Discover Cost-Saving Solutions for Electrical Plugs & Sockets (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for electrical plugs & sockets
Navigating the global market for electrical plugs and sockets presents a unique set of challenges for international B2B buyers, particularly those sourcing components across diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The myriad of plug types, voltage specifications, and safety standards can complicate procurement processes, often leading to compatibility issues that can disrupt operations. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify these complexities, providing valuable insights into the various types of plugs and sockets available, their applications, and essential supplier vetting practices.
By delving into key topics such as regional standards, cost considerations, and the latest innovations in electrical infrastructure, this guide empowers buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. Whether you are looking to source Type C sockets for European markets or Type D plugs for African installations, understanding the nuances of electrical compatibility is crucial for ensuring seamless integration into your projects.
Furthermore, we will explore the implications of regulatory compliance and safety certifications, which are particularly pertinent in today’s increasingly interconnected world. With this knowledge, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of the electrical supply market with confidence, optimizing their sourcing strategies while minimizing risks associated with international procurement.
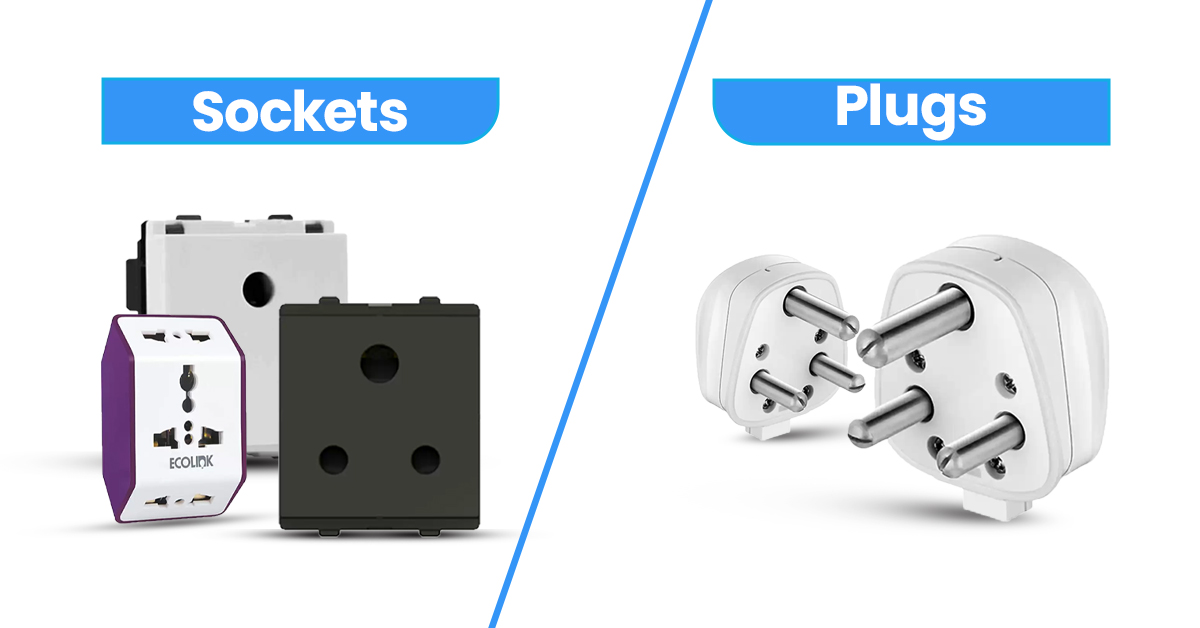
Understanding electrical plugs & sockets Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type C | Two round pins, commonly known as the “Euro” plug. | Widely used in Europe, Africa, and Asia for consumer electronics. | Pros: Universally compatible with many devices; Cons: Not suitable for high-power applications. |
| Type G | Three rectangular prongs, often found in the UK and some Middle Eastern countries. | Common in the UK for heavy-duty appliances and industrial applications. | Pros: High safety due to grounding; Cons: Bulkier design may not fit all devices. |
| Type E/F | Two round pins with a grounding pin; Type F is also known as “Schuko.” | Popular in Germany, France, and surrounding countries for residential and commercial use. | Pros: Versatile compatibility; Cons: May require adapters for non-European devices. |
| Type I | Flat pins in a V-shape, used in Australia, New Zealand, and parts of China. | Suitable for appliances and electronics in the Southern Hemisphere. | Pros: Good for high-power devices; Cons: Limited compatibility outside its region. |
| Type N | Similar to Type C but with an additional grounding pin, used in Brazil and South Africa. | Used for residential and commercial electrical installations. | Pros: Enhanced safety; Cons: Limited availability of compatible devices outside its region. |
What Are the Characteristics of Type C Plugs and Sockets?
Type C plugs, recognized by their two round pins, are a staple in many countries across Europe, Africa, and Asia. Their design allows for compatibility with a wide range of devices, making them ideal for consumer electronics. For B2B buyers, the versatility of Type C plugs means they can source a single type of adapter for multiple devices, reducing inventory complexity. However, businesses should consider that Type C is not suitable for high-power applications, which may necessitate additional solutions for certain equipment.
Why Is Type G a Preferred Choice in the UK and Middle East?
Type G plugs feature three rectangular prongs and are commonly used in the UK and some Middle Eastern countries. Their robust design makes them suitable for heavy-duty appliances, often utilized in industrial settings. B2B buyers appreciate the added safety features of Type G plugs, particularly the grounding mechanism that minimizes electrical hazards. However, the bulkiness of Type G plugs may limit compatibility with some devices, making it essential for buyers to ensure their equipment can accommodate this type.
How Do Type E/F Plugs Benefit European Businesses?
Type E/F plugs, characterized by two round pins and a grounding pin, are prevalent in Germany, France, and other parts of Europe. Their compatibility with various devices makes them a practical choice for businesses operating in these regions. B2B buyers benefit from the versatility of Type E/F plugs, as they can use them across multiple applications without needing various adapters. However, it is important to note that while they are widely used, businesses may need adapters for devices from outside Europe.
What Are the Advantages of Type I Plugs in Australia and New Zealand?
Type I plugs, with their unique V-shaped pins, are primarily found in Australia, New Zealand, and parts of China. They are well-suited for high-power devices, making them a preferred choice for businesses in these regions. B2B buyers can leverage Type I plugs for various applications, from consumer electronics to industrial machinery. However, their limited compatibility outside their region may require additional investment in adapters for international operations.
Why Choose Type N Plugs for Brazilian and South African Markets?
Type N plugs, which feature a similar design to Type C but with an additional grounding pin, are used in Brazil and South Africa. Their enhanced safety features make them suitable for both residential and commercial installations. For B2B buyers, Type N plugs offer a reliable option for powering devices in these markets. However, buyers should be aware of the limited availability of compatible devices outside these regions, which could impact sourcing strategies.
Key Industrial Applications of electrical plugs & sockets
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Electrical Plugs & Sockets | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Powering machinery and tools | Ensures operational efficiency and minimizes downtime | Voltage compatibility, durability, and safety ratings |
| Construction | Temporary power supply for tools and lighting | Facilitates continuous work on-site | Weather resistance, compliance with local regulations |
| Hospitality | Guest room and common area electrical installations | Enhances guest experience and satisfaction | Aesthetic design, energy efficiency, and safety features |
| Telecommunications | Data center equipment connections | Supports reliable data transmission and uptime | Compatibility with high-power requirements and cooling needs |
| Agriculture | Powering irrigation and farming equipment | Improves productivity and operational reliability | Resistance to environmental factors and voltage stability |
How are Electrical Plugs & Sockets Utilized in Manufacturing?
In the manufacturing sector, electrical plugs and sockets are critical for powering machinery and tools. These connections ensure that heavy equipment operates efficiently and without interruption, thereby minimizing downtime. Buyers should consider the voltage compatibility and durability of the plugs, as machinery often operates under rigorous conditions. Additionally, safety ratings are vital to prevent electrical hazards in high-output environments.
What Role Do Electrical Plugs & Sockets Play in Construction?
In construction, electrical plugs and sockets are essential for providing temporary power to tools and lighting on job sites. They enable continuous work by supplying energy to various devices, from power drills to site lighting. When sourcing, businesses must prioritize weather-resistant products that can withstand harsh conditions, as well as compliance with local regulations to ensure safety and reliability.
How Do Electrical Plugs & Sockets Enhance Hospitality?
The hospitality industry relies heavily on electrical plugs and sockets for guest room and common area installations. These components are integral to powering amenities such as lighting, televisions, and charging stations, directly impacting guest satisfaction. Buyers should focus on aesthetic designs that blend with interior decor, energy efficiency to reduce operational costs, and safety features to protect guests from electrical issues.
Why Are Electrical Plugs & Sockets Important in Telecommunications?
In telecommunications, electrical plugs and sockets are vital for connecting data center equipment. Reliable electrical connections support data transmission and ensure high uptime, which is crucial for maintaining service quality. When sourcing these products, businesses must ensure compatibility with high-power requirements and consider cooling needs to prevent overheating of connected devices.
How Are Electrical Plugs & Sockets Used in Agriculture?
In agriculture, electrical plugs and sockets are used to power irrigation systems and farming equipment. Efficient electrical connections are necessary to enhance productivity and ensure operational reliability during critical planting and harvesting periods. Buyers should look for products that are resistant to environmental factors, such as moisture and dirt, and that provide stable voltage to avoid equipment malfunctions.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘electrical plugs & sockets’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Voltage Compatibility Issues in International Markets
The Problem: One of the most pressing challenges B2B buyers face when sourcing electrical plugs and sockets is the confusion surrounding voltage compatibility across different regions. For instance, a manufacturer in Europe may need to export products to South America or Africa, where the voltage requirements differ significantly. This mismatch can lead to equipment failure, safety hazards, and increased costs due to the need for additional voltage converters or adapters. Buyers may find it difficult to navigate the diverse voltage standards, resulting in costly delays and potential damage to their brand reputation.
The Solution: To effectively manage voltage compatibility, it’s crucial to conduct thorough research on the electrical standards of the target market. Buyers should leverage resources like international electrical standards organizations and industry-specific databases to identify the voltage and frequency specifications required for their products. Additionally, consider sourcing multi-voltage plugs and sockets that can adapt to different electrical environments. When specifying products, include clear labeling on the packaging indicating the voltage range and compatibility to ensure users can safely utilize the equipment. Collaborating with local distributors can also provide insights into specific regional needs, ensuring compliance and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Scenario 2: Addressing Safety Standards and Compliance Concerns
The Problem: Safety compliance is a critical pain point for B2B buyers, especially when dealing with electrical plugs and sockets. Different countries have distinct safety regulations that must be adhered to, such as CE marking in Europe or SANS standards in South Africa. Failure to comply can lead to legal liabilities, product recalls, and severe financial losses. Buyers may find it challenging to ensure that their products meet these varying standards, particularly when importing or exporting electrical components.
The Solution: To navigate safety standards effectively, buyers should engage with third-party testing laboratories that specialize in electrical safety compliance. Obtain certifications that align with the target market’s regulations, and ensure that your suppliers can provide the necessary documentation proving compliance. It’s also advisable to incorporate safety features such as surge protection and child-proof designs in your products to enhance their marketability. Regularly review changes in regulations and participate in industry forums to stay informed about evolving compliance requirements. By prioritizing safety and compliance, you not only mitigate risks but also build trust with your customers.
Scenario 3: Overcoming Sourcing Challenges for Diverse Product Lines
The Problem: Many B2B buyers struggle with sourcing a diverse range of electrical plugs and sockets to meet the demands of various applications. For instance, a company may need to supply both residential and industrial-grade products but faces difficulties in finding a reliable supplier that can provide a comprehensive selection. This issue can lead to project delays, increased costs due to multiple suppliers, and inconsistency in product quality.
The Solution: To overcome sourcing challenges, consider establishing long-term partnerships with manufacturers who specialize in a wide range of electrical components. This approach not only streamlines the purchasing process but also allows for better negotiation on pricing and terms. When evaluating suppliers, prioritize those who offer custom solutions, such as tailored designs for specific applications or bulk ordering options to reduce costs. Utilize digital platforms and marketplaces that aggregate multiple suppliers, making it easier to compare options and ensure quality. Furthermore, engaging in direct communication with manufacturers can foster innovation and adaptability, allowing you to meet customer needs effectively and efficiently.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for electrical plugs & sockets
When selecting materials for electrical plugs and sockets, international B2B buyers must consider several factors, including performance, durability, compliance with standards, and cost. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the manufacturing of these devices: thermoplastics, thermosetting plastics, metals, and rubber. Each material has distinct properties and implications for use in various global markets, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Key Properties of Thermoplastics in Electrical Plugs and Sockets?
Thermoplastics, such as polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and nylon, are widely used in electrical plugs and sockets due to their excellent insulation properties and flexibility. They typically have a temperature rating ranging from -40°C to 85°C, making them suitable for various environments. Additionally, thermoplastics exhibit good resistance to chemicals and moisture, which is crucial for applications in humid regions.
Pros and Cons of Thermoplastics:
– Pros: Cost-effective, lightweight, and easy to mold, allowing for complex designs. They also provide good electrical insulation.
– Cons: Limited heat resistance compared to thermosetting plastics, which can lead to deformation under high temperatures.
Impact on Application:
Thermoplastics are ideal for residential and commercial electrical applications where moderate temperature and humidity levels are expected. However, they may not be suitable for high-load industrial environments.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers must ensure compliance with regional standards such as IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) and ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) when sourcing thermoplastic components, especially for markets in Europe and the Middle East.
How Do Thermosetting Plastics Perform in Electrical Applications?
Thermosetting plastics, like phenolic and epoxy resins, are known for their superior heat resistance and mechanical strength. They can withstand temperatures up to 150°C without deforming, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications. Their rigidity also contributes to enhanced durability and longevity.
Pros and Cons of Thermosetting Plastics:
– Pros: Excellent thermal stability and mechanical strength, making them ideal for high-load applications.
– Cons: More expensive than thermoplastics and typically more complex to manufacture, which can increase lead times.
Impact on Application:
These materials are particularly beneficial in industrial settings where plugs and sockets may be exposed to extreme conditions, including high temperatures and mechanical stress.
Considerations for International Buyers:
For regions like Africa and South America, where electrical infrastructure may be less reliable, sourcing thermosetting plastics that meet local standards can enhance product reliability and safety.
What Role Do Metals Play in Electrical Plug and Socket Manufacturing?
Metals, particularly copper and aluminum, are commonly used for the conductive components of plugs and sockets. Copper is favored for its excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance, while aluminum is lighter and more cost-effective.
Pros and Cons of Metals:
– Pros: High conductivity and durability, with the ability to handle high electrical loads.
– Cons: Prone to corrosion if not properly coated, and can be heavier, impacting the overall weight of the device.
Impact on Application:
Metal components are essential for high-performance applications where electrical efficiency is critical. They are commonly used in industrial and commercial settings.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with local electrical standards, such as DIN in Europe or NEMA in the United States, is crucial. Buyers should also consider the environmental impact of sourcing metals, particularly in regions with strict regulations.
How Does Rubber Enhance the Safety and Functionality of Electrical Devices?
Rubber is often used as an insulating material and for protective casings in electrical plugs and sockets. Its flexibility and resistance to wear and tear make it an excellent choice for outdoor and industrial applications.
Pros and Cons of Rubber:
– Pros: Excellent electrical insulation properties and resistance to environmental factors such as moisture and UV light.
– Cons: Can degrade over time with exposure to certain chemicals and extreme temperatures.
Impact on Application:
Rubber is particularly useful in applications where moisture resistance is critical, such as outdoor plugs and sockets.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure that rubber materials comply with local safety standards and environmental regulations, especially in markets like Europe, where compliance is strictly monitored.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Electrical Plugs and Sockets
| Material | Typical Use Case for electrical plugs & sockets | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermoplastics | Residential and commercial applications | Cost-effective and easy to mold | Limited heat resistance | Low |
| Thermosetting Plastics | Industrial applications | Excellent thermal stability | More expensive and complex to manufacture | High |
| Metals | High-performance industrial settings | High conductivity and durability | Prone to corrosion if not coated | Medium |
| Rubber | Outdoor and moisture-prone environments | Excellent insulation and moisture resistance | Can degrade over time with chemical exposure | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides actionable insights for international B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions tailored to their specific market needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for electrical plugs & sockets
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Electrical Plugs and Sockets?
The manufacturing of electrical plugs and sockets involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets safety and performance standards. Understanding these stages is essential for international B2B buyers looking to source quality components.
-
Material Preparation: The process begins with the selection of high-grade materials, typically thermoplastics for the casing and copper or brass for the conductors. Suppliers often rely on certified vendors to ensure that raw materials comply with international standards. Buyers should verify the material specifications to ensure durability and safety.
-
Forming: In this stage, materials are shaped into the desired forms. For instance, plastic casings are often produced through injection molding, while metal components may be stamped or extruded. This stage requires precision machinery and skilled operators to achieve the correct dimensions and tolerances.
-
Assembly: After forming, components are assembled. This may involve automated systems for mass production or manual assembly for smaller batches. Key factors during assembly include ensuring that electrical contacts are secure and that the plugs fit correctly into sockets. Quality control measures should be in place to catch any defects early.
-
Finishing: The final stage includes surface treatments, such as coating or polishing, to enhance aesthetics and functionality. This may involve applying anti-corrosive finishes to metal parts or ensuring that plastic surfaces are free from imperfections. Finishing processes can significantly affect the product’s longevity and performance.
What International Standards Govern the Quality Assurance of Electrical Plugs and Sockets?
Quality assurance in the manufacturing of electrical plugs and sockets is governed by various international standards that ensure safety, reliability, and performance. Understanding these standards is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when sourcing products globally.
-
ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and emphasizes continuous improvement. Manufacturers certified under ISO 9001 are likely to have structured processes in place, enhancing product quality and customer satisfaction.
-
CE Marking: In Europe, the CE mark indicates compliance with safety, health, and environmental protection standards. For B2B buyers in Europe, ensuring that plugs and sockets bear the CE mark is essential for legal compliance.
-
UL and CSA Certifications: In North America, Underwriters Laboratories (UL) and the Canadian Standards Association (CSA) provide safety certification for electrical products. Buyers should verify these certifications to ensure safety and compliance with local regulations.
-
IEC Standards: The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) develops international standards for electrical and electronic devices. Compliance with IEC standards is often a requirement for international trade.
How Do Quality Control Checkpoints Ensure Product Reliability?
Quality control (QC) is integral to the manufacturing process, particularly for electrical components where safety is paramount. Several checkpoints are critical in maintaining quality throughout production.
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival at the manufacturing facility. Ensuring that materials meet specified standards before production begins is crucial for preventing defects.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, various checks are performed to monitor production quality. This can include measuring dimensions, testing electrical conductivity, and ensuring assembly accuracy.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before products are shipped, a final inspection is conducted. This includes functional testing and visual inspections to ensure that the products are free from defects and meet all specifications.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in the Industry?
Testing is vital to ensure that electrical plugs and sockets perform reliably under various conditions. Here are some common testing methods employed by manufacturers:
-
Electrical Testing: This includes tests for insulation resistance, dielectric strength, and earth continuity. These tests ensure that the plugs and sockets can safely handle electrical loads without risk of failure.
-
Mechanical Testing: This assesses the physical durability of the components, including stress tests to determine how well they withstand bending, twisting, and other mechanical forces.
-
Environmental Testing: Products are subjected to extreme temperatures, humidity, and exposure to chemicals to ensure they can perform in different environmental conditions. This is particularly relevant for products intended for outdoor use.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is essential for ensuring product reliability. Here are some actionable steps to consider:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. This helps identify potential risks and ensures compliance with international standards.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should ask for documentation that outlines the supplier’s quality control processes, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC stages. This transparency can help assess the supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s practices. These services can conduct on-site inspections and provide detailed reports on compliance with industry standards.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
Navigating the complexities of international quality control can be challenging, especially for buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Here are some nuances to consider:
-
Regional Standards: Different regions may have varying standards and regulations. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local compliance requirements to avoid legal issues.
-
Cultural Differences in Quality Assurance: Understanding cultural attitudes towards quality and safety can help buyers communicate more effectively with suppliers. For instance, some regions may prioritize cost over quality, which can impact product reliability.
-
Logistics and Supply Chain Risks: Global supply chains can introduce risks related to quality control. Buyers should assess the entire supply chain, from raw material sourcing to final product delivery, to ensure that quality is maintained at every stage.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing electrical plugs and sockets, ensuring that they meet both safety standards and performance expectations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘electrical plugs & sockets’
Introduction
Sourcing electrical plugs and sockets for your business requires careful consideration and strategic planning. This guide provides a practical checklist to help B2B buyers navigate the complexities of procurement, ensuring that you select the right products that meet your technical requirements while also aligning with international standards. Whether you are in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe, following these steps will facilitate a smoother sourcing process.
1. Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, it is essential to clearly outline your technical requirements. This includes understanding the voltage, amperage, and type of electrical plugs and sockets that are compatible with your operations.
- Key Factors to Consider:
- Identify the standard plug types used in your target market (e.g., Type C for Europe, Type G for the UK).
- Ensure compatibility with existing electrical systems to avoid costly modifications.
2. Research Regulatory Standards and Compliance
Understanding the regulatory standards applicable in your region is crucial for compliance and safety. Different countries have varying electrical codes and safety regulations.
- What to Look For:
- Verify if the plugs and sockets comply with IEC standards or local regulations.
- Check for certifications like CE marking in Europe or SANS in South Africa that ensure product safety and reliability.
3. Identify Potential Suppliers
Finding reputable suppliers is a critical step in the sourcing process. A robust supplier network can provide you with quality products and reliable service.
- How to Proceed:
- Utilize online platforms like Alibaba, Global Sources, or regional trade shows to discover potential suppliers.
- Look for suppliers with a proven track record in your industry and positive reviews from other B2B buyers.
4. Evaluate Supplier Certifications and Quality Assurance
Before making a commitment, it’s vital to assess the certifications and quality assurance measures of potential suppliers. This step helps mitigate risks associated with product quality and reliability.
A stock image related to electrical plugs & sockets.
- Key Actions:
- Request copies of certifications, such as ISO 9001, which indicate adherence to quality management principles.
- Inquire about their quality control processes to ensure that products meet your specifications consistently.
5. Request Samples and Conduct Testing
Obtaining samples is an important step to verify the quality and suitability of the plugs and sockets for your specific needs.
- Why This Matters:
- Testing samples allows you to assess the durability, safety, and functionality of the products.
- Ensure that the samples perform well under your operational conditions before placing larger orders.
6. Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you have selected potential suppliers, the next step is to negotiate terms, pricing, and delivery schedules. This ensures that you achieve the best value for your investment.
- Negotiation Tips:
- Discuss bulk purchase discounts or payment terms that work for your budget.
- Clarify lead times and logistics to avoid delays in your supply chain.
7. Establish a Long-term Relationship
Building a long-term relationship with reliable suppliers can enhance your sourcing efficiency and provide stability in your supply chain.
- Focus Areas:
- Maintain open communication and provide feedback on product performance.
- Explore opportunities for collaboration on future projects or product developments to foster a stronger partnership.

A stock image related to electrical plugs & sockets.
By following this practical sourcing checklist, international B2B buyers can effectively procure electrical plugs and sockets that meet their operational needs while ensuring compliance with local regulations and standards.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for electrical plugs & sockets Sourcing
When sourcing electrical plugs and sockets, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. This analysis will explore the key cost components, price influencers, and provide actionable tips for international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Electrical Plugs and Sockets?
-
Materials: The primary materials used in manufacturing electrical plugs and sockets include plastics, metals (like copper and aluminum), and insulating materials. The quality and source of these materials can significantly impact costs. For instance, high-grade materials that comply with international safety standards may incur higher costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary dramatically based on the manufacturing location. Countries with lower labor costs may offer cheaper products; however, this may come at the expense of quality. It’s crucial to balance cost with the reliability of labor practices.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations such as utilities, equipment maintenance, and administrative costs. Efficient production processes can help mitigate these overhead costs, allowing for competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling and molds can be substantial, particularly for custom designs. These costs are often amortized over the production run, meaning larger orders can benefit from lower per-unit costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing robust QC measures ensures product safety and compliance with international standards. While this can add to costs, it is essential for preventing costly recalls and ensuring customer satisfaction.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary based on the origin and destination of the products. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and Incoterms will influence overall logistics expenses.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on market demand, competition, and brand positioning.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Electrical Plugs and Sockets?
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often lead to significant discounts. Suppliers are more willing to negotiate prices for bulk purchases, which can drastically reduce costs per unit.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized products, such as specific designs or additional features, usually have higher price points. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the additional costs.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Products that meet international safety certifications (e.g., CE, UL) generally command higher prices due to the rigorous testing and compliance processes involved.
-
Supplier Factors: The reliability and reputation of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a proven track record may charge more but offer better quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial in determining who bears the cost and risk at various stages of shipping. This can affect the total cost of acquisition.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Sourcing?
-
Negotiate Terms: Don’t hesitate to negotiate prices and terms, especially for large orders. Suppliers may offer discounts for upfront payments or longer contract durations.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with maintenance, potential failures, and compliance. A slightly higher upfront cost may lead to lower overall expenses.
-
Research Market Prices: Conduct thorough market research to understand the going rates for various types of plugs and sockets. This knowledge can empower you during negotiations.
-
Consider Regional Variations: Be mindful of price variations based on geography. For instance, electrical components sourced from Europe may be pricier than those from Asia, but they may also offer superior quality.
-
Stay Informed on Compliance Requirements: Ensure that the products meet the necessary certifications for your region to avoid costly penalties and rejections upon import.
Conclusion
Sourcing electrical plugs and sockets requires a nuanced understanding of cost structures and market dynamics. By considering the outlined cost components and price influencers, B2B buyers can make more strategic purchasing decisions that align with their business needs and budgets. Always remember to stay informed and leverage negotiation as a tool for securing the best possible pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing electrical plugs & sockets With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternative Solutions to Electrical Plugs and Sockets
In today’s globalized economy, the reliance on electrical plugs and sockets is ubiquitous; however, several alternatives exist that can serve similar purposes. As international B2B buyers, especially from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it’s vital to explore these alternatives to make informed decisions that align with your operational needs, budget constraints, and technological advancements.
Comparison Table of Electrical Plugs & Sockets vs. Alternative Solutions
| Comparison Aspect | Electrical Plugs & Sockets | Wireless Charging Solutions | Power Over Ethernet (PoE) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Reliable for direct power | Limited to compatible devices | High data and power transfer |
| Cost | Low initial investment | Higher setup costs | Moderate installation costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple and widely adopted | Requires compatible devices | Needs specialized equipment |
| Maintenance | Minimal maintenance | Low maintenance | Regular updates required |
| Best Use Case | General household and industrial use | Mobile devices and gadgets | Networking equipment and smart devices |
Evaluating Wireless Charging Solutions
Wireless charging technology eliminates the need for physical plugs and sockets by allowing devices to charge through electromagnetic fields. This solution is particularly advantageous for mobile devices, reducing wear and tear on physical connectors. However, it has limitations regarding the charging speed and compatibility with various devices. The initial investment in wireless charging pads and technology can be higher compared to traditional plugs, making it less appealing for large-scale industrial applications.
Analyzing Power Over Ethernet (PoE)
Power Over Ethernet is an innovative solution that allows electrical power and data to be transmitted over standard Ethernet cables. This dual functionality simplifies the installation process, especially in settings that require both internet and power, such as security cameras and VoIP phones. The main downside is the requirement for specialized network infrastructure, which can incur moderate setup costs. Additionally, regular updates and maintenance of the network equipment are essential to ensure optimal performance.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate solution for electrical connectivity hinges on specific use cases and operational demands. Electrical plugs and sockets remain the most practical choice for general applications due to their reliability and low cost. However, for businesses that prioritize mobility or are integrating smart technologies, exploring alternatives like wireless charging or Power Over Ethernet could yield significant benefits. As an international B2B buyer, it is crucial to assess the unique requirements of your operations, considering factors such as performance, cost, and ease of implementation, to make the best decision for your organization.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for electrical plugs & sockets
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Electrical Plugs and Sockets?
Understanding the critical technical specifications of electrical plugs and sockets is vital for B2B buyers to ensure compatibility, safety, and performance in their operations. Here are several essential properties to consider:
-
Material Grade
– The materials used in electrical plugs and sockets can significantly affect their durability and conductivity. Common materials include thermoplastics for housings and copper or brass for connectors. High-grade materials ensure better resistance to heat, corrosion, and mechanical stress, making them suitable for industrial applications. For buyers, selecting plugs and sockets made from high-quality materials minimizes the risk of failures and enhances the longevity of electrical installations. -
Current Rating (Amperage)
– The current rating indicates the maximum electrical current a plug or socket can safely carry. Ratings are often specified in amperes (A), such as 10A, 16A, or 32A. Understanding current ratings is crucial for ensuring that the chosen plugs and sockets match the electrical load requirements of specific devices or appliances. Selecting components with inadequate ratings can lead to overheating and potential fire hazards. -
Voltage Rating
– Voltage ratings, typically expressed in volts (V), denote the maximum voltage that a plug or socket can handle. Common voltage ratings include 110V, 220V, and 380V. Buyers must ensure that the voltage ratings of the plugs and sockets match the electrical systems in their respective countries. Mismatched voltage ratings can lead to equipment failure or serious safety risks. -
Pin Configuration and Size
– Different countries use various pin configurations and sizes in their electrical plugs and sockets. For example, Type C plugs (commonly used in Europe) have two round pins, while Type G plugs (used in the UK) have three rectangular pins. B2B buyers should be aware of the specific configurations to ensure compatibility with local electrical systems. This knowledge is particularly important for international sourcing and when expanding into new markets. -
IP Rating (Ingress Protection)
– The IP rating indicates the level of protection against dust and moisture. For example, an IP67 rating means that the device is dust-tight and can withstand immersion in water up to a certain depth. Understanding IP ratings is crucial for applications in harsh environments, such as outdoor installations or industrial settings, where exposure to elements can compromise electrical safety and functionality.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Electrical Plugs and Sockets Industry?
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B sector. Here are some common terms to know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– An OEM refers to a company that produces components or products that are then marketed under another company’s brand. For electrical plugs and sockets, working with OEMs can provide buyers access to high-quality products tailored to specific requirements without the need for in-house manufacturing. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for buyers to manage inventory costs and ensure that they meet supplier requirements. Higher MOQs can lead to better pricing, but they may also require significant upfront investment. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products or services. This is a vital step in procurement, allowing buyers to compare offers and negotiate better deals for electrical plugs and sockets. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Incoterms are a series of predefined commercial terms used in international trade to clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers. They define aspects such as shipping, insurance, and liability. Familiarity with Incoterms can help B2B buyers navigate international transactions more effectively, ensuring clarity in shipping costs and responsibilities. -
CE Marking
– The CE marking indicates that a product meets European health, safety, and environmental protection standards. For electrical plugs and sockets, CE marking is often mandatory for sale in Europe. Buyers should ensure that their products comply with these regulations to avoid legal issues and ensure market access.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed purchasing decisions, ensuring safety, compatibility, and cost-effectiveness in their electrical systems.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the electrical plugs & sockets Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in the Electrical Plugs & Sockets Sector?
The electrical plugs and sockets market is undergoing significant transformations driven by globalization, technological advancements, and increasing energy demands. In regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, B2B buyers are particularly influenced by the need for standardized products that ensure compatibility across diverse electrical systems. The rise of smart technology is also shaping the sector, with innovations like USB outlets and smart plugs becoming increasingly popular. This shift towards more integrated solutions is pushing manufacturers to adapt their offerings, catering to a tech-savvy audience.
Additionally, the focus on energy efficiency and sustainability is reshaping market dynamics. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing energy-efficient products that comply with international regulations and standards. For instance, the European Union’s Ecodesign Directive mandates that electrical devices meet specific environmental criteria, prompting suppliers to innovate in product design and material use. As a result, international B2B buyers are encouraged to seek suppliers who not only provide high-quality products but also demonstrate a commitment to sustainability and compliance with environmental standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Ensure Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in Electrical Plugs & Sockets?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are critical considerations for B2B buyers in the electrical plugs and sockets sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly concerning waste and energy consumption, has become a focal point for many companies. Buyers should look for manufacturers that utilize eco-friendly materials and sustainable practices in their production processes. This includes the use of recyclable materials and adherence to certifications such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment Directive).
Moreover, establishing ethical supply chains is essential to mitigate risks associated with labor practices and material sourcing. International buyers should conduct thorough due diligence on their suppliers to ensure compliance with labor laws and ethical sourcing guidelines. By prioritizing suppliers with transparent practices and sustainability certifications, businesses can not only enhance their brand reputation but also contribute positively to the environment and society.
What Is the Historical Evolution of the Electrical Plugs & Sockets Sector?

A stock image related to electrical plugs & sockets.
The evolution of electrical plugs and sockets dates back to the late 19th century, coinciding with the widespread adoption of electrical power. Initially, plugs were designed with simple two-prong configurations, primarily for low-voltage applications. As electrical demands grew, so did the complexity and variety of plug designs to accommodate different voltages and safety standards.
By the mid-20th century, standardized plug types began to emerge, with organizations like the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) playing a pivotal role in establishing global standards. The introduction of safety features, such as grounding pins and tamper-resistant designs, marked significant advancements in plug and socket technology, enhancing user safety. This historical context is vital for B2B buyers as it highlights the importance of adhering to established standards and the continuous need for innovation in product design to meet evolving market demands.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of electrical plugs & sockets
-
How do I choose the right electrical plugs and sockets for my international business needs?
Selecting the right electrical plugs and sockets involves understanding the specific requirements of the countries you are targeting. Research the plug types and voltage specifications used in these regions, as they can vary significantly. For example, Type C is widely used in Europe, while Type G is common in the UK. Additionally, consider the local electrical standards and safety regulations. It’s essential to partner with suppliers who are knowledgeable about these requirements and can provide the necessary certifications for compliance. -
What is the best way to vet suppliers of electrical plugs and sockets?
Vetting suppliers involves a thorough assessment of their credibility and capability. Start by checking their business registration, certifications, and industry reputation through reviews and references. Request samples to evaluate product quality, and inquire about their manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols. Additionally, consider their experience in international trade, especially in your target regions, to ensure they understand the specific logistics and regulatory challenges involved. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for electrical plugs and sockets?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for electrical plugs and sockets can vary widely depending on the supplier and the product type. Generally, MOQs can range from 100 to 1,000 units, but some suppliers may offer lower quantities for sample orders or prototypes. When negotiating with suppliers, express your volume needs and seek flexibility if you anticipate scaling your orders in the future. Understanding your supplier’s production capacity can also help in planning your inventory efficiently. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing electrical plugs and sockets internationally?
Payment terms for international transactions can vary significantly based on the supplier’s policies and the country of origin. Common terms include a deposit (usually 30-50%) upon order confirmation, with the balance due before shipment or upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer credit terms for established relationships. It’s crucial to discuss and agree on payment methods (e.g., wire transfer, letters of credit) to protect both parties and ensure secure transactions. -
How can I customize electrical plugs and sockets for my brand?
Customization options for electrical plugs and sockets often include branding (logos, colors), specific features (USB ports, tamper-resistant designs), and compliance with regional standards. Discuss your customization needs with potential suppliers early in the negotiation process. Many manufacturers have the capability to produce bespoke designs, but be prepared for potential minimum order requirements and longer lead times for custom products. Ensure you have clear specifications and samples before finalizing your order. -
What are the key quality assurance (QA) measures to consider when sourcing electrical plugs and sockets?
Quality assurance is critical in ensuring the safety and reliability of electrical plugs and sockets. Look for suppliers who follow international quality standards such as ISO 9001. Request documentation regarding their QA processes, including testing for durability, safety, and compliance with regional electrical standards. Regular audits and inspections during production can also help maintain quality. Consider third-party testing for additional assurance, especially if you are entering highly regulated markets. -
What logistics challenges should I be aware of when importing electrical plugs and sockets?
Importing electrical plugs and sockets can involve several logistics challenges, including customs clearance, tariffs, and compliance with local regulations. Understand the import duties applicable in your target market, and ensure that your products meet local safety standards to avoid delays. Partnering with a reliable freight forwarder can streamline the shipping process and help navigate regulatory requirements. Additionally, consider the impact of lead times on your supply chain, especially if you’re sourcing from overseas. -
How do I handle returns and warranty claims for electrical plugs and sockets?
Establishing clear return and warranty policies is crucial when sourcing electrical plugs and sockets. Discuss these terms with your supplier upfront to understand their procedures for handling defective products or returns. A typical warranty period ranges from one to three years, depending on the product. Ensure that your customers are aware of the return process and any conditions that may apply. Having a robust after-sales support system will enhance customer satisfaction and strengthen your business relationships.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for electrical plugs & sockets
In the rapidly evolving landscape of electrical plugs and sockets, strategic sourcing stands out as a critical factor for international B2B buyers. By understanding the diverse types of plugs and sockets prevalent in various regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, businesses can mitigate risks and enhance operational efficiency. Establishing relationships with reliable suppliers not only ensures compliance with local standards but also fosters innovation in product offerings, such as energy-efficient and smart solutions.
What Are the Key Benefits of Strategic Sourcing for Electrical Products?
Investing in strategic sourcing can lead to significant cost savings and improved supply chain resilience. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to quality, sustainability, and adaptability to market changes. Furthermore, keeping abreast of emerging trends in plug and socket technology will allow businesses to stay competitive in their respective markets.
How Can B2B Buyers Prepare for Future Trends?
As the demand for standardized and versatile electrical solutions increases, proactive engagement with manufacturers and distributors will be vital. International B2B buyers are encouraged to leverage data-driven insights to forecast trends and identify opportunities for collaboration.
In conclusion, a forward-thinking approach to strategic sourcing will not only enhance procurement efficiency but also support broader business objectives. Embrace the potential of new technologies and partnerships to position your business for success in the global marketplace.