Top 5 Battery Manufacturer List and Guide: How To Solve Scenario …
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for battery manufacturer
Navigating the global market for battery manufacturing poses significant challenges for B2B buyers, especially when it comes to sourcing reliable suppliers that meet stringent quality and sustainability standards. With the increasing demand for diverse battery types—from lithium-ion for electric vehicles to lead-acid batteries for industrial applications—buyers must be well-informed to make effective purchasing decisions. This comprehensive guide serves as a vital resource, detailing the various battery types, their applications, and the intricacies involved in supplier vetting.
Our aim is to empower international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including countries like Nigeria and Brazil—by providing actionable insights into the battery manufacturing landscape. The guide covers essential aspects such as cost considerations, market trends, and the importance of certifications, ensuring that buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing with confidence. By equipping you with the knowledge needed to evaluate potential suppliers and understand market dynamics, this guide fosters informed purchasing decisions that align with your business goals and sustainability initiatives.
As the battery industry continues to evolve, being equipped with the right information will not only enhance your supply chain efficiency but also position your business for long-term success in a competitive global market.
Top 10 Battery Manufacturer Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. East Penn Manufacturing – Lead-Acid Batteries
Domain: eastpennmanufacturing.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
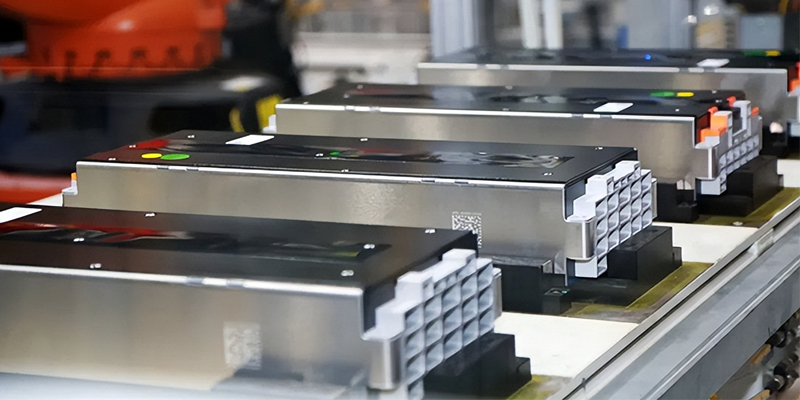
Introduction: East Penn Manufacturing is the world’s largest single-site, family-owned lead-acid battery manufacturer. Their product lines include: 1. Motive Power: Deka® batteries for material handling needs. 2. Transportation: Batteries for cars, trucks, boats, tractors, and other moving applications. 3. Reserve Power: Energy storage solutions for UPS, telecommunications, outside plant, and renewable energy. …
2. Clarios – Advanced Low-Voltage Batteries
Domain: clarios.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Clarios manufactures advanced low-voltage batteries, including AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat), lithium-ion, and supercapacitors. Their products are designed for various applications such as automotive, commercial vehicles, powersports, and leisure activities. Clarios emphasizes sustainable, next-generation performance and offers multi-battery systems with a chemistry-agnostic approach integrated with a…
3. CATL – Advanced Battery Solutions
Domain: catl.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: 宁德时代(CATL)提供多种电池解决方案,包括:1. 乘用车解决方案:为电动汽车提供超快充、长寿命、高比能等先进技术。2. 商用车解决方案:定制化解决方案,适用于公交、客运、旅游等场景,帮助客户降低成本。3. 储能系统解决方案:基于磷酸铁锂化学体系,提供安全、高效、经济的锂电储能系统,促进能源结构优化。4. 二轮车、电动港口、工程机械、特种车辆等多种行业应用。
4. Crown Battery – Motive Power Batteries
Domain: crownbattery.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Crown Battery offers a wide range of batteries and charging systems for various applications including:
1. **Motive Power Batteries**: Designed for industrial applications such as electric forklifts, pallet jacks, and automated guided vehicles.
2. **Industrial Charging Systems**: Energy-efficient chargers for material handling applications.
3. **Electric Mining Machinery**: Batteries built for…
5. Natron Energy – BluePack™, BlueRack™, BlueTray™
Domain: natron.energy
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Natron Energy offers three key products: 1. BluePack™ Critical Power Battery – designed for critical power applications. 2. BlueRack™ 250 Battery Cabinet – a cabinet solution for battery storage. 3. BlueTray™ 4000 – a high-capacity battery solution. All products are based on unique Prussian blue electrode chemistry and are intended strictly for commercial and industrial use.
Understanding battery manufacturer Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lead-Acid Battery | Cost-effective, robust, and widely available. | Automotive, industrial, backup power. | Pros: Low cost, established technology. Cons: Heavier, shorter lifespan. |
| Lithium-Ion Battery | High energy density, lightweight, rechargeable. | Consumer electronics, electric vehicles. | Pros: Long lifespan, fast charging. Cons: Higher cost, sensitive to temperature. |
| Nickel-Cadmium Battery | Rechargeable, performs well in extreme conditions. | Power tools, emergency lighting. | Pros: Durable, reliable in cold weather. Cons: Memory effect, environmental concerns. |
| Flow Battery | Scalable, long cycle life, and easy to maintain. | Renewable energy storage, grid applications. | Pros: Long-term energy storage, low degradation. Cons: High initial investment, complex setup. |
| Solid-State Battery | Enhanced safety, higher energy density. | Electric vehicles, portable electronics. | Pros: Safer than liquid batteries, longer lifespan. Cons: Still in development, higher production costs. |
What are the Key Characteristics of Lead-Acid Batteries for B2B Buyers?
Lead-acid batteries are one of the oldest and most established battery technologies, known for their robustness and cost-effectiveness. These batteries are commonly used in automotive applications, industrial machinery, and as backup power sources. For B2B buyers, the low initial investment is a significant advantage, but it’s essential to consider their shorter lifespan and heavier weight compared to newer technologies. Buyers should evaluate the total cost of ownership, including replacement frequency and disposal regulations.
How Do Lithium-Ion Batteries Stand Out in the Market?
Lithium-ion batteries have revolutionized energy storage with their high energy density and lightweight design, making them ideal for consumer electronics and electric vehicles. B2B buyers appreciate their long lifespan and fast charging capabilities, which can enhance productivity in various applications. However, the higher upfront costs and sensitivity to temperature fluctuations are crucial factors to consider. Businesses should assess their usage patterns to maximize the benefits of lithium-ion technology while mitigating risks associated with thermal management.
Why are Nickel-Cadmium Batteries Still Relevant for Certain Applications?
Nickel-cadmium batteries are rechargeable and excel in extreme conditions, making them suitable for power tools and emergency lighting systems. Their durability and reliability in cold weather are significant advantages for B2B applications in harsh environments. However, buyers must be aware of the memory effect, which can reduce capacity over time, and the environmental concerns related to cadmium disposal. Companies should weigh these factors against their specific operational needs when considering nickel-cadmium solutions.
What Advantages Do Flow Batteries Offer for Energy Storage?
Flow batteries are gaining traction for their scalability and long cycle life, particularly in renewable energy storage and grid applications. They allow for easy maintenance and low degradation over time, making them an attractive option for businesses looking to invest in sustainable energy solutions. However, the high initial investment and complex setup can be barriers for some buyers. Companies should conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis to determine if flow batteries align with their long-term energy strategy.
How Do Solid-State Batteries Change the Landscape for B2B Applications?
Solid-state batteries represent the next generation of energy storage technology, offering enhanced safety and higher energy density. This makes them particularly appealing for electric vehicles and portable electronics. B2B buyers should be aware that while solid-state batteries promise longer lifespans and reduced risks of leakage or combustion, they are still in development and may come with higher production costs. Companies should stay informed about advancements in this technology to leverage its potential benefits in the future.
Key Industrial Applications of battery manufacturer
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Battery Manufacturer | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Electric and Hybrid Vehicles | Enhances vehicle performance and range | Compliance with local regulations and standards |
| Renewable Energy | Energy Storage Systems | Stabilizes power supply and optimizes energy use | Scalability and compatibility with existing systems |
| Telecommunications | Backup Power Supply | Ensures uninterrupted service during outages | Reliability and service life of batteries |
| Industrial Equipment | Powering Heavy Machinery | Increases operational efficiency and uptime | Durability and capacity to handle high demand |
| Consumer Electronics | Rechargeable Batteries for Devices | Reduces costs and environmental impact | Battery chemistry and size compatibility |
How Are Batteries Used in the Automotive Sector for Electric and Hybrid Vehicles?
Battery manufacturers play a crucial role in the automotive sector, particularly in the production of lithium-ion batteries that power electric and hybrid vehicles. These batteries not only enhance vehicle performance but also extend driving ranges, addressing one of the primary concerns of consumers: range anxiety. For B2B buyers in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing batteries that comply with local regulations and environmental standards is essential. Additionally, manufacturers should consider the availability of after-sales support and warranty options to ensure long-term reliability.
What Role Do Batteries Play in Renewable Energy Systems?
In renewable energy applications, battery manufacturers provide energy storage systems that stabilize power supply and optimize energy usage. These batteries are integral for balancing intermittent energy sources like solar and wind, ensuring that energy is available when needed. For buyers in regions with developing energy infrastructures, such as parts of the Middle East and Africa, scalability and compatibility with existing renewable systems are critical. Buyers should also evaluate the lifecycle and efficiency of the batteries to ensure sustainable energy solutions.
How Do Batteries Ensure Reliability in Telecommunications?
Battery manufacturers supply backup power solutions for telecommunications infrastructure, ensuring uninterrupted service during power outages. This is vital for maintaining communication networks, especially in regions prone to power instability. For B2B buyers in Europe and the Middle East, reliability and service life are paramount, as any downtime can lead to significant financial losses. Buyers should look for batteries that offer advanced monitoring features and efficient energy management systems.
In What Ways Are Batteries Used to Power Industrial Equipment?
In the industrial sector, battery manufacturers provide solutions that power heavy machinery and equipment, enhancing operational efficiency and minimizing downtime. These batteries are designed to withstand rigorous conditions and high demand, making them essential for industries such as manufacturing and construction. Buyers, particularly in South America and Africa, should prioritize durability and capacity when sourcing batteries, ensuring they can handle the specific requirements of their operations.
Why Are Rechargeable Batteries Essential for Consumer Electronics?
Battery manufacturers produce rechargeable batteries that are widely used in consumer electronics, providing a cost-effective and environmentally friendly solution. These batteries not only reduce operational costs but also minimize environmental impact through reduced waste. For international B2B buyers, understanding the nuances of battery chemistry and size compatibility is crucial to ensure that the batteries meet the specific needs of their devices. Buyers should also consider the supply chain reliability and the manufacturer’s ability to provide ongoing support.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘battery manufacturer’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Quality Assurance and Reliability Concerns in Battery Supply Chains
The Problem: B2B buyers often face significant challenges in ensuring the quality and reliability of battery products, especially when sourcing from manufacturers across different regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East. Concerns about inconsistent product quality can arise from variations in manufacturing standards, material sourcing, and local regulations. This can lead to operational inefficiencies, increased costs due to returns or replacements, and ultimately, a negative impact on end-user satisfaction.
The Solution: To mitigate these risks, buyers should prioritize manufacturers that adhere to international quality standards and certifications, such as ISO 9001. Conducting thorough due diligence before selecting a battery manufacturer is crucial. This includes requesting quality assurance documentation, customer testimonials, and performance metrics. Additionally, establishing a direct line of communication with the manufacturer can facilitate transparency regarding production processes and quality control measures. Buyers should also consider implementing a pilot testing phase for new battery products, allowing them to evaluate performance in real-world conditions before committing to larger orders. This proactive approach ensures that the products meet the necessary standards and reduces the likelihood of quality-related issues.
Scenario 2: Navigating Diverse Battery Technologies for Specific Applications
The Problem: The battery market is saturated with various technologies, including lithium-ion, lead-acid, and nickel-cadmium, each suitable for different applications. B2B buyers can become overwhelmed when trying to select the right battery technology for their specific needs, such as for electric vehicles, renewable energy storage, or industrial machinery. Misalignment between battery specifications and application requirements can lead to performance issues and operational downtime, causing frustration and financial loss.
The Solution: To effectively navigate the complexities of battery technologies, buyers should engage in comprehensive needs assessments that outline their specific application requirements, including energy capacity, discharge rates, and environmental conditions. Collaborating with experienced battery manufacturers who offer expert consultations can provide valuable insights into the most suitable battery types for their applications. Additionally, utilizing detailed product catalogs and comparison tools available from manufacturers can help buyers make informed decisions. By leveraging these resources, buyers can align their technical requirements with the appropriate battery technology, enhancing operational efficiency and minimizing the risk of product failure.
Scenario 3: Managing Supply Chain Disruptions and Lead Times
The Problem: Global supply chain disruptions have become increasingly common, impacting the availability and lead times for battery products. B2B buyers may find themselves facing long wait times for critical components, which can halt production lines or delay project timelines. Such disruptions can be particularly detrimental in industries like automotive and renewable energy, where timely delivery of batteries is essential for maintaining competitive advantage.
The Solution: To manage supply chain risks effectively, B2B buyers should establish strategic partnerships with multiple battery manufacturers across different regions. This diversification allows buyers to mitigate the impact of disruptions by having alternative sources for battery supply. Implementing robust inventory management practices, such as just-in-time inventory systems, can also help maintain optimal stock levels and reduce reliance on single suppliers. Furthermore, maintaining regular communication with manufacturers regarding their production capacities and potential delays can provide early warning signals, enabling buyers to adjust their procurement strategies accordingly. By adopting a proactive approach to supply chain management, buyers can ensure consistent access to battery products, safeguarding their operations against unforeseen disruptions.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for battery manufacturer
What Are the Key Materials Used in Battery Manufacturing?
Selecting the right materials for battery manufacturing is critical for ensuring product performance, longevity, and compliance with international standards. Below are analyses of four common materials used in battery production, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Does Lead-Acid Material Perform in Battery Applications?
Lead-acid batteries are widely used due to their established technology and cost-effectiveness. Key properties include a temperature rating of -40°C to 60°C and a high discharge current capability, making them suitable for automotive and stationary applications.
Pros include durability and a relatively low manufacturing cost, which makes them an attractive option for budget-conscious buyers. However, cons include weight and environmental concerns related to lead disposal. In terms of application impact, lead-acid batteries are compatible with various media, including automotive and backup power systems.
For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, compliance with local environmental regulations is crucial. Standards such as ASTM and DIN are often referenced, and buyers should ensure that lead-acid batteries meet these requirements to avoid legal issues.
What Role Does Lithium-Ion Material Play in Modern Batteries?
Lithium-ion batteries are known for their high energy density and lightweight properties, making them ideal for consumer electronics and electric vehicles. They typically operate within a temperature range of -20°C to 60°C and exhibit excellent cycle stability.
The key advantages of lithium-ion batteries include a longer lifespan and lower self-discharge rates compared to other battery types. However, they come with disadvantages such as higher manufacturing complexity and cost. The application impact is significant, as lithium-ion batteries are essential in renewable energy storage and electric mobility.
International buyers should be aware of the varying standards for lithium-ion batteries, such as UN 38.3 for transportation safety and IEC 62133 for safety requirements. These standards are crucial for ensuring compliance and safety in markets across Europe and the Middle East.
How Do Nickel-Cadmium Batteries Compare in Performance?
Nickel-cadmium (NiCd) batteries are known for their robustness and ability to perform in extreme temperatures, ranging from -40°C to 60°C. They also exhibit excellent cycle performance and can be rapidly charged.
While advantages include durability and the ability to deliver high discharge currents, disadvantages involve environmental concerns due to cadmium toxicity and a relatively lower energy density compared to lithium-ion batteries. NiCd batteries find applications in power tools and medical devices, where reliability is paramount.
For international B2B buyers, especially in regions with strict environmental regulations, understanding the implications of cadmium use is vital. Compliance with standards such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) is essential for market entry in Europe and other regions.
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Using Nickel-Metal Hydride Batteries?
Nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries are commonly used in hybrid vehicles and consumer electronics. They operate efficiently within a temperature range of -20°C to 60°C and offer a higher energy density than NiCd batteries.
The key advantages of NiMH batteries include their ability to store more energy and a lower environmental impact compared to NiCd batteries. However, they are generally more expensive and have a shorter cycle life than lithium-ion batteries. Their application is primarily in hybrid vehicles and energy storage systems.
International buyers should consider certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management when sourcing NiMH batteries. Compliance with these standards can enhance marketability and trust among consumers in Europe and the Middle East.
Summary of Material Selection for Battery Manufacturing
| Material | Typical Use Case for battery manufacturer | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lead-Acid | Automotive, backup power systems | Cost-effective and durable | Environmental concerns | Low |
| Lithium-Ion | Electric vehicles, renewable energy storage | High energy density, lightweight | Higher manufacturing complexity | High |
| Nickel-Cadmium | Power tools, medical devices | Robust performance in extremes | Toxicity and environmental issues | Medium |
| Nickel-Metal Hydride | Hybrid vehicles, consumer electronics | Higher energy density | Shorter cycle life | Medium |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection considerations for battery manufacturers, particularly for international B2B buyers navigating diverse regulatory landscapes.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for battery manufacturer
What Are the Key Stages in Battery Manufacturing Processes?
The manufacturing of batteries is a complex process that involves several critical stages. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers aiming to source reliable battery products.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in battery manufacturing is material preparation, which involves sourcing and processing raw materials. For lead-acid batteries, this includes lead oxide, sulfuric acid, and other components. Lithium-ion batteries require lithium, cobalt, nickel, and graphite, among others. These materials must be of high purity to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the batteries. Suppliers often conduct rigorous material testing to ensure compliance with international standards, which helps in minimizing defects in the final product.
2. Forming
Following material preparation, the forming stage involves creating the battery components. For lead-acid batteries, this typically means casting lead grids, mixing active materials, and preparing separators. In lithium-ion batteries, electrode materials are coated onto metal foils and then dried. This stage is crucial as the quality of the components directly impacts the efficiency and safety of the battery.
3. Assembly
The assembly stage is where the various components come together. In lead-acid batteries, the plates are stacked and inserted into the battery casing, followed by the addition of electrolyte. For lithium-ion batteries, cells are assembled into modules and then integrated into battery packs. This stage often involves automation to enhance precision and reduce human error. Manufacturers may also implement techniques such as ultrasonic welding or laser welding to ensure strong connections within the battery.
4. Finishing
The final stage, finishing, includes sealing, labeling, and packaging the batteries. This stage often requires rigorous inspection to ensure that each battery meets quality standards. In addition, manufacturers may conduct tests to verify the batteries’ performance under various conditions, such as temperature fluctuations and cycling.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Battery Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a fundamental aspect of battery manufacturing, ensuring that products meet both safety and performance standards. For B2B buyers, understanding the quality assurance processes can help in selecting reliable suppliers.
Relevant International Standards for Battery Manufacturing
To maintain high standards of quality, battery manufacturers often adhere to international certifications such as ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems. Additionally, industry-specific standards like CE marking for European markets and API standards for performance and safety are crucial. B2B buyers should look for suppliers that have these certifications, as they indicate a commitment to quality and safety.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint assesses the quality of raw materials before production begins. Suppliers should provide certificates of analysis to confirm material quality.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During production, IPQC ensures that processes are followed correctly and that any defects are identified early. This can include real-time monitoring of equipment and periodic sampling of products.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, FQC involves comprehensive testing of the finished batteries. This includes performance tests, safety assessments, and environmental simulations to ensure the products meet specified standards.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Battery Quality Control?
Battery manufacturers employ various testing methods to validate the quality of their products. Common testing techniques include:
-
Cycle Life Testing: Evaluates how many charge and discharge cycles a battery can undergo before its capacity significantly degrades.
-
Temperature and Humidity Testing: Simulates extreme environmental conditions to ensure the battery performs reliably under various climates.
-
Electrical Testing: Measures voltage, current, and resistance to ensure the battery operates within specified parameters.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial in ensuring product reliability. Here are several methods to validate QC:
-
Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing and quality control practices. Buyers should look for transparency in operations and adherence to quality standards.
-
Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed quality reports that outline testing methodologies, results, and any corrective actions taken for defective products.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control processes. This is particularly important for international buyers who may not have the ability to perform onsite inspections.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding quality control nuances is vital:
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have specific regulations regarding battery manufacturing. Buyers should ensure that suppliers comply with local laws and standards to avoid legal issues.
-
Cultural Differences: Communication can vary significantly across cultures. Establishing clear expectations and understanding local practices can help mitigate misunderstandings related to quality assurance.
-
Supply Chain Transparency: Buyers should prioritize suppliers who provide clear visibility into their supply chain. This includes information about raw material sourcing, manufacturing practices, and logistics, which can all impact product quality.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices in the battery industry, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that lead to successful partnerships and reliable products. This knowledge not only helps in mitigating risks but also enhances overall supply chain efficiency.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘battery manufacturer’
Introduction
In the rapidly evolving battery manufacturing sector, sourcing the right supplier is pivotal for B2B buyers. This practical checklist aims to guide international buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, through the essential steps to procure batteries effectively. By following this checklist, you can ensure that you partner with reliable manufacturers who meet your specific needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to suppliers, clearly outline your technical requirements for the batteries you need. This includes specifications such as battery type (e.g., lithium-ion, lead-acid), capacity, voltage, and intended application (e.g., automotive, renewable energy). A well-defined specification helps in filtering potential suppliers who can meet your precise needs.
Step 2: Research Potential Manufacturers
Conduct thorough research to identify manufacturers that specialize in the type of batteries you require. Utilize industry databases, trade shows, and online platforms to gather information. Look for companies with a proven track record, strong market presence, and a diverse product line that aligns with your specifications.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verify that potential suppliers possess relevant certifications and quality standards. Certifications such as ISO 9001 or those specific to battery manufacturing indicate a commitment to quality and safety. This step is crucial as it reassures you of the manufacturer’s adherence to industry standards, which can mitigate risks in quality and compliance.
Step 4: Assess Production Capacity and Capabilities
Inquire about the production capacity of the manufacturers to ensure they can meet your order volume and timeline. Evaluate their technological capabilities, including automation and quality control processes. A manufacturer with robust production capabilities can handle fluctuations in demand and ensure timely delivery.
Step 5: Request Samples and Conduct Testing
Once you narrow down your options, request product samples to assess quality firsthand. Conduct performance testing under conditions similar to your intended application. This step allows you to evaluate the battery’s reliability, lifespan, and overall performance before making a substantial investment.
Step 6: Review Pricing Structures and Payment Terms
Discuss pricing models and payment terms with shortlisted suppliers. Ensure that you understand the total cost, including shipping, taxes, and any additional fees. Transparent pricing and favorable payment terms can significantly impact your budgeting and cash flow management.
Step 7: Establish Communication and Support Channels
Finally, assess the communication and support channels offered by potential suppliers. Reliable manufacturers should provide clear lines of communication and responsive customer service. Establishing a good relationship with your supplier can facilitate smoother transactions and prompt resolution of any issues that may arise.
By adhering to this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing battery manufacturers with confidence, ensuring they select partners that align with their business objectives and market demands.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for battery manufacturer Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Battery Manufacturing?
When sourcing batteries, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting and negotiation. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of battery chemistry significantly impacts material costs. For instance, lithium-ion batteries require lithium, cobalt, and nickel, while lead-acid batteries primarily use lead and sulfuric acid. Prices of raw materials fluctuate based on market demand and geopolitical factors.
-
Labor: Labor costs are influenced by the location of the manufacturing facility. Regions with higher labor costs, such as parts of Europe, may lead to increased pricing. Additionally, skilled labor is essential for quality assurance and complex manufacturing processes, which can further drive labor expenses.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses utilities, maintenance, and administrative costs. Overhead can vary significantly depending on the efficiency of production processes and the scale of operations.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling is significant, especially for customized battery designs. Tooling costs can be amortized over large production runs, making economies of scale a vital consideration.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product reliability and safety requires rigorous testing and certification processes. Investments in QC can add to upfront costs but are essential for maintaining brand reputation and compliance with international standards.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling fees must be factored into the total cost. This includes transportation from the manufacturer to the buyer, which can vary significantly based on distance, mode of transport, and Incoterms used.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically apply a profit margin to cover their risks and investments. Understanding typical margins in the industry can aid buyers in evaluating offers.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Battery Sourcing?
Several factors influence the pricing of batteries, making it essential for buyers to navigate these variables effectively:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) and volume discounts play a significant role. Larger orders often qualify for reduced pricing, which can be advantageous for businesses with predictable demand.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom battery designs tailored to specific applications can incur higher costs due to additional engineering and manufacturing processes. Buyers should assess whether standard products meet their needs to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Materials: The type and quality of materials used will directly affect price. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who can provide high-quality materials while remaining cost-effective.
-
Quality and Certifications: Batteries used in critical applications may require specific certifications (e.g., ISO, UL). Suppliers with robust certifications might charge a premium, but this can be justified by reduced risk and enhanced reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, production capacity, and historical performance can influence pricing. Established suppliers may command higher prices due to their reliability and quality assurances.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms affects cost and risk distribution. Understanding the implications of terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) is vital for accurate pricing analysis.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Achieve Cost Efficiency in Battery Sourcing?
-
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers about pricing and terms. Leverage volume and long-term contracts to negotiate better deals.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but the total cost of ownership, including maintenance, operational efficiency, and disposal costs.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East should consider currency fluctuations and import duties, which can significantly impact the final cost.
-
Research and Benchmarking: Conduct thorough market research to benchmark prices and identify competitive suppliers. Utilize platforms that aggregate data on pricing and suppliers to inform decision-making.
-
Long-term Partnerships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and service, particularly for repeat orders and customized solutions.
Disclaimer
The pricing insights provided herein are indicative and subject to market fluctuations and supplier discretion. Buyers are encouraged to conduct due diligence and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing battery manufacturer With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Battery Manufacturers
In the rapidly evolving energy landscape, businesses often seek alternatives to traditional battery manufacturing to meet their power needs. While battery manufacturers provide reliable solutions, exploring alternative technologies can offer innovative, cost-effective, and sustainable options. This analysis compares battery manufacturing with energy storage systems and fuel cell technologies, providing B2B buyers with insights to make informed decisions.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Battery Manufacturer | Energy Storage Systems | Fuel Cell Technologies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High energy density, reliable output | Variable based on technology | Continuous power generation |
| Cost | Moderate to high initial investment | Varies; often lower long-term costs | High initial investment, lower operating costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized installation | Can be integrated with existing grids | Complex installation and maintenance |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed | Low to moderate; depends on system | Regular maintenance and monitoring |
| Best Use Case | Transportation, backup power, consumer electronics | Renewable energy integration, grid support | Long-duration applications, remote locations |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
Energy Storage Systems
Energy storage systems, such as pumped hydro or compressed air energy storage, provide a robust alternative to traditional battery solutions. These systems excel in scalability and can store large amounts of energy generated from renewable sources like wind and solar. Their cost-effectiveness often improves over time as technology advances, making them a viable choice for businesses seeking long-term energy solutions. However, implementation can be complex, requiring significant infrastructure investments and site-specific considerations.
Fuel Cell Technologies
Fuel cells convert chemical energy directly into electricity, offering a continuous power supply with minimal emissions. They are particularly advantageous for applications requiring long-duration energy output, such as in remote locations or for backup power in critical infrastructure. While the operating costs may be lower over time, the initial investment can be substantial, and the technology requires skilled technicians for maintenance. Additionally, fuel cells’ dependence on hydrogen or other fuels can impact their overall feasibility and sustainability.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Energy Solution?
When selecting an energy solution, B2B buyers should assess their unique operational requirements, budget constraints, and long-term energy strategy. Battery manufacturers provide a well-established, reliable option for various applications, particularly in transportation and backup power. Conversely, energy storage systems and fuel cells may offer enhanced sustainability and lower operating costs over time, making them attractive for businesses focused on renewable energy integration. By carefully evaluating the performance, cost, and implementation factors of each alternative, buyers can determine the best fit for their specific needs and goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for battery manufacturer
What Are the Essential Technical Properties in Battery Manufacturing?
When engaging with battery manufacturers, understanding key technical specifications is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are several critical properties that define battery quality and performance:
1. Capacity (Ah – Ampere-Hours)
Capacity refers to the total amount of electric charge a battery can store, measured in ampere-hours (Ah). This specification is vital for B2B buyers, as it directly impacts the battery’s runtime and efficiency in applications ranging from consumer electronics to industrial machinery. A higher capacity indicates longer usage between charges, which is particularly important for applications with high energy demands.
2. Voltage (V)
Voltage is the potential difference that drives the flow of current in a battery. It is typically expressed in volts (V). Different applications require different voltage levels; for example, electric vehicles often operate on higher voltage systems. Understanding the voltage requirements ensures compatibility with existing systems and helps avoid performance issues.
3. Cycle Life
Cycle life is the number of complete charge and discharge cycles a battery can undergo before its capacity falls below a specified percentage (often 80% of its original capacity). For B2B buyers, selecting batteries with longer cycle lives can lead to lower long-term costs and reduced frequency of replacements, making it a critical factor in the total cost of ownership.
4. Self-Discharge Rate
This property indicates how quickly a battery loses its charge when not in use. A lower self-discharge rate is preferable, as it means the battery will retain its charge longer during storage. This is particularly significant for applications requiring infrequent use, such as emergency backup systems.
5. Thermal Stability
Thermal stability refers to a battery’s ability to operate safely and effectively under varying temperature conditions. It is essential for applications exposed to extreme environments, such as automotive and aerospace sectors. Batteries with high thermal stability minimize the risk of overheating and failure, enhancing safety and reliability.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Battery Manufacturing?
Familiarity with industry jargon can facilitate smoother transactions and clearer communications. Here are several essential terms relevant to battery manufacturing:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In battery manufacturing, OEMs often provide batteries for various applications, including automotive and industrial equipment. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and ensure product quality.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ represents the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell in a single order. This term is crucial for B2B buyers, as it can affect inventory management and cash flow. Knowing the MOQ can help in planning purchases, especially when entering new markets or launching new products.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that a buyer sends to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products or services. For battery manufacturers, submitting an RFQ can streamline the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare offers and make informed decisions based on pricing, lead times, and other conditions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers involved in cross-border battery procurement, as they dictate shipping responsibilities, risk transfer, and cost allocation.
5. BMS (Battery Management System)
A BMS is an electronic system that manages a rechargeable battery by monitoring its state, controlling its environment, and facilitating communication between the battery and other devices. For buyers, understanding BMS is essential as it impacts battery performance, longevity, and safety, particularly in complex applications like electric vehicles and renewable energy systems.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can enhance their understanding of battery products, leading to more strategic purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the battery manufacturer Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Battery Manufacturing Sector?
The global battery manufacturing sector is experiencing significant growth driven by the increasing demand for electric vehicles (EVs), renewable energy storage solutions, and portable electronics. In emerging markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the adoption of EVs is accelerating as governments implement stricter emissions regulations and provide incentives for sustainable practices. This shift presents substantial opportunities for international B2B buyers looking to source advanced battery technologies and materials.
Key trends include the rise of lithium-ion batteries, which dominate the market due to their efficiency and longevity. Additionally, innovations in solid-state batteries are on the horizon, promising enhanced safety and energy density. Other emerging technologies include battery recycling and second-life applications, which are gaining traction in response to environmental concerns and resource scarcity. As a result, international buyers should stay informed about advancements in battery chemistries and consider sourcing from manufacturers that prioritize innovation.
Moreover, the trend towards digitalization in manufacturing processes is reshaping supply chains. Technologies such as IoT and AI are being integrated to optimize production and logistics, making it crucial for buyers to partner with manufacturers that leverage these technologies to enhance efficiency and reduce lead times. Given the competitive landscape, international buyers must adopt a proactive sourcing strategy to navigate the complexities of this dynamic market.
How Do Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact Battery Manufacturers?
Sustainability has become a central theme in the battery manufacturing sector, particularly as consumers and regulatory bodies emphasize the need for responsible sourcing and production practices. The environmental impact of battery production, including resource extraction and waste management, necessitates a focus on ethical supply chains. Buyers should prioritize manufacturers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through certifications and transparent sourcing practices.
One notable trend is the increasing use of recycled materials in battery production. This not only reduces the ecological footprint but also addresses the growing concerns over the depletion of raw materials, such as lithium and cobalt. Manufacturers are seeking partnerships with suppliers that provide recycled components or sustainable alternatives, which can significantly enhance the value proposition for international buyers.
Additionally, certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and the Responsible Minerals Initiative (RMI) signal a manufacturer’s dedication to sustainable practices. Buyers should look for these credentials when evaluating potential suppliers to ensure that their sourcing aligns with environmental and ethical standards. By prioritizing sustainability, B2B buyers can not only meet regulatory requirements but also enhance their brand reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious customers.
What Is the Brief Evolution of Battery Manufacturing Relevant to Today’s B2B Context?
The battery manufacturing industry has evolved significantly over the past century, transitioning from simple lead-acid technologies to sophisticated lithium-ion systems. Initially, batteries were primarily used for automotive applications, but the advent of consumer electronics in the late 20th century catalyzed the development of compact and efficient battery solutions. This evolution laid the groundwork for today’s diverse battery market, which encompasses applications ranging from electric vehicles to renewable energy storage.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards sustainability and innovation, driven by technological advancements and increasing environmental awareness. The rise of electric mobility and renewable energy sources has further accelerated this transformation, prompting manufacturers to invest heavily in research and development. As a result, today’s battery manufacturers are not only competing on performance and price but also on their commitment to ethical sourcing and sustainability practices, making these factors critical considerations for B2B buyers in the sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of battery manufacturer
-
How do I choose the right battery manufacturer for my business needs?
When selecting a battery manufacturer, consider factors such as the type of batteries you need (e.g., lead-acid, lithium-ion), the manufacturer’s reputation, production capacity, and certifications. Assess their ability to meet your specific requirements, such as quality standards, customization options, and delivery timelines. Additionally, explore their experience in your industry and their ability to provide reliable after-sales support. Engage in discussions with potential suppliers to gauge their responsiveness and willingness to collaborate on solutions tailored to your business. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for battery manufacturers?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly among battery manufacturers based on the type of battery and the production process. Generally, MOQs may range from a few hundred to several thousand units. Custom-designed batteries typically have higher MOQs due to the specialized production requirements. It’s advisable to communicate your needs directly with manufacturers to negotiate MOQs that align with your purchasing capabilities while ensuring you receive the best pricing and service. -
What payment terms should I expect when working with battery manufacturers?
Payment terms with battery manufacturers can differ widely. Common arrangements include upfront payments, partial payments upon order confirmation, and the remainder upon delivery. Some manufacturers may offer credit terms based on your business’s creditworthiness and history. It’s crucial to discuss and agree upon payment terms upfront to avoid misunderstandings later. Additionally, inquire about any available discounts for bulk purchases or early payments, which can help optimize your procurement costs. -
What quality assurance measures should I look for in a battery manufacturer?
Quality assurance is vital in battery manufacturing. Look for manufacturers that adhere to international quality standards such as ISO 9001 or ISO 14001. Ensure they have rigorous testing procedures in place for their products, including performance, safety, and durability tests. Request documentation of their quality control processes and certifications. Engaging in regular audits and inspections, or visiting their production facilities, can also provide insights into their commitment to maintaining high-quality standards. -
How can I verify the reliability of a battery manufacturer?
To verify a battery manufacturer’s reliability, research their market reputation through customer reviews, case studies, and industry references. Check their history, including years in operation and experience in your specific market segment. Engaging in direct communication with other clients can provide valuable insights into their experiences. Additionally, consider their financial stability and capacity to fulfill large orders consistently, as well as their ability to provide timely customer support. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing batteries internationally?
When sourcing batteries from international manufacturers, consider shipping options, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Evaluate the reliability of the manufacturer’s logistics partners and their ability to handle international shipments efficiently. Understand the lead times involved in production and shipping, and factor these into your inventory planning. It’s also wise to discuss packaging requirements to ensure batteries are protected during transit, as well as any potential storage needs upon arrival. -
Can battery manufacturers customize products for specific applications?
Many battery manufacturers offer customization options to meet specific application needs. This may include variations in battery chemistry, size, capacity, and connectors. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to explore their capabilities in customization. It’s important to provide detailed specifications and any unique operational conditions your batteries must meet. Collaborating closely with the manufacturer during the design phase can help ensure that the final product aligns perfectly with your application. -
What are the environmental regulations I should be aware of when sourcing batteries?
Environmental regulations regarding battery production and disposal vary by region. It’s essential to be aware of regulations such as the European Union’s Battery Directive, which sets standards for the environmental impact of batteries. Ensure that your chosen manufacturer complies with local and international environmental standards, including proper recycling practices and waste management. Request documentation proving adherence to these regulations, as this not only safeguards the environment but also enhances your business’s reputation among environmentally conscious consumers.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for battery manufacturer
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Battery Supply Chain?
In today’s competitive market, strategic sourcing is vital for battery manufacturers aiming to optimize their supply chains and reduce costs. By partnering with reputable manufacturers, such as East Penn and Tesla, international buyers can ensure access to high-quality products that meet diverse industry needs, from automotive to renewable energy storage. Understanding the nuances of various battery technologies—such as lithium-ion, lead-acid, and nickel-cadmium—enables buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational requirements.
Furthermore, as sustainability becomes increasingly important, sourcing from manufacturers committed to environmentally friendly practices can enhance brand reputation and meet regulatory demands. The global battery market is poised for substantial growth, particularly in emerging regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, where demand for energy storage solutions is surging.
What Steps Should International Buyers Take Next?
As you navigate this dynamic landscape, consider leveraging comprehensive market insights and establishing strategic relationships with leading manufacturers. Embrace the opportunity to innovate and expand your product offerings by integrating advanced battery technologies into your operations. Engaging with suppliers who prioritize quality and sustainability will not only elevate your supply chain but also position your business for long-term success in the evolving battery market.