Discover 7 Essential Types of Locks for Your Business Needs (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for type of locks
In today’s interconnected world, sourcing the right types of locks presents a unique challenge for international B2B buyers. With security being a top priority for businesses across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the diverse options available is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. This comprehensive guide delves into various types of locks, from traditional deadbolts to modern smart locks, highlighting their specific applications and suitability for different environments.
Buyers will find detailed insights into the functionality and security levels of each lock type, enabling them to assess which solutions best meet their operational needs. Additionally, the guide addresses crucial factors such as supplier vetting, cost considerations, and compliance with regional security standards. By equipping B2B buyers with actionable information, this resource empowers them to navigate the complexities of the global lock market confidently.
Whether you’re securing a commercial facility in South Africa or a retail outlet in Brazil, understanding the nuances of lock types can significantly impact your security strategy. This guide serves as a roadmap, ensuring that you not only protect your assets effectively but also enhance your overall operational efficiency. Join us as we explore the myriad of locking solutions available and help you make choices that bolster your business’s security framework.
Understanding type of locks Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Deadbolt Locks | Thick metal bolt, high resistance to forced entry | Exterior doors of commercial buildings | Pros: High security; Cons: Requires professional installation. |
| Electronic Locks | Keyless entry, integration with smart systems | Office buildings, rental properties | Pros: Convenient access; Cons: Higher initial cost, requires power source. |
| Mortise Locks | Built into the door, robust locking mechanism | High-security entrances, hotels | Pros: Excellent security; Cons: More complex installation. |
| Padlocks | Portable, versatile locking mechanism | Locking storage units, outdoor equipment | Pros: Easy to use; Cons: Limited security for high-value items. |
| Smart Locks | Remote access via smartphone, compatibility with smart home systems | Short-term rentals, tech-savvy businesses | Pros: Enhanced control and monitoring; Cons: Vulnerable to hacking if not secured properly. |
What are the Key Characteristics of Deadbolt Locks?
Deadbolt locks are renowned for their security features, consisting of a solid metal bolt that extends deep into the door frame, making them highly resistant to forced entry. They are primarily used for securing exterior doors in commercial buildings, providing peace of mind for businesses. B2B buyers should consider the installation requirements and potential need for professional assistance, as proper installation is crucial for maximizing security benefits.
How Do Electronic Locks Enhance Security for Businesses?
Electronic locks provide a modern solution for businesses seeking keyless entry systems. They can be integrated with smart technology, allowing for remote access through mobile devices. This feature is particularly advantageous for office buildings and rental properties, where multiple users may need access. Buyers should evaluate the costs associated with installation and maintenance, as well as the necessity for a reliable power source to ensure uninterrupted access.
Why Choose Mortise Locks for High-Security Needs?
Mortise locks are embedded within the door, offering a robust locking mechanism that is difficult to tamper with. They are ideal for high-security applications, such as hotels and corporate offices, where security is paramount. When purchasing mortise locks, B2B buyers should consider the complexity of installation, as these locks often require specialized knowledge and tools, potentially increasing overall project costs.
In What Situations are Padlocks Most Effective?
Padlocks are versatile and portable, making them suitable for securing storage units, outdoor equipment, and lockers. Their ease of use allows for quick locking and unlocking, which is beneficial for businesses that require frequent access to secured items. However, buyers should be cautious about the security level of padlocks, as they may not provide adequate protection for high-value items. Evaluating the lock’s material and mechanism is crucial for ensuring appropriate security.
What Advantages Do Smart Locks Offer to Modern Businesses?
Smart locks represent the forefront of locking technology, allowing businesses to manage access remotely via smartphones or other devices. This feature is particularly appealing to short-term rental properties and tech-savvy businesses that prioritize convenience and monitoring. However, B2B buyers must consider the potential vulnerabilities associated with smart locks, such as hacking risks, and ensure that proper cybersecurity measures are in place to protect their systems.
Key Industrial Applications of type of locks
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Type of Locks | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Securing machinery and equipment | Prevents unauthorized access and ensures safety compliance | Durability, resistance to tampering, and ease of use |
| Healthcare | Locking medication cabinets and patient records | Protects sensitive information and controlled substances | Compliance with health regulations and reliability |
| Retail | Securing stockrooms and cash registers | Reduces theft and enhances inventory management | Versatility in lock types, ease of access, and security |
| Logistics and Warehousing | Locking storage units and delivery vehicles | Ensures goods are protected during transport and storage | Weather resistance, portability, and theft deterrence |
| Hospitality | Securing guest rooms and service areas | Enhances guest safety and improves operational efficiency | Compatibility with keyless systems and ease of maintenance |
How Are Different Types of Locks Used in Manufacturing?
In the manufacturing sector, locks are crucial for securing machinery and sensitive equipment. Heavy-duty padlocks and electronic locks are often employed to prevent unauthorized access, which is essential for safety compliance and protecting proprietary technology. International buyers should consider the durability and resistance to tampering when sourcing locks, as equipment downtime due to security breaches can lead to significant financial losses.
Why Are Locks Vital in the Healthcare Industry?
Healthcare facilities utilize locks to secure medication cabinets and patient records, ensuring compliance with strict regulations governing the handling of sensitive information. Mortise locks and electronic keypad locks are commonly used for their reliability and ease of access. B2B buyers in this sector must prioritize locks that meet health regulations, offer reliable performance, and can withstand frequent use without compromising security.
What Role Do Locks Play in Retail Security?
In retail environments, locks are essential for securing stockrooms and cash registers. Combination locks and electronic locks help reduce theft and enhance inventory management by providing secure access to high-value items. For international B2B buyers, sourcing versatile lock types that offer both security and ease of access is critical to maintaining operational efficiency and customer trust.
How Do Locks Ensure Security in Logistics and Warehousing?
In logistics and warehousing, locks are used to secure storage units and delivery vehicles, safeguarding goods during transport and storage. Heavy-duty padlocks and electronic locking systems are preferred for their weather resistance and portability, which are vital for protecting cargo from theft and environmental damage. Buyers should focus on sourcing locks that are both robust and easy to use, as this will streamline operations and enhance security measures.
Why Are Locks Important in the Hospitality Sector?
In the hospitality industry, locks are used to secure guest rooms and service areas, significantly impacting guest safety and operational efficiency. Smart locks and traditional deadbolts are common, with many hotels adopting keyless systems for convenience. When sourcing locks, buyers should ensure compatibility with existing security systems and consider ease of maintenance to provide a seamless experience for guests while enhancing security measures.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘type of locks’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inadequate Security for High-Value Assets
The Problem:
B2B buyers often find themselves in situations where they need to secure valuable assets, such as expensive machinery, sensitive documents, or inventory. Traditional locks, such as cam locks or knob locks, may provide insufficient security for these high-value items. For instance, a manufacturing company in South Africa might use basic locks on their machinery storage, only to discover that these locks can be easily bypassed, leading to theft and significant financial loss. This vulnerability not only impacts their bottom line but also damages their reputation.
The Solution:
To enhance security, buyers should consider investing in high-security locks, such as mortise locks or electronic locks that meet industry standards. These locks offer superior resistance to forced entry and tampering. When sourcing these locks, it’s vital to look for those certified to standards such as BS3621, which ensures a level of security recognized in many regions, including Europe. Additionally, employing a multi-layered security approach can be effective; for example, combining deadbolt locks with an access control system can provide both physical and electronic security. Establishing a routine for regular maintenance and audits of lock systems can help ensure ongoing security and identify potential vulnerabilities before they lead to security breaches.
Scenario 2: Difficulties in Managing Access Control
The Problem:
In businesses with multiple employees or locations, managing who has access to which areas can become complicated and inefficient. For example, a logistics company in Brazil may face challenges with key distribution, where lost keys pose a security risk and require costly rekeying of locks. Additionally, the time spent on key management detracts from operational efficiency, leading to frustration among staff and increased risk of unauthorized access.
The Solution:
Implementing electronic or smart locks can significantly streamline access control. These locks allow for keyless entry, where access codes can be easily updated or revoked without the need to change physical locks. Businesses should consider locks that integrate with their existing security systems, allowing for remote management and real-time monitoring of access logs. When selecting these locks, ensure compatibility with mobile access options for added convenience. Training employees on the importance of access control and regularly reviewing access permissions can further enhance security and operational efficiency.
Scenario 3: Challenges with Compliance and Regulations
The Problem:
Many industries are subject to strict regulations regarding security measures, particularly those handling sensitive information or hazardous materials. For instance, a healthcare provider in the Middle East might struggle with compliance due to outdated locking mechanisms that fail to meet legal standards. Non-compliance can lead to severe penalties, reputational damage, and loss of business, creating a pressing need for reliable and compliant security solutions.
The Solution:
B2B buyers should conduct a thorough assessment of their current locking systems against regulatory requirements. Upgrading to locks that comply with local and international standards, such as high-security deadbolts or access control systems with audit trails, can mitigate compliance risks. It is crucial to work with reputable suppliers who understand these regulations and can provide locks that meet or exceed them. Regular training sessions for staff on compliance protocols and the proper use of locking mechanisms can further reinforce security practices within the organization. Establishing a compliance review process will help ensure that all security measures remain up-to-date with evolving regulations, minimizing risks associated with non-compliance.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for type of locks
When selecting locks for various applications, the choice of material significantly impacts performance, durability, and cost. Here, we analyze four common materials used in lock manufacturing: steel, brass, zinc alloy, and plastic. Each material has unique properties that cater to different security needs and environmental conditions.
What Are the Key Properties of Steel in Lock Manufacturing?
Steel is a widely used material for locks, especially in high-security applications. Its key properties include exceptional tensile strength and resistance to deformation under pressure. Steel locks can withstand high temperatures, making them suitable for environments prone to heat exposure. Additionally, they can be treated for corrosion resistance, enhancing their longevity in harsh conditions.
Pros and Cons of Steel Locks
The primary advantage of steel locks is their durability and resistance to physical attacks, which makes them ideal for external doors and high-security areas. However, they can be heavier and more expensive than other materials, potentially increasing manufacturing complexity. Furthermore, untreated steel is susceptible to rust, which can be a concern in humid climates.
How Does Brass Compare as a Material for Locks?
Brass is another popular material, known for its excellent corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. It is a copper-zinc alloy that provides a good balance between strength and malleability, allowing for intricate designs in lock mechanisms. Brass locks perform well in moderate temperature ranges and are often used in residential applications.
Pros and Cons of Brass Locks
Brass offers a classic look and is less prone to corrosion, making it suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications. However, it is softer than steel, which can make it more vulnerable to wear and breakage under heavy use. Additionally, brass locks can be more expensive than zinc alloy options, which may deter budget-conscious buyers.
What Are the Advantages of Zinc Alloy Locks?
Zinc alloy is commonly used for locks due to its cost-effectiveness and good mechanical properties. It is lightweight and can be easily molded into complex shapes, making it suitable for various lock designs. Zinc alloy locks typically have a decent level of corrosion resistance, especially when treated with protective coatings.
Pros and Cons of Zinc Alloy Locks
The main advantage of zinc alloy locks is their affordability and versatility, making them ideal for budget-sensitive projects. However, they are generally less durable than steel or brass, which may limit their use in high-security environments. Additionally, zinc alloy locks can be more susceptible to wear over time, particularly in demanding applications.
In What Situations Are Plastic Locks Appropriate?
Plastic locks, often made from high-strength polymers, are increasingly being used in specific applications, particularly in environments where corrosion is a concern. They are lightweight and can be manufactured in various colors and designs, appealing to aesthetic preferences.
Pros and Cons of Plastic Locks
Plastic locks are resistant to rust and corrosion, making them suitable for marine or humid environments. They are also cost-effective, which is attractive for large-scale projects. However, their durability is significantly lower than metal locks, limiting their use to low-security applications. They may not withstand heavy physical force, making them unsuitable for external doors.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Locks
| Material | Typical Use Case for type of locks | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | High-security external doors | Exceptional durability | Heavier and more expensive | High |
| Brass | Residential and decorative locks | Corrosion resistance and aesthetics | Softer, more wear-prone | Medium |
| Zinc Alloy | Budget-sensitive applications | Cost-effective and versatile | Less durable than steel or brass | Low |
| Plastic | Low-security internal locks | Rust and corrosion resistant | Limited durability under stress | Low |
In conclusion, the selection of lock materials should align with the specific security needs, environmental conditions, and budget considerations of international B2B buyers. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material will enable informed purchasing decisions that enhance security and functionality in diverse applications across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.

A stock image related to type of locks.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for type of locks
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Locks?
The manufacturing process for locks typically involves several stages, each critical to ensuring the final product meets quality and security standards. Understanding these stages can help international B2B buyers make informed decisions when sourcing locks.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Commonly Used in Lock Manufacturing?
The first step in manufacturing locks is selecting the right materials, which typically include steel, brass, zinc alloy, and plastic. Steel is often used for its strength and durability, while brass is favored for its corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. The material is prepared by cutting it into specific shapes and sizes using advanced machinery like laser cutters and CNC machines. These machines provide precision, ensuring that components fit perfectly during assembly.
How Is the Lock Formed?
Once the materials are prepared, the forming stage begins. This involves shaping the materials into the required components of the lock, such as the casing, bolt, and keyway. Techniques such as stamping, forging, and machining are employed. For instance, a die-casting process may be used to create complex shapes in zinc alloy locks, while forging is often used for high-security locks requiring robust construction.
What Does the Assembly Process Involve?
The assembly stage involves combining the formed components into a functioning lock. This is usually done in a clean environment to avoid contamination. Automated assembly lines are common, where machines and skilled laborers work together to insert components like springs and tumblers into the lock body. Quality checks are often performed at this stage to catch any defects early on.
What Finishing Techniques Are Used for Locks?
The finishing stage is essential for enhancing the lock’s durability and aesthetics. Finishing techniques may include polishing, plating, and applying protective coatings. For example, locks may be nickel-plated to improve corrosion resistance or powder-coated for added protection against wear and tear. This step not only affects the product’s lifespan but also its market appeal.
How Is Quality Assurance Integrated into the Lock Manufacturing Process?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of lock manufacturing, ensuring that products meet both international and industry-specific standards. B2B buyers must understand these QA measures to verify the reliability of their suppliers.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
For locks, compliance with international standards such as ISO 9001 is crucial. This standard outlines requirements for a quality management system, helping manufacturers ensure consistent quality in their products. Other relevant certifications include CE marking in Europe, which indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. B2B buyers should check that their suppliers hold these certifications to ensure product reliability.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process. These typically include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint ensures that raw materials meet specified standards before production begins. Materials are often tested for strength, corrosion resistance, and dimensional accuracy.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Conducted during the manufacturing process, IPQC involves monitoring key parameters like temperature and pressure during forming and assembly stages. Regular checks help catch defects early, minimizing waste and rework.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): This final checkpoint occurs before products are shipped. Locks are tested for functionality, durability, and security. Common testing methods include cycle testing, where the lock is opened and closed multiple times, and pull testing, which assesses the lock’s strength against forced entry.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
Verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is essential for B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Should Buyers Look for in Supplier Audits and Reports?
B2B buyers should request copies of quality control reports and audit findings. Reputable suppliers will conduct regular internal audits and may also undergo third-party inspections. These documents should detail the results of IQC, IPQC, and FQC processes, highlighting any non-conformities and corrective actions taken.
How Do Third-Party Inspections Ensure Quality?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s manufacturing and quality control processes. These inspections often include on-site evaluations of production facilities, material quality checks, and product testing. Buyers should ensure that the inspection agency is recognized and trusted within the industry.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate various quality control nuances when sourcing locks, especially from suppliers in different regions.
How Do Regional Standards Affect Quality Assurance?
Different regions may have specific standards and regulations affecting lock manufacturing. For instance, while CE marking is essential in Europe, South American markets may require compliance with local standards like ABNT. Understanding these regional differences is crucial for buyers to ensure their products meet local compliance requirements.
What Are the Challenges in Verifying Quality Across Borders?
Cross-border transactions can complicate quality verification. Language barriers, differing regulatory standards, and varying levels of supplier transparency can pose challenges. B2B buyers should establish clear communication channels and consider working with local partners or representatives to facilitate the verification process.
Conclusion: Ensuring Quality and Reliability in Lock Manufacturing
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in the lock industry, international B2B buyers can make informed sourcing decisions. Prioritizing suppliers who adhere to stringent quality standards and demonstrate robust quality control practices will ensure that the locks procured meet the necessary security and reliability requirements.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘type of locks’
Introduction
In today’s competitive global marketplace, sourcing the right type of locks is critical for ensuring security and compliance in various business operations. This practical guide aims to equip B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe with actionable steps to effectively procure locks that meet their specific needs. By following this checklist, you can streamline your sourcing process and make informed decisions that enhance security while optimizing costs.
Step 1: Define Your Security Requirements
Understanding your security needs is the first step in the procurement process. Evaluate the specific environments where the locks will be used, such as offices, warehouses, or retail locations. Consider factors like the level of foot traffic, potential threats, and access control requirements.
- Identify lock types: Determine whether you need deadbolts, electronic locks, or padlocks based on the security level required.
- Assess compliance needs: Ensure that the locks meet any regional security standards or regulations applicable to your industry.
Step 2: Research Available Lock Types
Familiarize yourself with the various types of locks available in the market. Each type serves different purposes and offers distinct features.
- Consider durability and resistance: Look for locks that withstand tampering, weather conditions, and wear over time.
- Evaluate technology: Explore advanced options like smart locks or electronic systems that can provide better control and monitoring capabilities.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a purchase, it’s essential to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region.
- Check certifications: Ensure suppliers have relevant certifications (e.g., ISO, ANSI) to guarantee product quality and reliability.
- Assess their track record: Look for suppliers with proven experience in providing locks to businesses similar to yours.
Step 4: Request Samples and Conduct Testing
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request samples of the locks you are considering. Testing the locks in real-world scenarios will help assess their performance and suitability.
- Conduct security assessments: Test locks for ease of use, durability, and resistance to forced entry.
- Involve end-users: Gather feedback from staff who will be using the locks to ensure they meet operational needs.
Step 5: Review Pricing and Payment Terms
Understanding the financial implications of your purchase is crucial. Compare pricing structures from different suppliers to ensure you get the best value.
- Consider total cost of ownership: Evaluate not just the initial purchase price but also installation costs, maintenance, and potential replacement needs.
- Negotiate terms: Discuss payment terms, warranties, and return policies to ensure favorable conditions for your procurement.
Step 6: Finalize Your Order and Monitor Delivery
Once you have made your selection, finalize your order while ensuring clear communication with the supplier regarding specifications and delivery timelines.
- Confirm order details: Double-check specifications, quantities, and delivery schedules to avoid errors.
- Track delivery: Monitor the shipment to ensure timely arrival and address any issues that may arise promptly.
Step 7: Implement and Train Staff on Lock Usage
After receiving the locks, it’s vital to implement them effectively and train staff on their proper use.
- Conduct training sessions: Ensure employees understand how to operate the locks and recognize potential security issues.
- Establish maintenance protocols: Set up regular checks and maintenance schedules to prolong the lifespan of the locks and enhance security.
By following this comprehensive sourcing checklist, B2B buyers can ensure they select the right locks tailored to their specific security needs while fostering a secure environment for their operations.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for type of locks Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Lock Manufacturing?
When considering the sourcing of locks, understanding the cost components is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary elements that contribute to the overall cost include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts pricing. For instance, locks made of stainless steel or brass tend to be more expensive due to their durability and corrosion resistance compared to those made from lower-grade metals or plastic.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region. Countries with higher labor costs, such as those in Western Europe, may have higher lock prices than those produced in regions with lower labor costs, like parts of Africa or South America.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory maintenance, utilities, and administrative expenses. Factories with advanced technology and automation may have lower per-unit overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for unique designs or specifications can add to the initial costs but may lead to savings in the long run through efficiency in production.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure product reliability and compliance with standards, which can increase costs but are essential for maintaining brand reputation and customer satisfaction.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary significantly depending on the distance, mode of transportation, and any tariffs or duties that may apply. International buyers should consider these factors in their total cost analysis.
-
Margin: Suppliers will add their profit margin to the base cost, which can vary widely based on market conditions and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Lock Sourcing?
Several factors influence the pricing of locks, especially for international B2B buyers:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Purchasing in bulk typically lowers the per-unit cost, making it advantageous for larger operations. Buyers should negotiate MOQ with suppliers to achieve better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom locks tailored to specific needs (e.g., smart locks with advanced features) can lead to higher costs. Understanding the necessity of such customizations versus off-the-shelf options is essential for cost efficiency.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Locks that meet specific industry standards (e.g., ANSI/BHMA certification) or that use higher-grade materials will come at a premium. Buyers should weigh the cost against the potential for reduced liability and increased security.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and geographical location can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to perceived quality, while newer suppliers might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: The terms of shipping can significantly impact overall costs. Buyers should understand the responsibilities and costs associated with different Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) to negotiate better terms with suppliers.
What Tips Can Help B2B Buyers Optimize Costs?
To ensure cost efficiency and effective negotiations, international B2B buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but the entire lifecycle cost, including installation, maintenance, and potential replacements. This broader perspective can highlight better long-term value.
-
Negotiation Tactics: Engage in discussions about pricing, especially if purchasing in bulk or establishing a long-term relationship. Suppliers may be willing to offer discounts or more favorable terms.
-
Research Local Market Conditions: Understand the local market dynamics in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This knowledge can provide leverage in negotiations and help identify the most competitive suppliers.
-
Consider Alternative Suppliers: Exploring multiple suppliers can uncover better pricing options. Establishing relationships with local suppliers may also reduce logistics costs and lead times.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Pricing for locks can vary widely based on the factors outlined above. As such, the prices discussed in this analysis are indicative and may not reflect current market conditions. Buyers should conduct thorough research and obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure they receive the best pricing for their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing type of locks With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Traditional Locks: What Are Your Options?
In the quest for security solutions, businesses often weigh the pros and cons of traditional locks against modern alternatives. While various types of locks offer physical security for doors and compartments, advancements in technology have introduced alternative methods that can provide comparable or enhanced security levels. This analysis will explore traditional locks, their functionalities, and how they stack up against alternative solutions such as electronic access systems and biometric security devices.
Comparison Table: Types of Locks vs. Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Type Of Locks | Electronic Access Systems | Biometric Security Devices |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Reliable physical barrier | High, with remote access | Very high, unique to individuals |
| Cost | Moderate initial cost; ongoing key replacement | Higher initial cost; lower ongoing | High initial cost; minimal ongoing |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple installation; requires manual key management | Requires wiring or network setup | Requires installation and calibration |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; may require key duplication | Moderate; software updates needed | Moderate; regular calibration and maintenance |
| Best Use Case | Traditional settings; homes, businesses | High traffic areas; offices | Secure environments; government, finance |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
How Do Electronic Access Systems Compare to Traditional Locks?
Electronic access systems provide a modern alternative to traditional locks by allowing entry through keypads, RFID cards, or smartphone applications. These systems can be programmed to grant access to multiple users without the need for physical keys, making them ideal for environments with high traffic or where access needs to be managed dynamically.
Pros:
– Enhanced convenience with keyless entry.
– Ability to track access logs and revoke access remotely.
– Integration with other security systems.
Cons:
– Higher upfront costs and potential vulnerability to hacking.
– Dependence on power supply and network connectivity.
What Are the Advantages of Biometric Security Devices Over Traditional Locks?
Biometric security devices, which utilize unique biological traits (like fingerprints or facial recognition) to grant access, represent one of the most secure methods of entry available today. These devices eliminate the need for keys or codes, as access is granted based on the individual’s unique attributes.
Pros:
– Extremely secure; difficult to replicate biometric data.
– Eliminates the risk of lost or stolen keys.
– Provides detailed access logs.
Cons:
– High initial investment and potential for technical issues.
– May require user training to ensure proper usage and maintenance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Security Needs
When selecting the best security solution, B2B buyers should consider the specific requirements of their business environment. Traditional locks may suffice for smaller operations or less critical access points, while electronic access systems and biometric devices may be better suited for larger, high-security environments where monitoring and flexibility are paramount. Assess factors such as cost, ease of implementation, and maintenance needs to determine the most suitable option for securing your assets effectively. Ultimately, the choice should align with your organization’s security objectives, budget constraints, and operational requirements.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for type of locks
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Locks for B2B Buyers?
Understanding the technical specifications of locks is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure they select the right products for their needs. Here are some key properties to consider:
1. Material Grade: What Should You Look For?

A stock image related to type of locks.
The material grade of a lock significantly impacts its durability and security. Common materials include stainless steel, brass, and zinc alloys. Stainless steel locks are often preferred for their corrosion resistance and strength, making them ideal for outdoor applications. Brass offers a good balance of aesthetics and durability, while zinc alloys are typically used for lighter-duty applications. Selecting the appropriate material ensures longevity and reliability, particularly in harsh environments.
2. Security Rating: Why Is It Important?
Locks are often rated based on their security features, which can range from basic to high-security levels. Common standards include ANSI/BHMA ratings in the U.S. and EN 12209 in Europe. A higher rating indicates enhanced resistance to picking, drilling, and forced entry. For international B2B buyers, understanding these ratings helps in selecting locks that meet specific security needs, especially in commercial settings where asset protection is paramount.
3. Tolerance Levels: How Do They Affect Lock Functionality?
Tolerance levels refer to the precision with which lock components are manufactured. High tolerance levels lead to smoother operation and reduce the likelihood of jamming or malfunction. When sourcing locks, it’s essential to inquire about the tolerance specifications to ensure that the locks will function correctly in their intended applications. This is particularly important in environments where reliability is critical, such as in high-traffic commercial spaces.
A stock image related to type of locks.
4. Key Control Systems: What Are the Benefits?
Key control systems, including restricted keyways and master key systems, are vital for managing access to secured areas. Restricted keyways prevent unauthorized duplication of keys, while master key systems allow for hierarchical access control. For B2B buyers, implementing these systems can enhance security protocols in multi-user environments, such as offices or shared facilities. Understanding these systems can also help in negotiating better terms with suppliers.
5. Lock Mechanism Type: Which Is Right for Your Application?
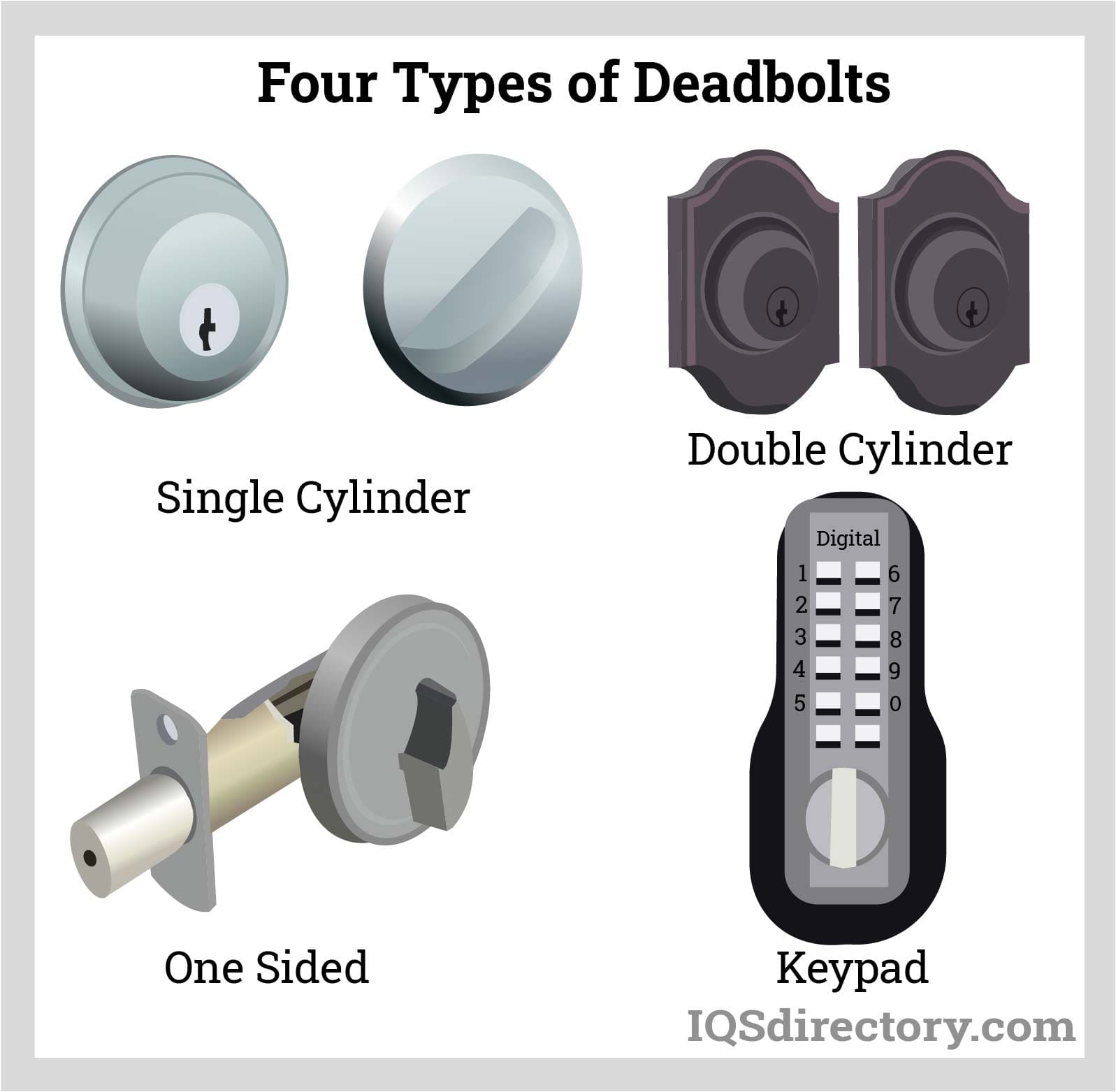
Different lock mechanisms—such as deadbolts, electronic locks, and mortise locks—offer varying levels of security and convenience. Deadbolts provide robust security for external doors, while electronic locks offer keyless entry and integration with smart home systems. For B2B buyers, choosing the right mechanism is essential for meeting specific security needs while considering user convenience and technology integration.
What Are the Common Trade Terms in the Lock Industry?
Familiarizing yourself with industry jargon can facilitate smoother negotiations and transactions. Here are some key terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): What Does It Mean?
OEM refers to companies that produce components that are later sold under another company’s brand name. Understanding OEM relationships can help B2B buyers identify reliable suppliers and assess the quality of locks based on the manufacturer’s reputation.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): How Does It Impact Your Purchase?
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is essential for B2B buyers, particularly for small to medium-sized enterprises, to plan their budgets and inventory effectively.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation): Why Is It Important?
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products. For international buyers, submitting an RFQ can streamline the procurement process and ensure competitive pricing, especially when sourcing locks from different regions.
4. Incoterms: What Do They Mean for International Trade?
Incoterms, or International Commercial Terms, are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers to understand shipping costs, risk management, and delivery obligations when importing locks from different countries.
5. Certification Standards: Why Should You Care?
Certification standards, such as ISO or CE marking, indicate that a product meets specific safety and quality benchmarks. For B2B buyers, sourcing certified locks not only ensures compliance with regulations but also enhances the credibility of their offerings in the market.
By understanding these essential technical properties and trade terminology, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance security and operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the type of locks Sector
What Are the Key Trends Influencing the Locks Market for B2B Buyers?
The global locks market is experiencing significant transformation driven by technological advancements, security concerns, and changing consumer preferences. Key trends include the rise of smart locks that integrate with IoT devices, enhancing security and convenience for both residential and commercial applications. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are increasingly seeking locks that offer not just security but also features like remote access and monitoring, which are particularly appealing in urban environments.
Emerging markets are witnessing a growing demand for electronic locks due to the surge in smart home technologies. In South Africa and Brazil, for instance, urbanization and rising disposable incomes are pushing the demand for advanced locking solutions. Additionally, the Middle East’s expanding construction sector presents opportunities for bulk procurement of high-security locks that meet international standards. B2B buyers must stay informed about these trends to make strategic sourcing decisions that align with market demands.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influence Your Lock Purchases?
Sustainability has become a pivotal consideration in the procurement of locks, with environmental impact and ethical supply chains gaining prominence among international buyers. The production of locks can involve materials and processes that contribute to environmental degradation. Therefore, sourcing from manufacturers who prioritize eco-friendly materials—such as recycled metals or sustainably sourced composites—is essential for businesses aiming to enhance their corporate social responsibility (CSR) profile.
Moreover, certification programs like ISO 14001 for environmental management systems can help buyers identify suppliers committed to reducing their ecological footprint. Buyers from Europe, in particular, are increasingly scrutinizing the sustainability practices of suppliers, which can directly influence purchasing decisions. By choosing suppliers with strong sustainability credentials, businesses not only contribute to environmental preservation but also strengthen their market position by appealing to a growing base of eco-conscious customers.
How Has the Locks Industry Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the locks industry has been marked by significant technological advancements and changes in consumer needs. From the rudimentary wooden locks of ancient civilizations to the sophisticated electronic and smart locks of today, the journey reflects broader societal changes. In the late 20th century, the introduction of electronic locks marked a turning point, paving the way for enhanced security features like keyless entry and integration with home automation systems.
Today, the focus is shifting towards smart locks that utilize biometric recognition and mobile app connectivity, catering to a tech-savvy generation that values convenience and security. For B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is crucial for making informed decisions about which types of locks to procure, ensuring they align with current market demands and technological advancements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of type of locks
-
How do I select the right type of lock for my business needs?
Selecting the right lock type depends on the specific security needs of your business. Consider factors such as the location, the value of items being protected, and the level of access control required. For high-security areas, deadbolts or mortise locks are recommended. For places needing frequent access by multiple individuals, electronic or smart locks might be ideal. Conduct a risk assessment to understand vulnerabilities and consult with a security expert if necessary to ensure optimal lock selection. -
What is the best lock type for outdoor use in humid climates?
For outdoor applications in humid climates, stainless steel padlocks or mortise locks with corrosion-resistant finishes are ideal. These locks are designed to withstand moisture and prevent rusting, ensuring durability and reliability. Additionally, consider using locks with sealed mechanisms to protect against dust and water ingress. Always verify the lock’s IP (Ingress Protection) rating for assurance against environmental factors. -
How can I verify the quality of locks from suppliers?
To ensure you are sourcing high-quality locks, check for certifications such as ANSI/BHMA or ISO standards, which indicate that the locks meet specific performance criteria. Request product samples and conduct physical tests for durability and functionality. Additionally, review supplier reputations through trade references, online reviews, and industry feedback. It’s also beneficial to inquire about their quality assurance processes and warranty terms. -
What are the common minimum order quantities (MOQ) for lock purchases?
Minimum order quantities for locks can vary significantly by supplier and lock type. Generally, for bulk purchases, MOQs may range from 50 to 100 units, while custom orders could have higher MOQs depending on the complexity of the customization. Always clarify MOQ terms during negotiations and consider discussing flexible ordering options with suppliers to accommodate your specific needs. -
What payment terms should I consider when sourcing locks internationally?
When engaging in international transactions, standard payment terms include net 30 or net 60 days, where payment is due within 30 or 60 days after delivery. However, for new suppliers, consider using secure payment methods like letters of credit or PayPal to mitigate risk. Always negotiate terms that protect your interests, and be aware of currency exchange rates and potential additional fees that might arise during international transactions. -
How do I handle logistics and shipping when importing locks?
When importing locks, it’s crucial to partner with reliable logistics providers experienced in international shipping. They can assist with customs clearance, ensuring compliance with local regulations. Evaluate shipping options such as air freight for speed or sea freight for cost-effectiveness. Always plan for potential delays, and consider insurance for high-value shipments to mitigate risks associated with loss or damage during transit. -
What customization options are available for locks?
Customization options for locks can include specific finishes, sizes, and keying systems. Some suppliers offer branding opportunities, allowing you to have your logo engraved on the locks. It’s also possible to request unique features such as electronic access control or biometric systems. When seeking customization, communicate your requirements clearly to ensure that the supplier can meet your specifications effectively. -
What are the best practices for lock maintenance and longevity?
To ensure the longevity of your locks, regular maintenance is essential. This includes cleaning locks periodically to remove dust and debris, lubricating moving parts with graphite or silicone-based lubricants, and checking for any signs of wear or damage. Conduct routine inspections to ensure all locking mechanisms function smoothly. Establish a maintenance schedule and train staff on proper handling to prevent unnecessary wear and tear.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for type of locks
As the global market for locks continues to evolve, strategic sourcing plays a pivotal role in ensuring that international B2B buyers can secure the best products for their specific needs. Understanding the various types of locks—from deadbolts to smart locks—enables businesses to make informed decisions that align with their security requirements, operational demands, and budget constraints.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Lock Procurement Process?
By leveraging strategic sourcing, businesses can identify reliable suppliers, negotiate favorable terms, and ensure compliance with regional security standards. This approach not only enhances security but also promotes cost savings and operational efficiency. For buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it is essential to consider local market dynamics and potential logistical challenges when sourcing locks.
What Does the Future Hold for Lock Technologies?
Looking ahead, the integration of smart technology in locks will likely reshape the landscape of security solutions. International B2B buyers should stay abreast of emerging trends and innovations, such as keyless entry systems and IoT compatibility, to enhance their security infrastructure.
In conclusion, prioritize strategic sourcing to navigate the complexities of the lock market effectively. Engage with trusted suppliers and stay informed about advancements to secure a competitive edge in your industry.