Discover the Best Types of Bolt Heads for Your Needs (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for types of bolt heads
In the dynamic landscape of international B2B procurement, sourcing the right types of bolt heads is a critical challenge that can significantly impact project success. With a myriad of options available, including hex, socket, and flange heads, making informed decisions becomes essential for optimizing performance and ensuring safety. This comprehensive guide delves into the diverse types of bolt heads, their specific applications across various industries, and practical insights for effective supplier vetting. By providing a detailed examination of cost factors, quality considerations, and regional supply chain dynamics, this resource equips international buyers—particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—with the knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of the global market.
Understanding the nuances of bolt head types not only enhances operational efficiency but also empowers businesses to establish stronger partnerships with suppliers. In regions such as South Africa and Indonesia, where local manufacturing capabilities may vary, having a clear grasp of available fastener types and their specifications can lead to better procurement strategies. This guide aims to serve as a valuable tool for B2B buyers, ensuring that they can confidently choose the right fasteners to meet their unique project requirements, ultimately fostering growth and innovation in their industries.
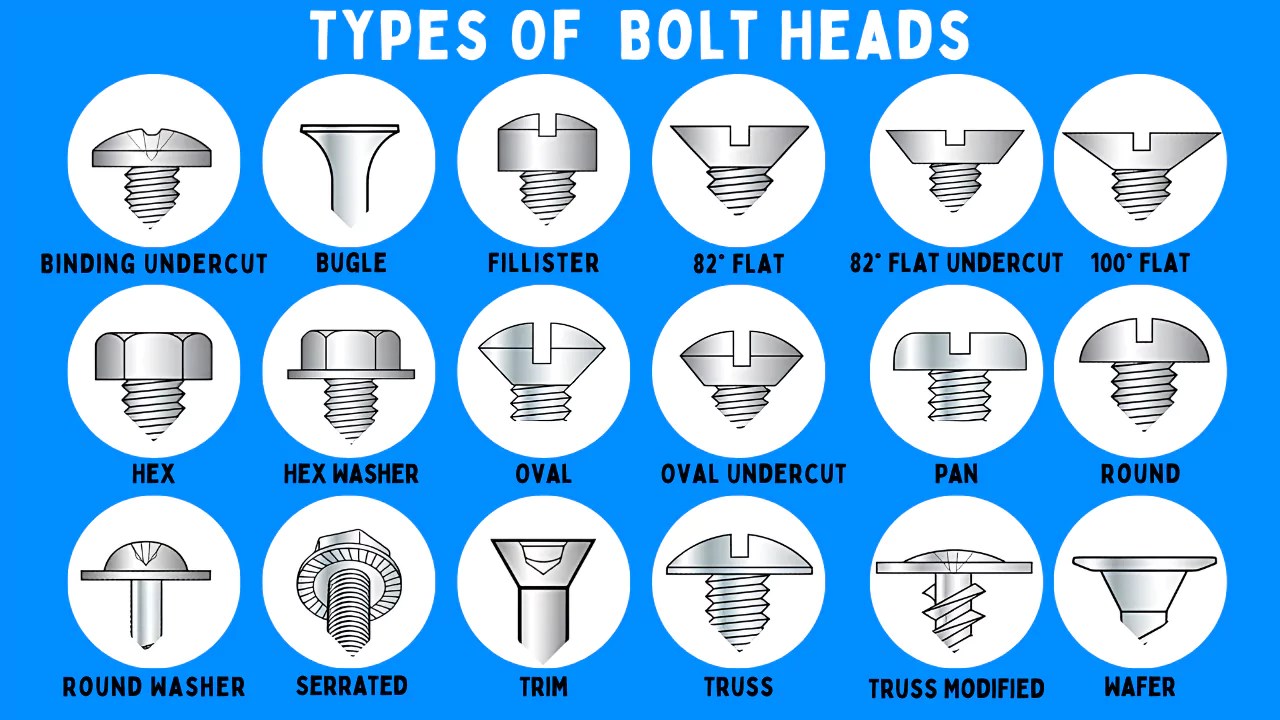
Understanding types of bolt heads Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hex Head Bolt | Six-sided head, commonly used with a wrench | Construction, machinery assembly | Pros: High torque, easy to install; Cons: Can be difficult to access in tight spaces. |
| Socket Cap Bolt | Cylindrical head with hex socket for Allen wrench | Precision machinery, automotive | Pros: Provides a clean finish, less protrusion; Cons: Requires specific tools for installation. |
| Carriage Bolt | Rounded head with a square neck to prevent rotation | Wood construction, railings | Pros: Prevents loosening, easy to install; Cons: Limited to applications where rotation is not an issue. |
| Flange Bolt | Integrated washer-like flange for load distribution | Heavy machinery, automotive | Pros: Reduces the need for separate washers; Cons: May require specific hole sizes for effective use. |
| Eye Bolt | Circular loop at the head for attaching cables or chains | Lifting, rigging, and construction | Pros: Versatile for various rigging applications; Cons: Limited to applications requiring a loop for attachment. |
What are the Characteristics of Hex Head Bolts and Their B2B Suitability?
Hex head bolts are characterized by their six-sided shape, allowing for easy fastening with a wrench. They are widely used in construction and machinery assembly due to their ability to handle high torque applications. When purchasing hex head bolts, B2B buyers should consider the material (such as stainless steel or carbon steel) for durability and corrosion resistance. It’s also essential to evaluate the bolt’s grade to ensure it meets the strength requirements for specific applications.
How Do Socket Cap Bolts Differ and Where are They Used?
Socket cap bolts feature a cylindrical head with a hex socket, typically requiring an Allen wrench for installation. This design allows for a low-profile fastening solution, making them suitable for precision machinery and automotive applications where space is limited. Buyers should focus on the material and finish of socket cap bolts to ensure compatibility with environmental conditions. Additionally, they should consider the torque specifications to avoid stripping the socket during installation.
Why Choose Carriage Bolts for Wood Construction?
Carriage bolts are easily identifiable by their rounded heads and square necks, which prevent them from rotating once installed. This makes them ideal for wood construction and railings, where a secure fit is crucial. When sourcing carriage bolts, B2B buyers should assess the required length and diameter based on the project specifications. It’s also advisable to consider the coating or finish to enhance resistance against weather elements, particularly in outdoor applications.
What Makes Flange Bolts a Preferred Choice in Heavy Machinery?
Flange bolts come with a built-in washer-like flange that helps distribute load and reduce the likelihood of loosening. They are commonly used in heavy machinery and automotive applications, where strength and stability are paramount. Buyers should ensure that the flange bolt’s dimensions match the specifications of the assembly to prevent issues during installation. Additionally, considering the material and corrosion resistance is vital for longevity in demanding environments.
In What Situations are Eye Bolts Most Effective?
Eye bolts are designed with a circular loop at the head, making them ideal for attaching cables or chains in lifting and rigging applications. They offer versatility in construction and are essential for tasks requiring secure connections. When purchasing eye bolts, B2B buyers should consider the load rating to ensure they can handle the intended weight. It’s also important to evaluate the material and finish to ensure they are suitable for the specific environmental conditions they will face.
Key Industrial Applications of types of bolt heads
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Types of Bolt Heads | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Assembly of vehicle components | Ensures safety and reliability in critical structures | Quality standards, corrosion resistance, certification |
| Construction | Structural connections in buildings | Provides stability and durability in construction | Material specifications, load-bearing capacity |
| Manufacturing | Machinery assembly and maintenance | Enhances operational efficiency and reduces downtime | Compatibility with machinery, ease of installation |
| Oil & Gas | Pipeline and rig assembly | Ensures leak-proof connections and operational safety | Resistance to extreme conditions, compliance regulations |
| Aerospace | Aircraft assembly and maintenance | Critical for safety and performance | Lightweight materials, aerospace-grade certifications |
How are Types of Bolt Heads Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, various types of bolt heads, such as hex and socket screws, are crucial for the assembly of vehicle components. They are used in critical areas where safety and reliability are paramount, such as the engine, suspension, and braking systems. International buyers from regions like Africa and South America must consider sourcing bolts that meet specific quality standards and certifications to ensure compliance with safety regulations. Additionally, the resistance to corrosion is vital due to varying environmental conditions.
What Role Do Bolt Heads Play in Construction?
In construction, bolt heads are integral to creating secure structural connections in buildings. Flange bolts, for example, distribute loads effectively, enhancing the stability of frameworks. Buyers in the Middle East and Europe should focus on sourcing materials that comply with local building codes and standards. Additionally, understanding the load-bearing capacity of different bolt heads is essential for ensuring the safety and longevity of structures, especially in seismic-prone areas.
Why are Bolt Heads Important in Manufacturing?
Manufacturing industries utilize various bolt heads in machinery assembly and maintenance, where efficiency and reliability are critical. The use of socket cap screws allows for easy installation and removal, facilitating routine maintenance. For B2B buyers in regions like South Africa, it is crucial to source bolts compatible with specific machinery to minimize downtime and ensure operational efficiency. Additionally, considering the ease of installation can lead to reduced labor costs.

A stock image related to types of bolt heads.
How Are Bolt Heads Used in Oil & Gas Applications?
In the oil and gas sector, bolt heads are essential for assembling pipelines and rigs, where leak-proof connections are a necessity. Using robust types like hex bolts ensures that components can withstand high pressure and extreme environmental conditions. International buyers must ensure that sourced products meet stringent compliance regulations and are resistant to corrosion and wear. This is particularly important in offshore applications where exposure to harsh elements is common.
What is the Significance of Bolt Heads in Aerospace?
Aerospace applications require the highest standards of precision and reliability, making the selection of bolt heads critical. Aircraft assembly often utilizes specialized bolt heads that comply with stringent aerospace-grade certifications. Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should prioritize sourcing lightweight materials that do not compromise structural integrity. Understanding the specific requirements for aerospace applications can significantly impact safety and performance, making it imperative for buyers to engage with reputable suppliers.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘types of bolt heads’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Selecting the Right Bolt Head Type for Specific Applications
The Problem: When sourcing fasteners for projects, many B2B buyers struggle with identifying the appropriate bolt head type that meets their specific application requirements. For instance, a construction firm may need a bolt that can withstand high torque without stripping, while a manufacturer might require a bolt head style that allows for easy access in confined spaces. This confusion can lead to delays in procurement, increased costs, and potential project failures due to inappropriate fastener selections.
The Solution: To effectively address this issue, buyers should invest time in understanding the different bolt head types and their applications. Create a detailed specification sheet that outlines the specific requirements for your project, including load capacities, material types, environmental conditions, and accessibility needs. Collaborate with suppliers who provide comprehensive catalogs or online tools that allow for easy comparison of bolt head styles such as hex, socket cap, and flange bolts. Additionally, utilizing a sample kit from suppliers can help assess the physical attributes and usability of different bolt heads before making bulk purchases. This proactive approach ensures the right fastener selection, ultimately saving time and resources.
Scenario 2: Complications Arising from Incompatible Bolt Head Drives
The Problem: A common pain point for B2B buyers is the incompatibility between the bolt head drive type and the tools available for installation. For instance, a buyer may purchase hex socket bolts only to find that their existing Allen wrenches are not compatible due to size variations. This oversight can result in project delays as teams scramble to procure the correct tools, leading to inefficiencies and additional costs.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, buyers should conduct a thorough inventory of existing tools before making any fastener purchases. When selecting bolt heads, ensure that the drive type aligns with the tools already in use. It is beneficial to standardize on a specific drive type across multiple projects to streamline tool requirements. Engage with suppliers who offer comprehensive tool and fastener kits that include both the fasteners and the appropriate installation tools. Additionally, consider investing in adjustable or multi-tool options that can accommodate various drive types, thereby enhancing operational flexibility and reducing downtime.
Scenario 3: Challenges with Corrosion Resistance in Bolt Head Types
The Problem: Buyers often encounter issues with the corrosion resistance of bolt heads, particularly in harsh environments such as coastal or industrial settings. For example, a manufacturing plant in South Africa may find that standard steel bolts rust quickly when exposed to moisture and chemicals, leading to compromised structural integrity and increased maintenance costs.
The Solution: To combat corrosion challenges, it is essential to specify bolt head types made from corrosion-resistant materials such as stainless steel, brass, or coated fasteners. When sourcing these fasteners, look for suppliers who provide detailed specifications regarding material properties and corrosion resistance ratings. Implement a systematic approach to assess the environmental conditions where the bolts will be used, and select appropriate coatings or treatments, such as galvanization or anodization, to enhance durability. Additionally, consider working with manufacturers that offer custom solutions tailored to specific environmental challenges, ensuring that the selected bolt heads maintain performance and safety standards over time.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for types of bolt heads
What Are the Key Properties of Steel Bolt Heads?
Steel is the most commonly used material for bolt heads due to its excellent mechanical properties. It typically offers high tensile strength, making it suitable for applications requiring significant load-bearing capabilities. Steel bolt heads can withstand high temperatures and pressures, which is essential in industries like construction and automotive. However, standard carbon steel is prone to corrosion, necessitating additional treatments such as galvanization or coating to enhance its resistance to environmental factors.
Pros and Cons of Steel Bolt Heads
Pros: High strength and durability, cost-effective, widely available, and easily manufactured.
Cons: Corrosion susceptibility unless treated, heavier than some alternatives, and potential for rusting in humid environments.
How Do Stainless Steel Bolt Heads Compare?
Stainless steel bolt heads are an excellent choice for applications exposed to corrosive environments, such as marine or chemical processing industries. The addition of chromium in stainless steel provides a protective layer that enhances corrosion resistance. Stainless steel also maintains its strength at elevated temperatures, making it versatile for various applications.
Pros and Cons of Stainless Steel Bolt Heads
Pros: Exceptional corrosion resistance, aesthetic appeal, and good strength at high temperatures.
Cons: Higher cost compared to carbon steel, more challenging to machine, and may not be suitable for high-load applications due to lower tensile strength.
What Advantages Do Aluminum Bolt Heads Offer?
Aluminum bolt heads are lightweight and resistant to corrosion, making them ideal for applications where weight reduction is critical, such as in aerospace and automotive sectors. Aluminum also has good thermal conductivity, which can be beneficial in applications requiring heat dissipation. However, aluminum’s lower tensile strength compared to steel means it is not suitable for high-load applications.
Pros and Cons of Aluminum Bolt Heads
Pros: Lightweight, excellent corrosion resistance, and good thermal conductivity.
Cons: Lower tensile strength, higher cost than carbon steel, and can be more prone to galling.
What Are the Considerations for Plastic Bolt Heads?
Plastic bolt heads are increasingly popular in applications where non-conductivity and corrosion resistance are essential, such as in electrical or chemical environments. They are lightweight and can be manufactured in various colors, which can be beneficial for aesthetic purposes. However, plastic bolt heads generally have lower mechanical strength and temperature resistance compared to metal alternatives.
Pros and Cons of Plastic Bolt Heads
Pros: Non-corrosive, lightweight, and good electrical insulation properties.
Cons: Limited mechanical strength, lower temperature resistance, and potential for degradation over time.
Summary Table of Bolt Head Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for types of bolt heads | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Construction, automotive | High tensile strength | Prone to corrosion without treatment | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Marine, chemical processing | Exceptional corrosion resistance | Higher cost, lower strength under load | Med |
| Aluminum | Aerospace, automotive | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower tensile strength, more expensive | Med |
| Plastic | Electrical, chemical environments | Non-corrosive and lightweight | Limited mechanical strength and temperature resistance | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides international B2B buyers with crucial insights into the properties, advantages, and limitations of various bolt head materials. Understanding these factors will aid in making informed purchasing decisions tailored to specific applications and regional compliance standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for types of bolt heads
What are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process for Bolt Heads?
The manufacturing process for bolt heads involves several key stages, each critical to ensuring the quality and functionality of the final product. Understanding these stages helps B2B buyers identify reliable suppliers and ensure that their products meet specific requirements.
Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation, which often involves selecting the appropriate raw materials, typically steel or stainless steel, depending on the intended application. Suppliers should utilize high-quality materials that comply with international standards. For instance, carbon steel is commonly used for standard bolts, while stainless steel is favored for corrosion resistance in harsh environments.
Buyers should inquire about the material specifications and certifications, such as ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) standards, to ensure that the materials meet the necessary requirements for their specific applications.
Forming Techniques: How are Bolt Heads Shaped?
Once the materials are prepared, the next stage is forming, where the raw materials are shaped into the desired bolt head profiles. Key techniques used in this process include:
-
Cold Heading: This method involves deforming metal at room temperature, which enhances its strength without compromising its structure. Cold heading is widely used for producing hexagonal and socket heads, as it allows for precise dimensions and high production rates.
-
Die Stamping: In this technique, a sheet of metal is cut and shaped using a series of dies. This method is particularly effective for producing complex shapes and is often used for custom bolt head designs.
-
Thread Rolling: This technique is employed to create threads on the bolt shaft. It involves rolling the metal through dies to form external threads, resulting in a stronger and more durable product compared to cutting threads.
B2B buyers should assess suppliers’ capabilities in these forming techniques to ensure they can meet specific design requirements.
Assembly and Finishing: What Steps Ensure Quality?
After forming, the next steps involve assembly (if necessary) and finishing. While many bolts are sold as standalone items, some applications may require additional components, such as washers or nuts. For these cases, assembly processes must be efficient and precise.
Finishing processes enhance the bolt’s durability and appearance. Common finishing techniques include:
- Plating: Applying a protective layer of zinc or other materials to prevent corrosion.
- Coating: Utilizing specialized coatings like powder or epoxy to enhance surface properties.
- Heat Treatment: Strengthening the bolts through processes like quenching and tempering to improve hardness and tensile strength.
B2B buyers should inquire about the types of finishing processes employed by suppliers, as these can significantly impact the performance and longevity of the bolts.
What International Standards and Quality Control Measures Should B2B Buyers Consider?
Quality assurance is essential in the manufacturing of bolt heads, as it directly influences product reliability and performance. B2B buyers should be aware of international standards and industry-specific regulations when evaluating suppliers.
Key International Standards: What Should Buyers Look For?
-
ISO 9001: This widely recognized standard focuses on quality management systems. Suppliers adhering to ISO 9001 demonstrate a commitment to continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
-
CE Marking: In the European market, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. It is crucial for buyers sourcing from or selling in Europe.
-
API Standards: For buyers in the oil and gas industry, API (American Petroleum Institute) standards ensure that bolts used in critical applications meet stringent safety and reliability requirements.
Buyers should request documentation proving compliance with these standards, as they serve as benchmarks for quality assurance.
What are the Quality Control Checkpoints in Bolt Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process. Key QC stages include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint ensures that the raw materials meet specified standards before production begins. Buyers should verify that suppliers conduct rigorous IQC procedures.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, ongoing inspections are essential to identify any deviations from specifications. This step helps maintain consistent quality throughout production.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipment, a final inspection is conducted to ensure that the finished products meet all specified requirements. This includes dimensional checks, visual inspections, and functional tests.
B2B buyers should consider suppliers that implement robust QC measures at each stage to ensure product integrity.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier QC practices is crucial. Here are some actionable steps:
Conduct Supplier Audits
Regular audits of suppliers can provide insight into their manufacturing processes and QC measures. Buyers should request documentation of previous audits, including findings and corrective actions taken.
Review Quality Control Reports
Buyers should ask for detailed QC reports that outline the testing methods used, results obtained, and any issues encountered during production. This transparency is vital for building trust and ensuring product quality.
Engage Third-Party Inspection Services
A stock image related to types of bolt heads.
Utilizing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s QC practices. These services often include factory audits, product inspections, and compliance checks against international standards.
What Quality Control Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
International buyers should be aware of specific nuances that could affect quality control:
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding cultural attitudes towards quality and compliance in different regions can help buyers navigate supplier relationships more effectively.
-
Regulatory Variations: Different countries may have varying regulations and standards, impacting product certification and acceptance in specific markets. Buyers must familiarize themselves with these regulations to ensure compliance.
-
Logistical Considerations: Shipping and handling can affect product quality. Buyers should ensure that suppliers have robust packaging and logistics processes to minimize damage during transit.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for bolt heads, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they source high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘types of bolt heads’
When sourcing different types of bolt heads for your B2B needs, it’s essential to have a clear and structured approach. This guide provides actionable insights to help you navigate the procurement process efficiently, ensuring that you select the right fasteners for your applications while building strong supplier relationships.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing precise technical specifications is critical in determining the right bolt head type for your project. Consider the following factors:
– Material Requirements: Assess whether you need stainless steel, carbon steel, or another material based on environmental conditions.
– Load and Stress Factors: Understand the load requirements and stress conditions to choose a bolt head that can handle your specific applications.
Step 2: Research Different Bolt Head Types
Familiarize yourself with the various types of bolt heads available in the market. Common types include hex, socket, and flange heads, each serving different functional purposes.
– Performance Characteristics: Investigate how each type performs under specific conditions, such as vibration or temperature changes, to ensure reliability.
– Industry Standards: Check for compliance with international standards like ISO or ASTM, which can impact the quality and performance of the fasteners.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region.
– Supplier Certifications: Verify that suppliers hold relevant certifications (e.g., ISO 9001) to ensure quality control.
– Industry Experience: Look for suppliers with a proven track record in your industry to enhance trust and reliability.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Always request samples before making bulk purchases. This step is vital for assessing the quality and compatibility of the bolt heads with your specific applications.
– Quality Assurance: Evaluate the samples for strength, dimensions, and finish to ensure they meet your specifications.
– Compatibility Check: Test how the bolt heads fit with corresponding nuts and other components in your assembly.
Step 5: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you’ve identified suitable suppliers and evaluated their products, engage in negotiations to finalize pricing and terms.
– Bulk Purchase Discounts: Inquire about volume discounts, especially if you plan to order large quantities.
– Payment Terms: Discuss payment options and terms to find a mutually beneficial arrangement that supports your cash flow needs.
Step 6: Establish a Quality Control Process
Implement a quality control process to ensure that all received bolt heads meet your specifications and quality standards.
– Inspection Procedures: Set up procedures for inspecting shipments upon arrival, including checking for damage and verifying quantities.
– Feedback Loop: Create a feedback mechanism to address any quality issues promptly with your suppliers.
Step 7: Build Long-Term Relationships
Focus on developing long-term relationships with reliable suppliers. This strategy can lead to better pricing, priority service, and improved collaboration on future projects.
– Regular Communication: Maintain open lines of communication to discuss new needs, product innovations, or changes in specifications.
– Partnership Opportunities: Explore opportunities for joint ventures or exclusive supply agreements that can enhance both parties’ business prospects.
By following this structured checklist, B2B buyers can effectively source the right types of bolt heads, ensuring they meet both technical requirements and business objectives.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for types of bolt heads Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Bolt Heads?
When sourcing bolt heads, international B2B buyers must understand the various cost components that contribute to the overall pricing. The primary elements include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts costs. For example, stainless steel bolts are more expensive than carbon steel due to corrosion resistance properties. Specialty materials, such as titanium or high-strength alloys, can further elevate costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can be influenced by local wage rates and skill levels. In countries with higher labor costs, such as many European nations, the overall cost of manufacturing bolt heads may increase.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses costs associated with factory operations, including utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. Efficient production facilities can minimize these overhead costs, affecting the final price.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling for production can be substantial, particularly for custom or complex designs. Buyers should inquire about the tooling costs to understand how they affect pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that bolt heads meet required standards involves rigorous QC processes. Additional testing and certification can add to costs, especially for industries with stringent safety and quality requirements.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs are crucial for international buyers. Factors such as distance, freight options, and customs duties can significantly influence total expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their risks and profit expectations. Understanding market conditions can help buyers negotiate better margins.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Bolt Head Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of bolt heads, and being aware of these can aid in making informed purchasing decisions:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Higher order volumes often lead to better pricing. Suppliers may offer discounts for bulk purchases, making it essential for buyers to assess their needs accurately.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom bolt heads designed to specific requirements can incur additional costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the potential price increase.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (such as ISO or ASTM) can command a premium price. Buyers in regulated industries should ensure compliance with relevant standards, which can affect sourcing decisions.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can also influence pricing. Established suppliers with proven track records may charge more for their products due to their commitment to quality and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is crucial for international transactions. Different terms can shift the responsibility for costs and risks between the buyer and seller, impacting the overall price.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Achieve Cost Efficiency in Bolt Head Sourcing?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can enhance cost efficiency:
-
Negotiation: Always negotiate with suppliers to secure better pricing. Utilize market research to substantiate requests for discounts or more favorable payment terms.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider the TCO rather than just the initial purchase price. Evaluate factors such as longevity, maintenance, and potential failure costs to determine the true value of bolt heads.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations and potential tariffs that can affect pricing. Working with suppliers who offer fixed pricing for longer contracts can mitigate these risks.
-
Supplier Diversification: Engaging multiple suppliers can foster competition and lead to better pricing and service levels. This strategy can also provide backup options in case of supply chain disruptions.
-
Local Partnerships: Establishing partnerships with local suppliers in the target regions can reduce logistics costs and lead to more favorable pricing structures due to lower shipping distances and tariffs.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
It is important to note that prices for bolt heads can vary significantly based on the aforementioned factors. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotations to ensure they are getting the best possible deal for their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing types of bolt heads With Other Solutions
Introduction: What Are the Alternatives to Traditional Bolt Heads?
In the realm of fastening solutions, bolt heads are a ubiquitous choice for connecting components in various applications. However, there are alternative solutions that may offer unique benefits based on the specific needs of a project. This analysis will compare traditional bolt heads with alternative fastening technologies, including threaded inserts and welding, to provide international B2B buyers with actionable insights for making informed decisions.
Comparison Table: Evaluating Bolt Heads Against Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Types Of Bolt Heads | Threaded Inserts | Welding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High tensile strength; reliable in dynamic loads | Moderate strength; suitable for static applications | Very high strength; ideal for permanent joins |
| Cost | Moderate; varies by material and size | Generally low; installation tools may add cost | High; requires skilled labor and equipment |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple; requires basic tools (wrench/screwdriver) | Moderate; requires precision for installation | Complex; requires specialized training and equipment |
| Maintenance | Low; easy to inspect and replace | Moderate; may require periodic checks | Low; permanent join with no maintenance needed |
| Best Use Case | Machinery, construction, automotive | Furniture assembly, electronic enclosures | Heavy machinery, structural applications |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What Are Threaded Inserts and Their Advantages?
Threaded inserts are cylindrical devices that allow for the creation of a strong threaded hole in softer materials, such as wood or plastic. These inserts can enhance the load-bearing capacity of a joint and facilitate easy replacement of damaged threads. The primary advantage of threaded inserts is their cost-effectiveness, especially in applications where the material may not support direct threading. However, they do require careful installation and may not be suitable for high-stress applications.
How Does Welding Compare to Bolt Heads?
Welding is a process that permanently joins materials by melting and fusing them together. This method provides exceptional strength and is ideal for applications that demand high durability, such as heavy machinery and structural components. The major drawback of welding is the initial investment in skilled labor and equipment, which can be significant. Additionally, once welded, components cannot be easily disassembled, making maintenance and repair more challenging compared to using bolt heads.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Fastening Solution for Your Needs
When selecting between bolt heads and alternative fastening solutions like threaded inserts or welding, B2B buyers should carefully assess their specific project requirements. Factors such as performance needs, cost constraints, ease of implementation, and maintenance expectations will guide the decision-making process. For applications requiring flexibility and ease of maintenance, bolt heads may be the best choice. Conversely, for projects demanding high strength and permanence, welding could be the superior option. By understanding the advantages and limitations of each solution, buyers can make informed choices that align with their operational needs and project objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for types of bolt heads
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Bolt Heads?
When selecting bolt heads for international projects, understanding specific technical properties is crucial. Here are some critical specifications that B2B buyers should consider:
1. Material Grade: Why Is It Important?
The material grade of a bolt head determines its strength, corrosion resistance, and suitability for specific applications. Common materials include stainless steel, carbon steel, and alloy steel. For example, stainless steel (often classified under ASTM A193) offers superior corrosion resistance, making it ideal for marine or chemical environments. Buyers should assess the environmental conditions their bolts will face to ensure longevity and reliability.
2. Tolerance: How Does It Affect Performance?
Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in dimensions and thread pitch of the bolt head. Tight tolerances ensure that the bolt fits precisely into its corresponding nut or hole, which is vital for maintaining structural integrity. Poor tolerances can lead to mechanical failure or premature wear. Understanding tolerance specifications can help buyers avoid costly replacements and downtime.
3. Coating and Finish: What Are the Options?
Bolt heads can come with various coatings, such as zinc plating, black oxide, or powder coating, which enhance corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. The choice of finish may also affect the bolt’s friction characteristics and compatibility with other materials. Buyers should consider the operational environment when selecting the appropriate coating to extend the life of their fasteners.
4. Load Rating: How Much Can It Handle?
The load rating indicates the maximum load a bolt head can sustain without failure. This property is vital for ensuring safety in structural applications. For instance, a bolt rated for 8.8 will have a different load capacity than one rated for 10.9. Understanding load ratings helps buyers select the right bolts for their specific applications and prevents catastrophic failures.
5. Head Style: Which One Is Best for Your Application?
Different bolt head styles, such as hex, socket, or pan, serve various functions and applications. For instance, hex heads allow for easy tightening with standard wrenches, while socket heads provide better access in tight spaces. Choosing the right head style can streamline installation and maintenance processes, enhancing overall project efficiency.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Bolt Heads?
Familiarity with industry jargon can facilitate smoother transactions and clearer communication between buyers and suppliers. Here are some essential trade terms every B2B buyer should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM specifications can help buyers ensure they are sourcing quality components that meet industry standards.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Being aware of MOQ can help buyers plan their purchases effectively and manage inventory costs, especially when sourcing from international suppliers.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and availability for specific products. Crafting a precise RFQ can expedite the procurement process, ensuring that buyers receive competitive quotes tailored to their needs.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding Incoterms can help international buyers navigate logistics and reduce unexpected costs.
5. Fastener Specifications

A stock image related to types of bolt heads.
Fastener specifications encompass all technical details related to a bolt or screw, including dimensions, material, and performance standards. Having a clear understanding of these specifications can assist buyers in making informed decisions, ensuring compatibility and performance in their applications.
In summary, understanding the technical properties and trade terminology associated with bolt heads can significantly enhance the purchasing decisions for international B2B buyers. By focusing on these key aspects, buyers can ensure they select the most suitable fasteners for their specific needs, ultimately leading to more successful projects and partnerships.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the types of bolt heads Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics for Bolt Heads in B2B Sourcing?
The global market for bolt heads is experiencing significant transformation driven by various factors, including industrial growth, technological advancements, and shifting consumer preferences. In regions such as Africa and South America, the demand for high-quality fasteners is growing as infrastructure projects and manufacturing sectors expand. The Middle East is witnessing a surge in construction and oil-related projects, further increasing the need for durable and reliable bolt heads. In Europe, stringent quality standards and regulations are pushing manufacturers to innovate, focusing on precision-engineered components that cater to specific applications.
Emerging technologies in manufacturing, such as 3D printing and automated assembly, are reshaping sourcing trends. These innovations enable suppliers to offer customized bolt heads that meet unique client specifications, which is particularly attractive to international B2B buyers looking for tailored solutions. Furthermore, digital platforms and e-commerce are streamlining the procurement process, allowing buyers from different regions to compare products and suppliers effortlessly. As global supply chains become more interconnected, B2B buyers are increasingly leveraging data analytics to forecast demand and optimize inventory management, ensuring they remain competitive in this dynamic market.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing the Bolt Heads Sector?
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of modern B2B sourcing practices, particularly in the fastener industry. The environmental impact of traditional manufacturing processes, including high energy consumption and waste generation, is prompting buyers to seek eco-friendly alternatives. Ethical sourcing is now a priority for many businesses, as consumers increasingly demand transparency regarding the materials and processes used in production. For bolt heads, this translates into a preference for suppliers who can demonstrate compliance with environmental standards and offer certifications such as ISO 14001.
Moreover, the use of sustainable materials, like recycled metals, is gaining traction. Buyers are encouraged to inquire about the sourcing practices of their suppliers, focusing on those who utilize green certifications or sustainable manufacturing processes. This not only helps mitigate environmental impact but also enhances brand reputation and customer loyalty. The emphasis on sustainability is reshaping supplier relationships, with buyers increasingly favoring partners that align with their ethical values.
What Is the Historical Context Behind the Evolution of Bolt Heads?
The evolution of bolt heads has been closely tied to advancements in engineering and manufacturing processes. Historically, the use of bolts can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where rudimentary fasteners were crafted from wood and metal to hold structures together. As industrialization progressed in the 18th and 19th centuries, the demand for more robust and standardized fasteners grew, leading to the development of various bolt head designs suited for different applications.
The introduction of mechanized manufacturing in the early 20th century allowed for mass production of bolts, enhancing their availability and affordability. Today, innovations such as cold heading, die stamping, and automated assembly lines have enabled the creation of highly specialized bolt heads tailored for specific industries, from automotive to construction. This historical context is essential for B2B buyers to understand the breadth of options available and the technological advancements that continue to shape the market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of types of bolt heads
-
How do I choose the right bolt head type for my application?
Selecting the appropriate bolt head type depends on several factors, including the materials you are fastening, the load requirements, and the environmental conditions. For example, hex bolts are ideal for high-torque applications, while carriage bolts work well in wood. Consider whether you need a flush finish (flat head) or a more prominent appearance (rounded head). Additionally, assess the accessibility of the fastening location; some heads require specific tools for installation. Consulting with suppliers and reviewing technical specifications can further guide your decision. -
What is the best bolt head type for high-stress applications?
For high-stress applications, hex bolts are often the best choice due to their robust design and ability to withstand significant torque. They provide a larger surface area for wrench engagement, ensuring a secure fit. Additionally, socket cap screws, which use an Allen wrench, are effective in tight spaces where traditional wrenches cannot reach. Always verify the tensile strength and material specifications to ensure the chosen bolt head type can handle the specific load and environmental conditions. -
How can I ensure the quality of bolt heads when sourcing internationally?
To ensure quality when sourcing bolt heads internationally, begin by vetting suppliers thoroughly. Look for certifications like ISO 9001, which indicates adherence to quality management standards. Request samples and conduct inspections, possibly utilizing third-party quality assurance services. Establish clear communication regarding specifications, standards, and performance metrics. Furthermore, consider visiting manufacturing facilities if feasible, to assess their production processes firsthand. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for bolt heads?
Minimum order quantities for bolt heads can vary significantly based on the supplier and the type of bolt head required. Generally, MOQs can range from a few hundred to several thousand pieces. For custom or specialized bolt heads, the MOQ may be higher due to production setup costs. Always inquire about MOQs during the initial discussions with suppliers, and negotiate terms that align with your purchasing strategy. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing bolt heads internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of bolt heads typically include options such as advance payment, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. Many suppliers may request a deposit upfront, especially for custom orders. It’s crucial to understand the terms clearly and negotiate favorable conditions that safeguard your interests. Consider using secure payment methods that offer buyer protection to mitigate risks associated with international transactions. -
How does shipping impact the cost of sourcing bolt heads from overseas?
Shipping can significantly impact the overall cost of sourcing bolt heads from overseas. Factors such as shipping method, weight, dimensions, and destination play a crucial role in determining freight costs. Additionally, customs duties and taxes may apply upon importation, depending on the country’s regulations. To optimize costs, consider bulk purchasing and exploring various shipping options, including air freight for urgent needs versus sea freight for more economical solutions. -
What customization options are available for bolt heads?
Customization options for bolt heads can include variations in size, material, coating, and specific head shapes to meet unique application requirements. Many suppliers offer services to tailor bolt heads based on your technical specifications, including finishes like zinc plating or anodizing for corrosion resistance. It’s advisable to discuss your customization needs early in the sourcing process to ensure the supplier can accommodate your requests within your timeframe and budget. -
What are the common logistical challenges when sourcing bolt heads internationally?
Logistical challenges in sourcing bolt heads internationally can include delays in shipping, customs clearance issues, and communication barriers with suppliers. To mitigate these challenges, establish a reliable logistics partner who understands international shipping regulations and can provide timely updates. Additionally, prepare for potential delays by planning ahead and allowing extra time for unforeseen circumstances. Regular communication with your supplier can also help address any issues proactively.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for types of bolt heads
What Are the Key Takeaways for International B2B Buyers on Bolt Heads?
In today’s competitive marketplace, understanding the various types of bolt heads is crucial for international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Strategic sourcing not only involves selecting the right fasteners based on application needs but also considers factors such as material quality, cost efficiency, and supplier reliability. By prioritizing these elements, buyers can enhance their procurement strategies, ensuring that they choose the most suitable bolt head types for their projects, whether it be hex bolts for robust applications or socket screws for precision tasks.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Improve Your Supply Chain?
Investing time in strategic sourcing can yield significant benefits, including reduced lead times and improved supply chain transparency. Buyers should actively seek partnerships with manufacturers that offer comprehensive product lines and customizable options to meet specific industry requirements. Leveraging local suppliers can also help mitigate logistical challenges, particularly in regions where access to global markets may be limited.
What’s Next for B2B Buyers in the Fastener Market?
As the fastener market evolves, staying informed about new materials and innovative manufacturing processes will be key. Buyers should keep an eye on emerging trends, such as sustainable materials and advanced manufacturing techniques, to remain competitive. By adopting a proactive approach to sourcing and fostering relationships with trusted suppliers, international B2B buyers can position themselves for long-term success in their respective industries. Embrace this opportunity to refine your sourcing strategy and ensure you are equipped with the best tools for your operational needs.