Master Alternating Current Power Supply: The Complete Guide (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for alternating current power supply
Navigating the complexities of sourcing an alternating current power supply can be daunting for international B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets like Nigeria and Colombia. The challenge lies not just in selecting the right technology, but also in ensuring that the chosen solution meets both operational needs and local regulatory standards. This comprehensive guide addresses these challenges by exploring various types of AC power supplies, their applications across different industries, and essential factors for supplier vetting.
In this guide, you will discover critical insights into the technical specifications of alternating current power supplies, including performance metrics such as voltage, frequency, and phase characteristics. Additionally, we delve into cost considerations, helping you understand the total cost of ownership, including installation and maintenance expenses. The guide also emphasizes the importance of aligning with reputable suppliers who can provide reliable products and support tailored to your regional context.
Empowering informed purchasing decisions is at the heart of this guide, aimed specifically at B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By equipping you with the knowledge to navigate the global market effectively, this resource ensures that your organization can harness the benefits of efficient power supply solutions, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and competitiveness in your sector.
Understanding alternating current power supply Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear AC Power Supply | Simple design, transformer-based, low noise output | Audio equipment, laboratory testing | Pros: Reliable, low ripple; Cons: Less efficient, bulkier. |
| Switching AC Power Supply | High efficiency, compact size, uses high-frequency switching | Telecommunications, computer systems | Pros: Lightweight, energy-efficient; Cons: Higher EMI, complexity. |
| Three-Phase AC Power Supply | Delivers three-phase power, higher efficiency for large loads | Industrial machinery, large-scale manufacturing | Pros: Balanced load, reduced losses; Cons: More complex setup. |
| Single-Phase AC Power Supply | Common household supply, simple design, lower power capacity | Residential applications, small businesses | Pros: Easy installation, cost-effective; Cons: Limited power output. |
| Programmable AC Power Supply | Adjustable output frequency and voltage, advanced features | Research and development, testing environments | Pros: Versatile, precise control; Cons: Higher cost, requires expertise. |
What are the Characteristics of Linear AC Power Supplies?
Linear AC power supplies are characterized by their straightforward design, which involves a transformer to step down voltage before rectification and filtering. They are primarily used in applications requiring low noise, such as audio equipment and laboratory testing. B2B buyers should consider their reliability and low ripple output, but also note their inefficiency and bulkiness compared to other types. For businesses prioritizing audio fidelity or sensitive measurements, a linear supply may be the ideal choice.
How Do Switching AC Power Supplies Work?
Switching AC power supplies utilize high-frequency switching techniques to convert power, resulting in higher efficiency and a more compact form factor. They are commonly found in telecommunications and computer systems, where space and energy savings are critical. Buyers should weigh the benefits of their lightweight design and energy efficiency against potential electromagnetic interference (EMI) and the complexity of the circuit. For tech-oriented businesses, the advantages often outweigh the drawbacks.
What are the Benefits of Three-Phase AC Power Supplies?
Three-phase AC power supplies are designed to provide a stable and efficient power source for industrial applications, supporting large machinery and manufacturing processes. They are distinguished by their ability to distribute power evenly across three conductors, reducing losses and improving performance. B2B buyers in manufacturing sectors should consider the reduced operational costs and improved efficiency, although the complexity of installation and maintenance may require specialized skills.
Why Choose Single-Phase AC Power Supplies?
Single-phase AC power supplies are the standard for residential and small commercial applications, providing sufficient power for basic needs. Their simple design allows for easy installation and cost-effectiveness, making them an attractive option for small businesses and home use. However, buyers should be aware of their limitations in power output, which might not suffice for larger equipment or operations. For businesses with straightforward power needs, single-phase supplies are a practical choice.
What are the Advantages of Programmable AC Power Supplies?
Programmable AC power supplies offer advanced features, allowing users to adjust output frequency and voltage according to specific testing requirements. They are particularly useful in research and development environments where precise control is necessary. B2B buyers should consider the flexibility and versatility of these supplies, though they typically come at a higher price point and may require technical expertise to operate effectively. For companies engaged in rigorous testing, the investment can lead to significant advantages in product development.
Key Industrial Applications of alternating current power supply
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Alternating Current Power Supply | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Powering Industrial Machinery | Ensures consistent operation of machines, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. | Voltage stability, compatibility with existing systems, and local support services. |
| Telecommunications | Supporting Data Centers | Provides reliable power for servers and network equipment, minimizing outages. | Scalability for future needs, efficiency ratings, and compliance with local regulations. |
| Construction | Operating Heavy Equipment | Powers cranes, mixers, and other heavy machinery on-site, enhancing project efficiency. | Power output requirements, portability, and durability in harsh environments. |
| Agriculture | Running Irrigation Systems | Facilitates consistent water supply for crops, increasing yield and efficiency. | Energy efficiency, adaptability to varying power sources, and maintenance support. |
| Healthcare | Supplying Medical Equipment | Ensures reliable operation of critical devices, improving patient care and safety. | Compliance with health standards, reliability, and emergency backup options. |
How is Alternating Current Power Supply Used in Manufacturing?
In the manufacturing sector, alternating current (AC) power supplies are essential for powering industrial machinery such as conveyor belts, robotic arms, and CNC machines. These systems require stable voltage to operate efficiently, and any fluctuations can lead to production delays or equipment damage. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing AC power supplies that can handle local voltage variations and comply with regional standards is crucial. Additionally, having local technical support and maintenance services can significantly reduce downtime and enhance operational reliability.
What Role Does AC Power Supply Play in Telecommunications?
Telecommunications infrastructure relies heavily on AC power supplies to support data centers, which host servers and networking equipment. A reliable AC power supply ensures uninterrupted service, minimizing the risk of outages that can lead to significant financial losses. For B2B buyers in the Middle East and Europe, it is important to consider the scalability of power solutions to accommodate future growth in data demands. Compliance with regional energy efficiency standards and the ability to integrate with existing systems are also critical factors in the sourcing process.
How is AC Power Supply Essential for Construction Projects?
In the construction industry, AC power supplies are vital for operating heavy machinery such as cranes, concrete mixers, and power tools. These machines require a stable power source to function optimally, especially on large job sites where power demands can fluctuate. Buyers from Europe and Africa should prioritize sourcing AC power systems that offer portability and ruggedness to withstand challenging site conditions. Additionally, ease of maintenance and support services are key considerations to ensure continuous operation throughout the project lifecycle.
In What Ways Does AC Power Supply Support Agriculture?
Agricultural operations utilize AC power supplies to run irrigation systems that are crucial for crop management. Reliable AC power enables consistent water delivery, which is essential for maximizing yield and minimizing waste. For international buyers in regions like South America, it is important to consider energy-efficient solutions that can adapt to varying power sources, especially in remote areas. Maintenance support and local availability of parts can also enhance the sustainability of agricultural operations.
How Does AC Power Supply Enhance Healthcare Services?
In the healthcare sector, alternating current power supplies are critical for the operation of medical equipment such as imaging devices, monitors, and surgical tools. A reliable power source ensures that these devices function correctly, directly impacting patient care and safety. For B2B buyers in Africa and the Middle East, sourcing AC power supplies that comply with stringent health regulations is essential. Additionally, options for backup power solutions can provide an extra layer of security, ensuring that critical equipment remains operational during power outages.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘alternating current power supply’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Power Supply Leading to Equipment Malfunction
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face challenges with inconsistent power supply when dealing with alternating current (AC) systems. This inconsistency can be particularly problematic in regions like Africa and parts of South America, where power outages or fluctuations in voltage can lead to equipment malfunction. For instance, a manufacturing plant relying on AC power may experience downtime or damage to sensitive machinery due to voltage spikes or drops, resulting in costly repairs and lost productivity.
The Solution:
To mitigate the impact of inconsistent power supply, it is crucial to invest in high-quality AC power supplies equipped with voltage regulation features. Buyers should look for products that offer automatic voltage regulation (AVR) to ensure stable output despite input fluctuations. Additionally, sourcing power supplies from reputable manufacturers that provide robust warranties and customer support can further ensure reliability. Implementing backup solutions such as uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) can also help maintain operations during outages, providing a buffer that protects sensitive equipment from sudden power loss.
Scenario 2: Complex Installation and Integration Challenges
The Problem:
Another significant pain point for B2B buyers is the complexity of installing and integrating alternating current power supplies into existing systems. In industries such as telecommunications or data centers, integrating new power supplies with legacy systems can be daunting. Misalignment in specifications can lead to operational inefficiencies, increased installation costs, and extended project timelines, which can be particularly frustrating for businesses aiming to optimize their operations.
The Solution:
To streamline the installation process, it’s essential to conduct a thorough compatibility assessment prior to purchasing any AC power supply. Buyers should collaborate with manufacturers or suppliers who offer detailed technical support and installation services. Additionally, utilizing modular AC power supply systems can facilitate easier integration, as they allow for incremental upgrades without extensive overhauls of existing infrastructure. Providing training for staff on the new systems can also reduce integration time and foster a smoother transition.
Scenario 3: Lack of Awareness About Energy Efficiency Standards
The Problem:
Many B2B buyers are not fully aware of the energy efficiency standards applicable to alternating current power supplies, which can lead to poor purchasing decisions. In regions like Europe and the Middle East, where regulations are increasingly focused on sustainability, failing to comply with energy efficiency standards can result in fines and increased operational costs. This lack of awareness can also hinder a company’s ability to promote its commitment to sustainability, which is an important factor for many customers today.
The Solution:
To address this issue, B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing AC power supplies that meet or exceed international energy efficiency standards such as ENERGY STAR or IEC 62040-3. Engaging with suppliers who provide clear documentation on the energy performance of their products is crucial. Additionally, conducting regular training sessions for procurement teams on the latest regulations and energy-efficient technologies can empower them to make informed decisions. By investing in energy-efficient power supplies, companies not only comply with regulations but also benefit from long-term cost savings through reduced energy consumption.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for alternating current power supply
What Are the Key Materials Used in Alternating Current Power Supply?
When selecting materials for alternating current (AC) power supplies, it is crucial to consider properties that directly impact performance, durability, and compliance with international standards. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the manufacturing of AC power supplies, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
Copper: The Preferred Conductor for AC Power Supplies
Key Properties: Copper boasts excellent electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and corrosion resistance. It can handle high temperatures without significant degradation, making it ideal for power applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of copper is its superior conductivity, which leads to lower energy losses in transmission. However, copper is more expensive than alternatives like aluminum, and its extraction and processing can have significant environmental impacts.
Impact on Application: Copper’s high conductivity ensures efficient power transmission, which is critical for applications requiring minimal energy loss. It is compatible with various media, including air and oil, used in cooling systems.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM B170 (for copper) is essential. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should also consider the availability of copper and its price volatility.
Aluminum: A Cost-Effective Alternative
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and has good electrical conductivity, though not as high as copper. It is also resistant to corrosion, particularly when treated with anodization.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of aluminum is its lower cost and weight compared to copper, making it easier to handle and install. However, aluminum has a higher electrical resistance, which can lead to increased energy losses.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is commonly used in overhead power lines and some transformer applications. Its compatibility with various insulating materials makes it versatile in different environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the relevant standards, such as ASTM B231 for aluminum conductors. In regions like the Middle East, where high temperatures are prevalent, ensuring that aluminum is adequately treated to resist corrosion is vital.
Steel: Structural Integrity and Support
Key Properties: Steel offers high tensile strength and durability, making it suitable for structural components in power supply systems. It is also resistant to impact and deformation.
Pros & Cons: The advantage of steel lies in its strength and ability to support heavy loads. However, it is prone to corrosion unless treated, and its weight can complicate installation.
Impact on Application: Steel is often used in the framework of power supply systems, including enclosures and mounting structures. Its compatibility with various protective coatings enhances its longevity in harsh environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM A36 for structural steel is important. Buyers in Europe may also need to consider EU regulations on material sourcing and environmental impact.
Thermoplastics: Insulation and Protection
Key Properties: Thermoplastics, such as PVC and nylon, are lightweight, flexible, and provide excellent electrical insulation. They can withstand a range of temperatures and are resistant to moisture.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of thermoplastics is their insulating properties, which are crucial for safety in electrical applications. However, they may not withstand extreme temperatures as well as metals, and their long-term durability can be a concern.
Impact on Application: Thermoplastics are widely used for insulation of wires and connectors in AC power supplies. Their compatibility with various chemicals and moisture makes them suitable for diverse environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards, such as UL 94 for flammability, is essential. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should consider the availability of high-quality thermoplastics that meet these standards.
Summary Table of Material Selection for AC Power Supply
| Material | Typical Use Case for Alternating Current Power Supply | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Conductors in power cables and transformers | Superior conductivity | High cost and environmental impact | High |
| Aluminum | Overhead power lines and some transformers | Cost-effective and lightweight | Higher resistance leads to losses | Medium |
| Steel | Structural components and enclosures | High strength and durability | Prone to corrosion, heavy weight | Medium |
| Thermoplastics | Insulation for wires and connectors | Excellent electrical insulation | May not withstand extreme temperatures | Low |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for alternating current power supplies, emphasizing the importance of aligning material properties with application requirements and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for alternating current power supply
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing an Alternating Current Power Supply?
Manufacturing an alternating current (AC) power supply involves several critical stages, each essential for ensuring the final product meets industry standards and customer requirements. The main stages of the manufacturing process include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for AC Power Supply Manufacturing?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. This involves sourcing high-quality raw materials such as copper for windings, silicon steel for transformers, and various electronic components like capacitors and diodes. Suppliers should be evaluated based on their ability to provide materials that comply with international standards such as ISO 9001. Additionally, traceability of materials is vital, especially for international buyers from regions like Africa and South America, where sourcing reliability may vary.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in AC Power Supply Production?
Forming processes typically include stamping, winding, and machining. For instance, copper windings are created using automated winding machines that ensure precision and consistency. Transformers are stamped from silicon steel sheets, which are then assembled into cores. Utilizing techniques such as CNC machining can enhance the accuracy of component manufacturing, reducing the likelihood of defects.
How Is Assembly Conducted for AC Power Supplies?
The assembly stage is where the prepared components come together. This includes soldering connections, mounting components onto printed circuit boards (PCBs), and integrating transformers. Advanced techniques such as surface mount technology (SMT) may be employed to ensure compact designs and improved performance. It’s crucial for B2B buyers to inquire about the assembly methods used, as these can significantly impact the reliability and efficiency of the power supply.
What Finishing Techniques Are Important in AC Power Supply Manufacturing?
Finishing processes involve testing and quality checks to ensure the power supply operates correctly. This may include conformal coating to protect PCBs from environmental factors and painting or encapsulating enclosures for aesthetic and protective purposes. The final product should be visually inspected for defects, and any non-compliant units should be reworked or discarded.
What Are the Key Quality Assurance Standards for AC Power Supplies?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing of AC power supplies. Adhering to international standards such as ISO 9001 guarantees that manufacturers implement effective quality management systems. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE marking and API standards ensure that products meet safety and performance criteria.
What Are the QC Checkpoints in AC Power Supply Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are critical throughout the manufacturing process. Common QC checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Conducting inspections during the manufacturing process helps identify defects early, minimizing rework costs.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The finished product undergoes comprehensive testing, including functional tests and stress testing, to ensure it meets all operational specifications.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for AC Power Supplies?
Testing methods can vary but typically include:
- Electrical Testing: Verifying the output voltage, current, and frequency to ensure they meet specifications.
- Thermal Testing: Monitoring the temperature of the unit under load to prevent overheating issues.
- Load Testing: Assessing the power supply’s performance under different load conditions to ensure reliability in real-world applications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential. Buyers can take several steps to ensure that manufacturers maintain high-quality standards:
- Audits: Conduct regular audits of the manufacturing facility to assess compliance with quality standards.
- Quality Reports: Request detailed quality reports that document testing results and any corrective actions taken.
- Third-Party Inspections: Employ third-party inspection services to conduct independent evaluations of the manufacturing process and product quality.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
Understanding the nuances of quality control and certification is especially important for buyers from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements, which can affect compliance and certification processes. For example, CE marking is mandatory for products sold in the European Union, while specific certifications may be required in Middle Eastern markets.
Buyers should also consider the implications of local laws and regulations when sourcing AC power supplies. Engaging with local experts or consultants can provide insights into navigating these complexities and ensuring compliance with both local and international standards.
Conclusion
In-depth knowledge of manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices is crucial for international B2B buyers looking to source AC power supplies. Understanding each stage of the manufacturing process, the relevant quality control standards, and the methods to verify supplier quality can significantly enhance the procurement experience. By ensuring compliance with international standards and conducting thorough supplier evaluations, businesses can secure reliable power supply solutions that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘alternating current power supply’
To effectively procure an alternating current (AC) power supply, B2B buyers must navigate a complex landscape of technical specifications, supplier evaluations, and compliance requirements. This practical sourcing guide provides a clear checklist to ensure you make informed decisions that align with your business needs and operational standards.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding the technical requirements of your application is crucial. Determine the voltage, current, and frequency specifications needed for your equipment. Additionally, consider whether you need a single-phase or three-phase power supply, as this will significantly impact your choice of suppliers and products.
- Voltage Requirements: Ensure you know the peak and RMS voltage requirements for your application.
- Current Ratings: Assess the maximum current your devices will draw to avoid under or over-specifying the power supply.
Step 2: Identify Your Compliance Needs
Different regions have specific regulatory standards for electrical equipment. Familiarize yourself with the compliance requirements relevant to your target markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
- Safety Standards: Look for certifications such as CE, UL, or IEC that demonstrate compliance with safety regulations.
- Environmental Regulations: Consider energy efficiency ratings and environmental impact assessments to ensure sustainability.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making any commitments, it’s crucial to thoroughly vet potential suppliers. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from businesses in similar industries or regions.
- Supplier Reputation: Investigate online reviews and ratings to gauge the reliability of suppliers.
- Experience and Expertise: Assess the supplier’s experience in providing AC power supplies that meet your specific industry standards.
Step 4: Request and Compare Quotations
Once you have a shortlist of suppliers, request detailed quotations that include pricing, lead times, and warranties. This step is essential for financial planning and to ensure you’re getting the best value for your investment.
- Cost Breakdown: Look for transparency in pricing, including any additional fees for shipping or installation.
- Warranty and Support: Evaluate the warranty terms and the level of technical support offered post-purchase.
Step 5: Conduct Site Visits or Virtual Assessments
If possible, arrange site visits to the supplier’s facilities or conduct virtual assessments to get a firsthand look at their operations. This can provide insights into their production capabilities and quality control processes.
- Production Capacity: Ensure the supplier can meet your volume needs without compromising quality.
- Quality Assurance Processes: Inquire about their testing protocols to ensure reliability and performance.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Finalize Agreements
Once you’ve selected a supplier, negotiate terms of delivery, payment schedules, and service agreements. Clear communication at this stage can prevent misunderstandings and ensure smooth transactions.
- Payment Terms: Discuss options such as upfront payments, milestones, or credit terms that align with your cash flow.
- Delivery Expectations: Set clear timelines for delivery and installation to avoid operational disruptions.
Step 7: Implement Quality Control Measures
After procurement, establish quality control measures to monitor the performance of the AC power supply in your operations. This ensures that the product continues to meet your specifications and performs reliably.
- Performance Monitoring: Regularly assess the efficiency and output of the power supply.
- Feedback Loop: Create a system for reporting issues and implementing corrective actions when necessary.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can ensure they are well-prepared to source an AC power supply that meets their operational needs while also complying with regional standards and supplier capabilities.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for alternating current power supply Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Alternating Current Power Supplies?
Understanding the cost structure of alternating current (AC) power supplies is vital for B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets such as Africa and South America. The cost components typically include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
-
Materials: The primary materials for AC power supplies include semiconductors, capacitors, inductors, transformers, and PCB (Printed Circuit Board) components. The prices of these materials can fluctuate based on global supply chain dynamics, which can impact your sourcing costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly across regions. For instance, manufacturing in countries with lower labor costs can lead to substantial savings, but it’s essential to consider the trade-off between cost and quality.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with running the manufacturing facility, such as utilities, equipment maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient operations can help minimize overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Depending on the complexity of the AC power supply design, tooling costs can be considerable. Custom tooling is often necessary for specialized products, which can lead to higher initial costs but may yield better long-term savings.
-
Quality Control (QC): Investing in robust QC processes is crucial, especially for international buyers who require compliance with specific standards. The cost of implementing rigorous testing and certification processes can affect the overall pricing but is necessary to ensure reliability.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary based on the origin of the product and the chosen shipping method. Buyers should factor in duties, tariffs, and insurance, which can add to the total cost.
-
Margin: Supplier profit margins typically range from 10% to 30%, depending on the market dynamics and the supplier’s positioning. Understanding these margins can aid in negotiating better pricing.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of AC Power Supplies?
Several factors influence the pricing of AC power supplies beyond the basic cost components:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Higher order volumes often lead to reduced per-unit pricing. Negotiating favorable terms can significantly lower costs, especially for buyers in regions like Nigeria and Colombia where bulk purchasing is feasible.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized products may incur additional costs, impacting pricing. Buyers should clearly define their specifications to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (like ISO or CE) can increase costs but are essential for compliance and reliability. International buyers should assess the importance of certifications in their markets.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their experience and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the International Commercial Terms (Incoterms) is crucial for international transactions. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers, affecting total landed costs.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Negotiating AC Power Supply Prices?
International B2B buyers should consider the following strategies to optimize their purchasing process:
-
Leverage Negotiation: Don’t hesitate to negotiate prices based on order volume, long-term relationships, or competitive pricing from other suppliers. Building rapport can often yield better terms.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate suppliers based on their total cost of ownership (TCO), not just the upfront price. Consider long-term factors such as energy efficiency and maintenance costs.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware that prices may vary based on regional economic conditions and currency fluctuations. Buyers in Africa or South America should consider currency risks in their negotiations.
-
Conduct Market Research: Stay informed about market trends and competitor pricing. This knowledge can empower you during negotiations and help you secure favorable terms.
Disclaimer on Indicative Pricing
Prices for AC power supplies can fluctuate based on the aforementioned factors and market conditions. It is advisable for buyers to request quotes from multiple suppliers and conduct thorough due diligence to ensure they are making informed purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing alternating current power supply With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Alternating Current Power Supply
In the quest for efficient power solutions, businesses often consider various alternatives to alternating current (AC) power supplies. While AC power is widely used due to its ability to transmit electricity over long distances with minimal losses, other solutions may offer unique advantages depending on specific applications and requirements. This section will compare alternating current power supplies with two viable alternatives: direct current (DC) power supplies and hybrid power solutions.
| Comparison Aspect | Alternating Current Power Supply | Direct Current Power Supply | Hybrid Power Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency in long-distance transmission; supports multiple loads simultaneously. | Excellent for low-voltage applications; stable output for sensitive electronics. | Combines benefits of AC and DC; versatile for various applications. |
| Cost | Generally lower installation costs due to established infrastructure. | Can be cost-effective for specific applications, but may require additional conversion equipment. | Higher initial costs but can lead to long-term savings through efficiency. |
| Ease of Implementation | Well-understood technology with widespread availability of components and support. | Requires careful planning for conversion and compatibility; limited infrastructure in some regions. | Complexity in design and installation can be a barrier, depending on the application. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance due to robust infrastructure; however, transformers can require periodic checks. | Generally low maintenance, but power conversion equipment may need regular service. | Maintenance can be complex due to the dual nature of the system, requiring expertise. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for residential and commercial power distribution; effective for large-scale energy transmission. | Best suited for electronic devices, renewable energy systems, and applications requiring stable voltage. | Suitable for applications needing both AC and DC; beneficial in hybrid renewable systems. |
Understanding Direct Current Power Supply: Pros and Cons
Direct current (DC) power supplies are an alternative that offers stable output, making them ideal for sensitive electronic devices like computers and battery systems. The primary advantage of DC is its ability to provide a constant voltage, which is crucial for devices that require consistent power levels. However, DC systems may necessitate additional equipment for voltage conversion and can be less efficient for long-distance transmission compared to AC. Moreover, the existing infrastructure for AC power can limit the widespread adoption of DC systems in some regions.
Evaluating Hybrid Power Solutions: Advantages and Challenges
Hybrid power solutions, which combine both AC and DC technologies, are emerging as a versatile alternative. These systems enable businesses to leverage the strengths of both power types, providing flexibility for various applications. For instance, hybrid systems can integrate renewable energy sources like solar panels, which typically produce DC, with traditional AC grids. However, the complexity of these systems can result in higher installation costs and require specialized knowledge for maintenance and operation. Despite these challenges, hybrid solutions can lead to significant long-term savings by optimizing energy use.
A stock image related to alternating current power supply.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Power Solution for Your Business
When selecting a power supply solution, B2B buyers must consider their specific needs, including performance requirements, cost constraints, and ease of implementation. While alternating current power supplies remain the standard for many applications, direct current and hybrid solutions offer unique benefits that can enhance operational efficiency and adaptability. Assessing the long-term implications of each option, including maintenance and scalability, will empower buyers to make informed decisions that align with their business goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for alternating current power supply
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Alternating Current Power Supply?
Understanding the technical specifications of alternating current (AC) power supplies is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when making purchasing decisions. Here are some essential properties to consider:
1. Voltage Rating
Voltage rating indicates the maximum voltage that the AC power supply can handle safely. It is typically expressed in volts (V) and can vary widely depending on the application. For international buyers, knowing the voltage rating is critical as it affects compatibility with local power grids. Ensuring the equipment aligns with regional standards can prevent costly operational failures.
2. Current Rating
The current rating refers to the maximum amount of electrical current the power supply can deliver, measured in amperes (A). This specification is vital for determining the load capacity of the power supply. Buyers should ensure that the current rating matches the requirements of their equipment to avoid overheating and potential damage.
3. Frequency
Frequency, measured in hertz (Hz), represents the number of cycles per second in an AC waveform. Most countries operate on either 50 Hz or 60 Hz systems. For B2B buyers, understanding the frequency is essential, as mismatches can lead to inefficient operation or equipment failure.
4. Power Factor
The power factor is a measure of how effectively the power supply converts electrical power into useful work output. It ranges from 0 to 1, where a higher power factor indicates a more efficient system. For international buyers, a good power factor can lead to reduced energy costs and improved system reliability, making it a key specification to consider.
5. Efficiency Rating
Efficiency rating indicates how much of the input power is converted into usable output power, often expressed as a percentage. Higher efficiency ratings lead to lower energy consumption and reduced operational costs. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers that offer high-efficiency power supplies to optimize their long-term energy expenses.
6. Thermal Management
Thermal management refers to the power supply’s ability to dissipate heat generated during operation. Effective thermal management is crucial for maintaining performance and reliability. Buyers should look for power supplies with built-in cooling mechanisms or robust design features that promote heat dissipation, especially in high-load applications.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the AC Power Supply Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation. Here are some common terms that B2B buyers should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and ensure product quality, particularly when sourcing specialized components for AC power systems.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is important for budgeting and inventory planning, especially for international buyers who may face shipping and storage costs. Understanding MOQ can aid in negotiating better terms and managing supply chain logistics.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products or services. B2B buyers should utilize RFQs to gather competitive pricing and ensure they are receiving the best value for their purchases, especially when sourcing AC power supplies from multiple vendors.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms used in international trade. They clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding the delivery of goods. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers to manage shipping logistics and mitigate risks associated with international transactions.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. This term is critical for project planning and inventory management. Buyers should inquire about lead times when negotiating with suppliers to ensure timely delivery aligns with their operational needs.
6. Warranty Period
Warranty period refers to the duration during which a product is guaranteed to be free from defects. Understanding warranty terms can protect B2B buyers from unexpected costs and ensure long-term reliability of their power supply systems. Always review warranty details before finalizing a purchase.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting alternating current power supplies, ensuring compatibility and efficiency for their operations.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the alternating current power supply Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Alternating Current Power Supply Sector?
The alternating current (AC) power supply sector is experiencing significant transformation driven by technological advancements and shifting market demands. For international B2B buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial. The global push for renewable energy sources is one of the primary drivers, as many countries aim to reduce their carbon footprints. This trend is leading to increased investments in AC power supply systems that can efficiently integrate with renewable energy technologies like solar and wind.
Emerging B2B technologies, such as smart grids and energy storage solutions, are reshaping sourcing strategies. Companies are increasingly looking for suppliers who can provide advanced AC power systems that offer real-time monitoring, energy efficiency, and compatibility with IoT devices. Moreover, the demand for high-performance AC power sources is rising in sectors like telecommunications and data centers, where uninterrupted power supply is critical.
Additionally, the geopolitical landscape is influencing sourcing trends. For instance, trade agreements and tariffs can affect the availability and cost of AC power supply components. Buyers in regions such as Nigeria and Colombia should consider local suppliers who understand the regional market dynamics and can provide tailored solutions that meet local regulatory requirements.
How Important Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in the AC Power Supply Industry?
Sustainability is a growing concern in the AC power supply sector, with increasing pressure on companies to minimize their environmental impact. International B2B buyers are now prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices. This includes sourcing materials that are recyclable and produced through environmentally friendly processes.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers should seek suppliers that adhere to international standards for labor practices and environmental management. Certifications like ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 50001 (Energy Management) are indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability and can provide reassurance to buyers regarding the ethical sourcing of materials.
Moreover, the adoption of “green” technologies, such as energy-efficient transformers and power supplies, is becoming a key differentiator in the market. Suppliers that can demonstrate their ability to provide such technologies will likely gain a competitive edge. For B2B buyers, aligning with suppliers that prioritize sustainability not only enhances corporate responsibility but also aligns with the growing consumer demand for environmentally friendly products.
What Is the Brief Evolution of the AC Power Supply Sector?
The AC power supply sector has evolved significantly since the late 19th century when Nikola Tesla and George Westinghouse championed alternating current for electrical transmission. Initially, AC power systems were limited to basic applications, but advancements in transformer technology allowed for efficient long-distance electricity transmission.
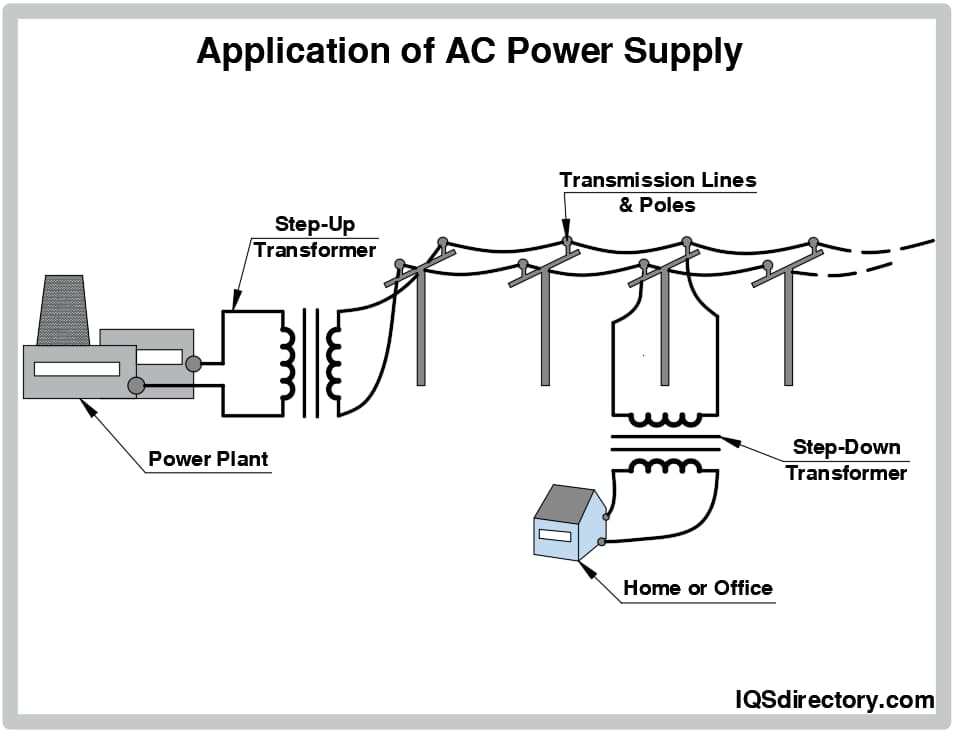
A stock image related to alternating current power supply.
In recent decades, the rise of digital technology and the internet of things (IoT) has further transformed the AC power supply landscape. Today, sophisticated power supply systems that integrate with smart technologies are becoming standard. This evolution is particularly relevant for B2B buyers looking to leverage modern solutions that enhance operational efficiency and sustainability in their power supply strategies.
As the sector continues to innovate, understanding these historical developments provides valuable insights into current trends and future opportunities for sourcing AC power supplies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of alternating current power supply
-
How do I determine the right alternating current power supply for my application?
Choosing the appropriate alternating current (AC) power supply involves assessing your specific needs, such as voltage requirements, power ratings, and load types. Start by identifying the input voltage from your local power grid and determine the required output voltage and current for your devices. Additionally, consider the frequency (typically 50Hz or 60Hz) relevant to your region. It’s also beneficial to consult with manufacturers or suppliers to ensure compatibility with your equipment. -
What are the key factors to consider when sourcing alternating current power supplies internationally?
When sourcing AC power supplies, key factors include supplier reliability, product certifications (like CE or UL), and compliance with local regulations. Research the manufacturer’s reputation through reviews and industry references. Additionally, assess logistical considerations such as shipping times and customs duties, especially for buyers in regions like Africa or South America, where import regulations can vary significantly. -
What should I know about payment terms when purchasing AC power supplies?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers. It’s crucial to clarify these terms upfront, including whether they accept letters of credit, advance payments, or payment upon delivery. For international transactions, consider using secure payment methods that protect both parties. Additionally, inquire about any payment milestones based on production stages, as this can help manage cash flow effectively. -
How can I ensure quality assurance when sourcing AC power supplies?
To ensure quality, look for suppliers who offer detailed product specifications and compliance certificates. Request samples for testing before placing a bulk order. Consider suppliers that conduct rigorous quality checks and provide warranties. Engaging third-party inspection services can also be beneficial, especially for large orders, to verify that products meet your standards before shipment. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) I should expect when sourcing AC power supplies?
The minimum order quantity (MOQ) often depends on the supplier’s production capabilities and your specific requirements. Many manufacturers set MOQs to ensure cost-effectiveness, which can range from a few units to hundreds. It’s advisable to discuss your needs directly with suppliers, as they may offer flexibility on MOQs for first-time customers or bulk orders. -
How do I vet suppliers for alternating current power supplies?
Vetting suppliers involves a comprehensive evaluation of their business practices and reputation. Start by checking their business licenses and certifications. Look for customer reviews and testimonials to gauge their reliability. Conduct virtual or in-person meetings to discuss your requirements and assess their responsiveness. Additionally, consider visiting their manufacturing facilities if possible, to better understand their production processes. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing AC power supplies?
Logistics is crucial for international purchases. Consider shipping options that best suit your timeline and budget, such as air freight for faster delivery or sea freight for cost savings. Ensure you understand the customs clearance processes in your country, which can affect delivery times. Collaborating with a freight forwarder can streamline logistics, helping you navigate paperwork and avoid delays. -
How can I customize my alternating current power supply to meet specific requirements?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for AC power supplies, including voltage levels, output configurations, and additional features like built-in protection mechanisms. To initiate customization, provide detailed specifications and discuss your needs with potential suppliers. Be prepared to engage in a collaborative design process, which may involve prototype testing before finalizing the product.

A stock image related to alternating current power supply.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for alternating current power supply
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers in AC Power Supply?
In conclusion, strategic sourcing in the realm of alternating current (AC) power supply is vital for international B2B buyers. By understanding the nuances of both linear and switching AC/DC power supplies, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance efficiency and reduce operational costs. Key factors such as voltage regulation, output stability, and compatibility with existing infrastructure should be prioritized when evaluating suppliers.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Supply Chain?
Leveraging strategic sourcing not only optimizes procurement processes but also fosters long-term partnerships with reliable manufacturers. This can lead to better pricing, improved service levels, and access to innovative technologies. Buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should actively seek suppliers that offer comprehensive solutions tailored to their unique market needs.
What’s Next for International B2B Buyers in AC Power Supply?
As the demand for energy-efficient solutions continues to rise, staying ahead of market trends will be crucial. Embrace the opportunity to engage with suppliers who prioritize sustainability and innovation. By doing so, you will not only ensure a robust supply chain but also contribute to a greener future. Take the next step today—evaluate your sourcing strategy and explore new partnerships that align with your business goals.