Master the Market for Large Industrial Air Compressors:
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for large industrial air compressor
In today’s fast-paced industrial landscape, the role of large industrial air compressors is critical for optimizing production processes and ensuring operational efficiency. These robust machines are integral to a variety of sectors, including manufacturing, construction, and energy, where they provide essential compressed air for powering tools, processes, and systems. Understanding the complexities of sourcing and selecting the right compressor can significantly impact not only productivity but also cost management and sustainability efforts.
This comprehensive guide is designed to equip international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, with the insights needed to navigate the global market for large industrial air compressors. It will cover a wide array of topics, including the different types of compressors available, materials used in manufacturing, quality control standards, leading suppliers, cost considerations, and market trends. Additionally, we address frequently asked questions to provide clarity on common concerns.
By leveraging the information presented in this guide, buyers will be empowered to make informed sourcing decisions that align with their operational needs and strategic goals. Whether you are a seasoned procurement professional or a new entrant in the industry, understanding the dynamics of large industrial air compressors will be essential for enhancing your supply chain efficiency and driving business success in a competitive global market.
Understanding large industrial air compressor Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rotary Screw Compressors | Continuous operation, high efficiency | Manufacturing, automotive | Pros: Reliable, low maintenance. Cons: Higher initial cost. |
| Reciprocating Compressors | Positive displacement, versatile sizes | Construction, oil & gas | Pros: Cost-effective, flexible. Cons: Noisy, less efficient at high volumes. |
| Centrifugal Compressors | High flow rates, multi-stage design | Power generation, chemical plants | Pros: Efficient for large volumes. Cons: Complex installation and maintenance. |
| Scroll Compressors | Compact design, low noise operation | HVAC, refrigeration | Pros: Quiet, energy-efficient. Cons: Limited capacity for large-scale needs. |
| Oil-Free Compressors | No oil contamination, high purity air | Pharmaceuticals, food processing | Pros: Clean air output, minimal maintenance. Cons: Higher operational costs. |
Rotary Screw Compressors
Rotary screw compressors utilize two interlocking helical rotors to compress air, allowing for continuous operation. They are ideal for industries requiring a steady supply of compressed air, such as manufacturing and automotive sectors. Buyers should consider the initial investment, which is typically higher than other types, but weigh this against their low maintenance requirements and energy efficiency. The long-term operational savings can justify the upfront costs, making them a preferred choice for many industrial applications.
Reciprocating Compressors
Reciprocating compressors operate by drawing air into a cylinder and compressing it with a piston. They are versatile and available in various sizes, making them suitable for applications in construction and oil & gas industries. While they are generally more cost-effective and easier to maintain, buyers should note that they can be noisy and less efficient at high volumes. For businesses with fluctuating air demands, these compressors offer flexibility and adaptability.
Centrifugal Compressors
Centrifugal compressors are designed for high flow rates and utilize a multi-stage process to achieve compression. They are commonly used in power generation and chemical plants where large volumes of air are necessary. Although they provide excellent efficiency for large-scale applications, buyers must consider the complexity of installation and ongoing maintenance. Their initial setup costs can be significant, so organizations should evaluate their long-term air demand to determine suitability.
Scroll Compressors
Scroll compressors feature a compact design with low noise levels, making them ideal for applications in HVAC and refrigeration. They operate using two spiral-shaped scrolls to compress air, resulting in a quiet and energy-efficient performance. However, their capacity is limited for large-scale industrial needs. Buyers should assess whether their air demands align with the scroll compressor’s capabilities, as this type is best suited for smaller, specialized applications.
Oil-Free Compressors
Oil-free compressors eliminate the risk of oil contamination, producing high-purity air essential for industries like pharmaceuticals and food processing. While they provide clean air output and require minimal maintenance, they typically come with higher operational costs. Buyers in sectors where air quality is paramount should consider these compressors despite the increased expenses, as they can help meet strict regulatory standards and ensure product integrity.
Related Video: How does an Air Compressor work? (Compressor Types) – Tutorial Pneumatics
Key Industrial Applications of large industrial air compressor
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of large industrial air compressor | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Pneumatic tools operation | Increases efficiency and productivity in assembly lines | Energy efficiency, maintenance support, and reliability |
| Food and Beverage | Packaging and bottling processes | Ensures consistent pressure for quality packaging | Compliance with hygiene standards, durability, and energy consumption |
| Oil and Gas | Pipeline pressure testing and maintenance | Enhances safety and operational efficiency | Robustness for harsh environments, service support, and availability of parts |
| Construction | Concrete spraying and compaction | Improves project timelines and reduces labor costs | Portability, ease of use, and power requirements |
| Automotive | Painting and coating applications | Achieves high-quality finishes and reduces rework | Precision control, environmental compliance, and reliability |
Manufacturing
In the manufacturing sector, large industrial air compressors are essential for powering pneumatic tools and equipment across assembly lines. They provide a reliable source of compressed air, enabling tasks such as fastening, drilling, and cutting. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, it is crucial to assess the energy efficiency of compressors to manage operational costs effectively. Additionally, considering maintenance support can minimize downtime, ensuring continuous production.
Food and Beverage
The food and beverage industry utilizes large industrial air compressors primarily in packaging and bottling processes. These compressors maintain consistent air pressure, which is vital for ensuring the integrity and quality of packaged products. For buyers in the Middle East and Europe, compliance with stringent hygiene standards is paramount. Therefore, sourcing compressors that are easy to clean and meet food safety regulations will be critical to maintain product quality and safety.
Oil and Gas
In the oil and gas sector, large industrial air compressors are used for pipeline pressure testing and maintenance tasks. They play a crucial role in enhancing safety by ensuring that pipelines are leak-free and operationally sound. Buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East should prioritize robustness in their compressors, as they often operate in harsh environments. Moreover, having access to reliable service support and spare parts is essential to prevent operational delays.
Construction
Large industrial air compressors are vital in the construction industry for applications such as concrete spraying and compaction. They facilitate the efficient delivery of materials, significantly improving project timelines and reducing labor costs. For international B2B buyers, especially from South America and Europe, considerations around portability and ease of use are essential. Additionally, understanding the power requirements will help ensure compatibility with existing equipment on-site.
Automotive
In the automotive industry, large industrial air compressors are integral to painting and coating processes. They provide the necessary air pressure for spray guns, enabling high-quality finishes and reducing the likelihood of rework. Buyers should focus on compressors with precision control features to ensure consistent application. Furthermore, understanding environmental compliance, particularly in Europe, is crucial for maintaining regulatory standards and avoiding penalties.
Related Video: Air Compressor (Basics, Parts, Diagram, Working & Applications) Explained with Animation
Strategic Material Selection Guide for large industrial air compressor
When selecting materials for large industrial air compressors, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that influence performance, durability, and compliance with regional standards. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in the construction of these compressors, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight and has excellent thermal conductivity. It can withstand moderate temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for various applications. Its natural corrosion resistance is beneficial in humid or chemically aggressive environments.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of aluminum is its low weight, which simplifies transportation and installation. However, it has lower strength compared to other metals, which may limit its use in high-pressure applications. Aluminum is also more expensive than some alternatives, impacting overall project budgets.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is compatible with many gases and can handle moderate levels of moisture. However, it may not be suitable for applications involving aggressive chemicals without proper coatings.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure that aluminum components meet international standards such as ASTM B221. In regions like Europe, compliance with REACH regulations is also critical. Buyers from Africa and South America should consider local availability and potential import tariffs.
Cast Iron
Key Properties:
Cast iron is known for its excellent durability and strength, with high-temperature and pressure ratings. It has good wear resistance and can absorb vibrations, which is advantageous in industrial settings.
Pros & Cons:
The primary benefit of cast iron is its robustness, making it ideal for high-load applications. However, it is heavy and can be more challenging to transport and install. Additionally, cast iron is prone to corrosion if not properly maintained, which can lead to increased lifecycle costs.
Impact on Application:
Cast iron is suitable for high-pressure air applications and can handle a variety of media, including oil-laden air. However, its susceptibility to rust in humid environments necessitates protective coatings or regular maintenance.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should verify that cast iron components comply with standards like ASTM A48. In regions such as the Middle East, where humidity can be high, additional corrosion protection may be required.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance and can withstand high temperatures and pressures. Its strength makes it suitable for demanding applications where durability is essential.
Pros & Cons:
Stainless steel’s primary advantage is its long lifespan and minimal maintenance needs due to its corrosion resistance. However, it is generally more expensive than aluminum and cast iron, which may impact budget considerations.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is compatible with various gases and fluids, making it versatile for different applications. Its resistance to corrosion is particularly beneficial in environments with high humidity or chemical exposure.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM A240. In Europe, adherence to the EU’s environmental regulations is crucial. Buyers from South America and Africa should consider local sourcing options to reduce costs.
Composite Materials
Key Properties:
Composite materials, often made from a combination of polymers and fibers, are lightweight and have excellent corrosion resistance. They can be engineered for specific pressure and temperature ratings, making them versatile.
Pros & Cons:
The main advantage of composites is their lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion, which can significantly reduce maintenance costs. However, they may not be suitable for high-pressure applications compared to metals and can be more expensive to manufacture.
Impact on Application:
Composites can be designed for specific media compatibility, making them suitable for specialized applications. However, their use may be limited in extreme temperature conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure that composite materials meet relevant standards, such as ASTM D3039. In regions like Turkey and Mexico, understanding local regulations regarding material use is essential for compliance.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for large industrial air compressor | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Lightweight components in moderate pressure applications | Low weight and good thermal conductivity | Lower strength than alternatives | Medium |
| Cast Iron | High-load, high-pressure applications | Excellent durability and strength | Heavy and prone to corrosion | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Corrosive environments and high-pressure applications | Long lifespan and minimal maintenance | Higher cost than other metals | High |
| Composite Materials | Specialized applications requiring lightweight and corrosion-resistant solutions | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Limited high-pressure capability | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides actionable insights for B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for large industrial air compressor
Manufacturing large industrial air compressors involves a series of meticulous processes designed to ensure durability, efficiency, and reliability. Buyers from diverse regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must understand these processes to make informed purchasing decisions.
Manufacturing Processes
The manufacturing of large industrial air compressors can be broken down into several key stages:
1. Material Preparation
The first step involves selecting high-quality materials. Common materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, and aluminum, chosen for their strength and resistance to corrosion. Suppliers should be scrutinized for their sourcing practices, ensuring that materials meet international standards and are suitable for the intended application.
2. Forming
In this stage, the prepared materials undergo various forming processes. Techniques include:
- Machining: Precision cutting, drilling, and milling to create essential components such as the compressor housing, rotors, and pistons.
- Casting: Used for parts that require complex shapes, ensuring a solid structure.
- Welding: Critical for assembling components, particularly in high-stress areas. The welding process must comply with industry standards to ensure integrity.
3. Assembly
The assembly process integrates all the manufactured components into a cohesive unit. This stage includes:
- Sub-assembly: Smaller components, such as valves and filters, are assembled before being integrated into the main unit.
- Final Assembly: The complete unit is assembled, often requiring specialized tooling and fixtures to ensure precision and alignment.
4. Finishing
Finishing processes enhance the compressor’s performance and longevity. Techniques include:
- Surface Treatment: Coatings and treatments to prevent corrosion and wear.
- Painting: Aesthetic and protective layers that also serve to identify brand and model.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical component in the manufacturing of large industrial air compressors. It ensures that products meet specified standards and perform reliably in the field.
International Standards
Buyers should look for compliance with international standards such as:
- ISO 9001: A standard that ensures effective quality management systems, focusing on customer satisfaction and continuous improvement.
- CE Marking: Indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area.
- API Standards: Relevant for compressors used in the oil and gas industry, ensuring they meet specific operational requirements.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) is performed at various stages throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspection of raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing checks during the manufacturing process to catch defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive inspection of the finished product before shipment, ensuring it meets all design and performance specifications.
Common Testing Methods
To validate the quality of large industrial air compressors, several testing methods are commonly employed:
- Pressure Testing: Ensures that the compressor can withstand its operating pressure without leaks.
- Performance Testing: Assesses the compressor’s efficiency and output under various operating conditions.
- Vibration Analysis: Used to detect any imbalances or mechanical issues that could affect performance.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse markets, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential. Here are actionable steps:
Conducting Audits
Regular audits of suppliers can help ensure compliance with quality standards. These can be either announced or unannounced and should focus on:
- Documentation Review: Check quality manuals, process flows, and compliance records.
- Facility Inspection: Evaluate the manufacturing environment and equipment used.
Requesting Quality Reports
Ask suppliers for detailed quality reports, which should include:
- Inspection Records: Documentation of IQC, IPQC, and FQC results.
- Non-Conformance Reports: Insights into any issues encountered during production and how they were resolved.
Engaging Third-Party Inspectors
Utilizing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s QC processes. These inspectors can conduct:
- Random Sampling: Evaluating a selection of products from a batch to determine overall quality.
- Certification Verification: Ensuring that suppliers hold valid certifications for the standards they claim to meet.
QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
International buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in QC and certification:
- Regulatory Compliance: Understand the local regulations that may differ significantly from international standards. For example, some countries may have additional certifications required for import.
- Cultural and Regional Differences: Be cognizant of varying quality expectations and practices in different regions. What is considered acceptable in one market may not be in another.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Establish clear communication channels with suppliers to ensure visibility into their quality processes and adherence to agreed-upon standards.
In summary, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for large industrial air compressors is vital for B2B buyers. By focusing on material selection, manufacturing techniques, and stringent QC protocols, buyers can ensure they are investing in reliable, high-quality equipment that meets their operational needs.
Related Video: Amazing factories | Manufacturing method and top 4 processes | Mass production process
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for large industrial air compressor Sourcing
In the procurement of large industrial air compressors, understanding the comprehensive cost and pricing structure is vital for B2B buyers. This analysis delves into the various cost components, price influencers, and actionable tips for international buyers, particularly those operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials, such as steel and aluminum, is a significant factor. Fluctuations in global commodity prices can impact the overall cost. Buyers should consider sourcing from regions with lower material costs or exploring alternative materials that may provide cost savings without compromising quality.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly by region. In countries with lower labor costs, manufacturers might offer competitive pricing. However, it’s crucial to assess the skill level and experience of the workforce, as these can directly affect the quality of the compressors produced.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, depreciation, and administrative costs associated with production. A thorough understanding of the manufacturer’s overhead can help buyers gauge pricing fairness.
-
Tooling: The cost associated with the tools and equipment necessary for production can be substantial, especially for custom compressors. Buyers should inquire about tooling costs and their impact on the overall price.
-
Quality Control (QC): Effective QC processes ensure the reliability and performance of the compressors. While rigorous QC may increase costs, it is essential for long-term operational efficiency. Buyers should evaluate suppliers’ QC practices and certifications.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary based on distance, mode of transport, and destination. Understanding logistics costs is critical, particularly for international buyers who must navigate tariffs and duties.
-
Margin: Manufacturer margins can differ based on their market positioning and cost structure. It is beneficial for buyers to understand the profit margins typically applied in the industry to assess the fairness of supplier pricing.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often yield better pricing due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate for favorable pricing based on their order quantities.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom features or specifications can significantly increase costs. Buyers should carefully assess their needs and only request customizations that are essential.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) can lead to increased costs but may be necessary for compliance and operational reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may charge a premium but can reduce risks associated with performance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms (e.g., FOB, CIF) is essential for clarifying responsibilities and costs associated with logistics. Buyers should ensure they fully comprehend the implications of the chosen Incoterms on total costs.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers to negotiate better terms. Understanding the cost structure can empower buyers during negotiations.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO), which includes purchase price, operating costs, maintenance, and potential downtime. A lower initial price may not always equate to the best long-term value.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and local market conditions that can affect pricing. Buyers should also consider local regulations and standards that may impact compressor specifications and costs.
Disclaimer
Prices for large industrial air compressors can vary widely based on the factors discussed. The information provided here serves as a guideline and may not reflect current market conditions. Buyers should conduct thorough market research and consult multiple suppliers to obtain accurate quotes tailored to their specific needs.
Spotlight on Potential large industrial air compressor Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘large industrial air compressor’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for large industrial air compressor
Key Technical Properties of Large Industrial Air Compressors
When investing in large industrial air compressors, understanding their technical specifications is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some of the essential properties to consider:
-
Compressor Type
The primary types of compressors are reciprocating, rotary screw, and centrifugal. Each type has unique performance characteristics and operational efficiencies. For instance, rotary screw compressors are often favored for continuous operations due to their durability and lower maintenance requirements, making them suitable for large-scale industrial applications. -
Pressure Rating
Measured in pounds per square inch (PSI), the pressure rating indicates the maximum pressure the compressor can produce. Higher pressure ratings allow for more demanding applications but may also require additional safety considerations. Buyers should align the pressure rating with the specific needs of their operations to ensure efficiency and safety.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Flow Rate (CFM)
The flow rate, measured in cubic feet per minute (CFM), defines the volume of air the compressor can deliver. This specification is vital for determining whether a compressor can meet the air demand of a particular application. An inadequate flow rate can lead to operational inefficiencies and increased wear on the equipment. -
Horsepower (HP)
Horsepower indicates the power output of the compressor’s motor. It is a critical factor in assessing the compressor’s capability to handle the required workload. Higher horsepower often translates to greater efficiency and longevity, but it can also lead to increased operational costs. -
Material Grade
The material used in the construction of the compressor, such as aluminum, cast iron, or steel, affects durability and performance. High-grade materials can withstand higher pressures and temperatures, contributing to a longer lifespan and reduced maintenance costs. Buyers should consider the operational environment when evaluating material grades. -
Noise Level (dBA)
Noise levels are an important consideration, especially in environments where sound regulations are in place. Measured in decibels A-weighted (dBA), lower noise levels contribute to a safer and more comfortable working environment. Opting for quieter models can enhance workplace conditions, particularly in urban settings or near residential areas.
Common Trade Terminology
Navigating the industrial air compressor market requires familiarity with specific terminology. Here are some key terms that B2B buyers should understand:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to the company that produces the original components of the compressor. When sourcing parts or complete systems, working with OEMs ensures compatibility and quality. Buyers should verify that parts are sourced from reputable OEMs to avoid issues with performance or warranty claims. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ represents the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their operational needs without overcommitting resources. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document soliciting price and terms from suppliers. This process helps buyers compare options and negotiate better deals. Including detailed specifications in the RFQ can lead to more accurate and competitive quotations.
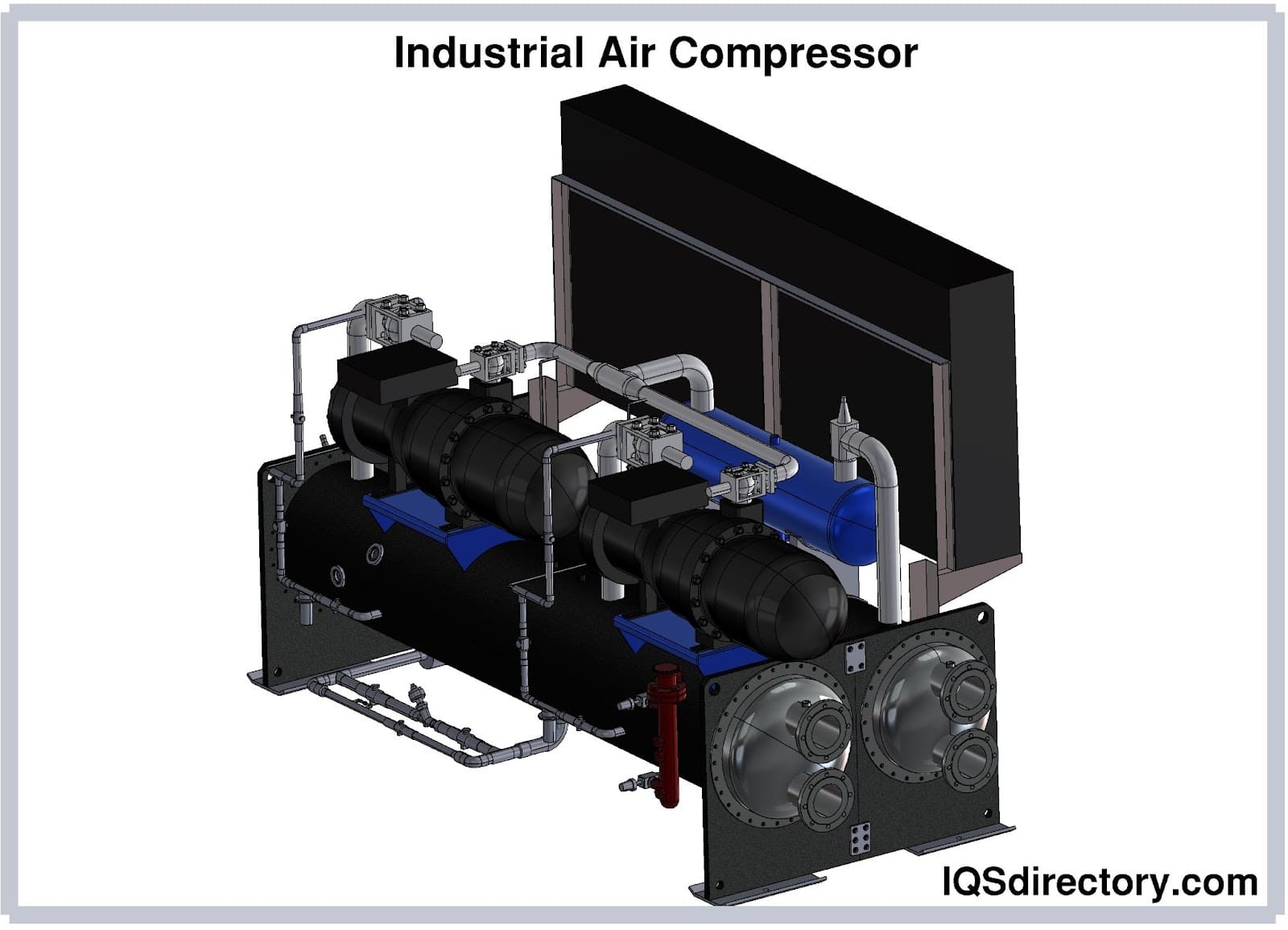
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined trade terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce that define responsibilities between buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for international transactions, as they clarify who is responsible for various costs and risks during transit. -
After-Sales Support
This term encompasses the services provided by suppliers after the purchase, including maintenance, repairs, and parts replacement. Strong after-sales support is vital for minimizing downtime and ensuring the long-term performance of the compressor. -
Warranty Period
The warranty period specifies the duration during which the manufacturer guarantees the product against defects. Understanding the warranty terms is essential for risk management and helps buyers make informed decisions regarding maintenance and potential repairs.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terminologies, international B2B buyers can navigate the complex landscape of large industrial air compressors more effectively, ensuring they make informed investments that align with their operational goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the large industrial air compressor Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global market for large industrial air compressors is experiencing a dynamic evolution driven by several key factors. One of the most significant drivers is the growing demand for energy-efficient solutions across various industries, including manufacturing, automotive, and construction. As businesses face increasing operational costs, the need for advanced compressors that reduce energy consumption has become paramount. Additionally, the rise of automation and Industry 4.0 technologies is influencing purchasing decisions, as companies seek compressors that can seamlessly integrate with smart systems for enhanced monitoring and maintenance.
Emerging trends in sourcing highlight the importance of digital platforms for procurement. B2B buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are increasingly leveraging online marketplaces and e-procurement systems to streamline their sourcing processes. This shift not only enhances transparency but also allows buyers to compare options and negotiate better terms. Moreover, as geopolitical tensions and supply chain disruptions become more prevalent, companies are diversifying their supplier bases to mitigate risks, focusing on local and regional suppliers to ensure continuity.
For international buyers, particularly those from Turkey and Mexico, understanding local regulations and standards is essential. Compliance with these standards not only facilitates smoother transactions but also enhances credibility in the marketplace. Additionally, the trend toward modular and customizable compressors is gaining traction, allowing businesses to tailor solutions to their specific operational needs, further driving demand in diverse markets.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a non-negotiable aspect of procurement strategies in the industrial air compressor sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and the operational efficiency of compressors are under scrutiny as businesses strive to meet corporate social responsibility goals. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing products that are designed with sustainability in mind, such as those that use recyclable materials and have lower carbon footprints.
Moreover, ethical sourcing is crucial in today’s global marketplace. Companies are expected to ensure that their supply chains adhere to ethical labor practices and sustainable resource management. This includes seeking suppliers who are certified by recognized environmental standards such as ISO 14001 or those that utilize green materials in their manufacturing processes. For B2B buyers from diverse regions, aligning procurement strategies with sustainability goals not only enhances brand reputation but also appeals to a growing base of environmentally conscious consumers.
Investing in compressors that feature energy-efficient technologies, such as variable speed drives and advanced control systems, can significantly reduce operational costs while minimizing environmental impact. Buyers should actively seek partnerships with manufacturers who prioritize sustainability and can provide documentation of their compliance with environmental standards.
Brief Evolution/History
The large industrial air compressor market has undergone significant transformations since its inception in the late 19th century. Initially driven by the steam engine, the development of electric motors in the early 20th century revolutionized the industry, making compressors more efficient and accessible. The post-World War II era saw rapid advancements in technology, with the introduction of rotary screw compressors that offered improved efficiency and reliability.
As industries evolved, so did the demand for specialized compressors tailored for specific applications, leading to increased innovation. The last two decades have marked a shift toward energy-efficient and environmentally friendly solutions, driven by regulatory changes and heightened awareness of climate issues. Today, the focus is on integrating smart technologies and sustainability practices, aligning with global efforts to reduce energy consumption and enhance operational efficiencies. For B2B buyers, understanding this historical context is essential to navigate current market dynamics and make informed procurement decisions.
Related Video: Incoterms for beginners | Global Trade Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of large industrial air compressor
-
What criteria should I use to vet suppliers of large industrial air compressors?
When vetting suppliers, consider their industry experience, reputation, and financial stability. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates quality management systems. Additionally, ask for references from previous clients in your region to gauge reliability and service quality. Evaluate their production capacity and whether they can meet your specific needs, especially if you’re considering bulk purchases. -
Can large industrial air compressors be customized to meet specific requirements?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for large industrial air compressors. You can tailor specifications such as capacity, power source, and additional features like variable speed drives or noise reduction technology. Discuss your exact needs with suppliers early in the negotiation process to ensure they can accommodate your requests and provide a detailed quote. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for these compressors?
MOQs can vary significantly depending on the manufacturer and the complexity of the order. Generally, for large industrial air compressors, MOQs may start from 5 to 10 units. Lead times can range from 4 to 12 weeks based on customization, production schedules, and shipping logistics. Always confirm these details during discussions to plan your procurement effectively. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing large industrial air compressors?
Payment terms can differ widely among suppliers. Common terms include a 30% upfront deposit, with the balance due upon delivery or installation. For international transactions, consider using secure payment methods like letters of credit or escrow services to mitigate risks. Ensure that all payment conditions are clearly outlined in the contract before proceeding. -
What quality assurance measures should suppliers provide?
Reputable suppliers should offer a comprehensive quality assurance plan that includes testing procedures, warranty details, and compliance with international standards. Request documentation of certifications and quality control processes. It’s also beneficial to inquire about after-sales support, such as service agreements and spare parts availability, to ensure ongoing reliability. -
How should I handle logistics and shipping for international purchases?
When arranging logistics, collaborate closely with your supplier to understand shipping methods and timelines. Consider factors like freight costs, customs duties, and local regulations in your country. Engaging a freight forwarder can simplify the process, ensuring that all necessary paperwork is completed and that the compressors arrive in good condition and on time. -
What should I do if there is a dispute with the supplier?
In the event of a dispute, first, review your contract to understand the terms and conditions agreed upon. Open a line of communication with the supplier to discuss the issue and seek a resolution. If necessary, consider mediation or arbitration as stipulated in your contract. Maintaining a professional demeanor and clear documentation can often lead to a favorable outcome. -
Are there specific certifications or regulations I should be aware of for importing compressors into my region?
Yes, it’s crucial to familiarize yourself with local regulations and standards for importing industrial equipment. This can include safety standards, energy efficiency certifications, and environmental regulations. Check with relevant authorities in your country to ensure compliance and avoid potential delays or fines. Suppliers should also be able to assist you in understanding these requirements.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for large industrial air compressor
As the demand for large industrial air compressors continues to grow across diverse markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, strategic sourcing has emerged as a pivotal approach for B2B buyers. By focusing on supplier reliability, cost-efficiency, and technological innovation, businesses can enhance operational efficiency and reduce total ownership costs.
Key takeaways include the importance of conducting thorough market research to identify reputable suppliers, understanding local regulations, and leveraging partnerships to foster collaborative growth. Investing in high-quality compressors not only ensures superior performance but also contributes to sustainability goals, aligning with global trends toward eco-friendly operations.
Looking ahead, B2B buyers should actively seek out suppliers who are willing to innovate and adapt to changing market dynamics. By prioritizing strategic sourcing, companies can secure a competitive edge while navigating the complexities of international trade.
Now is the time to act—evaluate your sourcing strategies, engage with potential suppliers, and position your business for success in the evolving landscape of industrial air compressors. Your next step could be the key to unlocking new opportunities and driving long-term growth.