Discover Cost-Saving Benefits of Power Transformers (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for power transformer
Navigating the global market for power transformers presents a unique set of challenges for international B2B buyers, especially those hailing from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As energy demands increase and infrastructure evolves, sourcing the right power transformer can significantly impact operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. This guide aims to demystify the complexities of power transformers, addressing key aspects such as types, applications, supplier vetting, and cost considerations.
Understanding the various types of power transformers, including step-up and step-down models, is crucial for making informed decisions that align with specific operational needs. Furthermore, this guide will explore the applications of power transformers in diverse sectors—from energy generation and transmission to industrial manufacturing—helping buyers identify the best fit for their requirements.
By providing insights on how to effectively vet suppliers, assess quality, and evaluate pricing structures, this comprehensive resource empowers B2B buyers to make confident purchasing decisions. Whether you are in Italy, France, or emerging markets across Africa and South America, our guide equips you with the knowledge needed to navigate the intricacies of the power transformer market, ensuring that your investment meets both current and future energy demands.
Understanding power transformer Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Step-Up Transformer | Increases voltage from primary to secondary winding | Power generation, renewable energy plants | Pros: Reduces transmission losses; Cons: Higher initial cost. |
| Step-Down Transformer | Decreases voltage from primary to secondary winding | Commercial and residential power distribution | Pros: Suitable for local distribution; Cons: Limited to lower voltage applications. |
| Three-Phase Transformer | Utilizes three sets of windings for balanced load distribution | Industrial facilities, large-scale operations | Pros: High efficiency; Cons: More complex installation. |
| Distribution Transformer | Steps down voltage for end-use applications | Urban infrastructure, residential areas | Pros: Excellent voltage regulation; Cons: Limited to lower power levels. |
| Autotransformer | Shares a single winding for both primary and secondary circuits | Voltage regulation in transmission networks | Pros: Compact design; Cons: Less isolation between circuits. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of Step-Up Transformers for B2B Buyers?
Step-up transformers are designed to elevate voltage levels from the primary to the secondary winding, making them crucial for reducing transmission losses in long-distance power delivery. They are commonly utilized in power generation stations and renewable energy plants, where electricity is generated at lower voltages. B2B buyers should consider the initial investment and operational efficiency, as these transformers can significantly enhance the overall power factor and reduce energy losses in transmission lines.
How Do Step-Down Transformers Meet B2B Application Needs?
Step-down transformers serve to lower voltage levels to make electricity suitable for commercial and residential use. They are essential in local distribution networks where high voltage from substations must be reduced to levels that end-users can safely utilize. Buyers should evaluate the transformer’s capacity and voltage regulation capabilities, as these factors directly impact the reliability of power supply in urban infrastructures and residential areas.
Why are Three-Phase Transformers Important for Industrial Applications?
Three-phase transformers are optimized for balancing electrical loads and are indispensable in industrial settings where large amounts of power are required. They consist of three primary and three secondary windings, providing high efficiency and improved voltage stability. B2B buyers in manufacturing or large-scale operations should assess the complexity of installation and maintenance needs, as well as the transformer’s ability to handle varying load demands effectively.
What Role Do Distribution Transformers Play in Urban Power Systems?
Distribution transformers are pivotal for stepping down voltage levels for end-use applications, particularly in urban settings. They ensure that electricity is delivered efficiently and safely to homes and businesses. When considering a purchase, B2B buyers should focus on the transformer’s voltage regulation performance and its ability to operate at full load consistently, as these factors are critical for maintaining service quality in densely populated areas.
How Do Autotransformers Provide Compact Solutions for Voltage Regulation?
Autotransformers utilize a single winding to serve both primary and secondary functions, offering a compact and cost-effective solution for voltage regulation in transmission networks. They are often employed where space is limited and efficiency is paramount. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of reduced size and cost against the potential drawbacks, such as less electrical isolation between circuits, which could pose risks in sensitive applications.
Key Industrial Applications of power transformer
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Power Transformer | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power Generation | Voltage stepping in renewable energy plants | Enhances energy efficiency and reduces transmission losses | Ensure compatibility with local grid standards and regulations |
| Oil and Gas | Voltage regulation for drilling operations | Provides reliable power supply to remote locations | Consider ruggedness and environmental protection features |
| Manufacturing | Power distribution in industrial plants | Supports machinery operation and increases production capacity | Focus on transformer size, capacity, and cooling methods |
| Telecommunications | Power supply for data centers | Ensures uninterrupted service and minimizes downtime | Evaluate transformer efficiency and redundancy options |
| Mining | Power supply for extraction and processing | Guarantees stable operations in harsh environments | Assess durability and maintenance needs in remote locations |
How Are Power Transformers Used in Power Generation?
In the power generation sector, power transformers play a crucial role in stepping up voltage levels produced by renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind farms, to match transmission requirements. This voltage adjustment minimizes losses during electricity transmission over long distances, enhancing overall energy efficiency. International buyers, particularly from regions with growing renewable energy initiatives like Africa and South America, should consider sourcing transformers that comply with local grid standards and are designed for high efficiency to maximize their investment.
What Is the Role of Power Transformers in the Oil and Gas Industry?
Power transformers are essential in the oil and gas sector for voltage regulation during drilling operations. These transformers ensure that remote drilling sites receive a reliable power supply, which is critical for the operation of heavy machinery and safety equipment. Buyers in this industry, especially from the Middle East, should prioritize sourcing transformers that are ruggedized and feature robust environmental protection, as these units must withstand harsh conditions and potential hazards.
How Do Power Transformers Support Manufacturing Operations?
In manufacturing, power transformers are pivotal for distributing electricity to various machinery and equipment. They provide the necessary voltage levels that enable efficient operation, thus increasing production capacity and reducing downtime. For international B2B buyers in Europe, such as Italy and France, it is crucial to focus on the size and capacity of transformers, ensuring they meet the specific demands of the production processes while also considering the cooling methods, which can affect performance and longevity.
Why Are Power Transformers Important for Telecommunications?
Power transformers serve a vital function in telecommunications, particularly in powering data centers where continuous operation is paramount. They help maintain stable power levels, which minimizes the risk of downtime and service interruptions. B2B buyers in this sector should evaluate the efficiency ratings of transformers and consider redundancy options to ensure uninterrupted service, as any power failure can lead to significant financial losses.
How Do Power Transformers Facilitate Mining Operations?
In the mining industry, power transformers provide essential power supply for extraction and processing activities. They ensure stable operations in often remote and challenging environments, where reliable electricity is critical for equipment operation. Buyers in the mining sector should assess the durability of transformers, as well as their maintenance needs, to ensure they can withstand the rigors of mining operations while delivering consistent performance.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘power transformer’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Ensuring Voltage Stability in Remote Installations
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, face challenges in maintaining voltage stability in remote installations. Power transformers are crucial for stepping up or down voltages, but in areas with unreliable power supply or fluctuating demand, buyers struggle to find transformers that can adapt effectively to these variations. The inability to maintain stable voltage can lead to equipment damage, increased operational costs, and inefficiencies in power distribution.
The Solution: To address voltage stability issues, buyers should consider investing in adaptive power transformers equipped with voltage regulation technology. These transformers automatically adjust their output based on real-time load conditions, ensuring that voltage remains within specified limits. When sourcing transformers, look for manufacturers that provide transformers with built-in Automatic Voltage Regulation (AVR) systems. Additionally, conducting a thorough site assessment can help identify specific voltage needs and potential fluctuations. Collaborating with an experienced supplier can also aid in selecting the right transformer type, such as a step-down transformer for reducing voltage at the distribution end, which is crucial for maintaining equipment safety and operational efficiency.
Scenario 2: Overcoming High Installation and Maintenance Costs
The Problem: A significant pain point for buyers in the Middle East and Europe is the high cost associated with the installation and maintenance of power transformers. These costs can be prohibitive, especially for small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) that require reliable power supply solutions but have limited budgets. Inadequate planning and poor specification of transformers can lead to frequent breakdowns, further escalating expenses.
The Solution: To mitigate installation and maintenance costs, buyers should focus on long-term investment strategies rather than just initial purchase prices. Engaging with reputable suppliers who offer comprehensive warranties and after-sales support can significantly reduce unexpected costs. It’s advisable to conduct a life cycle cost analysis before purchasing a transformer. This analysis should include installation, operational, and maintenance costs over the expected lifespan of the transformer. Additionally, opting for modular transformer designs can simplify maintenance and reduce costs, as they allow for easy upgrades or replacements of specific components without needing to replace the entire unit.
Scenario 3: Navigating Compliance and Regulatory Challenges
The Problem: International B2B buyers often encounter complex compliance and regulatory requirements when sourcing power transformers, especially in Europe and the Middle East. Regulations regarding efficiency standards, environmental impact, and safety can vary significantly between regions, leading to confusion and potential delays in project timelines. Non-compliance can result in penalties, project halts, or costly redesigns.
The Solution: To navigate these regulatory challenges, buyers should thoroughly research the specific compliance requirements for their region before procurement. Engaging with local regulatory bodies or industry associations can provide clarity on necessary certifications and standards, such as the IEC standards in Europe or local environmental regulations. Collaborating with suppliers who have a strong understanding of these regulations can also facilitate smoother procurement processes. Moreover, consider transformers that meet or exceed international efficiency standards, as they often come with built-in compliance features, thereby reducing the risk of non-compliance. Lastly, maintaining open communication with suppliers throughout the sourcing process can ensure that any regulatory changes are promptly addressed, minimizing project disruptions.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for power transformer
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Power Transformers?
Selecting the right materials for power transformers is crucial for optimizing performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Below, we analyze four common materials used in power transformers, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of Silicon Steel in Power Transformers?
Silicon steel, often used for transformer cores, exhibits excellent magnetic properties, which enhance energy efficiency. Its temperature rating typically reaches around 150°C, while it offers good corrosion resistance due to its silicon content. This material is essential for minimizing energy losses during operation.
Pros and Cons:
The primary advantage of silicon steel is its high permeability, which allows for efficient magnetic flux transfer. However, it can be relatively expensive and may require complex manufacturing processes, such as lamination, to reduce eddy current losses. Its performance can be affected by mechanical stress, making it less suitable for harsh environments.
Impact on Application:
Silicon steel is compatible with various insulating oils, making it ideal for oil-cooled transformers. However, it may not perform as well in dry-type transformers, which require different core materials.
Considerations for International Buyers:
B2B buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM or JIS. In Europe, particularly in Italy and France, adherence to environmental regulations regarding the use of silicon in manufacturing is essential.
How Does Copper Compare as a Conductor Material for Power Transformers?
Copper is widely recognized for its excellent electrical conductivity, with a conductivity rating of approximately 59.6 x 10^6 S/m. It also has a high melting point (around 1,085°C) and exhibits good corrosion resistance, especially when coated.
Pros and Cons:
The key advantage of copper is its superior electrical performance, which leads to reduced energy losses. However, it is more expensive than aluminum, another common conductor material. Additionally, copper is heavier, which can complicate the design and installation of transformers.
Impact on Application:
Copper’s compatibility with various cooling methods, including oil and air, makes it versatile. However, its weight may pose challenges in applications where weight-saving is critical.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in the Middle East and Europe must consider the availability of copper and its price fluctuations. Compliance with international standards for electrical safety and environmental impact is also vital.
What Role Does Insulating Oil Play in Power Transformer Performance?
Insulating oil, typically mineral oil, is crucial for cooling and insulating transformer components. It has a high dielectric strength, allowing it to withstand high voltages, and a temperature rating that can exceed 100°C.
Pros and Cons:
The main advantage of insulating oil is its dual function of cooling and insulation, which enhances transformer efficiency. However, it can pose environmental risks if leaks occur, leading to regulatory scrutiny. Additionally, the oil must be regularly tested and maintained to ensure optimal performance.
Impact on Application:
Insulating oil is compatible with various transformer designs, particularly oil-cooled transformers. Its performance may be affected by ambient temperatures, requiring careful selection based on geographic location.
Considerations for International Buyers:
B2B buyers should be aware of local regulations regarding the use and disposal of insulating oil, particularly in Europe, where environmental standards are stringent.
How Does Aluminum Compare as a Cost-Effective Alternative for Power Transformers?
Aluminum is a lighter and less expensive alternative to copper, with a conductivity rating of about 37.7 x 10^6 S/m. It has a melting point of around 660°C and is naturally resistant to corrosion due to its oxide layer.
Pros and Cons:
The primary advantage of aluminum is its cost-effectiveness and lightweight nature, which simplifies installation. However, its lower conductivity means that larger cross-sections are required to achieve the same performance as copper, potentially increasing material costs.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is suitable for various transformer designs, but it may not perform as well in high-temperature environments compared to copper.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should evaluate the total cost of ownership, including installation and maintenance, when considering aluminum. Compliance with local standards is also necessary, particularly in regions with strict electrical safety regulations.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Power Transformers
| Material | Typical Use Case for Power Transformer | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silicon Steel | Transformer cores | High magnetic permeability | Expensive and complex to manufacture | High |
| Copper | Conductors in transformers | Superior electrical conductivity | Higher cost and heavier weight | High |
| Insulating Oil | Cooling and insulation | Dual function of cooling and insulation | Environmental risks and maintenance | Medium |
| Aluminum | Cost-effective conductors | Lightweight and less expensive | Lower conductivity requiring larger sizes | Low |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for power transformer
What are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Power Transformers?
Manufacturing power transformers involves several key stages that ensure the final product meets both performance and safety standards. Understanding these stages is crucial for B2B buyers looking to source reliable transformers.
Material Preparation: What Materials are Used in Power Transformer Manufacturing?
The first step in manufacturing power transformers is the selection and preparation of materials. Common materials include:
- Core Steel: High-quality silicon steel is used for the core, which is essential for efficient electromagnetic induction.
- Copper or Aluminum Winding: These metals are chosen for their excellent electrical conductivity. The choice between them often depends on cost and application.
- Insulation Materials: Insulating paper, resin, and oil are critical for electrical insulation and heat dissipation. These materials must meet international safety standards.
Forming: How are Transformer Components Shaped?
Once materials are prepared, the next stage is forming. This involves:
- Cutting and Stamping: Core steel sheets are cut and stamped into specific shapes to form the core. Precision in this stage is vital for reducing losses during operation.
- Winding: The winding process involves carefully wrapping copper or aluminum wire around the core. This can be done using automated machines that ensure uniform tension and winding precision.
What Techniques are Used in the Assembly of Power Transformers?
The assembly stage is where various components come together to form the complete transformer.
- Core Assembly: The core is assembled using the stamped steel sheets, which are stacked and bonded together to create a magnetic circuit.
- Winding Assembly: The windings are then installed around the core. For larger transformers, this may require multiple layers and meticulous alignment to maintain efficiency.
- Tank Assembly: The assembled core and windings are placed in a tank, which is typically filled with oil for cooling and insulation. The tank must be sealed to prevent leaks and contamination.
What Finishing Processes are Involved in Power Transformer Manufacturing?
Finishing processes ensure that the transformer is ready for delivery and operation.
- Surface Treatment: Protective coatings are applied to prevent corrosion and enhance durability. This is especially important for transformers that will be used in harsh environmental conditions.
- Testing: Before shipping, transformers undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet performance specifications. This includes electrical tests, insulation resistance tests, and thermal imaging to detect hotspots.
What International Standards Govern Quality Assurance in Power Transformer Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the manufacturing of power transformers. Adherence to international standards ensures reliability and safety. Key standards include:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems, ensuring that manufacturers consistently produce quality products and services.
- CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area, CE marking indicates compliance with safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For transformers used in specific industries, such as oil and gas, compliance with American Petroleum Institute (API) standards may be required.
How is Quality Control Implemented During the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) is integrated at multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint verifies that raw materials meet specifications before they are used in production.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, ongoing inspections are conducted to ensure that processes remain within acceptable limits. This includes checking winding tension and insulation integrity.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once manufacturing is complete, the final product undergoes extensive testing to verify that it meets all performance criteria before shipment.
What Common Testing Methods are Used to Ensure Transformer Quality?
Several testing methods are employed to ensure that power transformers are safe and efficient:
- Dielectric Testing: This checks the insulation strength of the transformer to prevent electrical breakdown.
- Transformer Ratio Testing: This verifies the turns ratio of the transformer, ensuring proper voltage transformation.
- Temperature Rise Testing: This assesses the transformer’s ability to dissipate heat under load conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control is crucial to ensure product reliability. Here are actionable steps:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can help assess their adherence to quality standards and manufacturing processes.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should request detailed quality control reports from suppliers, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC phases.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspection services can provide unbiased evaluations of the manufacturing process and product quality.
What Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Consider Regarding Quality Certifications?
When sourcing power transformers internationally, buyers should be aware of the following nuances:
- Regional Certification Differences: Different regions may have specific requirements for certifications. For example, CE marking is essential in Europe, while UL certification may be required in North America.
- Language Barriers: Ensure that all documentation, including quality certifications, is available in a language that is comprehensible to the buyer to avoid misunderstandings.
- Cultural Considerations: Understanding the cultural context of your suppliers can facilitate smoother communication and negotiations regarding quality expectations and standards.
By comprehensively understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols associated with power transformers, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘power transformer’
In today’s rapidly evolving energy landscape, sourcing a power transformer requires careful consideration and strategic planning. This checklist is designed to assist international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, in making informed decisions during the procurement process.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, it’s essential to have a clear understanding of your technical requirements. Identify the type of power transformer needed based on your application—whether it’s a step-up, step-down, single-phase, or three-phase transformer. Consider factors such as voltage ratings, power ratings, and cooling methods (oil-cooled vs. dry-type).
- Voltage Requirements: Ensure the transformer can handle the operational voltage levels in your region.
- Power Capacity: Calculate the power capacity required to meet your operational needs.
Step 2: Conduct Market Research for Suppliers
Next, perform thorough market research to identify potential suppliers. Look for manufacturers and distributors with a strong track record in your region and sector.
- Industry Presence: Focus on suppliers with experience in the power transformer market specific to your geographical area.
- Product Range: Ensure they offer a variety of transformers to meet diverse operational needs.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Compliance with international standards and certifications is crucial for ensuring quality and reliability. Verify that potential suppliers hold relevant certifications such as ISO 9001, IEC standards, and any local regulations that apply.
- Quality Assurance: Certifications indicate a commitment to quality control processes.
- Regulatory Compliance: This ensures that the transformers meet safety and operational standards necessary for your market.
Step 4: Request and Analyze Technical Documentation
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request detailed technical documentation for their transformers. This should include specifications, installation guides, and maintenance manuals.
- Technical Clarity: Clear documentation aids in understanding the operational requirements and maintenance needs.
- Compatibility Assessment: Analyze if the proposed transformers are compatible with your existing systems.
Step 5: Assess After-Sales Support and Warranty
Evaluate the after-sales support offered by suppliers. A robust support system can significantly impact the long-term performance of your power transformer.
- Warranty Terms: Understand the warranty offered for the transformer and what it covers.
- Support Services: Check if the supplier provides installation, maintenance, and emergency support.
Step 6: Compare Pricing and Total Cost of Ownership
While price is an important factor, it should not be the sole criterion for selection. Compare the total cost of ownership, which includes installation, maintenance, and operational costs over the transformer’s lifespan.
- Long-term Value: A higher initial investment in quality equipment can lead to lower operational costs and fewer maintenance issues.
- Supplier Financing Options: Consider any financing or leasing options that may be available to ease upfront costs.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Finalize Purchase
Finally, once you’ve selected a supplier, negotiate the purchase terms. Discuss payment options, delivery timelines, and installation support.
- Clear Agreements: Ensure that all terms are documented clearly to avoid misunderstandings.
- Delivery and Logistics: Confirm the logistics involved in delivering and installing the transformer at your site.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing power transformers effectively, ensuring that they make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regional requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for power transformer Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Power Transformer Sourcing?
Understanding the cost structure of power transformers is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The major cost components include:
-
Materials: The primary materials used in power transformer manufacturing include copper or aluminum for windings, silicon steel for the core, and insulating materials such as oil or resin. The prices of these materials can fluctuate significantly based on global supply and demand.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary widely depending on the country and the skill level required for manufacturing. Countries with lower labor costs may provide cheaper sourcing options, but this can affect the overall quality of the transformer.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to facility maintenance, utilities, and indirect labor. Efficient manufacturing processes can help keep these costs low.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific transformer designs can be a significant upfront cost. Buyers should consider this when evaluating suppliers, especially for customized products.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes are essential to ensure that transformers meet industry standards. The costs associated with QC can vary depending on the complexity of the transformer and the certifications required.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, which include transportation and handling, play a vital role in the total cost. International shipping may involve customs duties and tariffs that can add to expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin on top of their costs, which varies based on market conditions, competition, and the value-added services they provide.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Power Transformer Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of power transformers. Understanding these can help buyers negotiate better deals:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in bulk or meeting the Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) can lead to significant discounts. Suppliers are often willing to reduce prices for larger orders due to lower per-unit production costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specific performance requirements can increase costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the associated price increase.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (such as ISO or IEC standards) can lead to higher prices but can also ensure better performance and reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their reliability and service.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms affects the total landed cost. Buyers should understand the implications of terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) on pricing and risk.
What Are Effective Tips for Negotiating Power Transformer Prices?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those in emerging markets, there are several strategies to optimize costs:
-
Conduct Market Research: Understanding current market prices for materials and transformers can provide leverage during negotiations. Utilize platforms and trade publications for up-to-date pricing.
-
Engage Multiple Suppliers: Soliciting quotes from several suppliers can create competitive tension and may lead to better pricing or terms.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): While the upfront cost is crucial, considering the TCO—factoring in maintenance, efficiency, and lifespan—can lead to better long-term financial decisions.
-
Leverage Long-term Relationships: Establishing long-term partnerships with suppliers can result in more favorable pricing and terms over time. Suppliers may offer discounts for repeat business or loyalty.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be cognizant of currency fluctuations, political factors, and economic conditions in both the supplier’s and buyer’s country, as these can significantly impact pricing.
What Should Buyers Keep in Mind Regarding Indicative Prices?
It is essential for buyers to remember that the prices for power transformers can vary widely based on the factors mentioned above. Indicative prices provided by suppliers may not reflect the final cost due to potential fluctuations in material prices, changes in labor costs, and other market dynamics. Always seek detailed quotes and clarify the specifics of what is included in the price to avoid surprises during procurement.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing power transformer With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Solutions for Power Transformers
In the realm of electrical energy transmission and distribution, power transformers are crucial for adjusting voltage levels and ensuring efficient power delivery. However, several alternative solutions and technologies exist that can also serve similar purposes. Understanding these alternatives allows B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific operational needs, budget constraints, and long-term objectives.
Comparison Table of Power Transformers and Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Power Transformer | Autotransformer | Voltage Regulator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency and reliability | Very efficient, especially for small voltage adjustments | Moderate efficiency, effective for steady voltage supply |
| Cost | Generally high initial investment | Lower initial cost compared to power transformers | Moderate cost; varies by application |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized installation | Easier to install than traditional transformers | Simple installation; often plug-and-play |
| Maintenance | Requires regular maintenance checks | Lower maintenance needs; simpler design | Minimal maintenance required |
| Best Use Case | Large-scale power transmission | Medium voltage applications and interconnections | Localized voltage stabilization in sensitive equipment |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What are Autotransformers and Their Advantages?
Autotransformers are a cost-effective alternative to traditional power transformers, particularly suitable for applications requiring voltage adjustments of less than 2:1. They utilize a single winding to serve as both the primary and secondary, which makes them more compact and lighter. The main advantages include lower costs and reduced copper losses due to their design. However, they do not provide galvanic isolation, which may pose risks in sensitive applications.
How do Voltage Regulators Function?
Voltage regulators are devices designed to maintain a constant output voltage regardless of variations in input voltage or load conditions. They are particularly beneficial for protecting sensitive electronic equipment from voltage fluctuations. Voltage regulators are typically simpler to install and maintain than power transformers, making them an attractive option for smaller applications or localized systems. However, their performance is limited to specific voltage ranges, and they may not be suitable for high power applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When deciding between power transformers and their alternatives, B2B buyers must consider various factors such as performance requirements, budget constraints, and specific application needs. Power transformers excel in high-voltage applications and large-scale power distribution, whereas autotransformers and voltage regulators offer more cost-effective and straightforward solutions for specific situations. By evaluating these aspects, buyers can select the most suitable technology that aligns with their operational goals and enhances overall efficiency in their electrical systems.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for power transformer
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Power Transformers?
When considering the procurement of power transformers, understanding their technical specifications is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and reliability. Below are some essential technical properties that international B2B buyers should be familiar with:
1. Material Grade
The materials used in the construction of power transformers, particularly the core and windings, significantly influence their efficiency and durability. Common materials include silicon steel for the core, which minimizes energy loss, and copper or aluminum for the windings. High-grade materials ensure lower losses and longer operational life, which are critical for reducing total cost of ownership.
2. Insulation Class
Insulation class refers to the temperature rating of the insulating materials used in the transformer. Common classes include A, B, F, and H, which correspond to maximum temperature limits (e.g., 105°C, 130°C, 155°C, and 180°C, respectively). Selecting the right insulation class is vital for ensuring that the transformer can withstand operational conditions without overheating, thereby enhancing reliability and longevity.
3. Voltage Rating
The voltage rating specifies the maximum voltage that the transformer can handle safely. This specification is critical for ensuring compatibility with the electrical grid and preventing equipment failure. B2B buyers must ensure that the voltage rating aligns with their operational requirements to avoid potential damage and costly downtime.
4. Efficiency Rating
Efficiency is a key performance metric for power transformers, typically expressed as a percentage. A higher efficiency rating indicates lower energy losses during operation, which translates to cost savings over time. For businesses aiming to optimize operational costs, selecting a transformer with a high efficiency rating is essential.
5. Impedance
Impedance affects voltage regulation and short-circuit performance. It is measured in ohms and is critical for matching the transformer with the electrical network. Understanding impedance helps buyers ensure that the transformer can handle load variations without compromising performance, thereby enhancing system stability.
6. Cooling Method
Power transformers can be oil-cooled or air-cooled, impacting their size, efficiency, and operational environment. Oil-cooled transformers generally offer better heat dissipation, making them suitable for high-capacity applications. Buyers should consider the cooling method in relation to their operational environment to prevent overheating and ensure optimal performance.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Power Transformer Industry?
Familiarity with industry-specific terminology can streamline negotiations and purchasing processes for B2B buyers. Here are some common trade terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is essential for buyers looking for quality assurance and reliable supply chains, particularly when sourcing transformers from different manufacturers.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers as it affects inventory management and cash flow. Knowing the MOQ can help businesses plan their purchasing strategy and avoid overstocking or understocking.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that an organization sends to suppliers to request pricing and other details for specific products or services. Crafting a precise RFQ can help buyers obtain accurate quotations, facilitating better comparisons between suppliers and ensuring they secure the best deal.
4. Incoterms
Incoterms, or International Commercial Terms, are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC). They clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding Incoterms is vital for international B2B transactions, as they mitigate risks and ensure that both parties understand their obligations.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the amount of time it takes from placing an order to the delivery of the product. This term is important for procurement planning, as longer lead times may affect project timelines and operational efficiency. Buyers should inquire about lead times when negotiating with suppliers to ensure timely delivery.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing power transformers, ultimately contributing to the efficiency and reliability of their electrical systems.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the power transformer Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in the Power Transformer Sector?
The power transformer market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for electricity in emerging economies, particularly in Africa and South America. The global push for renewable energy sources is also propelling the need for advanced transformer technologies that can efficiently handle fluctuating loads and voltage levels. With the rise of smart grids and automation in energy management, B2B buyers are increasingly looking for innovative solutions that offer enhanced monitoring and control capabilities.
In Europe, especially in countries like Italy and France, there is a notable trend towards the integration of digital technologies in power transformers. This includes the use of IoT-enabled devices that facilitate real-time data analysis and predictive maintenance, reducing operational downtime and improving efficiency. Additionally, the demand for compact and modular transformer designs is rising, as they are easier to integrate into existing infrastructures and can be tailored to specific applications.
Sourcing strategies are evolving as international B2B buyers prioritize long-term partnerships with manufacturers that can provide reliable, high-quality products. Companies are also increasingly interested in suppliers that can offer comprehensive service packages, including installation, maintenance, and technical support, which can significantly reduce total cost of ownership.
How Important is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in the Power Transformer Industry?
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration in the power transformer sector, as stakeholders increasingly recognize the environmental impacts associated with transformer production and operation. B2B buyers are now prioritizing suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices and can demonstrate a commitment to reducing their carbon footprint. This includes utilizing environmentally friendly materials in manufacturing processes and minimizing waste through efficient production techniques.
The importance of ethical sourcing cannot be overstated. Buyers are seeking suppliers that comply with international standards for labor rights and environmental protection. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety are becoming essential criteria in supplier selection. Furthermore, the use of ‘green’ materials, such as biodegradable insulating oils and recyclable components, is gaining traction, providing an added value proposition for environmentally-conscious businesses.
Investing in sustainability not only enhances brand reputation but also aligns with the global shift towards greener energy solutions, making it a strategic priority for international B2B buyers.
What is the Brief Evolution of Power Transformers in the B2B Context?
The evolution of power transformers can be traced back to the late 19th century, when the need for efficient electrical energy transmission became apparent. Initially, transformers were large and cumbersome, but advancements in materials and technology have led to the development of more compact and efficient models. The introduction of oil-cooled transformers in the mid-20th century allowed for better heat dissipation and improved performance in high-capacity applications.
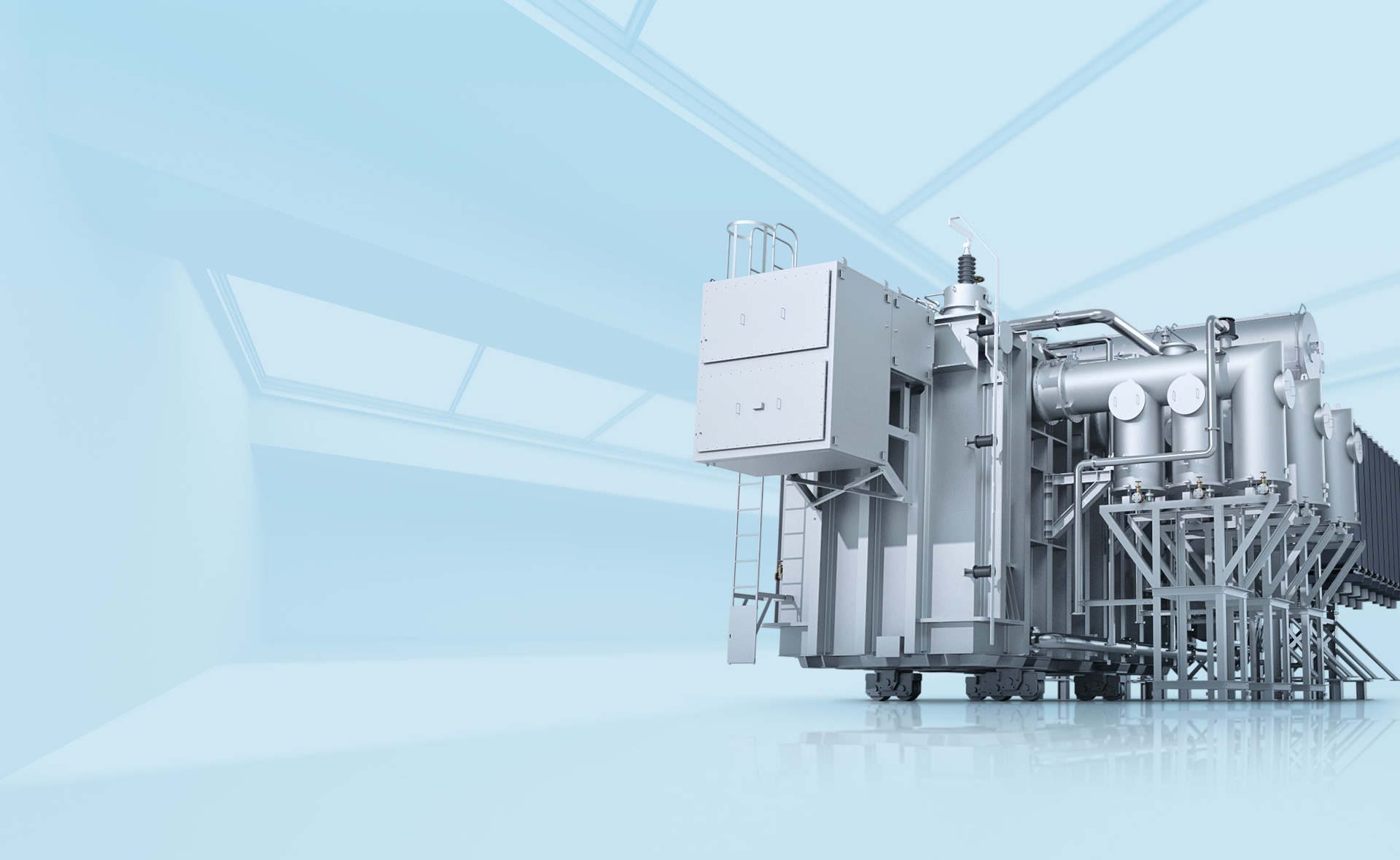
A stock image related to power transformer.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards digitalization and smart technologies. Modern power transformers are equipped with sensors and monitoring systems that provide real-time data, enabling predictive maintenance and enhancing operational efficiency. This transformation not only meets the demands of contemporary electrical grids but also supports the transition to renewable energy sources by facilitating better load management and integration of distributed energy resources.
As the market continues to evolve, B2B buyers must stay abreast of these changes to make informed sourcing decisions that align with their operational and sustainability goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of power transformer
-
How do I choose the right power transformer for my application?
Choosing the right power transformer involves understanding your specific application needs, such as voltage levels, phase requirements (single-phase or three-phase), and load characteristics. Consider factors like the transformer type (step-up or step-down), cooling method (oil-cooled or dry-type), and core design (core or shell type). Additionally, evaluate the environmental conditions and space availability for installation. Engaging with a knowledgeable supplier can help assess these requirements and ensure optimal performance. -
What are the key specifications to look for in a power transformer?
When sourcing a power transformer, focus on specifications such as voltage rating, power rating (in kVA or MVA), impedance, efficiency, and cooling method. It’s also essential to consider the transformer’s insulation class, noise levels, and dimensions. These specifications directly impact the transformer’s performance, durability, and suitability for your operational environment. Always request detailed technical documentation from suppliers to verify these specifications. -
How can I ensure the reliability of a power transformer supplier?
To ensure reliability, conduct thorough research on potential suppliers, including their industry reputation, years of experience, and certifications (e.g., ISO). Request references from previous clients and check for customer reviews and feedback. Additionally, assess their quality assurance processes and after-sales support. Engaging in direct communication with the supplier can also provide insights into their responsiveness and commitment to service. -
What customization options are available for power transformers?
Many manufacturers offer customization options to meet specific operational requirements. Common customizations include tailored voltage ratings, specialized cooling systems, and modifications in size or weight. It’s also possible to request features like enhanced insulation materials for harsh environments or additional safety devices. Discuss your needs with potential suppliers early in the procurement process to explore available customization options effectively. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for power transformers?
The MOQ for power transformers can vary significantly between manufacturers. Some suppliers may require a minimum order of several units, while others might accommodate single-unit orders, particularly for custom solutions. It’s advisable to clarify MOQs during initial discussions with suppliers, as this can impact your budgeting and project timelines. Understanding the MOQ will also help in assessing the supplier’s flexibility and willingness to cater to smaller projects.

A stock image related to power transformer.
-
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing power transformers internationally?
Payment terms can differ based on the supplier’s policies and the nature of the transaction. Common arrangements include partial upfront payments with the balance due upon delivery or payment in full before shipment. For international transactions, consider secure methods such as letters of credit or escrow services to mitigate risks. Always negotiate payment terms that align with your cash flow and project timelines. -
How do I ensure quality assurance during the procurement of power transformers?
To ensure quality assurance, establish clear specifications and standards before engaging suppliers. Request certifications, such as ISO 9001, and inquire about their quality control processes. It’s beneficial to conduct factory visits or audits if feasible. Additionally, consider requesting samples or trial units to assess performance before placing a larger order. Regular communication with the supplier throughout the production process can also help maintain quality standards. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing power transformers?
Logistics play a crucial role in the timely delivery of power transformers. Assess shipping options, including air freight and sea freight, based on cost and urgency. Ensure you understand the customs regulations and duties applicable in your country, as these can impact overall costs. Collaborate with logistics providers experienced in heavy equipment transport to manage the complexities of shipping, handling, and installation of transformers.

A stock image related to power transformer.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for power transformer
In the evolving landscape of the power transformer market, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical component for international B2B buyers. Understanding the diverse types of power transformers—such as step-up, step-down, single-phase, and three-phase—allows organizations to tailor their procurement strategies to meet specific operational needs. By leveraging insights into voltage adjustments, impedance matching, and the importance of galvanic isolation, buyers can enhance their energy efficiency and minimize operational risks.
The global demand for reliable power infrastructure continues to rise, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Buyers in these markets should prioritize sourcing from reputable manufacturers that comply with international standards and offer robust after-sales support. This approach not only ensures quality but also fosters long-term partnerships that can lead to innovation and cost savings.
Looking ahead, the power transformer market is poised for growth, driven by advancements in technology and a heightened focus on sustainable energy solutions. International B2B buyers are encouraged to adopt a proactive sourcing strategy that embraces these trends, ensuring their organizations remain competitive and responsive to future challenges. Engage with trusted suppliers today to secure your position in this dynamic market.