Unlock Efficiency: The Complete M Codes List for 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for m codes list
As international B2B buyers seek to optimize their manufacturing processes, understanding the intricate world of M codes becomes essential. M codes, or miscellaneous codes, play a pivotal role in controlling various machine functions across CNC (Computer Numerical Control) systems. However, the challenge lies in the variation of M codes among different machines and manufacturers, which can lead to confusion and inefficiencies when sourcing the right equipment or components. This guide is designed to demystify the M codes list, offering a comprehensive overview of types, applications, and supplier vetting processes that are crucial for making informed purchasing decisions.
In this guide, you will discover detailed insights into the most commonly used M codes, their functions, and how they can enhance your machining operations. We will explore best practices for evaluating suppliers, ensuring that you select partners who can provide the specific M codes relevant to your machinery. Additionally, we will discuss cost considerations and factors influencing pricing in various regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—specifically targeting countries like Colombia and Nigeria.
By equipping yourself with this knowledge, you can navigate the global market for M codes effectively, avoiding common pitfalls and maximizing your investment in CNC technology. This guide empowers you to make strategic decisions that align with your operational goals, ensuring that your manufacturing processes are both efficient and cost-effective.
Understanding m codes list Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard M-Codes | Universal codes such as M00 (Stop), M02 (End) | General CNC machining operations | Pros: Wide compatibility; Cons: May lack specific functions for advanced machines. |
| Custom M-Codes | Tailored codes for specific machine functions | Specialized CNC operations | Pros: Enhanced control; Cons: Limited availability and support. |
| Manufacturer-Specific M-Codes | Codes unique to specific CNC manufacturers | Proprietary machine operations | Pros: Optimized for specific machines; Cons: Requires detailed knowledge of manufacturer’s codes. |
| Advanced M-Codes | Codes for complex functions like multi-axis control | High-precision machining | Pros: Enables intricate designs; Cons: Requires skilled operators and advanced software. |
| Safety M-Codes | Codes designed to enhance operational safety | All CNC operations | Pros: Reduces risk of accidents; Cons: May slow down production if overused. |
What are Standard M-Codes and Their Applications?
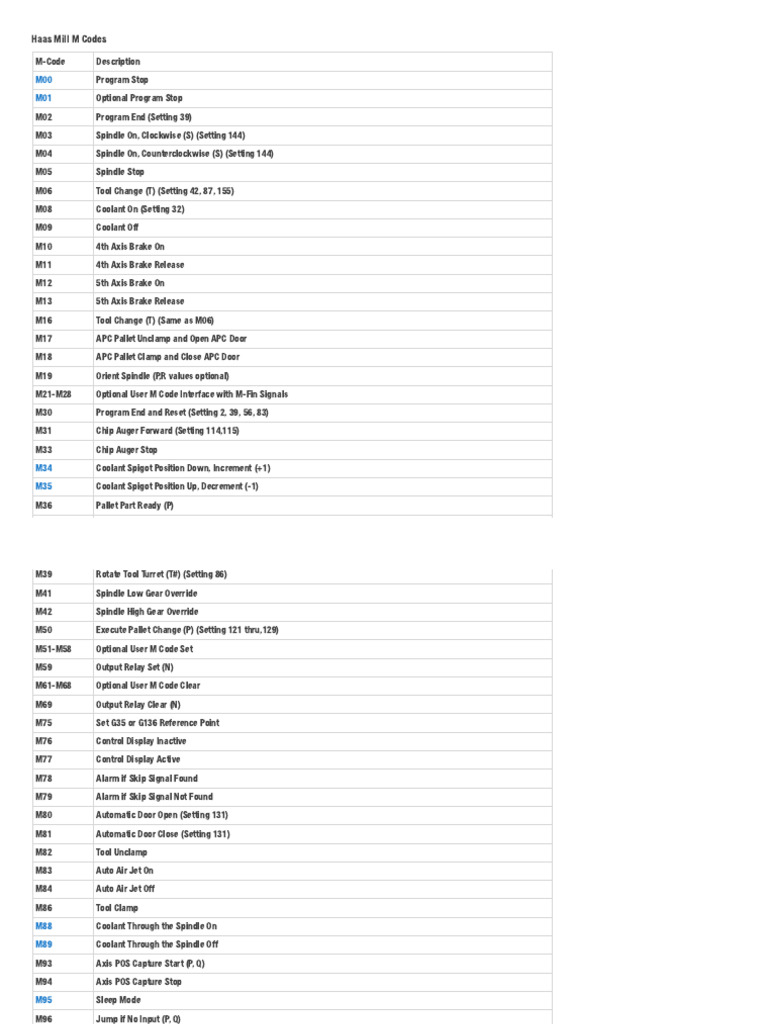
Standard M-codes are the foundational commands used across various CNC machines, including M00 for program stop and M02 for program end. They are widely recognized and utilized in general CNC machining operations, making them essential for any B2B buyer looking for compatibility with a range of machines. However, while their universality is a significant advantage, they may not provide the specialized functions needed for advanced manufacturing processes.
How Do Custom M-Codes Enhance CNC Operations?
Custom M-codes are specifically designed to control unique functions tailored to particular machines or processes. They are often employed in specialized CNC operations, where standard codes may fall short. For buyers, the primary advantage of custom M-codes lies in their ability to enhance control over specific tasks. However, the downside is that their availability can be limited, and support may not be as robust compared to standard M-codes.
What Makes Manufacturer-Specific M-Codes Unique?
Manufacturer-specific M-codes are unique to certain CNC machine brands and models. These codes are optimized for proprietary functions, making them essential for companies that invest in specialized equipment. While they allow for enhanced performance and efficiency, they also require buyers to have a detailed understanding of the manufacturer’s coding system, which may complicate training and operational consistency.
Why Are Advanced M-Codes Important for Precision Machining?
Advanced M-codes are designed for complex machining functions, including multi-axis control and intricate machining processes. They are crucial for high-precision applications, enabling manufacturers to create detailed and sophisticated components. However, the complexity of these codes often necessitates skilled operators and advanced software, which can be a barrier for some B2B buyers looking to streamline operations.
How Do Safety M-Codes Contribute to Operational Safety?
Safety M-codes are specifically created to enhance the safety of CNC operations. They can include commands that control emergency stops or safety interlocks, ensuring that operators can work in a secure environment. While these codes are beneficial in reducing the risk of accidents, their frequent use may slow down production processes. Thus, B2B buyers must find a balance between safety and efficiency when integrating these codes into their operations.
Key Industrial Applications of m codes list
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of m codes list | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace Manufacturing | Tool change automation for precision parts | Increased efficiency and reduced downtime | Compatibility with existing CNC machines and training support |
| Automotive Industry | Spindle control for multi-axis machining | Enhanced production speed and product quality | Supplier reliability and machine adaptability |
| Metal Fabrication | Coolant management for metal cutting | Improved tool life and surface finish | Availability of local service and parts for maintenance |
| Electronics Assembly | Automated program stops for assembly line optimization | Reduced errors and streamlined operations | Customization of M-codes to fit specific assembly needs |
| Oil and Gas Exploration | Pallet management for drilling operations | Maximized operational efficiency and safety | Compliance with industry standards and equipment specifications |
How is the M Codes List Utilized in Aerospace Manufacturing?
In aerospace manufacturing, the M codes list is crucial for automating tool changes, particularly for complex components that require high precision. M-codes such as M06 for tool changes and M03 for spindle control streamline the machining process, significantly reducing downtime between operations. For international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing CNC machines that support a comprehensive M code list can facilitate smoother operations and enhance productivity, ensuring compliance with stringent aerospace standards.
What Role Do M Codes Play in the Automotive Industry?
The automotive industry benefits greatly from M codes for spindle control, particularly when utilizing multi-axis CNC machining. M03 and M04 allow for precise spindle rotation, optimizing the manufacturing of intricate parts like engine components. B2B buyers from Europe and the Middle East must consider machine compatibility with various M codes to enhance production speed and maintain product quality, ultimately leading to a competitive advantage in the market.
How Does Metal Fabrication Leverage M Codes?
In metal fabrication, M codes are vital for managing coolant application during cutting processes. Codes like M08 for flood coolant and M09 for coolant off help in maintaining optimal temperatures, improving tool life, and achieving superior surface finishes. Buyers in regions such as Nigeria should prioritize CNC machines that offer customizable M codes, ensuring they can adapt the machining processes to specific materials and operational needs.
What Benefits Do M Codes Offer in Electronics Assembly?
M codes enhance the efficiency of electronics assembly lines by allowing automated program stops and restarts, using codes like M00 and M30. This automation reduces the likelihood of errors during assembly, ensuring high-quality outputs. B2B buyers from South America should look for CNC systems that can be easily programmed with M codes tailored to their specific assembly processes, ensuring a seamless integration into existing workflows.
How is the Oil and Gas Sector Improved by M Codes?
In the oil and gas exploration industry, M codes facilitate effective pallet management during drilling operations. Codes such as M32 and M33 allow for efficient pallet exchanges, maximizing operational efficiency and safety in challenging environments. International buyers, particularly from the Middle East, must ensure that the CNC machines they source comply with industry standards and support advanced M codes for enhanced safety and reliability in their operations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘m codes list’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Understanding Machine-Specific M-Codes
The Problem:
For international B2B buyers, especially those in regions like Africa or South America, sourcing CNC machines can be a complex process. Many buyers discover that M-codes are not standardized across different machine manufacturers. This discrepancy can lead to significant confusion, as the same M-code might perform different functions depending on the machine model. For instance, while one machine may use M06 for a tool change, another might assign it a completely different function. This lack of uniformity can result in operational inefficiencies and increased downtime, as operators struggle to adapt programs for machines that they are unfamiliar with.
The Solution:
To overcome this issue, it is crucial for buyers to obtain detailed documentation specific to the machines they are purchasing. Before finalizing any transaction, ensure that the seller provides a complete M-code list along with the machine’s operational manual. Additionally, buyers should invest in training sessions for their operators that focus on the specific M-codes of their new machines. Many manufacturers offer online resources, such as webinars or instructional videos, that can bridge knowledge gaps. Furthermore, creating a custom cheat sheet for frequently used M-codes based on the specific machines in use will help streamline operations and reduce errors. By prioritizing documentation and training, buyers can enhance their teams’ proficiency and reduce the risk of costly mistakes.
Scenario 2: The Challenge of Obsolete M-Codes
The Problem:
As technology evolves, many CNC machines become outdated, and their associated M-codes may become obsolete or less relevant. For B2B buyers in the Middle East or Europe, this can pose a challenge when trying to integrate newer software or machinery with existing systems. For example, a company may find that their legacy CNC machines are not compatible with the latest software updates, resulting in lost productivity as teams struggle to adapt old M-codes to new systems. This scenario can lead to frustration among operators and engineers who are trying to maintain efficiency while dealing with outdated technology.
The Solution:
To effectively address this pain point, companies should consider a two-pronged approach: retrofitting older machines and developing a phased upgrade plan. Retrofitting involves updating the machine’s software and hardware to support current M-codes. This can be a cost-effective solution that extends the life of existing equipment. Additionally, establishing a clear upgrade roadmap that includes timelines and budget considerations will help organizations transition smoothly to newer systems. Collaborating with a trusted CNC supplier who offers support for both old and new machines can provide access to necessary resources, including training and documentation. By planning for upgrades and considering retrofitting options, companies can ensure that their operations remain efficient and competitive in the evolving market.
Scenario 3: Navigating Compatibility Issues with Custom M-Codes
The Problem:
In many instances, international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Nigeria and Colombia, may require custom M-codes tailored to their specific manufacturing processes. However, navigating compatibility issues can be a significant hurdle. Custom M-codes may not be recognized by all CNC machines or might conflict with existing codes, leading to operational interruptions. This situation can frustrate teams that rely on precise programming for manufacturing, resulting in delays and increased costs.
The Solution:
To mitigate compatibility challenges, buyers should conduct thorough research on the machines they plan to use, specifically regarding support for custom M-codes. Engaging with manufacturers or software developers that specialize in CNC programming can provide insights into best practices for integrating custom codes. It is also advisable to implement a testing phase where new M-codes are trialed in a controlled environment before being fully deployed in production. Regular communication with machine tool builders about the intended use of custom M-codes can also help avoid potential issues. By taking proactive steps to ensure compatibility and conducting rigorous testing, B2B buyers can enhance their operational efficiency and minimize disruptions caused by custom M-codes.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for m codes list
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in M Codes?
When selecting materials for applications involving M codes, it is essential to consider their properties that directly impact performance. Here, we analyze four common materials: aluminum, stainless steel, titanium, and plastics.
How Does Aluminum Perform in M Code Applications?
Aluminum is a lightweight and versatile material widely used in CNC machining. It boasts excellent thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for various applications. Its temperature rating is generally around 660°C, which is adequate for many machining processes.
Pros: Aluminum is relatively inexpensive, easy to machine, and offers good strength-to-weight ratios. Its lightweight nature reduces energy consumption during transportation and machining.
Cons: However, aluminum has lower durability compared to metals like steel and can deform under high pressure. It may not be suitable for applications requiring high strength or resistance to wear.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with a range of media, including air and water, but may not perform well in highly corrosive environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM B221 for aluminum extrusions. In regions like Africa and South America, sourcing local suppliers can mitigate shipping costs.
What Are the Advantages of Using Stainless Steel in M Code Manufacturing?
Stainless steel is renowned for its strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion, making it a preferred choice for many industrial applications. It can withstand temperatures up to 1,600°C, depending on the grade.
Pros: The material’s high tensile strength and resistance to oxidation make it ideal for applications exposed to harsh environments. It also has a long lifespan, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
Cons: The primary drawback of stainless steel is its higher cost and complexity in machining. It often requires specialized tools and techniques, which can increase manufacturing time and expenses.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a variety of media, including chemicals and high-pressure environments, making it suitable for industries like oil and gas.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify compliance with standards such as ASTM A240 for stainless steel sheets. In Europe, certifications like EN 10088 are also important.
Why Choose Titanium for M Code Applications?
Titanium is a high-performance material known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance. It can endure temperatures up to 1,600°C, making it suitable for high-stress applications.
Pros: Titanium is incredibly durable and resistant to corrosion, making it ideal for aerospace and medical applications. Its biocompatibility is a significant advantage in medical devices.
Cons: The main limitation is its high cost and challenging machining properties, which require specialized equipment and techniques. This can lead to longer lead times and higher production costs.
Impact on Application: Titanium is compatible with a wide range of media, including aggressive chemicals, which is essential for industries like aerospace and marine.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of compliance with standards such as ASTM B348 for titanium and its alloys. In regions like the Middle East, sourcing from certified suppliers is crucial due to stringent regulations.
What Role Do Plastics Play in M Code Applications?
Plastics, such as polycarbonate and nylon, offer a lightweight and cost-effective alternative for many applications. They typically have lower temperature ratings, around 80-120°C, depending on the type.
Pros: Plastics are easy to machine and can be produced in various colors and shapes. They are also resistant to corrosion and chemical exposure, making them suitable for non-metal applications.
Cons: However, plastics generally lack the strength and durability of metals, making them unsuitable for high-stress applications. They can also deform under high temperatures.
Impact on Application: Plastics are compatible with non-aggressive media and are often used in consumer products and electronic housings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM D638 for tensile properties of plastics. In regions like South America, local regulations may dictate specific material requirements.
Summary Table of Material Selection for M Codes
| Material | Typical Use Case for m codes list | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Aerospace components | Lightweight and easy to machine | Lower durability under pressure | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Industrial machinery | High strength and corrosion resistance | Higher cost and machining complexity | High |
| Titanium | Aerospace and medical devices | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio | High cost and difficult to machine | High |
| Plastics | Consumer products | Cost-effective and easy to machine | Lacks strength for high-stress applications | Low |
This analysis provides international B2B buyers with actionable insights into material selection for M code applications, ensuring they can make informed decisions that align with their specific needs and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for m codes list
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process for M Codes?
The manufacturing process for M codes is an intricate journey that involves several key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each of these stages plays a vital role in ensuring the final product adheres to the specifications required by B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
How is Material Prepared for M Code Production?
Material preparation is the first stage of the manufacturing process. This involves selecting the appropriate raw materials based on the specifications of the M codes being implemented. Common materials include metals, plastics, and composites, depending on the intended application.
During this stage, manufacturers often conduct a thorough analysis of the materials, including chemical composition, mechanical properties, and surface conditions. This ensures that only high-quality materials are used, which is crucial for maintaining the integrity and performance of the final product.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in M Code Manufacturing?
Once the materials are prepared, the next step is forming. This can involve various techniques such as CNC machining, injection molding, or 3D printing, depending on the complexity of the components being produced.
A stock image related to m codes list.
CNC machining is particularly relevant for M codes, as it allows for high precision and repeatability. The use of M codes in CNC machines facilitates specific operations like tool changes and spindle control, enhancing the manufacturing process’s efficiency. Buyers should inquire about the types of machines and techniques used by suppliers to ensure they align with their quality expectations.
How Does Assembly Fit into the M Code Production Process?
After forming, the assembly stage involves putting together various components to create the final product. This may include integrating electronic components, mechanical parts, or software systems.
Quality assurance during assembly is critical. Manufacturers often implement real-time monitoring systems to detect any discrepancies or defects as components are assembled. B2B buyers should seek suppliers who have robust assembly protocols and who utilize M codes effectively to enhance operational consistency.
What Finishing Processes Are Commonly Applied to M Code Products?
Finishing processes are the final stage in the manufacturing of M codes and can include surface treatments, coatings, and final inspections. These processes not only enhance the aesthetic appeal of the product but also improve its durability and functionality.
Common finishing techniques include anodizing, painting, and plating. Each of these methods can significantly affect the performance of the final product. Buyers should request information about the finishing processes used by suppliers to ensure they meet specific industry standards and customer expectations.
How is Quality Assurance Implemented in M Code Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of manufacturing M codes, ensuring that products meet both international and industry-specific standards. B2B buyers must understand these QA processes to make informed purchasing decisions.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider for M Code Quality Assurance?
International standards such as ISO 9001 play a significant role in quality assurance for M code manufacturing. ISO 9001 establishes a framework for consistent quality management systems, ensuring that suppliers adhere to stringent quality controls throughout the production process.
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) for European markets and API (American Petroleum Institute) for oil and gas components are crucial. Buyers should confirm that suppliers possess the necessary certifications relevant to their industry to ensure compliance and reliability.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are essential to maintaining product quality throughout the manufacturing process. Key QC checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Conducting inspections during various stages of production to identify defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Performing comprehensive inspections and testing of finished products before shipment.
These checkpoints help prevent defects from reaching the customer, ensuring that B2B buyers receive high-quality products.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
To ensure the reliability of suppliers, B2B buyers should actively verify the quality control processes in place. This can be achieved through several methods:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits to assess the manufacturing processes, quality control systems, and overall operational standards of potential suppliers.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports from suppliers that outline their QC processes, inspection results, and compliance with relevant standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures and product quality.
By taking these steps, international buyers can gain confidence in their supplier’s ability to deliver high-quality M codes that meet their specific requirements.
What Quality Control Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
International buyers must be cognizant of various nuances in quality control that may affect their procurement processes. Different regions may have unique standards and expectations regarding product quality. For instance, buyers in Europe may face stricter regulatory requirements compared to those in Africa or South America.
Moreover, language barriers and cultural differences can impact communication regarding quality expectations. Buyers should establish clear communication channels with suppliers and consider working with local representatives who understand the regional nuances.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures associated with M codes is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing, alongside robust quality assurance protocols, buyers can ensure they are sourcing high-quality products that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘m codes list’
To effectively source an “M codes list” for CNC machines, international B2B buyers need a clear and actionable checklist. This guide provides essential steps to ensure that you select the right resources tailored to your specific machining needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Identifying your specific requirements is crucial before sourcing an M codes list. Consider the type of CNC machines you operate and their unique programming needs. This will help you narrow down the M codes that are relevant to your operations and ensure compatibility with your machinery.
- Machine Type: Different machines (e.g., milling, turning) may require different sets of M codes.
- Manufacturer Variability: M codes can vary significantly between manufacturers, so identify the specific brands you work with.
Step 2: Research Reliable Sources for M Codes
Gathering M codes from credible sources is vital for ensuring the accuracy of the information. Look for official documentation from machine manufacturers or reputable CNC resources.
- Manufacturer Manuals: Always refer to the official manuals provided by your machine’s manufacturer for the most accurate M codes.
- Industry Websites: Utilize trusted industry websites and forums that specialize in CNC machining for additional insights and community support.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers of M Codes
Before committing to any supplier for M code lists, conduct thorough evaluations. This helps ensure that you are getting a reliable and comprehensive resource.
- Request Documentation: Ask suppliers for their documentation to confirm the accuracy of their M codes.
- Check References: Seek references or testimonials from other businesses in your sector to gauge the supplier’s reliability.
Step 4: Verify Compatibility with Your CNC Systems
Not all M codes will be applicable to every CNC machine, making it essential to verify compatibility. This step can prevent costly errors and downtime in your operations.
- Cross-Reference Codes: Cross-reference the M codes list with your machine’s specifications to ensure they align.
- Test Codes: If possible, run a few test programs using the M codes to verify their functionality in your system.
Step 5: Assess Ongoing Support and Updates
The landscape of CNC programming can evolve, and having access to ongoing support is invaluable. Ensure that your supplier provides updates and assistance when needed.
- Support Channels: Inquire about the availability of customer support channels for troubleshooting or queries.
- Update Policy: Check if the supplier regularly updates their M codes list to include new codes or modifications.
Step 6: Consider Training and Resources for Your Team
Implementing a new M codes list may require additional training for your operators. Assess whether your supplier offers training resources or documentation to facilitate this transition.
- Training Materials: Look for suppliers that provide manuals, guides, or workshops to help your team understand the M codes effectively.
- Hands-On Training: If possible, arrange for hands-on training sessions for your operators to enhance their proficiency with the new codes.
Step 7: Finalize Your Purchase and Agreement Terms
Once you have thoroughly vetted suppliers and found a suitable M codes list, finalize your purchase. Make sure to review the terms of the agreement to ensure clarity on deliverables and support.
- Contract Clarity: Ensure the contract clearly outlines the scope of the M codes provided and any support included.
- Payment Terms: Agree on payment terms that are favorable for both parties, ensuring you receive value for your investment.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively source a reliable M codes list that meets their machining needs, minimizing risks and enhancing operational efficiency.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for m codes list Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in M Codes List Sourcing?
Understanding the cost structure associated with sourcing M codes lists is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The materials involved in the production of CNC machinery and tools can significantly affect costs. High-quality materials often lead to better performance and longevity, justifying a higher price point.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary by region and are influenced by the skill level required for programming and machine operation. For instance, countries with higher wage standards may present a different labor cost structure compared to those in Africa or South America.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing practices can minimize overhead, impacting the final price.
-
Tooling: The cost of specialized tooling required for different M codes can add to the overall expense. Custom tooling may be necessary for unique specifications, which can increase costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of M codes requires rigorous QC processes. This is especially critical for international buyers who may face compliance issues in their home markets.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can fluctuate based on the geographical location of the supplier and the buyer. International shipping may include tariffs, taxes, and insurance, affecting the total cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their costs and desired profit. The margin can vary significantly based on the supplier’s position in the market and the competitive landscape.
How Do Pricing Influencers Affect M Codes List Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of M codes lists, which can vary based on the buyer’s needs and market conditions:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Negotiating favorable MOQs can help international buyers manage their budgets effectively.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom M codes tailored to specific machinery can incur additional costs. Buyers should clearly communicate their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials and the presence of quality certifications (e.g., ISO standards) can impact pricing. Buyers should assess whether higher-priced materials justify the benefits they offer.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, experience, and reliability play a critical role in pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium, but their reliability can mitigate risks associated with sourcing.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the International Commercial Terms (Incoterms) is essential for managing shipping costs and responsibilities. Buyers should negotiate terms that minimize their risk and optimize cost-efficiency.
What Tips Can International B2B Buyers Use for Cost-Efficiency?
To maximize cost-efficiency when sourcing M codes lists, international buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Effective Negotiation Techniques: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better negotiation outcomes. Buyers should be prepared to discuss pricing openly and seek volume discounts.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond initial pricing, buyers should evaluate the TCO, which includes maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential downtime costs. This holistic view helps in making informed purchasing decisions.
-
Awareness of Pricing Nuances: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should be aware of regional pricing differences. Understanding local market dynamics can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Research and Comparison: Conduct thorough market research to compare prices and offerings from multiple suppliers. This can uncover competitive pricing and better product specifications.
-
Consider Long-Term Relationships: Establishing long-term partnerships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and reliability over time. Suppliers may be more willing to offer discounts or better terms for repeat business.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for M codes lists can vary widely based on the factors discussed above. The information provided is indicative and should not be considered a definitive pricing guide. Buyers are encouraged to conduct their due diligence and engage directly with suppliers to obtain accurate quotes tailored to their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing m codes list With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to the M Codes List: What Are Your Options?
In the realm of CNC machining and automation, the use of M Codes is prevalent for controlling machine functions. However, B2B buyers should consider alternative solutions that might better suit their operational needs or offer enhanced functionality. This analysis will compare the M Codes list against two viable alternatives: G Codes and Custom CNC Software Solutions.
Comparison Table: M Codes List vs. Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | M Codes List | G Codes | Custom CNC Software Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Standardized control codes, effective for most CNC machines. | High precision control, optimized for specific tasks. | Tailored solutions can outperform standard codes with advanced features. |
| Cost | Generally low-cost, included with CNC machines. | Low to moderate; may require additional training. | Higher initial investment due to customization and development. |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to implement; most machines come pre-configured. | Requires understanding of both G and M codes, moderate learning curve. | Implementation can be complex; requires skilled personnel for setup. |
| Maintenance | Low; minimal updates needed. | Low; however, understanding interactions with M codes is crucial. | Ongoing maintenance required, including updates and troubleshooting. |
| Best Use Case | General CNC operations; suitable for most standard tasks. | Ideal for specific machining tasks requiring high precision. | Best for complex, specialized applications needing customization. |
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of G Codes?
G Codes serve as an alternative to M Codes, providing a different set of commands to control CNC machines. They excel in precision and are often used for complex machining tasks. One of the significant advantages of G Codes is their widespread use across various machine types, making them a versatile option. However, they require a solid understanding of both G and M codes, which can present a learning curve for operators unfamiliar with these systems. Additionally, while G Codes are generally cost-effective, they may necessitate additional training for staff, potentially increasing overall operational costs.
How Do Custom CNC Software Solutions Compare?
Custom CNC software solutions represent a more advanced alternative to the traditional M Codes list. These solutions can be tailored to specific operational needs, allowing for enhanced functionality and efficiency. Businesses that require specialized applications, such as intricate part production or unique machining processes, may find that custom software significantly improves performance. However, the main drawback is the higher initial investment and complexity involved in implementation. Ongoing maintenance and updates are also necessary to ensure optimal performance, which can add to the total cost over time.
Making the Right Choice for Your Business Needs
When selecting between the M Codes list and alternative solutions, B2B buyers must consider their specific operational requirements, budget constraints, and the complexity of their machining tasks. For businesses engaged in standard CNC operations, the M Codes list offers a reliable and cost-effective solution. In contrast, organizations focused on precision machining or those needing custom workflows might benefit more from G Codes or tailored CNC software solutions. Evaluating these aspects will help buyers choose the solution that aligns best with their production goals and operational efficiencies.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for m codes list
What Are the Key Technical Properties Related to M Codes?
When dealing with M codes in CNC machining, understanding their technical properties is crucial for optimizing operations. Here are several key specifications that international B2B buyers should be aware of:
-
Compatibility and Standardization
M codes can vary significantly across different manufacturers and machines. This lack of standardization means that buyers must ensure compatibility with their existing equipment. Understanding the specific M codes used by a machine’s control software—like Mach3 or Fanuc—is essential for seamless operations and avoiding costly mistakes. -
Programming Flexibility
The ability to customize M codes allows manufacturers to tailor their machinery for specific tasks. For example, businesses might require unique M codes for special tool changes or operations, which enhances operational efficiency. Buyers should inquire about the programming capabilities of the CNC machines they consider to ensure they can meet their production needs. -
Operational Efficiency
M codes control various machine functions that can directly impact production speed and quality. For example, M00 (Program Stop) and M30 (Program End) are critical for managing workflow. Buyers should assess how the use of specific M codes can streamline their processes, reduce downtime, and improve overall productivity. -
Integration with Software
The integration of M codes with CAD/CAM software is vital for efficient programming and operation. Understanding how M codes interact with design software helps buyers create more accurate machining processes. Evaluating software compatibility can lead to better design-to-production transitions, which is essential for maintaining competitiveness. -
Error Handling and Diagnostics
M codes play a significant role in error management and diagnostics within CNC machines. Codes like M98 (Sub-Program Call) and M99 (Sub-Program End) can aid in program control and troubleshooting. Buyers should consider how a machine’s M code functionality supports error detection and correction to minimize production disruptions.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B landscape. Here are several important terms related to M codes and CNC machining:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding the OEM landscape helps buyers identify reliable sources for machinery and components, ensuring quality and performance. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest amount of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For international buyers, knowing the MOQ is essential for managing inventory costs and production schedules. It allows for better planning and ensures that procurement aligns with production needs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that suppliers use to provide pricing and terms for a specific quantity of goods or services. Issuing an RFQ helps B2B buyers compare costs and services from different suppliers, facilitating informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including shipping, risk, and insurance. Understanding these terms is vital for international buyers to mitigate risks and clarify logistical arrangements in their contracts. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the duration between the initiation of a process and its completion. For B2B buyers, knowing the lead time for machinery and parts is crucial for effective planning and meeting production deadlines.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, optimize their procurement processes, and enhance operational efficiency in CNC machining.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the m codes list Sector
What are the Current Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the M Codes List Sector?
A stock image related to m codes list.
The global market for CNC machining and M codes is witnessing significant growth driven by advancements in automation, artificial intelligence, and Industry 4.0. International B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly adopting CNC technologies to enhance operational efficiency and product quality. In these regions, there’s a notable shift towards digitization and smart manufacturing, which are essential for staying competitive in the global market.
Emerging trends include the integration of IoT (Internet of Things) technologies in CNC machinery, enabling real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. This is particularly relevant for buyers in developing regions like Nigeria and Colombia, where operational uptime is critical. Additionally, the rise of cloud-based solutions allows for better data management and collaboration across supply chains, making it easier for international buyers to source machinery and components from diverse suppliers.
Sourcing trends are also evolving, with buyers increasingly favoring local suppliers to mitigate risks associated with long supply chains. This preference not only reduces lead times but also supports local economies. Furthermore, there is a growing emphasis on customized solutions, as companies seek M codes that cater to specific operational needs, enhancing flexibility and adaptability in production processes.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the M Codes List Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a central pillar in the sourcing strategies of international B2B buyers. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including those governed by M codes, is under scrutiny. Buyers are increasingly aware of the carbon footprints associated with CNC machining and are seeking suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly practices.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, with companies focusing on supply chains that uphold labor rights and fair trade practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 9001 for quality management are becoming prerequisites for suppliers in the M codes sector. Buyers from Europe and the Middle East, in particular, are demanding transparency in sourcing to ensure compliance with stringent regulatory standards.
Additionally, there is a rising trend towards using sustainable materials and technologies in the manufacturing process. For instance, selecting cutting tools and coolant fluids that are biodegradable or recyclable can significantly reduce environmental impact. This shift not only aligns with global sustainability goals but also enhances brand reputation, making ethical sourcing a strategic advantage for B2B buyers.
What is the Brief Evolution and History of M Codes in CNC Machining?
The concept of M codes, or miscellaneous codes, emerged alongside the development of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining in the mid-20th century. Initially, these codes were designed to control various non-motion-related machine functions, providing a way to automate processes that were previously manual. As CNC technology evolved, so did the complexity and variety of M codes, with manufacturers developing proprietary codes tailored to specific machines and applications.
Over the years, the standardization of M codes has improved, allowing for better interoperability across different CNC machines. This evolution has enabled international B2B buyers to leverage a broader range of CNC solutions, making it easier to integrate new technologies into existing operations. Today, M codes play a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency and precision of machining processes, reflecting the ongoing innovation within the industry.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of m codes list
-
How do I choose the right M-code list for my CNC machine?
Selecting the appropriate M-code list for your CNC machine involves understanding the specific machine model and its manufacturer. Each machine may have a unique set of M-codes, so it’s crucial to consult the machine’s manual or reach out to the manufacturer for the correct codes. Additionally, consider the type of machining operations you will perform, as some M-codes are specific to certain functions, such as tool changes or coolant control. This knowledge will ensure you optimize your machine’s performance and maintain production efficiency. -
What are the most common M-codes used in CNC machining?
Some of the most commonly used M-codes in CNC machining include M00 (Program Stop), M03 (Spindle Start Clockwise), M05 (Spindle Stop), and M06 (Tool Change). These codes control basic machine functions and are essential for various operations. Familiarizing yourself with these fundamental M-codes will help you operate CNC machines more effectively. Always refer to the specific M-code documentation for your machine, as codes can vary significantly among different manufacturers. -
How can I ensure the quality of M-code implementations in my operations?
To ensure quality M-code implementations, start by conducting thorough testing of the codes in a controlled environment before full-scale production. Utilize simulation software to evaluate how the M-codes interact with your machining processes. Additionally, develop a quality assurance (QA) protocol that includes regular reviews and updates of the M-code list as per any changes in machine configuration or operational requirements. Engaging with experienced technicians can also provide insights into best practices for M-code applications. -
What factors should I consider when sourcing M-code lists internationally?
When sourcing M-code lists internationally, consider the compatibility of the codes with your CNC machinery, which may vary by region. Evaluate the supplier’s reputation and expertise in providing M-code lists that align with your specific machine types. Additionally, assess factors such as lead times, shipping logistics, and language barriers that may affect communication and understanding. It’s also advisable to inquire about after-sales support, as this can be crucial for troubleshooting issues that may arise during implementation. -
How do I vet suppliers for M-code lists to ensure reliability?
Vetting suppliers for M-code lists involves researching their credentials, customer reviews, and industry experience. Request references and case studies that demonstrate their expertise in providing M-codes for your specific machinery. Additionally, engage in direct communication to assess their knowledge of CNC operations and M-code applications. Look for suppliers who offer comprehensive technical support and have a clear understanding of international trade regulations, particularly if you are importing from regions like Africa or South America. -
What are the typical payment terms for international transactions involving M-code lists?
Payment terms for international transactions can vary widely depending on the supplier and the agreement reached. Common terms include advance payment, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. It is crucial to clarify these terms before finalizing any agreements, ensuring that they align with your cash flow and procurement strategy. Additionally, consider the implications of currency fluctuations and transaction fees when dealing with international suppliers, as these can affect the overall cost of the M-code list. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing M-code lists?
When importing M-code lists, logistics considerations include understanding customs regulations in your country and ensuring that all documentation is in order for smooth processing. Evaluate shipping options for reliability and cost-effectiveness, and consider potential delays that may arise due to international shipping. It’s also beneficial to work with logistics partners who have experience in handling technical documentation, as this can streamline the import process and minimize complications. -
Can I customize M-code lists for my specific machining needs?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for M-code lists to better fit your specific machining processes. Custom M-codes can be developed to control unique machine functions or to integrate with specific tooling setups. When requesting customization, provide detailed specifications of your machining requirements and any existing codes you currently use. Collaborating closely with your supplier during this process will help ensure that the customized M-code list meets your operational needs effectively.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
A stock image related to m codes list.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for m codes list
In today’s competitive landscape, understanding and effectively utilizing M-Codes is essential for international B2B buyers involved in CNC machining. The strategic sourcing of M-Code knowledge can greatly enhance operational efficiency and reduce downtime, particularly for manufacturers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By familiarizing themselves with the specific M-Codes relevant to their machines, businesses can streamline processes such as tool changes, coolant management, and program execution, leading to improved productivity and cost savings.
How Can Strategic Sourcing of M-Codes Benefit Your Business?
Investing in a comprehensive understanding of M-Codes not only minimizes the risk of errors but also fosters better communication with suppliers and machine operators. This knowledge empowers buyers to make informed decisions when purchasing CNC machinery or negotiating contracts with manufacturers. Additionally, as the global market evolves, leveraging M-Code expertise will be crucial for adapting to new technologies and maintaining a competitive edge.
What’s Next for International B2B Buyers?
As you move forward, consider integrating M-Code training into your operational strategy and seek out suppliers who prioritize transparency and education. Embrace the opportunity to collaborate with technical experts and industry peers to exchange insights and best practices. The future of manufacturing lies in informed decision-making—equip your business with the knowledge necessary to thrive in a rapidly changing environment.