Discover Cost-Effective Label Machinery Solutions (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for label machinery
Navigating the global market for label machinery can be a complex endeavor for B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The challenge lies not only in sourcing the right labeling solutions but also in ensuring they meet the diverse regulatory and operational requirements of different regions. This guide aims to simplify the process by providing a comprehensive overview of various types of label machinery, their applications across industries, and key considerations for supplier vetting.
From semi-automatic label applicators to advanced labeling systems for high-volume production, understanding the specifications and functionalities of different machines is crucial. Additionally, we will discuss the importance of evaluating supplier credentials, assessing total cost of ownership, and recognizing the impact of technological advancements in labeling solutions. By arming international B2B buyers with actionable insights, this guide empowers them to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Whether you are looking to enhance your product presentation, comply with regional labeling standards, or streamline your production process, this resource will serve as a valuable tool in navigating the competitive landscape of label machinery. Embrace the opportunity to elevate your labeling processes and gain a competitive edge in your market.
Understanding label machinery Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Semi-Automatic Label Applicators | High-speed application, adjustable settings, easy operation | Bottling, packaging, food and beverage | Pros: Cost-effective, efficient for medium volumes. Cons: Limited automation, requires operator presence. |
| Fully Automatic Labeling Machines | High throughput, integrated systems for multiple labels | Large-scale manufacturing, pharmaceuticals | Pros: Very high speed, minimal labor required. Cons: Higher initial investment, complex setup. |
| Label Printers | Print-on-demand capability, versatile label sizes | Retail, logistics, product labeling | Pros: Customizable labels, low cost for short runs. Cons: Slower than applicators, limited to label printing. |
| Label Rewinders | Neatly rewinds labels for easier handling | Pre-printed labels, distribution centers | Pros: Reduces waste, improves organization. Cons: Limited to rewinding, not for application. |
| Flat Surface Label Applicators | Designed for flat or tapered surfaces, versatile container types | E-commerce, packaging, specialty goods | Pros: Adaptable to various container shapes. Cons: Slower than cylindrical applicators. |
What Are Semi-Automatic Label Applicators and Their B2B Suitability?
Semi-automatic label applicators are designed for high-speed label application while requiring minimal operator involvement. These machines can apply labels to cylindrical containers like bottles and jars at rates of up to 1500 labels per hour. They are ideal for medium-volume production environments, such as food and beverage industries, where efficiency and accuracy are paramount. When considering a purchase, B2B buyers should evaluate their production volume, the types of containers they use, and the ease of operation.
Why Choose Fully Automatic Labeling Machines for Large Scale Production?
Fully automatic labeling machines are engineered for high throughput and can apply multiple labels simultaneously. These systems are typically integrated with other production line equipment, making them suitable for large-scale manufacturing, such as in pharmaceuticals and cosmetics. While they offer significant advantages in speed and labor savings, B2B buyers must consider the higher upfront costs and potential complexity in setup and maintenance. A thorough assessment of production needs and available space is crucial before investing.
How Do Label Printers Benefit B2B Operations?
Label printers provide a versatile solution for businesses that require print-on-demand capabilities. They allow companies to create customized labels in various sizes, making them suitable for retail and logistics applications. While they are cost-effective for short runs, B2B buyers should be aware that label printers generally operate at slower speeds compared to applicators. Thus, businesses with high-volume needs may need to consider integrating a printer with other labeling machinery for optimal efficiency.
What Role Do Label Rewinders Play in Labeling Processes?
Label rewinders are essential for managing pre-printed labels, allowing businesses to neatly rewind large quantities for easy handling and storage. They are particularly useful in distribution centers and printing facilities where organization and waste reduction are priorities. Although they do not apply labels, their value lies in improving workflow efficiency. Buyers should assess their label handling processes to determine if a rewinder will enhance their operations.
Why Opt for Flat Surface Label Applicators?
Flat surface label applicators are versatile machines designed to apply labels to a variety of flat or tapered surfaces, such as boxes and bags. They are particularly beneficial for e-commerce businesses and specialty goods manufacturers, where packaging diversity is common. While they provide adaptability, B2B buyers should consider their application speed, as these machines may not match the efficiency of cylindrical applicators. Evaluating the types of products and packaging used will help buyers make informed decisions.
Key Industrial Applications of label machinery
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Label Machinery | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food & Beverage | Automated labeling for bottles, cans, and pouches | Increases efficiency and accuracy in production | Speed of labeling, compatibility with various container shapes |
| Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics | Serialization and compliance labeling for products | Ensures regulatory compliance and enhances traceability | Ability to print variable data, security features for anti-counterfeiting |
| Logistics & Shipping | Labeling for packages and pallets | Streamlines logistics operations and improves tracking | Durability of labels, ease of application on various surfaces |
| Chemicals & Hazardous Materials | Safety labeling for containers and barrels | Enhances safety and compliance with regulations | Customizability for specific safety standards and labeling requirements |
| Retail & E-commerce | Product labeling for retail display and online sales | Improves brand visibility and customer engagement | Versatility in label design, integration with printing technology |
How is Label Machinery Used in the Food & Beverage Industry?
In the food and beverage sector, label machinery is essential for the automated labeling of bottles, cans, and pouches. This equipment not only enhances the speed of production but also ensures that labels are applied accurately, reducing wastage and the risk of mislabeling. Buyers in this industry should prioritize machines that can handle various container shapes and sizes while maintaining high labeling speeds to meet production demands.
What Role Does Label Machinery Play in Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics?
Label machinery in pharmaceuticals and cosmetics is crucial for serialization and compliance labeling. This ensures that products meet regulatory requirements and enhances traceability throughout the supply chain. Buyers must consider machines that offer the capability to print variable data, such as batch numbers and expiration dates, and include security features that prevent counterfeiting, which is increasingly important in these sectors.
How Can Logistics & Shipping Benefit from Label Machinery?
In logistics and shipping, label machinery is used for labeling packages and pallets. This application streamlines logistics operations by improving tracking and inventory management. Businesses should look for durable labeling solutions that can withstand various environmental conditions and ensure that labels adhere well to different surfaces, facilitating smoother operations from warehousing to delivery.
Why is Safety Labeling Important in Chemicals & Hazardous Materials?
For chemicals and hazardous materials, safety labeling is a critical application of label machinery. These labels provide essential information regarding handling, storage, and emergency procedures, thus enhancing safety and compliance with regulations. Buyers should seek machines that allow for customization to meet specific safety standards and can produce labels that are durable and resistant to chemicals.
How Does Label Machinery Enhance Retail & E-commerce?
In the retail and e-commerce sectors, label machinery is vital for creating product labels that enhance brand visibility and customer engagement. Efficient labeling systems can produce high-quality labels that are visually appealing and informative. When sourcing label machinery, businesses should consider the versatility of label designs and the ability to integrate with current printing technologies to streamline their operations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘label machinery’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inefficient Labeling Processes Leading to Downtime
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face challenges with inefficient labeling processes that lead to significant downtime in production lines. For example, a beverage manufacturer in South America may use a manual labeling system that cannot keep up with production demands. As a result, employees spend excessive time aligning labels and ensuring they stick correctly, which disrupts workflow and leads to delays in product distribution. This inefficiency not only affects productivity but also increases labor costs and can result in lost sales opportunities.
The Solution:
Investing in semi-automatic or fully automatic label applicators can significantly enhance labeling efficiency. For example, machines like the AP380 Label Applicator can apply labels at speeds of up to 1,500 per hour, allowing for quick adjustments to production needs. Buyers should look for machinery that offers easy setup and operation, such as a touchscreen interface for intuitive use. Additionally, selecting machines with integrated features like label-liner rewinders can prevent label waste and keep workspaces organized. When sourcing machinery, consider your production volume and label specifications to choose a model that meets your operational requirements without compromising speed or accuracy.
Scenario 2: Compatibility Issues with Existing Equipment
The Problem:
One common issue that B2B buyers encounter is the compatibility of new label machinery with their existing production equipment. A company in Africa looking to upgrade its labeling technology may find that new label applicators do not integrate well with its current conveyor systems. This lack of compatibility can lead to additional costs for retrofitting or replacing existing equipment, ultimately delaying the labeling process and straining budgets.
The Solution:
To avoid compatibility issues, it is crucial to conduct a thorough analysis of current equipment before purchasing new label machinery. Buyers should engage with suppliers who offer custom solutions tailored to their existing setups. It’s advisable to request detailed specifications and compatibility reports for any new machinery. Additionally, consider modular labeling systems that can be easily adapted to fit various production lines. When discussing options with suppliers, ask for demonstrations or case studies of how other clients have successfully integrated new machinery with existing systems. This proactive approach can help mitigate risks and ensure a smoother transition to new labeling technologies.
Scenario 3: Rising Quality Control Standards and Compliance Challenges
The Problem:
As global markets become more competitive, B2B buyers are increasingly challenged by rising quality control standards and compliance regulations. For instance, a pharmaceutical company in Europe must ensure that all labels comply with strict regulations regarding legibility, durability, and information accuracy. Failing to meet these standards can lead to costly recalls and damage to brand reputation, creating significant pressure on manufacturers to maintain high-quality labeling practices.
The Solution:
To address these quality control challenges, businesses should invest in label machinery equipped with advanced quality assurance features. Look for machines that offer real-time monitoring and feedback mechanisms to ensure labels are applied correctly every time. Additionally, incorporating software solutions that track compliance with labeling regulations can streamline the process. Buyers should also prioritize sourcing from manufacturers that provide comprehensive training and support, ensuring that staff are well-versed in operating the machinery and understanding compliance requirements. By establishing a robust quality control system that includes reliable labeling machinery, businesses can enhance product integrity and avoid regulatory pitfalls.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for label machinery
What Are the Key Materials Used in Label Machinery?
When selecting label machinery, understanding the materials used in their construction is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Here, we analyze four common materials used in label machinery, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
How Does Stainless Steel Benefit Label Machinery?
Key Properties: Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures. It is particularly beneficial in environments where hygiene is critical, such as food and pharmaceutical industries.
Pros & Cons: The durability of stainless steel makes it a preferred choice for long-term investments; however, it can be more expensive than other materials. Manufacturing complexity can also increase due to the need for specialized welding techniques. While it provides excellent compatibility with a variety of media, its higher cost may be a barrier for smaller manufacturers.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel’s resistance to corrosion and ease of cleaning make it ideal for applications involving liquids and food products, ensuring compliance with health and safety regulations.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America may need to consider local availability and cost variations. Compliance with international standards such as ASTM or DIN is essential, especially in industries governed by strict regulations.
What Are the Advantages of Aluminum in Label Machinery?
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and has good thermal conductivity. It is suitable for applications requiring quick heat dissipation.
Pros & Cons: One of the main advantages of aluminum is its lower cost compared to stainless steel, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious buyers. However, it is less durable and can be prone to deformation under high stress or impact.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is often used in label machinery that operates at moderate temperatures and does not require extreme strength. It is compatible with a wide range of labeling materials but may not be suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: In regions like Europe and the Middle East, where lightweight machinery is preferred for efficiency, aluminum can be a favorable choice. Buyers should verify compliance with local standards, particularly if the machinery will be used in regulated industries.
How Does Plastic Compare as a Material for Label Machinery?
Key Properties: Plastics, particularly high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and polycarbonate, offer good chemical resistance and lightweight characteristics. They are also less prone to rust.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of plastic is its cost-effectiveness and versatility. However, plastics may not withstand high temperatures and can degrade over time when exposed to certain chemicals. This limits their use in more demanding environments.
Impact on Application: Plastic components are often used in label machinery for non-critical applications or where weight savings are essential. They can be suitable for packaging and consumer goods but may not be ideal for industrial settings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in emerging markets may find plastics appealing due to their lower cost. However, they should assess the long-term durability and compliance with local regulations, especially in sectors like food and pharmaceuticals.
What Role Does Carbon Steel Play in Label Machinery?
Key Properties: Carbon steel is known for its strength and durability, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. It is less resistant to corrosion compared to stainless steel but can be treated for enhanced performance.
Pros & Cons: The strength of carbon steel allows for robust machinery construction, but it is heavier and more susceptible to rust. This can lead to higher maintenance costs over time, particularly in humid environments.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is often used in the structural components of label machinery, especially in industries requiring heavy-duty performance. However, it may require additional coatings or treatments to enhance its corrosion resistance.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions with high humidity or corrosive environments, such as coastal areas in South America and Africa, should be cautious with carbon steel. Understanding local environmental conditions and compliance with relevant standards is crucial for ensuring longevity.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Label Machinery
| Material | Typical Use Case for label machinery | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Food and pharmaceutical labeling | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Aluminum | Lightweight machinery applications | Cost-effective and lightweight | Less durable under high stress | Medium |
| Plastic | Non-critical labeling applications | Versatile and cost-effective | Limited temperature resistance | Low |
| Carbon Steel | Heavy-duty structural components | High strength and durability | Prone to rust without treatment | Medium |
This guide serves as a comprehensive resource for international B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions when selecting materials for label machinery tailored to their specific needs and regional contexts.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for label machinery
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Label Machinery?
The manufacturing process of label machinery involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets industry standards and buyer requirements. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe make informed purchasing decisions.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Label Machinery?
The first stage involves selecting and preparing materials such as metals, plastics, and electronic components. Common materials include:
- Aluminum and Stainless Steel: Used for structural components due to their strength and corrosion resistance.
- High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE): Often used for parts that require durability and flexibility.
- Electronic Components: Sourced from reliable suppliers to ensure compatibility and performance.
Material quality is critical. Buyers should verify that suppliers adhere to international standards for material specifications, as this directly impacts the longevity and reliability of the machinery.
How Is Label Machinery Formed and Assembled?
The forming stage typically includes processes like cutting, bending, and machining of components. Key techniques include:
- CNC Machining: Provides precision in creating complex parts.
- Laser Cutting: Offers high accuracy for intricate designs.
- Injection Molding: Commonly used for plastic components, ensuring uniformity and scalability.
After forming, the assembly stage begins, where components are put together. This may involve:
- Automated Assembly Lines: Increase efficiency and reduce human error.
- Manual Assembly: Necessary for complex or delicate components that require skilled labor.
Buyers should inquire about the assembly techniques used by suppliers, as this can affect the machine’s performance and reliability.
What Finishing Techniques Are Commonly Used in Label Machinery?
Finishing processes enhance the functionality and aesthetics of label machinery. Common techniques include:
- Surface Treatment: Such as anodizing or powder coating, which improves corrosion resistance and appearance.
- Quality Control Checks: Conducted during the finishing stage to ensure that the machinery is free of defects.
Understanding these finishing techniques can help buyers evaluate the quality of the machinery they are considering.
What Are the Quality Assurance Standards for Label Machinery?
Quality assurance (QA) is a vital component of the manufacturing process, ensuring that the label machinery meets both international and industry-specific standards.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
International standards such as ISO 9001 provide a framework for quality management systems. Compliance with these standards indicates that a manufacturer has established processes to ensure quality throughout the manufacturing cycle. Other relevant certifications include:
- CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area, indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Certification: Relevant for equipment used in the oil and gas industry, ensuring quality in hazardous environments.
B2B buyers should request documentation of these certifications to confirm the reliability of potential suppliers.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) is integrated at multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process. Key checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspects materials upon receipt to ensure they meet specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitors processes during production to identify defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducts thorough testing of the finished machinery to verify performance and safety standards.
By understanding these checkpoints, buyers can better assess the thoroughness of a supplier’s quality assurance practices.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
Verifying a supplier’s quality control measures is crucial for ensuring the reliability of label machinery. Here are actionable strategies for B2B buyers:
What Are Effective Methods for Supplier Audits?
Conducting supplier audits is an effective way to assess quality control practices. Buyers should consider:
- On-Site Audits: Visiting the manufacturing facility to evaluate processes, equipment, and quality management systems.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent auditors to provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s practices.
How Can Buyers Utilize Quality Reports and Certifications?
Requesting quality reports and certifications from suppliers is essential. Buyers should look for:
- Test Reports: Details of performance testing, including speed, accuracy, and durability.
- Certification Documentation: Proof of compliance with international standards.
Having access to these documents enables buyers to verify the legitimacy of the supplier’s claims regarding quality and reliability.
What Are the QC Considerations for International Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control is vital. Key considerations include:
- Regional Compliance: Familiarizing oneself with local regulations that may affect machinery performance and safety standards.
- Cultural Differences: Recognizing that quality expectations may vary by region, which can impact supplier relationships and negotiations.
By being aware of these factors, buyers can ensure they select suppliers that align with their quality expectations and operational requirements.
Conclusion: Ensuring Quality in Label Machinery Procurement
In summary, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for label machinery is crucial for international B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, finishing, and quality assurance standards, buyers can make informed decisions that lead to successful procurement. Verifying supplier quality control through audits, reports, and certifications further enhances confidence in the machinery purchased, ultimately leading to better operational outcomes.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘label machinery’
To successfully procure label machinery that meets your business needs, it is essential to follow a structured approach. This checklist serves as a practical guide for international B2B buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, to ensure a smooth sourcing process.
A stock image related to label machinery.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline your requirements before beginning your search. Consider factors such as the types of products you will be labeling, the speed of labeling (labels per hour), and the maximum dimensions of containers and labels. This will help you narrow down your options and focus on machinery that can efficiently handle your specific needs.
Step 2: Research Available Label Machinery Types
Familiarize yourself with the different types of label machinery available in the market. For instance, consider whether you need semi-automatic or fully automatic machines based on your production volume. Understanding the capabilities of various models will help you make an informed decision that aligns with your operational workflow.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Look for suppliers with a proven track record of reliability and customer satisfaction, as this can significantly impact your production efficiency.
- Key Points to Assess:
- Reputation: Research online reviews and testimonials.
- Experience: Check how long the supplier has been in the industry.
Step 4: Verify Compliance and Certifications
Ensure that the machinery complies with local regulations and industry standards. Look for certifications such as ISO, CE, or specific health and safety certifications relevant to your region. This step is critical to avoid legal issues and ensure the machinery is safe to operate.
Step 5: Request Quotes and Compare Pricing
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request detailed quotes that include pricing, delivery times, and warranty conditions. Compare these aspects carefully, as the lowest price may not always indicate the best value. Consider total cost of ownership, including maintenance and operational costs over time.
Step 6: Assess After-Sales Support and Maintenance Services
Inquire about the after-sales support offered by the supplier, including installation services, training for your staff, and maintenance packages. Reliable after-sales service is essential for minimizing downtime and ensuring that your machinery operates efficiently.
- What to Look For:
- Training Programs: Ensure that your team is adequately trained to operate the machinery.
- Spare Parts Availability: Confirm that spare parts are readily available to avoid extended downtimes.
Step 7: Finalize Your Purchase Agreement
Once you are satisfied with all aspects of the procurement process, finalize your purchase agreement. Ensure that all terms are clearly outlined, including payment terms, delivery schedules, and any warranties. Having a well-defined contract protects both parties and helps mitigate potential disputes.
By following this checklist, international B2B buyers can streamline their sourcing process for label machinery and ensure they make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for label machinery Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Label Machinery Sourcing?
When sourcing label machinery, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting and negotiation. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: This encompasses the raw materials used in the manufacturing of label machinery, such as metals and plastics. Higher quality materials will naturally increase costs, but they also contribute to durability and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly by region and complexity of the machinery. Automated machines may require fewer operators, reducing ongoing labor costs, while custom machinery might necessitate more skilled labor during production.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations, such as utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. Efficient production processes can help mitigate overhead costs.
-
Tooling Costs: Specialized tools required for the production of specific machinery can add to initial costs. It’s essential to evaluate whether these costs are included in the quoted price or will be charged separately.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC measures ensures that machinery meets industry standards, which can involve additional costs. However, investing in QC can reduce long-term maintenance and operational issues.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs for shipping machinery can vary based on distance and method. International buyers should consider logistics when evaluating total costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a profit margin to their costs, which varies based on competition, market demand, and the uniqueness of the machinery.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Label Machinery Costs?
Several factors can influence the final pricing of label machinery, which international buyers should consider:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their operational needs to optimize pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom machinery designed to meet specific operational requirements can significantly increase costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the budget constraints.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Machinery that meets international quality standards or certifications may carry a premium price. However, these investments often yield long-term savings through reliability and efficiency.
-
Supplier Factors: Different suppliers may have varying pricing strategies based on their manufacturing capabilities, reputation, and market presence. Establishing relationships with reliable suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of shipping (e.g., FOB, CIF) is critical, as they dictate who bears the costs and risks during transportation. This can impact the overall cost of machinery.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Negotiating Label Machinery Prices?
International B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, can adopt several strategies to enhance their sourcing effectiveness:
-
Negotiate Wisely: Always seek to negotiate terms, including pricing, payment plans, and delivery schedules. Suppliers may have flexibility in their pricing based on order size and payment terms.
-
Assess Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but also the ongoing costs associated with operation, maintenance, and potential downtime. A lower initial price may lead to higher long-term costs if the machinery is less efficient or reliable.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Different regions may have varied pricing structures due to local manufacturing costs, tariffs, and taxes. Familiarizing oneself with these factors can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Request Detailed Quotes: Ensure that quotes are itemized to understand exactly what is included. This transparency can help identify areas for negotiation.
-
Leverage Local Networks: Utilize local contacts or industry associations to gain insights into reliable suppliers and average pricing, which can strengthen your negotiating position.
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices
Prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and can vary based on supplier negotiations, market conditions, and specific machinery requirements. It is essential for buyers to conduct thorough research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing label machinery With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Label Machinery
In the world of packaging and labeling, businesses often seek the most efficient solutions to meet their operational needs. While label machinery offers a reliable way to apply labels to products, there are alternative methods that can achieve similar outcomes. This section explores several viable alternatives, providing B2B buyers with a comprehensive comparison to help them make informed decisions.
Comparison of Label Machinery with Alternative Solutions
| Comparison Aspect | Label Machinery | Manual Labeling | Digital Printing Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High-speed application (up to 1500 labels/hour) | Slower (10-100 labels/hour) | Variable (depends on printer) |
| Cost | Initial investment varies ($1,395 – $2,395) | Low (minimal equipment needed) | Medium to high (depends on printer and materials) |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires setup and training | Very simple; no training required | Moderate; requires software knowledge |
| Maintenance | Regular upkeep needed for optimal performance | Minimal maintenance needed | Regular maintenance and software updates required |
| Best Use Case | High-volume production environments | Low-volume, artisanal products | Custom, short-run labels or variable data printing |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Manual Labeling?
Manual labeling involves applying labels by hand, making it a straightforward solution for businesses with lower production volumes. One of the primary advantages of this method is its low cost; it requires minimal equipment, making it accessible for small businesses or startups. Furthermore, it allows for flexibility in label placement and design, catering to unique product requirements. However, the downsides include significantly slower application speeds and a higher potential for human error, which can affect consistency and quality.
How Do Digital Printing Systems Compare to Label Machinery?
Digital printing systems offer an innovative alternative that allows businesses to print labels on-demand, eliminating the need for pre-printed stock. This method is particularly advantageous for companies requiring custom or variable data labels, such as QR codes or unique barcodes. Digital printing can also reduce waste by allowing for smaller print runs. However, the initial investment in digital printers can be substantial, and the speed may not match that of dedicated label machinery for high-volume applications. Additionally, operational complexity is higher, as it requires familiarity with design software and printer settings.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Labeling Solution for Your Business
Selecting the appropriate labeling solution depends on various factors, including production volume, budget, and specific labeling requirements. For businesses in high-demand markets, investing in label machinery may be the most efficient approach due to its speed and consistency. Conversely, if the production volume is low or if customization is paramount, manual labeling or digital printing systems may be more suitable. B2B buyers should carefully evaluate their operational needs and long-term goals to choose the solution that best aligns with their business strategy.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for label machinery
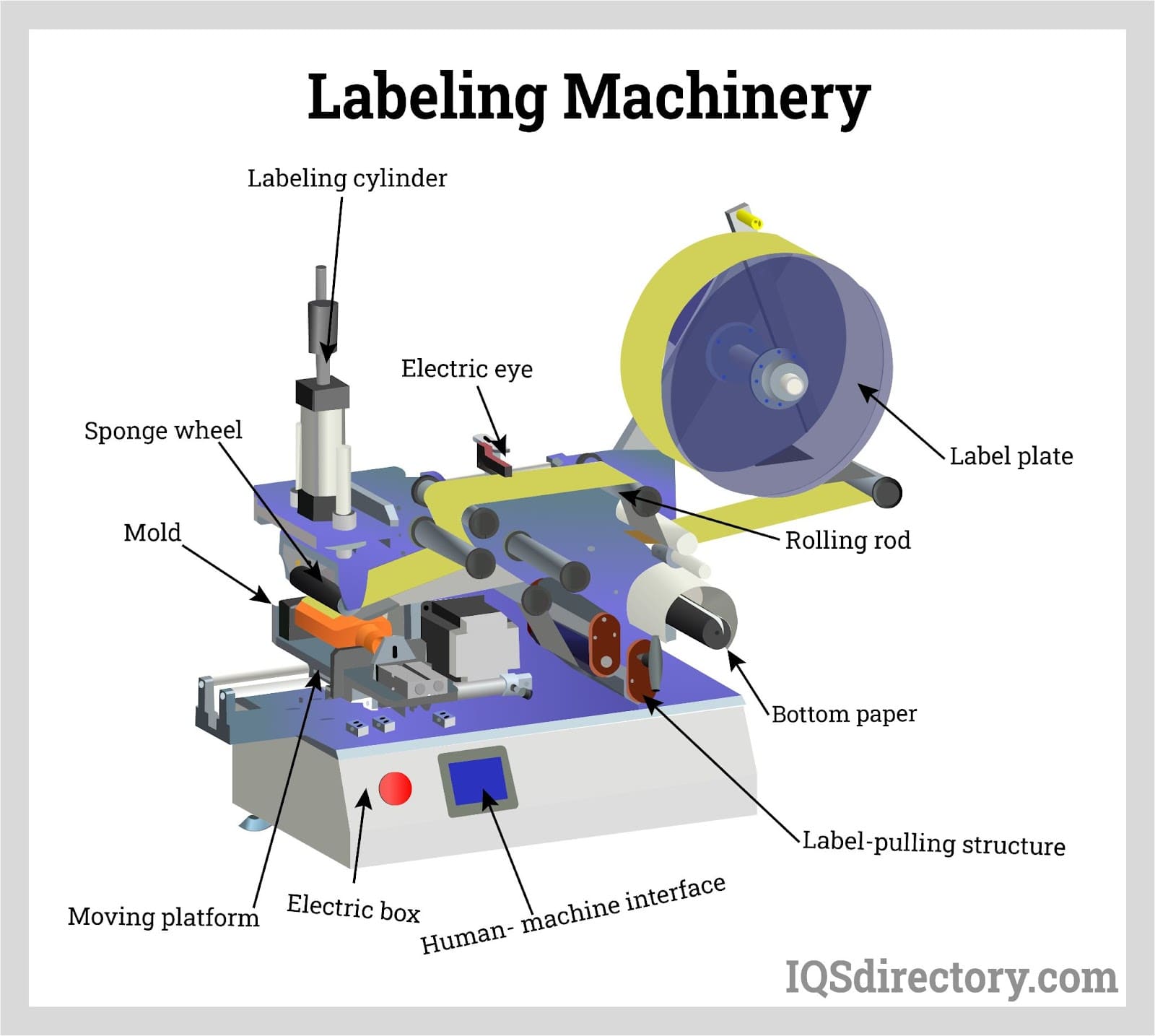
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Label Machinery?
When considering label machinery for your business, understanding its technical specifications is crucial for ensuring the right fit for your operational needs. Here are some essential properties to evaluate:
1. Label Application Speed
Label application speed, typically measured in labels per hour, indicates how quickly the machine can apply labels to products. For instance, some machines can apply up to 1,500 labels per hour. This property is vital for high-volume production environments where efficiency directly impacts profitability. Slow machines can bottleneck operations and lead to increased labor costs.
2. Container Compatibility
This specification refers to the types and sizes of containers that the labeling machine can handle. Machines may be designed for cylindrical containers (like bottles and jars) or flat surfaces (like boxes and pouches). Understanding container compatibility is essential for ensuring that your labeling machinery can accommodate your specific product range without requiring additional equipment.
3. Label Width Capacity
The maximum label width capacity indicates the largest label size the machine can apply. Some machines can handle labels up to 8.375 inches wide. This property is crucial for businesses that require larger labels for branding or regulatory information. Choosing a machine with the appropriate label width ensures compliance and enhances product visibility on shelves.
4. Material Grade and Build Quality
The material grade of the labeling machine affects its durability and performance. Machines made from high-grade materials are typically more robust and reliable, reducing the likelihood of breakdowns and maintenance costs. When selecting a labeling machine, it’s important to consider the environment in which it will operate, as some materials may not withstand harsh conditions.
5. Ease of Use and Setup
User-friendliness is an essential property, especially for businesses with varying levels of technical expertise. Machines that offer quick setup and intuitive operation reduce training time and increase productivity. Features like touchscreen controls and preset configurations can significantly enhance the user experience, making it easier for operators to manage the machinery.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Label Machinery?
Understanding industry jargon can help you navigate negotiations and supplier communications more effectively. Here are some common terms you should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In labeling machinery, it’s important to know if your supplier is an OEM or a reseller. This distinction can affect warranty, service, and the availability of replacement parts.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ specifies the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For labeling machinery, knowing the MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory management. Suppliers may set MOQs to ensure profitability, so understanding this term can help you negotiate better terms based on your purchasing power.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and other details for a specific product or service. When considering labeling machinery, submitting an RFQ can help you gather competitive offers and make informed decisions. It’s an essential step in the procurement process for B2B buyers.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized terms used in international trade to define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when importing labeling machinery from different countries. They clarify who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and risk during transit.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the machinery. For labeling machinery, longer lead times can disrupt production schedules. Knowing the lead time is essential for planning and ensuring that you have the necessary equipment when you need it.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring they select the right labeling machinery for their operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the label machinery Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Label Machinery Sector?

A stock image related to label machinery.
The label machinery sector is experiencing significant growth, driven by several global factors. First, the rise of e-commerce has led to increased demand for packaging and labeling solutions that enhance product visibility and brand recognition. Additionally, the trend toward automation in manufacturing processes is reshaping how companies approach labeling. Emerging technologies, such as AI and IoT, are enabling advanced labeling solutions that improve operational efficiency and reduce production costs.
For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial. The market is increasingly competitive, with suppliers offering a range of customizable labeling machines that cater to various industries, including food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who offer flexibility in machine configurations and the ability to integrate with existing production lines. Furthermore, the shift towards semi-automatic and fully automatic systems is becoming more prevalent, as businesses seek to streamline operations and reduce labor costs.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Trends in the Label Machinery Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor in B2B purchasing decisions within the label machinery sector. The environmental impact of production processes is under scrutiny, prompting buyers to seek machines that minimize waste and energy consumption. Ethical sourcing is equally important, as companies are increasingly held accountable for the sustainability of their supply chains. Buyers should look for suppliers that demonstrate commitment to sustainable practices, such as using recyclable materials and reducing emissions during manufacturing.
Green certifications and the use of eco-friendly materials in labeling machinery are gaining traction. For instance, machines that utilize biodegradable labels or those made from recycled components are becoming more desirable. This not only aligns with global sustainability goals but also enhances brand reputation among environmentally conscious consumers. As such, B2B buyers should engage suppliers who can provide transparency regarding their sourcing practices and sustainability credentials.
How Has the Label Machinery Sector Evolved Over Time?
The label machinery sector has evolved significantly over the past few decades, transitioning from manual labeling processes to sophisticated automated systems. Initially, labeling was a labor-intensive task, often resulting in inconsistent application and quality issues. With technological advancements, the introduction of semi-automatic and fully automatic labeling machines has revolutionized the industry, allowing for higher output rates and improved accuracy.
This evolution has been driven by the need for efficiency and the ability to meet consumer demands for quick turnaround times. Additionally, the integration of digital printing technology has enabled companies to produce labels on demand, reducing inventory costs and waste. As a result, international B2B buyers can now access a diverse range of labeling solutions that not only enhance productivity but also cater to the unique requirements of their businesses. Understanding this evolution is essential for making informed purchasing decisions in today’s dynamic market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of label machinery
-
How do I choose the right labeling machine for my business needs?
Selecting the appropriate labeling machine involves assessing your production requirements, including the types of containers and labels you use. Consider factors such as label application speed, precision, and compatibility with your existing machinery. For international buyers, it’s crucial to evaluate the machine’s adaptability to different container shapes and sizes, as well as whether it can handle varying label materials. Additionally, consult with suppliers about their customization options to ensure the machine aligns with your specific operational needs. -
What is the best labeling machine for small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs)?
For SMEs, semi-automatic labeling machines often provide the best balance between cost and efficiency. Models like Primera’s AP360 or AP380 are ideal, as they can apply labels to various container types at speeds of up to 1,500 labels per hour. When sourcing, consider machines that offer flexibility in label sizes and types, as well as ease of operation and maintenance, which is essential for businesses with limited technical support. -
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for labeling machinery?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their reputation, years of experience, and customer reviews. Check if they provide comprehensive after-sales support, including installation, training, and maintenance services. Additionally, verify their manufacturing certifications and compliance with international standards to ensure quality. For international buyers, assess the supplier’s ability to handle customs, shipping logistics, and any potential tariffs that may impact your investment. -
What are the common payment terms for purchasing labeling machinery internationally?
Common payment terms for international B2B transactions often include options such as Letters of Credit (LC), bank transfers, or payment through escrow services. It’s essential to negotiate terms that protect your investment, especially when dealing with overseas suppliers. Ensure you understand the total cost implications, including shipping, customs, and taxes, which can affect your budget. Always seek clarity on any potential upfront deposits and the conditions for payment upon delivery or installation.

A stock image related to label machinery.
-
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for imported labeling machines?
To ensure quality assurance for imported labeling machines, request detailed product specifications and certifications from the supplier. Conduct a pre-shipment inspection to verify that the machinery meets your operational standards. Establish a clear return and warranty policy to address any defects or performance issues post-delivery. Additionally, consider sourcing from suppliers who offer trial periods or demonstrations to assess the machine’s functionality before finalizing the purchase. -
What is the typical lead time for labeling machinery orders from international suppliers?
The lead time for labeling machinery can vary significantly depending on the supplier’s location, production capacity, and your specific requirements. Generally, expect a lead time of 4 to 12 weeks, factoring in manufacturing, quality checks, and shipping. For urgent needs, some suppliers may offer expedited options, but this can increase costs. Always communicate your timeline expectations upfront and confirm the supplier’s ability to meet them. -
How does customization impact the cost of labeling machinery?
Customization can significantly affect the cost of labeling machinery, as tailored solutions often require additional engineering and materials. While standard models may be more cost-effective, customized machines provide specific functionalities that can enhance efficiency and productivity in your operations. When negotiating with suppliers, request detailed quotes that break down the costs associated with customization options, so you can evaluate the return on investment. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing labeling machinery?
Logistics play a crucial role in the successful importation of labeling machinery. Ensure you have a reliable freight forwarder to manage shipping routes and customs clearance. Assess the total landed cost, including shipping fees, tariffs, and insurance. Additionally, consider the machine’s dimensions and weight, as these can influence shipping methods and costs. Establish a clear communication channel with your supplier regarding shipping timelines and any potential delays to avoid unexpected disruptions in your supply chain.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for label machinery
What Are the Key Takeaways for Strategic Sourcing in Label Machinery?
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of label machinery offers significant advantages for international B2B buyers. By focusing on reliable suppliers, understanding the nuances of different labeling technologies, and considering the specific needs of diverse markets, businesses can optimize their production processes and enhance product presentation. The ability to choose between semi-automatic and fully automatic solutions allows companies to tailor their investments based on production volume and operational efficiency.
How Can B2B Buyers Prepare for Future Trends in Label Machinery?
As the demand for sustainable and customizable labeling solutions continues to rise, buyers should remain proactive in exploring innovative technologies. Investing in adaptable labeling machines that can accommodate various container types and labeling styles will be crucial. Furthermore, understanding regional compliance requirements and consumer preferences in markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe will enable businesses to position themselves competitively.
What Steps Should International Buyers Take Now?
International B2B buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough market research and engage with suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to quality and innovation. Establishing partnerships with reputable manufacturers can lead to better pricing, improved support, and enhanced product offerings. As you plan your next sourcing strategy, consider the evolving landscape of label machinery and leverage these insights to drive your business forward. Your next step could be the key to unlocking new levels of efficiency and market presence.