Explore Different Plug Types: The Ultimate Sourcing Guide (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for different plug types
In today’s interconnected global market, sourcing the right electrical components, such as different plug types, can pose significant challenges for B2B buyers. With over 15 distinct plug and socket designs in use worldwide, understanding the compatibility and applications of each type is crucial for businesses looking to streamline their operations and avoid costly electrical mishaps. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, detailing the various plug types, their specific applications, and the voltage and frequency standards associated with each.
International B2B buyers, especially those operating in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, will find actionable insights into supplier vetting, cost considerations, and best practices for importing electrical components. By equipping buyers with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of global electrical standards, this guide empowers them to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs.
Whether you’re sourcing components for manufacturing, construction, or consumer electronics, understanding the nuances of different plug types is essential. This guide aims to bridge the knowledge gap, ensuring that businesses can confidently select the right products that comply with local regulations and enhance their market competitiveness. As you delve into the subsequent sections, expect to gain clarity on how to effectively manage the intricacies of sourcing electrical plugs and sockets across diverse markets.
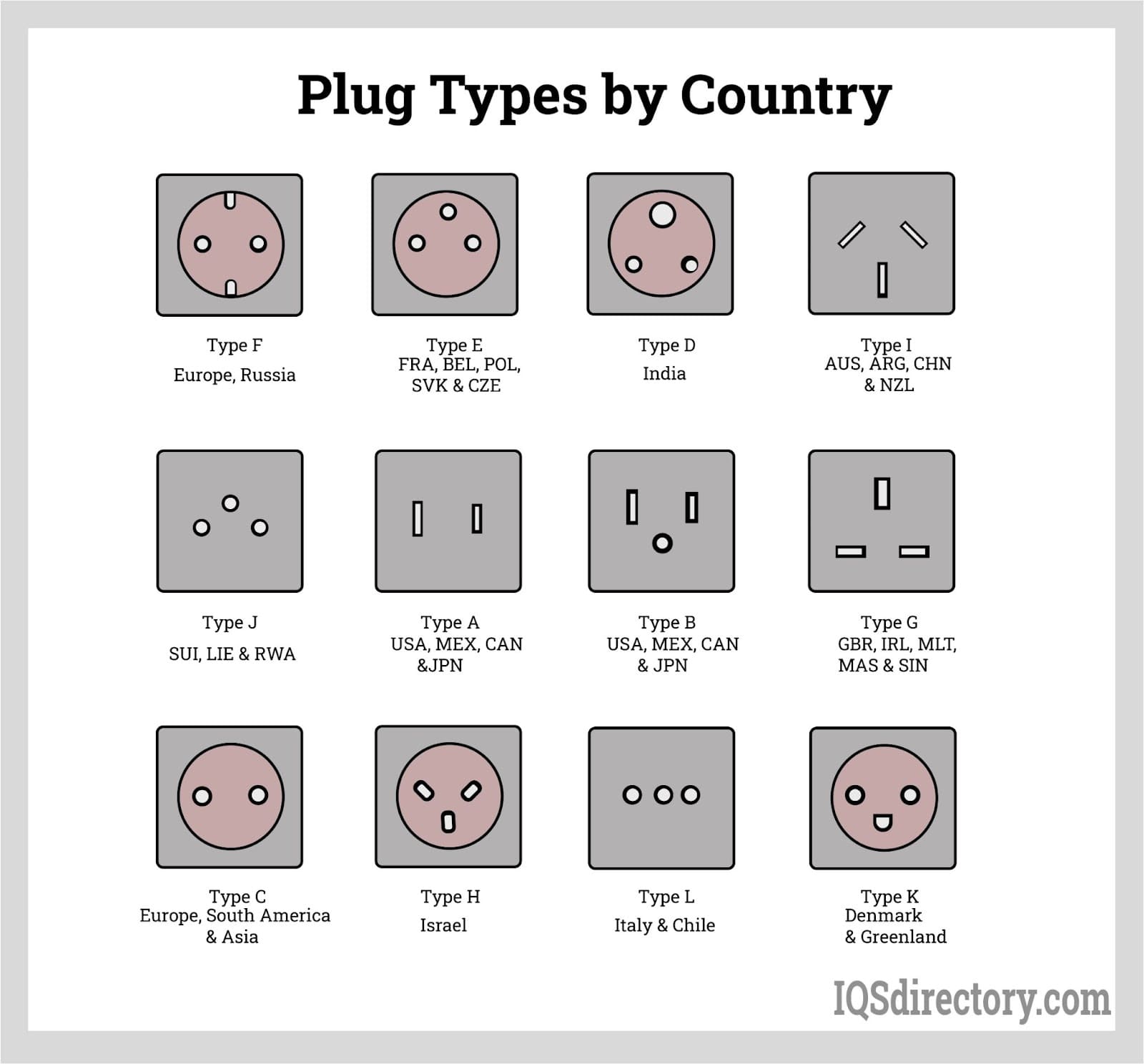
Understanding different plug types Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
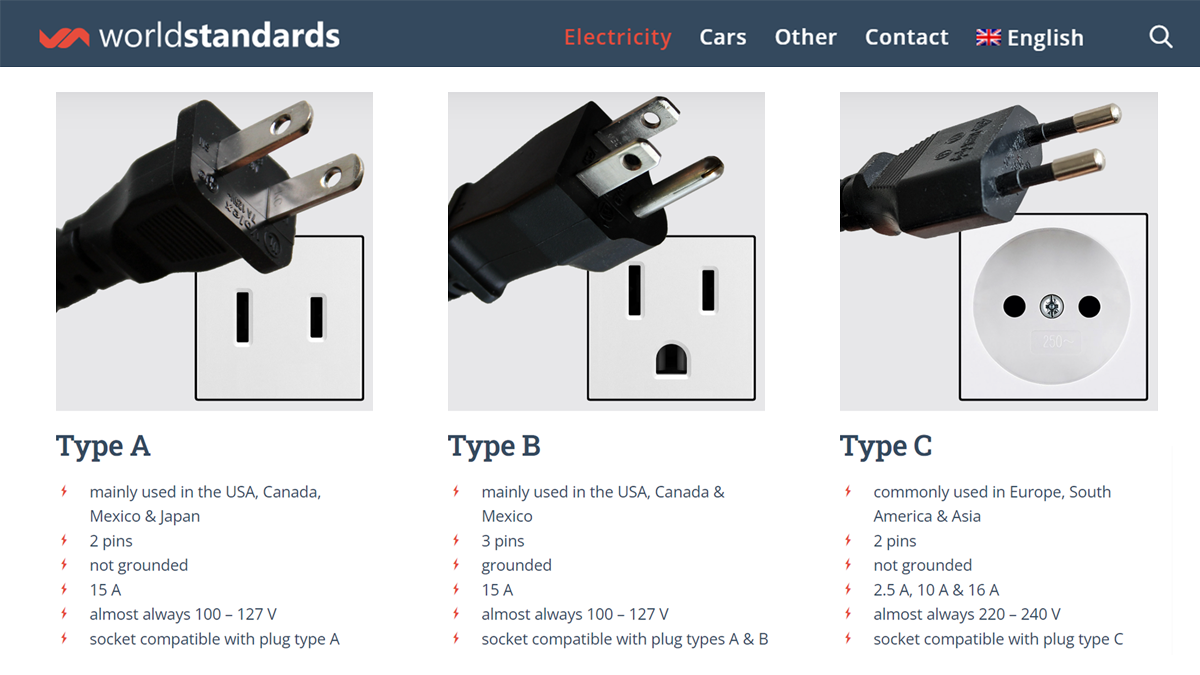
| Type C | 2 non-grounded pins, 2.5 A, 10 A & 16 A, 220-240 V | Widely used in Europe, Africa, and South America for general appliances | Pros: Commonly available, versatile; Cons: Non-grounded, limited to lower power applications |
| Type G | 3 grounded pins, 13 A, 220-250 V | Essential for UK, Ireland, and Middle Eastern markets, often used in industrial settings | Pros: Grounded for safety, high power capacity; Cons: Bulkier, may require adapters in other regions |
| Type I | 2 or 3 pins, 10 A, 220-240 V | Used in Australia, New Zealand, and parts of Asia for various electronics | Pros: Dual pin options for flexibility; Cons: Less compatibility in Europe and the Americas |
| Type E/F | 2 grounded pins, 16 A, 220-240 V | Common in France, Germany, and other European countries for household and commercial use | Pros: Grounded for safety, compatible with multiple types; Cons: Regional compatibility issues |
| Type N | 3 grounded pins, 10 A, 16 A, 20 A, 100-240 V | Primarily used in Brazil and South Africa for high-demand electrical equipment | Pros: High power capacity, versatile; Cons: Limited availability outside specific regions |
What are the Characteristics of Type C Plugs and Their Suitability for B2B Purchases?
Type C plugs feature two non-grounded pins and are commonly used across Europe, Africa, and South America. They support various amperages (2.5 A, 10 A, and 16 A) and operate at 220-240 V. These plugs are suitable for general appliances and electronics, making them a staple in both residential and commercial environments. B2B buyers should consider the widespread availability of Type C plugs, which can simplify sourcing and logistics. However, the lack of grounding may limit their use in high-power applications.
How Does Type G Plug Ensure Safety in B2B Applications?
Type G plugs are characterized by their three grounded pins and a power rating of 13 A, operating at 220-250 V. This type is essential in the UK, Ireland, and several Middle Eastern countries, often found in industrial and commercial settings. The grounding feature enhances safety, reducing the risk of electrical shock, which is crucial for B2B applications. Buyers should note that while Type G plugs offer high power capacity, their bulkiness may necessitate the use of adapters when connecting to devices from other regions.
Why Choose Type I Plugs for International B2B Operations?
Type I plugs are designed with either two or three pins and can handle 10 A at 220-240 V. They are primarily used in Australia, New Zealand, and parts of Asia. The dual pin options provide flexibility, making them suitable for a range of electronics and appliances. B2B buyers should consider Type I plugs for operations that require adaptability in power connections. However, compatibility issues may arise when trying to connect devices in Europe or the Americas, which could complicate international logistics.
What Makes Type E/F Plugs Ideal for European Businesses?
Type E/F plugs feature two grounded pins rated for 16 A and operate at 220-240 V, making them a common choice in France, Germany, and other European countries. Their grounding capability ensures safety and reliability in both residential and commercial applications. B2B buyers will find Type E/F plugs advantageous due to their compatibility with multiple plug types, facilitating easier integration of equipment. However, companies should be aware of regional compatibility issues when dealing with international partners.
How Do Type N Plugs Serve the Needs of Brazilian and South African Markets?
Type N plugs, with three grounded pins and power ratings of 10 A, 16 A, and 20 A, are primarily utilized in Brazil and South Africa. Their versatility and high power capacity make them suitable for demanding electrical equipment in various industries. B2B buyers should consider Type N plugs for operations requiring reliable power connections. However, the limited availability outside these regions may pose challenges in sourcing and compatibility when conducting international business.
Key Industrial Applications of different plug types
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of different plug types | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Power supply for machinery using Type C and Type F plugs | Ensures compatibility with local electrical standards, reducing downtime. | Verify voltage and amperage requirements for machines. |
| Construction | Temporary power connections on job sites with Type G plugs | Provides safe and reliable power to tools and equipment. | Assess weather resistance and durability of plugs. |
| Information Technology | Data centers using Type I plugs for servers | Supports high power demands with grounding for safety. | Ensure compliance with local electrical codes and standards. |
| Hospitality | Charging stations with Type A and Type B plugs in hotels | Enhances guest experience through accessible charging options. | Evaluate plug type compatibility with guest devices. |
| Healthcare | Medical equipment powered by Type D and Type E plugs | Guarantees safety and reliability for critical devices. | Confirm compatibility with medical device specifications. |
How are Different Plug Types Used in Manufacturing?
In the manufacturing sector, Type C and Type F plugs are commonly utilized for powering machinery and tools. These plugs are compatible with the standard voltages (220-240V) used in many African and European countries, ensuring minimal downtime due to electrical issues. Buyers should consider the specific voltage and amperage requirements of their equipment to avoid compatibility problems. Additionally, sourcing plugs that meet local safety standards can help prevent electrical hazards in the workplace.
What are the Benefits of Different Plug Types in Construction?
Construction sites often require temporary power solutions, where Type G plugs play a critical role. These plugs provide reliable electrical connections for power tools and lighting, ensuring safety and efficiency on-site. Businesses benefit from reduced project delays due to electrical failures. When sourcing plugs for construction, it is essential to assess their weather resistance and durability, as they will be exposed to various environmental conditions.
Why are Different Plug Types Important in Information Technology?
In the IT sector, especially in data centers, Type I plugs are essential for powering servers and networking equipment. These plugs support higher power demands while providing grounding for safety, which is critical in preventing equipment damage. For international B2B buyers, ensuring compliance with local electrical codes and standards is vital when sourcing plugs, as it can affect the overall safety and functionality of IT infrastructure.
How Do Different Plug Types Enhance Hospitality Services?
In the hospitality industry, hotels often provide charging stations equipped with Type A and Type B plugs to accommodate guests’ devices. This enhances the guest experience by ensuring easy access to charging options. For hotel managers, evaluating plug type compatibility with various guest devices is crucial to avoid customer dissatisfaction. Additionally, sourcing high-quality plugs can reduce maintenance costs and improve guest satisfaction.
What Role Do Different Plug Types Play in Healthcare?
Healthcare facilities frequently rely on Type D and Type E plugs to power medical equipment. These plugs ensure safety and reliability for critical devices, such as monitors and imaging equipment. Buyers in this sector must confirm that the plugs they source comply with medical device specifications and local electrical standards. This not only guarantees the safety of patients and staff but also enhances the efficiency of healthcare operations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘different plug types’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Multiple Plug Standards Across Regions
The Problem: As a B2B buyer operating in multiple markets, you may face the daunting challenge of dealing with various plug standards. For instance, if your company sources equipment from Europe for distribution in Africa, you might encounter devices that use Type C plugs while your local infrastructure primarily supports Type D or G sockets. This can lead to significant delays in product deployment, increased operational costs, and frustration among your logistics team when trying to fulfill orders.
The Solution: To mitigate these challenges, consider investing in universal plug adapters or sockets that accommodate multiple plug types. When sourcing equipment, ensure that the suppliers provide compatibility information regarding plug types and voltages. Additionally, you can establish partnerships with local electrical suppliers who can provide the necessary adapters or even modify equipment to fit local standards. Training your logistics team on the specific plug types used in each region will also enhance efficiency in handling products, ensuring they are ready for deployment without unnecessary delays.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Electrical Safety Compliance
The Problem: Electrical safety is paramount, especially when dealing with different plug types. A common scenario involves sourcing equipment that may not meet local electrical codes, particularly when importing from regions with different voltage and amperage standards. For example, equipment designed for Type I sockets in Australia may not be suitable for use in South America where Type C or N sockets are prevalent. This mismatch can lead to equipment malfunctions, safety hazards, and potential legal liabilities.
The Solution: To ensure compliance with local electrical safety standards, conduct thorough due diligence before purchasing equipment. This includes verifying that the equipment is certified for use in the target market and conforms to local voltage and amperage requirements. Collaborate with compliance consultants or local experts who can provide insights into safety standards and regulations specific to the countries you operate in. Additionally, consider sourcing from suppliers who offer equipment specifically designed for your target markets, which can reduce the risk of safety issues and streamline the approval process for installations.
Scenario 3: Managing Supply Chain Disruptions Due to Plug Type Variations
The Problem: International supply chains are often disrupted by unexpected variations in plug types, especially when dealing with last-minute orders or urgent equipment needs. A scenario might arise where a company in South Africa urgently requires medical equipment that was ordered from Europe, but the shipment arrives with European Type C plugs while the local infrastructure uses Type M. This not only delays critical operations but also incurs additional costs for retrofitting or purchasing adapters.
The Solution: To prevent such disruptions, implement a comprehensive sourcing strategy that includes a detailed analysis of plug type compatibility during the procurement process. Create a database of plug types used in your key markets and ensure that all suppliers are aware of these requirements during the order process. Furthermore, maintain a stock of essential adapters and converters tailored to the specific plug types you encounter frequently. By establishing a proactive approach to plug type compatibility, your organization can minimize supply chain disruptions and ensure that critical operations continue smoothly, regardless of last-minute changes in equipment needs.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for different plug types
When selecting materials for different plug types, international B2B buyers must consider various factors, including the properties of the materials, their suitability for specific applications, and compliance with regional standards. This analysis focuses on four common materials used in plug manufacturing: thermoplastics, thermosetting plastics, metals, and rubber. Each material offers distinct advantages and disadvantages that can impact performance and application.
What Are the Key Properties of Thermoplastics in Plug Manufacturing?
Thermoplastics, such as polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), are widely used in plug manufacturing due to their excellent electrical insulation properties and versatility. They can withstand temperatures ranging from -40°C to 85°C and offer good impact resistance. Additionally, thermoplastics are resistant to corrosion and chemicals, making them suitable for various environments.
Pros & Cons:
Thermoplastics are lightweight and cost-effective, which makes them an attractive option for manufacturers. However, they may not be as durable as other materials and can deform under high temperatures, limiting their use in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application:
Thermoplastics are ideal for standard plugs used in household and office environments where moderate electrical loads are present. Their compatibility with various media types, including water and oils, makes them versatile.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local electrical standards, such as IEC or ANSI, when selecting thermoplastic plugs.
How Do Metals Enhance Performance in Plug Types?
Metals, particularly copper and aluminum, are frequently used in the conductive components of plugs due to their superior electrical conductivity and durability. They can handle high temperatures and pressures, with copper rated for continuous use up to 90°C.
Pros & Cons:
Metal plugs are highly durable and provide excellent performance in high-load applications. However, they can be heavier and more expensive than plastic alternatives, which may affect shipping costs and installation.
Impact on Application:
Metal components are essential in industrial plugs that require robust performance under heavy electrical loads, such as those found in manufacturing facilities.
Considerations for International Buyers:
B2B buyers in the Middle East and Europe should be aware of corrosion resistance standards, especially in humid or coastal environments, where metal plugs may require additional coatings or treatments.
What Role Does Rubber Play in Plug Design?
Rubber is often used as an insulating material in plugs, providing excellent flexibility and resistance to environmental factors such as moisture and dust. It can typically withstand temperatures from -30°C to 70°C and is known for its durability.
Pros & Cons:
Rubber plugs are highly effective at preventing electrical shock and are ideal for outdoor use. However, they can be more expensive and may degrade over time if exposed to UV light.
Impact on Application:
Rubber is particularly suitable for plugs used in outdoor or industrial settings where exposure to harsh weather conditions is a concern.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in regions with extreme weather conditions, such as South Africa, should prioritize rubber plugs that comply with local safety standards to ensure reliability.
How Do Thermosetting Plastics Compare in Plug Applications?
Thermosetting plastics, such as phenolic resins, are known for their high thermal stability and mechanical strength. They can withstand temperatures up to 150°C without deforming, making them suitable for high-performance applications.
Pros & Cons:
These materials offer excellent durability and resistance to heat and chemicals. However, they are more complex to manufacture and generally more expensive than thermoplastics.
Impact on Application:
Thermosetting plastics are ideal for heavy-duty plugs used in industrial settings where high temperatures and mechanical stress are common.
Considerations for International Buyers:
B2B buyers in Europe should consider compliance with standards like DIN EN for thermosetting plastics to ensure product safety and reliability.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Plug Types
| Material | Typical Use Case for different plug types | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermoplastics | Household and office plugs | Lightweight and cost-effective | Less durable under high stress | Low |
| Metals | Industrial plugs | Excellent conductivity and durability | Heavier and more expensive | High |
| Rubber | Outdoor and industrial plugs | Flexible and moisture-resistant | Can degrade under UV exposure | Medium |
| Thermosetting Plastics | Heavy-duty industrial plugs | High thermal stability | More complex to manufacture | High |
By understanding the properties, advantages, and disadvantages of these materials, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific needs and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for different plug types
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Electrical Plugs?
The manufacturing process of electrical plugs involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets safety and performance standards. Understanding these stages is vital for B2B buyers looking to source plugs that comply with international standards.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in manufacturing electrical plugs is material selection and preparation. Common materials used include:
- Thermoplastics: For the plug body, providing insulation and durability.
- Copper or Brass: For conductors due to their excellent electrical conductivity.
- Nickel Coating: Often applied to terminals to prevent corrosion.
Materials are sourced based on international standards to ensure compatibility and safety. Buyers should verify the source and quality of these materials to ensure compliance with standards like ISO 9001.
2. Forming Techniques
Once materials are prepared, they undergo forming processes to create the different components of the plug. Key techniques include:
- Injection Molding: Used for shaping the plastic components. This process allows for high precision and consistency in production.
- Stamping and Machining: These methods are employed to create metal parts, such as pins and connectors, ensuring they meet specified dimensions and tolerances.
B2B buyers should inquire about the forming techniques used by suppliers to ensure they align with their quality expectations.
3. Assembly of Components
The assembly stage combines the formed components into a complete plug. This process typically involves:
- Automated Assembly Lines: Many manufacturers use robotics to increase efficiency and reduce human error.
- Manual Assembly: In some cases, particularly for complex plug types, skilled workers are involved to ensure precision.
Quality checks are integral during assembly, with specific focus on the alignment and secure fitting of components.
4. Finishing Processes
After assembly, plugs undergo finishing processes that enhance their performance and appearance. This may include:
- Surface Treatments: Such as polishing or coating to improve aesthetics and resistance to wear.
- Electrical Testing: Every plug is tested for electrical continuity and insulation resistance.
Buyers should ensure that manufacturers employ rigorous finishing processes to guarantee the longevity and safety of the plugs.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Plug Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a cornerstone of the manufacturing process for electrical plugs. It involves systematic monitoring and evaluation to ensure that products meet established standards.
International Standards Relevant to Plug Manufacturing
B2B buyers should be aware of the various international standards that govern plug manufacturing, including:
- ISO 9001: A globally recognized standard for quality management systems, ensuring consistent quality in production.
- IEC Standards: Specific to electrical devices, these standards cover safety and performance requirements for plugs.
- CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area, indicating compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
Understanding these standards can help buyers assess the credibility of potential suppliers.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspecting raw materials before production begins to ensure they meet specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitoring processes during production to catch defects early. This includes regular checks on dimensions and assembly integrity.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducting thorough inspections and tests on finished products before they are packaged and shipped.
B2B buyers should request detailed QC reports from suppliers to verify adherence to these checkpoints.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Plug Manufacturing?
Testing is a vital component of quality assurance in plug manufacturing. Several methods are employed to ensure the safety and functionality of plugs:
- Electrical Testing: Measures insulation resistance, continuity, and dielectric strength.
- Mechanical Testing: Assesses the durability of the plug under various conditions, including temperature and mechanical stress.
- Environmental Testing: Simulates conditions such as humidity and temperature extremes to ensure reliability in diverse climates.
B2B buyers should ensure that their suppliers conduct comprehensive testing and provide documentation of results.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
To ensure that suppliers adhere to stringent quality control measures, B2B buyers should consider the following approaches:
- Supplier Audits: Conduct regular audits of suppliers’ manufacturing processes and quality control systems. This helps to identify any gaps and ensure compliance with international standards.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Ask for documentation of quality control measures, including inspection and testing results.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engage independent organizations to assess suppliers’ quality control processes. This adds an extra layer of verification and assurance.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
When sourcing electrical plugs from manufacturers in different regions, international buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances:
- Regulatory Compliance: Different countries have varying regulations regarding electrical safety and quality. It’s crucial to ensure that the plugs meet the specific standards of the target market.
- Cultural Considerations: Understanding local manufacturing practices and quality expectations can enhance communication with suppliers.
- Logistics and Supply Chain: Be mindful of potential delays in shipping and customs that may affect product quality. Implementing quality checks at various stages of the supply chain can mitigate risks.
By focusing on these aspects, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing plugs, ensuring they receive high-quality products that comply with international standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘different plug types’
This sourcing guide aims to assist international B2B buyers in navigating the complexities of procuring various plug types required for electrical devices across different regions. Understanding the distinct specifications and regulations associated with plug types is essential for successful procurement and compliance with local standards.
Step 1: Identify Your Market Requirements
Understanding the plug types prevalent in your target market is critical. Different countries use various plug types, voltages, and frequencies, which can affect product compatibility. Research the specific plug requirements for your target countries, such as Type C for many African and South American nations or Type G for the UK and Saudi Arabia.
Step 2: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to suppliers, clearly outline the technical specifications of the plugs you need. This includes:
– Current Rating: Determine whether you require plugs rated for 10A, 16A, or higher.
– Grounding Requirements: Identify if you need grounded or ungrounded plugs based on safety standards in your market.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they can meet your requirements. Look for:
– Certifications: Verify that suppliers have relevant certifications (e.g., CE, UL) indicating compliance with safety standards.
– Experience: Consider suppliers with a proven track record in exporting plugs to your target regions.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Always request samples before placing a bulk order. Testing samples allows you to:
– Check Compatibility: Ensure the plugs work with the electrical systems in your target market.
– Assess Quality: Evaluate the build quality and durability of the plugs to avoid future issues.
Step 5: Understand Import Regulations and Tariffs
Research the import regulations and tariffs associated with electrical products in your target countries. This step is crucial because:
– Compliance: Non-compliance can lead to delays or penalties.
– Cost Management: Understanding tariffs helps in budgeting and pricing your products effectively.
Step 6: Negotiate Payment Terms and Delivery Schedules
When finalizing contracts, ensure you negotiate favorable payment terms and delivery schedules. Consider:
– Payment Methods: Secure payment methods that minimize risk, such as letters of credit.
– Lead Times: Confirm the expected lead times for delivery and plan accordingly to avoid disruptions in your supply chain.
Step 7: Establish a Quality Control Process
Implement a quality control process to monitor the incoming plugs. This can include:
– Inspection Criteria: Define clear inspection criteria that align with your specifications.
– Feedback Loop: Create a feedback mechanism with your suppliers to address any quality issues promptly.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing different plug types, ensuring compliance, quality, and compatibility with local electrical systems.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for different plug types Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Different Plug Types?
When sourcing different plug types, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall cost. For example, plugs made with high-quality thermoplastics or metals will have higher costs compared to those made from lower-grade materials. Additionally, the type of plug (e.g., Type C vs. Type G) influences material costs due to varying designs and specifications.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and supplier. For instance, manufacturing in countries with lower labor costs may reduce overall expenses, but this can also impact the quality and reliability of the plugs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, facility rent, and administrative costs associated with production. Efficient manufacturing processes can minimize overhead, thus lowering the cost per unit.
-
Tooling: Custom molds and tools for specific plug designs can be a significant upfront cost. Buyers should consider the amortization of these costs over the volume of plugs ordered.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that plugs meet international standards and certifications (e.g., CE, UL) may incur additional QC costs. However, investing in quality can reduce long-term liabilities and improve customer satisfaction.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs will vary based on the origin of the plugs and the delivery location. Factors like shipping method, distance, and volume can significantly influence logistics costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will apply a margin to cover their costs and profit. Understanding the typical margin for plug manufacturers can help buyers negotiate better prices.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Plug Type Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of plug types:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often attract discounts, making it essential for buyers to assess their needs accurately. Negotiating lower MOQs can also be beneficial for small to medium-sized enterprises.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom plug designs or specific certifications can lead to higher costs. Buyers should balance their requirements with the associated costs and consider standardized options when possible.
-
Materials Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications typically lead to increased costs. Buyers should evaluate the importance of these factors against their budget and intended application.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers with a track record may charge more due to their quality assurance processes, while newer or less reputable suppliers might offer lower prices but at higher risk.
-
Incoterms: The terms of trade can also affect pricing. Understanding the implications of different Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) is essential for calculating total costs and managing risk during transportation.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Negotiate Better Prices for Plug Types?
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: Consolidating orders or collaborating with other businesses to increase order volumes can lead to better pricing.
-
Negotiate Payment Terms: Flexible payment terms can improve cash flow and provide leverage during negotiations. Consider negotiating upfront payments for discounts or longer payment windows for larger orders.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Rather than just the purchase price, consider the TCO, including maintenance, replacement, and energy efficiency costs. This broader view can justify spending more upfront for higher-quality plugs.
-
Explore Alternative Suppliers: Diversifying suppliers can lead to competitive pricing and reduce dependency on a single source. Research suppliers from various regions, particularly emerging markets in Africa and South America.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of seasonal fluctuations, currency exchange rates, and political factors that can impact pricing. Being informed can provide leverage during negotiations.
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices
All prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and can fluctuate based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and other factors. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing different plug types With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Different Plug Types
As international B2B buyers navigate the complexities of electrical systems, understanding the alternatives to traditional plug types is crucial. While various plug types serve their unique functions, there are alternative solutions that can enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve compatibility across different markets. This section compares traditional plug types with alternative solutions, such as universal adapters and wireless power transfer technologies.
Comparison Table of Different Plug Types and Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Different Plug Types | Universal Adapters | Wireless Power Transfer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Varies by type; generally reliable for local use | Good for international compatibility; may limit power | High convenience; limited distance and speed |
| Cost | Moderate, varies by type | Generally low to moderate | Higher initial investment |
| Ease of Implementation | Standardized for regions | Easy to use; plug-and-play | Requires installation and compatible devices |
| Maintenance | Minimal; replace when worn | Minimal; replace if damaged | Regular checks; battery maintenance may be needed |
| Best Use Case | Regional electrical systems | Traveling between countries | Smart homes, modern devices |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Universal Adapters?
Universal adapters are designed to accommodate multiple plug types, allowing devices to connect to different outlets worldwide. Their primary advantage is versatility, making them ideal for international travelers and businesses operating across borders. However, the performance can be inconsistent, especially with high-wattage appliances, which may lead to overheating or malfunction. Additionally, while they are generally cost-effective, purchasing multiple units for different regions can add up.
How Does Wireless Power Transfer Compare to Traditional Plug Types?
Wireless power transfer is an innovative technology that allows devices to charge without the need for physical connections. This method offers significant advantages in terms of convenience, as users can simply place their devices on a charging pad. However, the technology is still evolving, and the distance over which power can be transferred is limited. Furthermore, wireless charging can require a higher initial investment compared to traditional plug types, and not all devices are compatible, which may restrict its application in a B2B context.
A stock image related to different plug types.
Conclusion: How Can B2B Buyers Make the Right Choice?
When choosing between traditional plug types and alternative solutions, B2B buyers must consider their specific operational needs. For businesses with a global footprint, universal adapters provide a practical solution for compatibility across different markets. In contrast, companies focused on integrating modern technologies may find wireless power transfer beneficial for enhancing convenience and reducing wear on physical connectors. Ultimately, the choice will depend on the specific requirements, budget constraints, and operational contexts of the buyer’s business.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for different plug types
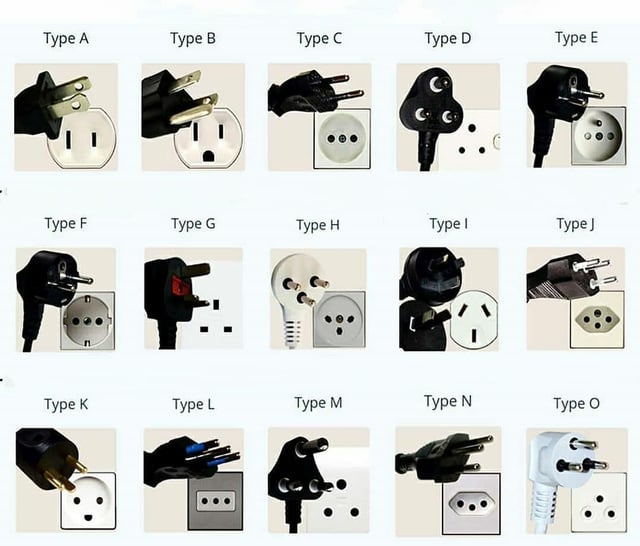
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Different Plug Types?
When selecting electrical plugs for international markets, understanding their technical properties is crucial for ensuring compatibility, safety, and reliability. Here are key specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
The materials used in plug manufacturing, such as thermoplastic or metal, directly affect durability and conductivity. High-quality materials can withstand wear and tear, especially in high-use environments. Buyers should prioritize plugs made from flame-retardant materials to enhance safety, particularly in regions with varying climate conditions. -
Current Rating
This specification indicates the maximum electrical current a plug can safely carry, measured in amperes (A). For instance, Type C plugs are rated for 2.5 A, while Type G can handle up to 13 A. Choosing the correct current rating ensures that the plug can support the intended load without overheating, which is essential for preventing electrical fires. -
Voltage Compatibility
Different regions operate on varying voltage standards, typically ranging from 100V to 240V. For example, plugs in Europe generally support 220-240V, while those in North America operate at 100-127V. Buyers should ensure that the plugs they select can handle the voltage levels prevalent in their target markets to avoid equipment damage. -
Pin Configuration
The shape and arrangement of pins are critical for compatibility with sockets. Each plug type has a unique design; for example, Type F features two round pins and a grounding clip, while Type G has three rectangular pins. Understanding these configurations helps in selecting the right plug for specific regions, preventing operational disruptions. -
Safety Certifications
Look for plugs that meet international safety standards, such as CE or UL certifications. These certifications ensure that the products comply with safety regulations, providing assurance to buyers about the reliability and safety of the electrical connections.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Electrical Plugs?
Navigating the international B2B market involves understanding specific trade terminologies that streamline transactions and communication. Here are some essential terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. For buyers, working with OEMs can ensure that they receive high-quality products tailored to their specifications, which is crucial in maintaining brand integrity. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ represents the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQs is vital for B2B buyers as it affects inventory management and cost efficiency. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to align with their purchasing power and storage capabilities. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products. Crafting a detailed RFQ ensures that all potential vendors provide comparable quotes, facilitating better decision-making based on price, quality, and delivery terms. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are standardized international trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers. Familiarity with Incoterms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) is crucial for understanding shipping costs, risk transfer, and liability during transportation. -
Certification Mark
This mark indicates that a product has been tested and meets specific safety and quality standards. For international buyers, recognizing certification marks can simplify compliance with local regulations and reassure consumers of product safety.

A stock image related to different plug types.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing different plug types for their international operations, ultimately ensuring compatibility, safety, and efficiency in their electrical applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the different plug types Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Plug Types Sector?
The global plug types market is experiencing a transformative phase driven by several key factors. Increased international trade and cross-border connectivity necessitate a uniform understanding of plug and socket compatibility, especially for B2B transactions. Regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are witnessing a surge in electronic imports, leading to a greater demand for diverse plug types. For instance, Type C and Type G plugs dominate in Europe and parts of Africa, while Type I is prevalent in Australia and New Zealand. Understanding these trends allows international buyers to make informed sourcing decisions.
Emerging technologies such as smart plugs, which offer energy efficiency and remote control features, are reshaping the market landscape. The rise of e-commerce platforms has made it easier for businesses to procure various plug types directly from manufacturers, often at competitive prices. Additionally, the growing trend of customization in plug designs to accommodate specific voltage requirements and safety standards presents new opportunities for B2B buyers. Suppliers that can offer tailored solutions will likely stand out in a crowded marketplace.
How Is Sustainability Influencing the Plug Types Market?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of sourcing strategies in the plug types sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly in plastic production and electronic waste, has prompted a shift towards more sustainable practices. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that adhere to green certifications and utilize eco-friendly materials in their products. Certifications such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) compliance are now essential for ensuring that products meet environmental standards.
Moreover, ethical sourcing is gaining traction as companies seek to enhance their corporate social responsibility profiles. Buyers are encouraged to engage with manufacturers that implement fair labor practices and transparent supply chains. This focus on sustainability not only addresses regulatory requirements but also resonates with environmentally conscious consumers and businesses, driving demand for ethically produced plug types.
How Have Plug Types Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of plug types is a reflection of technological advancement and the growing need for electrical safety. Initially, plugs were designed with minimal safety features, leading to frequent electrical hazards. Over time, regulations emerged to standardize designs, resulting in the creation of various plug types tailored to specific voltage and frequency requirements across different regions.
For instance, Type C plugs became widely adopted in Europe and parts of Africa due to their compatibility with higher voltage systems. Meanwhile, the introduction of grounding features in plugs such as Type G has significantly reduced the risk of electrical shock. Today, manufacturers are innovating further with smart technology integration, paving the way for the next generation of plug types that focus on energy efficiency and enhanced safety standards. This historical context is crucial for B2B buyers as they navigate the complexities of sourcing reliable and compliant electrical components.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of different plug types
-
How do I choose the right plug type for my product?
Selecting the appropriate plug type for your product involves understanding the target market’s electrical standards, including voltage, frequency, and outlet compatibility. For example, if you’re exporting to Europe, you might need Type C or Type F plugs, which support 220-240V. It’s essential to consult local regulations and standards to ensure compliance. Additionally, consider the product’s purpose; for high-power devices, grounding features in plugs (like Type E or G) are crucial for safety. Working with local distributors can also provide insights into consumer preferences. -
What is the best plug type for use in Africa?
In Africa, Type C and Type D plugs are the most commonly used. Type C plugs are versatile and found in many countries, while Type D plugs are specifically prevalent in countries like India and its neighbors. When sourcing plugs for African markets, consider the specific country requirements, as some nations may have unique standards. It’s advisable to conduct thorough market research or collaborate with local partners to identify the most suitable plug types for your products. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for different plug types?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can vary significantly based on the supplier and the plug type. Typically, MOQs range from 500 to 10,000 units, depending on the complexity of the design and the materials used. For customized plugs or those with specific safety certifications, MOQs may be higher due to the added production costs. It’s crucial to discuss MOQs upfront with potential suppliers to ensure they align with your business needs and market demand. -
How do I ensure the quality of plugs when sourcing internationally?
To ensure quality when sourcing plugs internationally, it is vital to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request samples to evaluate the product’s build quality, and check for compliance with international safety standards such as IEC or UL certifications. Establishing a quality assurance process is also crucial; consider third-party inspections or audits of the manufacturing facilities. Building a relationship with reliable suppliers who have a track record of quality can further enhance your confidence in the products you are sourcing.
A stock image related to different plug types.
-
What payment terms should I negotiate with international suppliers?
Negotiating favorable payment terms is essential for managing cash flow in international trade. Common practices include a deposit (20-30%) upfront, with the balance due upon shipment or delivery. Depending on the supplier’s reputation, you might consider letters of credit for larger orders to mitigate risk. Always clarify payment methods—wire transfers, PayPal, or escrow services—and ensure that terms are documented in the contract to avoid misunderstandings. -
How can I customize plug types for my specific needs?
Customization of plug types often involves specifying design elements like pin configuration, voltage ratings, and materials. Most manufacturers can accommodate customization requests, but it’s essential to discuss these needs during the initial negotiation phase. Providing detailed specifications and standards will facilitate the development process. Be aware that custom molds may incur additional costs and longer lead times, so factor these into your project timeline and budget. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing plugs?
Logistics play a crucial role in the successful importation of plugs. Consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and duties that may apply in your target market. Collaborating with a logistics partner experienced in electrical components can streamline the process. Additionally, ensure that the plugs are packaged correctly to prevent damage during transit. Understanding the lead times for production and shipping will help you plan better and avoid stockouts. -
How can I stay informed about changes in electrical standards and regulations?
Staying updated on electrical standards and regulations is vital for compliance and market success. Subscribe to industry newsletters, join trade associations, and participate in relevant conferences to network and gather insights. Monitoring regulatory bodies and standards organizations, such as the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), can provide timely updates on changes. Engaging with local experts and partners can also offer valuable perspectives on evolving market requirements.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for different plug types
In navigating the complexities of global markets, understanding the diverse plug types and their compatibility is essential for international B2B buyers. With over 15 different plug types utilized across various regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, strategic sourcing becomes crucial. Buyers must prioritize sourcing products that align with regional standards to avoid operational disruptions and enhance supply chain efficiency.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Business Operations?
Strategic sourcing not only mitigates risks associated with incompatible electrical systems but also leverages local suppliers who understand regional specifications. This approach can lead to cost savings, improved product quality, and enhanced supplier relationships. For instance, businesses in South Africa should consider plug type M compatibility, while those in Saudi Arabia should focus on type G to ensure seamless integration.
What Does the Future Hold for Plug Types and Sourcing Strategies?
Looking ahead, the shift towards more standardized solutions may emerge as manufacturers innovate in response to globalization. International B2B buyers are encouraged to stay informed about evolving standards and adapt their sourcing strategies accordingly. By embracing these changes, buyers can enhance their competitiveness and secure a more resilient supply chain. Engage with local suppliers and invest in research to ensure your business remains at the forefront of this dynamic landscape.