Discover the Best Type A Outlet: Your Ultimate Sourcing Guide (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for type a outlet
In today’s interconnected world, sourcing reliable Type A outlets can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers, especially those from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the nuances of Type A outlets—predominantly used in North America and parts of Asia—is crucial for businesses looking to expand their operations or enhance their product offerings. This guide provides an in-depth exploration of Type A outlets, including their specifications, applications, and the variety of devices compatible with them.
Navigating the complexities of sourcing electrical components involves evaluating supplier reliability, understanding regional electrical standards, and assessing cost implications. By offering comprehensive insights into the types of Type A outlets available, as well as practical advice on supplier vetting, this guide equips B2B buyers with the knowledge necessary to make informed purchasing decisions. Whether you are a manufacturer in Nigeria looking to integrate Type A outlets into your products or a distributor in Europe seeking to meet customer demand, understanding the global market landscape for Type A outlets is essential.
Armed with this information, businesses can not only streamline their procurement processes but also ensure compliance with safety and performance standards, ultimately leading to greater operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
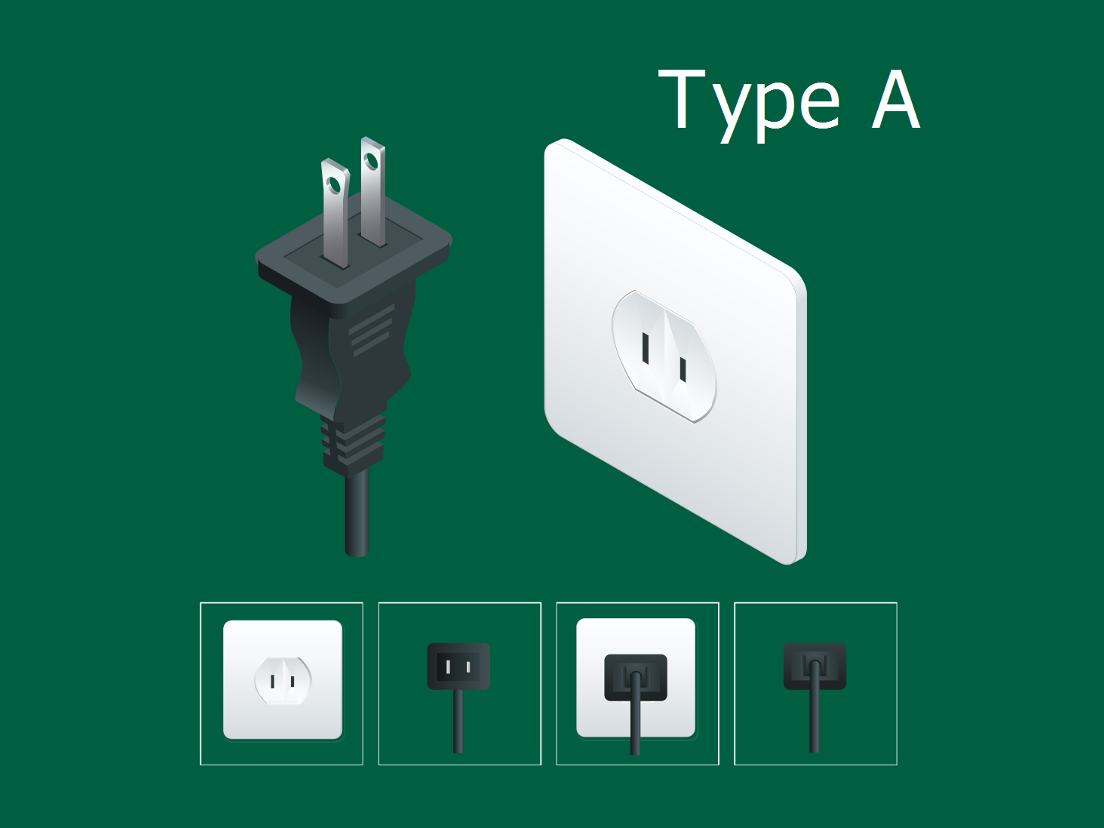
Understanding type a outlet Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type A | Ungrounded; two flat parallel prongs; polarized design | Small appliances, electronics | Pros: Simple design; widely available. Cons: Not suitable for high-power devices; safety concerns due to ungrounded nature. |
| Type B | Grounded; two flat parallel prongs plus a round grounding pin | Heavy-duty appliances, industrial use | Pros: Enhanced safety with grounding; suitable for higher loads. Cons: Less common in some regions; may require adapters. |
| Japanese Type A | Similar to Type A but with stricter dimensional standards | Consumer electronics in Japan | Pros: Compatible with North American outlets; strict safety regulations. Cons: May not fit older designs without modification. |
| Type A with Locking Mechanism | Features holes in prongs for securing plugs | Vending machines, industrial equipment | Pros: Prevents accidental disconnection; ideal for fixed installations. Cons: Limited availability; may require specialized sockets. |
| Type A Travel Adapter | Adapts Type A plugs for international use | Travel-related electronics | Pros: Versatile for global travel; compact design. Cons: Limited voltage conversion; check compatibility with local voltage. |
What Are the Characteristics of Type A Outlets?
Type A outlets, known as NEMA 1-15, are primarily used in North America and parts of Central and South America. They feature two flat parallel prongs that are often polarized to ensure correct insertion. These outlets are commonly found in residential and commercial settings for low-power devices, such as chargers and small appliances. When considering Type A outlets for B2B purchases, it’s essential to evaluate the safety implications of ungrounded plugs, especially in environments where electrical reliability is critical.
How Do Type B Outlets Differ From Type A?
Type B outlets are similar to Type A but include a grounding pin, which enhances safety by providing a path for fault currents. This makes them suitable for heavy-duty applications, such as industrial machinery and large appliances. B2B buyers should prioritize Type B outlets when sourcing equipment that requires higher power loads or when operating in environments with increased electrical hazards. Ensuring compatibility with Type B plugs can significantly reduce the risk of electrical failures.
What Makes Japanese Type A Unique?
The Japanese version of Type A outlets adheres to stricter regulations regarding dimensions and safety standards, making them slightly different from their North American counterparts. They are widely used for consumer electronics in Japan and can often fit into North American outlets. B2B buyers in electronics should consider these standards when importing devices to ensure compliance and functionality in both regions, as mismatched plugs can lead to compatibility issues.
Why Use Type A Outlets with Locking Mechanisms?
Type A outlets equipped with locking mechanisms are designed for applications where a secure connection is essential, such as in vending machines and industrial equipment. These outlets have holes in the prongs that allow for a locking mechanism to prevent accidental disconnection. When sourcing these types of outlets, B2B buyers should assess the specific needs of their operations, particularly in environments where equipment reliability is paramount.
How Can Type A Travel Adapters Benefit International Buyers?
Type A travel adapters allow for the use of Type A plugs in various international outlets, making them invaluable for businesses that operate globally. These adapters are compact and convenient, but buyers must ensure they are compatible with local voltage specifications to avoid damage to devices. For companies frequently engaging in international travel, investing in high-quality adapters can facilitate seamless operations and enhance productivity.
Key Industrial Applications of type a outlet
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of type a outlet | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Consumer Electronics | Charging devices like smartphones and tablets | Provides a convenient power source for daily use | Ensure compatibility with local voltage and frequency standards |
| Retail and Vending Machines | Powering vending machines and kiosks | Facilitates unattended sales and customer interaction | Look for durable, weather-resistant options for outdoor use |
| Hospitality | Supporting appliances in hotels and restaurants | Enhances guest experience with accessible charging ports | Consider safety regulations and grounding requirements in installations |
| Manufacturing | Operating small machinery and tools | Increases productivity by providing reliable power | Assess the load capacity and environmental conditions of the workspace |
| Education | Charging laptops and projectors in classrooms | Supports modern teaching methods and technology integration | Ensure sufficient outlet availability and compliance with local standards |
How is Type A Outlet Used in Consumer Electronics?
In the consumer electronics sector, type A outlets are predominantly used for charging devices such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops. These outlets provide a straightforward solution for powering personal devices, essential for both individual users and businesses. International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and South America, should ensure that the voltage and frequency match their devices to avoid damage and ensure optimal performance.
What Role Does Type A Outlet Play in Retail and Vending Machines?
Type A outlets are crucial for powering vending machines and kiosks, allowing them to operate independently in retail environments. This application enhances the customer experience by enabling self-service options and increasing sales opportunities. Buyers in this sector need to consider the durability of the outlet, especially if it will be used outdoors, to withstand environmental factors.
How is Type A Outlet Beneficial in the Hospitality Industry?
In the hospitality sector, type A outlets are utilized for powering various appliances, including mini-fridges, coffee makers, and charging stations in guest rooms. This availability enhances the guest experience, providing convenience and comfort. Buyers must be aware of local safety regulations and ensure proper installation to comply with grounding requirements, especially in older buildings.
What is the Application of Type A Outlet in Manufacturing?
In manufacturing, type A outlets are often employed to operate small machinery and hand tools. Reliable power supply is vital for maintaining productivity and operational efficiency. International buyers should evaluate the load capacity of the outlets to ensure they can handle the required power demands, considering environmental factors such as humidity and dust that may affect performance.
How is Type A Outlet Used in Educational Settings?
Educational institutions utilize type A outlets to support charging needs for laptops, projectors, and other electronic teaching aids. This integration of technology in classrooms is essential for modern education methodologies. Buyers in this sector must ensure that there are enough outlets available and that they meet local standards for safety and accessibility, facilitating an optimal learning environment.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘type a outlet’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Incompatibility with Local Electrical Standards
The Problem: International B2B buyers often face challenges when importing equipment that utilizes Type A outlets. Many devices are designed for specific regions, and when they arrive in countries with different electrical standards—such as those in Africa or South America—buyers encounter compatibility issues. This can lead to the inability to use essential equipment, causing delays in operations and additional costs for converters or adaptors.
The Solution: To mitigate this problem, buyers should conduct thorough research on the electrical standards of their destination country before purchasing equipment. It’s essential to verify whether the devices can operate on the local voltage and frequency. For Type A outlets, which typically operate at 120V and 60Hz, ensure that the devices are either dual voltage or have adapters that can handle local specifications. Investing in multi-standard equipment or purchasing local adapters and transformers will streamline operations and avoid unnecessary downtime. Additionally, establishing relationships with suppliers who are knowledgeable about international standards can further ease this process.
Scenario 2: Safety Risks Associated with Ungrounded Outlets
The Problem: Type A outlets are ungrounded, which poses significant safety risks, especially in industrial settings where equipment failure could lead to electric shocks or fires. B2B buyers must be aware that using devices that require grounding can be hazardous if plugged into a Type A outlet, leading to liability issues and potential harm to employees.
The Solution: Buyers should prioritize sourcing equipment that is compatible with ungrounded outlets or invest in devices that come with built-in safety features, such as circuit breakers or ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCI). When purchasing Type A plugs, consider using adapters that include grounding capabilities. This can help mitigate risks by ensuring that the equipment is grounded properly, especially in environments with high electrical loads. Furthermore, conducting regular safety audits and training employees on the risks associated with ungrounded outlets will enhance workplace safety and compliance with local regulations.
Scenario 3: Limited Availability of Type A Adapters in Certain Regions
The Problem: B2B buyers often find it challenging to acquire Type A adapters, especially in regions where this outlet type is less common. This scarcity can lead to operational disruptions when devices are unable to connect to power sources. For companies that rely on international travel or shipping of goods, this can severely impact productivity and project timelines.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should consider bulk purchasing Type A adapters and transformers from reputable suppliers or manufacturers. Establishing a partnership with local distributors who specialize in electrical equipment can ensure a steady supply of necessary adapters. Additionally, buyers should consider investing in universal power adapters that accommodate multiple plug types, including Type A. This not only simplifies logistics but also provides flexibility when operating in various regions. Lastly, maintaining an inventory of essential adapters as part of the operational toolkit will prevent delays and ensure that all equipment remains functional, regardless of location.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for type a outlet
When selecting materials for Type A outlets, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that influence performance, compliance, and cost-effectiveness. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in the manufacturing of Type A outlets, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What are the Key Properties of Plastic in Type A Outlets?
Plastic is one of the most commonly used materials for Type A outlets, particularly due to its insulation properties. High-grade thermoplastics, such as polycarbonate and nylon, are often employed.
- Key Properties: Excellent electrical insulation, lightweight, and good resistance to heat and chemicals.
- Pros: Cost-effective, easy to mold into complex shapes, and offers good durability against environmental factors.
- Cons: Less resistant to physical impacts compared to metals; may degrade under prolonged exposure to UV light.
- Impact on Application: Suitable for indoor use, but may not withstand extreme temperatures or harsh environmental conditions.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as IEC 60884-1 is essential. Buyers should verify whether the plastic used meets local safety regulations.
How Does Metal Affect the Performance of Type A Outlets?
Metal, particularly copper and aluminum, is often used for the conductive components of Type A outlets.
- Key Properties: High electrical conductivity, good thermal properties, and mechanical strength.
- Pros: Excellent durability and reliability in electrical performance; metals can withstand high temperatures without degrading.
- Cons: Higher cost than plastics and can corrode if not properly treated or coated.
- Impact on Application: Ideal for high-load applications where electrical efficiency is critical.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that metal components comply with corrosion resistance standards such as ASTM B117 for salt spray testing, especially in coastal regions.
What Role Does Rubber Play in Type A Outlet Design?
Rubber is often utilized in Type A outlets for grommets and seals to enhance safety and durability.
- Key Properties: Excellent flexibility, good electrical insulation, and resistance to wear and tear.
- Pros: Provides a secure fit and prevents dust and moisture ingress, enhancing safety.
- Cons: Can degrade over time with exposure to heat and certain chemicals, leading to potential failure.
- Impact on Application: Useful in environments where moisture or dust may be a concern.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Ensure that the rubber meets relevant standards for flame retardancy, such as UL 94, to comply with safety regulations.
How Do Composite Materials Enhance Type A Outlets?
Composite materials, which combine plastics and metals, are increasingly being used in the production of Type A outlets.
- Key Properties: Tailored properties depending on the composite; can offer a balance of strength, weight, and insulation.
- Pros: Enhanced durability and performance; can be engineered for specific applications, improving overall product life.
- Cons: More complex manufacturing processes can lead to higher costs.
- Impact on Application: Suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications, depending on the specific composite formulation.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Verify that composites meet local and international standards for electrical safety and environmental impact, such as RoHS compliance.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Type A Outlets
| Material | Typical Use Case for Type A Outlet | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plastic | Indoor residential and commercial | Excellent electrical insulation | Less impact resistance | Low |
| Metal | High-load applications | High electrical conductivity | Susceptible to corrosion | High |
| Rubber | Seals and grommets in outlets | Provides moisture and dust protection | Can degrade with heat exposure | Medium |
| Composite | Versatile applications | Tailored properties for specific needs | Higher manufacturing complexity | Medium to High |
This guide serves as a comprehensive resource for international B2B buyers seeking to make informed decisions regarding material selection for Type A outlets, ensuring compliance with relevant standards and suitability for their specific applications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for type a outlet
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process for Type A Outlets?
The manufacturing process of Type A outlets involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets safety and performance standards. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers assess the quality and reliability of their suppliers.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used?
The manufacturing of Type A outlets begins with material preparation. Typically, materials include:
- Plastic Resins: Used for the outlet casing, ensuring durability and insulation.
- Copper Alloys: Employed for the prongs, providing excellent conductivity and strength.
- Nickel or Tin Plating: Applied to the prongs to prevent corrosion and enhance electrical contact.
Suppliers must source materials that comply with international standards to ensure quality. Buyers should verify the origin and certification of these materials to ensure they meet their regional requirements.
How Are Type A Outlets Formed?
The forming stage involves shaping the prepared materials into the desired outlet configuration. This process may include:
- Injection Molding: Used for creating the plastic casing. High-quality molds ensure precision and uniformity.
- Stamping: Employed for shaping the metal prongs. This process allows for high-speed production while maintaining dimensional accuracy.
- Die Casting: Sometimes used for producing components that require more intricate designs.
Buyers should inquire about the machinery and techniques used by suppliers to ensure they employ modern, efficient methods that reduce waste and enhance quality.
What Is Involved in the Assembly of Type A Outlets?
Once individual components are formed, the assembly stage takes place. This includes:
- Component Integration: Prongs are inserted into the molded casing, ensuring they are properly aligned and securely fastened.
- Soldering or Welding: Connections between components may require soldering to ensure a solid electrical connection.
- Final Assembly: The outlet is assembled, including any additional features such as locking mechanisms or safety tags.
During this stage, manufacturers should implement stringent assembly protocols to prevent defects. B2B buyers can request details on the assembly line processes used by suppliers to gauge their efficiency and quality.
What Finishing Techniques Are Applied to Type A Outlets?
The finishing stage is crucial for enhancing the outlet’s appearance and functionality. Key techniques include:
- Surface Treatment: This may involve polishing, coating, or painting to improve aesthetics and resistance to wear.
- Quality Inspection: Before the final product is packaged, it undergoes a thorough inspection to ensure all features function correctly and meet design specifications.
B2B buyers should confirm that suppliers utilize finishing techniques that comply with international standards to ensure product longevity and safety.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Type A Outlet Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is vital for ensuring that Type A outlets are safe and reliable. Manufacturers typically adopt several international standards and implement multiple quality checkpoints throughout the production process.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
Understanding international standards is critical for B2B buyers when sourcing Type A outlets. Key standards include:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines a framework for quality management systems, ensuring continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
- CE Marking: Indicates that the product complies with EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For certain applications, adhering to American Petroleum Institute standards may be necessary.
Buyers should request documentation proving that suppliers comply with these standards to ensure product safety and marketability.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are essential in the manufacturing process to identify defects and ensure product integrity. Common checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Materials are inspected upon arrival to confirm compliance with specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections during production to monitor the manufacturing process and catch defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A thorough inspection of the finished product before packaging, ensuring it meets all design and safety standards.
B2B buyers should inquire about the specific QC protocols employed by suppliers to understand how they ensure product quality.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Type A Outlets?
Manufacturers employ various testing methods to ensure Type A outlets meet safety and performance requirements, including:
- Electrical Testing: Measures the outlet’s ability to handle voltage and current without overheating or failing.
- Durability Testing: Assesses the outlet’s resistance to wear, mechanical stress, and environmental conditions.
- Safety Testing: Ensures that the outlet meets safety standards, such as preventing electrical shocks or short circuits.
Buyers should request test reports and certifications from suppliers to verify that the products have undergone rigorous testing.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
Verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure they receive reliable products. Here are several strategies to consider:
What Should B2B Buyers Look for in Supplier Audits?
Conducting audits of potential suppliers can provide insight into their quality control processes. Key aspects to assess include:
- Compliance with Standards: Ensure that the supplier adheres to relevant international and industry-specific standards.
- Documentation Practices: Review their record-keeping to confirm that they document quality checks and testing results.
- Employee Training: Inquire about the training programs for employees involved in the manufacturing and quality assurance processes.
How Can Reports and Third-Party Inspections Help?
Requesting reports from suppliers can offer transparency regarding their quality control measures. B2B buyers should look for:
- Quality Assurance Reports: These documents should detail the QC processes and results of inspections and tests.
- Third-Party Inspection Certificates: Verification from independent organizations adds credibility and assurance of quality.
By implementing these strategies, B2B buyers can significantly mitigate risks associated with sourcing Type A outlets from international suppliers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘type a outlet’
The following guide serves as a practical checklist for international B2B buyers seeking to procure Type A outlets. These outlets are widely used in various regions, including North America and parts of South America, and understanding the procurement process can help ensure that your electrical needs are met efficiently and safely.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing precise technical specifications for Type A outlets is crucial for compatibility with your devices. Consider factors such as voltage ratings (typically 125V), amperage (15A), and the physical dimensions of the outlet. This ensures that the outlets will function correctly with your existing equipment, reducing the risk of damage or inefficiencies.
Step 2: Research Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Understanding the regulatory standards in your target market is essential. Type A outlets must comply with local electrical codes and standards, which can vary significantly between regions. Look for certifications such as UL (Underwriters Laboratories) in the U.S. or CE marking in Europe, indicating that the products meet safety and performance requirements.
Step 3: Identify Reliable Suppliers
Finding reputable suppliers is fundamental to successful procurement. Use platforms like Alibaba, Global Sources, or industry-specific trade shows to identify potential manufacturers. Assess their credentials, production capabilities, and customer reviews to ensure they have a proven track record in delivering quality Type A outlets.
- Tip: Request samples to evaluate the quality of the products before making large orders.
Step 4: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before finalizing a supplier, verify their certifications and quality management practices. Suppliers should ideally have ISO 9001 certification, ensuring they follow rigorous quality control processes. Additionally, check if they have specific certifications for electrical components, as this can influence the reliability and safety of the outlets.
Step 5: Request Detailed Quotations
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request detailed quotations that include pricing, minimum order quantities, lead times, and shipping options. This information will help you assess the total cost of ownership and choose the supplier that offers the best value for your investment.
- Important: Ensure that all costs, including shipping and taxes, are clearly outlined to avoid unexpected expenses.
Step 6: Conduct Site Visits or Virtual Inspections
If possible, arrange site visits to the manufacturing facilities or conduct virtual inspections. This step provides insights into the production processes and quality control measures in place. Observing the facility can also help you gauge the supplier’s commitment to safety and quality.
Step 7: Establish Clear Communication Channels
Effective communication is key to a successful procurement process. Establish clear lines of communication with your chosen supplier, specifying preferred contact methods and response times. This practice helps to resolve any issues quickly and maintain a smooth operational flow.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline the sourcing process for Type A outlets, ensuring that they meet their technical, regulatory, and operational needs effectively.
A stock image related to type a outlet.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for type a outlet Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Type A Outlets?
When considering the sourcing of Type A outlets, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The quality and type of materials used significantly influence the overall cost. Copper for conductors, high-grade plastics for the casing, and insulation materials are typical components. Suppliers that use lower-grade materials may offer cheaper options, but this could affect the durability and safety of the outlet.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary widely depending on the country of manufacture. Regions with lower labor costs, such as Southeast Asia, may offer more competitive pricing but could also result in varying quality levels.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with factory operations, such as utilities, equipment maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturers often pass savings onto buyers.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs for producing custom designs can be substantial. Buyers should consider whether the outlet design is standard or requires unique tooling, which can add to the upfront costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Investing in rigorous QC processes ensures that the products meet safety and performance standards. While this can increase costs, it reduces the risk of product recalls and customer dissatisfaction.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs are critical, especially for international buyers. Factors such as distance, shipping method (air vs. sea), and current freight rates will affect overall logistics costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include their desired profit margin in the pricing. Understanding typical margins in the industry can help buyers negotiate better deals.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Type A Outlet Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of Type A outlets:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their needs to optimize pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Outlets that require custom features (such as specific colors or additional safety features) will typically cost more. Standardized designs are more cost-effective.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Outlets manufactured from premium materials or those that meet international safety certifications (such as UL or CE) generally command higher prices. Buyers should weigh the benefits of certifications against costs.
-
Supplier Factors: Established suppliers with a good reputation may charge a premium for their products due to perceived reliability and quality assurance. New or lesser-known suppliers might offer lower prices but could pose risks related to quality and delivery.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms such as FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can affect total costs. Buyers should clarify these terms with suppliers to avoid unexpected expenses.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficient Sourcing?
International B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, can implement several strategies for more effective sourcing:
-
Negotiate Terms: Always negotiate pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Suppliers may have flexibility, especially if you can commit to larger volumes.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but also factors like shipping, import duties, and potential costs from low-quality products. A slightly higher initial cost may result in lower long-term expenses if the product is more reliable.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Transactions: Currency fluctuations can affect pricing. Buyers should keep an eye on exchange rates and consider locking in prices when favorable.
-
Research and Compare Suppliers: Take the time to compare multiple suppliers. Check for reviews, certifications, and past performance to ensure you’re getting the best value.
Conclusion: What to Keep in Mind About Pricing for Type A Outlets
While indicative prices for Type A outlets can vary widely based on the factors mentioned above, being informed and strategic in your sourcing approach can lead to significant savings. Always remember that the cheapest option is not necessarily the best, especially in terms of safety and reliability. By understanding the cost structure and leveraging negotiation tactics, B2B buyers can optimize their purchasing decisions in the competitive landscape of electrical components.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing type a outlet With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Type A Outlets for International B2B Buyers
In the realm of electrical solutions, selecting the right outlet type is crucial for ensuring compatibility, safety, and efficiency. While the Type A outlet, primarily used in North America and parts of Japan and South America, has its advantages, it is essential to explore viable alternatives. This analysis will compare the Type A outlet with two alternative solutions: the Type C outlet and the Type G outlet.
Comparison Table of Electrical Outlet Types
| Comparison Aspect | Type A Outlet | Type C Outlet | Type G Outlet |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Ungrounded, limited safety | Ungrounded, widely compatible | Grounded, higher safety |
| Cost | Generally low | Generally low | Higher initial installation cost |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple installation, widely available | Simple installation, but requires adapters in some regions | More complex due to grounding requirements |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance | Low maintenance | Moderate maintenance due to grounding checks |
| Best Use Case | Small appliances, low power | General appliances, travel | High-power appliances, safety-critical environments |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What are the Benefits of Using Type C Outlets?
The Type C outlet, known for its two round pins, is prevalent in Europe and parts of Asia. Its design allows for compatibility with various plug types, making it an excellent choice for international businesses that deal with multiple electrical devices. The ungrounded nature of Type C outlets limits their safety features compared to grounded options, but their widespread usage makes them highly accessible and cost-effective. For businesses with low-power devices, Type C outlets are a practical choice, although using adapters may be necessary for devices from regions utilizing different plug types.
Why Choose Type G Outlets for Safety and Reliability?
The Type G outlet, characterized by its three rectangular prongs and grounding capabilities, is primarily found in the UK and some other Commonwealth countries. This outlet type offers enhanced safety due to its grounding feature, which significantly reduces the risk of electrical shocks. While the installation cost is generally higher compared to Type A and C outlets, the long-term benefits of using Type G outlets in high-power or safety-critical applications make them an appealing option for businesses. However, companies must consider the more complex installation and maintenance requirements associated with grounding.
How to Choose the Right Electrical Outlet for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate electrical outlet type depends on various factors, including device compatibility, safety requirements, and installation costs. For international B2B buyers, understanding the specific needs of their equipment and the regions they operate in is paramount. If the primary concern is low-cost and low-power devices, the Type A or C outlets may suffice. However, for businesses that prioritize safety and plan to use high-power equipment, investing in Type G outlets could offer more significant long-term advantages.

A stock image related to type a outlet.
In conclusion, carefully evaluating the performance, cost, and safety features of each outlet type will empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational requirements and safety standards.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for type a outlet
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Type A Outlets?
Understanding the essential technical specifications of Type A outlets is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when sourcing electrical components for various applications. Here are the primary specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
Type A outlets are typically made from high-quality thermoplastic materials such as polycarbonate or nylon. These materials are chosen for their durability, heat resistance, and electrical insulation properties. For B2B buyers, selecting outlets made from superior material grades ensures long-term reliability and safety, reducing the risk of electrical failures or hazards.
2. Voltage and Amperage Ratings
Type A outlets are rated for 125 volts and 15 amps. This specification is critical for ensuring compatibility with devices and appliances designed for similar voltage and current levels. Buyers should ensure that their equipment can operate safely within these parameters to prevent overheating or damage.
3. Blade Dimensions
The two flat parallel prongs of Type A outlets have specific dimensions: each blade measures 1.5 mm thick and between 15.9 mm to 18.3 mm in length, with a spacing of 12.7 mm apart. Understanding these dimensions is vital for ensuring compatibility with various plugs and avoiding potential electrical issues.
4. Grounding Type
Type A outlets are ungrounded, meaning they do not provide a direct path to the ground for electrical faults. This property is significant for buyers in industries where grounding is essential for safety, as it may necessitate the use of alternative grounding solutions or the selection of grounded Type B outlets instead.
5. Polarization
Most modern Type A plugs are polarized, with one blade wider than the other, ensuring correct orientation when plugging in devices. This feature enhances safety by minimizing the risk of electrical shock. B2B buyers should consider this aspect when sourcing plugs and outlets to ensure proper device functionality.
What Are Common Trade Terminology and Jargon Related to Type A Outlets?
Familiarizing yourself with industry terminology can greatly facilitate smoother transactions and negotiations. Here are some key terms relevant to Type A outlets:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of Type A outlets, OEMs provide components designed specifically for compatibility with certain devices, ensuring quality and reliability.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to sell in one order. Understanding MOQ is crucial for B2B buyers looking to negotiate bulk purchases of Type A outlets, as it can affect inventory costs and supply chain management.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers asking for pricing and terms for specific products, such as Type A outlets. It is a vital tool for B2B buyers to ensure competitive pricing and favorable terms from different manufacturers or distributors.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms is essential for B2B buyers importing Type A outlets, as they dictate aspects like shipping costs, risk management, and delivery responsibilities.
5. UL Listing (Underwriters Laboratories)
A UL listing indicates that a product has been tested for safety and meets specific standards. For Type A outlets, ensuring they have UL certification is important for compliance with safety regulations, especially in regions like North America.
6. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order until the product is delivered. Understanding lead times for Type A outlets can help B2B buyers plan their inventory and project timelines effectively, ensuring they meet customer demands without delays.
By grasping these technical specifications and trade terminologies, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing Type A outlets, enhancing their operational efficiency and safety standards.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the type a outlet Sector
What are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Type A Outlet Sector?
The global market for Type A outlets is influenced by a variety of factors, including the increasing demand for electronic devices and the need for standardized power solutions in international trade. Key drivers include technological advancements in energy efficiency, the growth of smart homes, and the push for universal compatibility in electrical appliances. B2B buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must stay informed about the latest regulations and standards concerning electrical outlets. These regions often face varying voltage requirements and electrical infrastructure challenges that can affect sourcing decisions.
Emerging trends in sourcing for Type A outlets include a shift towards suppliers that offer innovative solutions, such as integrated USB ports and enhanced safety features. The rise of e-commerce platforms has also transformed traditional procurement processes, allowing buyers to compare products and suppliers more efficiently. Additionally, the focus on sustainability is reshaping the supply chain, prompting manufacturers to adopt greener practices and materials. For international buyers, understanding these dynamics is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions and ensuring compliance with local regulations.
How is Sustainability Influencing the Sourcing of Type A Outlets?
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor in the sourcing of Type A outlets, driven by increasing environmental awareness among consumers and businesses. The production and disposal of electrical components can significantly impact the environment, leading to greater scrutiny of supply chains. Ethical sourcing practices are essential for B2B buyers to ensure that materials are procured responsibly and that manufacturers adhere to environmental regulations.
Buyers should prioritize suppliers that offer ‘green’ certifications, such as Energy Star or RoHS compliance, which indicate adherence to environmental standards. Additionally, the use of recyclable materials and eco-friendly packaging can enhance a company’s brand reputation and appeal to a growing demographic of environmentally conscious consumers. As the demand for sustainable products rises, companies that integrate ethical sourcing into their procurement strategies will not only meet regulatory requirements but also position themselves competitively in the marketplace.
What is the Evolution of the Type A Outlet and its Relevance to B2B Buyers?
The Type A outlet, known as NEMA 1-15, was first introduced in the early 20th century and has undergone several modifications to enhance safety and functionality. Initially designed for basic electrical needs, the Type A outlet has evolved to accommodate modern technology, including polarized plugs that prevent incorrect insertion. This evolution is particularly relevant for B2B buyers who must ensure that their electrical products meet current safety standards and compatibility requirements.
Understanding the historical context of the Type A outlet can provide valuable insights into the future of electrical components. As technology continues to advance, the demand for innovative solutions—such as smart outlets that integrate with home automation systems—will likely shape future sourcing trends. For international buyers, being aware of these historical developments can inform strategic sourcing decisions and help anticipate market shifts.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of type a outlet
-
How do I choose the right type A outlets for my business needs?
When sourcing type A outlets, consider the voltage and frequency compatibility of your devices, as they typically operate at 120V and 60Hz. Assess the quality certifications (such as UL or CE) to ensure safety and reliability. Additionally, evaluate the manufacturer’s reputation and customer reviews to gauge performance. It’s wise to conduct a small test order to verify that the outlets meet your specific requirements before committing to larger quantities. -
What is the best supplier for type A outlets in Africa or South America?
Identifying the best supplier involves researching established manufacturers with a proven track record in electrical components. Look for suppliers who specialize in type A outlets and have experience exporting to your region. Utilize platforms like Alibaba or Global Sources to compare offerings, and consider reaching out to local distributors for recommendations. Always request samples and verify certifications to ensure compliance with local standards. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for type A outlets?
MOQs for type A outlets can vary significantly between suppliers, often ranging from 100 to 1,000 units. Smaller manufacturers might accommodate lower MOQs, while larger companies may have stricter requirements. When negotiating with suppliers, inquire about the possibility of lower MOQs for initial orders, especially if you are testing the market or introducing new products. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing type A outlets?
Payment terms can differ based on the supplier and your negotiation leverage. Common terms include a 30% deposit upfront with the balance due upon shipment, or net 30 days after delivery. Always clarify terms before placing an order and consider using secure payment methods such as letters of credit for larger transactions to mitigate risks.

A stock image related to type a outlet.
-
How do I ensure quality assurance for type A outlets?
To ensure quality assurance, request that suppliers provide certification documents that verify compliance with international safety standards. Conduct factory audits or hire third-party inspection services to assess manufacturing processes. Additionally, establish a clear quality control agreement that outlines testing protocols for the outlets before shipment, including electrical safety tests and durability assessments. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing type A outlets?
When importing type A outlets, consider shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations in your country. Air freight is faster but more expensive, while sea freight is cost-effective for larger orders. Ensure that the supplier provides all necessary documentation, such as invoices and certificates of origin, to facilitate smooth customs clearance. Also, factor in potential tariffs and taxes that may apply. -
What are the common issues with type A outlets that I should be aware of?
Common issues with type A outlets include compatibility problems with devices requiring grounding, as type A outlets are ungrounded. Additionally, the potential for wear and tear due to frequent plugging and unplugging can lead to poor connections. It’s essential to educate your team about proper usage and consider investing in higher-quality outlets designed for durability to mitigate these risks. -
How can I customize type A outlets for my specific applications?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for type A outlets, such as different colors, branding, or additional features like integrated USB ports. When discussing customization, provide detailed specifications and intended applications to the supplier. Be prepared to meet minimum order quantities for customized products and allow additional lead time for production and testing of the modified outlets.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for type a outlet
In the evolving landscape of international business, understanding the nuances of Type A outlets is crucial for B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By strategically sourcing electrical components and devices that are compatible with Type A outlets, businesses can enhance operational efficiency and ensure seamless connectivity for their products and services.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Improve Your Supply Chain?
The strategic sourcing of electrical components allows companies to mitigate risks associated with voltage and frequency discrepancies, particularly when dealing with cross-border transactions. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who offer reliable products that meet international standards, ensuring safety and compliance in their respective markets.
What is the Future Outlook for Type A Outlets in Global Trade?
Looking ahead, the demand for Type A-compatible devices is expected to grow, particularly as businesses expand into emerging markets. International B2B buyers must stay informed about technological advancements and regulatory changes that could impact the sourcing of electrical goods.
By fostering strong supplier relationships and investing in quality products, businesses can position themselves for success in a competitive marketplace. Embrace the opportunities that come with strategic sourcing, and ensure that your company is prepared to meet the demands of a globalized economy.