Discover Cost-Effective Solutions with Linear Bearings (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for linear bearing
In today’s fast-paced manufacturing landscape, sourcing high-quality linear bearings can present significant challenges for international B2B buyers. Factors such as varying quality standards, supplier reliability, and logistical complexities can complicate the procurement process. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the global market for linear bearings, providing actionable insights tailored specifically for businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key markets like the UAE and South Africa.
Within these pages, readers will explore a wide array of linear bearing types, from ball bearings to roller bearings, and their various applications in industries ranging from automation to aerospace. The guide delves into critical aspects of supplier vetting to ensure that your chosen partner meets both quality and compliance standards. Additionally, it addresses cost considerations and emerging trends in the linear bearing market that can impact purchasing decisions.
Arming B2B buyers with this knowledge not only simplifies the sourcing process but also enhances decision-making capabilities, ultimately leading to more efficient operations and improved product outcomes. Whether you’re a seasoned procurement professional or new to the field, this guide serves as your essential resource for navigating the complexities of acquiring linear bearings in a globalized economy.
Understanding linear bearing Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear Ball Bearings | Utilize balls for reduced friction and smooth movement | Automation, CNC machinery, robotics | Pros: High speed, low friction. Cons: Require lubrication and maintenance. |
| Linear Roller Bearings | Use cylindrical rollers for increased load capacity | Heavy machinery, transportation equipment | Pros: Higher load capacity. Cons: More friction than ball bearings. |
| Linear Slide Bearings | Often made from plastic or composite materials | Light-duty applications, packaging machines | Pros: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant. Cons: Limited load capacity. |
| Profile Rail Systems | Feature a rail and carriage design for stability | Industrial automation, assembly lines | Pros: High rigidity and precision. Cons: Higher initial cost. |
| Self-Lubricating Bearings | Designed to operate without external lubrication | Food processing, medical equipment | Pros: Low maintenance, suitable for harsh environments. Cons: Typically higher upfront costs. |
What Are Linear Ball Bearings and Their Applications?
Linear ball bearings are designed to provide smooth motion along a linear path, utilizing small balls to minimize friction. They are ideal for applications requiring high speeds and precision, such as automation systems, CNC machinery, and robotics. When purchasing, consider the need for regular lubrication and maintenance, as these bearings can wear out if not properly cared for. Their efficiency in dynamic applications makes them a popular choice among B2B buyers focused on performance.
How Do Linear Roller Bearings Compare?
Linear roller bearings utilize cylindrical rollers instead of balls, offering greater load capacity and rigidity. This makes them suitable for heavy-duty applications in industries like construction and transportation equipment. While they provide enhanced durability under load, they also generate more friction than ball bearings, which can affect speed. Buyers should evaluate their specific load requirements and consider the trade-off between performance and friction when selecting roller bearings.
What Are Linear Slide Bearings and Their Benefits?
Linear slide bearings are typically constructed from lightweight materials like plastic or composite, making them ideal for light-duty applications such as packaging machines and conveyor systems. Their corrosion-resistant properties are advantageous in environments prone to moisture. However, their load capacity is limited compared to metal bearings. Buyers should consider the operational environment and load requirements, as these factors will influence the suitability of slide bearings for their applications.
Why Choose Profile Rail Systems?
Profile rail systems combine a rail and carriage to provide high rigidity and precision in linear motion applications. They are widely used in industrial automation and assembly lines, where accurate positioning is crucial. While they tend to have a higher upfront cost, their long-term durability and reduced maintenance needs can make them a cost-effective choice over time. B2B buyers should weigh initial costs against potential savings in maintenance and downtime.
What Are the Advantages of Self-Lubricating Bearings?
Self-lubricating bearings are engineered to function without the need for external lubrication, making them an excellent choice for industries like food processing and medical equipment, where hygiene and maintenance are critical. Their low maintenance requirements appeal to buyers seeking reliability in harsh environments. However, these bearings often come with a higher initial investment, which should be factored into the overall budget.
Key Industrial Applications of linear bearing
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Linear Bearing | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | CNC Machining Equipment | Enhanced precision and reduced wear over time | Ensure compatibility with existing machinery; consider load capacity and environmental factors. |
| Food and Beverage | Automated Packaging Lines | Increased efficiency and reduced operational costs | Compliance with food safety standards; evaluate lubrication options to prevent contamination. |
| Robotics and Automation | Robotic Arm Movement Systems | Improved accuracy and speed in production processes | Look for high load ratings and durability; assess integration with control systems. |
| Medical Equipment | Surgical Equipment and Hospital Beds | Reliability and precision in critical applications | Check for biocompatibility and ease of sterilization; ensure compliance with medical standards. |
| Aerospace | Aircraft Control Surfaces and Landing Gear Mechanisms | Enhanced safety and performance under extreme conditions | Focus on weight reduction and corrosion resistance; prioritize suppliers with aerospace certifications. |
How Are Linear Bearings Used in Manufacturing Applications?
In the manufacturing sector, linear bearings play a critical role in CNC machining equipment, enabling smooth and precise movement of cutting tools. This application addresses common issues such as wear and tear, which can lead to inaccuracies in machining. For international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and South America, sourcing linear bearings that offer high load capacity and compatibility with existing machinery is essential. Additionally, understanding the environmental conditions in which these bearings will operate can influence material selection, ensuring longevity and performance.
What Are the Benefits of Linear Bearings in Food and Beverage Industries?
Automated packaging lines in the food and beverage industry utilize linear bearings to facilitate the swift and accurate movement of packaging machinery. This application significantly boosts operational efficiency while minimizing downtime. For buyers in the Middle East and Europe, sourcing linear bearings that comply with food safety standards is paramount. Furthermore, evaluating lubrication options to prevent contamination is crucial to maintaining hygiene and product integrity in food processing environments.
How Do Linear Bearings Enhance Robotics and Automation?
In robotics and automation, linear bearings are fundamental components in robotic arm movement systems, allowing for precise positioning and high-speed operations. This application directly contributes to improved accuracy and speed in production processes, which is vital for maintaining competitive advantage. International buyers, especially in Europe, should focus on sourcing bearings with high load ratings and durability, ensuring they can withstand the rigors of automated operations. Additionally, compatibility with control systems is a key consideration for seamless integration.
Why Are Linear Bearings Important in Medical Equipment?
In the medical sector, linear bearings are used in surgical equipment and hospital beds, where reliability and precision are critical. These applications ensure that medical devices function correctly during crucial procedures, enhancing patient safety. Buyers in Africa and South America must prioritize sourcing linear bearings that meet stringent biocompatibility standards and are easy to sterilize. Understanding local regulations and compliance requirements is vital for ensuring that medical equipment adheres to safety protocols.
How Do Aerospace Applications Benefit from Linear Bearings?
Linear bearings are integral to aircraft control surfaces and landing gear mechanisms, where they enhance safety and performance under extreme conditions. This application requires bearings that can withstand high loads while being lightweight, contributing to overall aircraft efficiency. For international buyers in the aerospace sector, focusing on suppliers with relevant certifications and a proven track record in aerospace applications is essential. Additionally, considering materials that offer corrosion resistance is crucial for maintaining performance over time.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘linear bearing’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Performance in High-Load Applications
The Problem:
International B2B buyers often encounter the issue of inconsistent performance from linear bearings, especially in high-load applications. This can lead to frequent machinery breakdowns, increased downtime, and ultimately, a loss of productivity. Buyers might find that bearings fail prematurely or do not meet the required specifications for load-bearing capacities, resulting in operational inefficiencies. For companies in sectors like manufacturing or logistics, where reliability is paramount, this inconsistency can severely impact overall business performance.
The Solution:
To mitigate this issue, it is crucial to choose the right type of linear bearing based on the specific application requirements. Buyers should conduct a thorough analysis of the load conditions, including dynamic and static loads, and ensure that the selected bearings can handle these stresses. Collaborating with manufacturers that provide detailed product specifications and load ratings is essential. Additionally, consider sourcing bearings that are designed for high-load applications, such as those with robust steel construction or those utilizing advanced materials that offer enhanced durability. Regular maintenance checks and lubrication can also prolong the life of linear bearings, ensuring consistent performance under load.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Finding the Right Replacement Parts
The Problem:
B2B buyers frequently face challenges when searching for replacement linear bearings that match their existing systems. This is particularly true for older machinery or specialized applications where standard bearings may not fit. The inability to find compatible components can lead to extended machine downtime and costly delays in production schedules, which is especially critical for businesses in competitive markets like automotive or aerospace.
The Solution:
To streamline the replacement process, buyers should maintain a comprehensive inventory of part numbers and specifications for all linear bearings used in their operations. Engaging with suppliers who offer custom solutions can also prove beneficial. Many manufacturers provide specialized bearings tailored to unique specifications, and reaching out to them with detailed requirements can expedite the sourcing process. Furthermore, utilizing digital platforms that allow for easy cross-referencing of parts can help identify suitable replacements quickly. Establishing a relationship with local distributors or manufacturers can also facilitate quicker turnaround times for replacement parts.
Scenario 3: Environmental Challenges Affecting Bearing Longevity
The Problem:
In regions with extreme environmental conditions—such as high humidity, dust, or corrosive substances—linear bearings can suffer from reduced longevity and performance. Buyers in industries like food processing or pharmaceuticals, where cleanliness and compliance with health regulations are critical, may find that standard bearings fail to meet their operational demands. This can lead to increased maintenance costs and potential disruptions in production.
The Solution:
To combat environmental challenges, it is advisable to invest in specialized linear bearings designed for harsh conditions. For instance, selecting bearings with corrosion-resistant coatings or those made from stainless steel can significantly enhance durability. Additionally, consider using sealed or shielded bearings that prevent contaminants from entering the bearing assembly. Buyers should also evaluate the lubrication methods used; opting for self-lubricating bearings can reduce maintenance frequency and ensure consistent operation in challenging environments. Regularly reviewing and updating the bearing selection based on environmental factors will help maintain operational efficiency and reduce unexpected failures.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for linear bearing
When selecting materials for linear bearings, it is essential to consider the specific requirements of the application, including environmental conditions, load capacities, and compatibility with various media. Below, we analyze four common materials used in linear bearings, highlighting their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
What are the Key Properties of Steel in Linear Bearings?
Steel is the most commonly used material for linear bearings due to its excellent mechanical properties. It typically offers high tensile strength, good wear resistance, and the ability to withstand high loads. Steel linear bearings can operate effectively at temperatures ranging from -40°C to 120°C, depending on the specific alloy used.
Pros: Steel bearings are durable and cost-effective, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. They are also readily available and can be manufactured to precise specifications.
Cons: The primary drawback of steel is its susceptibility to corrosion, especially in humid or chemically aggressive environments. Additional coatings or treatments may be necessary, which can increase manufacturing complexity and costs.
Impact on Application: Steel linear bearings are ideal for applications involving heavy loads and moderate speeds. However, they may not be suitable for environments where moisture or corrosive substances are present.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should consider local climate conditions when selecting steel bearings. Compliance with standards such as ASTM or DIN for material specifications is crucial to ensure quality and performance.
How Does Aluminum Perform in Linear Bearings?
Aluminum is another popular choice for linear bearings, particularly in applications where weight reduction is critical. Aluminum bearings are lightweight and offer good corrosion resistance, especially when anodized.
Pros: The lightweight nature of aluminum makes it an excellent choice for portable or mobile applications. It also has good thermal conductivity, which can be advantageous in heat-sensitive environments.
Cons: Aluminum has lower load-bearing capacity compared to steel, which can limit its use in heavy-duty applications. Additionally, it can be more expensive than steel, depending on the alloy.
Impact on Application: Aluminum linear bearings are well-suited for applications in the aerospace, automotive, and electronics industries, where weight savings are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in the Middle East and Europe should verify that aluminum bearings meet local compliance standards, such as JIS or ISO, to ensure compatibility with their systems.
What are the Benefits of Plastic in Linear Bearings?
Plastic, particularly high-performance polymers like PTFE or PEEK, is increasingly used in linear bearings due to its low friction properties and resistance to corrosion and chemicals.
Pros: Plastic bearings are lightweight, self-lubricating, and can operate in a wide temperature range. They are also resistant to moisture and various chemicals, making them suitable for food processing and medical applications.
Cons: While plastic bearings are durable, they may not handle high loads as effectively as metal bearings. They can also be more expensive, depending on the specific polymer used.
Impact on Application: Plastic linear bearings are ideal for applications in clean environments, such as food and pharmaceutical industries, where contamination must be minimized.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like South Africa should ensure that plastic bearings comply with relevant food safety standards, such as FDA or USDA regulations.
Why Choose Ceramic for Linear Bearings?
Ceramic materials, including silicon nitride and zirconia, are known for their exceptional hardness and wear resistance. They are often used in specialized applications that require high precision and low friction.
Pros: Ceramic bearings are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and can operate at higher temperatures than metals. They also have excellent electrical insulating properties.
Cons: The primary limitation of ceramic bearings is their brittleness, which can lead to failure under shock loads. Additionally, they are typically more expensive than metal or plastic options.
Impact on Application: Ceramic linear bearings are suitable for high-speed applications and environments that require minimal lubrication, such as in aerospace and high-performance machinery.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe should verify that ceramic bearings meet industry-specific standards for performance and safety, ensuring they are suitable for their intended applications.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Linear Bearings
| Material | Typical Use Case for Linear Bearing | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy-duty applications | High strength and durability | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Lightweight applications | Lightweight and good corrosion resistance | Lower load capacity | Medium |
| Plastic | Food and medical applications | Self-lubricating and corrosion-resistant | Limited load capacity | High |
| Ceramic | High-speed precision applications | High hardness and wear resistance | Brittle and expensive | High |
This strategic material selection guide aims to provide international B2B buyers with actionable insights to make informed decisions when sourcing linear bearings, considering both performance requirements and regional compliance standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for linear bearing
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Linear Bearings?
The manufacturing of linear bearings involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets industry standards and buyer requirements. Below are the main stages of the manufacturing process:
-
Material Preparation: The first stage involves selecting the appropriate materials, typically high-carbon steel, stainless steel, or polymer composites. The materials undergo rigorous inspection to ensure they meet specifications regarding hardness, tensile strength, and corrosion resistance. For instance, stainless steel is often preferred for environments subject to moisture or corrosive substances.
-
Forming: This stage includes the shaping of components through methods such as machining, forging, or casting. Advanced CNC machines are frequently used to achieve high precision in dimensions. The manufacturing process may also involve heat treatment to enhance the mechanical properties of the materials, ensuring the bearings can withstand heavy loads and high speeds.
-
Assembly: After forming, the various components (such as races, balls, and seals) are assembled. This step requires precision to ensure proper alignment and function. Automation tools, such as robotic arms, are increasingly used to enhance efficiency and reduce human error during assembly.
-
Finishing: The finishing stage includes processes like grinding, polishing, and coating. These techniques not only improve the aesthetic quality of the bearings but also enhance their performance characteristics, such as reducing friction and increasing lifespan. For example, applying a PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) coating can significantly reduce friction and wear.
How Is Quality Assurance Integrated into Linear Bearing Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is crucial in ensuring that linear bearings meet international standards and customer specifications. Here are the key aspects of QA in this context:
-
International Standards Compliance: Manufacturers often adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems. Compliance with these standards ensures that processes are in place for continuous improvement, customer satisfaction, and product quality.
-
Industry-Specific Certifications: Depending on the application, certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne), API (American Petroleum Institute), or FDA (Food and Drug Administration) may be necessary. These certifications demonstrate that the bearings are safe for use in specific industries like food processing or oil and gas.
-
Quality Control Checkpoints:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, regular checks are conducted to identify any deviations from the required specifications.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): The finished products undergo rigorous testing to assess functionality, load capacity, and durability before they are shipped to clients.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Linear Bearing Quality Assurance?
To ensure the reliability and performance of linear bearings, various testing methods are employed:
-
Load Testing: Bearings are subjected to various loads to evaluate their performance under stress. This includes both static and dynamic load tests to simulate real-world conditions.
-
Wear Testing: This involves running the bearings in conditions that mimic operational environments to assess wear rates over time.
-
Dimensional Inspection: Using precision measuring tools, manufacturers check critical dimensions to ensure that the bearings meet exact specifications.
-
Lubrication Testing: For bearings designed to operate under specific lubrication conditions, tests are performed to determine the effectiveness of the lubrication under different operational speeds and loads.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is essential. Here are actionable steps to ensure quality compliance:
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can help assess their adherence to quality standards and manufacturing processes. This can be done in-person or through virtual audits.
-
Request Quality Assurance Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation of their quality assurance processes, including results from any testing conducted, compliance certificates, and records of any past non-conformities.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Independent third-party inspections can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures. This is particularly important for buyers who may not have the resources to conduct thorough audits themselves.
-
Review Compliance with Local Regulations: Buyers should ensure that suppliers comply with local regulations in their respective countries, which can vary significantly. For instance, regulations in the UAE might differ from those in South Africa or Brazil.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate various quality control nuances when sourcing linear bearings:
-
Cultural and Regulatory Differences: Understanding the cultural and regulatory landscape of the supplier’s country is vital. For example, some regions may have less stringent quality regulations, which could impact product reliability.
-
Time Zone and Communication Challenges: Coordinating quality assurance processes across different time zones can lead to delays in communication. Establishing clear lines of communication and setting regular check-ins can mitigate these issues.
-
Supply Chain Resilience: Buyers should assess the robustness of the supplier’s supply chain. Disruptions in the supply chain can affect quality and delivery times, so ensuring that suppliers have contingency plans in place is crucial.
-
Sustainability Practices: Increasingly, buyers are looking for suppliers who prioritize sustainability in their manufacturing processes. This not only impacts the environment but can also enhance brand reputation and customer loyalty.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices associated with linear bearings, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and establish long-term relationships with reliable suppliers.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘linear bearing’
The procurement of linear bearings is a critical aspect for B2B buyers, especially those operating in industries that require precision and reliability. This guide provides a structured checklist to streamline your sourcing process, ensuring you make informed decisions that align with your operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outlining your technical specifications is the first step in sourcing linear bearings. This includes understanding load capacities, speed requirements, and environmental conditions in which the bearings will operate. A well-defined specification helps narrow down your options and ensures compatibility with existing systems.
- Consider factors like:
- Maximum load and speed ratings.
- Operating temperature and environmental conditions (e.g., humidity, exposure to chemicals).
Step 2: Research Different Types of Linear Bearings
Familiarize yourself with the various types of linear bearings available, such as ball bearings, roller bearings, and self-lubricating options. Each type has unique advantages and is suited for specific applications. Understanding these differences is essential for selecting the right bearing for your needs.
- Key types to explore include:
- Linear Ball Bearings: Best for high-speed applications.
- Roller Bearings: Ideal for heavy loads and durability.
- Self-Lubricating Bearings: Suitable for maintenance-free environments.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, thoroughly vet potential suppliers. A reputable supplier will provide not just products, but also value-added services such as technical support and after-sales service. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions.
- What to look for:
- Supplier certifications (ISO, CE, etc.).
- Customer testimonials and reviews.
- Availability of technical support.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request samples of the linear bearings for testing. This step is crucial to ensure that the bearings meet your operational requirements. Testing samples in your specific application can prevent costly mistakes later on.
- Testing should focus on:
- Load capacity and durability under actual working conditions.
- Noise levels and friction characteristics.
Step 5: Verify Compliance with Industry Standards
Ensure that the linear bearings comply with relevant industry standards and regulations. Compliance guarantees that the bearings meet safety and quality requirements, reducing risks associated with failures.
- Important standards may include:
- ISO standards for manufacturing quality.
- Specific industry regulations (e.g., FDA for food applications).
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Before finalizing your order, negotiate the terms and pricing with the supplier. Consider not only the price of the bearings but also the cost of shipping, lead times, and payment terms. A well-negotiated contract can lead to significant cost savings.
- Key points to negotiate:
- Bulk order discounts.
- Warranty and return policies.
- Delivery timelines.
Step 7: Establish a Long-term Relationship
After the purchase, focus on establishing a long-term relationship with your supplier. Open lines of communication can facilitate better service, quicker responses to issues, and opportunities for future collaborations.
- To foster this relationship:
- Provide feedback on product performance.
- Stay updated on new product developments and innovations.
By following this structured checklist, international B2B buyers can ensure a comprehensive and effective sourcing process for linear bearings, leading to enhanced operational efficiency and product reliability.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for linear bearing Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Linear Bearing Sourcing?
When sourcing linear bearings, understanding the comprehensive cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the cost. Common materials such as stainless steel, plastic, or specialized alloys vary in price. For example, bearings made from high-grade stainless steel will typically command a higher price than those made from standard carbon steel due to enhanced durability and corrosion resistance.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can affect the overall price. Manufacturers in regions with higher labor costs may pass these expenses onto buyers, while suppliers in emerging markets may offer more competitive pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes the costs associated with running a manufacturing facility, such as utilities, maintenance, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturers with optimized operations can provide better pricing.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs for custom or complex designs can be significant. Buyers should inquire about these costs upfront, especially if they require unique specifications or modifications to standard products.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that the bearings meet specified standards. Suppliers with established quality certifications (like ISO) may charge a premium, but this often results in long-term cost savings through reduced failure rates.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs can vary widely based on the origin of the product, destination, and chosen shipping method. Understanding the Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) can help buyers manage these costs effectively.
-
Margin: Supplier profit margins can vary based on market demand and competition. Buyers should assess multiple suppliers to understand the pricing landscape.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Linear Bearing Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of linear bearings, making it essential for buyers to consider these aspects:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often lead to bulk pricing discounts. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to optimize their costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications typically increase costs. However, if these specifications lead to improved performance or longer life, the initial higher cost may be justified.
-
Material Selection: The choice between standard and high-performance materials directly influences pricing. While high-performance materials may have a higher upfront cost, their longevity can lead to lower total ownership costs.
-
Quality and Certifications: Bearings that meet international quality standards may incur higher costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of investing in certified products against potential risks from lower-quality options.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of a supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while newer suppliers might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms can significantly affect landed costs. Buyers should clarify responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and duties to avoid unexpected expenses.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Linear Bearing Sourcing?
To maximize cost-efficiency when sourcing linear bearings, international buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Pricing: Don’t hesitate to negotiate with suppliers. Building a relationship can lead to better pricing and terms, especially for repeat orders.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial purchase price. Consider factors such as maintenance, performance, and lifespan when calculating TCO. Higher-quality bearings may have a higher upfront cost but could result in savings over time due to reduced failure rates and maintenance needs.
-
Conduct Market Research: Stay informed about market trends and pricing fluctuations in different regions. This knowledge can empower buyers during negotiations and help identify the best sourcing opportunities.
-
Leverage Local Suppliers: For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, exploring local suppliers can reduce shipping costs and lead times. Additionally, local suppliers may offer better support and service.
-
Consider Long-Term Partnerships: Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to favorable pricing, priority service, and improved collaboration on custom solutions.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for linear bearings can fluctuate based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific requirements. Buyers should seek multiple quotes and conduct thorough due diligence to ensure they are obtaining the best value for their investment.
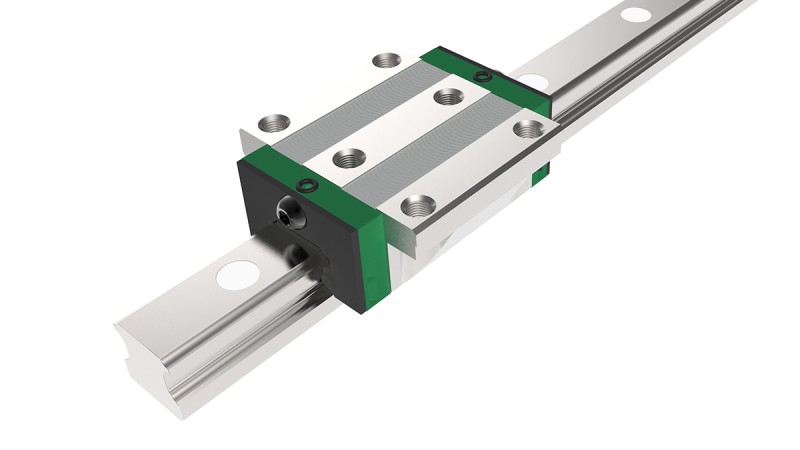
A stock image related to linear bearing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing linear bearing With Other Solutions
When exploring options for linear motion systems, it is essential to consider alternatives to linear bearings that might meet specific operational requirements or budget constraints. Different technologies can offer varying benefits and drawbacks, making it crucial for international B2B buyers to analyze their options carefully.
| Comparison Aspect | Linear Bearing | Alternative 1: Linear Guide Rail System | Alternative 2: Pneumatic Actuators |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and low friction; supports heavy loads | Excellent rigidity; suitable for long strokes | High speed and quick response; good for repetitive tasks |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; lower long-term costs due to durability | Higher upfront cost; but reduced operational costs over time | Lower initial cost; higher long-term costs due to maintenance |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires precise alignment; installation can be complex | Easier to install due to modular design | Simple setup; requires air supply and control systems |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; periodic lubrication necessary | Low maintenance; typically self-lubricating | Regular maintenance required for air supply and seals |
| Best Use Case | Precision engineering, automation, and robotics | Heavy machinery and manufacturing lines | Applications requiring fast movements, like packaging and assembly |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Linear Guide Rail Systems?
Linear guide rail systems provide a robust alternative to linear bearings. They excel in applications requiring high rigidity and load-bearing capacity, making them suitable for heavy machinery and manufacturing lines. The modular design of these systems allows for easier installation, which can reduce downtime during setup. However, they come with a higher initial investment, which may be a concern for budget-conscious buyers. Additionally, while they often have low maintenance needs, the cost of replacement parts can accumulate over time.
How Do Pneumatic Actuators Compare to Linear Bearings?
Pneumatic actuators are another viable alternative, particularly in scenarios that demand rapid movements and high speed. They are straightforward to install and operate, making them ideal for assembly lines and packaging applications. The initial cost can be lower than that of linear bearings, but ongoing maintenance expenses can add up, especially if the air supply system is not properly maintained. Furthermore, pneumatic actuators may not provide the same level of precision as linear bearings, which could be a drawback in applications requiring tight tolerances.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Linear Motion Solution?
For international B2B buyers, the decision to choose linear bearings or one of the alternatives should be guided by specific operational requirements, budget constraints, and long-term maintenance considerations. Buyers should evaluate the precision needed, the type of loads handled, and the expected lifespan of the solution. By conducting a thorough analysis of their unique needs and comparing the performance, cost, and maintenance requirements of each option, businesses can select the most suitable linear motion system that aligns with their operational goals and financial resources.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for linear bearing
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Linear Bearings?
Understanding the technical properties of linear bearings is crucial for B2B buyers in industries such as manufacturing, automotive, and automation. Here are some key specifications that are essential to consider:
1. Material Grade: Why Does It Matter?
The material of linear bearings typically includes stainless steel, plastic, or bronze. Stainless steel bearings are favored for their corrosion resistance and durability, making them ideal for harsh environments. Plastic bearings, on the other hand, are lightweight and often self-lubricating, suitable for applications requiring lower loads. Knowing the material grade helps buyers assess the bearing’s suitability for their specific application.
2. Load Capacity: How Much Weight Can They Handle?
Load capacity refers to the maximum weight a linear bearing can support without failure. This specification is critical for applications involving heavy machinery or automated systems. Buyers should evaluate both dynamic (moving load) and static (stationary load) capacities to ensure the bearing can withstand operational demands without premature wear or failure.
3. Tolerance: Why Is Precision Important?
Tolerance is the allowable variation in dimensions that ensure the bearing fits correctly within the assembly. High precision is vital for applications requiring accurate movement and positioning. A tighter tolerance often results in improved performance and longevity, making it a key consideration for B2B buyers focused on efficiency and reliability.
4. Speed Rating: What Is the Maximum Operating Speed?
Speed rating indicates the maximum speed at which a linear bearing can operate effectively. This specification is crucial for applications in sectors like robotics and conveyor systems, where high-speed movement is essential. Buyers must match the speed rating to the requirements of their machinery to avoid overheating or failure.
5. Lubrication Type: How Does It Affect Maintenance?
Linear bearings can be lubricated or lubrication-free. Lubricated bearings require periodic maintenance, while self-lubricating options minimize downtime and maintenance costs. Understanding lubrication types helps buyers choose products that align with their operational maintenance capabilities and budget.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in Linear Bearing Transactions?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): What Does It Mean?
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of linear bearings, knowing whether a product is OEM can indicate quality and compatibility with existing systems. Buyers should consider OEM products for enhanced reliability.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Why Is It Important?
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory management. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to align with their production needs without incurring excess inventory costs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation): How to Use It Effectively?
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit pricing and terms for specific products. For buyers, preparing a clear and detailed RFQ can lead to better pricing and terms, ensuring a competitive edge in procurement.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms): What Are They?
Incoterms are predefined commercial terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers avoid misunderstandings and ensures compliance with international trade regulations.
5. Lead Time: What Should You Expect?
Lead time is the time it takes from placing an order until the product is delivered. Understanding lead times allows buyers to plan their production schedules effectively and manage supply chain expectations.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terminology, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs in their linear bearing procurement processes.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the linear bearing Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in the Linear Bearing Sector?
The linear bearing market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing automation across various industries, including manufacturing, automotive, and aerospace. International B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of several key trends shaping this sector. First, the demand for precision engineering is on the rise, as companies seek to enhance the efficiency and reliability of their machinery. This trend is particularly evident in regions like the UAE and South Africa, where industrial sectors are rapidly evolving.
Moreover, the integration of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and smart manufacturing systems, is influencing sourcing strategies. These technologies enable real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance of linear bearing systems, thereby reducing downtime and operational costs. Buyers should consider suppliers that not only provide high-quality linear bearings but also offer digital solutions that align with these technological advancements.

A stock image related to linear bearing.
Another emerging trend is the focus on customization. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who can offer tailored solutions to meet specific application requirements. This has led to the rise of companies that specialize in providing bespoke linear bearings and systems, catering to niche markets within the broader industrial landscape.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Decisions in the Linear Bearing Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor for B2B buyers in the linear bearing sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and the importance of ethical supply chains are now at the forefront of sourcing decisions. Companies are increasingly seeking suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to reducing their carbon footprint and implementing sustainable practices.
Buyers should prioritize suppliers that use eco-friendly materials and processes, such as those certified with green certifications like ISO 14001 or using recyclable components in their products. The adoption of maintenance-free and self-lubricating linear bearings is another example of how sustainability is being integrated into product design, reducing the need for additional lubricants that can harm the environment.
Furthermore, transparency in the supply chain is vital. Buyers are encouraged to engage with suppliers who provide clear documentation regarding their sourcing practices, ensuring that materials are ethically sourced and that labor practices meet international standards. This not only helps in building a responsible brand image but also aligns with the growing consumer demand for sustainability in industrial products.
How Has the Linear Bearing Sector Evolved Over Time?
The linear bearing sector has undergone significant evolution since its inception, adapting to the changing demands of various industries. Initially, linear bearings were primarily mechanical devices designed for basic linear motion applications. However, as technology advanced, so did the complexity and functionality of these bearings.
In the past two decades, innovations in materials science have led to the development of high-performance linear bearings that offer improved load capacities, reduced friction, and enhanced durability. The introduction of self-lubricating and maintenance-free options has further transformed the market, catering to industries that require low-maintenance solutions.
As automation and precision engineering have gained prominence, linear bearings have become integral components in sophisticated machinery and systems. This evolution reflects a broader trend in industrial manufacturing, where efficiency, reliability, and sustainability are paramount. International B2B buyers should be aware of these historical developments as they navigate current market dynamics and sourcing trends, allowing them to make informed decisions that align with both their operational needs and sustainability goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of linear bearing
-
How do I choose the right linear bearing for my application?
Selecting the appropriate linear bearing involves assessing factors such as load capacity, speed requirements, and environmental conditions. For high-load applications, consider linear ball bearings or roller bearings, which provide superior load-carrying capabilities. Additionally, evaluate the material of the bearing; stainless steel or specialized plastics are ideal for harsh environments. Understanding your application’s specific needs will guide you in choosing the most effective linear bearing. -
What are the benefits of using linear bearings over traditional bearings?
Linear bearings offer enhanced performance in linear motion applications, providing low friction and high precision. They are designed for smooth and accurate movement along a rail, making them ideal for automated systems. Compared to traditional bearings, linear bearings can support heavier loads and allow for longer stroke lengths without sacrificing accuracy. This results in improved efficiency and longer service life in machinery. -
What customization options are available when sourcing linear bearings?
Many suppliers offer customization options for linear bearings, including dimensions, material types, and load capacities. Depending on your specific needs, you can request features such as self-lubrication, corrosion resistance, or specific coatings to enhance performance in unique environments. It is advisable to communicate your requirements clearly to suppliers to ensure they can meet your specifications accurately. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for linear bearings?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly among suppliers, often ranging from 10 to 100 units. High-volume manufacturers may offer lower MOQs, while specialized or custom bearing providers may require larger orders. To optimize costs, consider consolidating orders with other components or negotiating with suppliers to meet their MOQ while still fulfilling your requirements. -
How can I ensure the quality of linear bearings when sourcing internationally?
To ensure quality, work with reputable suppliers that provide certifications and quality assurance processes. Request samples for testing before placing large orders, and consider suppliers who adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001. Building relationships with suppliers through visits or audits can also help assure product quality and reliability in international transactions. -
What are the payment terms typically offered by suppliers of linear bearings?
Payment terms can vary based on the supplier and the nature of the transaction. Common options include upfront payment, partial payment upon order confirmation, and the balance upon delivery. For international transactions, consider using secure payment methods such as letters of credit or escrow services to protect your investment. Always clarify payment terms in advance to avoid misunderstandings. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing linear bearings?
When importing linear bearings, consider shipping methods, delivery times, and customs regulations in your country. Air freight is faster but more expensive, while sea freight offers cost savings for larger orders. Ensure that all necessary documentation, including invoices and certificates of origin, is prepared to facilitate smooth customs clearance. Working with a freight forwarder can help streamline the logistics process. -
How can I vet potential suppliers of linear bearings effectively?
To vet suppliers, start by researching their reputation within the industry through reviews and testimonials. Evaluate their experience, product range, and compliance with international standards. Request references from previous clients and inquire about their production capabilities and lead times. Engaging in direct communication with potential suppliers can also provide insights into their reliability and customer service practices.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for linear bearing
Why is Strategic Sourcing Essential for Linear Bearings?
In today’s competitive landscape, strategic sourcing is pivotal for international B2B buyers looking to procure linear bearings. By leveraging supplier diversity and understanding global supply chain dynamics, businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can enhance their operational efficiency and reduce costs. The right sourcing strategy not only ensures access to high-quality products but also fosters sustainable relationships with suppliers, which can lead to innovation and better service levels.
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers?
Buyers should focus on quality, compatibility, and long-term performance when selecting linear bearings. Consideration of factors such as load capacity, lubrication requirements, and environmental conditions is crucial for optimizing machinery performance. Additionally, engaging with manufacturers who offer customization can significantly enhance the fit for specific applications, thereby improving operational outcomes.
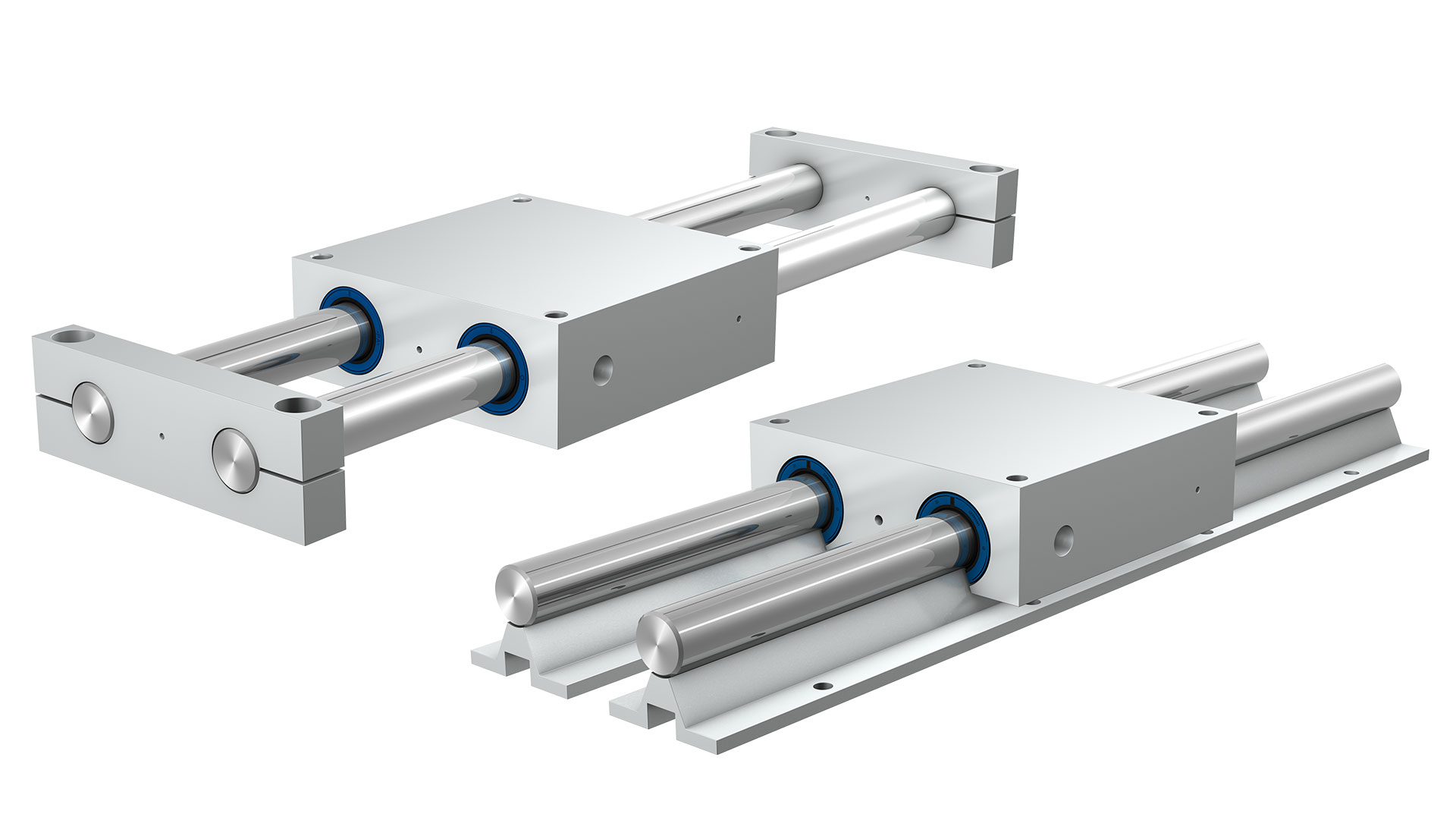
A stock image related to linear bearing.
What Does the Future Hold for Linear Bearings?
As industries evolve, the demand for advanced linear bearing solutions will continue to rise. Buyers should remain proactive by exploring new technologies and materials, such as self-lubricating and corrosion-resistant bearings, which are gaining traction in sectors such as food processing and pharmaceuticals.
How Can You Move Forward?
Now is the time to evaluate your sourcing strategies and align them with future industry trends. By establishing strong partnerships with reliable suppliers, particularly those with a global footprint, you can ensure your operations remain agile and competitive. Engage with experts in the field to explore innovative solutions and optimize your supply chain for maximum efficiency.