Discover Cost-Saving EMI EMC Shielding Materials (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for emi emc shielding materials
In an increasingly interconnected world, the challenge of sourcing effective EMI and EMC shielding materials has become paramount for international B2B buyers. With the rise of sophisticated electronic devices, ensuring protection against electromagnetic interference is critical to maintaining operational integrity. This guide aims to simplify the complex landscape of EMI shielding materials, providing valuable insights into their types, applications, and the factors influencing their effectiveness.
Buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like Mexico and France, will find actionable strategies for vetting suppliers, understanding cost implications, and selecting appropriate materials tailored to their specific needs. The guide covers a comprehensive range of topics, including the various metals and materials used in EMI shielding, such as copper, aluminum, and specialized alloys, as well as the importance of customized solutions like gaskets and enclosures.
By leveraging this resource, B2B buyers can make informed purchasing decisions that not only enhance the performance of their electronic devices but also align with their budgetary constraints. Ultimately, navigating the global market for EMI and EMC shielding materials becomes less daunting, empowering businesses to protect their technological investments effectively.
Understanding emi emc shielding materials Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metal Gaskets | Customizable, effective for sealing gaps | Medical devices, electronics, automotive | Pros: Versatile, high shielding effectiveness. Cons: Can be costly if highly customized. |
| Copper Alloys | High conductivity, excellent corrosion resistance | Telecommunications, aerospace, automotive | Pros: Durable, effective against both RF and magnetic waves. Cons: Heavier than alternatives. |
| Aluminum Foils | Lightweight, easy to shape and form | Consumer electronics, packaging | Pros: Cost-effective, good for lower frequency applications. Cons: Limited effectiveness at higher frequencies. |
| Mu-Metal | Exceptional magnetic shielding properties | Medical equipment, sensitive electronics | Pros: Malleable, high shielding effectiveness. Cons: Expensive and not suitable for all environments. |
| Conductive Fabrics | Flexible, lightweight, often used in hybrid solutions | Wearable technology, consumer electronics | Pros: Lightweight, adaptable to various designs. Cons: May not provide the same level of shielding as metals. |
What Are the Characteristics of Metal Gaskets for EMI Shielding?
Metal gaskets are a prominent choice for EMI shielding due to their ability to create a tight seal between surfaces, preventing electromagnetic interference from penetrating electronic devices. These gaskets can be tailored in size, shape, and material composition to meet specific application requirements, making them highly versatile. Key purchasing considerations include the environment in which they will be used (e.g., exposure to moisture or temperature extremes) and the level of shielding effectiveness required. While they offer high performance, the customization can lead to increased costs.
Why Are Copper Alloys Preferred in EMI Shielding Applications?
Copper alloys, particularly beryllium copper, are favored for their exceptional conductivity and corrosion resistance. They are particularly effective in applications requiring a robust solution to both radiofrequency and magnetic interference, making them suitable for industries such as telecommunications and aerospace. When purchasing, buyers should consider the alloy’s specific properties, such as tensile strength and resistance to environmental factors, to ensure optimal performance. Although heavier than alternatives like aluminum, their durability often justifies the weight.
How Does Aluminum Foil Function as an EMI Shielding Material?
Aluminum foil is widely used for EMI shielding due to its lightweight nature and ease of manipulation into various shapes. It is particularly effective for lower frequency applications, making it a common choice in consumer electronics and packaging. Buyers should evaluate the specific frequency ranges and environmental conditions of their applications when considering aluminum. While it is a cost-effective solution, its shielding effectiveness diminishes at higher frequencies, which may necessitate additional protective measures.
What Makes Mu-Metal an Effective Shielding Material?
Mu-metal is renowned for its superior ability to shield against magnetic interference, making it ideal for sensitive applications such as medical devices and high-precision electronics. Its malleability allows it to be formed into thin sheets, enhancing its adaptability for various designs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of mu-metal’s high shielding effectiveness against its higher cost and potential limitations in harsh environments. Understanding the specific shielding requirements of their applications is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions.
Why Consider Conductive Fabrics for EMI Shielding?
Conductive fabrics are increasingly popular in the EMI shielding landscape due to their flexibility and lightweight properties. They are particularly well-suited for wearable technology and consumer electronics where traditional metal shields may be impractical. When evaluating conductive fabrics, buyers should consider the fabric’s conductivity level and its compatibility with the intended device design. While they offer unique advantages in terms of weight and adaptability, they may not achieve the same level of shielding effectiveness as traditional metal options, making it essential to assess application-specific needs.
Key Industrial Applications of emi emc shielding materials
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of EMI EMC Shielding Materials | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Shielding for avionics and communication systems | Ensures operational reliability and safety of aircraft systems | Compliance with international safety standards and certifications |
| Medical Devices | EMI shielding in diagnostic and therapeutic equipment | Protects sensitive electronics, ensuring accurate readings and patient safety | Material biocompatibility and regulatory compliance |
| Telecommunications | Protection for cellular towers and communication devices | Minimizes signal interference, enhancing service quality | Durability against environmental factors and ease of installation |
| Automotive | Shielding for electronic control units (ECUs) | Reduces malfunction risks, improving vehicle safety and performance | Cost-effective sourcing and compatibility with existing components |
| Consumer Electronics | EMI shielding in smartphones and laptops | Enhances user experience by reducing static and noise | Lightweight materials and design flexibility for compact devices |
How Are EMI EMC Shielding Materials Used in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace sector, EMI EMC shielding materials are crucial for protecting avionics and communication systems from electromagnetic interference. These materials ensure that critical systems operate reliably, which is vital for flight safety. Buyers in this industry must consider compliance with rigorous international safety standards, as well as the ability of materials to withstand extreme environmental conditions. Sourcing from manufacturers with certifications in aerospace applications can further enhance reliability.
What Role Do EMI EMC Shielding Materials Play in Medical Devices?
In medical devices, EMI shielding is essential for diagnostic and therapeutic equipment to function accurately and safely. These materials protect sensitive electronic components from interference that could lead to incorrect readings or equipment failure, which can have serious consequences for patient safety. International buyers should prioritize sourcing biocompatible materials that meet stringent regulatory requirements, ensuring that the devices are safe for use in medical environments.
How Do Telecommunications Industries Benefit from EMI EMC Shielding Materials?
Telecommunications companies utilize EMI shielding for cellular towers and communication devices to minimize signal interference. This shielding enhances the quality and reliability of communication services, which is critical in a competitive market. Buyers should focus on sourcing durable materials that can withstand various environmental factors, as well as ensuring that installation processes are straightforward to minimize downtime during upgrades or repairs.
Why Are EMI EMC Shielding Materials Important in Automotive Applications?
In the automotive industry, EMI shielding is vital for electronic control units (ECUs) to prevent electromagnetic interference that could lead to malfunctions. This shielding not only enhances vehicle performance but also significantly improves safety by ensuring that critical systems function without interruption. B2B buyers should seek cost-effective sourcing options that also consider compatibility with existing automotive components, allowing for seamless integration during manufacturing or retrofitting.
How Do Consumer Electronics Manufacturers Use EMI EMC Shielding Materials?
For consumer electronics like smartphones and laptops, EMI shielding is essential to reduce static and background noise, significantly improving user experience. The shielding materials must be lightweight and flexible to fit into compact designs without compromising performance. International buyers should prioritize suppliers that offer customizable shielding solutions to meet specific design requirements, ensuring that the final products are both effective and appealing to consumers.
3 Common User Pain Points for ’emi emc shielding materials’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inadequate EMI Shielding Leading to Device Malfunction
The Problem:
International B2B buyers often face the challenge of purchasing EMI shielding materials that fail to meet the specific requirements of their devices. This can lead to electromagnetic interference (EMI) that disrupts the performance of sensitive electronic equipment, such as medical devices or aviation instruments. For instance, a company in South America may invest in low-cost shielding options that do not provide adequate protection against high-frequency interference, resulting in costly device failures and potential safety hazards.
The Solution:
To effectively source the right EMI shielding materials, buyers should begin by conducting a thorough assessment of the electromagnetic environment in which their devices will operate. This involves identifying the types of interferences present and the frequency ranges that require protection. Next, buyers should specify shielding materials based on their effectiveness, conductivity, and environmental compatibility. For example, materials like copper or beryllium copper are highly recommended for their superior shielding properties. Additionally, collaborating with manufacturers who offer customized solutions can ensure that the shielding is tailored to fit the device specifications, thus maximizing performance and reliability.
Scenario 2: High Costs Associated with Inefficient EMI Shielding Solutions
The Problem:
Cost management is a significant concern for B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and the Middle East, where budgets may be tighter. Many buyers initially opt for cheaper EMI shielding materials, only to find that they require frequent replacements or repairs due to poor performance. This not only inflates the overall project costs but can also lead to operational delays and lost revenue as devices remain out of service longer than anticipated.
The Solution:
To mitigate costs while ensuring effective EMI shielding, buyers should focus on the long-term value of materials rather than just upfront prices. Investing in high-quality materials like stainless steel or aluminum can provide durability and longevity, ultimately reducing the need for replacements. Buyers should also negotiate with suppliers for bulk purchasing discounts or explore local manufacturers who can offer competitive pricing without compromising on quality. Furthermore, conducting a cost-benefit analysis that factors in the potential operational savings from reduced downtime can provide compelling justification for selecting more expensive, yet effective, EMI shielding solutions.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Finding Reliable Suppliers for Customized EMI Shielding Solutions
The Problem:
Many international B2B buyers struggle to find reliable suppliers who can provide customized EMI shielding solutions that fit their specific needs. This challenge is particularly evident in Europe, where diverse regulatory standards and industry specifications can complicate the sourcing process. Buyers may encounter suppliers who offer generic solutions that do not address the unique requirements of their applications, leading to inadequate shielding and compliance issues.
The Solution:
To overcome this barrier, buyers should prioritize establishing relationships with manufacturers known for their expertise in EMI shielding. This includes conducting thorough research to identify suppliers with a proven track record of delivering customized solutions. Engaging in dialogue with potential suppliers about specific application needs and compliance requirements is crucial. Buyers should also request samples or prototypes to test the materials before committing to larger orders. Attending industry trade shows and networking events can also be beneficial for connecting with reputable suppliers who can provide tailored solutions, ensuring that the selected materials meet both performance standards and regulatory compliance.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for emi emc shielding materials
What Are the Key Properties of Common EMI Shielding Materials?
When selecting materials for EMI shielding, it is critical to understand their properties, advantages, and limitations. Below, we analyze four common materials used in EMI shielding, focusing on their performance characteristics, suitability for various applications, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Copper: The Versatile Shielding Solution
Key Properties: Copper is known for its excellent electrical conductivity and malleability, making it a top choice for EMI shielding. It effectively blocks both radio and magnetic waves, with a high shielding effectiveness rating.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of copper is its versatility and effectiveness in a variety of applications, including consumer electronics and medical devices. However, copper is prone to corrosion, which can limit its lifespan unless treated or alloyed with other materials.
Impact on Application: Copper is ideal for environments where high conductivity is required, such as in medical devices. However, it may not be suitable for outdoor applications without protective coatings due to its susceptibility to corrosion.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN, particularly regarding corrosion resistance. In regions like Africa and South America, local climatic conditions may necessitate additional protective measures.
2. Aluminum: The Lightweight Alternative
Key Properties: Aluminum boasts a high strength-to-weight ratio and is resistant to corrosion, making it an excellent choice for EMI shielding in various applications. It is also easy to fabricate into different shapes.
Pros & Cons: The lightweight nature of aluminum makes it cost-effective and suitable for portable devices. However, its lower conductivity compared to copper can be a drawback in applications requiring high shielding effectiveness.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for consumer electronics and automotive applications where weight is a concern. Its corrosion resistance makes it a good option for outdoor use, but it may not perform as well in high-frequency applications compared to copper.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should consider local regulations on material sourcing and recycling. Standards compliance is essential, especially for automotive and aerospace applications.
3. Stainless Steel: The Durable Shield
Key Properties: Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance and durability, making it suitable for harsh environments. It has a lower conductivity than copper and aluminum but is still effective for many EMI shielding applications.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of stainless steel is its robustness and resistance to high temperatures, which is beneficial in industrial settings. However, its higher cost and weight compared to aluminum can be limiting factors for portable applications.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is often used in industrial equipment and outdoor electronics where durability is paramount. Its performance in shielding effectiveness is adequate for many applications but may not meet the requirements for high-frequency devices.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the stainless steel used complies with local standards for corrosion resistance and mechanical properties. In regions like Africa and South America, sourcing high-quality stainless steel can be challenging.
4. Mu-Metal: The Specialized Shielding Material
Key Properties: Mu-metal is an alloy primarily composed of nickel and iron, known for its high magnetic permeability. This makes it particularly effective at shielding against low-frequency magnetic fields.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of mu-metal is its effectiveness in specialized applications, such as medical imaging equipment. However, it is more expensive and less versatile than other materials, limiting its use to specific applications.
Impact on Application: Mu-metal is ideal for applications requiring high magnetic field attenuation, such as MRI machines. Its specialized nature means it may not be suitable for general-purpose shielding.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific applications for mu-metal and the associated costs. Compliance with medical device standards is critical in regions like Europe, where regulations are stringent.
Summary Table of EMI Shielding Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for EMI EMC Shielding Materials | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Medical devices, consumer electronics | High conductivity and versatility | Prone to corrosion | Med |
| Aluminum | Automotive, portable electronics | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower conductivity than copper | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Industrial equipment, outdoor electronics | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and weight | High |
| Mu-Metal | Medical imaging equipment, specialized electronics | High magnetic permeability | Expensive and less versatile | High |
This guide provides a clear understanding of the strengths and weaknesses of various EMI shielding materials, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs and regional requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for emi emc shielding materials
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of EMI EMC Shielding Materials?
Manufacturing EMI EMC shielding materials involves several critical stages, each aimed at ensuring the final product meets the required specifications for performance, durability, and compliance. Understanding these stages can help international B2B buyers make informed decisions when selecting suppliers.
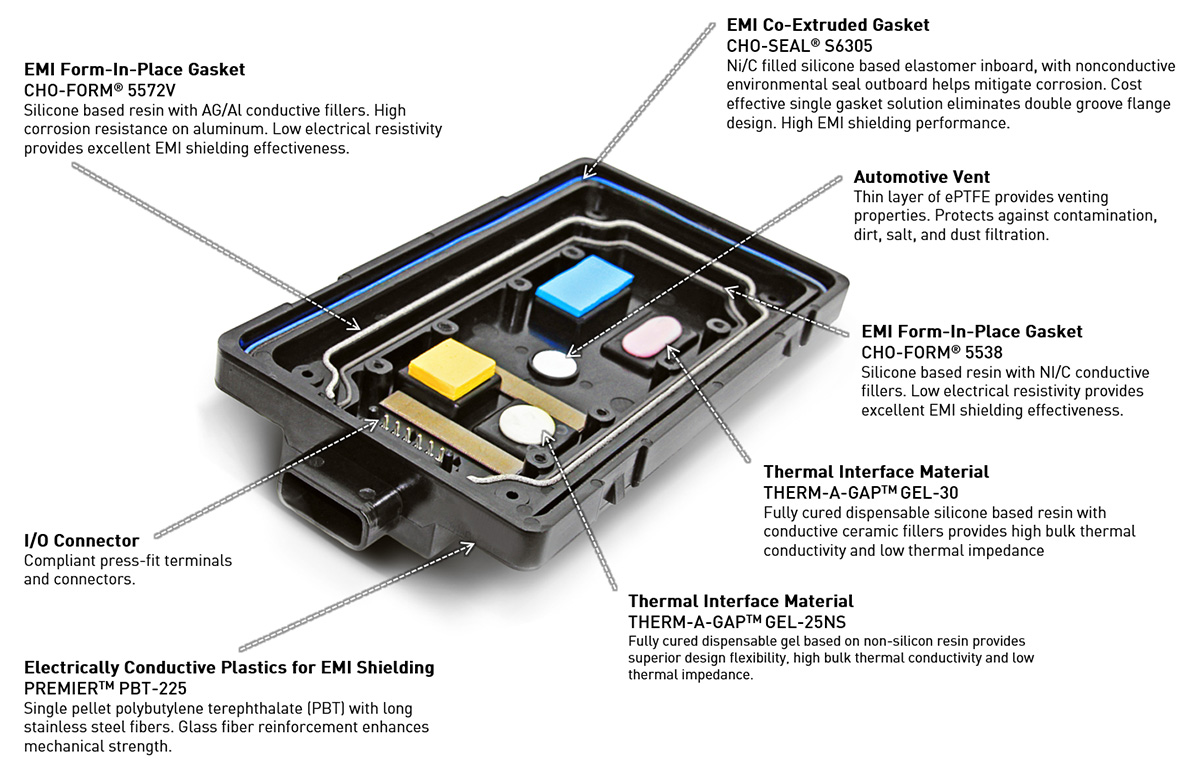
A stock image related to emi emc shielding materials.
Material Preparation: How Are Raw Materials Processed for EMI Shielding?
The first stage of manufacturing involves sourcing high-quality raw materials suitable for EMI shielding. Common materials include metals like copper, aluminum, and specialized alloys such as beryllium copper and Mu-metal. The raw materials undergo several processes:
- Material Selection: Buyers should ensure that the selected materials have the necessary electrical and mechanical properties, such as conductivity, corrosion resistance, and malleability.
- Cutting and Shaping: Raw materials are cut into specific dimensions using techniques such as laser cutting or stamping. This precision is crucial for achieving the desired fit and performance in the final product.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in EMI Shielding Manufacturing?
Once the materials are prepared, they are subjected to various forming techniques to achieve the desired shapes and structures. Key forming methods include:
- Metal Etching: A chemical process that removes material to create intricate designs and patterns. This technique is especially useful for producing detailed components like gaskets and electronic enclosures.
- Photochemical Machining: This process combines photographic and chemical techniques to shape metals, allowing for rapid prototyping and adjustments to design.
- Mechanical Forming: Techniques such as bending, rolling, and pressing are used to shape materials into final forms. Ensuring the right parameters during these processes is vital for maintaining structural integrity.
How Is Assembly Conducted in EMI Shielding Production?
The assembly stage involves bringing together various components to create the final EMI shielding product. This can include:
- Gasket Assembly: Gaskets made from rubber or metal are often integrated into electronic enclosures to enhance shielding effectiveness.
- Integration with Electronic Components: EMI shielding materials are assembled with circuit boards and other electronics. This requires precise alignment and fitting to ensure optimal shielding performance.
- Sealing and Finishing: Final assembly processes may include sealing components to prevent environmental ingress and enhance durability.
What Finishing Techniques Are Commonly Applied to EMI Shielding Products?
Finishing processes play a crucial role in enhancing the performance and aesthetics of EMI shielding materials. Common techniques include:
- Coating: Applying protective coatings to prevent corrosion and enhance durability. For instance, pre-tinplated steel offers additional rust resistance.
- Surface Treatment: Techniques like anodizing aluminum can improve its electrical properties and resistance to wear.
- Quality Testing: After finishing, products undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet specified performance standards.
What Quality Assurance Processes Should B2B Buyers Expect in EMI Shielding Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process for EMI shielding materials. Buyers should be aware of the following QA practices:
What Are the International Standards for Quality Assurance in EMI Shielding?
International standards such as ISO 9001 are essential for ensuring consistent quality in manufacturing processes. Compliance with these standards indicates that a manufacturer adheres to best practices in quality management systems.
Additionally, specific industry certifications may apply, such as CE marking for products sold in Europe and API standards for certain industrial applications. Buyers should inquire about these certifications to ensure compliance with regional regulations.
How Are Quality Control Checkpoints Integrated Throughout the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process to catch defects early. Key checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet the required specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Regular checks during the manufacturing stages help identify issues before they escalate. This includes monitoring dimensions and material properties during forming and assembly.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The final product undergoes comprehensive testing, including EMI shielding effectiveness tests, to verify performance metrics.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used to Ensure EMI Shielding Performance?
To assess the effectiveness of EMI shielding materials, various testing methods are employed:
- Shielding Effectiveness Testing: This involves measuring the attenuation of electromagnetic waves through the shielding material. Common methods include the use of a spectrum analyzer to evaluate performance across different frequencies.
- Environmental Testing: Products may undergo tests to assess their performance under extreme conditions, such as high temperatures or humidity, to ensure durability.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Measures?
When sourcing EMI shielding materials, B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify supplier quality control measures:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting site visits to assess manufacturing capabilities and QC processes can provide valuable insights.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation of their quality control measures, including testing results and compliance certificates.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s production quality and adherence to standards.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding local regulations and certification nuances is crucial. Some considerations include:
- Regional Compliance: Different regions may have specific requirements for EMI shielding products. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these regulations to ensure compliance.
- Language Barriers: Documentation and communication may vary in language, so establishing clear channels of communication with suppliers is essential.
- Logistical Challenges: Understanding the logistics of sourcing materials across borders can help mitigate delays and ensure timely delivery.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for EMI EMC shielding materials is essential for international B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming techniques, assembly, and finishing, along with rigorous quality control measures, buyers can ensure they partner with suppliers that deliver reliable and compliant shielding solutions.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ’emi emc shielding materials’
To help international B2B buyers effectively procure EMI EMC shielding materials, this guide provides a practical checklist designed to streamline the sourcing process. Ensuring your electronic devices are protected from electromagnetic interference is critical, especially in high-stakes industries such as telecommunications, medical devices, and aerospace. Follow these steps to enhance your procurement strategy and ensure you select the right materials for your needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by outlining the technical requirements for your EMI shielding needs. Consider factors such as the frequency range of the interference you wish to block, the environmental conditions (e.g., humidity, temperature), and the mechanical properties required for your application. This clear definition will guide you in selecting the right materials and shielding designs.
- Frequency Range: Identify specific frequencies that need shielding to ensure you choose compatible materials.
- Environmental Factors: Assess whether your devices will be exposed to harsh conditions, which might dictate the choice of more durable materials.
Step 2: Research Available Materials
Investigate the various materials available for EMI shielding, each with unique properties. Common options include copper, aluminum, stainless steel, and specialized alloys like beryllium copper and mu-metal. Understanding the pros and cons of each material helps you align your choice with your technical specifications.
- Conductivity and Shielding Effectiveness: Ensure the material can effectively block the electromagnetic waves relevant to your application.
- Cost Considerations: Balance material performance with your budget constraints, especially if sourcing in regions with different price points.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, thoroughly vet potential suppliers. Request detailed company profiles, inquire about their production capabilities, and ask for case studies or references from similar industries or geographic areas. A well-established supplier will have a proven track record and be able to meet your specific needs.
- Certifications and Standards: Verify if the supplier adheres to industry-specific certifications, such as ISO or NEMA ratings, which can indicate reliability and quality.
- Customer Reviews: Look for testimonials or reviews from previous clients to gauge the supplier’s reputation and service reliability.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request samples of the shielding materials you’re considering. Testing these samples in your specific application will provide insights into their performance and compatibility. This step is crucial to ensure that the materials meet your shielding effectiveness requirements.
- Compatibility Testing: Check how well the materials integrate with your existing devices or components.
- Performance Evaluation: Assess the shielding effectiveness through controlled tests to confirm the materials’ capabilities.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Engage in discussions with your selected suppliers to negotiate pricing, delivery timelines, and payment terms. Clear communication on these aspects can prevent misunderstandings later in the procurement process.
- Volume Discounts: Inquire about discounts for bulk orders or long-term contracts, which can significantly reduce costs.
- Lead Times: Understand the supplier’s lead times to ensure that your project timelines can be met without delays.
Step 6: Finalize Purchase Agreements
Once negotiations are complete, finalize the purchase agreements with the chosen supplier. Ensure that all specifications, terms, and conditions are clearly documented to avoid any future disputes.
- Documentation: Include detailed descriptions of the materials, quantities, pricing, and delivery schedules in the agreement.
- Quality Assurance Clauses: Incorporate clauses for quality assurance and potential penalties for non-compliance with the agreed standards.
Step 7: Monitor Delivery and Quality Control
Upon receiving the materials, conduct a thorough inspection to ensure they meet the agreed-upon specifications. This includes checking for any physical damage during transit and verifying the quantity and quality of the materials received.
- Quality Checks: Implement your quality control procedures to assess the materials’ performance before they are integrated into your products.
- Feedback Loop: Establish a feedback mechanism with the supplier to address any issues that may arise post-delivery.
By following this structured checklist, international B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategy for EMI EMC shielding materials, ensuring that they select the most suitable options for their specific applications.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for emi emc shielding materials Sourcing
In sourcing EMI/EMC shielding materials, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers. This analysis delves into the key components of costs, price influencers, and actionable buyer tips, particularly for stakeholders in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Key Cost Components for EMI Shielding Materials?
When evaluating the cost of EMI shielding materials, several core components contribute to the total expenditure:
-
Materials: The type of shielding material significantly affects cost. Metals such as copper, aluminum, stainless steel, and specialized alloys (e.g., beryllium copper, Monel) have varying price points influenced by market demand and availability. As a buyer, selecting a material that balances performance and cost is essential.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the workforce involved in manufacturing and assembling the shielding materials. Regions with higher labor costs may influence overall pricing, making it critical to consider the location of your suppliers.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility operations. Suppliers with efficient manufacturing processes can offer more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific EMI shielding applications can add to upfront costs. However, investing in quality tooling can yield long-term savings through enhanced production efficiency.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure compliance with international standards, especially for critical applications in sectors like aerospace and medical devices. While this adds to costs, it is essential for ensuring product reliability.
A stock image related to emi emc shielding materials.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary widely based on the supplier’s location and the chosen Incoterms. Understanding these can help in negotiating better terms.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include their profit margin in the pricing. This can vary based on market competition and the supplier’s positioning.
How Do Price Influencers Affect EMI Shielding Material Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of EMI shielding materials, which B2B buyers should consider:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders typically result in lower per-unit costs. Negotiating for better pricing based on volume can lead to significant savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Tailored solutions often come at a premium. Clearly defining your specifications can help avoid unnecessary costs associated with revisions and customizations.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and compliance with industry certifications (e.g., ISO, RoHS) can increase costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of premium materials against their specific application requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The reliability and reputation of suppliers play a significant role in pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer better quality assurance and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the shipping terms can significantly affect the final cost. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can shift costs between the buyer and supplier.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Sourcing EMI Shielding Materials?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the following tips can help optimize costs:
-
Negotiate Wisely: Use volume commitments and long-term partnerships as leverage in negotiations. Suppliers are often willing to offer better pricing for reliable, repeat business.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Analyze the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the initial purchase price. Consider long-term factors like durability, maintenance, and operational efficiencies.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences and market dynamics. For instance, fluctuations in metal prices can affect costs, so staying informed about market trends is vital.
-
Request Samples and Prototypes: Before committing to large orders, request samples to evaluate quality and performance. This can prevent costly mistakes later.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
It is important to note that prices for EMI shielding materials can vary significantly based on market conditions, material choices, and supplier negotiations. Therefore, obtaining multiple quotes and conducting thorough market research is advisable to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing emi emc shielding materials With Other Solutions
When it comes to shielding electronic devices from electromagnetic interference (EMI), various solutions exist beyond traditional EMI shielding materials. Understanding the alternatives can help international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific needs, environmental conditions, and budget constraints. Below, we compare EMI shielding materials with two viable alternatives: RF shielding technology and electronic enclosures.
Comparison Table of EMI Shielding Materials and Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | EMI EMC Shielding Materials | RF Shielding Technology | Electronic Enclosures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High effectiveness across a range of frequencies, tailored to specific applications. | Effective for high-frequency signals but may not cover all frequencies. | Provides physical protection and can include EMI shielding features. |
| Cost | Varies significantly based on material type; can be expensive. | Generally lower initial costs but may require additional components. | Moderate to high costs depending on material and design complexity. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires careful design and integration into devices. | Can be easier to apply in existing setups with some adjustments. | May require custom designs and installation, depending on device size. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; durability depends on material choice. | Requires monitoring of shielding effectiveness over time. | Low maintenance if properly sealed; however, access may be limited. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for sensitive electronics in medical or aerospace applications. | Suitable for telecommunications and broadcasting industries. | Best for general electronic devices needing both physical and EMI protection. |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of RF Shielding Technology?
RF shielding technology utilizes specialized materials and designs to block radiofrequency signals. One of its main advantages is the flexibility in application, allowing for easy integration into existing systems. It typically incurs lower initial costs compared to dedicated EMI materials, making it attractive for budget-conscious buyers. However, it may not provide the comprehensive protection required for all electronic devices, particularly those sensitive to a wide range of frequencies.
How Do Electronic Enclosures Compare for EMI Protection?
Electronic enclosures serve the dual purpose of protecting electronic components from environmental factors and providing EMI shielding. They can be designed to meet specific NEMA ratings, which is a significant advantage for buyers in sectors like manufacturing or energy. However, the cost can be moderate to high, depending on the material and design complexity. Additionally, while they offer good overall protection, their effectiveness in EMI shielding can be compromised if not designed with appropriate materials and configurations.
Conclusion: How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
For B2B buyers, selecting the right EMI shielding solution involves assessing the specific requirements of their applications. Consider the performance needs, budget, and implementation capabilities of each option. EMI shielding materials are often the best choice for high-stakes environments like medical devices or aerospace technology, while RF shielding technology may suit telecommunications applications better. Electronic enclosures provide a versatile solution for general electronic devices but may require careful design considerations to ensure effective EMI protection. By evaluating these factors, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and budgetary constraints.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for emi emc shielding materials
What Are the Key Technical Properties of EMI/EMC Shielding Materials?
When evaluating EMI/EMC shielding materials, it’s crucial to understand certain technical properties that can significantly impact performance and application suitability. Here are some essential specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the quality and composition of the metal or alloy used in shielding. Higher-grade materials typically offer better conductivity, corrosion resistance, and durability. For B2B buyers, selecting the right material grade is fundamental, as it directly affects the longevity and effectiveness of the shielding solution, especially in demanding environments like those found in aerospace or medical applications.
2. Shielding Effectiveness (SE)
Shielding effectiveness quantifies how well a material can attenuate electromagnetic interference (EMI). It is measured in decibels (dB) and indicates the material’s ability to block specific frequencies. For international buyers, understanding SE is critical when assessing products for their specific applications, ensuring that the selected shielding material meets regulatory and operational requirements.
3. Thickness
The thickness of the shielding material plays a vital role in its performance. Thicker materials generally provide better shielding but may also increase weight and cost. B2B buyers must balance thickness against other factors such as flexibility and application needs, particularly in industries where weight is a critical consideration, such as automotive or aerospace.
4. Conductivity
Conductivity refers to how well a material can conduct electricity and is a crucial factor in EMI shielding. Materials with higher conductivity typically offer better performance in blocking electromagnetic waves. Buyers should prioritize materials with optimal conductivity for their specific applications, particularly in high-frequency environments where effective shielding is paramount.
5. Galvanic Compatibility
This term describes how different metals interact when in contact, particularly in the presence of moisture. Incompatible metals can lead to galvanic corrosion, compromising the shielding’s integrity. B2B buyers must consider galvanic compatibility when designing assemblies that involve multiple materials, especially in humid or corrosive environments common in regions like the Middle East or coastal areas of Europe.
6. Durability
Durability encompasses the material’s resistance to wear, corrosion, and environmental factors. High durability is essential for applications exposed to harsh conditions, such as industrial machinery or outdoor electronics. Buyers should assess the expected lifespan of the shielding solution in their specific application to avoid costly replacements and ensure reliability.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in EMI/EMC Shielding?
Understanding industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B landscape. Here are some common terms related to EMI/EMC shielding materials:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of EMI shielding, OEMs often provide customized solutions tailored to specific needs. Buyers should engage with reputable OEMs to ensure quality and compatibility with their applications.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for B2B buyers to manage inventory effectively and avoid excess costs. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their demand patterns to optimize procurement efficiency.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing information for specific products or services. It helps buyers compare costs and make informed purchasing decisions. Crafting a clear RFQ is essential for ensuring suppliers provide accurate and relevant quotes for EMI shielding materials.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. They specify who pays for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, impacting overall costs. B2B buyers should familiarize themselves with Incoterms to negotiate favorable shipping terms and understand their liabilities.
5. EMI/RFI (Electromagnetic Interference/Radio Frequency Interference)
EMI and RFI refer to disturbances that can disrupt electronic devices. Understanding these terms helps buyers appreciate the importance of effective shielding solutions in protecting sensitive equipment from interference that could lead to malfunctions or failures.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they select the right EMI/EMC shielding materials for their unique needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the emi emc shielding materials Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the EMI/EMC Shielding Materials Sector?
The EMI/EMC shielding materials market is experiencing significant growth driven by the rising demand for electronic devices across various industries, including automotive, telecommunications, and healthcare. International B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should note that advancements in technology are leading to the development of more effective shielding materials, including the use of composites and innovative metal alloys. For instance, the integration of beryllium copper and aluminum in shielding solutions is gaining traction due to their lightweight properties and superior conductivity.
Emerging trends such as the miniaturization of electronic devices and the proliferation of wireless technologies are pushing manufacturers to seek advanced EMI shielding solutions that can fit within compact designs while maintaining high performance. Additionally, the rise of smart devices necessitates improved shielding techniques to mitigate interference from multiple signal sources. Buyers should also be aware of the increasing importance of customization in shielding products, as tailored solutions can enhance performance and reduce costs.
Furthermore, the global market is witnessing shifts towards localized sourcing strategies. This trend is particularly relevant for buyers in Africa and South America, where establishing regional partnerships can lead to reduced lead times and logistics costs. By understanding these dynamics, international B2B buyers can better navigate the complexities of the EMI shielding materials market and make informed sourcing decisions.
How Can International Buyers Ensure Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in EMI Shielding Materials?
Sustainability has become a crucial factor in the procurement of EMI shielding materials. Buyers must consider the environmental impact of their sourcing decisions, especially as regulations around electronic waste and carbon emissions tighten globally. Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on sustainable practices, such as utilizing recyclable materials and reducing energy consumption in the production process.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, particularly for buyers in emerging markets. Ensuring that suppliers adhere to fair labor practices and sustainable material sourcing is vital for maintaining brand integrity and compliance with international standards. B2B buyers should seek suppliers that possess certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety, as these indicate a commitment to ethical practices.
In addition, the growing demand for ‘green’ materials in EMI shielding applications is leading to innovations in eco-friendly alternatives. For instance, some manufacturers are exploring the use of bio-based polymers and composite materials that offer effective shielding capabilities with a lower environmental footprint. By prioritizing sustainability and ethical sourcing, international buyers can not only align with consumer expectations but also enhance their competitive advantage in the market.
What Is the Evolution of EMI Shielding Materials and Its Relevance to Current B2B Trends?
The evolution of EMI shielding materials dates back to the early days of electronics when basic metal enclosures were utilized to protect sensitive components from electromagnetic interference. Over the decades, the industry has progressed significantly, driven by technological advancements and the growing complexity of electronic devices. The introduction of specialized materials like mu-metal and beryllium copper has expanded the range of options available for effective shielding.
As electronic devices became more compact and integrated, the demand for advanced shielding solutions increased. This led to the development of innovative materials and techniques, such as photochemical etching and chemical milling, which allow for precise fabrication of intricate designs that meet modern shielding requirements. Today, the focus is not only on performance but also on sustainability and ethical sourcing, reflecting the changing landscape of global manufacturing practices.
Understanding this historical context can provide international B2B buyers with insights into current market dynamics and help them identify reliable suppliers that are committed to innovation and responsible practices. By leveraging the lessons learned from the past, buyers can make strategic decisions that align with both their operational goals and the evolving expectations of their customers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of emi emc shielding materials
-
How do I solve electromagnetic interference issues in my devices?
To effectively address electromagnetic interference (EMI) issues, start by assessing the specific types of interference your devices are experiencing. Choose appropriate EMI shielding materials based on the frequencies involved and the environment in which the devices will operate. Common solutions include metal enclosures, gaskets, and specialized coatings that can block or redirect EMI. Collaborating with suppliers who offer customizable options can help tailor solutions to your specific needs, ensuring optimal performance and reliability. -
What is the best EMI shielding material for high-frequency applications?
For high-frequency applications, materials such as copper and aluminum are highly effective due to their excellent conductivity and flexibility. Copper provides superior shielding effectiveness and can be alloyed with other metals for enhanced performance. Aluminum, being lightweight and cost-effective, is also widely used. When selecting a material, consider the application’s specific requirements, including environmental factors and budget constraints, to ensure you choose the most suitable option. -
What factors should I consider when sourcing EMI shielding materials internationally?
When sourcing EMI shielding materials internationally, consider factors such as material specifications, compliance with local regulations, and supplier reliability. Research potential suppliers by reviewing their certifications and previous projects. Additionally, assess the logistics involved, including shipping times and costs, as well as payment terms and currency exchange rates. Clear communication regarding your requirements can also help avoid misunderstandings and ensure timely delivery. -
How can I customize EMI shielding solutions for my specific needs?
Customization of EMI shielding solutions can be achieved by collaborating closely with your supplier. Discuss your specific application requirements, including size, shape, material composition, and any environmental considerations. Many suppliers offer design services that allow you to create tailored solutions, such as gaskets or enclosures, that meet your unique specifications. Ensure that you provide detailed information about the intended use and performance expectations to achieve the best results. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for EMI shielding products?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for EMI shielding products can vary significantly between suppliers and depend on the specific materials and customization options. Many manufacturers may have MOQs ranging from 100 to 1,000 units, particularly for customized products. However, some suppliers may offer lower MOQs for standard items. It’s crucial to communicate your needs with potential suppliers to negotiate MOQs that align with your project requirements and budget.
A stock image related to emi emc shielding materials.
-
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing EMI shielding materials?
Payment terms for EMI shielding materials can vary by supplier and region. Common terms include full payment upfront, a deposit followed by balance upon delivery, or net payment terms (e.g., 30 days after invoice). When sourcing internationally, be aware of additional factors such as currency conversion and potential tariffs. Discuss payment options early in the negotiation process to ensure mutual understanding and to facilitate a smooth transaction. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) in my EMI shielding materials?
To ensure quality assurance (QA) in your EMI shielding materials, verify that the supplier adheres to international quality standards, such as ISO 9001. Request documentation of their quality control processes, including testing methods for shielding effectiveness and material durability. Additionally, consider asking for samples before placing large orders to assess the product’s quality firsthand. Establishing a clear QA agreement with the supplier can further enhance confidence in the materials provided. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing EMI shielding materials?
When importing EMI shielding materials, logistics considerations include shipping methods, lead times, customs clearance processes, and potential duties or tariffs. Choose a reliable freight forwarder familiar with international trade regulations to facilitate smooth transportation. Be aware of packaging requirements to prevent damage during transit, and ensure all necessary documentation is in order for customs. Planning ahead for these logistics can help avoid delays and additional costs, ensuring timely delivery of your materials.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for emi emc shielding materials
Why Is Strategic Sourcing Essential for EMI Shielding Materials?
In the rapidly evolving landscape of electronic devices, strategic sourcing of EMI shielding materials is crucial for international B2B buyers. This process not only ensures compliance with industry standards but also enhances product reliability and performance across diverse applications, from consumer electronics to critical medical devices. Understanding the specific needs related to electromagnetic interference (EMI) will enable buyers to select appropriate materials—such as copper, aluminum, or specialized alloys—tailored to their unique operational environments.
How Can Buyers Optimize Their Sourcing Strategies?
Buyers should prioritize a thorough assessment of material properties, including conductivity, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness. Collaborating with manufacturers who offer customizable solutions can further streamline the sourcing process. By leveraging local suppliers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, buyers can mitigate logistical challenges and foster sustainable partnerships that enhance supply chain resilience.
What’s Next for International Buyers in EMI Shielding?
Looking ahead, the demand for effective EMI shielding solutions will only grow as technology advances. International buyers must stay informed about emerging materials and innovations in shielding technologies. Engaging in proactive sourcing strategies and maintaining open lines of communication with suppliers will position businesses for success in this competitive market. Take action now to secure your supply chain and ensure your products are equipped to meet future challenges.