Discover 5 Types of Heat Exchangers to Cut Costs (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for types of heat exchangers
In today’s competitive global marketplace, international B2B buyers face the daunting challenge of sourcing the right types of heat exchangers that meet specific operational requirements while ensuring cost-effectiveness. With diverse applications ranging from HVAC systems to chemical processing, the selection of heat exchangers is critical for optimizing energy efficiency and enhancing system performance. This comprehensive guide is designed to navigate buyers through the complex landscape of heat exchangers, covering essential topics such as types, applications, supplier vetting, and cost considerations.
By exploring the various classifications of heat exchangers—including their construction, flow configurations, and cooling mediums—this guide empowers B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including countries like Mexico and the UAE), to make informed purchasing decisions. Each section is meticulously crafted to provide actionable insights that not only clarify the technical aspects of heat exchangers but also address practical concerns such as supplier reliability and pricing strategies.
With a focus on enhancing procurement strategies, this guide serves as a valuable resource for businesses aiming to improve their operational efficiencies and reduce waste. By leveraging the information presented here, buyers can confidently approach their sourcing decisions, ensuring they select the most suitable heat exchangers for their unique needs.
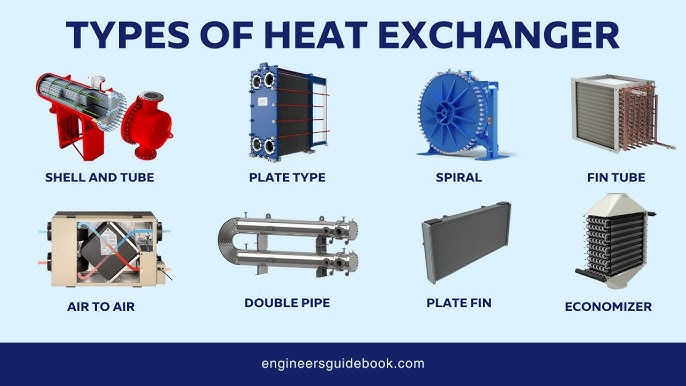
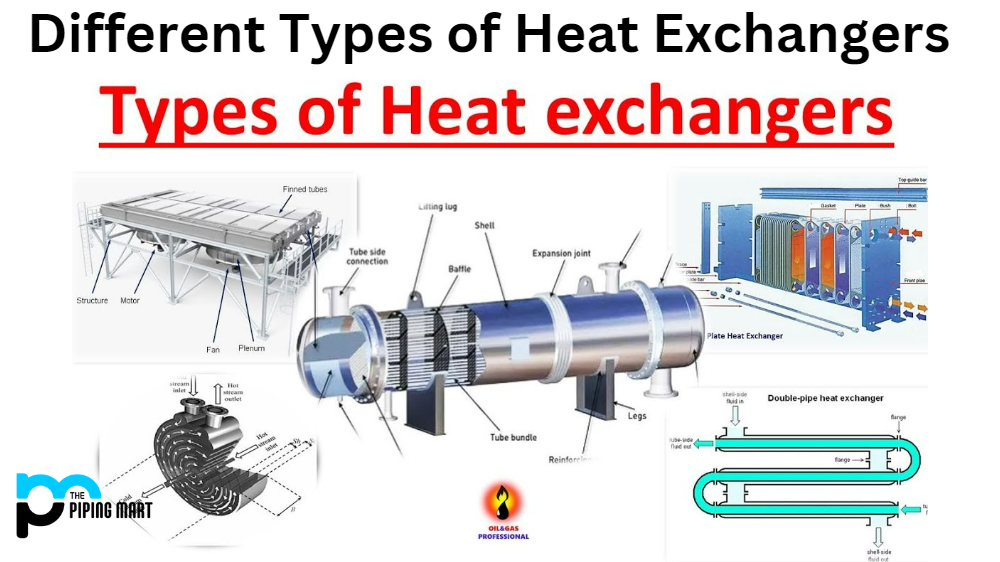
Understanding types of heat exchangers Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger | Comprises multiple tubes within a shell; versatile | Petrochemical, HVAC, food processing | Pros: High efficiency, adaptable to various fluids. Cons: Space-intensive, potential for fouling. |
| Plate Heat Exchanger | Thin plates stacked to facilitate heat transfer | Chemical processing, refrigeration | Pros: Compact design, high surface area. Cons: Limited pressure handling, potential for leakage. |
| Finned-Tube Heat Exchanger | Tubes with fins to increase surface area | Power generation, HVAC, automotive | Pros: Enhanced heat transfer, effective in low-temperature applications. Cons: Higher initial cost, maintenance complexity. |
| Double Pipe Heat Exchanger | Simple design with one pipe inside another | Small-scale applications, oil & gas | Pros: Easy to construct, cost-effective for low capacities. Cons: Limited efficiency, not suitable for large volumes. |
| Air-Cooled Heat Exchanger | Uses air to cool fluids, eliminating water use | HVAC, industrial cooling | Pros: Water conservation, low operational costs. Cons: Dependent on ambient conditions, less efficient in high humidity. |
What Are the Characteristics of Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers?
Shell and tube heat exchangers consist of a series of tubes housed within a cylindrical shell. This design allows for effective heat transfer between two fluids, with one fluid flowing through the tubes and the other around them. They are particularly suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature applications, making them a staple in petrochemical industries. B2B buyers should consider factors such as maintenance requirements and potential fouling, which can impact efficiency and operational costs over time.
How Do Plate Heat Exchangers Stand Out?
Plate heat exchangers utilize thin plates to create a large surface area for heat transfer while maintaining a compact footprint. This design is highly effective in applications requiring efficient heat exchange, such as chemical processing and refrigeration. Buyers should evaluate the material compatibility and pressure ratings, as these units may not handle extreme pressures as well as shell and tube designs. The compact nature also means they can be easier to clean and maintain, offering long-term operational benefits.
What Are the Benefits of Finned-Tube Heat Exchangers?
Finned-tube heat exchangers are designed with extended surfaces (fins) that maximize heat transfer efficiency, particularly in low-temperature environments. They are widely used in power generation and HVAC applications. For B2B buyers, the advantages include enhanced heat transfer rates, which can lead to energy savings. However, they come with a higher upfront investment and may require more intricate maintenance due to the fin structure, which can accumulate debris over time.
Why Choose Double Pipe Heat Exchangers for Small Applications?
Double pipe heat exchangers feature a straightforward design, where one pipe is nested inside another, allowing for heat exchange between two fluids. They are ideal for small-scale applications and industries like oil and gas. Buyers appreciate their cost-effectiveness and ease of construction. However, they may not be suitable for large volume applications due to lower efficiency compared to more complex designs. Understanding the specific heat transfer needs is crucial for making an informed purchasing decision.
What Advantages Do Air-Cooled Heat Exchangers Offer?
Air-cooled heat exchangers use ambient air to cool fluids, eliminating the need for water in the cooling process. This makes them particularly advantageous in regions facing water scarcity or high operational costs associated with water use. They find applications in HVAC systems and industrial cooling. B2B buyers should consider the environmental conditions, as performance can be affected by humidity and temperature. While they have lower operational costs, initial installation and maintenance should also be evaluated against other cooling solutions.
Key Industrial Applications of types of heat exchangers
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of types of heat exchangers | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Processing | Heat exchangers in chemical reactors for temperature control | Enhances reaction efficiency and product quality | Material compatibility, pressure ratings, and heat transfer efficiency |
| HVAC and Refrigeration | Air-cooled heat exchangers for building climate control | Reduces energy consumption and improves comfort | Energy efficiency ratings, installation space, and maintenance needs |
| Oil and Gas | Shell and tube heat exchangers for crude oil cooling | Increases operational safety and efficiency | Corrosion resistance, design standards, and capacity requirements |
| Food and Beverage | Plate heat exchangers for pasteurization processes | Ensures food safety and extends product shelf life | Hygiene standards, ease of cleaning, and thermal efficiency |
| Power Generation | Regenerative heat exchangers in gas turbine systems | Maximizes energy recovery and minimizes emissions | Operating temperature limits, material durability, and efficiency ratings |
How Are Heat Exchangers Used in Chemical Processing?
In the chemical processing industry, heat exchangers play a crucial role in maintaining optimal temperatures within reactors. By effectively transferring heat, they enhance reaction rates, leading to improved yields and product quality. For international B2B buyers, sourcing heat exchangers for this sector requires careful consideration of material compatibility, especially in corrosive environments, as well as pressure ratings to ensure safety and reliability under operational conditions.
What Role Do Heat Exchangers Play in HVAC and Refrigeration?
In HVAC and refrigeration systems, air-cooled heat exchangers are essential for regulating indoor climates. These devices transfer heat from indoor air to the outside, significantly reducing energy consumption while enhancing comfort levels. Buyers should focus on energy efficiency ratings and the physical space available for installation, as well as maintenance requirements to ensure long-term performance and reliability.
A stock image related to types of heat exchangers.
How Are Heat Exchangers Utilized in Oil and Gas?
Shell and tube heat exchangers are commonly employed in the oil and gas sector for cooling crude oil and other fluids. Their design allows for high-pressure applications, making them ideal for the demanding conditions of this industry. B2B buyers must prioritize sourcing materials with high corrosion resistance and adherence to design standards to ensure safety and efficiency in operations.
What Is the Importance of Heat Exchangers in Food and Beverage Production?
In the food and beverage industry, plate heat exchangers are widely used in pasteurization processes to ensure food safety. They provide efficient heat transfer while maintaining hygiene standards, crucial for extending product shelf life. Buyers should consider hygiene certifications, ease of cleaning, and thermal efficiency when sourcing these heat exchangers to comply with regulatory requirements and ensure product quality.
How Do Heat Exchangers Contribute to Power Generation?
Regenerative heat exchangers are utilized in gas turbine systems to maximize energy recovery by transferring heat from exhaust gases back into the system. This process minimizes emissions and enhances overall efficiency. For international buyers in the power generation sector, it is vital to assess operating temperature limits and material durability to ensure the longevity and effectiveness of these systems.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘types of heat exchangers’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Selecting the Right Heat Exchanger for Unique Applications
The Problem: Many international B2B buyers struggle to identify the most suitable type of heat exchanger for their specific applications. For instance, a manufacturer in South America may require a heat exchanger capable of efficiently operating under high pressure and temperature conditions, yet they may be unaware of which design—such as shell and tube or plate heat exchangers—would best meet those needs. This indecision can lead to costly mistakes, including purchasing an inefficient model that results in increased operational costs or frequent breakdowns.
The Solution: To effectively address this challenge, buyers should conduct a thorough needs assessment that considers factors such as the type of fluids involved, temperature ranges, pressure conditions, and space constraints. Collaborating with suppliers who offer customization options can also help in selecting the ideal heat exchanger. For example, when sourcing a shell and tube heat exchanger, inquire about the materials of construction to ensure compatibility with your specific fluids. Additionally, utilizing simulation software during the design phase can optimize performance and mitigate risks. Engaging with experienced engineers during the selection process can provide valuable insights tailored to the unique operational environment, ultimately leading to more informed purchasing decisions.
Scenario 2: Managing Maintenance and Operational Efficiency
The Problem: A common pain point for B2B buyers, particularly in industries like petrochemicals or HVAC, is the maintenance of heat exchangers. Buyers often face unexpected downtime due to fouling, corrosion, or leakage, which can significantly affect productivity and lead to financial losses. For instance, a buyer in the UAE might find that the heat exchanger in their cooling system requires frequent cleaning, disrupting operations and increasing labor costs.
The Solution: Implementing a proactive maintenance strategy is crucial for ensuring operational efficiency. Buyers should prioritize selecting heat exchangers that are designed for easy maintenance—such as those with removable components or those that allow for quick access to critical areas. Regular monitoring through advanced diagnostic tools can help identify potential issues before they escalate. Additionally, consider investing in heat exchangers with anti-fouling coatings or designs that minimize fouling potential, thus reducing the frequency of maintenance. Training staff on proper operational protocols can also enhance the longevity of the equipment and prevent costly outages.
Scenario 3: Navigating Regulatory Compliance and Environmental Standards
The Problem: International buyers face the challenge of navigating complex regulatory environments when sourcing heat exchangers. For example, a company in Europe must ensure that their chosen heat exchanger complies with the EU’s stringent environmental regulations regarding energy efficiency and emissions. Failure to adhere to these standards can lead to hefty fines and damage to the company’s reputation.
The Solution: Buyers should stay informed about local and international regulations that affect their industry. Engaging with suppliers who possess a deep understanding of compliance issues is critical. When evaluating heat exchangers, request documentation that verifies compliance with relevant standards, such as ISO or ASME certifications. Additionally, consider the energy efficiency ratings of the heat exchangers, as higher efficiency models not only meet regulatory requirements but also reduce operational costs over time. Collaborating with environmental consultants can provide further insights into compliance strategies, ensuring that your heat exchanger selection aligns with both regulatory demands and corporate sustainability goals.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for types of heat exchangers
What Are the Key Materials Used in Heat Exchangers?
When selecting materials for heat exchangers, international B2B buyers must consider various factors, including the specific application, operating conditions, and regional compliance standards. Below, we analyze four common materials used in heat exchangers, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
How Does Stainless Steel Perform in Heat Exchanger Applications?
Key Properties: Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, high-temperature tolerance, and strength. It typically withstands temperatures up to 900°C and pressures exceeding 100 bar, making it suitable for various applications.
Pros & Cons: The durability of stainless steel ensures a long lifespan, reducing maintenance costs. However, it is more expensive than other materials like carbon steel. Manufacturing complexity can also increase due to the need for specialized welding techniques.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including aggressive chemicals and high-pressure steam. Its corrosion resistance makes it ideal for industries such as petrochemicals and pharmaceuticals.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM A312 or DIN 17440. In regions like the UAE and Europe, where corrosion resistance is crucial, stainless steel is often preferred despite its higher cost.
What Advantages Do Copper and Copper Alloys Offer?
Key Properties: Copper exhibits excellent thermal conductivity, making it highly efficient for heat transfer. It can handle temperatures up to 200°C and is resistant to corrosion in many environments.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of copper is its superior heat transfer efficiency, which can lead to smaller and lighter heat exchangers. However, copper is susceptible to corrosion in certain conditions, such as when exposed to ammonia or acidic environments, and is generally more expensive than carbon steel.
Impact on Application: Copper is often used in HVAC systems and refrigeration due to its thermal efficiency. However, its limitations in specific chemical environments may restrict its use in some applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B88 is essential. Buyers from South America and Africa should consider local environmental conditions, as copper’s corrosion resistance may vary significantly.
How Does Carbon Steel Compare in Heat Exchanger Design?
Key Properties: Carbon steel is favored for its strength and affordability, with a temperature tolerance of up to 400°C and pressure ratings that can exceed 50 bar.
Pros & Cons: The cost-effectiveness of carbon steel makes it an attractive option for large-scale applications. However, it is prone to corrosion, requiring protective coatings or regular maintenance, which can increase long-term costs.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is suitable for applications involving water and steam but may not perform well in corrosive environments. It is widely used in power generation and oil and gas industries.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers need to ensure compliance with standards like ASTM A106 or API 5L. In regions like the Middle East, where high temperatures are common, carbon steel may require additional protective measures.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Heat Exchanger Manufacturing?
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and can handle temperatures up to 150°C. Its thermal conductivity is also high, making it efficient for heat exchange.
Pros & Cons: The lightweight nature of aluminum allows for easier installation and transport. However, it has a lower temperature and pressure tolerance compared to stainless steel and carbon steel, limiting its application scope.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is commonly used in automotive and HVAC applications where weight reduction is critical. However, it may not be suitable for high-pressure or high-temperature applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B221 is crucial. Buyers in Europe may favor aluminum for its lightweight properties, especially in automotive applications.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Heat Exchangers
| Material | Typical Use Case for types of heat exchangers | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Petrochemical, pharmaceuticals | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Copper | HVAC, refrigeration | Superior thermal conductivity | Corrosion susceptibility in certain environments | Med |
| Carbon Steel | Power generation, oil & gas | Cost-effective for large applications | Prone to corrosion, requires maintenance | Low |
| Aluminum | Automotive, HVAC | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower temperature and pressure tolerance | Med |
This strategic material selection guide offers valuable insights for international B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance with local standards.
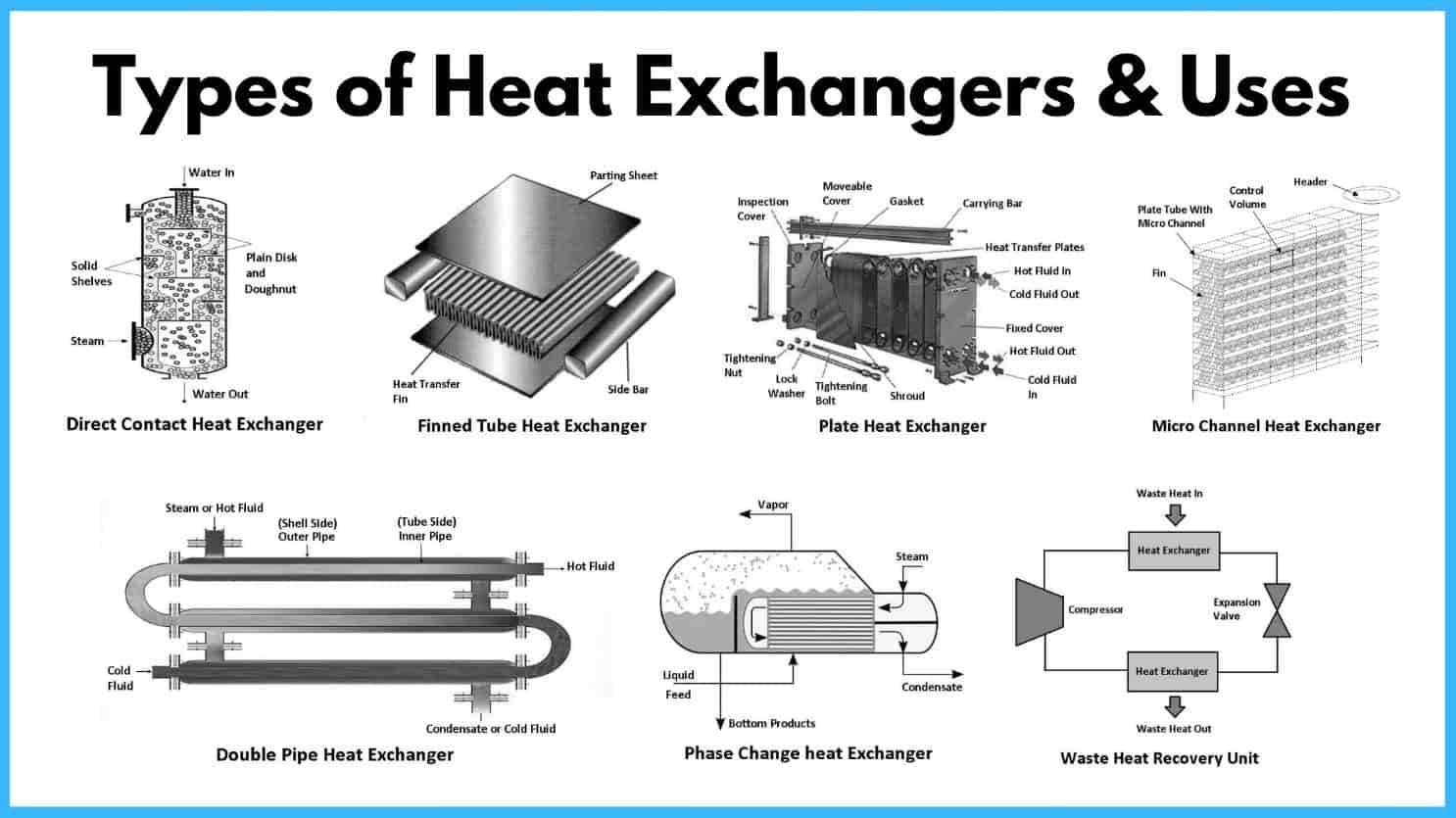
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for types of heat exchangers
What Are the Main Manufacturing Processes for Heat Exchangers?
Manufacturing heat exchangers involves several critical stages to ensure that the final product meets performance and safety standards. Understanding these processes is essential for B2B buyers looking for reliable suppliers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
How is Material Prepared for Heat Exchangers?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. Common materials used for heat exchangers include stainless steel, carbon steel, and copper alloys. The choice of material depends on the application’s temperature and pressure requirements, as well as the fluids involved.
-
Material Selection: B2B buyers should evaluate the corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity of the materials. For example, stainless steel is preferred for corrosive environments, while copper may be chosen for its superior thermal conductivity.
-
Cutting and Shaping: Sheets and tubes are cut to size using laser cutting or water jet cutting technologies. Precision in this step is crucial to ensure that all parts fit correctly during assembly.
-
Surface Treatment: Depending on the application, materials may undergo surface treatments like passivation or coating to enhance their resistance to corrosion and fouling.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Heat Exchangers?
Once the materials are prepared, forming techniques are employed to create the specific shapes required for heat exchangers.
-
Bending and Rolling: Tubes are often bent or rolled to achieve the desired shapes. The accuracy of this process is vital to prevent leaks and ensure efficient heat transfer.
-
Welding: Various welding techniques, such as TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) and MIG (Metal Inert Gas), are used to join components. The choice of welding method can affect the integrity of the joints, making quality control essential.
-
Finning: For certain types of heat exchangers, fins are added to enhance surface area and improve heat transfer efficiency. This process often involves precision stamping or extrusion.
How is Assembly Conducted for Heat Exchangers?
The assembly of heat exchangers is a critical phase that requires meticulous attention to detail.
-
Component Assembly: All individual components—tubes, shells, and baffles—are assembled according to design specifications. This step often involves the use of jigs and fixtures to maintain alignment.
-
Sealing: Sealing techniques are employed to ensure that there are no leaks between different sections. Gaskets or welds are commonly used, depending on the design.
-
Pressure Testing: Once assembled, heat exchangers undergo pressure tests to verify their integrity. This is a crucial step, especially for applications involving high pressures or hazardous fluids.
What Finishing Processes Are Common for Heat Exchangers?
Finishing processes play a significant role in the performance and longevity of heat exchangers.
-
Cleaning: After assembly, heat exchangers are thoroughly cleaned to remove any contaminants that could affect performance. This may involve chemical cleaning or high-pressure water jets.
-
Coating: Heat exchangers may receive protective coatings to enhance corrosion resistance. This is particularly important for those used in aggressive environments.
-
Final Inspection: A final inspection is conducted to ensure that the heat exchanger meets all specifications. This includes dimensional checks and visual inspections for weld quality.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Heat Exchangers?
Quality assurance is critical in the manufacturing of heat exchangers to ensure reliability and compliance with international standards.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
International quality standards such as ISO 9001 provide a framework for quality management systems. Compliance with these standards indicates a commitment to quality and continuous improvement.
-
ISO 9001: This standard focuses on meeting customer requirements and enhancing satisfaction. Manufacturers adhering to ISO 9001 often have documented processes that facilitate consistency in production.
-
Industry-Specific Certifications: Depending on the application, certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) for Europe or API (American Petroleum Institute) for the oil and gas industry may be necessary. These certifications ensure that products meet specific safety and performance requirements.
What are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints During Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are crucial for identifying defects early in the manufacturing process.
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This step involves inspecting raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet specified standards. Buyers should verify the material certifications provided by suppliers.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During production, regular inspections are conducted to monitor the manufacturing process. This includes checking dimensions, weld quality, and adherence to design specifications.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipping, a final inspection is performed to verify that the heat exchanger meets all technical and safety requirements. This may include pressure testing and performance evaluations.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
To ensure that suppliers maintain high-quality standards, B2B buyers should consider several verification strategies.
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess manufacturing processes and quality control systems. This firsthand observation can provide insights into the supplier’s capabilities.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting quality assurance documentation, including inspection reports and test certificates, can help buyers understand the quality metrics achieved during production.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspectors can offer an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality control measures. This is particularly beneficial for international buyers, ensuring compliance with local and international standards.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers should be aware of specific nuances in quality control that can affect their purchasing decisions.
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding cultural attitudes towards quality and compliance can help buyers navigate potential communication gaps with suppliers from different regions.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different countries have varying regulations regarding manufacturing and safety standards. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these regulations to ensure that the products they purchase comply with local laws.
-
Logistical Considerations: Quality assurance can also be impacted by logistics. Delays in shipping or customs can affect the final product’s integrity. Buyers should work closely with suppliers to ensure timely and safe delivery.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for heat exchangers is vital for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, finishing, and rigorous quality control, buyers can make informed decisions that lead to successful procurement outcomes.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘types of heat exchangers’
A stock image related to types of heat exchangers.
In the competitive landscape of international B2B procurement, sourcing the right type of heat exchanger is crucial for enhancing operational efficiency and maintaining cost-effectiveness. This guide serves as a practical checklist for buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, to streamline their procurement process.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by clearly outlining the technical requirements for your heat exchanger. This includes factors such as the type of fluids involved, operating temperatures, pressure ratings, and flow configurations (e.g., counterflow or crossflow). Establishing these specifications early ensures that you can accurately communicate your needs to potential suppliers.
- Fluids and Phases: Specify whether the fluids are single or multiphase.
- Temperature and Pressure: Identify the maximum and minimum operating conditions.
Step 2: Identify Your Application Needs
Understand the specific application for which the heat exchanger will be used. Different industries may have unique requirements based on environmental conditions, regulatory standards, and performance expectations. This will help narrow down the types of heat exchangers suitable for your application.
- Industry Standards: Research any specific standards or certifications required in your industry.
- Performance Metrics: Determine key performance indicators such as heat transfer efficiency and maintenance needs.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct a thorough evaluation. Look for established companies with a proven track record in manufacturing the type of heat exchanger you need. Request detailed company profiles, product catalogs, and case studies to gauge their expertise.
- References and Reviews: Seek testimonials from existing clients in similar industries.
- Quality Assurance: Check for certifications like ISO or industry-specific standards that validate their manufacturing processes.
Step 4: Request Detailed Quotations
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request detailed quotations that include pricing, lead times, and terms of service. Ensure that the quotes reflect your technical specifications and application needs. This will facilitate a straightforward comparison between suppliers.
- Breakdown of Costs: Ask for a detailed breakdown of costs, including shipping and installation if applicable.
- Warranty and Support: Inquire about warranty terms and after-sales support options.
Step 5: Assess Delivery and Installation Capabilities
Confirm the supplier’s ability to meet your delivery timelines and installation requirements. Delays in delivery can disrupt your operations, so it’s essential to establish realistic timelines. Additionally, ensure that the supplier offers installation services or guidance.
- Logistics and Shipping: Discuss the logistics involved in transporting the heat exchanger to your location.
- Installation Expertise: Verify if the supplier provides installation training or support for your team.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Finalize Contracts
Once you have chosen a supplier, engage in negotiations to finalize the terms of the contract. This includes payment terms, delivery schedules, and penalties for non-compliance. Clear agreements can prevent misunderstandings and foster a positive supplier relationship.
- Flexibility: Aim for terms that provide flexibility in case of unforeseen circumstances.
- Legal Review: Consider having legal counsel review the contract to ensure all aspects are covered.
Step 7: Plan for Ongoing Maintenance and Support
Finally, develop a maintenance plan to ensure the longevity and efficiency of your heat exchanger. Discuss maintenance schedules and support services with your supplier to keep your equipment running optimally.
- Training Programs: Consider training programs for your staff on maintenance best practices.
- Spare Parts Availability: Confirm the availability of spare parts and support for future repairs.
By following these steps, international B2B buyers can effectively navigate the procurement process for heat exchangers, ensuring they select the right equipment tailored to their specific needs and applications.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for types of heat exchangers Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Heat Exchangers?
Understanding the cost structure of heat exchangers is essential for international B2B buyers. The main components influencing the overall cost include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials, such as stainless steel, carbon steel, or specialized alloys, significantly impacts pricing. High-quality materials enhance durability and efficiency but may increase initial costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and complexity of manufacturing. Skilled labor is often necessary for precision in assembly and quality assurance, especially for customized solutions.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory operation, maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be substantial, particularly for custom designs. However, these costs are amortized over larger production runs, making it crucial to consider volume when negotiating.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring compliance with industry standards and certifications (e.g., ASME, TEMA) can add to costs. However, investing in QC can prevent costly failures and enhance product reliability.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs vary based on distance, mode of transport, and shipping terms. International buyers must factor in potential tariffs and import duties as well.
-
Margin: Supplier profit margins can fluctuate based on market demand, competition, and negotiation outcomes. Understanding market conditions can aid buyers in securing better deals.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Heat Exchanger Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of heat exchangers, especially for international buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Bulk purchasing often leads to lower unit costs. Buyers should evaluate their needs and negotiate MOQs to optimize their purchasing strategy.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs tailored to specific applications may incur additional costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the potential for increased expenses.
-
Materials: The choice of materials affects both the performance and price of heat exchangers. Premium materials can lead to higher upfront costs but may provide long-term savings through improved efficiency.
-
Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality products with necessary certifications typically command higher prices. Buyers should assess whether the added cost aligns with their operational requirements and risk management strategies.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can impact pricing. Established suppliers may offer higher prices but can provide better support and assurance of quality.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is crucial for international transactions. They determine responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and duties, affecting total costs.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Negotiating Heat Exchanger Prices?
For international B2B buyers, especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the following tips can enhance negotiation outcomes:
-
Negotiate Terms: Engage in discussions about pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Flexibility on both sides can lead to mutually beneficial agreements.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just initial purchase price. Consider maintenance, energy efficiency, and lifespan when assessing value.
-
Research Market Prices: Conduct thorough market research to understand current pricing trends. Knowledge of competitor offerings can empower buyers in negotiations.
-
Leverage Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can result in better pricing and service. Long-term partnerships often yield favorable terms.
-
Consider Local Suppliers: For buyers in Africa and South America, local suppliers may offer competitive pricing due to reduced logistics costs. Evaluate their capabilities and product offerings.
Conclusion: How to Approach Heat Exchanger Sourcing with Confidence
While indicative prices for heat exchangers can vary widely based on the factors discussed, an informed approach will help buyers make strategic sourcing decisions. Understanding the cost components, price influencers, and negotiation tactics is vital for achieving the best value in this critical industrial sector.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing types of heat exchangers With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives to Heat Exchangers
When considering thermal management solutions, businesses often evaluate various technologies to optimize energy efficiency and operational performance. Heat exchangers are well-regarded for their effectiveness in transferring heat between fluids, but alternatives exist that may provide specific advantages depending on the application. This section will compare types of heat exchangers against two viable alternatives: cooling towers and heat pumps.
| Comparison Aspect | Types Of Heat Exchangers | Cooling Towers | Heat Pumps |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency in heat transfer; suitable for various fluids | Effective for large-scale cooling, especially in HVAC | Can both heat and cool efficiently; versatile |
| Cost | Varies widely; generally higher initial investment for complex designs | Lower initial costs; ongoing water and energy costs | Higher upfront cost, but lower operational costs over time |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized installation; complex designs may need custom solutions | Relatively easy to install; requires water supply and drainage | Installation complexity varies with type; may require retrofitting |
| Maintenance | Regular cleaning and inspection needed; parts may require replacement | Low maintenance; periodic cleaning and water treatment necessary | Routine maintenance needed; refrigerant management is critical |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for chemical processing, power generation, and food production | Best for large facilities needing cooling (e.g., industrial plants) | Suitable for residential and commercial heating and cooling needs |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Cooling Towers?
Cooling towers are designed to dissipate heat from water-cooled systems, making them an efficient choice for large-scale cooling applications. Their primary advantage lies in their cost-effectiveness; they have lower initial setup costs compared to heat exchangers and can handle substantial thermal loads. However, they do rely on a continuous water supply and can be less efficient in arid climates where water scarcity may be an issue. Additionally, they require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance, particularly in managing water quality to prevent scaling and biological growth.
How Do Heat Pumps Compare to Heat Exchangers?
Heat pumps serve dual functions by transferring heat from one location to another, effectively heating or cooling a space. They are particularly advantageous for their versatility and energy efficiency, often yielding lower operational costs over time compared to traditional heating systems. However, heat pumps typically require a higher upfront investment and may need complex installation, especially in retrofitting existing structures. Their effectiveness can also diminish in extreme temperature conditions, which may limit their applicability in certain regions.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When selecting the right thermal management solution, B2B buyers must consider several factors including performance requirements, budget constraints, and specific application needs. Heat exchangers excel in industries requiring precise temperature control and efficiency, while cooling towers may be more suitable for large-scale cooling needs. Heat pumps present an excellent option for energy-conscious buyers looking for versatile heating and cooling systems. By assessing their operational demands and long-term goals, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their strategic objectives, ultimately leading to improved energy efficiency and cost-effectiveness in their operations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for types of heat exchangers
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Heat Exchangers?
Understanding the technical specifications of heat exchangers is essential for international B2B buyers, particularly when making informed purchasing decisions. Here are critical specifications that should be considered:
1. Material Grade
The material used in heat exchangers significantly affects their durability, thermal conductivity, and resistance to corrosion. Common materials include stainless steel, carbon steel, and copper. For industries operating in harsh environments, selecting a material with high corrosion resistance is crucial to ensure longevity and reduce maintenance costs.
2. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the permissible limits of variation in a physical dimension. In heat exchangers, tight tolerances are vital for ensuring that components fit properly, which can prevent leaks and enhance performance. B2B buyers should prioritize manufacturers that adhere to strict tolerance standards, as this directly impacts the efficiency of heat transfer.
3. Pressure Rating
Pressure rating indicates the maximum pressure a heat exchanger can withstand during operation. Different applications require different pressure ratings, and exceeding this limit can lead to catastrophic failures. International buyers must assess the pressure requirements of their specific applications to ensure compliance and safety.
4. Heat Transfer Efficiency
This specification measures how effectively a heat exchanger can transfer heat between fluids. Efficiency is often expressed as a percentage, with higher numbers indicating better performance. Understanding this metric is essential for buyers looking to optimize energy use and reduce operating costs, particularly in energy-intensive industries.
5. Flow Configuration
Heat exchangers can be classified based on their flow configurations—counterflow, cocurrent, and crossflow. Each type has its advantages and disadvantages regarding efficiency and application suitability. Buyers should consider the specific needs of their operations and select a heat exchanger design that maximizes thermal performance.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Heat Exchanger Industry?
Familiarizing oneself with industry jargon is crucial for smooth transactions and effective communication in the B2B marketplace. Here are several essential terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding the role of OEMs is vital for buyers, as it affects the sourcing and quality of components used in heat exchangers. Collaborating with reputable OEMs can ensure higher quality and reliability.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For international buyers, understanding MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory management. Negotiating favorable MOQs can lead to better pricing and reduced holding costs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a standard business process where buyers invite suppliers to submit price quotes for specific products or services. Crafting a detailed RFQ can help buyers obtain competitive pricing and ensure that all necessary specifications are covered, aiding in informed decision-making.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping responsibilities, risk management, and cost implications, which are critical for international procurement.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the period from when an order is placed until it is fulfilled. In the heat exchanger industry, understanding lead times is essential for project planning and inventory management. Buyers should communicate clearly with suppliers to establish realistic expectations and avoid delays.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can enhance their purchasing strategies and ensure they select the most suitable heat exchangers for their specific applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the types of heat exchangers Sector
What Are the Key Trends Influencing the Heat Exchangers Market?
The global heat exchangers market is witnessing significant growth, driven by a surge in demand across various sectors, including HVAC, chemical processing, and power generation. As industries focus on enhancing energy efficiency and reducing operational costs, the need for advanced heat exchangers is becoming increasingly critical. International B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of several key trends shaping the market.
One prominent trend is the integration of digital technologies such as IoT and AI in heat exchanger design and operation. These technologies facilitate real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, allowing businesses to optimize performance and minimize downtime. Additionally, the shift towards renewable energy sources is influencing the development of specialized heat exchangers tailored for applications in solar thermal systems and geothermal energy.
Another essential aspect is the growing emphasis on modular and compact designs. With space constraints in urban areas and the need for flexible manufacturing setups, buyers are increasingly seeking heat exchangers that can be easily installed and scaled. Furthermore, sustainability is a crucial consideration, with many suppliers adopting eco-friendly materials and processes to appeal to environmentally conscious buyers.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact Heat Exchanger Procurement?
The environmental impact of heat exchangers extends beyond their operation; it also encompasses their manufacturing and end-of-life disposal. As global awareness of climate change rises, B2B buyers are urged to consider sustainability in their procurement strategies. This involves sourcing heat exchangers made from materials that are recyclable or have a lower carbon footprint.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as buyers should evaluate the supply chain practices of their suppliers. A transparent and responsible supply chain reduces risks associated with labor practices and environmental degradation. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and other ‘green’ certifications can guide buyers in selecting suppliers committed to sustainability.
Moreover, the use of innovative materials, such as heat exchangers designed with advanced alloys or composites, can enhance thermal performance while minimizing environmental impact. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who invest in research and development to create ‘green’ heat exchangers that not only meet regulatory requirements but also exceed industry standards for environmental stewardship.
What Is the Historical Context of Heat Exchangers in B2B Markets?
The evolution of heat exchangers dates back to the early 19th century when the first designs were implemented in steam engines and industrial processes. As industries expanded, the need for efficient heat transfer mechanisms became apparent, leading to innovations in design and materials. By the mid-20th century, heat exchangers had become integral to various applications, particularly in the chemical and petrochemical sectors.
Today, heat exchangers have evolved into sophisticated devices that play a crucial role in energy management and sustainability efforts across industries. B2B buyers must recognize this historical context as it informs current trends and innovations, enabling them to make informed purchasing decisions that align with both technological advancements and sustainability goals. Understanding the trajectory of heat exchanger development can also help buyers anticipate future trends and adapt their sourcing strategies accordingly.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of types of heat exchangers
-
How do I choose the right type of heat exchanger for my industry?
Selecting the appropriate heat exchanger depends on various factors, including the type of fluids involved, temperature ranges, and specific industry applications. For instance, shell and tube heat exchangers are ideal for high-pressure environments, while plate heat exchangers offer compact designs for lower pressure applications. Conduct a thorough analysis of your operational requirements, considering efficiency, maintenance needs, and space constraints. Consulting with a specialized supplier can also provide insights into the best options tailored to your business needs. -
What is the best heat exchanger for energy recovery applications?
For energy recovery, regenerative heat exchangers are often the most effective choice. They can capture and reuse heat from exhaust gases or other waste streams, significantly improving overall energy efficiency. Alternatively, shell and tube heat exchangers can also be utilized in these applications if designed for specific temperature and pressure conditions. When considering options, evaluate the heat recovery potential and compatibility with existing systems to ensure optimal performance. -
What factors should I consider when vetting heat exchanger suppliers?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their experience and reputation in the industry. Look for certifications that demonstrate adherence to international quality standards, such as ISO 9001. Additionally, consider their product range, customization capabilities, and after-sales support. It’s also beneficial to request case studies or references from previous clients to gauge their performance and reliability. Engaging with suppliers who understand regional regulations and logistical challenges can further enhance your sourcing process. -
How can I customize a heat exchanger to meet specific operational requirements?
Most suppliers offer customization options for heat exchangers, which can include adjustments in materials, sizes, and configurations. To initiate this process, provide detailed specifications, such as desired flow rates, temperatures, and the nature of the fluids involved. Collaborate closely with the supplier’s engineering team to ensure that the design aligns with your operational needs. Keep in mind that customized solutions may have longer lead times and potentially higher costs, so plan accordingly. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for heat exchangers?
Minimum order quantities for heat exchangers can vary significantly between suppliers and depend on the type of heat exchanger being purchased. Typically, larger suppliers may have higher MOQs due to production costs, while smaller manufacturers might accommodate smaller orders. Always clarify MOQ policies upfront during negotiations to avoid unexpected costs. If you require a lower quantity, consider discussing potential stock items or options for batching orders with other buyers to meet MOQ requirements. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing heat exchangers internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely based on the supplier and the nature of your agreement. Common terms include net 30 or net 60 days, where payment is due within 30 or 60 days of invoice receipt. Some suppliers may request a deposit before production begins, especially for customized orders. It’s essential to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow needs and ensure clarity in the contract to avoid disputes. Also, consider using secure payment methods to protect your transaction.
A stock image related to types of heat exchangers.
-
How do I ensure quality assurance for heat exchangers sourced internationally?
To ensure quality assurance, request certifications and testing reports from the supplier, such as ASME or PED compliance. Implementing a third-party inspection can provide additional verification of quality before shipment. Establishing a clear quality control process that includes specifications and acceptance criteria in your contract is crucial. Engage with suppliers who offer warranties and robust after-sales support to address any quality issues that may arise post-purchase. -
What logistical considerations should I keep in mind when importing heat exchangers?
When importing heat exchangers, consider factors such as shipping methods, customs clearance, and lead times. Evaluate the total landed cost, which includes shipping, duties, and taxes, to avoid unexpected expenses. Collaborating with logistics providers experienced in handling industrial equipment can streamline the process. Additionally, ensure compliance with local regulations regarding imports, as this can impact delivery timelines and costs. Planning for potential delays can help manage expectations and maintain operational efficiency.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for types of heat exchangers
In conclusion, understanding the diverse types of heat exchangers is crucial for international B2B buyers aiming to optimize energy efficiency and reduce operational costs. By strategically sourcing the right heat exchanger—whether it be shell and tube, plate, or finned-tube—organizations can significantly enhance their thermal management processes. Each type offers unique advantages tailored to specific applications, making it essential for buyers to evaluate their specific needs against the performance characteristics of various heat exchangers.
Moreover, as industries worldwide increasingly prioritize sustainability and energy conservation, the demand for efficient heat exchangers is expected to rise. Buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should leverage this trend by engaging with manufacturers who offer innovative solutions that align with these goals.
Investing in strategic sourcing not only ensures access to high-quality products but also fosters long-term partnerships that can lead to enhanced technological advancements. As you move forward, consider how the right heat exchanger can transform your operations and contribute to a more sustainable future. Engage with suppliers who understand your market’s unique challenges and can provide tailored solutions that will drive your business success.