Top 6 Shaft Manufacturers List and Guide: How To Solve Scenario 1…
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for Shaft Manufacturers
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing reliable shaft manufacturers can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers. The need for precision-engineered shafts that meet specific application requirements is paramount, especially in industries such as energy, automotive, and marine. This guide delves into the multifaceted world of shaft manufacturing, offering insights into various types of shafts, their applications across different sectors, and strategies for effective supplier vetting.
By exploring the nuances of manufacturing processes, quality standards, and cost considerations, this comprehensive resource empowers buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—particularly in markets such as Saudi Arabia and Brazil—to make informed purchasing decisions. With a focus on identifying reputable manufacturers who can deliver on time and to specification, this guide ensures that you can navigate the complexities of the global market with confidence.
Whether you are seeking custom solutions or off-the-shelf products, understanding the critical factors influencing shaft manufacturing will equip you with the knowledge needed to enhance operational efficiency and drive success in your projects.
Top 10 Shaft Manufacturers Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Empower Manufacturing – Custom Shaft Precision Solutions
Domain: empowermfg.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
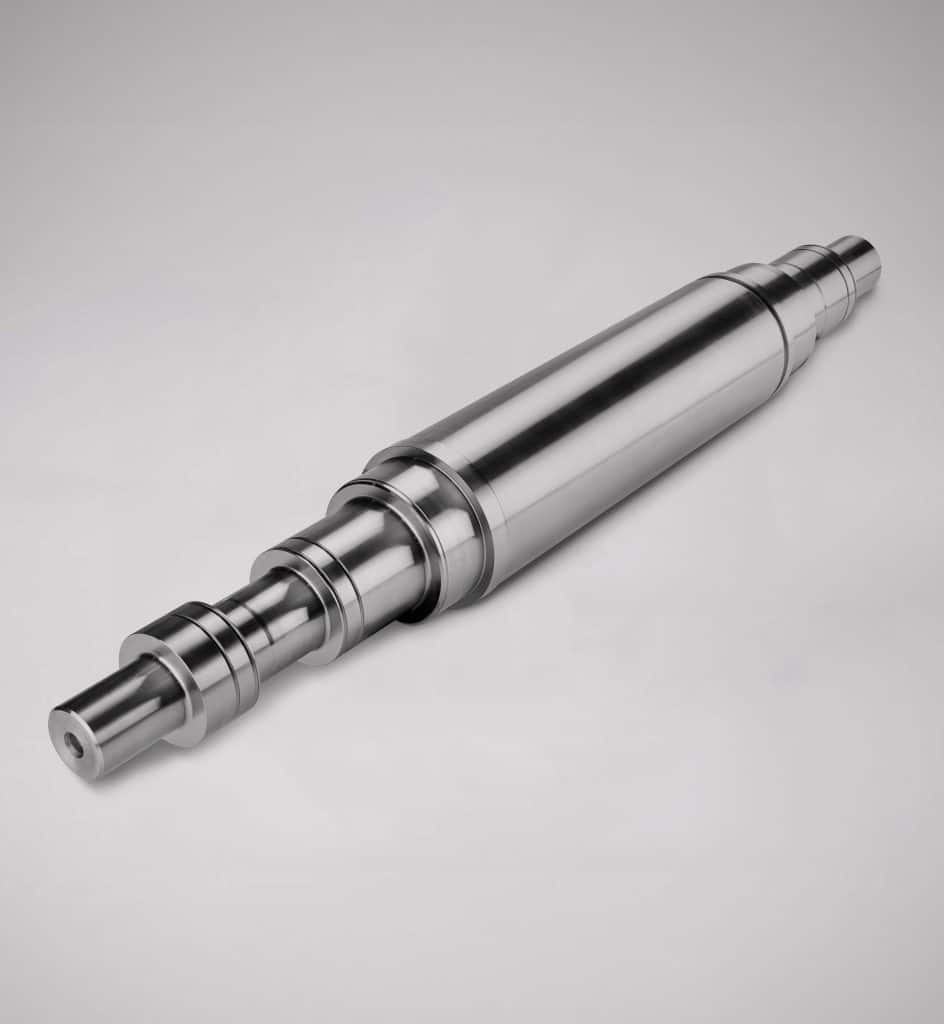
Introduction: Empower Manufacturing specializes in custom shaft manufacturing with over 40 years of experience. Key product details include:
– Precision capabilities: TIR of .001″ and ground diameters up to 0.0001″ tolerance.
– Shaft dimensions: Diameters up to 24″ and turned lengths up to 120″, with OD grinding up to 168″ long.
– Material: Massive inventory of cold-drawn 1045 steel for quick turnaround on larg…
2. Western Machine – Shaft Manufacturing Solutions
Domain: westernmachine.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Shaft Manufacturing Services for Heavy Industry, providing comprehensive solutions including dimensional inspection, non-destructive testing, shaft design with strength calculations, metallurgical analysis, reverse engineering, CNC turning and machining, custom tooling, hydrostatic testing, and project management. Capable of manufacturing various types of shafts (e.g., rotor, armature, ship, drive…
3. GLForge – Custom Forged Steel & Stainless Steel Shafts
Domain: glforge.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Custom Forged Steel & Stainless Steel Shaft Manufacturing Services include:
– Types of Forged Products: Forged shafts, crankshafts, eccentric shafts, rotor shafts, forged blocks, rectangles, flats, rounds, discs, sleeves, hubs, spindles, and fluid ends.
– Materials Used: 13-8 Stainless Steel, 15-5 Stainless Steel, 17-4 Stainless Steel, 316 & 316L Stainless Steel, Nitronic 50 Stainless Steel, Carbo…
4. WM Berg – Precision Shafting Components
Domain: wmberg.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: WM Berg manufactures several types of precision shafting components, including shafts, shaft wipers, shaft seals, shaft adapters, hubs, clamps, and Woodruff keys. The shafting is used in applications ranging from general machinery to aircraft instruments, robotic surgical equipment, and other linear and rotary motion systems. The precision shafts are available in inch and metric sizes, made from 3…
5. HM Manufacturing – Custom Shafts
Domain: hmmanufacturing.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Custom shafts manufactured to project specifications; capabilities include milling, hobbing, turning, grinding, and broaching; can be paired with splines, sprockets, pulleys, and gearboxes; heat treatment available for specific hardness. Dimensions: Diameter from ½’’ to 24’’, straightness up to 0002’’/inch, length up to 63’’. Surface finish: Turning 16 µin/N5, Grinding 2 µin/N2. Diameter tolerance…
6. Winpretec – Custom Machined Shafts
Domain: winpretec.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Custom manufactured machined shafts including ship propeller shafts, marine shafts, large diameter shafts, generator shafts, shaft balancing, and shaft straightening. Capabilities include: lengths up to 570″ long, available in all alloys, and 3 plane computerized dynamic balancing with certified reports. Applications served include ship shafts, marine shafts, large diameter shafts for various indu…
Understanding Shaft Manufacturers Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Custom Shaft Manufacturers | Tailored solutions with precise specifications; often utilize CNC machining. | Automotive, aerospace, industrial machinery | Pros: High precision, tailored designs. Cons: Longer lead times for complex designs. |
| Precision Shaft Manufacturers | Focus on ultra-fine tolerances and quality assurance; often ISO certified. | Marine, oil & gas, energy sectors | Pros: Exceptional quality and reliability. Cons: Potentially higher costs. |
| Heavy-Duty Shaft Manufacturers | Designed for extreme conditions; robust materials and construction methods. | Mining, construction, heavy equipment | Pros: Durability under stress. Cons: May require more maintenance. |
| Standard Shaft Manufacturers | Production of widely used shaft types; often in bulk with set specifications. | General manufacturing, consumer goods | Pros: Cost-effective, quick turnaround. Cons: Limited customization options. |
| Specialty Shaft Manufacturers | Focus on niche applications; may offer unique materials or designs. | Aerospace, medical devices, custom machinery | Pros: Innovative solutions for specific needs. Cons: Higher costs and longer lead times. |
What Are the Characteristics of Custom Shaft Manufacturers?
Custom shaft manufacturers provide bespoke solutions tailored to the unique requirements of clients. Utilizing advanced CNC machining and engineering expertise, they can create shafts that meet specific dimensions and performance standards. This type of manufacturer is suitable for industries such as automotive and aerospace, where precision is critical. Buyers should consider lead times, as custom solutions may take longer to produce, but the result is often a high-quality product that fits their exact needs.
How Do Precision Shaft Manufacturers Ensure Quality?
Precision shaft manufacturers are characterized by their commitment to achieving ultra-fine tolerances and maintaining stringent quality assurance processes. Often ISO certified, these manufacturers employ advanced technologies and skilled labor to produce shafts with minimal deviations. They are particularly suited for high-stakes industries such as marine and oil & gas, where reliability is paramount. While the quality comes at a premium, buyers benefit from the assurance that their components will perform reliably under demanding conditions.
What Makes Heavy-Duty Shaft Manufacturers Unique?
Heavy-duty shaft manufacturers focus on producing shafts designed to withstand extreme operational conditions. They often utilize robust materials and construction methods, ensuring that their products can endure significant stress and wear. These manufacturers are essential for industries like mining and construction, where equipment operates in harsh environments. While these shafts are durable and reliable, buyers should be aware that they may necessitate more frequent maintenance due to their demanding applications.
When Should Buyers Consider Standard Shaft Manufacturers?
Standard shaft manufacturers produce shafts based on widely accepted specifications, making them a cost-effective solution for general manufacturing and consumer goods. They typically operate on a high-volume basis, allowing for quick turnaround times. However, buyers may find limited customization options with this type of manufacturer. For businesses looking for reliable and affordable solutions without the need for specialized features, standard shaft manufacturers present an attractive option.
What Are the Advantages of Specialty Shaft Manufacturers?
Specialty shaft manufacturers cater to niche applications and often provide unique materials or innovative designs tailored to specific industry needs. They are particularly valuable in sectors such as aerospace, medical devices, and custom machinery, where standard solutions may not suffice. While they can offer groundbreaking solutions, buyers should consider the potential for higher costs and longer lead times associated with these specialized products.
Key Industrial Applications of Shaft Manufacturers
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Shaft Manufacturers | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oil & Gas | Drill shafts for exploration and extraction | Enhanced efficiency and reliability in drilling operations | Material specifications, corrosion resistance, and compliance with industry standards |
| Renewable Energy | Rotor shafts for wind turbines | Increased energy production and operational longevity | Precision tolerances, weight considerations, and environmental durability |
| Marine | Propeller shafts for vessels | Improved fuel efficiency and reduced maintenance costs | Customization capabilities, material strength, and resistance to marine environments |
| Automotive | Drive shafts for vehicles | Enhanced performance and reduced vibration | Tolerance levels, weight distribution, and regulatory compliance |
| Manufacturing | Shafts for CNC machinery and conveyor systems | Increased productivity and reduced downtime | Lead times, precision engineering, and compatibility with existing systems |
How Are Shaft Manufacturers Used in the Oil & Gas Sector?
In the oil and gas industry, shaft manufacturers produce drill shafts essential for exploration and extraction activities. These shafts must endure extreme conditions, including high pressure and corrosive environments. By sourcing high-quality, durable materials, businesses can ensure that their drilling operations are efficient and reliable, minimizing downtime and maximizing productivity. Buyers should consider material specifications, corrosion resistance, and compliance with industry standards to ensure optimal performance.
What Role Do Shaft Manufacturers Play in Renewable Energy?
Shaft manufacturers are critical in the renewable energy sector, particularly for wind turbines where rotor shafts are designed to convert wind energy into electrical power. The precision and durability of these shafts directly impact the energy production efficiency and operational longevity of wind farms. International buyers should prioritize suppliers who can meet stringent precision tolerances and provide shafts that withstand environmental challenges, ensuring sustainability and reliability in energy generation.
How Are Shafts Essential in the Marine Industry?
In the marine sector, propeller shafts are vital for the propulsion systems of vessels. These shafts must be engineered to enhance fuel efficiency while minimizing maintenance costs. The unique challenges posed by marine environments necessitate sourcing materials that resist corrosion and withstand the rigors of oceanic conditions. Buyers should look for manufacturers that offer customization capabilities and demonstrate expertise in material strength to ensure optimal performance in marine applications.
Why Are Shafts Important in the Automotive Industry?
Shaft manufacturers provide drive shafts that are crucial for the performance of vehicles. These components must be designed to reduce vibration and ensure smooth power transfer from the engine to the wheels. Automotive buyers must consider tolerance levels and weight distribution to enhance vehicle performance while adhering to regulatory compliance standards. Working with manufacturers that specialize in automotive applications can lead to significant improvements in vehicle efficiency and customer satisfaction.
How Do Shaft Manufacturers Contribute to Manufacturing Operations?
In manufacturing, shafts are integral components of CNC machinery and conveyor systems. Their role is to facilitate movement and operations, thereby increasing overall productivity. Buyers in this sector should focus on sourcing shafts with precision engineering and compatibility with existing systems to minimize downtime and enhance operational efficiency. Additionally, lead times are crucial; therefore, partnering with manufacturers that can deliver quickly without compromising quality is essential for maintaining competitive advantage.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘Shaft Manufacturers’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Achieving Precision Tolerances for Critical Applications
The Problem: Many B2B buyers in sectors like aerospace, automotive, and energy often face challenges when it comes to precision tolerances in shaft manufacturing. These industries require components with ultra-fine tolerances to ensure reliable performance and safety. For instance, a buyer may order a shaft for a turbine that must adhere to strict dimensional specifications. If the manufacturer fails to meet these tolerances, it could lead to equipment failures, costly downtimes, or even catastrophic incidents, jeopardizing not just finances but also safety.
The Solution: To overcome this issue, buyers should prioritize partnering with shaft manufacturers that have a proven track record in precision engineering. Look for manufacturers who are ISO certified and can demonstrate their capabilities through detailed case studies or testimonials. During the sourcing process, specify the exact tolerances required and ask for documentation that outlines their quality assurance processes. Additionally, consider involving the manufacturer in the design phase to leverage their engineering expertise, ensuring that the design can be feasibly produced to the required specifications. This proactive collaboration will minimize the risk of errors and enhance the overall quality of the final product.
Scenario 2: Long Lead Times Affecting Project Schedules
The Problem: In industries such as oil & gas, construction, and manufacturing, project timelines are often tight, making long lead times for shaft manufacturing a significant pain point. A buyer may find themselves in a situation where a critical shaft component is delayed, causing a ripple effect that stalls the entire project. This situation can lead to increased costs, strained relationships with clients, and missed deadlines.
The Solution: To mitigate this risk, buyers should seek manufacturers with robust inventory management and efficient production capabilities. When evaluating potential suppliers, inquire about their lead times for various products, and assess their capacity to handle rush orders. Establishing a reliable relationship with a manufacturer that holds a diverse inventory of materials can significantly reduce wait times. Additionally, consider discussing long-term partnerships that include agreed-upon delivery timelines. This approach not only ensures timely access to components but also fosters a collaborative environment where both parties can work together to meet project demands.
Scenario 3: Challenges in Customization for Unique Applications
The Problem: Many buyers encounter hurdles when attempting to source custom shafts designed for specific applications. Industries such as marine, aerospace, and renewable energy frequently require unique dimensions or materials that standard manufacturers may not provide. This lack of customization can lead to subpar performance or compatibility issues, ultimately impacting operational efficiency.
The Solution: To address customization challenges, buyers should focus on collaborating with manufacturers known for their engineering capabilities and flexibility in design. During the initial discussions, clearly articulate the unique requirements of your application, including environmental conditions, load specifications, and any industry standards that need to be met. Request examples of previous custom projects to gauge the manufacturer’s experience and adaptability. Additionally, consider utilizing reverse engineering services if existing components are available, as this can simplify the design process and ensure a more accurate fit. Engaging manufacturers early in the design phase can lead to innovative solutions tailored to your specific needs, thereby enhancing the overall performance and longevity of the shafts in your operations.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for Shaft Manufacturers
What Are the Key Properties of Common Shaft Materials?
Shaft manufacturers often choose materials based on specific application requirements, including mechanical properties, environmental conditions, and cost considerations. Here, we analyze four common materials used in shaft manufacturing: carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and composite materials.
How Does Carbon Steel Perform in Shaft Manufacturing?
Key Properties: Carbon steel is known for its high tensile strength and hardness, making it suitable for applications that require durability. It typically has good wear resistance and can withstand high pressures, but its performance can be affected by temperature fluctuations.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of carbon steel is its cost-effectiveness and availability, making it a popular choice for various industrial applications. However, it is prone to corrosion if not properly treated, which can limit its use in harsh environments. The manufacturing complexity is moderate, as it can be easily machined and welded.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel shafts are commonly used in automotive, industrial machinery, and oil & gas applications. However, they may require protective coatings or treatments in corrosive environments, such as those found in marine or chemical processing industries.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East should ensure compliance with local standards, such as ASTM or DIN, especially when dealing with oil and gas applications. Understanding the local climate and its impact on material performance is also crucial.
What Advantages Does Stainless Steel Offer for Shaft Applications?
Key Properties: Stainless steel provides excellent corrosion resistance and maintains its strength at elevated temperatures. It is also non-magnetic and has a smooth surface finish, which is beneficial for applications requiring clean environments.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of stainless steel is its durability and resistance to oxidation, making it suitable for marine and chemical applications. However, it is more expensive than carbon steel and can be more challenging to machine due to its toughness.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel shafts are ideal for environments exposed to moisture, chemicals, or extreme temperatures. They are widely used in the food processing, pharmaceutical, and aerospace industries, where hygiene and reliability are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe and South America should consider the specific grades of stainless steel (like 304 or 316) that comply with international standards. Additionally, understanding local regulations regarding food safety or environmental impact can influence material selection.
How Does Aluminum Compare as a Shaft Material?
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and has good corrosion resistance, making it suitable for applications where weight reduction is critical. It also has decent thermal and electrical conductivity.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its low weight, which can enhance the efficiency of machinery. However, it has lower tensile strength compared to steel, making it less suitable for high-load applications. Manufacturing complexity is relatively low, but care must be taken to avoid galling during machining.
Impact on Application: Aluminum shafts are often used in aerospace, automotive, and lightweight machinery applications. They are particularly effective in reducing overall system weight, which can lead to energy savings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of specific alloy grades and their properties, as well as compliance with international standards. In regions like Brazil, understanding the local market for aluminum can also impact pricing and availability.
What Role Do Composite Materials Play in Shaft Manufacturing?
Key Properties: Composite materials, often made from a combination of fibers and resins, offer excellent strength-to-weight ratios and can be tailored for specific applications. They are resistant to corrosion and fatigue.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of composites is their ability to be engineered for specific performance characteristics, such as flexibility or rigidity. However, they can be more expensive and complex to manufacture compared to metals.
Impact on Application: Composite shafts are increasingly used in aerospace and high-performance automotive applications where weight and performance are critical. They can also be beneficial in corrosive environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must consider the availability of composite materials in their region and any specific certifications required for high-performance applications. Understanding the local manufacturing capabilities for composites is also essential.
Summary Table of Shaft Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for Shaft Manufacturers | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Automotive, industrial machinery | Cost-effective and durable | Prone to corrosion | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, aerospace | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and machining complexity | High |
| Aluminum | Aerospace, lightweight machinery | Lightweight and corrosion resistant | Lower tensile strength | Medium |
| Composite | Aerospace, high-performance automotive | Tailored performance characteristics | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for shaft manufacturing, catering to the needs of international B2B buyers across various regions. By understanding the properties, advantages, limitations, and regional considerations for each material, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific application requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for Shaft Manufacturers
What Are the Key Stages in the Shaft Manufacturing Process?
The manufacturing of shafts involves several critical stages that ensure precision and reliability. Understanding these stages is vital for B2B buyers looking to partner with reputable shaft manufacturers.
Material Preparation: How Is the Right Material Selected and Prepared?
The process begins with material selection, which is crucial for the performance of the final product. Common materials used include high-tensile steels such as 1045 carbon steel and alloy steels, known for their durability and strength. Material preparation involves sourcing quality raw materials, often subjected to metallurgical analysis to confirm their suitability for the intended application.
Once the material is selected, it is cut to size, typically using techniques like band sawing or shearing. This ensures that the raw material meets the initial dimensional requirements before moving on to the next stage.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape Shafts?
The forming stage primarily involves subtractive manufacturing techniques such as CNC turning, milling, and grinding. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines play a pivotal role in achieving the high precision required for shafts. During this stage, the material is shaped into the desired form, with features like grooves and keyways added as necessary.
Advanced techniques such as hydrostatic testing may also be employed to assess the integrity of the shaft during this phase. This ensures that any potential defects are identified early, minimizing wastage and rework later in the process.
Assembly: How Are Shafts Prepared for Final Use?
In some cases, shafts may require additional components such as sleeves, bearings, or couplings. This assembly stage involves careful alignment and fitting of these components to ensure optimal performance. Precision is key, as misalignment can lead to operational failures.
The assembly process may also include reverse engineering of existing shafts when OEM specifications are unavailable. This allows manufacturers to replicate critical components accurately, ensuring compatibility and performance.
Finishing: What Processes Ensure a High-Quality Surface?
Finishing processes are essential for enhancing the surface quality and functional characteristics of the shafts. Techniques such as grinding, polishing, and coating are employed to achieve the desired surface finish. These processes not only improve aesthetics but also increase resistance to wear and corrosion.
Heat treatment may also be applied to enhance the mechanical properties of the shafts, such as hardness and tensile strength. This step is particularly important for applications involving high dynamic loads, such as in the aerospace and automotive industries.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Standard in Shaft Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a fundamental aspect of shaft manufacturing that ensures products meet specified standards and customer expectations. International and industry-specific standards guide these QA processes.
How Do International Standards Like ISO 9001 Affect Shaft Quality Control?
ISO 9001:2015 certification is a benchmark for quality management systems in manufacturing. This standard ensures that manufacturers implement consistent processes for quality control, from material selection to final inspection. A certified manufacturer demonstrates a commitment to quality, making them a more attractive partner for B2B buyers.
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) and API (American Petroleum Institute) may also apply, particularly for manufacturers serving sectors like oil and gas. Compliance with these standards indicates that the products meet safety and performance requirements relevant to specific applications.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Shaft Manufacturing?
Quality control in shaft manufacturing typically involves several checkpoints throughout the production process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials for compliance with specifications. Any non-conforming materials are rejected or returned.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, continuous monitoring is essential. This includes dimensional checks and process validations to ensure that the shaft is being produced within the specified tolerances.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): The final inspection verifies that the completed shafts meet all design and quality specifications. This may involve dimensional inspections, non-destructive testing (NDT), and functional testing.
B2B buyers should request documentation of these quality checks, including inspection reports and testing results, to verify the manufacturer’s commitment to quality.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is critical. Here are some strategies:
What Steps Should Buyers Take to Conduct Supplier Audits?
Conducting supplier audits is one of the most effective ways to assess a manufacturer’s quality control practices. An audit should evaluate:
- Compliance with international standards such as ISO 9001.
- The effectiveness of their quality management system.
- The training and qualifications of personnel involved in manufacturing and quality control.
Buyers can either conduct these audits themselves or engage third-party inspection agencies to ensure an unbiased assessment.
How Important Are Third-Party Inspections and Certifications?
Third-party inspections provide an additional layer of assurance regarding the quality of the products. Buyers should look for manufacturers who allow independent inspections and can provide relevant certifications that validate their adherence to quality standards.
Moreover, maintaining open communication about quality control processes and sharing testing results can foster trust between manufacturers and buyers, ultimately leading to stronger business relationships.
What Are the Specific Quality Control Challenges for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers often face unique challenges in verifying quality control, including:
-
Cultural and Language Barriers: These can complicate communication regarding quality expectations and standards.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have varying compliance requirements, making it essential for buyers to understand local regulations affecting quality standards.
-
Logistical Issues: Shipping delays and customs regulations can impact the timely receipt of quality documentation and samples.
By being proactive and establishing clear communication channels with suppliers, B2B buyers can navigate these challenges effectively, ensuring they receive high-quality shafts that meet their operational needs.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices of shaft manufacturers is crucial for B2B buyers. By focusing on these aspects, buyers can make informed decisions that lead to successful partnerships and high-quality products.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘Shaft Manufacturers’
Introduction
This sourcing guide aims to equip B2B buyers with actionable steps to effectively procure shaft manufacturing services. The process of selecting the right supplier is crucial for ensuring quality, reliability, and cost-effectiveness in your projects. By following this checklist, buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing and make informed decisions that align with their operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the cornerstone of any successful procurement process. Detail the exact requirements, including dimensions, materials, and tolerances needed for your shafts. This clarity helps suppliers understand your needs and ensures that you receive accurate quotes and proposals.
- Consider application-specific requirements: Identify the industry standards your shafts must meet, such as those for aerospace or marine applications.
- Include performance metrics: Specify factors such as load capacity, durability, and any environmental conditions that could impact performance.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Thorough research on potential suppliers is vital to identify those who can meet your specific requirements. Look for manufacturers with a proven track record in shaft production, especially in your industry.
- Check online reviews and testimonials: Use platforms like LinkedIn or industry forums to gather insights from other buyers.
- Evaluate their portfolio: A robust portfolio of past projects can indicate the supplier’s experience and capability.
Step 3: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that the suppliers you consider hold relevant industry certifications. Certifications such as ISO 9001:2015 demonstrate a commitment to quality management and operational excellence.
- Request documentation: Ask for copies of certifications and any quality control processes they follow.
- Understand compliance standards: Familiarize yourself with the certifications relevant to your industry to ensure compliance.
Step 4: Evaluate Manufacturing Capabilities
Understanding a supplier’s manufacturing capabilities is essential for assessing whether they can meet your specifications. Investigate the technologies and processes they use in shaft manufacturing.
- Inquire about machinery and technology: Ensure they have modern CNC equipment and the ability to achieve tight tolerances.
- Assess production capacity: Confirm that the supplier can handle your order volume within your required timeframe.
Step 5: Request Detailed Quotes
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request detailed quotes that outline pricing, lead times, and terms. This step allows for transparent comparisons between different manufacturers.
- Look for breakdowns in pricing: Ensure the quote specifies costs for materials, labor, and any additional services such as testing or finishing.
- Clarify payment terms: Understand the payment structure to avoid any potential cash flow issues.
Step 6: Conduct On-Site Visits or Audits
If possible, conduct on-site visits to the manufacturing facilities of your shortlisted suppliers. This step provides an opportunity to assess their operations firsthand.
- Evaluate production processes: Observe quality control measures, cleanliness, and adherence to safety standards.
- Meet the team: Building relationships with the engineering and production teams can enhance collaboration.
Step 7: Check References and Past Projects
Finally, before making a commitment, check references and review past projects similar to yours. This step provides additional assurance of the supplier’s capability and reliability.
- Ask for client testimonials: Request contact information for previous clients to discuss their experiences.
- Review case studies: Analyze projects that required similar specifications to gauge the supplier’s problem-solving capabilities.
By following this structured checklist, B2B buyers can ensure a thorough and effective sourcing process for shaft manufacturing services, ultimately leading to better project outcomes and supplier relationships.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for Shaft Manufacturers Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Shaft Manufacturing?
Understanding the cost structure of shaft manufacturing is essential for B2B buyers seeking to optimize their sourcing strategies. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of raw materials, such as carbon steel or specialized alloys, significantly impacts the overall cost. High tensile strength materials may incur higher upfront costs but can lead to longer-lasting products, thereby reducing long-term operational expenses.
-
Labor: Skilled machinists and engineers are crucial for precision manufacturing. Labor costs vary by region, with countries in Africa and South America often offering competitive rates compared to Europe and the Middle East. The complexity of the shaft design can also influence labor hours required.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the costs of operating machinery, utilities, and facility maintenance. Manufacturers with advanced technologies and efficient processes may have lower overhead costs, which can translate to better pricing for buyers.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling and fixturing are often required for specific shaft designs. The initial investment in specialized tools can be substantial but is necessary for achieving tight tolerances and high-quality outputs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC measures, including dimensional inspections and non-destructive testing, ensure that shafts meet industry standards. While these processes add to the cost, they are critical for reducing the risk of failure in demanding applications.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary dramatically based on distance, shipping method, and Incoterms. International buyers should consider logistics in their total cost calculations, especially for bulky items like shafts.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically apply a profit margin that reflects their operational efficiencies and market conditions. Understanding the competitive landscape can help buyers assess whether the margins are justified.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Shaft Manufacturing Costs?
Several factors influence pricing in shaft manufacturing, including:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their project needs to maximize cost efficiency.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized shafts with unique specifications generally incur higher costs due to the additional engineering and manufacturing processes involved. Buyers should balance the need for customization with budget constraints.
-
Material Choices: The type and quality of materials significantly affect pricing. High-performance materials may require a higher initial investment but can lead to reduced maintenance costs over time.
-
Quality Certifications: Compliance with international standards (e.g., ISO certifications) can increase costs but is often necessary for applications in regulated industries such as aerospace and oil & gas.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, production capacity, and geographic location can all influence pricing. Buyers should evaluate suppliers based on their ability to deliver on time and meet quality standards.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international buyers. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can affect the total landed cost of the shafts.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Negotiating Shaft Prices?
To navigate the complexities of shaft sourcing effectively, consider these tips:
-
Leverage Negotiation: Use your purchasing power to negotiate better terms. Discuss volume discounts or longer-term contracts that may incentivize suppliers to offer lower pricing.
-
Assess Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial purchase price. Consider factors like maintenance, downtime, and replacement costs to understand the true cost of ownership.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and import duties that can affect total costs. Establish clear communication with suppliers regarding pricing adjustments related to these factors.
-
Request Multiple Quotes: Obtain quotes from several manufacturers to benchmark prices and services. This can provide leverage during negotiations.
-
Build Long-Term Relationships: Developing strong relationships with suppliers can lead to preferential pricing and priority service in the future.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for shaft manufacturing can vary widely based on the factors mentioned above. Buyers should obtain specific quotes tailored to their project requirements to ensure accurate budgeting.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing Shaft Manufacturers With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Solutions to Shaft Manufacturing
In the world of industrial operations, selecting the right component or method for transferring energy efficiently can significantly impact productivity and cost. While traditional shaft manufacturers offer precision-engineered solutions, there are alternative technologies that can achieve similar outcomes. This analysis evaluates the benefits and drawbacks of shaft manufacturers compared to alternative methods, providing valuable insights for B2B buyers seeking the best solution for their needs.
| Comparison Aspect | Shaft Manufacturers | 3D Printing of Shafts | Couplings and Gear Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision with tight tolerances | Variable precision; limited by material | Effective energy transfer but less flexible |
| Cost | Generally higher initial investment | Lower initial costs, but variable costs based on complexity | Moderate; often requires additional components |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized knowledge and equipment | User-friendly for prototyping; can be complex for mass production | Easier to integrate with existing systems |
| Maintenance | Durable; requires periodic checks | Material-dependent; can be less durable | Relatively low maintenance; depends on wear |
| Best Use Case | Heavy-duty applications with stringent specs | Rapid prototyping and low-volume runs | Applications needing flexible energy transfer |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of 3D Printing for Shafts?
3D printing is an innovative manufacturing process that allows for the rapid creation of components from digital models. The primary advantage of 3D printing is its ability to produce complex geometries that may be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional methods. It is particularly beneficial for low-volume production runs and prototyping, where time and cost efficiency are crucial. However, the material properties of 3D-printed shafts can vary significantly, which might lead to performance issues in high-load applications. Additionally, while initial costs may be lower, the long-term durability of printed components can be a concern, especially under demanding operating conditions.
How Do Couplings and Gear Systems Compare?
Couplings and gear systems are alternative methods for transferring rotational power between components. These systems can be effective in applications where flexibility in energy transfer is needed. The main advantage of couplings is their ability to accommodate misalignment between shafts, which can enhance the overall system’s reliability. They are generally easier to implement and integrate with existing machinery. However, couplings and gears may not provide the same level of precision as custom-manufactured shafts, and their performance can be limited in applications requiring tight tolerances or high strength. Furthermore, they may need additional components, increasing the overall complexity of the system.
How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When selecting the most suitable option for their specific needs, B2B buyers should consider several factors, including the operational environment, required precision, and budget constraints. For applications demanding high durability and precision, partnering with a reputable shaft manufacturer is often the best choice. Conversely, for projects that require rapid prototyping or lower volumes, 3D printing may provide the necessary flexibility and cost savings. Couplings and gear systems offer a practical solution for industries where adaptability and ease of integration are paramount. Ultimately, understanding the unique requirements of the project and evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of each option will enable buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for Shaft Manufacturers
What Are the Key Technical Properties Important for Shaft Manufacturing?
When engaging with shaft manufacturers, understanding critical technical specifications is essential for ensuring the product meets operational needs. Here are some vital properties to consider:
-
Material Grade: The choice of material significantly affects the shaft’s performance and durability. Common materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel. Each material grade offers varying tensile strengths and resistance to wear and corrosion, making it crucial to select the appropriate grade based on the shaft’s application environment.
-
Tolerance: Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension. High precision is often required, with tolerances as tight as ±0.0001 inches. This specification is vital in applications where shafts must fit perfectly with other components to function correctly, thereby preventing equipment failure and extending the lifespan of machinery.
-
Surface Finish: The surface finish of a shaft affects its performance, particularly in reducing friction and wear. A smoother finish can lead to better efficiency and reduced energy consumption. Manufacturers often specify surface roughness levels (measured in microinches) that are necessary for the intended application, influencing both cost and longevity.
-
Length and Diameter: These dimensions are fundamental to the shaft’s application and must be precisely defined. Length and diameter determine the shaft’s capacity to transmit torque and accommodate loads. Custom dimensions often require advanced machining capabilities, highlighting the importance of working with a manufacturer that can meet specific requirements.
-
Heat Treatment: This process enhances the material’s properties, such as hardness and strength, making it more suitable for demanding applications. Understanding the heat treatment processes, such as quenching and tempering, is crucial for ensuring that the shaft can withstand operational stresses.
-
Load Capacity: This property indicates the maximum load a shaft can bear without failure. It is essential to consider both static and dynamic loads to ensure the shaft performs adequately under various conditions. Proper load calculations help in avoiding premature failure and extending equipment life.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Shaft Manufacturing?
Familiarity with industry jargon can streamline communication and negotiations with shaft manufacturers. Here are several key terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): This term refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM specifications is crucial for ensuring that replacement shafts meet the standards required for compatibility and performance.
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): This is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B buyers, knowing the MOQ helps in budgeting and planning inventory, especially when sourcing custom shafts that may require longer lead times.
-
RFQ (Request for Quote): An RFQ is a document that a buyer sends to suppliers to solicit price quotations for specific products or services. Including detailed specifications in an RFQ can lead to more accurate quotes and better procurement decisions.
-
Incoterms: Short for International Commercial Terms, these are predefined commercial terms used in international trade. They clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding these terms is vital for effective supply chain management and cost control.
-
CNC (Computer Numerical Control): This technology is used for machining parts with high precision. CNC machining is crucial for producing custom shafts that require tight tolerances and complex geometries, making it an essential term in discussions about manufacturing capabilities.
-
Lead Time: This refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order until the product is delivered. Understanding lead times is essential for planning project timelines and ensuring that operations remain uninterrupted.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when engaging with shaft manufacturers, ultimately enhancing their supply chain efficiency and product reliability.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Shaft Manufacturers Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in Shaft Manufacturing?
The global shaft manufacturing sector is experiencing significant growth, driven by various factors including industrial expansion, technological advancements, and increasing demand for high-precision components. Key industries such as automotive, aerospace, energy, and marine are propelling this growth, particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. For instance, countries like Saudi Arabia and Brazil are ramping up their investments in infrastructure and energy projects, creating a robust demand for custom shaft solutions.
Emerging B2B technologies such as advanced CNC machining, additive manufacturing, and IoT integration are transforming traditional manufacturing processes. These technologies enable manufacturers to achieve tighter tolerances, reduce lead times, and enhance overall efficiency. Additionally, the rise of Industry 4.0 is fostering a shift toward data-driven decision-making, allowing manufacturers to optimize production schedules and inventory management.
International B2B buyers are increasingly focusing on suppliers that offer comprehensive services, including reverse engineering and failure analysis, to mitigate risks associated with equipment downtime. The trend towards customization is also evident, as clients seek tailored solutions that meet specific operational requirements, further emphasizing the need for collaboration between manufacturers and buyers.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting Shaft Manufacturing?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of modern manufacturing practices, with environmental impact and ethical sourcing gaining prominence in the decision-making processes of B2B buyers. Shaft manufacturers are increasingly adopting sustainable materials and practices to minimize their ecological footprint. This includes utilizing recycled metals and eco-friendly coatings, which not only reduce waste but also appeal to environmentally conscious customers.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. International buyers are now prioritizing partnerships with manufacturers who adhere to ethical labor practices and environmental regulations. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 9001 (Quality Management) are becoming essential for suppliers aiming to establish credibility in global markets. These certifications demonstrate a commitment to continuous improvement in environmental performance and product quality, aligning with the values of modern businesses.
Furthermore, as regulations around emissions and sustainability tighten globally, manufacturers are compelled to innovate and invest in greener technologies. This shift not only meets regulatory requirements but also enhances brand reputation and customer loyalty among environmentally aware consumers.
What Is the Evolution of Shaft Manufacturing and Its Importance in B2B?
Shaft manufacturing has evolved significantly over the decades, transitioning from rudimentary techniques to advanced, precision-engineered solutions. Initially, shafts were primarily produced through manual machining processes, which limited accuracy and consistency. However, the introduction of CNC technology revolutionized the industry, enabling manufacturers to produce highly complex and precise shafts at scale.
The integration of computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) has further enhanced design capabilities, allowing for intricate geometries and optimized performance characteristics. This evolution is critical for B2B buyers who require reliable and durable components to ensure the smooth operation of machinery across various sectors, including oil and gas, aerospace, and heavy machinery.
Today, the emphasis is on customized solutions that cater to specific operational challenges, underscoring the importance of collaboration and innovation in the shaft manufacturing sector. Understanding this evolution helps international buyers make informed decisions about sourcing partners, emphasizing the need for quality, precision, and ethical practices in their supply chains.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of Shaft Manufacturers
-
How do I select the right shaft manufacturer for my project?
Choosing the right shaft manufacturer involves evaluating several factors. Look for a company with a solid reputation and extensive experience in your industry. Assess their capabilities, such as precision machining, material selection, and customization options. It’s also essential to verify their quality assurance processes, certifications (like ISO 9001), and ability to meet your specific tolerances and lead times. Request references and case studies to understand their previous work and customer satisfaction levels. -
What customization options are available for manufactured shafts?
Shaft manufacturers typically offer a range of customization options to meet specific project requirements. This includes variations in diameter, length, material type, and surface treatments. Many manufacturers also provide design services, allowing you to collaborate on strength calculations, stress analysis, and other engineering aspects. If you require unique features such as keyways or grooves, ensure that your chosen manufacturer has the necessary capabilities to deliver tailored solutions. -
What are the common minimum order quantities (MOQs) for shaft manufacturing?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly among shaft manufacturers. Some may have MOQs as low as one or two units for custom designs, while others might require larger quantities, especially for mass-produced items. It’s essential to discuss your needs upfront and understand the implications of MOQ on pricing and lead times. If you are a smaller buyer, look for manufacturers willing to accommodate lower quantities or consider forming partnerships with other buyers for bulk orders. -
What payment terms should I expect when working with international shaft manufacturers?
Payment terms for international transactions can vary widely depending on the manufacturer and your relationship with them. Common terms include upfront deposits (often 30-50%) with the balance due upon completion or delivery. Some manufacturers may offer credit terms for established clients. It’s advisable to clarify payment methods (wire transfer, letters of credit, etc.) and any potential currency exchange considerations. Always ensure that the terms align with your cash flow management and project timelines. -
How do I ensure quality assurance in shaft manufacturing?
To ensure quality assurance, inquire about the manufacturer’s quality control processes. A reputable manufacturer should have a comprehensive QA program in place, including inspections at various stages of production, non-destructive testing, and adherence to industry standards. Request documentation of their quality certifications and ask about their approach to addressing defects or failures. Engaging in a pre-production meeting to discuss quality expectations can also help mitigate risks. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing shafts internationally?
Logistics is crucial when sourcing shafts internationally. Consider the shipping methods available, estimated delivery times, and costs associated with freight and customs duties. It’s vital to understand the manufacturer’s ability to handle transportation logistics, including packaging and documentation for customs clearance. Additionally, discuss the incoterms (International Commercial Terms) to clarify responsibilities for shipping costs and risks during transit. -
What industries commonly utilize custom shaft manufacturing?
Custom shaft manufacturing serves a diverse range of industries, including automotive, aerospace, marine, oil and gas, renewable energy, and heavy machinery. Each sector has unique requirements regarding material properties, tolerances, and performance specifications. Understanding the specific needs of your industry can guide you in selecting a manufacturer with relevant experience and capabilities, ensuring the shafts produced meet the operational demands of your application. -
How can I evaluate the reliability of a shaft manufacturer?
Evaluating the reliability of a shaft manufacturer involves researching their track record, financial stability, and customer reviews. Look for testimonials, case studies, and industry recognition that demonstrate their ability to deliver on promises. It’s also beneficial to visit their facilities if possible, assess their equipment and technology, and meet their engineering team. Establishing open communication and transparency during initial discussions can further indicate their reliability and commitment to customer satisfaction.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for Shaft Manufacturers
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Shaft Manufacturing Operations?
In today’s competitive landscape, effective strategic sourcing is crucial for B2B buyers seeking reliable shaft manufacturing partners. By prioritizing suppliers who offer comprehensive services—from design and engineering to precision machining and quality assurance—you can ensure that your components meet the demanding standards of industries such as oil and gas, aerospace, and renewable energy.
Collaboration with experienced manufacturers not only streamlines your supply chain but also enhances product performance through advanced engineering solutions and rapid turnaround times. Engaging with suppliers that leverage cutting-edge technology and maintain rigorous quality control processes will significantly reduce downtime and operational risks associated with subpar components.
As you look to the future, consider the potential of global partnerships that foster innovation and resilience. By investing in relationships with reputable shaft manufacturers, especially those with a proven track record in international markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, you can elevate your operations and ensure sustained success.
Take the next step in your sourcing strategy—explore partnerships that align with your operational goals and drive your projects forward. The right supplier can make all the difference in achieving your business objectives.