Discover Power Plug Types: The Ultimate Sourcing Guide (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for power plug types
In an increasingly interconnected world, international B2B buyers face the challenge of navigating diverse power plug types when sourcing electrical equipment. Understanding the various plug and socket configurations is crucial for ensuring compatibility and safety across different regions, especially in markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the various power plug types used globally, detailing their applications, compatibility, and electrical specifications.
By exploring the intricacies of power plug types, buyers will gain insights into critical factors such as voltage requirements, grounding options, and the implications of different plug configurations. This knowledge is essential for making informed purchasing decisions, minimizing operational disruptions, and enhancing product compatibility. The guide also delves into the vetting process for suppliers, helping businesses identify reliable sources that meet their specific needs, as well as an analysis of cost considerations associated with different plug types.
International buyers, particularly those from regions like Saudi Arabia and Brazil, will find actionable strategies to streamline their procurement processes, ensuring that their electrical devices operate safely and efficiently in their respective markets. By equipping themselves with the right information, B2B buyers can enhance their supply chain resilience and drive operational success in a complex global landscape.
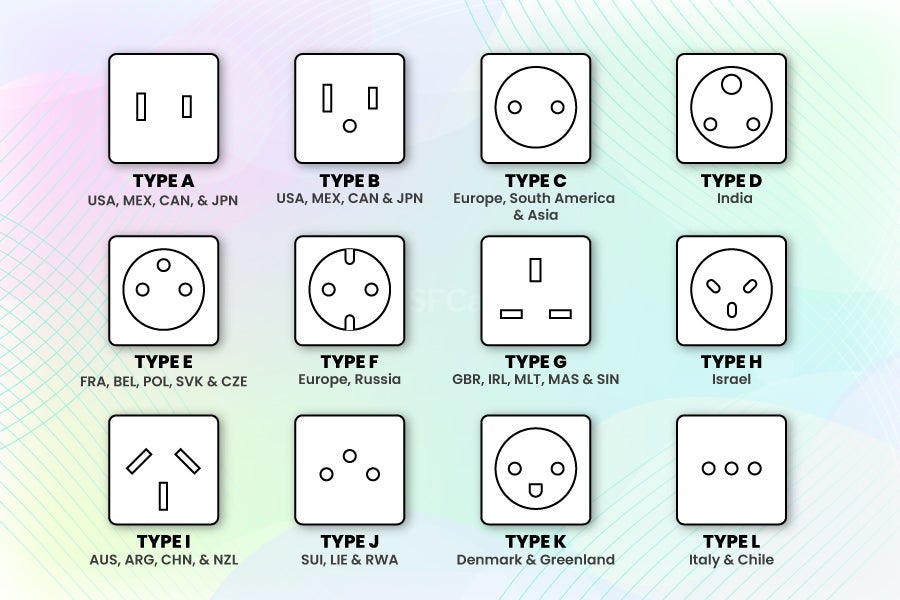
Understanding power plug types Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type C | 2 pins, not grounded, 10A-16A, 220-240V | Common in Europe, Africa, South America | Pros: Widely used, versatile. Cons: Not grounded, lower safety in high-power applications. |
| Type G | 3 pins, grounded, 13A, 220-250V | Predominant in UK, Middle East, and parts of Asia | Pros: High safety due to grounding. Cons: Bulkier design may not fit all devices. |
| Type N | 3 pins, grounded, 10A-20A, 100-240V | Brazil, South Africa | Pros: Supports multiple amperage ratings. Cons: Limited compatibility outside specific regions. |
| Type F | 2 pins, grounded, 16A, 220-240V | Common in Germany, Russia, and other European countries | Pros: Grounded, high current capacity. Cons: Compatibility with Type C may vary. |
| Type I | 2 or 3 pins, grounded options, 10A-15A, 220-240V | Used in Australia, New Zealand, and Argentina | Pros: Versatile with grounding options. Cons: Limited availability in some regions. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of Type C Power Plugs?
Type C plugs feature two round pins and are commonly used across Europe, Africa, and South America. They are rated for 10A to 16A and operate on a voltage range of 220-240V. While they are versatile and widely accepted, Type C plugs are not grounded, which raises safety concerns for high-power applications. B2B buyers should consider the availability of compatible sockets and the specific power requirements of their equipment when selecting this plug type.
Why Choose Type G Power Plugs for Your Business?
Type G plugs are distinguished by their three rectangular pins and grounding feature, making them a safe choice for businesses operating in the UK, Middle East, and parts of Asia. Rated for 13A and voltages between 220-250V, they provide a robust connection for various devices. While their grounded design enhances safety, the bulkier shape may limit compatibility with some devices. Buyers should weigh the benefits of enhanced safety against potential limitations in device compatibility.
What Makes Type N Plugs Ideal for Brazil and South Africa?
Type N plugs are characterized by three pins and are used primarily in Brazil and South Africa, with ratings ranging from 10A to 20A. They support a voltage range of 100-240V, making them versatile for different applications. Their grounding feature provides enhanced safety, but compatibility issues may arise outside their primary regions. B2B buyers should ensure that their equipment is compatible with Type N sockets and consider the specific amperage requirements for their operations.
How Do Type F Plugs Benefit European Businesses?
Type F plugs, or “Schuko” plugs, are widely used in Germany, Russia, and other European countries. They feature two grounded pins and are rated for 16A at 220-240V, making them suitable for high-power devices. Their grounding capability enhances safety, but compatibility with Type C sockets can vary. Businesses should consider the plug type compatibility of their devices and the electrical infrastructure of their operating regions when opting for Type F plugs.
Why Consider Type I Plugs for Operations in Australia and New Zealand?
Type I plugs are used in Australia, New Zealand, and Argentina, featuring two or three pins with grounding options. They are rated for 10A to 15A and operate at voltages between 220-240V. The versatility of Type I plugs makes them suitable for various applications, but their availability may be limited in certain regions. B2B buyers should evaluate their equipment’s compatibility with Type I sockets and consider the grounding options available for enhanced safety.
Key Industrial Applications of power plug types
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of power plug types | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Machinery and Equipment Power Supply | Ensures compatibility with local power standards | Verify plug type and voltage requirements specific to the region |
| Telecommunications | Network Equipment and Data Centers | Facilitates reliable power supply for critical operations | Consider redundancy and surge protection in power plug specifications |
| Construction | Power Tools and Heavy Machinery | Enhances operational efficiency and safety | Assess durability and safety ratings of plugs for site conditions |
| Healthcare | Medical Equipment Power Connections | Guarantees safety and compliance with medical standards | Ensure plugs meet international safety certifications and standards |
| Hospitality | Appliances in Hotels and Restaurants | Improves guest experience and operational reliability | Evaluate compatibility with local power grids and appliance specifications |
How Are Power Plug Types Used in Manufacturing?
In the manufacturing sector, power plug types are crucial for connecting machinery and equipment to local power supplies. Different regions utilize various plug types, which can lead to compatibility issues if not properly addressed. For international B2B buyers, it’s essential to verify that the machinery sourced complies with local voltage and plug type standards to avoid operational disruptions. Ensuring the correct power plug type not only enhances the efficiency of manufacturing processes but also minimizes downtime due to electrical incompatibilities.
What Role Do Power Plug Types Play in Telecommunications?
Telecommunications rely heavily on network equipment and data centers that require a stable and reliable power supply. The use of appropriate power plug types ensures that equipment is compatible with local electrical systems, which is vital for uninterrupted operations. For B2B buyers in this sector, sourcing power plugs that offer redundancy and surge protection can significantly enhance the resilience of network operations. Additionally, understanding the specific plug types used in different regions is essential to maintain compliance and operational standards.
How Are Power Plug Types Relevant in Construction?
In construction, power tools and heavy machinery often require specific power connections to function efficiently. Different countries have varying plug types and voltage specifications, necessitating careful consideration during equipment sourcing. B2B buyers must assess the durability and safety ratings of power plugs, especially in harsh site conditions. By ensuring compatibility with local power supply standards, businesses can enhance operational efficiency and ensure the safety of their workforce.
How Do Power Plug Types Impact Healthcare Equipment?
In the healthcare industry, power plug types are critical for the safe operation of medical equipment. Hospitals and clinics must ensure that all devices comply with local electrical standards to maintain patient safety and meet regulatory requirements. B2B buyers in this sector should prioritize sourcing plugs that adhere to international safety certifications, as this guarantees compliance and reliability in critical situations. The right power plug type not only enhances the functionality of medical devices but also contributes to overall patient care.

A stock image related to power plug types.
Why Are Power Plug Types Important in the Hospitality Sector?
In the hospitality industry, the use of power plug types is essential for the seamless operation of appliances in hotels and restaurants. Ensuring compatibility with local power grids improves guest experiences and operational reliability. For B2B buyers, evaluating the specifications of plugs used in appliances is critical for maintaining service quality. Additionally, understanding local plug types helps avoid potential electrical issues that could disrupt service and affect customer satisfaction.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘power plug types’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Identifying Compatible Power Plug Types Across Regions
The Problem:
B2B buyers frequently encounter challenges when trying to identify the correct power plug types for their equipment across different regions. For instance, a company sourcing electronic devices for distribution in Africa and Europe may realize that the devices come with plugs that are incompatible with local sockets. This not only leads to delays in product launches but also increases costs due to the need for additional adapters or plug modifications. The lack of standardized plug types can create confusion and frustration, making it critical for buyers to thoroughly understand regional requirements before making procurement decisions.
The Solution:
To address this issue, B2B buyers should invest in comprehensive market research that includes a detailed understanding of the plug types used in their target markets. Create a compatibility chart that lists the different plug types (e.g., Type C, Type G, etc.) alongside the countries that utilize them. Additionally, consider partnering with local distributors who have expertise in the electrical standards of each region. They can provide valuable insights on which products need modifications or additional adapters. Utilizing resources like international standards organizations or plug and socket databases can also help streamline the sourcing process, ensuring that the right products are selected from the outset.
Scenario 2: Safety Concerns with Plug Type Compatibility
The Problem:
Another significant pain point for B2B buyers is the safety concerns associated with using incompatible plug types and voltages. For example, equipment designed for a Type F socket (common in Europe) may be inadvertently plugged into a Type G socket (used in the UK). This mismatch can lead to electrical faults, posing risks not only to the equipment but also to personnel. Such incidents can result in costly damages, liability issues, and damage to the company’s reputation.
The Solution:
To mitigate safety risks, it’s essential to implement a rigorous quality control process during the procurement stage. Ensure that all electrical equipment is certified for use in the intended regions, adhering to local standards and regulations. Additionally, educate your team on the importance of using the correct plug types. Consider investing in universal power adapters or multi-socket power strips that can accommodate various plug types, ensuring safer usage across different settings. Regular training sessions on electrical safety standards and plug compatibility can further enhance workplace safety and reduce the likelihood of accidents.
Scenario 3: Increased Costs Due to Plug Type Mismanagement
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face unexpected costs related to plug type mismanagement. For instance, a company importing electronic devices may find that a significant portion of its budget is consumed by purchasing additional adapters or modifying equipment to fit local sockets. This situation is particularly prevalent when buyers fail to consider the plug types during the initial sourcing phase, leading to unplanned expenses that can strain financial resources.
The Solution:
To prevent budget overruns, B2B buyers should adopt a proactive approach by integrating plug type considerations into their product development and sourcing strategies. Conduct a thorough analysis of the product lifecycle and identify potential compatibility issues early on. When negotiating with suppliers, clearly communicate the required plug types and standards to avoid misunderstandings. Additionally, consider bulk purchasing of universal adapters or plug types that cater to multiple markets. This can help reduce long-term costs while ensuring product compatibility. By anticipating and addressing plug type issues upfront, companies can maintain control over their budgets and avoid unnecessary expenditures.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for power plug types
What Are the Key Materials Used in Power Plug Types?
When selecting materials for power plug types, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that impact performance, durability, and compliance with regional standards. Here, we analyze four common materials: thermoplastic, thermosetting plastic, metal alloys, and rubber. Each material has unique properties that influence its suitability for different applications.
How Does Thermoplastic Material Perform in Power Plugs?
Thermoplastics, such as polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and polycarbonate, are widely used in power plugs due to their excellent insulation properties and ease of molding. These materials typically have a temperature rating of up to 105°C and can withstand moderate pressure.
Pros: Thermoplastics are lightweight, cost-effective, and easy to manufacture, making them suitable for mass production. They also exhibit good electrical insulation, which is crucial for safety.
Cons: However, thermoplastics may not offer the same level of durability as other materials and can become brittle over time, especially when exposed to UV light or extreme temperatures.
Impact on Application: Thermoplastics are suitable for indoor applications where exposure to harsh environmental conditions is limited.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM D256 (impact resistance) and UL 94 (flammability) is essential. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure that the selected thermoplastics meet local safety regulations.
What Are the Benefits of Thermosetting Plastics in Power Plugs?
Thermosetting plastics, including phenolic and epoxy resins, are known for their high thermal stability and resistance to deformation under heat. They can typically handle temperatures up to 150°C, making them ideal for high-performance applications.
Pros: These materials provide excellent mechanical strength and electrical insulation, ensuring long-term reliability in demanding environments. They are also resistant to chemicals and moisture.
Cons: The manufacturing process for thermosetting plastics is more complex and costly compared to thermoplastics. Once set, these materials cannot be re-molded, limiting design flexibility.
Impact on Application: Thermosetting plastics are particularly beneficial in environments with high heat or chemical exposure, such as industrial settings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should look for compliance with international standards like IEC 60695 for fire hazard testing. This is especially relevant for buyers in the Middle East, where high temperatures are common.
Why Are Metal Alloys Important for Power Plug Types?
Metal alloys, such as brass and aluminum, are often used in the conductive components of power plugs due to their excellent electrical conductivity and mechanical strength. Brass, for instance, has a high corrosion resistance and can withstand high temperatures.
Pros: Metal alloys provide superior durability and reliability, ensuring a long service life. They are also capable of handling higher current loads, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Cons: The primary drawback is the higher cost associated with metal components compared to plastics. Additionally, they may require additional coatings to prevent corrosion, especially in humid environments.
Impact on Application: Metal alloys are essential for plugs used in industrial and outdoor applications where durability and electrical performance are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM B16 (brass alloys) is crucial, particularly for buyers in Europe and South America, where stringent quality regulations exist.
How Does Rubber Material Enhance Power Plug Performance?
Rubber is often used for the insulation and outer casing of power plugs, providing flexibility and resistance to environmental factors. It can typically withstand temperatures ranging from -40°C to 90°C.
Pros: Rubber offers excellent shock absorption and is resistant to moisture, making it ideal for outdoor applications. Its flexibility allows for easier handling and installation.
Cons: However, rubber can degrade over time when exposed to UV light and extreme temperatures, leading to potential safety hazards.
Impact on Application: Rubber is particularly useful for plugs designed for outdoor use or in environments where moisture is a concern.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that rubber materials comply with standards such as ASTM D412 (tensile strength) and IEC 60529 (ingress protection), especially in regions like Africa and the Middle East where environmental conditions can vary significantly.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Power Plug Types
| Material | Typical Use Case for Power Plug Types | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermoplastic | Indoor residential plugs | Lightweight and cost-effective | Less durable over time | Low |
| Thermosetting Plastic | Industrial and high-performance plugs | High thermal stability | Complex manufacturing process | High |
| Metal Alloys | Heavy-duty and industrial plugs | Superior durability and conductivity | Higher cost and corrosion risk | High |
| Rubber | Outdoor and moisture-prone plugs | Excellent shock absorption | Degrades under UV exposure | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide assists international B2B buyers in making informed decisions regarding power plug types, ensuring compliance with regional standards while optimizing for performance and cost.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for power plug types
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Power Plug Types?
Manufacturing power plugs involves several critical stages, each requiring specific techniques and materials to ensure quality and compliance with international standards. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when selecting suppliers.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Power Plug Production?
The manufacturing process begins with the selection of appropriate materials. Common materials include:
- Plastics: High-quality thermoplastics, such as polycarbonate or nylon, are used for insulation and casing due to their durability and electrical resistance.
- Conductors: Copper is the preferred choice for electrical conductors due to its excellent conductivity. Some manufacturers may also use aluminum, but it is less common.
- Metal Components: Contacts and pins are typically made from brass or nickel-plated copper to prevent corrosion and enhance conductivity.
Before production, materials undergo rigorous quality checks to ensure they meet industry specifications. This stage may include testing for electrical resistance, tensile strength, and thermal stability.
How Are Power Plugs Formed and Assembled?
The forming stage involves several techniques to shape and assemble the components of power plugs. Key processes include:
- Injection Molding: This is the primary method for creating the plastic casing of the plug. Heated plastic is injected into a mold, where it cools and solidifies into the desired shape.
- Die Casting: For metal components, die casting is often employed. Molten metal is poured into a mold, creating precise and durable parts.
- Machining: After forming, components may require machining to ensure precise dimensions and proper fit. This can include drilling holes or threading.
During the assembly phase, components are carefully combined. Automated assembly lines often enhance efficiency, but manual inspection remains crucial to ensure each plug meets quality standards.
What Finishing Techniques Are Used for Power Plugs?
Finishing processes enhance the durability and aesthetics of power plugs. Common techniques include:
- Surface Treatment: Metal parts may undergo plating (such as nickel or chrome) to improve corrosion resistance and conductivity.
- Coating: Some plugs are coated with a protective layer to prevent wear and tear.
- Labeling: Proper labeling is essential for compliance with international standards, including safety warnings and electrical ratings.
These finishing processes not only improve the product’s appearance but also its safety and longevity, which are critical for B2B buyers seeking reliable products.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Power Plug Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in ensuring that power plugs are safe and reliable. Various international and industry-specific standards guide the QA process.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
B2B buyers should look for manufacturers that comply with international quality standards, such as:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is essential for ensuring consistent quality in manufacturing processes.
- IEC 60884: This standard specifies safety requirements for plugs and socket-outlets, providing guidelines for electrical and mechanical safety.
- CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area, CE marking signifies compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
Understanding these standards can help buyers assess the credibility of potential suppliers.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Power Plug Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) in power plug manufacturing typically involves several checkpoints throughout the production process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials and components to ensure they meet specified standards before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, ongoing inspections are conducted to monitor production quality, focusing on critical dimensions and electrical performance.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once production is complete, a final inspection assesses the entire batch. This may include functional testing, visual inspections, and certification checks.
These checkpoints are crucial for minimizing defects and ensuring that only high-quality products reach the market.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers must conduct due diligence to ensure their suppliers adhere to robust quality control practices. Here are several strategies to verify supplier QC:
What Steps Can Buyers Take to Conduct Supplier Audits?
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits provides firsthand insight into the supplier’s manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and compliance with standards.
- Requesting Documentation: Suppliers should provide documentation, including quality control reports, certifications, and test results. This transparency is essential for building trust.
How Can Third-Party Inspections Enhance Quality Assurance?
Engaging third-party inspection services can further enhance quality assurance. These independent inspectors can conduct thorough assessments at various stages of production, ensuring compliance with international standards. This adds an extra layer of credibility and reliability for B2B buyers.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Power Plugs?
Testing methods are critical for verifying the safety and functionality of power plugs. Common methods include:
- Electrical Testing: This includes measuring insulation resistance, continuity, and dielectric strength to ensure safe operation.
- Mechanical Testing: Assessing mechanical strength and durability involves applying stress tests to ensure the plug can withstand regular use.
- Environmental Testing: Products may undergo testing for temperature variations, humidity, and exposure to chemicals to evaluate their resilience under different conditions.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of QC and certification is essential. Different countries may have specific requirements regarding plug types, voltage specifications, and safety standards.
- Regional Compliance: Buyers should ensure that their suppliers are aware of and compliant with regional regulations, such as those set by the Saudi Standards, Metrology and Quality Organization (SASO) in Saudi Arabia or the National Institute of Metrology, Quality and Technology (Inmetro) in Brazil.
- Documentation for Customs: Ensure that all certifications and quality control documents are readily available for customs clearance to avoid delays and complications.
A stock image related to power plug types.
By understanding these manufacturing processes, quality assurance measures, and regional compliance requirements, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing power plugs, ensuring safety, reliability, and compliance with international standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘power plug types’
When sourcing power plug types for international markets, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it’s essential to follow a structured approach. This checklist will guide B2B buyers through the critical steps necessary for effective procurement of power plug types that meet technical and regulatory requirements.
Step 1: Identify Your Market Needs
Understanding the specific power plug types required for your target market is crucial. Different countries utilize various plug types, voltages, and frequencies, affecting compatibility with electrical devices. Research the local standards in your target regions, such as Type C in much of Europe and Type G in the UK, to ensure you meet local consumer needs.
Step 2: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to suppliers, outline the technical specifications for the power plugs you need. Consider factors such as:
– Voltage and Amperage: Ensure the plugs can handle the required electrical load.
– Design Features: Decide if you need grounded plugs, which provide additional safety, or specific dimensions for compatibility.
Step 3: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that potential suppliers comply with international standards and certifications. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management and IEC standards for electrical safety. This step is vital to guarantee that the products meet the necessary safety and performance criteria, reducing the risk of defects.
Step 4: Request Samples for Quality Assurance
Before making a bulk purchase, request samples from shortlisted suppliers. Testing these samples allows you to evaluate the quality, durability, and overall performance of the plugs. Make sure to check:
– Material Quality: Assess whether the materials used are robust and suitable for long-term use.
– Compatibility: Confirm that the samples fit the sockets in your intended markets.
Step 5: Evaluate Supplier Reliability and Capacity
Assess the reliability and production capacity of your potential suppliers. This includes:
– Delivery Times: Ensure they can meet your timelines, particularly if you have a tight schedule.
– Production Capabilities: Verify that they can scale up production if demand increases.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have selected a supplier, negotiate terms that protect your interests. Discuss:
– Pricing: Ensure pricing is competitive but also reflective of quality.
– Payment Terms: Establish clear payment timelines to manage cash flow effectively.
Step 7: Implement a Risk Management Strategy
Develop a risk management plan to address potential issues that may arise during the procurement process. Consider factors such as:
– Political and Economic Stability: Be aware of the political climate in your supplier’s country, as instability can affect supply chains.
– Logistics Challenges: Plan for logistics and transportation issues that could delay delivery.
By following this structured checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing power plug types, ensuring compliance and compatibility with local standards while minimizing risks associated with international procurement.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for power plug types Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Power Plug Types Sourcing?
Understanding the cost structure associated with sourcing power plug types is essential for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts cost. For instance, plugs made from high-quality plastics and metals will generally be more expensive than those made from lower-grade materials. Additionally, the type of plug—whether it’s a basic Type C or a more complex Type G—can also dictate material costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region. For buyers in Africa and South America, sourcing from local manufacturers may reduce labor costs compared to sourcing from Europe or North America. However, it’s important to consider the skill level and experience of the workforce, as this can affect the quality and durability of the products.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facilities, equipment, and utilities. Efficient manufacturing processes in regions with lower overhead can result in significant savings. Buyers should inquire about the manufacturing capabilities of suppliers to assess potential overhead impacts.
-
Tooling: Custom designs or specific specifications may require unique tooling, which can be a substantial upfront cost. Understanding the tooling requirements early in the negotiation process can help avoid unexpected expenses later.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that power plugs meet international safety standards is crucial, particularly for buyers in Europe and the Middle East. QC processes add to the overall cost, but investing in rigorous QC can prevent costly returns and safety issues in the future.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary widely based on the distance from the supplier, the mode of transport, and the volume of the order. For international buyers, understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is vital, as they dictate who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to the cost of production. This margin can vary based on supplier reputation, market demand, and buyer relationships. Negotiating effectively can help buyers achieve better pricing.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Power Plug Types Sourcing?
Several factors influence the pricing of power plugs beyond the basic cost components:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders typically result in lower unit prices. Buyers should assess their needs and consider consolidating orders to take advantage of bulk pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized plugs or those meeting specific regional standards may incur additional costs. Buyers should clarify their specifications upfront to avoid misunderstandings and unexpected costs.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: High-quality materials and certifications (like CE, UL) can increase costs but are essential for compliance in many markets. Buyers should weigh the importance of these factors against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge higher prices but offer better guarantees and service. Conducting thorough supplier evaluations can save money in the long run.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms can significantly affect the total landed cost. For instance, opting for FOB (Free on Board) may be more cost-effective for buyers who can handle logistics, while DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) may simplify the process but at a higher price.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficient Sourcing?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, here are some actionable tips:
-
Negotiate Terms: Always negotiate pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Suppliers may have flexibility that can lead to significant savings.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond initial pricing. TCO includes shipping, customs duties, and potential warranty claims. Assessing TCO can provide a clearer picture of overall costs.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Different markets have varying pricing strategies. Being aware of these can help in negotiations and prevent overpaying.
-
Build Long-Term Relationships: Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, priority service, and early access to new products.
-
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Keeping abreast of trends in the electrical components market can help buyers anticipate changes in pricing and availability.
Disclaimer
The prices and cost factors discussed are indicative and can vary based on several variables, including market conditions, supplier negotiations, and regional economic factors. It is advisable to conduct thorough research and obtain multiple quotes before making purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing power plug types With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Power Plug Types
As global trade continues to expand, the need for effective power solutions becomes increasingly critical, especially for international B2B buyers. While traditional power plug types serve as a primary means of connecting electrical devices, exploring alternatives can offer innovative solutions that enhance efficiency and compatibility. This section evaluates the conventional power plug types against two viable alternatives: Universal Plug Adapters and Wireless Power Transfer Systems.
Comparison Table of Power Plug Types and Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Power Plug Types | Universal Plug Adapters | Wireless Power Transfer Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Reliable for fixed installations | Offers compatibility across multiple plugs | Provides flexibility without physical connections |
| Cost | Generally low initial cost | Moderate cost, varies by brand and features | Higher initial investment, but cost-effective over time |
| Ease of Implementation | Widely standardized, easy to source | Simple to use, plug-and-play functionality | Requires specific devices, may need infrastructure |
| Maintenance | Minimal maintenance required | Low maintenance; replace as needed | Minimal, but requires technology upgrades |
| Best Use Case | Fixed installations in specific regions | Travel and multi-region usage | Dynamic environments requiring mobility |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Universal Plug Adapters?
Universal plug adapters are designed to accommodate various power plug types, making them an ideal solution for international travelers and businesses operating across different regions. Their primary advantage lies in their versatility; they allow users to connect devices from various countries without needing multiple adapters. However, they do not convert voltage, which can lead to equipment damage if the voltage differs significantly. Additionally, while they are generally affordable, the cost can accumulate if multiple units are needed for various devices.
How Do Wireless Power Transfer Systems Compare?
Wireless power transfer systems represent a cutting-edge alternative to traditional plug types, leveraging electromagnetic fields to transmit energy without physical connectors. This method enhances convenience, particularly in environments where mobility is crucial, such as manufacturing floors or hospitals. The key benefits include reduced wear on connectors and increased safety from electrical hazards. However, the initial investment is significantly higher, and the technology may require specialized devices, limiting its immediate applicability in all scenarios. Furthermore, efficiency can vary based on distance and alignment, which can be a consideration for B2B buyers.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Power Solution?
When selecting the right power solution, B2B buyers must consider their specific operational needs, budget constraints, and the environments in which their products will be used. Traditional power plug types offer reliability and low costs, making them suitable for static installations. In contrast, universal plug adapters provide flexibility for businesses with diverse international operations, while wireless power transfer systems present a modern solution for dynamic and mobile environments. Ultimately, the choice should align with the company’s strategic goals, ensuring the selected power solution meets both current and future needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for power plug types
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Power Plug Types?
Understanding the technical properties of power plugs is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure compatibility, safety, and reliability in their electrical systems. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
– The material used in manufacturing plugs significantly affects durability and conductivity. Common materials include copper for conductors and polycarbonate or thermoplastic for housings. High-grade materials can withstand higher temperatures and resist corrosion, ensuring longer service life and reducing maintenance costs. -
Current Rating (Amperage)
– The current rating indicates the maximum amount of electrical current a plug can safely carry. It is essential for preventing overheating and potential fire hazards. Common ratings include 10 A, 16 A, and 20 A. Buyers should match the current rating to their specific application to ensure safety and compliance with local regulations. -
Voltage Rating
– Voltage ratings specify the maximum voltage a plug can handle, typically ranging from 100V to 250V. Understanding voltage requirements is vital to avoid equipment damage and ensure operational efficiency. For example, plugs used in Europe and parts of Africa often accommodate 220V to 240V systems. -
Pin Configuration and Size
– Different regions utilize various pin configurations and sizes, which affect compatibility with sockets. For instance, Type C plugs have two round pins, while Type G features three rectangular pins. Ensuring the correct configuration prevents connection issues and enhances safety. -
Grounding Mechanism
– Grounded plugs include an additional pin to prevent electrical shocks. This feature is especially important in industrial applications and areas with high moisture levels. Buyers should prioritize grounded plugs for equipment used in environments where electrical safety is paramount. -
Environmental Ratings
– Environmental ratings, such as IP (Ingress Protection) ratings, indicate the plug’s resistance to dust and water. For instance, IP67-rated plugs can withstand immersion in water. This specification is vital for outdoor or industrial applications where plugs may be exposed to harsh conditions.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Power Plugs?
Familiarizing yourself with key industry terminology can streamline the procurement process and enhance communication with suppliers. Here are some essential trade terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable sources for power plugs that meet specific industry standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– The minimum quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for buyers to understand their purchasing limits and negotiate better pricing, especially when sourcing plugs in bulk. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– A document sent to suppliers requesting a quote for specific products. An RFQ is essential for B2B buyers to gauge pricing and terms from multiple suppliers, enabling informed decision-making. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– A series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms can help buyers understand shipping responsibilities, risk management, and cost allocations. -
Certification Standards
– These are regulatory standards that power plugs must meet to ensure safety and compatibility. Common certifications include CE (European Conformity) and UL (Underwriters Laboratories). Understanding these standards is vital for compliance and market access. -
Lead Time
– The time it takes from placing an order to receiving the goods. Knowing lead times helps B2B buyers plan their inventory and production schedules, ensuring they meet project timelines.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they procure the right power plugs for their operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the power plug types Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Power Plug Types Sector?
The global market for power plug types is undergoing significant transformation, driven by several key factors. The increasing globalization of trade has led to a surge in demand for standardized power solutions that can cater to diverse regional requirements. For international B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of plug types is critical, especially as the number of types—currently at 15—continues to evolve. Countries like Brazil and Saudi Arabia are experiencing rapid urbanization and industrial growth, necessitating efficient power solutions that comply with local regulations and standards.
A stock image related to power plug types.
Emerging trends in the sector include the rise of smart plugs and IoT-enabled devices, which allow for improved energy management and automation. B2B buyers should be aware of how these innovations can enhance operational efficiency and reduce energy costs. Additionally, the push for universal plug designs is gaining momentum, driven by companies seeking to simplify logistics and reduce inventory complexity. This trend is particularly relevant for buyers looking to streamline their supply chains across multiple countries.
Moreover, sustainability is becoming a pivotal concern, with manufacturers increasingly focusing on eco-friendly production methods and materials. Buyers should look for suppliers who prioritize sustainable practices, as this can significantly influence market competitiveness and brand reputation.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Power Plug Types Market?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are no longer optional but essential components of the power plug types market. The environmental impact of electrical products is a growing concern, particularly given the increasing amount of electronic waste. B2B buyers must consider the lifecycle of power plugs, including the materials used in production and the end-of-life disposal methods. Selecting suppliers who engage in responsible sourcing can mitigate environmental risks and enhance corporate social responsibility.
Certifications such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) are critical in ensuring that products comply with environmental standards. Buyers should actively seek out manufacturers who hold these certifications, as they indicate a commitment to minimizing environmental footprints. Additionally, the use of recycled materials in the production of power plugs is becoming more prevalent, appealing to eco-conscious consumers and businesses alike.
Investing in suppliers that prioritize sustainability not only aligns with global trends but can also lead to cost savings in the long term. As regulations around environmental impact tighten, ensuring compliance with these standards can also safeguard against potential penalties and enhance market positioning.
What Is the Brief Evolution of Power Plug Types in the Global Market?
The evolution of power plug types has been driven by technological advancements and the need for standardization across different regions. The earliest plugs were simple two-pin designs, primarily used in North America. As global trade expanded, the diversity of electrical systems led to the development of various plug types, each tailored to specific voltage and frequency requirements.
By the mid-20th century, international organizations began addressing the need for standardization, but progress has been slow due to the entrenched nature of existing systems. Today, with the advent of globalization and increasing interconnectivity, there is a growing push for universal plug solutions that can accommodate the needs of multiple regions simultaneously. This evolution reflects the ongoing challenges faced by international B2B buyers in navigating the complex landscape of power plug types while seeking efficiency and compliance in their sourcing strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of power plug types
-
How do I solve compatibility issues with different power plug types?
To address compatibility issues, first identify the plug types used in your target markets. Use resources such as global plug charts or databases to determine the specific types (e.g., Type C, Type G) for each country. Consider sourcing multi-type adapters or universal sockets that accommodate various plug configurations. When negotiating with suppliers, ensure they can provide products that meet local standards, including voltage and frequency specifications. This proactive approach minimizes disruptions in logistics and ensures smooth operations in your international ventures. -
What is the best power plug type for international shipping?
The best power plug type for international shipping largely depends on your target markets. For example, Type C plugs are prevalent in Europe and South America, while Type G is used in the UK and parts of the Middle East. If your products will be used across multiple regions, consider manufacturing with interchangeable plug options or including adapters. This flexibility not only enhances product usability but also broadens your market appeal, making it easier for clients to integrate your products into their existing systems. -
What factors should I consider when vetting suppliers for power plugs?
When vetting suppliers, assess their compliance with international safety standards such as IEC and UL certifications. Check for their production capabilities, including quality control processes, to ensure product reliability. Additionally, consider their experience in exporting to your target regions, as this can influence shipping times and customs clearance. Request product samples and certifications before committing to a larger order to verify quality and compatibility with your specifications. -
How can I customize power plug types for specific markets?
Customization of power plugs can be achieved by collaborating with manufacturers who offer design flexibility. Discuss your specific market needs, such as unique voltage requirements or additional safety features. Ensure that the manufacturer is familiar with local regulations and standards to avoid compliance issues. Additionally, consider the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for custom designs, as some suppliers may have different thresholds, impacting your budget and inventory management. -
What are the typical payment terms when sourcing power plugs internationally?
Payment terms can vary significantly based on supplier policies and your negotiating power. Common arrangements include a 30% deposit upfront, with the balance due upon shipment or delivery. For first-time orders, consider using secure payment methods such as letters of credit or escrow services to mitigate risks. Clarify terms in writing to avoid misunderstandings and ensure compliance with international trade regulations, which can affect payment processing. -
What quality assurance practices should I implement when sourcing power plugs?
Implementing a robust quality assurance (QA) process is crucial. Start with pre-production inspections to ensure materials meet your specifications. Conduct in-process inspections during manufacturing to monitor quality control. Finally, arrange for a third-party inspection before shipment to verify that the products conform to safety standards and your requirements. Establish clear QA guidelines with your supplier to ensure consistency and reliability in the final products, which can enhance customer satisfaction. -
How do logistics and shipping affect the sourcing of power plug types?
Logistics and shipping play a pivotal role in the sourcing process. Factors such as shipping routes, customs regulations, and tariffs can significantly impact delivery times and costs. Choose suppliers who have experience in international shipping to navigate these complexities efficiently. Additionally, assess the reliability of shipping partners to ensure timely delivery, as delays can affect your business operations. Proper logistics planning can also help mitigate risks associated with damaged goods or customs issues. -
What are the most common challenges faced when importing power plugs?
Common challenges when importing power plugs include compliance with local electrical standards, navigating complex customs procedures, and managing shipping delays. Additionally, fluctuations in currency exchange rates can affect overall costs. To mitigate these issues, conduct thorough market research to understand local regulations and work with experienced customs brokers. Establish strong relationships with suppliers and logistics partners to ensure smoother transactions and reduce the likelihood of unexpected hurdles in the import process.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for power plug types
What Are the Key Takeaways for International B2B Buyers?
Understanding the diverse landscape of power plug types is crucial for international B2B buyers operating in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With 15 distinct plug types globally, including widely used types like C, G, and N, buyers must ensure compatibility for their products. This strategic sourcing consideration not only mitigates risks associated with electrical incompatibility but also enhances customer satisfaction through seamless integration.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Business Operations?
Strategic sourcing for power plugs involves not just selecting the right type but also establishing reliable supplier relationships. Buyers should focus on suppliers who can provide high-quality, compliant products tailored to their specific regional needs. This approach can lead to cost savings, improved supply chain efficiency, and enhanced product reliability.
What’s Next for International B2B Buyers?
As global markets continue to evolve, the demand for standardized and adaptable solutions will grow. International B2B buyers are encouraged to proactively assess their sourcing strategies and explore innovative options, such as universal plug designs. By doing so, they can position themselves competitively and better serve their diverse customer bases. Embrace the future of power connectivity—your strategic decisions today will pave the way for success tomorrow.