bears shipping and insurance costs. Understanding these terms can lead to significant savings.
What Are the Best Practices for Negotiating Prices?
B2B buyers can employ several strategies to negotiate better pricing on oxidant oxidizing agents:
-
Conduct a Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Analysis: Evaluate not just the purchase price, but all associated costs, including logistics, storage, and potential wastage. This comprehensive view can inform negotiations and justify higher upfront costs for higher quality or more reliable products.
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: If possible, consolidate purchases across multiple departments or projects to meet volume thresholds that unlock better pricing.
-
Build Relationships with Suppliers: Establishing strong partnerships can lead to better terms, flexibility in pricing, and priority during shortages.
-
Stay Informed About Market Trends: Awareness of global supply chain dynamics and raw material prices can empower buyers during negotiations.
-
Be Prepared for Pricing Nuances: Different regions may have varying pricing structures due to local market conditions, regulations, and tariffs. For buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these nuances is crucial for effective sourcing.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
It is essential to note that pricing for oxidant oxidizing agents can fluctuate due to market conditions, raw material availability, and regional regulations. Buyers should seek updated quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing and consider the factors outlined above when evaluating offers.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing oxidant oxidizing agent With Other Solutions
When considering the use of oxidant oxidizing agents in various industrial applications, it is essential to explore alternative solutions that can offer similar benefits. These alternatives may provide different performance characteristics, cost implications, or ease of implementation, making it crucial for B2B buyers to evaluate their specific needs and operational contexts.
| Comparison Aspect | Oxidant Oxidizing Agent | Alternative 1: Hydrogen Peroxide | Alternative 2: Chlorine Gas |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Highly effective in oxidation reactions, particularly in water treatment and organic synthesis. | Effective for disinfection and bleaching, but less potent in strong oxidizing applications. | Strong oxidizing agent, effective for large-scale disinfection and wastewater treatment. |
| Cost | Moderate, varies based on concentration and application. | Generally lower cost, particularly in bulk. | Cost-effective for large volumes but requires careful handling due to toxicity. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specific handling and storage protocols due to its reactive nature. | Easy to implement, often used in ready-to-use formulations. | Requires specialized equipment for safe handling and application. |
| Maintenance | Regular monitoring required for safe storage and effectiveness. | Minimal maintenance; stable in storage, but must be used promptly. | Requires maintenance of storage and delivery systems to manage toxicity risks. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for applications requiring high oxidation levels, such as industrial wastewater treatment. | Best for smaller-scale disinfection, cleaning, and oxidation processes. | Suitable for large-scale disinfection and water treatment facilities. |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Hydrogen Peroxide as an Alternative?
Hydrogen peroxide is a versatile oxidizing agent widely used for disinfection and bleaching. It decomposes into water and oxygen, making it an environmentally friendly option. Its effectiveness in low concentrations makes it ideal for applications in healthcare and food processing. However, it is less effective than strong oxidizers like chlorine or oxidant oxidizing agents in high-demand applications, and its stability can be a concern, as it needs to be stored properly to maintain efficacy.
How Does Chlorine Gas Compare in Performance and Cost?
Chlorine gas is a powerful oxidizing agent commonly used in water treatment and disinfection. It is highly effective in killing bacteria and other pathogens, making it a popular choice for municipal water supplies. Chlorine’s cost-effectiveness for large-scale applications is a significant advantage. However, it poses safety risks due to its toxicity and corrosiveness, requiring specialized handling and storage protocols. This complexity can increase operational risks and necessitate additional training for personnel.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Oxidizing Solution for Your Business Needs?
Selecting the right oxidizing agent depends on various factors, including the specific application, budget, and safety considerations. B2B buyers should assess their operational requirements, including performance needs and cost constraints. For applications requiring high levels of oxidation, oxidant oxidizing agents may be necessary despite their moderate cost and handling challenges. Conversely, for smaller-scale disinfection tasks, hydrogen peroxide could be a more cost-effective and simpler solution, while chlorine gas may be optimal for large-scale operations despite its handling complexities. Ultimately, understanding the unique advantages and limitations of each alternative will empower buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their specific operational contexts.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for oxidant oxidizing agent
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Oxidizing Agents?
Understanding the essential technical properties of oxidizing agents is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in industries such as chemical manufacturing, water treatment, and energy production. Here are some critical specifications:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the classification of an oxidizing agent based on its purity and chemical composition. For instance, industrial-grade oxidizers may contain impurities that are acceptable for manufacturing processes, while laboratory-grade oxidizers must meet stringent quality standards. Selecting the appropriate grade is vital for ensuring product efficacy and compliance with safety regulations.
2. Oxidation State
The oxidation state indicates the degree of oxidation of an element within a compound. For oxidizing agents, a higher oxidation state typically correlates with a stronger ability to gain electrons and oxidize other substances. Understanding the oxidation state helps buyers assess the reactivity and suitability of the oxidizing agent for specific applications, such as disinfection or chemical synthesis.
3. Concentration
Concentration measures the amount of oxidizing agent present in a solution, often expressed in molarity (moles per liter). Higher concentrations can enhance the effectiveness of the oxidizer but may also increase handling risks. Buyers must evaluate the concentration based on their operational requirements and safety protocols to prevent accidents during storage and usage.
4. Stability and Shelf Life
Stability refers to how well an oxidizing agent retains its properties over time under various environmental conditions. Shelf life is the period during which the product remains effective and safe to use. Buyers should consider these factors to avoid using degraded agents that could lead to suboptimal performance or hazardous situations.
5. Packaging and Storage Requirements
Oxidizing agents often require specific packaging and storage conditions to prevent reactions with other substances or environmental factors. For instance, some may need to be stored in cool, dry places away from flammable materials. Understanding these requirements is essential for maintaining safety and compliance throughout the supply chain.
Which Trade Terms Are Commonly Used in Oxidizing Agent Transactions?
Familiarity with industry jargon can streamline communication and negotiations between buyers and suppliers. Here are some common trade terms related to oxidizing agents:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces components or products that are used in another company’s end products. In the context of oxidizing agents, buyers may source these chemicals from OEMs to ensure compatibility with their manufacturing processes.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For oxidizing agents, MOQs can vary widely based on the chemical’s nature and market demand. Understanding MOQs helps buyers plan their inventory and budget accordingly.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that a buyer sends to potential suppliers requesting pricing and other relevant details for a specific quantity of oxidizing agents. This process enables buyers to compare offers and select suppliers that meet their budget and quality standards.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms used in international trade that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Knowing the applicable Incoterms for oxidizing agents can help buyers manage logistics and costs effectively.
5. CAS Number (Chemical Abstracts Service Number)
A CAS number is a unique identifier for a specific chemical substance. This number helps buyers precisely identify the oxidizing agent they need, ensuring that they receive the correct product for their application.
By understanding these key properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing oxidizing agents, ensuring compliance and optimizing their operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the oxidant oxidizing agent Sector
What are the Key Market Trends Influencing the Oxidant and Oxidizing Agent Sector?
The global market for oxidizing agents is evolving rapidly, driven by various factors such as industrial growth, environmental regulations, and technological advancements. In regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the demand for oxidizing agents is primarily fueled by their applications in water treatment, chemical manufacturing, and the production of pharmaceuticals. The growing focus on sustainable practices is also shaping sourcing trends, with buyers increasingly looking for eco-friendly oxidizing agents that meet regulatory standards.
Emerging technologies, such as the use of advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) in wastewater treatment, are enhancing the efficiency of oxidizing agents. These processes leverage oxidizing agents like ozone and hydrogen peroxide to break down contaminants effectively. Additionally, the rise of digital platforms for sourcing chemicals is making it easier for international buyers to find reliable suppliers, compare prices, and access product specifications. This digital transformation is particularly beneficial for buyers in Africa and South America, where traditional sourcing methods may be less developed.
Furthermore, the market dynamics are shifting as suppliers respond to fluctuating raw material costs and increased competition. Buyers should remain vigilant about market trends, including the potential impact of geopolitical factors on supply chains, which can affect pricing and availability. Leveraging insights from industry reports and engaging with suppliers that offer flexibility and transparency will be crucial for making informed purchasing decisions.
How Does Sustainability Impact Sourcing in the Oxidant Sector?
Sustainability has become a pivotal consideration for B2B buyers in the oxidant and oxidizing agent sector. The environmental impact of these chemicals—especially concerning their production, usage, and disposal—cannot be overstated. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability, which includes minimizing harmful emissions and reducing waste through responsible production practices.
Ethical sourcing is gaining traction as companies recognize the importance of maintaining transparent supply chains. Buyers are encouraged to seek out suppliers with certifications that validate their environmental practices, such as ISO 14001 or Green Seal certification. These certifications not only reflect compliance with environmental regulations but also indicate a proactive approach to sustainability.
Moreover, the adoption of ‘green’ oxidizing agents, such as hydrogen peroxide and ozone, is on the rise. These alternatives offer effective solutions with lower environmental footprints compared to traditional oxidizing agents. By incorporating these materials into their operations, international buyers can enhance their sustainability profiles while meeting regulatory requirements, ultimately leading to improved market competitiveness.
How Has the Oxidant Sector Evolved Over Time?
The history of oxidizing agents dates back to the early chemical discoveries of the 18th and 19th centuries, where substances like chlorine and oxygen were identified for their reactive properties. Initially, these agents were primarily utilized in industrial processes, such as bleaching and disinfection. As chemical understanding deepened, the role of oxidizing agents expanded into various applications, including energy production, environmental remediation, and pharmaceuticals.
In recent decades, there has been a significant shift towards more sustainable practices within the sector. The development of green chemistry principles has led to innovative formulations and processes that minimize environmental impact while maximizing efficiency. This evolution reflects a broader trend within the chemical industry, where sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming integral to business strategies.
For international B2B buyers, understanding this historical context is essential for navigating the current landscape. It highlights the ongoing innovation and the importance of aligning purchasing decisions with sustainability goals, ensuring long-term viability in a competitive market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of oxidant oxidizing agent
-
How do I identify the right oxidizing agent for my application?
To identify the appropriate oxidizing agent for your specific application, consider the chemical reaction you aim to facilitate. Assess the oxidation states of reactants and the desired products. Factors such as the reaction environment (e.g., temperature, pressure), safety concerns, and regulatory compliance must also be evaluated. For industrial applications, common oxidizing agents include hydrogen peroxide, ozone, and potassium permanganate. Consulting with a chemical engineer or supplier can provide insights tailored to your unique requirements. -
What is the best oxidizing agent for water treatment processes?
For water treatment, chlorine and ozone are among the most effective oxidizing agents. Chlorine is widely used due to its cost-effectiveness and ability to eliminate pathogens. Ozone, while more expensive, offers superior disinfection capabilities and leaves no residual chemicals. The choice between these agents will depend on factors such as budget, regulatory requirements, and the specific contaminants present in the water. Engaging with a water treatment specialist can help optimize your selection. -
What are the key factors to consider when sourcing oxidizing agents internationally?
When sourcing oxidizing agents globally, consider factors such as supplier reliability, product quality, regulatory compliance, and shipping logistics. Verify supplier certifications and quality assurance processes to ensure safety and efficacy. Additionally, understand the import regulations of your country, including any restrictions on specific chemicals. Cultivating relationships with suppliers who have a proven track record in your region can facilitate smoother transactions and minimize risks. -
How can I verify the quality of oxidizing agents before purchase?
To verify the quality of oxidizing agents, request certificates of analysis (CoA) from suppliers, which confirm the product’s specifications and purity levels. Additionally, consider third-party testing for critical applications where quality is paramount. Engaging in pilot testing with smaller quantities can also help assess performance in your specific application. Building a network of trusted suppliers and seeking recommendations can further enhance your sourcing process. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for oxidizing agents?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for oxidizing agents can vary significantly based on the supplier and the specific chemical. Generally, bulk suppliers may have higher MOQs, while specialty chemical suppliers might offer smaller quantities for niche applications. Discussing your needs directly with suppliers can help negotiate favorable terms. Additionally, consider forming purchasing groups with other businesses to meet MOQs while ensuring cost-effectiveness. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing oxidizing agents internationally?
Payment terms for international transactions of oxidizing agents can vary widely. Common terms include advance payment, letters of credit, or net 30/60 days, depending on the supplier’s policies and your relationship. It’s crucial to clarify payment terms upfront and consider using escrow services for larger transactions to mitigate risks. Engaging with suppliers who have experience in your region can also provide insights into standard practices and expectations.
A stock image related to oxidant oxidizing agent.
-
What logistics considerations are important when transporting oxidizing agents?
When transporting oxidizing agents, consider factors such as compliance with hazardous materials regulations, appropriate packaging, and labeling requirements. Ensure your logistics partner is experienced in handling chemicals to prevent incidents during transit. Additionally, evaluate the shipping method (air, sea, or land) based on urgency and cost, and account for potential delays due to customs clearance. Establishing a reliable supply chain network can streamline the logistics process. -
How can I customize oxidizing agents for specific industrial applications?
Customization of oxidizing agents often involves adjusting concentration levels, formulations, or combining agents for synergistic effects. Collaborate with your supplier to discuss your specific application requirements and any modifications needed. Some suppliers may offer tailored solutions or technical support to develop a product that meets your needs. Engaging in a dialogue about your application challenges can lead to innovative solutions that enhance operational efficiency.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for oxidant oxidizing agent
In the dynamic landscape of international trade, the strategic sourcing of oxidizing agents offers significant advantages to B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the role of oxidizing agents in various industrial applications—from water purification to energy storage—can help businesses optimize their processes and improve product quality.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Supply Chain Efficiency?
Effective sourcing strategies enable companies to secure high-quality oxidizing agents while managing costs and mitigating risks. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate reliability, compliance with safety standards, and a commitment to sustainability. Engaging with multiple suppliers can also provide leverage in negotiations, ensuring competitive pricing and supply chain resilience.
What Does the Future Hold for International Buyers of Oxidizing Agents?
As industries evolve, the demand for innovative oxidizing solutions will continue to grow. International B2B buyers are encouraged to stay informed about emerging trends, regulatory changes, and advancements in chemical technologies. By leveraging strategic sourcing, businesses can position themselves for future growth and capitalize on new opportunities in the global market.
In conclusion, investing in strategic sourcing practices is essential for maximizing the potential of oxidizing agents. Take proactive steps today to enhance your supply chain and drive your business forward in this competitive landscape.