Discover the Best Solutions: Different Types of Bolts (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for different types of bolts
In the ever-evolving landscape of global manufacturing and construction, sourcing the right types of bolts can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers. With a diverse range of applications, from automotive to construction, understanding the specific requirements for bolts—such as material strength, threading, and size—becomes crucial for effective procurement. This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of bolts available in the market, their applications, and best practices for supplier vetting and cost considerations.
By addressing critical aspects of bolt selection, including the differences between hex bolts, carriage bolts, and specialty fasteners, this guide empowers buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to make informed purchasing decisions. Whether you are looking for fasteners that withstand harsh environments or those that meet stringent safety standards, the insights provided here will enhance your sourcing strategy.
Additionally, we will explore key factors to consider when evaluating suppliers, ensuring that you establish partnerships that align with your quality and cost objectives. This guide is designed to streamline your procurement process, reduce risks, and ultimately drive your business’s success in an increasingly competitive global market.
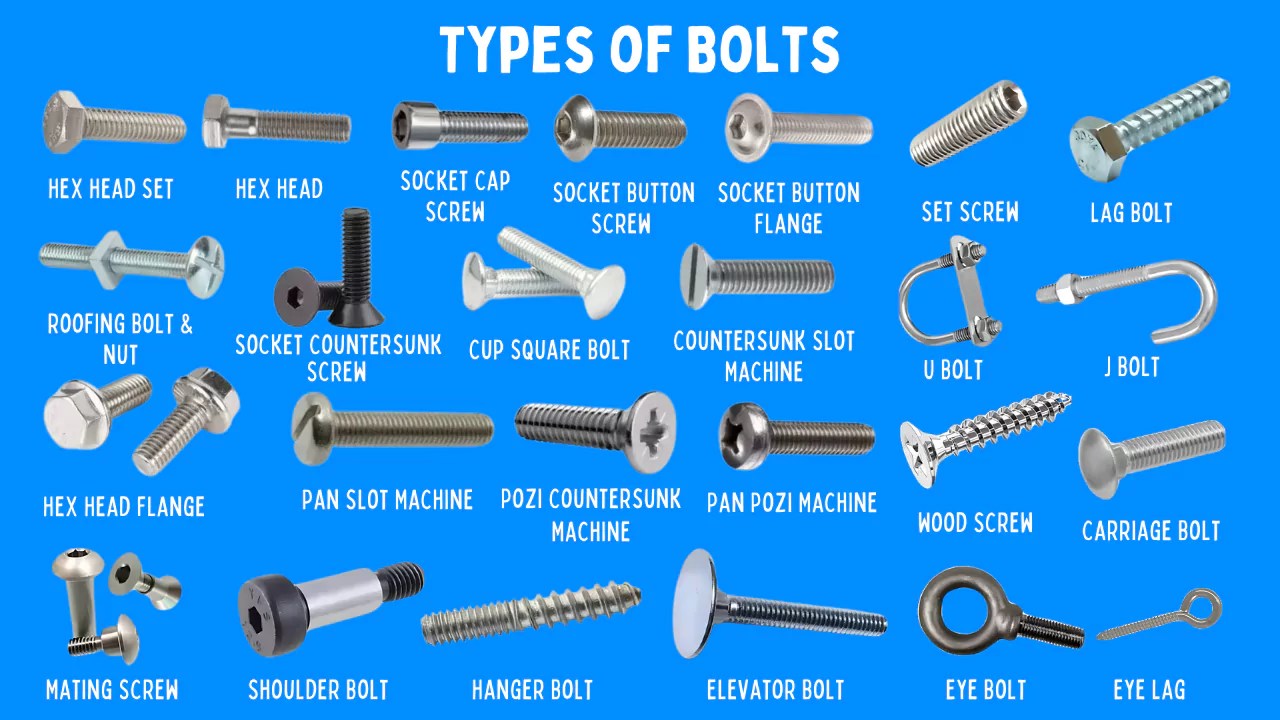
Understanding different types of bolts Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hex Bolts | Hexagonal head, external threads | Machinery, automotive, construction | Pros: High strength, easy to install. Cons: Requires a wrench, can loosen under vibration. |
| Carriage Bolts | Rounded head, square neck prevents rotation | Wood and metal structures, furniture | Pros: Smooth finish, ideal for soft materials. Cons: Limited to non-rotating applications. |
| Lag Bolts | Wood thread, pointed tip for easy driving | Wood construction, furniture assembly | Pros: Strong grip in wood, easy installation. Cons: Not suitable for metal applications. |
| Flange Bolts | Flange under the head acts like a built-in washer | Automotive, heavy machinery | Pros: Load distribution, reduces loosening. Cons: Higher cost due to additional features. |
| Eye Bolts | Circular ring at the head for attaching ropes or chains | Lifting, rigging, marine applications | Pros: Versatile for lifting, easy to use. Cons: Limited load capacity compared to other bolts. |
What are Hex Bolts and Their Applications?
Hex bolts are characterized by their hexagonal heads and external threads, making them suitable for various applications, especially in machinery and automotive sectors. These bolts provide high tensile strength and are designed for use with a nut or tapped hole. B2B buyers should consider the material and coating options, such as zinc-plated or stainless steel, to ensure corrosion resistance in specific environments. Proper installation practices, including torque specifications, are essential to prevent loosening due to vibration.
Why Choose Carriage Bolts?
Carriage bolts feature a rounded head and a square neck that prevents rotation, making them ideal for fastening wood and metal structures. Their smooth finish allows for a clean aesthetic, which is beneficial in furniture assembly. When purchasing carriage bolts, buyers should evaluate the length and diameter needed for their specific application, as well as the material to ensure durability. They are best suited for non-rotating applications where a flush finish is desired.
What Makes Lag Bolts Ideal for Wood Construction?
Lag bolts are designed with wood threads and a pointed tip, allowing for easy driving into wooden structures. They provide a strong grip, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications such as furniture assembly and construction. B2B buyers should ensure they select the correct size and length to match their project requirements. While they excel in wood applications, lag bolts are not recommended for use with metal, limiting their versatility.
How Do Flange Bolts Enhance Load Distribution?
Flange bolts come with a built-in flange that acts like a washer, distributing the load more evenly across the surface. This feature reduces the risk of loosening, making them particularly useful in automotive and heavy machinery applications. When sourcing flange bolts, buyers should consider the bolt’s strength rating and the specific load requirements of their application. While they may be more expensive than standard bolts, the benefits often outweigh the costs in critical applications.
What are the Benefits of Eye Bolts?
Eye bolts are designed with a circular ring at the head, making them ideal for attaching ropes or chains in lifting and rigging applications. Their versatility allows for use in various sectors, including marine and construction. B2B buyers should assess the load capacity and material of eye bolts to ensure they meet safety standards. While they offer ease of use and flexibility, their load capacity is typically lower compared to other bolt types, which should be considered in heavy-duty applications.
Key Industrial Applications of different types of bolts
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of different types of bolts | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Use of hex bolts in engine assembly and chassis construction | Ensures structural integrity and safety of vehicles | Material quality, corrosion resistance, and certification standards |
| Construction and Infrastructure | Application of lag bolts for securing wooden structures | Provides durable connections for safety and longevity | Load capacity, environmental conditions, and compliance with local regulations |
| Oil and Gas | Eye bolts for lifting and securing heavy equipment on rigs | Enhances safety during operations and maintenance | Load ratings, material specifications, and resistance to harsh environments |
| Aerospace | Use of shoulder bolts in aircraft assembly for pivot mechanisms | Critical for performance and safety of aircraft | Compliance with aerospace standards and traceability of materials |
| Electronics Manufacturing | Application of machine screws in assembling electronic devices | Ensures precision and reliability in device function | Thread specifications, material compatibility, and volume pricing for bulk orders |
How Are Different Types of Bolts Used in Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive sector, hex bolts are integral to engine assembly and chassis construction. These bolts provide the necessary strength and durability to withstand high-stress environments, ensuring vehicle safety and performance. International buyers should prioritize sourcing hex bolts that meet specific material quality standards and corrosion resistance, particularly in regions with diverse climates, such as Africa and South America. Additionally, certification standards must be adhered to in order to comply with safety regulations.
What Role Do Lag Bolts Play in Construction and Infrastructure?
Lag bolts are commonly used in construction to secure wooden structures, such as beams and frames. Their robust design provides a strong connection, essential for the safety and longevity of buildings. B2B buyers in the construction industry must consider the load capacity of lag bolts and their compatibility with local building codes. Furthermore, understanding the environmental conditions where the construction will take place is crucial, as it influences the choice of materials and finishes to prevent deterioration over time.
Why Are Eye Bolts Essential in the Oil and Gas Industry?
Eye bolts are utilized in the oil and gas industry for lifting and securing heavy equipment on drilling rigs. Their design allows for safe and efficient rigging, which is critical in high-risk environments. When sourcing eye bolts, businesses should focus on load ratings and material specifications to ensure they can withstand harsh conditions, such as extreme temperatures and corrosive substances. Additionally, compliance with industry safety standards is paramount to mitigate risks associated with equipment failure.
How Are Shoulder Bolts Critical in Aerospace Applications?
In aerospace manufacturing, shoulder bolts are often used in the assembly of aircraft, specifically in pivot mechanisms. These bolts are designed to allow for rotational movement while providing a secure connection, making them vital for aircraft performance and safety. International buyers must ensure that the shoulder bolts meet stringent aerospace standards and that there is traceability of materials used. This is particularly important for businesses in Europe and the Middle East, where regulatory compliance is strictly enforced.
What Are the Applications of Machine Screws in Electronics Manufacturing?
Machine screws are widely used in the assembly of electronic devices, where precision and reliability are key. They help secure components in place, ensuring the functionality of devices ranging from consumer electronics to industrial machinery. For B2B buyers in this sector, it is essential to consider thread specifications and material compatibility to prevent issues such as stripping or loosening over time. Additionally, negotiating volume pricing for bulk orders can significantly impact overall procurement costs, particularly for companies in emerging markets.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘different types of bolts’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Sourcing the Right Type of Bolt for Unique Applications
The Problem:
International B2B buyers often struggle to source the appropriate type of bolt for specialized applications. For instance, a company in South America may require bolts that can withstand high temperatures and corrosive environments, such as those found in oil and gas industries. However, they might find it challenging to identify suppliers who provide high-quality, industry-specific bolts that meet both regional standards and project requirements. This can lead to delays in production, increased costs, and potential project failures.
The Solution:
To effectively source the right type of bolt, B2B buyers should begin by conducting thorough research on the specific requirements of their applications, including load capacity, environmental resistance, and material composition. Utilizing online platforms and industry directories can help identify manufacturers and suppliers who specialize in the desired type of bolts, such as stainless steel or high-strength alloy bolts. Additionally, engaging with industry experts or joining relevant trade associations can provide insights into recommended suppliers and best practices. Requesting samples and certifications from potential suppliers can further ensure that the bolts meet the necessary quality standards before making bulk orders.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Compatibility of Bolts with Existing Equipment
The Problem:
Another common challenge faced by B2B buyers is ensuring that the bolts they purchase are compatible with their existing equipment or assembly processes. For example, a manufacturing company in Africa may need to replace bolts in their machinery but discovers that the new bolts do not fit the existing threading or size specifications. This oversight can result in costly downtime and the need for additional modifications, affecting overall productivity.
The Solution:
To prevent compatibility issues, buyers should maintain detailed records of the specifications of all components used in their machinery, including bolt dimensions, thread types, and material grades. Prior to purchasing new bolts, it is crucial to consult the machinery’s technical documentation or directly contact the manufacturer for recommendations. Using tools such as calipers to measure existing bolts can help ensure accurate specifications are communicated to suppliers. Additionally, buyers should consider working with suppliers who offer custom solutions, allowing for tailored bolts that fit specific machinery requirements, reducing the risk of future compatibility problems.
Scenario 3: Managing Inventory and Reducing Waste with Bolt Types
The Problem:
Effective inventory management is a significant pain point for B2B buyers dealing with different types of bolts. Companies in the Middle East often find themselves overstocking various types of bolts, leading to waste and increased holding costs. Conversely, they may run out of essential bolts, causing delays in production and project timelines. This imbalance can be particularly problematic in industries with fluctuating demand.
The Solution:
To optimize inventory management and reduce waste, buyers should implement a just-in-time (JIT) inventory system. This involves closely monitoring usage rates and aligning bolt orders with actual project needs. Utilizing inventory management software can provide real-time data on stock levels, helping buyers make informed purchasing decisions. Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can also facilitate quicker turnaround times for bolt orders, allowing companies to maintain minimal stock levels while ensuring they have the necessary components on hand. Additionally, conducting periodic reviews of bolt usage can identify which types are consistently in demand, allowing for more strategic purchasing and storage decisions.
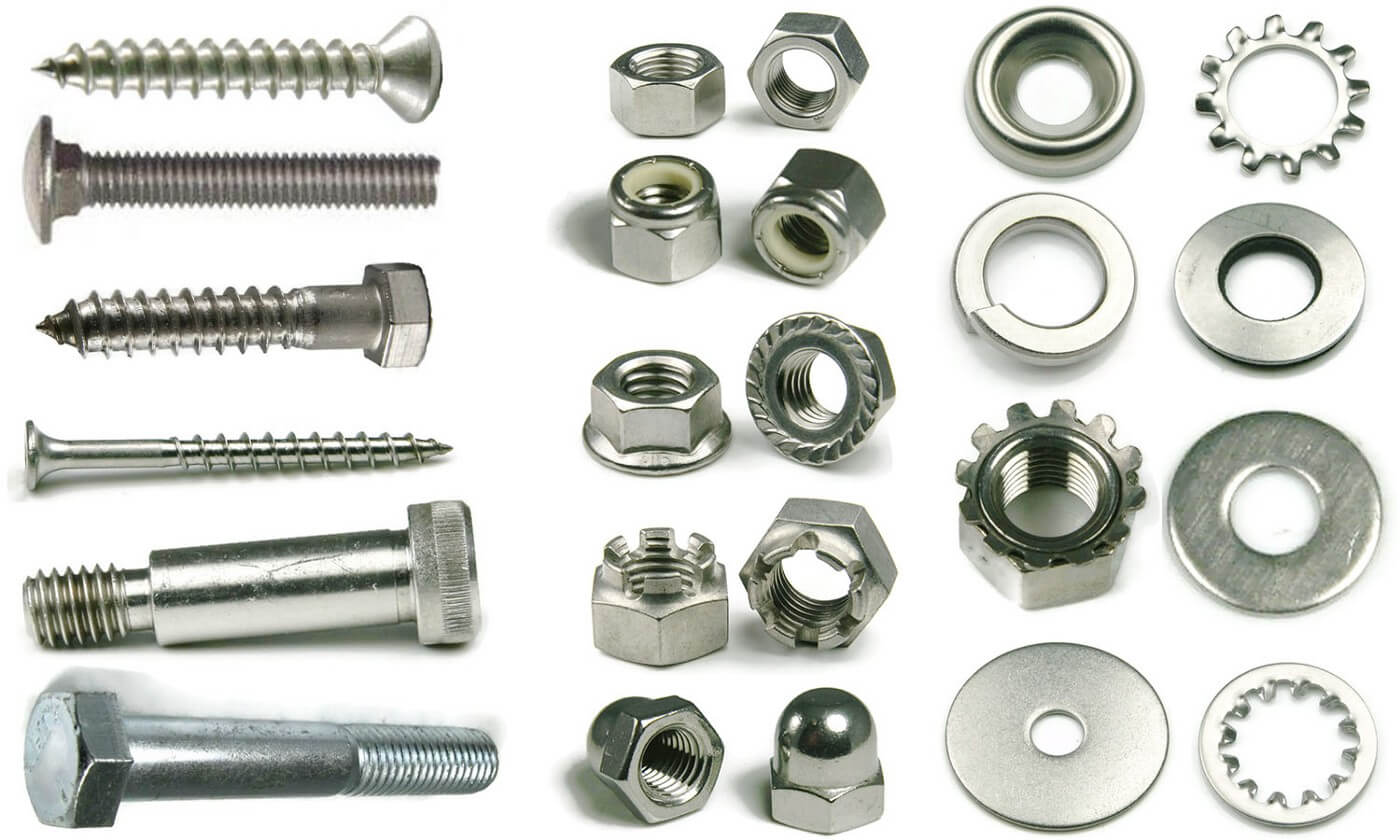
Strategic Material Selection Guide for different types of bolts
What Are the Key Properties of Steel Bolts?
Steel is the most commonly used material for bolts due to its excellent mechanical properties. Its high tensile strength allows it to withstand significant loads, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, from automotive to construction. Steel bolts can be treated to enhance their properties further, such as through heat treatment or galvanization, which improves corrosion resistance.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of steel bolts is their durability and strength, which ensures long-lasting performance in demanding environments. However, they can be susceptible to rust and corrosion if not properly treated, particularly in humid or saline conditions, which are common in regions such as Africa and the Middle East. The cost of steel bolts is generally moderate, but specialized treatments can increase manufacturing complexity and cost.
Impact on Application: Steel bolts are compatible with various media, including air, water, and some chemicals, but their performance can degrade in highly corrosive environments. Buyers in regions with high humidity or exposure to seawater should consider stainless steel or coated variants to ensure longevity.
How Do Stainless Steel Bolts Compare in Performance?
Stainless steel bolts are known for their superior corrosion resistance, making them ideal for applications in marine environments or areas with high moisture levels. The alloying elements, primarily chromium, provide a protective layer that prevents rusting.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of stainless steel bolts is their ability to resist corrosion and staining, which significantly extends their lifespan. However, they are generally more expensive than carbon steel bolts, which can be a consideration for budget-conscious buyers. Manufacturing stainless steel bolts can also be more complex due to the material’s properties, potentially leading to longer lead times.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel bolts are suitable for applications involving exposure to water, chemicals, and extreme temperatures. International buyers should ensure compliance with relevant standards, such as ASTM A193 or DIN 1.4401, to guarantee quality and performance.
What Are the Benefits of Using Alloy Steel Bolts?
Alloy steel bolts are made from a combination of steel and other elements, such as nickel, chromium, or molybdenum, which enhance their mechanical properties. These bolts are often used in high-stress applications, such as in the aerospace and automotive industries.
Pros & Cons: The primary benefit of alloy steel bolts is their high strength-to-weight ratio, making them ideal for applications where weight is a concern. However, they can be more expensive than standard steel bolts and may require specialized manufacturing processes, which can increase overall costs.
Impact on Application: Alloy steel bolts are particularly effective in environments that experience extreme temperatures and pressures. Buyers should be aware of the necessary certifications for alloy steel, such as ASTM A325, to ensure compliance with international standards.
Why Are Plastic and Composite Bolts Gaining Popularity?
Plastic and composite bolts are emerging as alternatives to traditional metal bolts, particularly in applications where weight reduction and corrosion resistance are critical. These materials are often used in industries such as electronics and automotive, where non-conductivity is also a benefit.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of plastic and composite bolts is their lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion. They are also non-magnetic, which is beneficial in certain applications. However, they typically have lower tensile strength compared to metal bolts, which limits their use in high-load applications. The manufacturing process can also be less straightforward, affecting lead times and costs.
Impact on Application: Plastic bolts are suitable for applications involving sensitive electronic components or environments where metal fasteners could cause interference. International buyers should consider the specific material properties and compliance with standards like ISO 9001.
| Material | Typical Use Case for different types of bolts | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Construction, automotive | High strength and durability | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Marine, chemical processing | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost than carbon steel | High |
| Alloy Steel | Aerospace, automotive | High strength-to-weight ratio | More expensive, complex mfg. | High |
| Plastic/Composite | Electronics, automotive | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Lower tensile strength | Medium |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for different types of bolts
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Different Types of Bolts?
The manufacturing process of bolts encompasses several critical stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Understanding these stages is crucial for B2B buyers, as it can significantly impact product quality and performance.
Material Preparation
The first stage involves selecting and preparing the raw materials, typically high-grade steel or alloys, which determine the bolt’s strength and durability. The materials are sourced based on international standards such as ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) or ISO specifications. Buyers should verify that suppliers adhere to these standards to ensure product reliability.
A stock image related to different types of bolts.
The material is then cut into appropriate sizes, often using techniques like shearing or sawing. This step is vital for maintaining consistency in dimensions, which is a prerequisite for the subsequent forming processes.
How Are Bolts Formed Using Different Techniques?
Once the raw materials are prepared, the next step is forming. This can be achieved through various methods, including cold heading, hot forging, and metal stamping.
-
Cold Heading: This technique involves deforming the metal at room temperature, using high-speed machinery. Cold heading is efficient for producing large volumes of bolts with precise dimensions. It is commonly used for hex bolts and socket screws.
-
Hot Forging: In this method, the metal is heated to a malleable state, allowing for complex shapes to be formed. Hot forging is ideal for larger bolts that require enhanced strength, such as structural bolts used in construction.
-
Metal Stamping: This cold-working process transforms metal sheets into predefined shapes using dies. It is particularly effective for producing washers and specialized bolt types like elevator bolts.
Each forming technique has its advantages, and B2B buyers should consider the intended application of the bolts when choosing suppliers that specialize in specific manufacturing processes.
What Quality Assurance Practices Should Be Implemented in Bolt Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in bolt manufacturing to ensure that products meet the necessary specifications and standards. The following QA practices are essential for maintaining product integrity.
What International Standards Govern Bolt Manufacturing?
International standards such as ISO 9001 play a crucial role in ensuring consistent quality across manufacturing processes. ISO 9001 focuses on quality management systems (QMS) and emphasizes continuous improvement, which is critical for suppliers serving global markets.
Other industry-specific standards, such as CE marking in Europe and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for bolts used in the oil and gas industry, also provide essential guidelines for quality assurance. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers comply with these standards to avoid potential liabilities.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Bolt Production?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are vital in the manufacturing process. Common checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial inspection ensures that raw materials meet specified standards before production begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, regular checks are performed to monitor the forming process and ensure adherence to specifications.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the bolts are manufactured, they undergo rigorous testing and inspection to ensure they meet all quality standards before shipment.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Bolt Quality Assurance?
Various testing methods are employed to verify the quality and performance of bolts. Some common methods include:
-
Tensile Testing: Measures the strength of the bolt by applying a pulling force until it fails. This test is crucial for ensuring that the bolt can withstand the loads it will encounter in application.
-
Hardness Testing: Assesses the material’s hardness, which correlates with its ability to resist wear and deformation.
-
Dimensional Inspection: Uses gauges and measurement tools to verify that the bolts meet specified dimensions and tolerances.
-
Surface Finish Inspection: Checks for surface defects, such as cracks or pits, which could compromise the bolt’s performance.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers should be proactive in verifying the quality control measures of their suppliers. Here are actionable steps:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can help ensure compliance with quality standards and manufacturing processes. This can be done through on-site visits or third-party auditing services.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed quality reports that outline their QC processes, testing results, and any certifications they hold.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies can provide unbiased assessments of product quality, especially for large orders.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control is essential. Consider the following:
-
Cultural Differences: Quality expectations and manufacturing practices can vary significantly across regions. Buyers should be aware of these differences to establish effective communication with suppliers.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that suppliers are compliant with both local and international regulations. This is particularly important for bolts used in critical applications like construction and aerospace.
-
Supply Chain Transparency: In regions with complex supply chains, transparency is vital. Buyers should seek suppliers who provide clear information about their sourcing and manufacturing processes.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for different types of bolts is critical for international B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming techniques, and rigorous quality control measures, buyers can ensure they procure reliable and high-performance products tailored to their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘different types of bolts’
This sourcing guide aims to provide international B2B buyers with a practical checklist for procuring various types of bolts. Whether you are sourcing for construction, manufacturing, or other industrial applications, following these steps will ensure that you make informed decisions, optimize costs, and secure reliable products.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is critical for sourcing the right type of bolt. Consider factors such as size, material, thread type, and load capacity. This step will help you avoid compatibility issues and ensure that the bolts meet the specific requirements of your projects.
- Material Considerations: Determine if you need carbon steel, stainless steel, or other materials based on environmental conditions and load requirements.
- Thread Types: Choose between coarse or fine threads depending on the application and load distribution needed.
Step 2: Research Industry Standards and Compliance
Understanding industry standards is essential for ensuring quality and safety. Familiarize yourself with relevant standards such as ISO, ASTM, or local certifications that apply to your region.
- Quality Assurance: Verify that the bolts meet the required specifications by checking for compliance certificates.
- Regional Standards: Different regions may have specific requirements; ensure that your suppliers are familiar with these standards, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct a thorough evaluation. This involves checking their reputation, product range, and customer service.
- Supplier References: Request case studies and references from similar industries to gauge reliability and product performance.
- Certifications: Look for ISO certifications or other quality assurance indicators that demonstrate the supplier’s commitment to quality.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Always request samples before placing bulk orders. Testing samples can help confirm that the bolts meet your specifications and quality standards.
- Performance Testing: Check for tensile strength, corrosion resistance, and compatibility with your existing materials.
- Field Testing: If possible, conduct field tests to assess how the bolts perform under actual working conditions.
Step 5: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you have identified potential suppliers, it’s time to negotiate pricing and contract terms. Ensure that you understand all costs involved, including shipping, tariffs, and payment terms.
- Bulk Discounts: Inquire about discounts for larger orders, which can significantly reduce your overall costs.
- Payment Flexibility: Discuss payment terms that work for both parties, especially if you are dealing with international suppliers.
Step 6: Plan for Logistics and Delivery
Logistics can significantly impact your project timelines. Discuss delivery times, shipping methods, and any potential delays with your supplier.
- Shipping Options: Evaluate air freight versus sea freight based on urgency and cost-effectiveness.
- Customs Regulations: Ensure that your supplier is compliant with customs regulations in your target market to avoid delays.
Step 7: Establish a Relationship for Future Sourcing
Building a long-term relationship with your suppliers can lead to better pricing and reliability in future transactions. Keep open lines of communication and provide feedback on product performance.
- Supplier Loyalty: Consider loyalty programs or long-term contracts that can benefit both parties.
- Regular Reviews: Schedule regular performance reviews to ensure that the supplier continues to meet your standards.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline the sourcing process for different types of bolts, ensuring that their procurement efforts are efficient and effective.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for different types of bolts Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Bolt Manufacturing?
Understanding the cost structure of bolt manufacturing is essential for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of raw materials—such as stainless steel, carbon steel, or alloy steel—significantly impacts the cost. High-quality materials enhance durability and corrosion resistance but come at a premium price.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region. For instance, labor is typically less expensive in parts of Africa and South America compared to Europe. This can influence the overall pricing strategy of manufacturers.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, rent, and indirect labor costs. Facilities in developed regions may have higher overheads, affecting the final price of bolts produced.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in molds and dies for production can be substantial. Custom tooling for unique bolt designs adds to the cost but is often necessary for specialized applications.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that bolts meet specific standards requires rigorous testing and inspection processes, which can add to the cost but is essential for maintaining product integrity.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary significantly based on the shipping method, distance, and any tariffs or duties applied. Buyers should be aware of these costs, especially when sourcing from overseas suppliers.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can vary based on their market position and pricing strategy. Understanding these margins can help buyers negotiate better deals.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Bolt Pricing for International Buyers?
Several factors influence the pricing of bolts, particularly for international B2B buyers:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Bulk purchases often lead to lower per-unit costs. Negotiating higher MOQs can yield significant savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized bolts tailored to specific applications may incur additional costs. Standardized products usually offer better pricing due to streamlined production processes.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-grade materials and certified products (e.g., ISO standards) typically command higher prices but offer greater reliability and compliance with international standards.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record but offer better quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) affect shipping responsibilities and costs. Understanding these terms can help buyers avoid unexpected expenses.
What Buyer Tips Can Help in Achieving Cost-Efficiency?
To navigate the complexities of bolt sourcing, international B2B buyers should consider the following tips:
-
Negotiate Wisely: Always negotiate pricing and terms. Leverage your purchasing power and be open to discussing volume discounts or long-term contracts.
-
Assess Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial purchase price. Consider the long-term costs associated with maintenance, replacements, and potential downtimes caused by inferior products.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Pricing can vary widely based on regional factors. For example, sourcing from local suppliers in South America may reduce logistics costs, while sourcing from Europe could provide access to higher quality materials.
-
Be Informed About Market Trends: Staying updated on the latest trends in bolt manufacturing and pricing can provide a competitive edge in negotiations and sourcing decisions.
-
Evaluate Supplier Stability: Choose suppliers with a history of reliability and quality. A stable supplier can mitigate risks associated with sourcing, such as delays or product failures.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for bolts can fluctuate based on market conditions, currency exchange rates, and geopolitical factors. Buyers should always request formal quotes and verify current pricing from suppliers to ensure accuracy and relevance to their specific sourcing needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing different types of bolts With Other Solutions
When considering the most effective solutions for fastening applications, it is crucial for B2B buyers to evaluate not just the different types of bolts, but also viable alternatives that could meet their specific needs. This analysis will provide insights into how various fastening methods compare, enabling buyers to make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and application suitability.
| Comparison Aspect | Different Types of Bolts | Self-Drilling Screws | Metal Brackets |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High tensile strength; suitable for various materials. | Excellent for quick assembly; creates its own pilot hole. | Provides structural support; can bear significant loads. |
| Cost | Moderate; bulk purchasing can reduce expenses. | Generally lower cost; fewer components required. | Higher initial investment; cost-effective for long-term use. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires pre-drilled holes and nuts for assembly. | Easy to install without pre-drilling; saves time. | Installation may require additional tools and techniques. |
| Maintenance | Durable but may require periodic checks for loosening. | Generally low-maintenance; can be replaced easily. | Low maintenance; however, may corrode over time if not treated. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for heavy-duty applications in construction and machinery. | Best for quick repairs and lightweight applications. | Suitable for structural applications, shelving, and equipment stabilization. |
How Do Self-Drilling Screws Compare to Different Types of Bolts?
Self-drilling screws are a popular alternative to traditional bolts, especially for applications where speed and ease of installation are critical. These screws come with a drill point that allows them to create their own hole in the material, eliminating the need for pre-drilling. This feature significantly reduces assembly time, making them an attractive option for projects requiring rapid deployment. However, they may not provide the same tensile strength as bolts, making them less suitable for heavy-duty applications.
What Are the Advantages of Using Metal Brackets Instead of Bolts?
Metal brackets serve a different purpose compared to bolts but can be an excellent alternative for specific applications. They provide robust structural support and are ideal for stabilizing shelves, equipment, or other installations where load-bearing capacity is crucial. While they may require a higher initial investment, their longevity and durability can lead to lower costs over time. However, the installation process can be more complex, requiring additional tools and expertise, which could be a drawback for some buyers.
Making the Right Choice: Which Fastening Solution Should You Choose?
In conclusion, selecting the right fastening solution involves a careful analysis of the specific requirements of your project. For B2B buyers, understanding the strengths and weaknesses of different types of bolts, self-drilling screws, and metal brackets is essential. Buyers should consider factors such as load requirements, assembly speed, maintenance, and overall costs. By aligning the choice of fastener with the unique demands of their applications, businesses can optimize their operational efficiency and ensure long-lasting results.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for different types of bolts
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Bolts That B2B Buyers Should Know?
Understanding the technical properties of bolts is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly when sourcing materials for manufacturing or construction projects. Here are some essential specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
Material grade indicates the strength and durability of a bolt. Common grades include ASTM A307 for general-purpose bolts, ASTM A325 for structural steel connections, and ASTM A490 for high-strength applications. Choosing the right material grade affects not only the bolt’s performance but also its suitability for specific applications, impacting overall project integrity.
2. Thread Count and Pitch
Thread count refers to the number of threads per inch (TPI) on a bolt, while pitch is the distance between threads. These specifications are critical for ensuring proper fit and compatibility with nuts and other fasteners. A mismatch can lead to mechanical failure, making it essential for buyers to understand these terms when selecting bolts.
3. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance defines the acceptable limits of variation in bolt dimensions, including length, diameter, and thread specifications. Tight tolerances are often necessary for precision applications, while looser tolerances may suffice for general use. Understanding tolerance requirements can help buyers avoid costly rework or failures in assembly.
4. Corrosion Resistance
Many bolts are treated or coated to enhance their resistance to corrosion. Common treatments include galvanization, black oxide, or the use of stainless steel. For B2B buyers operating in humid or corrosive environments, selecting the appropriate corrosion-resistant bolts is vital for maintaining long-term structural integrity.
5. Strength Class
Strength class, such as metric grades 8.8, 10.9, or 12.9, indicates the load-carrying capacity of a bolt. This classification helps buyers determine the bolt’s suitability for high-stress applications, ensuring that they select the right fasteners for their specific projects.
What Are Common Trade Terms Every B2B Buyer Should Understand?
Navigating the terminology related to bolts and fasteners can significantly impact procurement processes. Here are some key terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for buyers seeking quality assurance and compatibility with existing systems.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Recognizing MOQ helps B2B buyers plan their inventory and budget, ensuring they meet both supplier requirements and project needs without overcommitting resources.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting price quotes for specified products, including bolts. Utilizing RFQs allows buyers to compare pricing and terms from multiple vendors, ultimately aiding in informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international shipping. Familiarity with these terms, such as FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight), is essential for B2B buyers to understand shipping costs and liability.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the goods. Understanding lead time is vital for project planning and inventory management, allowing buyers to schedule deliveries to align with project timelines.
In conclusion, grasping both the technical properties and trade terminology related to bolts equips B2B buyers with the insights needed to make informed decisions, ensuring successful procurement processes and project outcomes.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the different types of bolts Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Bolts Sector?
The global bolts market is experiencing significant growth, driven by an expanding construction sector, increased automotive production, and a rising demand for industrial machinery. In regions such as Africa and South America, infrastructural development projects are catalyzing the need for robust fastening solutions. Meanwhile, in Europe and the Middle East, stringent regulations around safety and quality assurance are pushing buyers to seek high-grade bolts that meet international standards.
Emerging technologies are reshaping sourcing strategies. Automation in manufacturing processes, such as die stamping and cold forming, is leading to more efficient production lines and reduced costs. Buyers are increasingly leveraging online platforms for procurement, allowing them to compare products and suppliers more effectively. Furthermore, the rise of Industry 4.0 is encouraging the adoption of smart manufacturing technologies, which enhance transparency and traceability in the supply chain.
B2B buyers should also be aware of the fluctuating raw material prices, particularly steel, which is essential for bolt production. This volatility necessitates strategic sourcing practices, such as long-term contracts and diversified supplier bases, to mitigate risks. Understanding local market dynamics, including tariffs and trade regulations, is vital for international buyers, especially when engaging with suppliers across different continents.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shape the Bolts Market?
Sustainability is becoming a crucial consideration for B2B buyers in the bolts sector. The environmental impact of bolt production, particularly in terms of energy consumption and waste generation, is prompting companies to seek more eco-friendly alternatives. Buyers are increasingly interested in suppliers who utilize sustainable practices, such as recycling scrap metal and reducing carbon emissions during manufacturing.
Ethical sourcing is gaining traction as businesses recognize the importance of responsible supply chains. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate compliance with labor standards and environmental regulations. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and Fair Trade can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability and ethical practices.
Furthermore, the adoption of ‘green’ materials, such as biodegradable coatings or recycled metals, is becoming more common in bolt production. B2B buyers can enhance their brand reputation and customer loyalty by sourcing from suppliers who prioritize sustainable materials and practices. Emphasizing these values can not only meet regulatory requirements but also align with the growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible products.
What is the Evolution of the Bolts Sector and Its Relevance for B2B Buyers?
The bolts sector has evolved significantly since its inception during the Industrial Revolution. Originally crafted by blacksmiths, bolts are now produced through advanced manufacturing processes like metal stamping and powder metallurgy. These advancements have enabled higher precision and consistency in bolt production, catering to the diverse needs of modern industries.
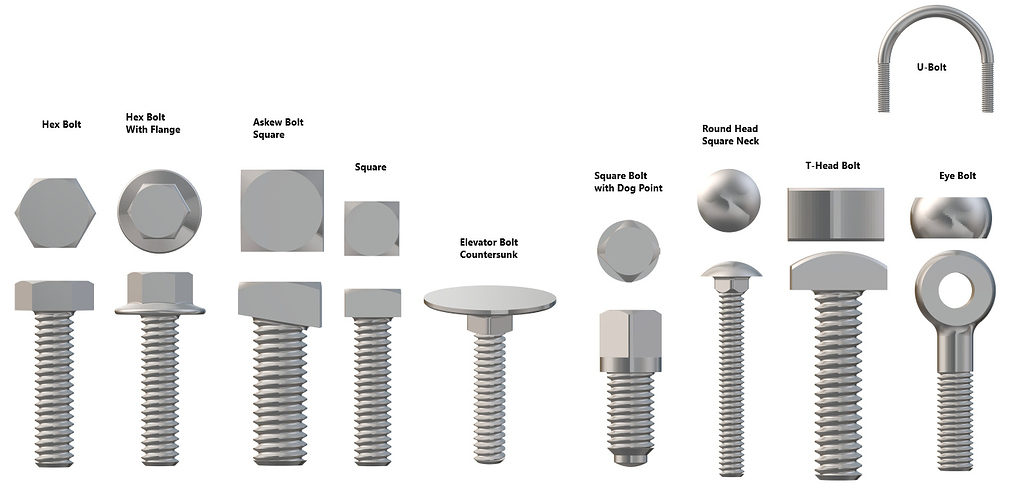
As the demand for specialized fasteners has grown, the industry has seen the emergence of various bolt types, including hex bolts, carriage bolts, and flange bolts, each designed for specific applications. This diversification allows B2B buyers to select the most suitable fastening solution for their projects, enhancing overall efficiency.
Understanding the historical context of bolt manufacturing provides valuable insights into current market trends and future innovations. As technology continues to advance, the bolts sector is likely to see further developments in materials and production techniques, making it essential for international buyers to stay informed about these changes to make informed purchasing decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of different types of bolts
-
How do I select the right type of bolt for my application?
Selecting the right type of bolt involves understanding the specific requirements of your application. Consider factors such as load capacity, environmental conditions (e.g., corrosion resistance), and the materials being fastened. Common bolt types include hex bolts for heavy-duty applications, carriage bolts for wood, and eye bolts for lifting. Additionally, consulting with a supplier or manufacturer can provide insights tailored to your specific needs and ensure compliance with industry standards. -
What is the best material for bolts used in outdoor applications?
For outdoor applications, stainless steel bolts are often recommended due to their excellent corrosion resistance. Other suitable materials include galvanized steel, which provides a protective coating against rust, and brass for aesthetic applications. The choice of material should also consider the environmental conditions, such as humidity and exposure to chemicals, ensuring long-lasting performance and reliability. -
What are the common minimum order quantities (MOQs) for bolts in international trade?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for bolts can vary significantly based on the supplier, the type of bolt, and the material. Typically, MOQs range from 500 to 1,000 units for standard bolts. For customized bolts or specialized materials, MOQs can be higher. It is advisable to negotiate with suppliers and consider consolidating orders with other buyers to meet MOQ requirements while optimizing shipping costs. -
How can I verify the quality of bolts before making a purchase?
To verify bolt quality, request certifications such as ISO 9001 or ASTM standards from suppliers. Conducting a factory audit or quality inspection can also be beneficial. Additionally, ask for samples to assess material properties and manufacturing precision. Building a relationship with reliable suppliers who have a proven track record in quality assurance will help mitigate risks associated with subpar products. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing bolts internationally?
Payment terms in international B2B transactions typically include options like advance payment, letters of credit, or open account terms. It’s common to encounter a 30% deposit with the balance due upon shipment. Understanding the payment terms can help manage cash flow and mitigate risks. Always clarify these terms in your contract and consider the political and economic stability of the supplier’s country before proceeding. -
How can I ensure timely delivery of bolts across international borders?
To ensure timely delivery, work with suppliers who have established logistics partnerships and experience in international shipping. Discuss lead times and shipping methods upfront, and consider using freight forwarders who specialize in customs clearance. Always account for potential delays due to customs inspections and plan orders well in advance of your project timelines. -
What are the advantages of customizing bolts for specific applications?
Customizing bolts allows you to tailor specifications such as size, material, and finish to meet unique application requirements. This can enhance performance, improve assembly efficiency, and reduce failure rates in critical applications. Additionally, custom bolts can help differentiate your products in competitive markets, providing a unique selling point that may attract more clients. -
How do I handle logistics challenges when importing bolts?
Handling logistics challenges when importing bolts involves thorough planning and coordination with your suppliers and logistics partners. Ensure that all documentation, including invoices, packing lists, and customs declarations, is complete and accurate. Familiarize yourself with import regulations in your country and consider using local customs brokers to navigate the complexities of international trade, ensuring a smooth delivery process.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use

A stock image related to different types of bolts.
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for different types of bolts
A stock image related to different types of bolts.
In the world of strategic sourcing, understanding the diverse types of bolts and their applications is essential for international B2B buyers. Bolts serve as critical fasteners in various industries, from construction to automotive, making it imperative to select the right type based on material, load requirements, and environmental conditions. Key takeaways include the importance of assessing supplier capabilities, considering regional manufacturing strengths, and evaluating cost-effectiveness without compromising quality.
Moreover, leveraging strategic sourcing can lead to enhanced supply chain resilience and reduced operational costs. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, establishing relationships with local and international suppliers can facilitate access to innovative bolt technologies, including advanced materials and manufacturing processes like cold forming and powder metallurgy.
As we move forward, it’s vital to stay informed about market trends and emerging technologies that can enhance product performance. Engage with trusted suppliers, attend industry trade shows, and participate in relevant forums to network and share insights. By adopting a proactive sourcing strategy, you can ensure that your business remains competitive and well-equipped to meet the demands of an ever-evolving market landscape.