Define Broaching Machine: The Complete Buyer’s Guide (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for define broaching machine
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, sourcing a broaching machine that meets specific operational needs can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers. The broaching process is known for its precision and efficiency, making it essential for industries requiring intricate shapes and high-quality finishes. However, with a multitude of options available, understanding the various types of broaching machines, their applications, and the nuances of supplier selection is critical for making informed purchasing decisions.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of broaching machines, covering essential topics such as the different types—linear, rotary, surface, and internal broaching—as well as their respective applications across various sectors like automotive, aerospace, and general engineering. Additionally, we will explore vital aspects of supplier vetting, cost considerations, and maintenance practices that can enhance the longevity and efficiency of your investment.
By equipping B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe with actionable insights, this guide aims to empower you to navigate the global market effectively. Whether you’re in the UAE looking for advanced manufacturing solutions or in South America seeking cost-effective options, understanding the landscape of broaching machines will enable you to optimize your procurement strategy and drive operational success.
Understanding define broaching machine Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear Broaching | Utilizes a straight-line motion for cutting | Automotive, aerospace, machinery | Pros: High precision; efficient for internal cuts. Cons: Limited to linear shapes. |
| Rotary Broaching | Involves simultaneous rotation of tool and workpiece | Custom shapes, gears, and splines | Pros: Versatile; produces complex shapes in one pass. Cons: May require more setup time. |
| Surface Broaching | Cuts flat surfaces, often with a stationary broach | General engineering, appliance manufacturing | Pros: Excellent surface finish; efficient. Cons: Limited to surface applications only. |
| Pull Broaching | Broach is drawn through the workpiece | High-volume production, automotive parts | Pros: Efficient for vertical setups; consistent results. Cons: Requires robust machine design. |
| Push Broaching | Broach is pushed through the workpiece | Specialized applications, less common | Pros: Simpler setup for specific tasks. Cons: Not as widely applicable; limited tool options. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Linear Broaching Machines?
Linear broaching machines are designed for precision cutting using a straight-line motion. This method is particularly effective for producing internal features such as keyways and splines. Industries like automotive and aerospace frequently utilize linear broaching due to its ability to deliver high accuracy and efficiency in a single pass. When purchasing, buyers should consider the machine’s capacity for various workpiece sizes and the types of broaches available.
How Do Rotary Broaching Machines Differ from Other Types?
Rotary broaching machines stand out by employing simultaneous rotation of both the tool and the workpiece. This technique allows for the creation of intricate shapes, such as hexagons or custom profiles, making it ideal for applications in gear manufacturing and specialized components. Buyers should evaluate the machine’s adaptability to different shapes and its ability to handle various materials, as this can impact overall production efficiency.
What Are the Applications of Surface Broaching Machines?
Surface broaching machines are specifically designed to achieve smooth and precise finishes on flat surfaces. This method is commonly used in general engineering and appliance manufacturing, where surface quality is critical. Buyers should focus on the machine’s ability to handle different material types and its compatibility with various broach designs to ensure optimal performance in their specific applications.
What Makes Pull Broaching Machines Suitable for High-Volume Production?
Pull broaching machines are characterized by their ability to draw the broach through the workpiece, making them ideal for high-volume production environments, particularly in the automotive sector. This method ensures consistent results and is efficient for vertical setups. When considering a purchase, buyers should assess the machine’s structural integrity and the ease of fixture adjustments to accommodate different workpieces.
Why Are Push Broaching Machines Less Common in the Market?
Push broaching machines operate by pushing the broach through the workpiece, which is less common compared to pull broaching. While they can be beneficial for specialized applications, their limited versatility means they are not as widely adopted in the industry. Buyers should carefully consider whether their specific needs align with the capabilities of push broaching machines, as well as the availability of suitable broach tools.
Key Industrial Applications of define broaching machine
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Define Broaching Machine | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Internal keyway broaching for gears and shafts | High precision and reduced production time | Material compatibility, machine size, and tooling costs |
| Aerospace | External broaching of complex shapes in components | Enhanced performance and reduced weight | Certification requirements, tolerances, and lead times |
| Machinery Manufacturing | Surface broaching for flat surfaces on parts | Improved surface finish and dimensional accuracy | Broach design, material hardness, and maintenance support |
| Oil & Gas | Broaching for creating slots in pipe fittings | Increased reliability and lower failure rates | Environmental considerations, durability, and sourcing local suppliers |
| Agriculture Equipment | Broaching for producing fittings and connectors | Cost savings through efficient production | Customization options, scalability, and logistics support |
How is Broaching Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, broaching machines are essential for producing internal keyways in gears and shafts. This application allows manufacturers to achieve high precision in the machining of components that require intricate shapes and tight tolerances. By using broaching, companies can significantly reduce production time compared to traditional machining methods, enabling faster assembly and improved overall efficiency. International buyers should consider the compatibility of materials with broaching processes, the size of the broaching machine needed, and the costs associated with tooling to ensure optimal production outcomes.
What are the Aerospace Applications of Broaching Machines?
In aerospace manufacturing, broaching is commonly employed for external broaching of complex shapes in components such as brackets and housings. This method is favored for its ability to create lightweight parts that meet stringent performance standards. The precision achieved through broaching contributes to enhanced aerodynamics and fuel efficiency, which are critical in this industry. Buyers in the aerospace sector must be aware of specific certification requirements, the need for high tolerances, and the importance of timely lead times to maintain production schedules.
How Does Machinery Manufacturing Benefit from Broaching?
Machinery manufacturing relies on broaching machines to achieve superior surface finishes and dimensional accuracy on flat surfaces. This capability is crucial for components that require tight fits and functional performance. By utilizing surface broaching, manufacturers can streamline their processes, reducing the number of machining operations needed and ultimately lowering production costs. When sourcing broaching machines for this application, buyers should focus on broach design, the hardness of the materials being machined, and the availability of maintenance support to ensure long-term operational efficiency.
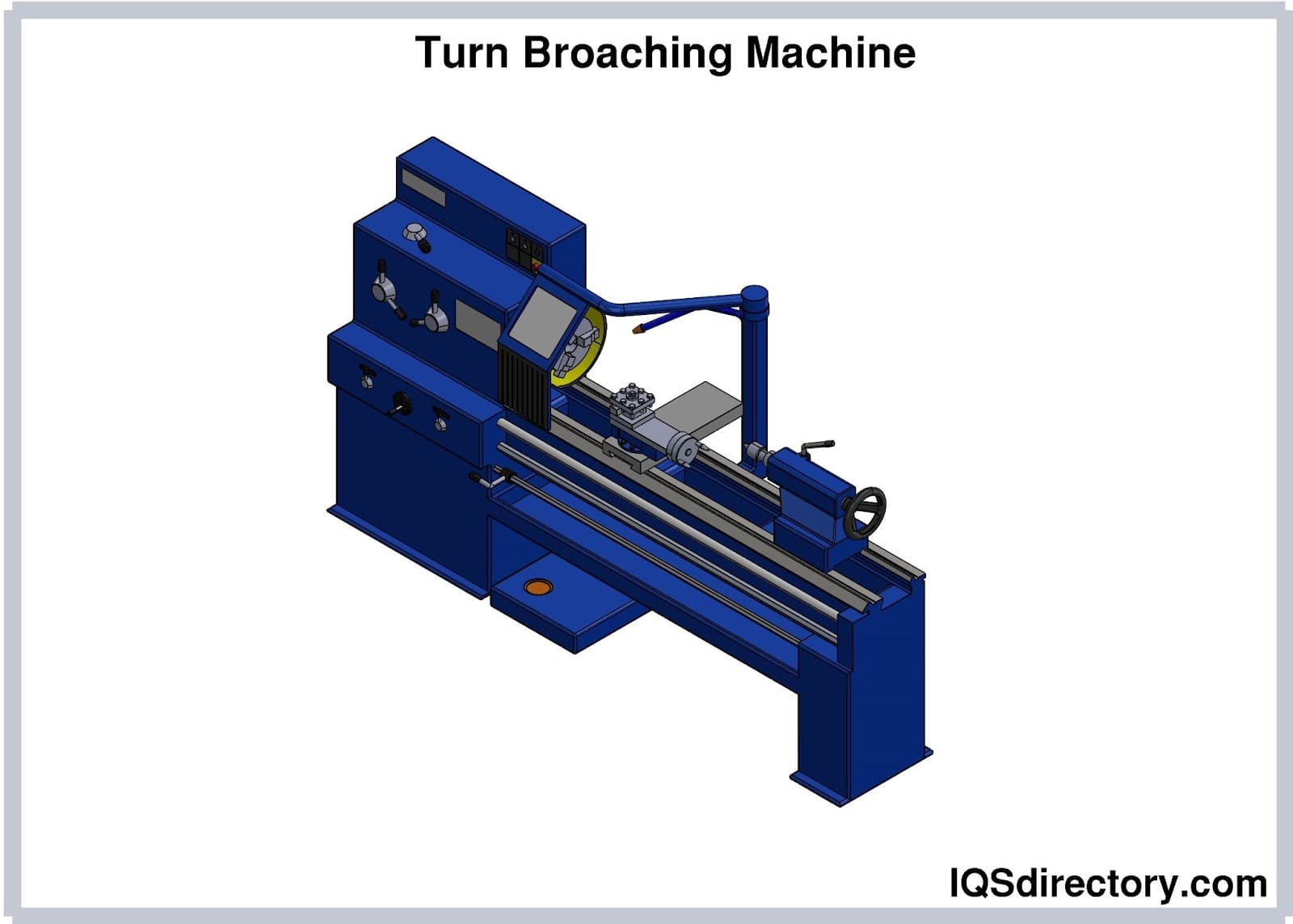
A stock image related to define broaching machine.
What Role Does Broaching Play in the Oil & Gas Sector?
In the oil and gas industry, broaching is utilized for creating slots in pipe fittings, which are essential for secure connections in high-pressure environments. The reliability of these fittings is paramount, as failures can lead to costly downtime and safety hazards. Broaching not only enhances the durability of these components but also contributes to lower failure rates. Buyers should take into account environmental considerations, the durability of the broaching tools, and the importance of sourcing local suppliers to mitigate logistical challenges.
How is Broaching Applied in Agriculture Equipment Manufacturing?
Broaching machines are vital in the agricultural equipment sector for producing fittings and connectors that require precise geometries. The efficiency of broaching allows manufacturers to save costs by reducing the time and materials needed for production. Buyers looking to invest in broaching technology should evaluate customization options available for specific applications, the scalability of the machines for varying production volumes, and the logistics support offered by suppliers to ensure smooth operations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘define broaching machine’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Selecting the Right Broaching Machine for Specific Needs
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with selecting the appropriate broaching machine that meets their specific production requirements. This challenge can stem from a lack of understanding of the different types of broaching machines available, such as linear, rotary, and surface broaching machines. Buyers may feel overwhelmed by the various options and end up purchasing a machine that does not fully align with their operational needs, leading to inefficiencies, increased costs, and wasted time.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, buyers should begin by conducting a thorough needs assessment. This involves identifying the types of materials they will be broaching, the complexity of the shapes required, and the volume of production. Engaging with a knowledgeable supplier who specializes in broaching machines can also provide valuable insights.
Buyers should request demonstrations or trials of different machines to evaluate their performance in real-world scenarios. When specifying their needs, they should consider factors such as the machine’s stroke length, speed, and compatibility with various broach types. Additionally, buyers should ensure that the machine can accommodate future production demands, allowing for scalability. This proactive approach not only ensures the purchase of the right machine but also enhances overall operational efficiency.
Scenario 2: High Maintenance Costs and Downtime
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face the issue of high maintenance costs and unplanned downtime associated with broaching machines. As these machines are critical for precision machining, any malfunction can halt production and lead to significant financial losses. Buyers may find themselves frequently investing in repairs or replacements of broaches, which can be expensive and time-consuming.
The Solution: To mitigate maintenance costs and downtime, buyers should implement a robust preventive maintenance program. This program should include regular inspections and servicing of the broaching machine to ensure all components are functioning optimally. Buyers should also keep a detailed log of machine performance and maintenance activities to identify patterns that may indicate potential issues.
Investing in high-quality broaches made from durable materials can also reduce long-term costs. Buyers should consider broaches that are specifically designed for the materials they are working with, as these will have a longer lifespan and require less frequent sharpening. Additionally, establishing relationships with suppliers who offer maintenance services and support can be invaluable. This proactive maintenance approach not only prolongs the life of the machine but also minimizes unexpected production interruptions.
Scenario 3: Lack of Skilled Operators
The Problem: A significant pain point for B2B buyers is the shortage of skilled operators capable of effectively running broaching machines. This skill gap can result in inefficient operations, increased error rates, and higher production costs. Buyers may struggle to find qualified personnel or may need to invest in training programs, which can divert resources away from core business activities.
The Solution: To address the lack of skilled operators, companies should invest in comprehensive training programs that focus on the specific operational requirements of broaching machines. This training should cover not only the technical aspects of operating the machinery but also best practices for tool selection and maintenance.
Additionally, buyers can collaborate with equipment suppliers who often provide training as part of their sales package. This partnership can ensure that operators are well-equipped to handle the machines safely and efficiently from the start. Implementing a mentorship program, where experienced operators train newer employees, can also foster a culture of knowledge-sharing within the organization. By prioritizing training and development, companies can build a skilled workforce that enhances productivity and reduces operational risks associated with inexperienced handling of broaching machines.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for define broaching machine
What Are the Key Materials for Broaching Machines?
When selecting materials for broaching machines, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that influence performance, durability, and cost. Below, we analyze four common materials used in broaching applications, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
How Does Steel Perform in Broaching Applications?
Key Properties: Steel, particularly high-speed steel (HSS) and alloy steel, is known for its excellent hardness and wear resistance. These properties enable it to withstand high temperatures and pressures during the broaching process.
Pros & Cons: Steel is durable and can be manufactured into various shapes, making it suitable for diverse applications. However, it can be costly, especially high-speed variants, and may require additional treatments to enhance corrosion resistance.
Impact on Application: Steel broaches are ideal for high-volume production of components requiring precise cuts, such as automotive parts. However, compatibility with corrosive media must be evaluated, as untreated steel can degrade in harsh environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards like ASTM for steel grades. In regions like the UAE and Europe, certifications for quality and performance are crucial.
What Role Does Carbide Play in Broaching?
Key Properties: Tungsten carbide is exceptionally hard and offers superior wear resistance, making it ideal for broaching operations that require high precision and durability.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of carbide is its longevity, often outlasting steel broaches in demanding applications. However, carbide is more brittle and can be prone to chipping under high stress, which may limit its use in certain scenarios.
Impact on Application: Carbide broaches excel in cutting hard materials, making them suitable for specialized applications in aerospace and military sectors. They are less effective in softer materials, where steel might be more appropriate.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific grades of carbide that meet their application needs. Compliance with local regulations regarding material safety and environmental impact is also essential.
How Effective Are Aluminum Alloys in Broaching?
Key Properties: Aluminum alloys are lightweight and exhibit good corrosion resistance. They are easier to machine than steel, which can lead to lower production costs.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of aluminum is its ease of machining, which allows for faster production times. However, aluminum is not as durable as steel or carbide, making it less suitable for high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum broaching is ideal for industries like consumer electronics and automotive, where weight reduction is critical. However, it may not perform well in high-temperature environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like South America and Africa should consider the availability of aluminum alloys that meet international standards. Compliance with ISO and local regulations is vital for ensuring quality.
What Are the Benefits of Using Plastic in Broaching?
Key Properties: Engineering plastics, such as polycarbonate and nylon, offer excellent chemical resistance and are lightweight.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of using plastics is their versatility and cost-effectiveness for low-volume production. However, they lack the strength and heat resistance of metals, limiting their use in high-load applications.
Impact on Application: Plastic broaches are suitable for producing non-metal components, such as in the electronics industry. They are not suitable for applications requiring high precision or durability.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the selected plastics comply with industry-specific standards, such as UL for electrical applications. Understanding local environmental regulations regarding plastic use is also critical.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Broaching Machines
| Material | Typical Use Case for define broaching machine | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Automotive parts, machinery components | High durability and versatility | Higher cost for high-speed variants | Medium |
| Carbide | Aerospace, military applications | Superior wear resistance | Brittle and prone to chipping | High |
| Aluminum Alloys | Consumer electronics, automotive lightweight parts | Easy to machine and lightweight | Less durable under high stress | Low |
| Plastic | Non-metal components, electronics | Cost-effective and versatile | Limited strength and heat resistance | Low |
By carefully considering these materials and their properties, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific application needs and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for define broaching machine
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of a Broaching Machine?
The manufacturing process of broaching machines involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure precision and efficiency. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers from diverse regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, make informed decisions when selecting suppliers.
How Is Material Prepared for Broaching Machines?
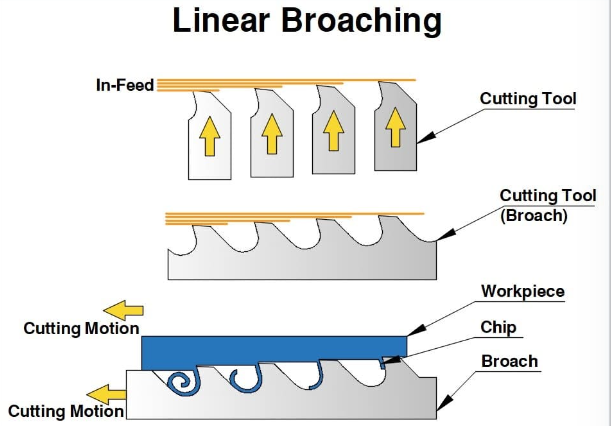
A stock image related to define broaching machine.
Material preparation is the first step in the manufacturing process. Typically, high-quality alloy steel or high-speed steel is chosen for its durability and cutting capabilities. The raw materials undergo rigorous inspection to ensure they meet specifications before being cut into manageable sizes. This stage is crucial, as the quality of the raw material directly impacts the performance of the broaching machine.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Broaching Machine Manufacturing?
The forming stage includes various machining processes, such as forging, casting, or CNC machining, to shape the machine components. Key components, such as the machine frame, broach holder, and drive mechanisms, must be manufactured with high precision. CNC machining is often employed for its ability to produce intricate geometries and tight tolerances, which are essential for the accurate functioning of the broaching machine.
How Is the Assembly of Broaching Machines Conducted?
Assembly involves piecing together the various components manufactured in the previous stages. Skilled technicians align and secure parts, ensuring they operate cohesively. This stage often includes integrating electrical components, hydraulic systems, and safety features, which are critical for the machine’s overall functionality. Proper assembly techniques help mitigate issues such as misalignment, which can lead to increased wear or failure during operation.
What Finishing Techniques Are Commonly Applied?
Finishing processes are the final touch in the manufacturing of broaching machines. These techniques can include surface grinding, heat treatment, and coating applications. Surface grinding improves the smoothness of critical components, while heat treatment enhances the hardness and wear resistance of the broach. Coatings, such as TiN (Titanium Nitride), are applied to reduce friction and improve tool life. Each of these finishing techniques contributes to the overall durability and efficiency of the broaching machine.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Broaching Machine Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing process of broaching machines. Adhering to international standards not only ensures product reliability but also builds trust with international buyers.
What International Standards Are Relevant for Broaching Machine Quality?
ISO 9001 is a widely recognized standard for quality management systems, ensuring consistent quality in products and services. Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking for European markets and API standards for the oil and gas sector may also apply. These certifications demonstrate compliance with safety and performance standards, which is crucial for buyers operating in regulated industries.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints During Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are established throughout the manufacturing process. These include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to verify they meet required specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring occurs during manufacturing to identify and rectify issues immediately.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The completed broaching machine undergoes a thorough inspection to ensure it meets all design and functional specifications.
Implementing these checkpoints helps ensure that each machine produced is of the highest quality.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Quality Assurance?
Testing methods for broaching machines can include dimensional inspections, performance testing, and fatigue testing. Dimensional inspections ensure that all components meet specified tolerances, while performance tests evaluate the machine’s operational capabilities. Fatigue testing assesses the durability of the machine under prolonged use, providing insights into its reliability and lifespan.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control is vital. Here are some actionable steps:
What Audit Practices Should Buyers Consider?
Conducting audits of potential suppliers can provide insight into their manufacturing and quality assurance processes. Buyers should request access to quality management documentation, including ISO certifications and internal QC reports. Regular audits help ensure that the supplier adheres to quality standards and continuously improves their processes.
How Important Are Third-Party Inspections?
Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased evaluation of a supplier’s quality practices. These inspections can occur at various stages of production, providing an additional layer of assurance. Buyers can request reports from these inspections to assess compliance with agreed-upon standards.
What Are the Quality Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers must be aware of the specific quality certifications required in their region. For instance, while ISO 9001 is recognized globally, certain markets may require additional certifications, such as CE marking for products sold in Europe. Understanding these nuances can help buyers avoid compliance issues and ensure that their suppliers meet all necessary regulations.
Conclusion
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for broaching machines are intricate and vital for ensuring product reliability. By understanding the stages of manufacturing and the importance of quality control, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing broaching machines. This knowledge not only aids in selecting the right suppliers but also enhances the overall efficiency and success of their operations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘define broaching machine’
In the competitive landscape of international B2B sourcing, understanding the intricacies of acquiring a broaching machine is essential. This guide offers a practical checklist for buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, to streamline their procurement process and ensure they make informed decisions.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the specifications required for the broaching machine. This includes the type of broaching (linear, rotary, or surface), the materials you intend to process, and the dimensions of the workpieces. Knowing your technical requirements helps narrow down options and ensures compatibility with your production needs.
Step 2: Research and Identify Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify reputable suppliers. Look for manufacturers with a strong track record in broaching machinery. Utilize industry directories, trade shows, and online platforms to compile a list of potential suppliers. Pay attention to their geographical location, as this can impact shipping costs and lead times.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications and Standards
Before proceeding, verify the certifications and standards upheld by potential suppliers. Look for ISO certifications, adherence to safety standards, and other industry-specific qualifications. These certifications not only reflect the quality of the machinery but also the reliability of the supplier in delivering consistent performance.
Step 4: Request Detailed Quotations
Reach out to selected suppliers and request detailed quotations. Ensure that the quotes include specifications, pricing, delivery timelines, and warranty information. Comparing multiple quotations will provide insights into market pricing and help identify the best value for your investment.
Step 5: Assess After-Sales Support and Maintenance
Evaluate the after-sales support offered by the suppliers. Reliable support can significantly impact the longevity and performance of the broaching machine. Inquire about maintenance services, availability of spare parts, and the responsiveness of the technical support team. A supplier with robust after-sales support can enhance your operational efficiency.
Step 6: Visit Supplier Facilities (If Possible)
If feasible, arrange to visit the facilities of shortlisted suppliers. Observing the manufacturing process and the working conditions can provide invaluable insights into the supplier’s operational capabilities and commitment to quality. Additionally, meeting the team in person can strengthen your business relationship.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Finalize the Purchase
Once you have evaluated all aspects, engage in negotiations to finalize the purchase terms. Discuss payment options, delivery schedules, and any potential discounts for bulk orders. Clear communication during this phase ensures that both parties are aligned, minimizing the risk of misunderstandings.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can approach the procurement of broaching machines with confidence, ensuring they select the right equipment and supplier to meet their specific needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for define broaching machine Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Broaching Machine Sourcing?
When sourcing a broaching machine, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The total cost encompasses several components:
-
Materials: The primary materials involved in broaching machines include high-speed steel or alloy steel for the broaches, and robust metals for the machine body. The choice of materials significantly impacts durability and performance, leading to variations in pricing.
-
Labor: Labor costs account for both the manufacturing of the broaching machine and the assembly processes. Skilled labor is necessary for precision machining and quality assurance, which can vary by region. In countries with a higher cost of living, labor costs are typically more expensive.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses associated with factory operations, such as utilities, equipment maintenance, and administrative costs. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize overhead and reduce overall pricing.
-
Tooling: The cost of specialized tooling, including broaches and fixtures, can be substantial. Buyers should consider the longevity and sharpening services of broaches, as well-maintained tools can extend the life of the investment.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the machine meets international standards requires robust QC processes, which may add to the cost. Certifications such as ISO and CE can influence pricing but provide assurance of quality and reliability.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary significantly based on the machine’s size and weight, as well as the shipping method chosen. For international buyers, understanding Incoterms is essential to manage these costs effectively.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include their profit margin in the pricing. This margin varies based on market conditions, competition, and the buyer’s negotiation capabilities.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Broaching Machine Costs?
Several factors can influence the price of broaching machines:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Ordering in bulk can lead to significant discounts. Suppliers often have MOQs that can affect pricing flexibility, especially for smaller buyers.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom machines designed for specific applications can increase costs. Buyers should balance the need for customization with the potential for increased pricing.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher-quality materials often come with a premium price. Additionally, machines certified for specific industry standards may cost more but can reduce long-term risks associated with failures.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and location of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers with a history of reliability may charge higher prices but offer better service and support.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms can prevent unexpected costs. Terms such as FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost Insurance and Freight) can influence the final price and the responsibilities of each party.
What Buyer Tips Can Help in Negotiating Broaching Machine Prices?
-
Negotiate Wisely: Engage in discussions about pricing, especially if purchasing in bulk or if you can offer a long-term contract. Leverage your position as a buyer to negotiate better terms.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership: Evaluate not just the purchase price, but also the long-term costs associated with maintenance, tooling, and operational efficiency. A higher upfront cost may lead to lower overall costs if the machine is more efficient and durable.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should consider currency fluctuations, import duties, and local regulations that can affect pricing. Building relationships with local distributors may also provide cost advantages.
-
Research Market Trends: Stay informed about market conditions and trends in the broaching machine industry. Knowing when to buy can help you secure better deals and pricing.
-
Seek Multiple Quotations: Always obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to compare pricing and service offerings. This can provide leverage in negotiations and help ensure you receive a competitive price.
Disclaimer on Pricing
Prices for broaching machines can vary widely based on the factors discussed above. It is advisable to conduct thorough research and obtain detailed quotations tailored to specific requirements before making purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing define broaching machine With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternatives for Broaching Machines
When it comes to precision machining, selecting the right method is crucial for achieving desired results in terms of efficiency, cost, and quality. While broaching machines are recognized for their ability to create intricate shapes with high accuracy, several alternative machining methods can also meet similar objectives. Understanding these alternatives allows B2B buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their specific operational needs.
Comparison Table of Broaching Machine Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Define Broaching Machine | CNC Machining | EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision for complex shapes | Versatile but variable precision | Extremely high precision for complex geometries |
| Cost | Moderate to high initial investment | Moderate initial costs; tooling can be expensive | High initial setup costs; operational costs vary |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled operators; setup can be complex | User-friendly with software; training needed | Specialized training required for operators |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed for broaches | Routine maintenance for machines | Minimal maintenance; consumable parts needed |
| Best Use Case | High-volume production of intricate internal/external features | Custom parts and prototypes across various industries | Precision components in aerospace, medical devices, and mold-making |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What are the advantages and disadvantages of CNC Machining compared to broaching machines?
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is a highly versatile alternative that excels in creating a wide range of components, from simple to complex geometries. Its user-friendly software interface allows for rapid adjustments and prototyping, making it ideal for both small and large production runs. However, while CNC machines can achieve high precision, they may not match the efficiency of broaching for specific intricate cuts, particularly in high-volume applications. Additionally, the tooling costs can add up, impacting the overall expense.
How does EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) compare to a broaching machine?
EDM is renowned for its ability to produce extremely precise components, especially for hard materials that are difficult to machine using traditional methods. It excels in creating complex shapes and fine details that may be challenging for both broaching and CNC machining. However, EDM requires a higher initial investment and can have longer production times due to its slower cutting process. The operational costs can also fluctuate based on the materials used and the need for consumables like electrodes.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Machining Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate machining solution hinges on several factors, including production volume, component complexity, and budget constraints. For B2B buyers, understanding the distinct advantages and limitations of each method—broaching, CNC machining, and EDM—will aid in aligning their choice with operational goals. Broaching machines stand out in high-volume applications requiring intricate shapes, while CNC offers flexibility for varied projects, and EDM provides unmatched precision for specialized components. By assessing specific needs and production capabilities, buyers can make strategic decisions that enhance productivity and cost-effectiveness.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for define broaching machine
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of a Broaching Machine?
Understanding the technical properties of a broaching machine is crucial for international B2B buyers looking to invest in high-precision metalworking equipment. Here are some key specifications that should be considered:
1. Material Grade of the Broach
The material used in the broach significantly affects its performance and longevity. High-speed steel (HSS) and carbide are common materials. HSS broaches are versatile and cost-effective, while carbide broaches offer superior wear resistance and longer life, making them ideal for high-volume production. Selecting the appropriate material grade can lead to reduced downtime and lower operational costs.
2. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension. In broaching, tight tolerances (e.g., ±0.001 inches) are critical for ensuring that parts fit correctly and function properly. For industries such as automotive and aerospace, where precision is non-negotiable, understanding the tolerance levels achievable with a specific broaching machine is vital for maintaining quality standards.
3. Broaching Stroke Length
The stroke length determines how far the broach can travel through the workpiece in a single pass. A longer stroke length allows for the machining of thicker materials or larger features, which is particularly beneficial for manufacturers dealing with diverse product sizes. Buyers should assess their production needs to select a machine with an appropriate stroke length to maximize efficiency.
4. Cutting Speed
Cutting speed, measured in surface feet per minute (SFPM), impacts the efficiency and finish quality of the broaching process. Different materials require different cutting speeds; for instance, aluminum can be machined faster than steel. Understanding the optimal cutting speeds for various materials can enhance productivity and reduce tool wear.
5. Fixture Types
Fixtures hold the workpiece in place during broaching operations. The choice of fixture affects the stability and accuracy of the machining process. Common types include dedicated fixtures, which are tailored for specific parts, and universal fixtures that can accommodate various shapes. Selecting the right fixture can lead to improved precision and reduced setup time.
6. Power Requirements
The power of a broaching machine, typically measured in horsepower (HP), indicates its capacity to perform heavy-duty cutting operations. Machines with higher power ratings can handle tougher materials and larger workloads. Buyers should match the power requirements of the machine with their production needs to ensure optimal performance.
What Are Common Trade Terminology and Jargon Related to Broaching Machines?
Navigating the world of broaching machines requires familiarity with specific trade terminology. Here are essential terms that B2B buyers should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the broaching industry, understanding whether a machine is an OEM product can affect warranty, support, and parts availability. This information is crucial for ensuring the reliability of equipment purchased.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For broaching machines and parts, knowing the MOQ can help buyers plan their budgets and inventory. This is particularly important for international buyers who may face higher shipping costs for small orders.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. When considering the purchase of a broaching machine, submitting an RFQ allows buyers to compare offers and negotiate better deals, ensuring they receive the best value for their investment.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in global trade. Understanding these terms helps buyers clarify shipping costs, risks, and delivery obligations when purchasing broaching machines from overseas suppliers.
5. CNC (Computer Numerical Control)
CNC refers to the automated control of machining tools by means of a computer. Broaching machines can be CNC-operated to improve precision and efficiency. Familiarity with CNC technology is essential for buyers looking to integrate modern manufacturing processes into their operations.
By comprehensively understanding these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when investing in broaching machines, ensuring they select equipment that meets their specific production needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the define broaching machine Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Define Broaching Machine Sector?
Market Overview & Key Trends: What Are the Global Drivers for Broaching Machines?
The define broaching machine sector is experiencing notable growth driven by advancements in precision engineering and the increasing demand for complex machining processes across various industries. International B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are witnessing a surge in applications for broaching technology in automotive, aerospace, and general manufacturing. The rising emphasis on automation and Industry 4.0 technologies is also shaping market dynamics, with buyers increasingly looking for smart machines that integrate with existing manufacturing systems.
Emerging trends such as the adoption of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology in broaching machines are enhancing precision and reducing production times. Furthermore, the integration of IoT (Internet of Things) capabilities allows for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, which can significantly lower operational costs. Buyers should also be aware of regional disparities in market maturity; for instance, European manufacturers tend to prioritize high-tech solutions, while buyers in Africa and South America may focus on cost-effective, reliable machines suitable for diverse applications.
Another critical trend is the shift towards customized solutions, where manufacturers are tailoring broaching machines to meet specific buyer requirements. This trend is particularly relevant for international buyers who often seek specialized features to address unique machining challenges in their local markets.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Decisions in the Broaching Machine Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a focal point for B2B buyers in the define broaching machine sector, influencing sourcing decisions significantly. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including energy consumption and waste generation, is under increasing scrutiny. Buyers are now looking for suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, such as using eco-friendly materials and minimizing emissions during production.
Ethical sourcing is equally important; suppliers that prioritize fair labor practices and maintain transparent supply chains are becoming preferred partners. For instance, certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety can help buyers identify responsible manufacturers.
Moreover, “green” materials, such as those derived from recycled sources or with lower carbon footprints, are gaining traction. Buyers should consider evaluating suppliers based on their environmental credentials and the sustainability of their manufacturing processes. This focus not only aligns with global sustainability goals but can also enhance brand reputation and customer loyalty in increasingly eco-conscious markets.
What Is the Evolution of Broaching Technology and Its Relevance to B2B Buyers?
The history of broaching technology dates back to the early 19th century when it was primarily used for producing internal shapes and features in metal components. Over the years, broaching machines have evolved significantly, transitioning from manual operations to highly automated CNC systems. This evolution has made broaching one of the most efficient machining processes available, capable of producing complex geometries with exceptional accuracy.
For B2B buyers, understanding the historical context of broaching technology can provide insights into its reliability and capabilities. As the industry continues to innovate with the integration of advanced materials and automation, buyers can leverage these advancements to improve production efficiency and reduce costs. The ongoing evolution of broaching machines ensures that they remain a vital component of modern manufacturing, catering to the increasing demands for precision and scalability in production processes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of define broaching machine
-
How do I choose the right broaching machine for my manufacturing needs?
Selecting the right broaching machine involves evaluating your specific production requirements, such as the types of materials you will be broaching and the complexity of the shapes you need. Consider the machine’s capacity, including its stroke length and speed, as well as the types of broaches it can accommodate (e.g., internal, external, rotary). Additionally, assess the machine’s reliability, maintenance needs, and compatibility with your existing production processes. It’s also beneficial to consult with suppliers who can provide insights based on industry best practices. -
What are the key features to look for in a broaching machine?
When sourcing a broaching machine, prioritize features such as versatility (ability to perform different broaching types), ease of operation, and accuracy of cuts. Look for machines with robust construction to ensure durability and longevity, as well as advanced control systems for precision. Additionally, consider the availability of customization options to meet specific production requirements and the machine’s compatibility with various broach sizes and shapes. -
What is the typical lead time for ordering a broaching machine?
Lead times for broaching machines can vary significantly based on the manufacturer, customization needs, and current demand. Generally, standard machines may take 4-8 weeks for delivery, while customized units could require 10-16 weeks or longer. It is advisable to discuss lead times directly with suppliers and factor in potential delays due to international shipping, especially when importing to regions like Africa or South America. -
How can I vet suppliers when purchasing a broaching machine?
To effectively vet suppliers, start by researching their reputation in the industry through reviews, testimonials, and case studies. Evaluate their experience in manufacturing broaching machines and their ability to provide after-sales support. Request references from past clients and inquire about warranty terms and service agreements. Additionally, consider visiting their facilities if possible or attending industry trade shows to assess their capabilities firsthand.
A stock image related to define broaching machine.
-
What are the common payment terms for international purchases of broaching machines?
Payment terms for international transactions typically include options such as advance payment, letters of credit, or installment payments based on milestones. It’s crucial to negotiate terms that provide security for both parties, ensuring you receive the machine as agreed while protecting the supplier’s interests. Always clarify the currency of payment and any additional costs, such as taxes or tariffs, that may apply during the importation process. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) when sourcing broaching machines?
Minimum order quantities can vary widely among suppliers, with some manufacturers requiring a MOQ for custom machines, while others may allow single-unit purchases for standard models. It’s important to discuss your specific needs with suppliers to understand their MOQ policies. If you are a smaller operation, consider seeking suppliers who specialize in low-volume orders or those willing to negotiate terms based on your capabilities and needs. -
How do I ensure quality assurance when sourcing a broaching machine?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed specifications and certifications for the broaching machine from your supplier. Inquire about their quality control processes and whether they conduct regular inspections during production. It can be beneficial to arrange for third-party inspections or audits, especially for international purchases, to verify compliance with industry standards. Establishing a clear agreement on performance benchmarks and post-sale support will also help maintain quality. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing a broaching machine?
When importing a broaching machine, consider factors such as shipping methods, customs clearance, and local regulations in your destination country. Evaluate the total landed cost, which includes shipping, tariffs, and handling fees. Partnering with a reliable logistics provider who understands international shipping can facilitate the process and help navigate any potential hurdles. Additionally, ensure you have adequate insurance coverage for the machine during transit to mitigate risks associated with damage or loss.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for define broaching machine
In the landscape of metalworking, understanding the strategic sourcing of broaching machines is crucial for international B2B buyers. Broaching offers unparalleled precision and efficiency, making it a valuable process for industries that demand high-quality components, such as automotive and aerospace. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who offer comprehensive support, including the selection of appropriate broaches, maintenance services, and tailored solutions for unique operational needs.
What Are the Key Considerations for Strategic Sourcing in Broaching Machines?
When sourcing broaching machines, consider factors such as machine capability, the range of broaches offered, and the supplier’s expertise in your specific industry. Additionally, evaluate logistics, support infrastructure, and the potential for long-term partnerships that can enhance your production capabilities.
How Can International Buyers Benefit from Strategic Sourcing?
For buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, strategic sourcing not only reduces costs but also fosters innovation and efficiency in manufacturing processes. As industries evolve, embracing the latest broaching technologies will be pivotal in maintaining competitiveness.
Looking ahead, the demand for advanced broaching solutions will only increase. Engage with reputable suppliers to explore innovative broaching technologies that can drive your business forward and meet the ever-growing market expectations. Take action today to secure your competitive edge in the global marketplace.