Discover the Benefits of Electromagnetic Coil Solutions (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for electromagnetic coil
In the complex landscape of global commerce, sourcing high-quality electromagnetic coils can be a daunting challenge for B2B buyers, particularly those operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As industries increasingly rely on electromagnetic coils for applications ranging from electric motors to transformers, understanding the nuances of these essential components becomes paramount. This guide aims to demystify the electromagnetic coil market, providing insights into various types, materials, and applications that cater to diverse industry needs.
By exploring the intricacies of supplier vetting, cost considerations, and performance specifications, we empower international B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. Whether you are based in Nigeria, Germany, or Brazil, this comprehensive resource serves as a strategic tool to navigate the complexities of sourcing electromagnetic coils.
Equipped with actionable insights and industry best practices, buyers can confidently assess supplier capabilities, evaluate product quality, and negotiate favorable terms. This guide not only highlights the critical factors in selecting the right electromagnetic coils for your applications but also emphasizes the importance of aligning procurement strategies with market trends. As you delve deeper into this guide, you will gain a robust understanding of how to optimize your sourcing processes and enhance the efficiency of your operations.
Understanding electromagnetic coil Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solenoid Coils | Wire tightly wrapped around a core to produce linear motion | Automotive actuators, industrial automation | Pros: High efficiency, compact size. Cons: Limited to linear applications. |
| Inductor Coils | Passive components that store energy in a magnetic field | Power supplies, filtering applications | Pros: Excellent for energy storage. Cons: Can be bulky and costly. |
| Voice Coils | Winding attached to speaker cones, generating sound waves | Audio equipment, loudspeakers | Pros: High fidelity sound reproduction. Cons: Sensitive to heat and overload. |
| Air Core Coils | Coils without a magnetic core, using air for insulation | RF applications, inductive sensing | Pros: Lightweight, low cost. Cons: Lower inductance compared to core coils. |
| Closed Core Coils | Wound on a magnetic core, creating a closed magnetic loop | Transformers, inductors, inductive charging | Pros: High efficiency, reduced magnetic leakage. Cons: Heavier and more expensive due to core material. |
What are Solenoid Coils and Their B2B Relevance?
Solenoid coils are characterized by their tightly wrapped wire around a core, typically metal, which generates a magnetic field when electricity passes through. They are primarily used in automotive actuators and industrial automation applications. For B2B buyers, solenoid coils offer high efficiency and compact design, making them ideal for space-constrained environments. However, their use is mostly limited to linear motion applications, which may not suit all operational needs.
How Do Inductor Coils Function in B2B Applications?
Inductor coils serve as passive components that store energy in a magnetic field, effectively opposing sudden changes in current. They find extensive use in power supplies and filtering applications across various industries. B2B buyers should consider inductor coils for their superior energy storage capabilities. However, they can be bulkier and more expensive than other coil types, which may impact budget and space considerations.
What Makes Voice Coils Essential for Audio Equipment?
Voice coils are specialized windings attached to speaker cones, essential for converting electrical signals into sound waves. They are widely utilized in audio equipment and loudspeakers, making them crucial for businesses in the entertainment and sound engineering sectors. While voice coils provide high-fidelity sound reproduction, buyers must be mindful of their sensitivity to heat and potential overload, which can affect durability and performance.
Why Choose Air Core Coils for RF Applications?
Air core coils are distinct for their lack of a magnetic core, relying on air insulation. They are particularly suitable for RF applications and inductive sensing technologies. B2B buyers may appreciate their lightweight and low-cost attributes. However, it’s important to note that air core coils exhibit lower inductance compared to their core-based counterparts, which may limit their effectiveness in certain applications.
What are the Advantages of Closed Core Coils in Industrial Use?
Closed core coils are wound on a magnetic core, forming a closed loop that significantly enhances magnetic efficiency. They are commonly used in transformers and inductors, making them vital for inductive charging applications. Buyers will benefit from their high efficiency and reduced magnetic leakage. However, the added weight and cost due to the core material should be factored into purchasing decisions, particularly in cost-sensitive projects.
Key Industrial Applications of electromagnetic coil
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Electromagnetic Coil | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Wireless Power Transfer (WPT) Systems | Enhances efficiency in electric vehicle charging | Ensure compatibility with existing systems and regulations |
| Manufacturing | Induction Heating Systems | Reduces energy consumption and improves processing speed | Look for suppliers with certifications for safety and efficiency |
| Electronics | Transformers for Power Supply Units | Ensures stable voltage and current for devices | Consider the core material and winding techniques used |
| Medical Devices | Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Equipment | Provides high-quality imaging for diagnostics | Verify compliance with medical standards and reliability |
| Renewable Energy | Wind Turbine Generators | Increases energy output and system efficiency | Evaluate the environmental conditions of the installation site |
How Are Electromagnetic Coils Used in Automotive WPT Systems?
In the automotive sector, electromagnetic coils are integral to wireless power transfer (WPT) systems, which enable efficient charging of electric vehicles (EVs). By creating a magnetic field that induces current in a receiver coil, these systems eliminate the need for physical connectors, enhancing user convenience. For international buyers, especially from regions like Africa and South America where EV infrastructure is developing, sourcing high-quality electromagnetic coils that meet local standards for safety and efficiency is critical. Buyers should consider the coil’s compatibility with various EV models and the efficiency ratings of the WPT system.
What Role Do Electromagnetic Coils Play in Induction Heating Systems?
In manufacturing, electromagnetic coils are utilized in induction heating systems to heat materials rapidly and efficiently. These systems generate heat directly within the workpiece, resulting in faster processing times and reduced energy consumption. For buyers, particularly in Europe and the Middle East, it is essential to source coils that provide consistent heating performance and are compliant with energy efficiency regulations. Additionally, understanding the specific power requirements and thermal management needs of the induction system is crucial for optimal performance.
How Are Electromagnetic Coils Used in Power Supply Transformers?
Electromagnetic coils are foundational in transformers used in power supply units, ensuring a stable voltage and current supply for various electronic devices. By transforming high voltage to low voltage, these coils protect sensitive electronics from damage while ensuring efficient operation. For B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Germany, sourcing transformers requires attention to the core material and winding techniques, which significantly impact efficiency and heat generation. It’s also important to consider the transformer’s size and weight, especially for applications with space constraints.
What Is the Importance of Electromagnetic Coils in MRI Equipment?
In the medical field, electromagnetic coils are essential components of MRI machines, providing the necessary magnetic fields for high-resolution imaging. These coils must be designed to meet stringent medical standards for reliability and safety, which is a significant consideration for buyers in Africa and the Middle East, where healthcare infrastructure is rapidly evolving. Ensuring that suppliers comply with international medical device regulations and can offer robust after-sales support is critical for maintaining operational efficiency and patient safety.
How Do Electromagnetic Coils Enhance Wind Turbine Generators?
In renewable energy applications, particularly wind energy, electromagnetic coils are used in generators to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy efficiently. The effectiveness of these coils directly impacts the energy output of the turbine, making it essential for buyers to focus on sourcing high-performance coils that can withstand harsh environmental conditions. Buyers from regions with significant wind energy potential should evaluate the coil’s durability and efficiency ratings, as well as the supplier’s experience in the renewable energy sector to ensure long-term reliability and performance.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘electromagnetic coil’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Sourcing High-Quality Electromagnetic Coils
The Problem:
B2B buyers, especially those in industries reliant on electromagnetic coils—such as automotive, manufacturing, and electronics—often struggle with sourcing high-quality coils that meet specific application requirements. In regions like Africa and South America, limited access to reputable suppliers can lead to the procurement of subpar coils, resulting in equipment failures, increased maintenance costs, and production delays. Furthermore, the risk of counterfeit products complicates the selection process, leaving buyers uncertain about quality assurance and reliability.
The Solution:
To overcome these challenges, B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing from established manufacturers with a proven track record in electromagnetic coil production. It is essential to conduct thorough research and verify certifications such as ISO 9001, which ensures quality management systems are in place. Engaging with industry-specific forums or networks can also help buyers identify reliable suppliers. Additionally, consider requesting samples or prototypes before placing bulk orders, enabling you to evaluate performance firsthand. Utilizing platforms that aggregate supplier reviews can also guide buyers toward reputable sources, ultimately ensuring the procurement of high-quality electromagnetic coils.
Scenario 2: Complex Specifications Leading to Miscommunication
The Problem:
Electromagnetic coils come with a myriad of specifications, including inductance values, resistance, and core materials, which can be overwhelming for B2B buyers. Miscommunication regarding these specifications between engineers and procurement teams often leads to the ordering of unsuitable products. For instance, a buyer in the Middle East may specify an air core coil for a high-frequency application, not realizing that a ferrite core coil would be more appropriate, resulting in inefficiencies and potential project failures.
The Solution:
To mitigate specification-related issues, B2B buyers should foster a collaborative environment between engineering and procurement teams. Establishing clear communication channels and using standardized terminology can significantly reduce misunderstandings. It is advisable to create a detailed specification document that includes all relevant parameters, such as expected operating conditions and environmental factors. Furthermore, involving suppliers early in the design process can provide valuable insights into the most suitable coil types for specific applications. Training sessions or workshops on electromagnetic coil technologies can also empower procurement teams to make informed decisions, ensuring alignment with engineering requirements.
Scenario 3: Performance Issues Due to Inadequate Testing
The Problem:
In many cases, B2B buyers face performance-related issues with electromagnetic coils due to inadequate testing and validation before deployment. This is particularly prevalent in sectors like renewable energy and telecommunications, where electromagnetic coils are critical for system efficiency. Buyers may find that coils fail to operate as expected under real-world conditions, leading to costly downtimes and a negative impact on overall productivity.
The Solution:
To address performance concerns, B2B buyers must implement rigorous testing protocols before integrating electromagnetic coils into their systems. This includes both laboratory testing and real-world simulations to evaluate the coils under various operational conditions. Collaborating with suppliers who offer comprehensive testing services can enhance confidence in product reliability. Additionally, investing in advanced testing equipment or partnering with third-party testing facilities can provide objective validation of coil performance. Establishing a feedback loop with suppliers post-deployment allows for continuous improvement and adjustments based on operational data, ensuring that coils perform optimally in their intended applications.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for electromagnetic coil
What Are the Key Materials for Electromagnetic Coils?
When selecting materials for electromagnetic coils, it’s essential to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and how they align with specific applications. Here, we analyze four common materials: copper, aluminum, ferrite, and silicon steel.
How Does Copper Perform in Electromagnetic Coils?
Key Properties: Copper is known for its excellent electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and resistance to corrosion. It typically operates efficiently at temperatures up to 200°C and can handle moderate pressure.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of copper is its high conductivity, which allows for efficient energy transfer and minimal energy loss. However, copper is relatively expensive compared to other materials, and its weight can be a disadvantage in applications requiring lightweight components.
Impact on Application: Copper coils are ideal for applications where high efficiency is crucial, such as in transformers and inductors. However, they may not be suitable for environments with high humidity or corrosive elements unless adequately insulated.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should consider the availability of copper and the associated costs. Compliance with standards such as ASTM B170 for copper wire may also be necessary, especially in Europe.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Electromagnetic Coil Design?
Key Properties: Aluminum offers good electrical conductivity, though not as high as copper. It is lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and can operate effectively at temperatures up to 150°C.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of aluminum is its low cost and lightweight nature, making it suitable for applications where weight is a concern. However, its lower conductivity means that larger gauge wires may be necessary, which can complicate manufacturing.
Impact on Application: Aluminum coils are often used in applications where weight and cost are critical, such as in automotive and aerospace sectors. However, they may not perform as efficiently as copper coils in high-power applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the different aluminum grades and their compliance with standards like DIN EN 60228. This is particularly relevant for European buyers focused on quality and performance.
Why Are Ferrite Materials Important for Electromagnetic Coils?
Key Properties: Ferrite cores are made from ferrimagnetic ceramic compounds that provide high magnetic permeability and low electrical conductivity. They are effective at high frequencies, typically operating well in temperatures up to 130°C.
Pros & Cons: Ferrite cores significantly reduce core losses and improve efficiency in high-frequency applications. However, they can be brittle and may require careful handling during manufacturing.
Impact on Application: Ferrite coils are commonly used in high-frequency transformers and inductors, particularly in telecommunications and RF applications. Their ability to minimize energy loss makes them suitable for energy-efficient designs.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as JIS C 2550 is crucial for buyers in Japan and other regions. Additionally, understanding the specific ferrite material grades is essential for ensuring compatibility with application requirements.
How Does Silicon Steel Enhance Electromagnetic Coils?
Key Properties: Silicon steel is a ferromagnetic material that enhances magnetic properties while reducing energy losses. It can operate effectively at temperatures up to 200°C and has excellent mechanical strength.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of silicon steel is its high magnetic permeability, which improves the efficiency of electromagnetic coils. However, it can be more expensive than other materials and may require complex manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application: Silicon steel is commonly used in power transformers and large inductors where efficiency is paramount. Its properties make it suitable for applications requiring high magnetic flux density.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must ensure compliance with international standards such as IEC 60404 for magnetic materials. This is particularly important for buyers in Europe, where regulatory compliance is strictly enforced.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Electromagnetic Coils
| Material | Typical Use Case for Electromagnetic Coil | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | High-efficiency transformers | Excellent electrical conductivity | Higher cost and weight | High |
| Aluminum | Automotive and aerospace applications | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower conductivity requires larger gauge | Medium |
| Ferrite | High-frequency transformers | Low core losses at high frequencies | Brittle and requires careful handling | Medium |
| Silicon Steel | Power transformers and large inductors | High magnetic permeability | More expensive and complex manufacturing | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides international B2B buyers with actionable insights into the properties, advantages, and considerations necessary for making informed decisions in their electromagnetic coil applications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for electromagnetic coil
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Electromagnetic Coils?
The manufacturing process for electromagnetic coils involves several critical stages, each essential for ensuring the final product meets the required specifications. Here’s a breakdown of the main stages:
Material Preparation
The first step in manufacturing electromagnetic coils is selecting the appropriate materials. Common materials include copper or aluminum wire for the winding and ferromagnetic cores made from ferrite or silicon steel. The choice of materials directly impacts the coil’s efficiency, inductance, and thermal performance.
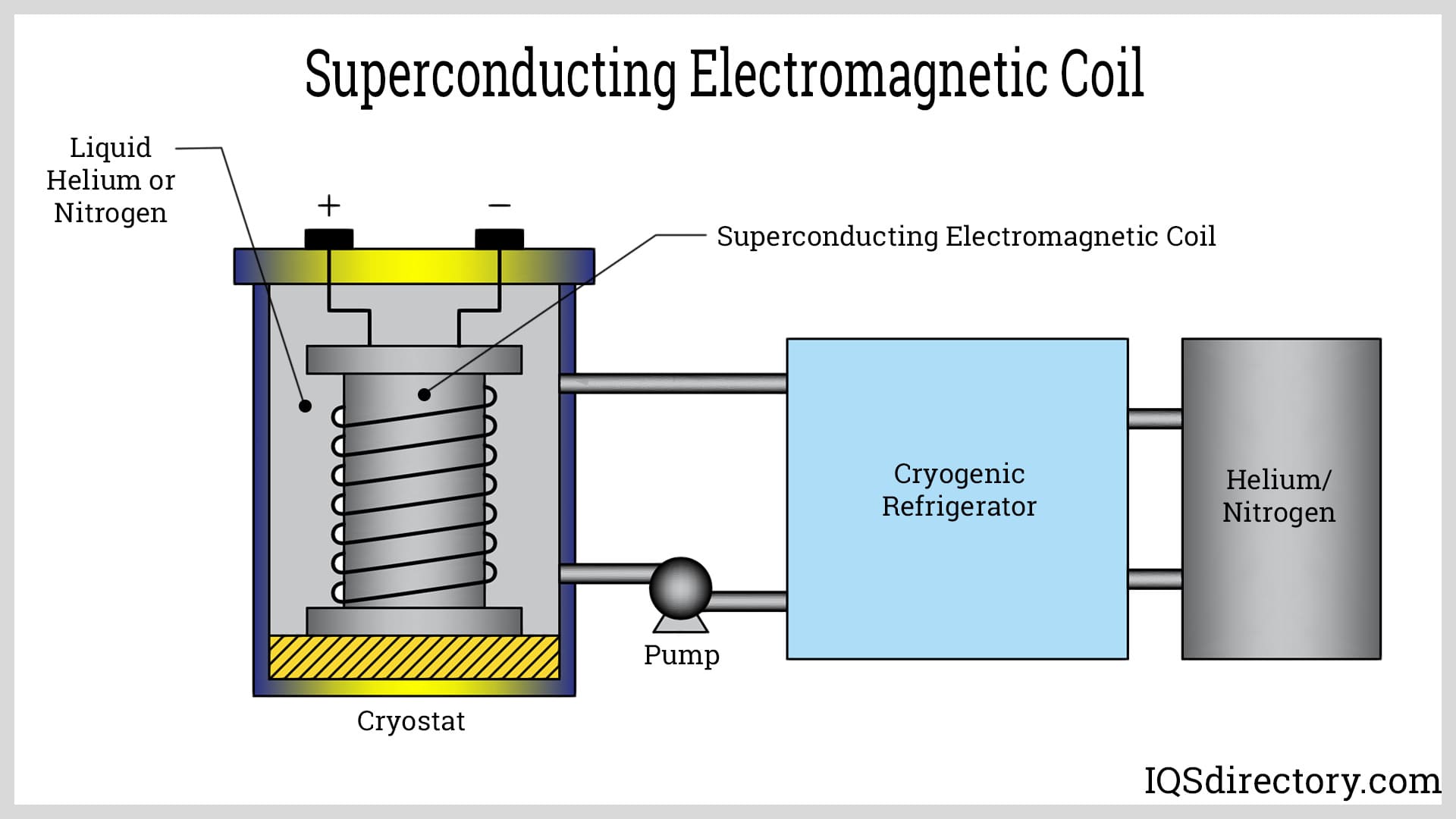
A stock image related to electromagnetic coil.
Once selected, the wires are prepped by cutting them to the desired length and removing any insulation. Additionally, the cores may undergo processes such as heat treatment to enhance their magnetic properties.
Forming the Coil
The forming stage involves winding the prepared wire around the magnetic core. This can be achieved using automated winding machines, which ensure precision in the number of turns and tension applied to the wire. The type of coil configuration—such as toroidal, solenoid, or multilayer—will depend on the intended application and performance requirements.
In this stage, manufacturers may also employ techniques like multi-layer winding to increase the coil’s inductance and performance. Attention to detail during this phase is crucial, as uneven winding can lead to performance issues and inefficiencies.
Assembly of Components
After forming, the next step is the assembly of the coil with other components, such as connectors or housing. This may involve soldering, crimping, or using adhesives to secure the connections. During assembly, manufacturers must ensure that the components are compatible and that the coil is properly insulated to prevent short circuits.
Quality control begins at this stage, where each assembly is checked for any defects that could compromise performance.
Finishing Processes
The final stage in the manufacturing process involves finishing techniques that enhance the coil’s durability and performance. This may include processes such as electroplating to improve corrosion resistance, encapsulation to protect against environmental factors, and insulation coating to enhance safety.
Manufacturers often conduct final inspections to ensure that the coils meet all specifications and performance criteria before packaging for shipment.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Electromagnetic Coil Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in the manufacturing of electromagnetic coils, ensuring that products meet international standards and specific industry requirements. Here’s how QA is typically structured:
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
B2B buyers must be aware of several international quality standards when sourcing electromagnetic coils:
- ISO 9001: This is a widely recognized quality management standard that ensures organizations consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- CE Marking: Essential for products sold in the European market, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For coils used in oil and gas applications, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is crucial for safety and reliability.
Understanding these standards helps buyers evaluate potential suppliers and ensure that their products are compliant with necessary regulations.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control in electromagnetic coil manufacturing typically involves several checkpoints, including:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint assesses the quality of raw materials before they enter the production process. Suppliers must provide certification for materials, which should be verified against industry standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During production, regular inspections are performed to monitor the winding process, assembly, and finishing stages. This ensures any defects are caught early, reducing waste and ensuring high quality.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly and finishing, a final inspection is conducted. This may include electrical testing, visual inspections, and performance assessments to verify that the coil meets all specifications.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Electromagnetic Coils?
Various testing methods are employed to ensure electromagnetic coils perform as expected:
-
Electrical Testing: This includes checking resistance, inductance, and insulation resistance to ensure the coil functions correctly under operational conditions.
-
Thermal Testing: Coils are subjected to temperature variations to assess performance under different thermal conditions. This is critical for applications where coils may be exposed to high heat.
-
Mechanical Testing: This involves assessing the mechanical integrity of the coil, ensuring it can withstand vibrations and physical stress during operation.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, verifying the quality control processes of potential suppliers is essential. Here are several strategies to ensure quality:
-
Conducting Supplier Audits: Periodic audits of suppliers can help verify compliance with quality standards and processes. Buyers should establish a checklist based on ISO and industry-specific standards to evaluate their suppliers effectively.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation regarding their quality control processes, including any certifications obtained and results from testing. This transparency helps build trust and accountability.
-
Engaging Third-Party Inspection Services: Utilizing third-party inspectors can provide an unbiased assessment of the manufacturing process and final products. This is particularly useful for buyers in regions with different compliance standards, such as Africa and South America.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate various quality control nuances when sourcing electromagnetic coils:
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding the local culture can impact communication and expectations regarding quality. Buyers should be aware of how different regions prioritize quality assurance and manufacturing practices.
-
Regulatory Variability: Compliance requirements can differ significantly between regions. Buyers from Europe may have stricter regulations compared to those in Africa or South America, so it’s essential to ensure that suppliers are aware of and compliant with the relevant standards in the buyer’s region.
-
Supply Chain Transparency: Establishing a transparent supply chain is crucial for maintaining quality. Buyers should work closely with suppliers to understand their sourcing of materials and the manufacturing processes involved.
By focusing on these aspects, international B2B buyers can ensure they are sourcing high-quality electromagnetic coils that meet their specific needs and comply with global standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘electromagnetic coil’
The following guide provides a structured approach for international B2B buyers looking to procure electromagnetic coils. This step-by-step checklist will ensure that you make informed decisions that align with your technical requirements and business objectives.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is crucial for selecting the right electromagnetic coil for your application. Consider the coil type (e.g., solenoid, inductor, or voice coil), wire gauge, number of turns, and the desired inductance or resistance values. Additionally, determine the operational environment—temperature, humidity, and exposure to chemicals can significantly influence performance.
Step 2: Identify Your Application Requirements
Different applications demand different electromagnetic coil characteristics. Whether for automotive, industrial, or consumer electronics, understanding your specific application will help narrow down your options. For instance, consider:
– Power requirements: AC vs. DC operation.
– Magnetic field strength: Required for effective operation.
– Size constraints: Ensure the coil fits within your design specifications.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct thorough evaluations to ensure they meet your quality and reliability standards. Request documentation such as company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries. Pay attention to:
– Experience: Suppliers with extensive experience in your sector may better understand your unique needs.
– Quality certifications: Look for ISO certifications or other relevant quality standards.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
It’s essential to verify that your potential suppliers hold relevant industry certifications. Certifications ensure that the supplier adheres to quality management standards and can consistently deliver reliable products. Common certifications to look for include:
– ISO 9001: Indicates a quality management system.
– RoHS Compliance: Ensures that the materials used are free from hazardous substances.
Step 5: Request Prototypes or Samples
Before finalizing your order, request prototypes or samples of the electromagnetic coils. Testing these samples in your application can help identify any potential issues before mass production. Evaluate the coils based on:
– Performance: Does it meet your specifications under real-world conditions?
– Durability: Assess how well the coil withstands environmental factors.
Step 6: Discuss Pricing and Payment Terms
Once you have identified a suitable supplier, engage in discussions regarding pricing and payment terms. Understanding the total cost of ownership is vital, which includes not just the purchase price but also shipping costs, tariffs, and potential import duties. Negotiate payment terms that align with your cash flow needs, such as:
– Advance payments: Often required for custom orders.
– Net terms: Discuss payment timelines that work for both parties.
Step 7: Establish Clear Communication Channels
Effective communication is critical throughout the procurement process. Establish clear channels for updates on order status, shipping, and any potential issues. Regular communication can help mitigate misunderstandings and ensure timely delivery of your electromagnetic coils. Consider:
– Dedicated account managers: They can provide personalized support.
– Regular status updates: Set expectations for how often you’ll receive updates during the order process.
By following this checklist, international B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing electromagnetic coils and ensure they make decisions that positively impact their operations.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for electromagnetic coil Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components of Electromagnetic Coil Sourcing?
Understanding the cost structure of electromagnetic coils is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts pricing. Commonly used materials like copper and ferrite can fluctuate in price due to market conditions. For instance, copper prices are subject to global demand, while ferrite costs depend on the manufacturing process and purity levels required.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region. Countries with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but this could also reflect the skill level and quality of workmanship. For buyers in regions like Africa or South America, sourcing from local manufacturers can reduce labor costs but may require careful vetting for quality assurance.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative expenses. Buyers should inquire about these overheads, as they can vary significantly between suppliers and impact the final pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific coil designs can be a significant upfront cost. Buyers should consider whether the supplier has the necessary tooling capabilities for their requirements, as this can affect lead times and pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing robust QC processes ensures that coils meet specific standards, which can add to costs. Suppliers with certifications (like ISO 9001) often have higher QC costs, but they provide assurance of product reliability.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs are essential factors, especially for international transactions. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and customs duties can significantly affect total costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding the competitive landscape can help buyers assess whether the offered margin is justified.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Electromagnetic Coil Pricing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of electromagnetic coils:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often lead to reduced per-unit costs. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their needs to capitalize on volume discounts.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specific performance specifications can increase costs. Buyers should clearly communicate their requirements to avoid unexpected price increases.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials or those with industry certifications can lead to increased prices. However, investing in quality can reduce long-term operational costs due to enhanced performance and reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer better quality assurance and customer service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for international buyers. They dictate who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly impact total costs.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Their Sourcing Strategy?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, here are actionable tips to optimize sourcing:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Leverage your position as a buyer to negotiate better terms. Discuss volume discounts, payment terms, and delivery schedules to create a win-win situation.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but also installation, maintenance, and operational costs. A cheaper initial price may lead to higher TCO if the product has lower reliability or requires frequent replacement.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences. For example, sourcing from Europe may have higher initial costs but potentially lower logistics and compliance costs compared to sourcing from Asia.
-
Conduct Supplier Assessments: Before finalizing a supplier, conduct thorough assessments to ensure they meet quality standards and can deliver on time. This can save costs associated with poor-quality products or delays.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for electromagnetic coils can vary widely based on the factors mentioned above. It is crucial for buyers to conduct their own market research and obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure they receive competitive pricing tailored to their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing electromagnetic coil With Other Solutions
Understanding the Importance of Alternative Solutions for Electromagnetic Coils
When considering electromagnetic coils for various applications, it’s crucial to evaluate alternative technologies that can meet similar needs. This analysis helps international B2B buyers identify the most effective and economical solutions tailored to their specific requirements. By comparing electromagnetic coils with other viable alternatives, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals.
Comparison Table of Electromagnetic Coils and Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Electromagnetic Coil | Inductive Sensors | Permanent Magnets |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency for energy storage and conversion; excellent for AC applications | Good for position sensing, but may have lower accuracy over distance | Excellent static magnetic field, but limited in dynamic applications |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment with ongoing maintenance costs | Generally lower initial cost but may require calibration | Lower long-term cost due to no power requirement |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires careful design and installation, particularly for power applications | Easier to install; often plug-and-play solutions | Simple installation but may need specific arrangements for application |
| Maintenance | Requires regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance | Low maintenance, but calibration may be needed | Virtually maintenance-free |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for energy transformation in motors, transformers, and inductors | Best suited for position sensing and proximity applications | Effective in applications requiring a consistent magnetic field without power |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What are Inductive Sensors and How Do They Compare?
Inductive sensors are electronic devices that use electromagnetic fields to detect the presence of metallic objects. They are particularly effective in automation and industrial applications. One of the main advantages of inductive sensors is their ease of installation; they often come as ready-to-use modules, reducing the complexity typically associated with electromagnetic coils. However, their performance can diminish with distance, making them less suitable for applications requiring precise control or long-range detection.
How Do Permanent Magnets Function in Comparison?
Permanent magnets generate a consistent magnetic field without the need for an external power source. This characteristic makes them advantageous for applications where energy efficiency is crucial. The installation of permanent magnets is straightforward, and they typically require no maintenance, leading to lower long-term costs. However, their static nature limits their use in dynamic applications where variable magnetic fields are required, such as in motors and transformers.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate technology for your application involves assessing various factors, including performance requirements, cost considerations, and maintenance capabilities. For applications demanding dynamic control and energy transformation, electromagnetic coils are typically the best choice. In contrast, if your needs lean toward static magnetic fields or simplified sensor installations, inductive sensors or permanent magnets may be more suitable. By understanding these alternatives and their unique attributes, B2B buyers can make strategic decisions that enhance operational efficiency and effectiveness in their respective markets.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for electromagnetic coil
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Electromagnetic Coils?
Understanding the essential technical properties of electromagnetic coils is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure compatibility and performance in their applications. Here are some key specifications:
1. Material Grade
The material used in electromagnetic coils, typically copper or aluminum, significantly affects conductivity and overall performance. Copper coils are preferred for high-efficiency applications due to their superior conductivity, while aluminum offers a lightweight alternative. Buyers should assess the material grade based on their application requirements and cost considerations.
2. Inductance Value
Inductance, measured in henries (H), defines a coil’s ability to store energy in a magnetic field. It is crucial for applications such as transformers and inductors. Higher inductance values generally indicate greater energy storage capacity, which can be critical in power supply designs. B2B buyers must ensure the inductance meets the specific needs of their electrical circuits.
3. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible deviation in inductance values, typically expressed as a percentage. A lower tolerance indicates higher precision, which is essential in applications where exact inductance is required, such as in RF circuits. Buyers should consider tolerance levels to ensure product reliability and performance consistency.
4. Core Type
The type of core used (ferrite, air, or laminated steel) plays a vital role in the performance of electromagnetic coils. Ferrite cores are preferred for high-frequency applications due to lower core losses, while air cores are used in high-frequency inductors. Understanding core types helps buyers select coils that minimize energy losses and optimize efficiency.
5. Operating Temperature Range
The operating temperature range indicates the conditions under which the coil can function effectively without degradation. Coils with a wider temperature range are suitable for diverse environments, making them versatile for various industries. B2B buyers should evaluate the operating temperature specifications against their application environments.
6. Wire Gauge
The gauge of wire used in the coil winding affects both the resistance and current-carrying capacity. Thicker wire (lower gauge number) can handle higher currents, making it suitable for applications requiring higher power. Buyers should select wire gauge based on electrical load requirements and thermal management considerations.
Which Trade Terminology Should B2B Buyers Understand?
Familiarity with industry-specific terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation. Here are some common terms relevant to electromagnetic coils:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM produces components that are used in another company’s final product. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for buyers to ensure quality and compatibility of electromagnetic coils within their systems.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the minimum number of units a supplier requires a buyer to purchase. This term is vital for budget planning and inventory management, especially for international buyers who may face different MOQ standards across suppliers.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products. For B2B buyers, issuing an RFQ for electromagnetic coils can help compare pricing, lead times, and terms from various manufacturers, aiding in informed decision-making.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized shipping terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Understanding these terms helps B2B buyers navigate shipping costs, risks, and insurance arrangements effectively.
5. Tolerance Specification
This term refers to the acceptable range of variation in product specifications. Knowledge of tolerance specifications is essential for ensuring that the purchased coils meet the required performance standards in their applications.
6. Lead Time
Lead time is the period between placing an order and receiving the product. For B2B buyers, understanding lead times for electromagnetic coils is crucial for project planning and ensuring that production schedules are met.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring the selection of the right electromagnetic coils for their specific needs and applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the electromagnetic coil Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Electromagnetic Coil Sector?
The electromagnetic coil market is experiencing significant transformation driven by technological advancements and increasing demand across various sectors, including automotive, telecommunications, and renewable energy. One of the key drivers is the rise of electric vehicles (EVs) and the growing need for efficient power management systems. This trend is particularly pronounced in regions like Europe, where stringent emissions regulations are pushing manufacturers towards electric solutions. In Africa and South America, the adoption of renewable energy sources is catalyzing the need for electromagnetic coils in energy storage systems and smart grid technologies.
International B2B buyers should also pay attention to emerging sourcing trends such as the shift towards localized supply chains. Companies are increasingly seeking suppliers within their regions to mitigate risks associated with global supply chain disruptions, which were highlighted during the COVID-19 pandemic. In the Middle East, there is a growing emphasis on investing in local manufacturing capabilities, which presents opportunities for international buyers to forge partnerships with regional suppliers.
Furthermore, as industries evolve, there is a notable shift towards the integration of smart technology into electromagnetic coils. Innovations such as wireless power transfer (WPT) systems and advanced sensing capabilities are becoming more prevalent, enhancing the functionality and efficiency of coils. Buyers looking to invest in electromagnetic coils should focus on suppliers that offer cutting-edge technology and can adapt to the rapid pace of change in this sector.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Be Integrated into Electromagnetic Coil Procurement?

A stock image related to electromagnetic coil.
The environmental impact of manufacturing electromagnetic coils is a significant concern for B2B buyers today. The production processes often involve materials that can be harmful to the environment, such as certain metals and plastics. Consequently, there is a pressing need for suppliers to adopt sustainable practices, including the use of recycled materials and energy-efficient manufacturing processes. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability by providing transparent information about their sourcing practices.
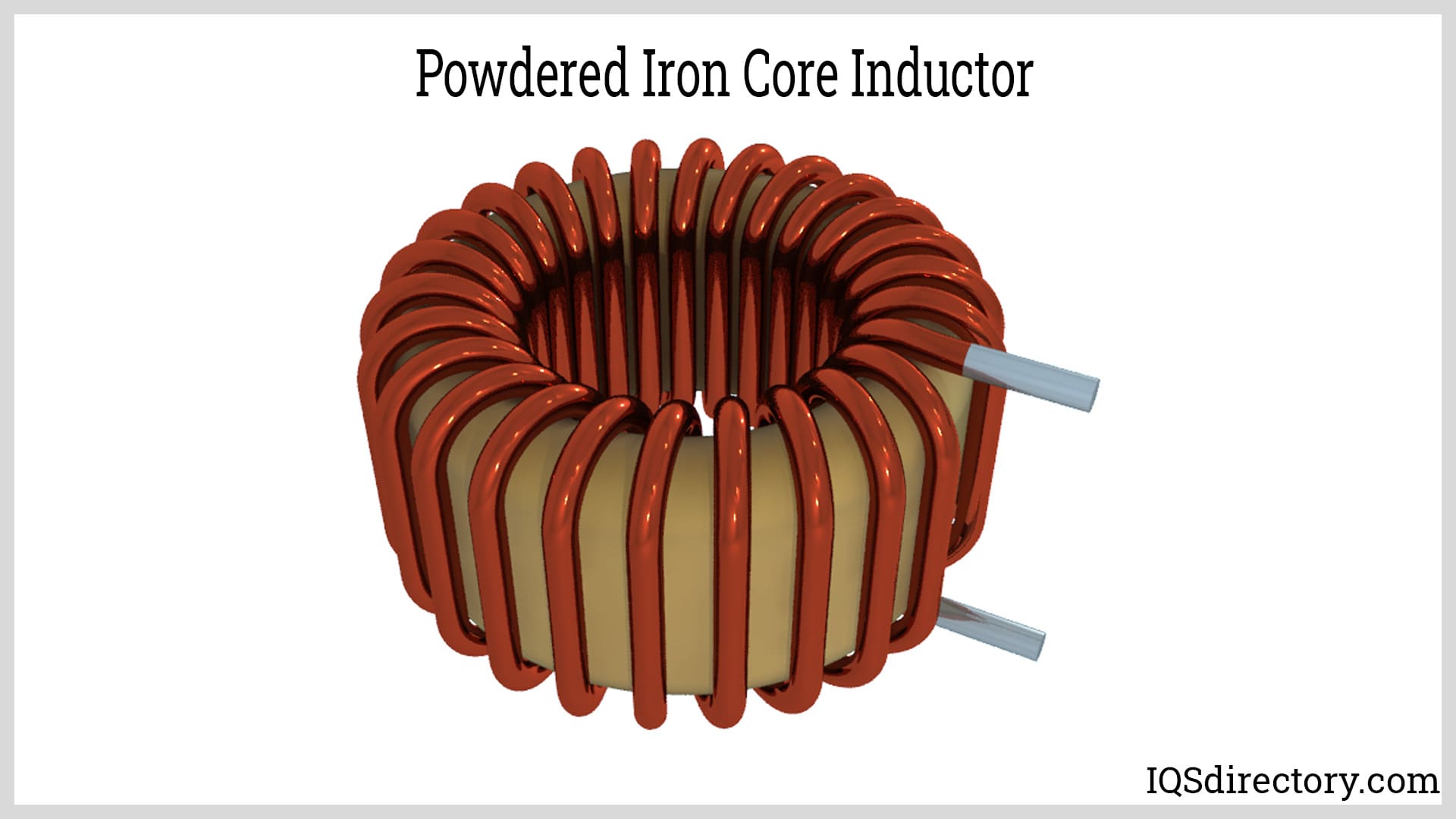
A stock image related to electromagnetic coil.
Ethical sourcing is not only about minimizing environmental impact; it also encompasses the social responsibility of suppliers. Companies that adhere to ethical labor practices and ensure fair treatment of workers contribute to a more sustainable supply chain. Buyers in regions like Europe, where corporate social responsibility is increasingly prioritized, should seek partnerships with manufacturers that hold recognized certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management or Fair Trade certifications.
Moreover, the trend towards ‘green’ certifications is gaining traction. Suppliers offering products made from eco-friendly materials or that have undergone environmentally friendly manufacturing processes can provide a competitive advantage in the marketplace. As B2B buyers become more conscious of their supply chain’s environmental footprint, choosing suppliers that align with these values will be critical for long-term success.
What Is the Historical Context of Electromagnetic Coils in B2B Applications?
The history of electromagnetic coils dates back to the early 19th century, with the foundational principles established by physicists such as Michael Faraday and Joseph Henry. These pioneers laid the groundwork for understanding electromagnetism, leading to the development of inductors and transformers that are integral to modern electrical engineering.
Over the decades, electromagnetic coils have evolved from simple components used in basic electrical circuits to complex devices essential for advanced applications, including telecommunications and industrial automation. The introduction of digital technologies in the late 20th century further revolutionized coil applications, paving the way for innovations like smart sensors and wireless power systems.
For B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is crucial. It highlights the importance of selecting suppliers who not only offer current technologies but also possess a deep understanding of the historical context and future potential of electromagnetic coils, ensuring they remain at the forefront of innovation in a rapidly changing market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of electromagnetic coil
-
How do I choose the right electromagnetic coil for my application?
Choosing the right electromagnetic coil involves understanding your specific application requirements, including voltage, current, frequency, and the desired magnetic field strength. Consider whether you need a solenoid, inductor, or transformer coil based on the functionality required. Additionally, evaluate the core material (ferrite, air, etc.) that best suits your operational frequency and efficiency needs. Consulting with manufacturers about your unique specifications can ensure you select a coil that meets all operational criteria effectively. -
What types of electromagnetic coils are commonly used in industrial applications?
The most common types of electromagnetic coils in industrial applications include solenoid coils, inductor coils, and voice coils. Solenoid coils are used for linear motion applications, while inductors are crucial for energy storage and filtering in circuits. Voice coils are specifically used in audio equipment to convert electrical signals into sound. Understanding the specific role each type plays in your application will help you make informed purchasing decisions. -
What are the key factors to consider when vetting suppliers of electromagnetic coils?
When vetting suppliers, consider their manufacturing capabilities, quality certifications (such as ISO 9001), and industry experience. Request samples to evaluate the quality of their coils and ensure they meet your specifications. It’s also crucial to check customer reviews and case studies to gauge reliability and service. Establishing clear communication and understanding their lead times and support services will also aid in choosing the right supplier for your needs. -
What minimum order quantities (MOQ) should I expect when sourcing electromagnetic coils?
Minimum order quantities for electromagnetic coils can vary significantly among suppliers. Generally, MOQs can range from a few hundred units to several thousand, depending on the complexity of the coil and the manufacturer’s production capabilities. If you require lower quantities, consider negotiating with suppliers or exploring manufacturers that specialize in custom orders. Understanding your own usage rates will help you make a more informed decision regarding MOQs. -
How can I customize electromagnetic coils to fit my specific needs?
Customizing electromagnetic coils typically involves collaborating with manufacturers to specify parameters such as size, wire gauge, core material, and winding configuration. Providing detailed specifications and application contexts can help manufacturers design coils tailored to your needs. Be prepared to discuss testing and validation processes to ensure the customized coils meet your performance standards before finalizing production. -
What payment terms should I negotiate with suppliers for electromagnetic coils?
Payment terms can vary by supplier, but common practices include upfront deposits, net 30/60/90 days, or payment upon delivery. Consider negotiating terms that align with your cash flow and project timelines. It’s wise to establish a secure payment method and include clauses for quality assurance and returns in your agreements. Understanding the supplier’s payment policies can help prevent misunderstandings and build a strong working relationship. -
How do I ensure quality assurance when purchasing electromagnetic coils internationally?
To ensure quality assurance, request certifications and quality control documentation from suppliers. Implement a pre-shipment inspection process to verify that coils meet your specifications. Collaborating with third-party inspection services can provide additional assurance, especially for international shipments. Establishing clear quality standards upfront and maintaining open communication throughout the process will help mitigate risks related to product quality. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing electromagnetic coils?
Logistics considerations include selecting the right shipping method (air vs. sea), understanding import regulations in your country, and ensuring that suppliers provide necessary shipping documentation. Factor in lead times for production and shipping, and plan for customs clearance to avoid delays. Additionally, consider the packaging to prevent damage during transit. Working with a reliable logistics partner can streamline the import process and ensure timely delivery of your coils.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for electromagnetic coil
What Are the Key Takeaways for International B2B Buyers of Electromagnetic Coils?
Strategic sourcing of electromagnetic coils is essential for B2B buyers aiming to enhance their product offerings while ensuring cost efficiency. Understanding the different types of coils—such as solenoids, inductors, and voice coils—enables buyers to select the most suitable components for their specific applications. Prioritizing suppliers who utilize high-quality materials like ferrite can significantly improve performance and reliability, especially in demanding environments common in markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Improve Your Supply Chain?
By adopting a strategic sourcing approach, businesses can foster long-term partnerships with manufacturers who are adept in producing electromagnetic coils tailored to their needs. This not only streamlines procurement processes but also enhances innovation through collaborative development efforts. Buyers should evaluate suppliers based on their production capabilities, certifications, and responsiveness to market trends.
What’s Next for B2B Buyers in the Electromagnetic Coil Market?
Looking ahead, as technology advances and industries evolve, the demand for sophisticated electromagnetic coils is expected to grow. B2B buyers should stay informed about emerging trends and technologies, such as wireless power transfer and smart sensors, which leverage electromagnetic coils for enhanced functionality. Engage with suppliers who can provide insights and adapt to these changes, ensuring your business remains competitive and future-ready.