Discover Gear Reducers: The Ultimate Sourcing Guide (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for gear reducers
In today’s global marketplace, sourcing reliable gear reducers poses a significant challenge for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in dynamic regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Gear reducers are essential components that optimize machinery performance by reducing speed and increasing torque, making them crucial for various applications, from industrial manufacturing to energy generation. However, navigating the complexities of supplier selection, understanding the myriad types of gear reducers, and evaluating costs can be daunting for procurement professionals seeking to make informed purchasing decisions.
This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of gear reducers, covering key topics such as different types of gear reducers, their applications across various industries, and practical strategies for supplier vetting. It also offers insights into cost considerations, ensuring that buyers can effectively balance quality and budget constraints. By providing a thorough understanding of gear reducer specifications and market dynamics, this guide empowers B2B buyers to make strategic sourcing decisions that align with their operational needs.
With a focus on actionable insights tailored for buyers from diverse regions, including Spain and Nigeria, this resource is designed to facilitate smarter procurement processes. Whether you are looking to enhance operational efficiency or seeking innovative solutions for specific machinery, this guide equips you with the knowledge necessary to navigate the global market for gear reducers successfully.
Understanding gear reducers Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Worm Gear Reducers | High torque output, compact design | Conveyor systems, material handling | Pros: High reduction ratios; Cons: Limited efficiency due to sliding friction. |
| Helical Gear Reducers | Helical teeth for smoother operation | Automotive, aerospace, and industrial machinery | Pros: Quiet operation; Cons: More complex and expensive to manufacture. |
| Planetary Gear Reducers | Multiple gears rotating around a central sun gear | Robotics, automotive, and aerospace applications | Pros: High torque density; Cons: Can be more complex to assemble and maintain. |
| Bevel Gear Reducers | Transmit power between shafts at angles | Power transmission in machinery and vehicles | Pros: Efficient power transfer; Cons: Requires precise alignment for optimal performance. |
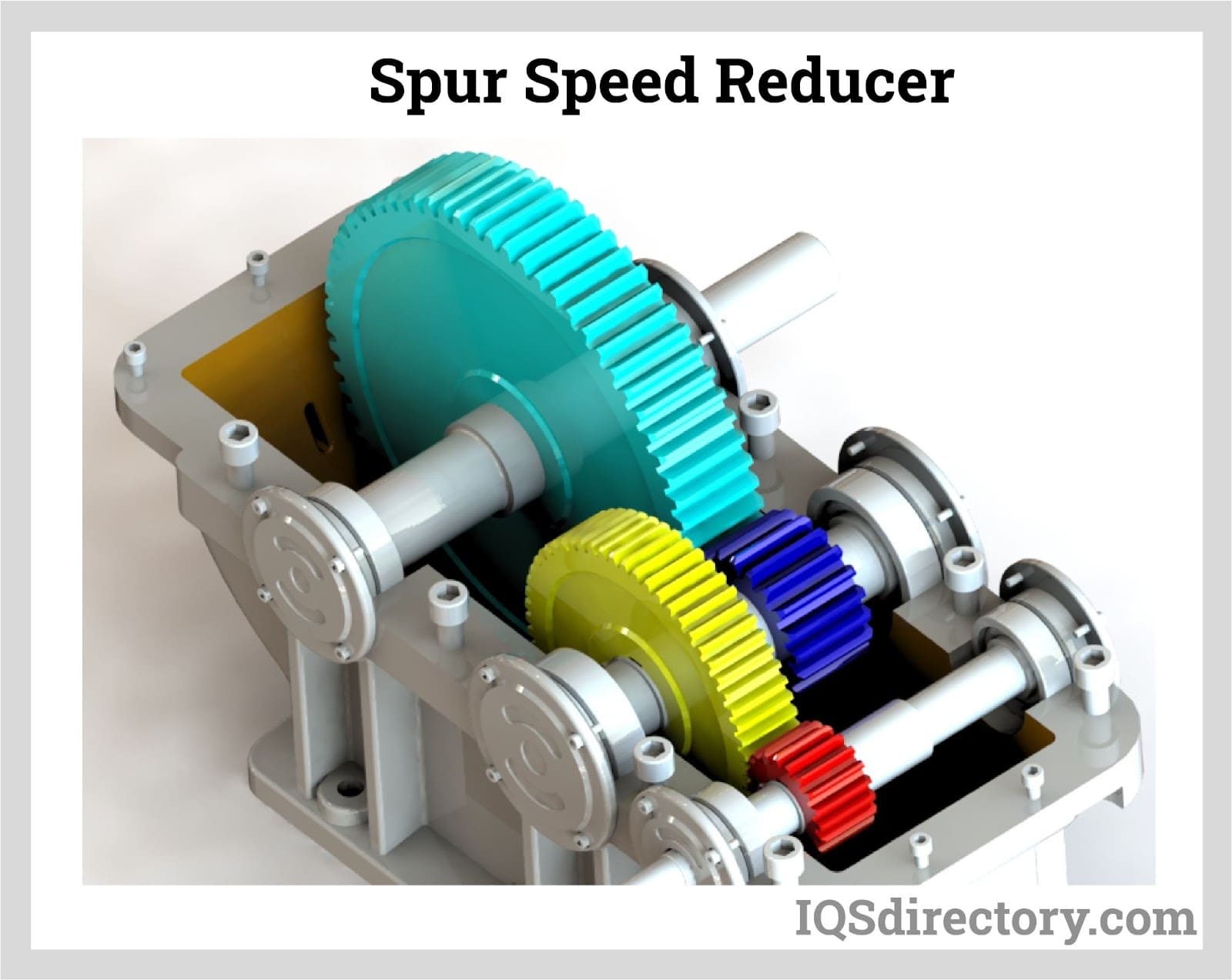
| Spur Gear Reducers | Simple design with parallel teeth | General machinery and industrial equipment | Pros: Cost-effective and easy to manufacture; Cons: Noisy operation at high speeds. |
What Are Worm Gear Reducers and When to Use Them?
Worm gear reducers are characterized by their unique design, which features a worm (screw) that meshes with a gear (worm wheel). This configuration allows for high torque output and a compact footprint, making them ideal for applications like conveyor systems and material handling. When considering a worm gear reducer, B2B buyers should evaluate the torque requirements, space constraints, and the potential for efficiency losses due to sliding friction, which can affect performance in high-load scenarios.
How Do Helical Gear Reducers Differ from Other Types?
Helical gear reducers utilize gears with angled teeth, which offer a smoother and quieter operation compared to spur gears. They are commonly used in automotive and aerospace applications where noise reduction is critical. Buyers should consider the complexity of design and manufacturing, as helix angles can increase production costs. However, the benefits of reduced vibration and higher efficiency often justify the investment.
What Are the Advantages of Planetary Gear Reducers?
Planetary gear reducers consist of a central sun gear surrounded by multiple planet gears, allowing for higher torque density in a smaller package. This makes them suitable for demanding applications in robotics and aerospace. When purchasing planetary gear reducers, B2B buyers should assess the required torque and speed ratios, as well as the complexity of assembly and maintenance, which can influence operational efficiency.
Why Choose Bevel Gear Reducers?
Bevel gear reducers are designed to transmit power between shafts that are not parallel, typically at a 90-degree angle. This capability makes them essential in power transmission for machinery and vehicles. Buyers should focus on alignment precision during installation, as improper alignment can lead to increased wear and reduced efficiency. The efficiency of bevel gear reducers can be a significant advantage in applications requiring space-saving designs.
What Makes Spur Gear Reducers a Popular Choice?
Spur gear reducers are among the simplest and most widely used types of gear reducers, featuring parallel teeth that provide straightforward mechanical advantages. They are cost-effective and easy to manufacture, making them suitable for general machinery and industrial equipment. However, buyers should be aware of the potential for noise at high speeds, which could impact operations in noise-sensitive environments. Selecting the right spur gear reducer involves balancing cost, performance, and operational noise levels.
Key Industrial Applications of gear reducers
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of gear reducers | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Conveyor Systems | Enhanced efficiency and reduced operational costs | Compatibility with existing systems and load ratings |
| Agriculture | Agricultural Machinery (e.g., tractors, harvesters) | Improved torque and power management for heavy loads | Durability in harsh environments and maintenance support |
| Food and Beverage | Processing Equipment (e.g., mixers, blenders) | Consistent performance and hygiene compliance | Material standards for food safety and ease of cleaning |
| Mining and Construction | Heavy Equipment (e.g., crushers, drills) | Increased reliability and reduced downtime | Resistance to extreme conditions and heavy-duty design |
| Renewable Energy | Wind Turbines | Enhanced energy efficiency and performance optimization | Customization options for different turbine designs |
How Are Gear Reducers Used in Manufacturing?
In the manufacturing sector, gear reducers are critical for conveyor systems that transport materials and products throughout the production line. By reducing the speed of motors, they increase torque, allowing for smooth operation even under heavy loads. This application helps manufacturers minimize energy consumption and operational costs. International buyers must consider the compatibility of gear reducers with existing conveyor systems, ensuring they meet specific load ratings and dimensions.
What Role Do Gear Reducers Play in Agriculture?
Agricultural machinery, such as tractors and harvesters, heavily relies on gear reducers to manage the high torque demands associated with plowing and harvesting. These devices allow for efficient power transfer from the engine to the wheels or attachments, enhancing the machine’s overall performance. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should prioritize durability and the ability to operate in harsh conditions, as well as access to maintenance support to ensure longevity.
Why Are Gear Reducers Important in the Food and Beverage Industry?
In the food and beverage industry, gear reducers are utilized in processing equipment such as mixers and blenders. They ensure that machinery operates at the correct speed and torque, which is essential for maintaining product quality and consistency. Compliance with hygiene standards is critical, so buyers should focus on materials that meet food safety regulations and allow for easy cleaning. This is particularly relevant for international buyers looking to import equipment that aligns with local health standards.
How Do Gear Reducers Support Mining and Construction?
Heavy equipment used in mining and construction, such as crushers and drills, benefits significantly from gear reducers. These devices help manage the immense torque needed for breaking down materials, thereby increasing the equipment’s reliability and reducing downtime. Buyers should consider the gear reducer’s resistance to extreme conditions and its heavy-duty design, ensuring it can withstand the rigors of mining operations, especially in regions with challenging terrains.
What Benefits Do Gear Reducers Offer in Renewable Energy Applications?
In renewable energy, particularly in wind turbines, gear reducers play a crucial role in optimizing energy efficiency. They allow for the conversion of high-speed input from the turbine blades to a lower speed output that is suitable for generators. This optimization is essential for maximizing energy production. Buyers should look for customization options that fit specific turbine designs, ensuring that the gear reducers can handle the unique demands of different wind energy projects across various geographical locations.
A stock image related to gear reducers.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘gear reducers’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Misalignment and Vibration Issues
The Problem: One of the most common challenges faced by B2B buyers when using gear reducers is misalignment, which can lead to excessive vibration. This issue typically arises when the input and output shafts of the gear reducer are not properly aligned, causing uneven wear on gears, increased noise, and even potential equipment failure. This not only affects the performance of the machinery but can also lead to costly downtime, especially in high-demand sectors such as manufacturing and logistics.
The Solution: To address alignment issues, it is crucial to perform a thorough installation assessment. Buyers should invest in precise alignment tools or hire professionals who specialize in this area. Regular maintenance checks should also be scheduled to monitor alignment over time, as vibrations can change due to wear and tear. Additionally, opting for gear reducers with built-in alignment features or flexible couplings can significantly reduce the risk of misalignment. It’s important to communicate with suppliers about your specific requirements to ensure you select a gear reducer that minimizes these risks.
Scenario 2: Limited Load Capacity Leading to Breakdowns
The Problem: Many buyers underestimate the load capacity required for their operations, which can result in gear reducer failures. This is particularly prevalent in industries like construction and agriculture, where gear reducers are subjected to high torque and heavy loads. A gear reducer that cannot handle the operational demands will lead to breakdowns, causing delays and increasing operational costs.
The Solution: To avoid this scenario, B2B buyers should conduct a comprehensive load analysis before purchasing gear reducers. This analysis should take into account peak load conditions and the operational environment. Consulting with manufacturers about the duty cycle and torque requirements of your application is crucial. Buyers should also consider gear reducers that offer safety margins beyond the expected load to accommodate unexpected surges. By sourcing gear reducers designed for higher load capacities or those that are customizable for specific applications, buyers can enhance reliability and reduce the frequency of breakdowns.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Sourcing the Right Gear Reducer Type
The Problem: International buyers often face challenges in sourcing the appropriate type of gear reducer for their unique applications. With a myriad of options available—such as worm gears, helical gears, and planetary gears—making the right choice can be overwhelming. This confusion can lead to the selection of an inappropriate gear reducer, resulting in inefficiencies and increased operational costs.
The Solution: To navigate the complexities of gear reducer selection, buyers should start by clearly defining their application requirements, including speed, torque, and space constraints. Engaging in discussions with technical experts or suppliers who understand the specific needs of different industries can be invaluable. Requesting product samples or detailed specifications can also aid in making informed decisions. Additionally, buyers should consider gear reducers that offer modular designs, allowing for future adjustments or upgrades without needing to replace the entire system. By investing time in understanding the different types of gear reducers available and their specific applications, buyers can ensure they select the most efficient and cost-effective solution for their operations.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for gear reducers
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Gear Reducers?
When selecting materials for gear reducers, international B2B buyers must consider several factors, including mechanical properties, environmental resistance, and cost-effectiveness. Here, we analyze four common materials used in gear reducer manufacturing: steel, aluminum, plastic, and cast iron.
How Does Steel Perform as a Material for Gear Reducers?
Key Properties: Steel is known for its high tensile strength, excellent wear resistance, and ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 300°C and can handle significant loads.
Pros & Cons: The durability of steel makes it suitable for heavy-duty applications, but it can be more expensive than other materials. Manufacturing complexity is moderate, requiring specialized machining processes. Steel gear reducers are ideal for applications where high torque and longevity are essential.
Impact on Application: Steel is compatible with various media, including oils and lubricants, making it suitable for industrial settings. However, its susceptibility to corrosion necessitates protective coatings or treatments, especially in humid or corrosive environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM or DIN is crucial. Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East may prefer steel for its robustness, while those in South America and Africa might focus on cost-effectiveness and availability.
What Advantages Does Aluminum Offer for Gear Reducers?
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and has good corrosion resistance, with a temperature rating of around 150°C. It is also easier to machine compared to steel.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its weight, which can reduce the overall mass of machinery. However, it is less durable than steel and may not be suitable for high-load applications. Manufacturing is simpler, but the cost can be moderate to high depending on the alloy used.
Impact on Application: Aluminum gear reducers are often used in applications where weight savings are critical, such as in aerospace or portable machinery. Its corrosion resistance makes it suitable for outdoor applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that aluminum gear reducers meet local standards. In regions with high humidity, such as parts of Africa, aluminum may be preferred for its resistance to corrosion.
What Role Do Plastics Play in Gear Reducers?
Key Properties: Engineering plastics, such as nylon or acetal, offer good wear resistance and are lightweight. They can operate in temperatures ranging from -40°C to 120°C.
Pros & Cons: Plastics are cost-effective and can be molded into complex shapes, making them suitable for customized applications. However, they have lower strength and durability compared to metals, limiting their use in high-torque situations.
Impact on Application: Plastic gear reducers are often used in low-load applications, such as in consumer electronics or small machinery. They are not suitable for high-temperature environments or where heavy loads are present.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should check for compliance with standards like JIS or ISO. In regions like South America, where cost is a significant factor, plastics may be a preferred choice for less demanding applications.
Why Is Cast Iron a Reliable Choice for Gear Reducers?
Key Properties: Cast iron is known for its excellent wear resistance and ability to absorb vibrations. It operates well under high temperatures, typically up to 200°C.
Pros & Cons: The durability and vibration-damping properties of cast iron make it suitable for heavy-duty applications. However, it is heavy and can be brittle, making it less suitable for portable applications. Manufacturing processes can be complex and costly.
Impact on Application: Cast iron gear reducers are ideal for industrial machinery that requires stability and durability. They are compatible with various lubricants and can withstand harsh operating conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with industry standards is critical. Buyers in Europe may prefer cast iron for its durability, while those in Africa may need to consider shipping costs due to its weight.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Gear Reducers
| Material | Typical Use Case for gear reducers | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy-duty industrial applications | High strength and durability | Higher cost than other materials | High |
| Aluminum | Aerospace and portable machinery | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Less durable than steel | Medium to High |
| Plastic | Consumer electronics and small machinery | Cost-effective and customizable | Lower strength and durability | Low |
| Cast Iron | Industrial machinery | Excellent wear resistance | Heavy and brittle | Medium |
By understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of these materials, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific application requirements and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for gear reducers
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Gear Reducers?
The manufacturing process for gear reducers involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets performance and durability standards. Understanding these stages can help international B2B buyers make informed decisions when selecting suppliers.
-
Material Preparation: The first step involves sourcing high-quality raw materials, typically metals such as steel or aluminum, known for their strength and durability. Suppliers should provide material certifications to verify that the materials meet industry standards. Buyers should look for suppliers who use materials with a proven track record in gear reducer applications.
-
Forming: During this stage, materials are shaped into the required components using techniques such as forging, machining, and casting. Machining is particularly important for achieving precise dimensions and tolerances. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is commonly used for its accuracy and efficiency. Buyers should inquire about the machinery and technologies used by suppliers to ensure they are utilizing advanced manufacturing processes.
-
Assembly: After forming, components like gears, shafts, and housings are assembled. This process often requires skilled labor to ensure that parts fit together correctly and function as intended. Automated assembly lines may also be employed for consistency and efficiency. It is advisable for buyers to confirm the assembly techniques and workforce training standards with potential suppliers.
-
Finishing: The finishing stage includes processes such as heat treatment, surface hardening, and coating. Heat treatment improves the mechanical properties of the gear components, while surface coatings can enhance resistance to wear and corrosion. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers have capabilities for both standard and custom finishes to meet specific application requirements.
How Is Quality Assurance Managed in Gear Reducer Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is a vital aspect of the manufacturing process for gear reducers, ensuring that products meet international and industry-specific standards. Here are the key elements of quality assurance:
-
International and Industry Standards: Many gear reducer manufacturers adhere to ISO 9001, which outlines quality management principles. Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) for European markets and API (American Petroleum Institute) for oil and gas applications are crucial. Buyers should verify the certifications held by suppliers to ensure compliance with relevant standards.
-
Quality Control Checkpoints: A robust quality control system includes several checkpoints:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, ongoing inspections are conducted to catch defects early in the process.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): Once assembly is complete, gear reducers undergo rigorous testing to ensure they function correctly and meet performance specifications. -
Common Testing Methods: Various testing methods are employed to assess gear reducer performance, including:
– Load Testing: Ensures the gear reducer can handle specified loads without failure.
– Noise and Vibration Testing: Identifies any operational issues that could affect performance or lifespan.
– Dimensional Inspection: Confirms that all components meet specified tolerances and dimensions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Measures?
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to ensure that their suppliers maintain high-quality standards. Here are actionable strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting audits of potential suppliers allows buyers to assess their manufacturing processes and quality control measures firsthand. This includes evaluating their facilities, equipment, and workforce training.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should request detailed quality reports that outline testing results, failure rates, and compliance with international standards. These documents provide insights into the supplier’s quality management system and performance history.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased evaluation of supplier capabilities. These inspections can cover everything from material quality to final product testing, providing assurance to buyers.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
When sourcing gear reducers from international suppliers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several nuances must be considered:
-
Cultural and Regulatory Differences: Understanding local manufacturing practices and regulatory requirements can help buyers navigate potential challenges. For instance, compliance with EU regulations may differ significantly from standards in other regions. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local quality standards and practices.
-
Logistics and Supply Chain Considerations: Importing gear reducers from overseas may involve additional logistics and supply chain complexities. Buyers should account for lead times, shipping methods, and customs regulations that could affect delivery schedules. Establishing clear communication with suppliers about these factors is essential.
-
Language and Communication Barriers: Language differences can lead to misunderstandings regarding quality requirements and specifications. Buyers should ensure that they have a clear line of communication with suppliers, possibly employing bilingual staff or translators if necessary.
-
Post-Purchase Support and Warranty: Lastly, it is crucial to understand the warranty and post-purchase support offered by suppliers. This includes maintenance services, replacement parts availability, and response times for addressing quality issues. A strong support system can significantly enhance the overall purchasing experience.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when selecting gear reducer suppliers, ultimately leading to improved operational efficiency and product reliability.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘gear reducers’
Introduction
Procuring gear reducers can be a complex process, particularly for international B2B buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This guide serves as a comprehensive checklist to streamline your sourcing efforts, ensuring that you make informed decisions that align with your operational needs and budget constraints.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before you begin sourcing, it’s essential to clearly outline your technical requirements. Consider factors such as torque, gear ratio, size, and type of gear reducer (e.g., worm, helical, planetary). Having precise specifications helps narrow down potential suppliers and ensures that the gear reducer meets your machinery’s operational demands.
- Torque Capacity: Determine the maximum torque the reducer must handle.
- Gear Ratio: Specify the desired input and output speeds.
- Physical Dimensions: Ensure the reducer fits within your existing equipment.
Step 2: Research and Identify Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers who specialize in gear reducers. Look for companies with a strong reputation in the industry and those that cater to your specific regional needs.
- Industry Directories: Utilize platforms like IQS Directory or industry-specific marketplaces.
- Supplier Reviews: Read customer testimonials and case studies to gauge reliability.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, it’s crucial to vet them thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. This step helps ensure you partner with a reputable vendor who can meet your quality and delivery standards.
- Certifications: Verify that suppliers have relevant certifications (e.g., ISO 9001).
- Experience: Inquire about their experience with similar projects and industries.
Step 4: Request Samples and Specifications
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request samples or detailed specifications of the gear reducers they offer. This step allows you to assess the quality and compatibility of the products with your existing systems.
- Testing: If possible, conduct tests on samples to ensure they meet your performance criteria.
- Documentation: Review technical data sheets for detailed specifications.
Step 5: Assess Pricing and Payment Terms
Pricing can vary significantly among suppliers, so it’s vital to compare quotes while considering the total cost of ownership. Look beyond the initial purchase price to include shipping, installation, and potential maintenance costs.
- Payment Terms: Evaluate the flexibility of payment options and any associated fees.
- Long-term Costs: Consider the expected lifespan and efficiency of the gear reducer to calculate long-term savings.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Finalize Contracts
After selecting a supplier, it’s time to negotiate the terms of your purchase. Discuss delivery timelines, warranties, and after-sales support to ensure you receive the best possible deal.
- Warranties: Ensure clear terms on warranties and support for repairs or replacements.
- Delivery Times: Confirm lead times and conditions for urgent orders.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Effective communication is crucial throughout the procurement process and post-purchase. Establish a clear line of communication with your supplier to address any questions or issues that may arise.
- Regular Updates: Schedule periodic updates to monitor order status and delivery.
- Feedback Mechanism: Create a system for providing feedback on product performance and supplier service.
By following this step-by-step checklist, international B2B buyers can efficiently navigate the procurement of gear reducers, ensuring that they select the right products that align with their operational requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for gear reducers Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Gear Reducers Sourcing?
When sourcing gear reducers, understanding the cost structure is essential for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the pricing of gear reducers. Common materials such as aluminum, cast iron, and stainless steel vary in cost. Higher-grade materials often lead to increased durability and performance, which can justify a higher price point.
-
Labor: Labor costs can fluctuate based on the region of production. Regions with higher labor costs, such as parts of Europe, may lead to increased overall expenses. Conversely, sourcing from regions with lower labor costs, like some parts of Africa or South America, can offer savings but may affect quality.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses all indirect costs associated with production, including utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce these costs, impacting the final price.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs involve the creation and maintenance of molds and dies necessary for manufacturing gear reducers. Custom tooling can lead to higher initial costs but can be amortized over larger production runs, making it more cost-effective in the long term.
-
Quality Control (QC): Investing in quality control processes ensures that the products meet required specifications and standards. This can involve additional costs but reduces the risk of defects and associated returns.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs, including shipping and handling, play a crucial role in the final price. Different Incoterms can affect who bears these costs, influencing the overall expense for the buyer.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their costs and profit. Understanding the supplier’s margin expectations can aid in negotiations.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Gear Reducers Pricing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of gear reducers, making it essential for buyers to be aware of them:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Purchasing in bulk can lead to discounts. Suppliers often have a minimum order quantity, so negotiating for larger orders can yield better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom gear reducers designed to meet specific application needs may incur higher costs. Buyers should assess whether custom specifications are necessary or if standard options suffice.
-
Materials Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (such as ISO standards) increase costs. Buyers should weigh the importance of these factors against their budget and application requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and location can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer better quality and service, which can be beneficial in the long run.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) affects shipping costs and responsibilities. Buyers should select terms that minimize their risk and expenses.
What Are Some Effective Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Gear Reducers Sourcing?
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can enhance cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiation: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Don’t hesitate to negotiate on price, terms, and conditions based on volume or long-term purchasing commitments.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but the total cost of ownership, including installation, maintenance, and operational costs. A higher initial investment in a quality gear reducer may result in lower long-term costs.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Currency fluctuations can impact pricing. Consider locking in prices or negotiating in a stable currency to mitigate risks associated with exchange rate changes.
-
Research and Benchmarking: Conduct thorough market research to understand average pricing and features of various gear reducers. Benchmarking against competitors can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Quality vs. Cost: Striking a balance between quality and cost is crucial. Investing in higher-quality gear reducers can lead to improved performance and reduced downtime, ultimately saving money.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
A stock image related to gear reducers.
Prices for gear reducers can vary significantly based on the factors discussed above. It is essential for buyers to conduct thorough due diligence and obtain multiple quotes to ensure they are making informed purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing gear reducers With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Gear Reducers: What Are Your Options?
When considering gear reducers for your operations, it’s essential to explore viable alternatives that may better suit your specific needs. Understanding the various options available can empower international B2B buyers—especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—to make informed decisions. Below, we compare gear reducers with two alternative solutions: Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) and Hydraulic Drives.
Comparison Table of Gear Reducers and Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Gear Reducers | Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) | Hydraulic Drives |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High torque, efficient speed reduction | Flexible speed control, less torque loss | High torque output, adjustable speed |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment, lower long-term maintenance | Higher upfront costs, potential energy savings | High installation and maintenance costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Straightforward installation for standard setups | Requires electrical expertise for installation | More complex; may need hydraulic specialists |
| Maintenance | Regular lubrication needed; generally low | Minimal, mainly electrical components | Frequent fluid checks and maintenance needed |
| Best Use Case | Fixed-speed applications in manufacturing | Applications requiring variable speeds | Heavy-duty applications, such as construction machinery |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Variable Frequency Drives?
Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) are increasingly popular in various industries due to their ability to control motor speed and torque efficiently. VFDs can adjust the motor speed according to the load requirements, leading to significant energy savings. However, they come with a higher upfront cost and require skilled electrical technicians for installation. Additionally, while VFDs excel in applications needing variable speed, they may not deliver the same level of torque as gear reducers in fixed-speed applications.
How Do Hydraulic Drives Compare?
Hydraulic Drives utilize pressurized fluid to transmit power, allowing for high torque output and adjustable speeds. They are particularly advantageous in heavy-duty applications, such as construction or mining, where significant force is required. However, the complexity of installation and ongoing maintenance can be drawbacks, as they necessitate regular checks of hydraulic fluid levels and potential leaks. The initial investment is also higher, making it less suitable for smaller operations or applications with limited budgets.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
Selecting the right solution depends on your specific operational requirements. Gear reducers offer a reliable and cost-effective method for applications needing consistent speed and torque. In contrast, VFDs provide flexibility and energy savings for operations with variable speed needs, while hydraulic drives excel in demanding, high-torque environments. International B2B buyers should assess their unique circumstances, including budget, application requirements, and available technical expertise, to make the best decision for their operations. By carefully weighing these alternatives, you can enhance your operational efficiency and achieve your business goals effectively.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for gear reducers
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Gear Reducers?
Understanding the essential technical properties of gear reducers is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly when making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
The material used in the construction of gear reducers significantly impacts durability and performance. Common materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, and aluminum. For instance, stainless steel is preferred in food and beverage applications due to its resistance to corrosion. Selecting the right material ensures longevity and reduces maintenance costs, which is especially important for industries in Africa and South America that may face harsh operating conditions.
2. Torque Rating
Torque rating indicates the maximum torque the gear reducer can handle without failure. This specification is vital for ensuring that the reducer can manage the load requirements of your machinery. A higher torque rating typically means a more robust design, essential for applications in heavy industries such as mining and manufacturing prevalent in the Middle East and Africa.
3. Efficiency
Efficiency refers to the ratio of output power to input power, often expressed as a percentage. Gear reducers with higher efficiency ratings minimize energy loss, leading to lower operational costs. For international buyers, particularly those in Europe focusing on sustainability, investing in high-efficiency gear reducers can also align with environmental regulations.
4. Gear Ratio
The gear ratio is the relationship between the input speed and output speed of the reducer. It determines how much the speed is reduced and affects the output torque. Selecting the appropriate gear ratio is critical for optimizing performance in applications ranging from automotive to industrial machinery, making it a key consideration for B2B buyers.
5. Operating Temperature Range
This specification defines the environmental conditions in which the gear reducer can operate effectively. Understanding the operating temperature range is essential for applications exposed to extreme temperatures, ensuring that the gear reducer will perform reliably without overheating or freezing, which is particularly relevant for regions with diverse climates.
Which Trade Terminology Should B2B Buyers Know?
Familiarity with industry terminology can streamline the purchasing process and facilitate better negotiations. Here are some essential terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for buyers seeking quality components for their machinery. Engaging with reputable OEMs can ensure that the gear reducers meet industry standards and specifications.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is important for buyers to understand their purchasing flexibility and manage inventory costs. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa, negotiating MOQs can lead to more favorable terms and cost savings.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that a buyer sends to suppliers to request pricing and other details for specific products. This process is essential for comparing offers and ensuring that you obtain the best value for your investment. It’s a standard practice in B2B transactions, especially when sourcing gear reducers from multiple suppliers.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce. They clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international transactions, particularly for buyers in South America and Africa, to avoid potential legal and financial complications.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving it. This term is vital for supply chain management and planning, especially in industries that require timely delivery of components for production processes. Buyers should consider lead times when selecting suppliers to ensure they can meet their project deadlines.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, streamline procurement processes, and foster better supplier relationships.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the gear reducers Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Gear Reducers Sector?
The global gear reducers market is witnessing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for efficient power transmission across various industries, including manufacturing, automotive, and renewable energy. Key trends include a shift towards automation and IoT integration, enabling real-time monitoring and optimization of gear performance. This is particularly relevant for international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where modernization efforts are critical for competitive advantage.
Emerging technologies, such as advanced materials and smart gear systems, are shaping sourcing strategies. For instance, gear reducers made from lightweight composites can improve efficiency and reduce energy consumption, appealing to buyers focused on cost-effective solutions. Additionally, manufacturers are increasingly offering customization options, allowing businesses to tailor gear reducers to specific operational needs. This trend emphasizes the importance of establishing strong partnerships with suppliers who can provide both standard and bespoke solutions.
Furthermore, sustainability is becoming a crucial factor in sourcing decisions. Buyers are looking for suppliers that prioritize eco-friendly production processes and materials, reflecting a broader commitment to corporate social responsibility. This trend is particularly relevant in Europe, where regulations on environmental impact are stringent, compelling suppliers to innovate and adhere to higher standards.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact Your Gear Reducers Procurement?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are paramount in today’s B2B landscape, especially in the gear reducers sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including carbon emissions and resource depletion, has prompted buyers to seek suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices. This focus on sustainability not only mitigates risks but also enhances brand reputation, a vital consideration for companies operating in global markets.
Buyers should prioritize suppliers that hold certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and those that utilize recycled or sustainably sourced materials in their gear reducers. The demand for ‘green’ products is growing, particularly in Europe and North America, where consumers are increasingly aware of the environmental implications of their purchases. This trend offers a competitive edge to businesses that can demonstrate their commitment to sustainability.
Additionally, ethical supply chains are crucial for minimizing risks associated with labor practices and sourcing materials. By selecting suppliers that adhere to ethical standards, buyers can ensure compliance with international regulations and avoid potential disruptions. This is especially relevant for buyers from regions with diverse regulatory environments, such as Africa and South America, where ethical sourcing can significantly impact long-term business sustainability.
What Is the Historical Context of Gear Reducers and Their Evolution in B2B Markets?
The evolution of gear reducers dates back to the early mechanical innovations of the industrial revolution, where simple gear systems were employed to transmit power efficiently. Over the decades, gear reducer technology has advanced significantly, with innovations such as worm gears, planetary gears, and helical designs emerging to meet the growing demands for efficiency and reliability.
In recent years, the integration of digital technologies has transformed gear reducers into smart systems capable of real-time performance monitoring. This evolution has enabled international B2B buyers to optimize their operations and reduce maintenance costs, aligning with the broader trend of Industry 4.0. As the market continues to evolve, understanding the historical context of gear reducers can provide valuable insights into current trends and future opportunities in sourcing strategies.
By keeping abreast of these market dynamics and sourcing trends, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that not only enhance operational efficiency but also align with their sustainability goals and ethical standards.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of gear reducers
-
How do I choose the right gear reducer for my application?
Selecting the appropriate gear reducer involves understanding your application’s specific requirements, including load capacity, speed, torque, and the type of motion required (linear or rotary). Consider the environment where the gear reducer will operate, such as temperature and humidity levels, to ensure durability. Reviewing technical specifications and consulting with suppliers for recommendations based on your machinery can significantly streamline the selection process. -
What is the best gear reducer type for high torque applications?
For high torque applications, planetary gear reducers are often the best choice due to their compact design and ability to handle substantial loads efficiently. They provide higher torque density and can be customized for specific requirements. Additionally, worm gear reducers are also suitable for applications requiring significant torque reduction, especially where space is limited. -
What are the key factors to consider when sourcing gear reducers internationally?
When sourcing gear reducers globally, key factors include the supplier’s reputation, product quality, compliance with international standards, and delivery capabilities. It’s crucial to assess the supplier’s experience in your industry and their ability to provide technical support. Additionally, consider logistical aspects, such as shipping times and costs, as well as any potential tariffs or trade regulations affecting your purchase. -
How can I vet suppliers for gear reducers?
Vetting suppliers involves checking their certifications, customer reviews, and previous project portfolios. Request samples or prototypes to assess product quality firsthand. Engage in direct communication to gauge their responsiveness and expertise. Utilizing platforms like Alibaba or industry-specific directories can help you identify reputable suppliers, while networking within your industry can provide valuable insights and recommendations. -
What customization options are available for gear reducers?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for gear reducers, including specific gear ratios, materials, and mounting configurations. Custom designs can enhance performance and adapt to unique application requirements. When discussing customization, be clear about your specifications and operational conditions to ensure the manufacturer can meet your needs effectively. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for gear reducers?
The MOQ for gear reducers can vary significantly based on the manufacturer and the type of gear reducer required. Some suppliers may have a low MOQ for standard products, while custom designs may require larger quantities. It’s advisable to inquire directly with potential suppliers about their MOQ policies to plan your procurement strategy accordingly.

A stock image related to gear reducers.
-
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing gear reducers internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely depending on the supplier and the nature of the transaction. Common terms include full payment upfront, a deposit with the balance upon delivery, or letter of credit arrangements. It’s crucial to establish clear payment terms before finalizing the order to avoid any misunderstandings. Consider using secure payment methods to protect your transaction. -
How do I ensure quality assurance when buying gear reducers?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed product specifications and quality certifications from your suppliers. Implement quality checks at various stages of the manufacturing process, and consider third-party inspections before shipment. Establish a return policy for defective products and maintain open communication with the supplier for any concerns post-delivery to ensure a satisfactory resolution.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for gear reducers
The landscape of gear reducers is evolving, driven by advancements in technology and increasing demand across various sectors. For international B2B buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, strategic sourcing is essential to navigate this complex market. Key takeaways include understanding the diverse types of gear reducers available—such as worm, helical, and planetary gear systems—and their specific applications in industries like manufacturing, automotive, and food processing.
Investing in quality gear reducers not only enhances operational efficiency but also reduces downtime and maintenance costs. By forming strategic partnerships with reputable suppliers, buyers can ensure access to the latest innovations and customized solutions that meet their unique operational needs.
Looking ahead, the integration of smart technologies and sustainability in gear reducer design will become increasingly important. Buyers are encouraged to stay informed about these trends and proactively engage with suppliers to leverage new opportunities. Embrace the future of gear reducers by prioritizing strategic sourcing to optimize performance and drive your business forward.