Enhance Efficiency: The Ultimate Cold Room Guide (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cold room
Navigating the complexities of sourcing cold rooms for commercial use can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Cold rooms are essential for maintaining the integrity of perishable goods and can significantly impact operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. However, selecting the right cold room involves understanding various factors, including the types available, their applications, supplier vetting processes, and cost implications.
This comprehensive guide is designed to empower B2B buyers by providing valuable insights into the global market for cold rooms. We will explore the different types of cold rooms, including walk-in refrigerators and freezers, and discuss their specific applications across various industries. Additionally, we will delve into the critical considerations for selecting the right supplier, ensuring that they meet the unique needs of your business while also adhering to international standards.
By addressing common questions and concerns, this guide will equip you with the knowledge necessary to make informed purchasing decisions. Whether you are a buyer in a bustling urban center or a remote location, understanding the landscape of cold room solutions will help you navigate the market with confidence, ultimately enhancing your operational capabilities and ensuring the longevity of your perishable goods.
Understanding cold room Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Walk-In Cold Room | Large, insulated space; customizable shelving; easy access | Food storage in restaurants, warehouses | Pros: High capacity, energy-efficient; Cons: Requires significant upfront investment and space. |
| Walk-In Freezer | Maintains temperatures below freezing; robust insulation | Frozen food storage, pharmaceuticals | Pros: Ideal for long-term storage; Cons: Higher energy costs and more complex installation. |
| Cold Storage Room | Versatile temperature settings; can be configured for various goods | Flowers, beverages, and perishables | Pros: Flexible use; Cons: Temperature control can be challenging without proper design. |
| Cold Clean Room | HEPA filtration for air cleanliness; controlled temperature and humidity | Biotechnology, pharmaceuticals | Pros: Maintains sterile environment; Cons: Higher operational costs due to filtration systems. |
| Modular Cold Room | Prefabricated panels; quick assembly; customizable size | Temporary storage solutions, events | Pros: Fast installation; Cons: May lack durability compared to permanent structures. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Walk-In Cold Rooms?
Walk-in cold rooms are designed for substantial storage needs, providing ample space for a variety of products, particularly in food service and logistics. Their customizable shelving allows for efficient organization, making restocking straightforward. For B2B buyers, it’s crucial to consider the room’s insulation quality and energy efficiency, as these factors significantly impact operating costs.
How Do Walk-In Freezers Differ from Other Cold Rooms?
Walk-in freezers are specifically engineered to maintain sub-zero temperatures, making them ideal for businesses that require long-term frozen storage, such as food distributors and pharmaceutical companies. When purchasing a walk-in freezer, buyers should assess the required temperature range, energy consumption, and potential installation challenges, as these units often involve more complex mechanical systems.
What Makes Cold Storage Rooms Versatile?
Cold storage rooms can be tailored for various temperature settings, accommodating everything from fresh produce to beverages. This flexibility is particularly advantageous for businesses that deal with multiple product types. However, B2B buyers must ensure the room is designed with effective temperature control systems to prevent spoilage and maintain product integrity.
Why Are Cold Clean Rooms Important for Certain Industries?
Cold clean rooms combine temperature control with air quality management, making them essential in sectors like biotechnology and pharmaceuticals, where product sterility is paramount. When investing in a cold clean room, buyers should consider the costs associated with advanced filtration systems and ensure that the room’s design meets specific regulatory requirements.
What Are the Benefits of Modular Cold Rooms?
Modular cold rooms offer a quick and efficient solution for businesses needing temporary or flexible cold storage. Their prefabricated panels allow for rapid assembly, making them ideal for events or seasonal storage needs. However, potential buyers should weigh the benefits of quick setup against the durability and long-term reliability of these structures compared to traditional cold rooms.
Key Industrial Applications of cold room
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Cold Room | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food and Beverage | Storage of perishable goods | Ensures food safety and extends shelf life | Temperature control, insulation quality, and energy efficiency |
| Pharmaceuticals | Vaccine and drug storage | Maintains efficacy of temperature-sensitive products | Compliance with regulatory standards and monitoring systems |
| Agriculture | Cold storage for fruits and vegetables | Reduces spoilage and maintains freshness | Humidity control and capacity for bulk storage |
| Floral Industry | Storage of cut flowers and plants | Preserves quality and extends product lifespan | Temperature range and ventilation requirements |
| Chemical Industry | Storage of temperature-sensitive chemicals | Prevents degradation and ensures safety | Material compatibility and safety features |
How are Cold Rooms Utilized in the Food and Beverage Industry?
In the food and beverage sector, cold rooms are essential for storing perishable goods such as meat, dairy, and produce. They provide a controlled environment that maintains optimal temperatures, preventing spoilage and ensuring compliance with health regulations. International buyers should consider the energy efficiency of the cold room, as well as its insulation quality, to minimize operational costs. Additionally, proper temperature monitoring systems are crucial for maintaining food safety standards.
What Role Do Cold Rooms Play in Pharmaceutical Storage?
Cold rooms are critical for the pharmaceutical industry, particularly for the storage of vaccines and temperature-sensitive medications. These facilities maintain precise temperature controls, which are vital for preserving the efficacy of these products. When sourcing cold rooms, buyers must ensure compliance with local regulatory standards, as well as consider the integration of advanced monitoring systems that provide alerts for any temperature fluctuations. This is particularly relevant for buyers in regions with diverse climate conditions.
How Do Cold Rooms Benefit Agricultural Operations?
In agriculture, cold rooms serve as vital storage facilities for fruits, vegetables, and other perishables. They help minimize spoilage and maintain the freshness of products during transportation and distribution. Buyers in this sector should focus on humidity control features, as excessive moisture can lead to spoilage. Additionally, the capacity to accommodate bulk storage is essential, particularly for larger operations in regions with high agricultural outputs.

A stock image related to cold room.
What Applications Exist for Cold Rooms in the Floral Industry?
The floral industry relies on cold rooms to store cut flowers and live plants, ensuring they remain fresh for extended periods. These facilities help maintain the ideal temperature and humidity levels, which are critical for preserving the quality of floral arrangements. Buyers should prioritize temperature range specifications and ventilation systems when sourcing cold rooms, as these factors directly impact the longevity of their products.
How Are Cold Rooms Used for Chemical Storage?
In the chemical industry, cold rooms are utilized for the storage of temperature-sensitive chemicals that require specific environmental conditions to prevent degradation. These facilities ensure that chemicals are stored safely, reducing risks associated with spoilage or hazardous reactions. Buyers should consider the compatibility of materials used in cold room construction with the chemicals stored, as well as the inclusion of safety features such as alarms and redundant systems to maintain operational integrity.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cold room’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Temperature Control Leading to Spoilage
The Problem: One of the most pressing challenges B2B buyers face with cold rooms is the inability to maintain consistent temperature control. Fluctuations can occur due to various factors, such as poor insulation, outdated mechanical systems, or inadequate installation. This inconsistency can lead to spoilage of perishable goods, resulting in financial losses, especially for businesses in the food service or pharmaceutical sectors.
The Solution: To combat temperature inconsistency, buyers should prioritize sourcing cold rooms with high-quality insulated panels and a robust mechanical design. When specifying a cold room, ensure it includes features such as redundant cooling systems that can kick in if the primary system fails. Additionally, work with reputable suppliers who provide comprehensive installation services. A site survey is essential to evaluate the ambient conditions and ensure proper ventilation. Regular maintenance checks and temperature monitoring systems with alarms can also help in maintaining optimal conditions, thus safeguarding your stock and minimizing spoilage.
Scenario 2: High Energy Costs Due to Inefficient Cold Room Design
The Problem: B2B buyers often experience soaring energy bills due to inefficient cold room designs. Poor insulation, outdated refrigeration technology, and improper placement can lead to excessive energy consumption. This is particularly concerning for businesses in regions like Africa or South America, where energy costs can significantly impact operational budgets.
The Solution: To mitigate high energy costs, invest in modern cold room designs that emphasize energy efficiency. Look for cold rooms with features like automatic door closers, energy-efficient compressors, and insulated flooring. When selecting a supplier, inquire about energy consumption ratings and request designs that comply with local energy efficiency standards. A professional installation that considers the specific ambient conditions of your location will also optimize performance. Additionally, consider integrating smart monitoring systems that track energy usage and identify areas for improvement, allowing you to make data-driven decisions that enhance efficiency.
Scenario 3: Inadequate Space Utilization Leading to Operational Inefficiencies
The Problem: Many businesses struggle with inadequate space utilization in their cold rooms, leading to operational inefficiencies. This is often a result of poor design choices or insufficient shelving options, making it difficult to organize and access products quickly. In fast-paced environments, such as restaurants or warehouses, this can slow down operations and impact service delivery.
The Solution: To improve space utilization, start by assessing your current storage needs and product types. Choose a cold room that allows for customizable shelving options made from durable materials like PVC or anodized aluminum, which can withstand the cold environment without deteriorating. Implement a first-in, first-out (FIFO) system to ensure older stock is used first, preventing waste. Additionally, consider installing features like adjustable racks and mobile shelving units that can be reconfigured as your inventory changes. Collaborate with suppliers who offer design consultation services to create a layout that maximizes efficiency, ensuring you have easy access to all products while maintaining an organized storage area.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cold room
What Are the Key Materials for Cold Room Construction?
When selecting materials for cold room construction, it’s essential to consider factors such as thermal efficiency, durability, and resistance to environmental conditions. Here, we analyze four common materials used in cold room applications: polyurethane foam, stainless steel, aluminum, and PVC. Each material has distinct properties that influence performance and suitability for various applications.
How Does Polyurethane Foam Perform in Cold Room Applications?
Key Properties: Polyurethane foam is known for its excellent thermal insulation properties, with a thermal conductivity rating as low as 0.020 W/mK. It is lightweight and can withstand a wide range of temperatures, making it ideal for cold room applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of polyurethane foam is its high insulation efficiency, which leads to lower energy costs. However, it can be susceptible to moisture absorption if not properly sealed, which may lead to degradation over time. Additionally, while it is relatively cost-effective, the manufacturing process can be complex, requiring specialized equipment.
Impact on Application: Polyurethane foam is particularly effective in maintaining consistent internal temperatures, crucial for perishable goods. However, buyers must ensure that the foam is adequately protected from moisture to prevent performance issues.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with local insulation standards, such as ASTM in the U.S. or EN in Europe, is vital. Buyers in regions with high humidity, like parts of Africa and South America, should prioritize moisture-resistant formulations.
What Are the Benefits of Using Stainless Steel in Cold Rooms?
Key Properties: Stainless steel is renowned for its strength, corrosion resistance, and ability to withstand extreme temperatures. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 1200°F (649°C) and is resistant to various chemicals.
Pros & Cons: The durability of stainless steel makes it ideal for high-traffic cold rooms, as it can withstand physical wear and tear. However, it is one of the more expensive materials, which may deter budget-conscious buyers. Additionally, its weight can complicate installation.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is suitable for environments requiring frequent cleaning and sanitation, such as food storage. Its resistance to corrosion ensures longevity in humid conditions, making it a preferred choice for cold rooms in tropical regions.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with food safety standards, such as those set by the FDA or local health authorities. In the Middle East and Europe, stainless steel grades must meet specific regulations (e.g., AISI 304 or 316).
How Does Aluminum Compare for Cold Room Use?
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has good thermal conductivity. It can handle temperature variations effectively, making it suitable for cold room applications.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of aluminum is its cost-effectiveness and ease of installation. However, it is less durable than stainless steel and may require additional coatings to enhance its resistance to corrosion in humid environments.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is particularly effective in cold rooms that require frequent access, as its lightweight nature allows for easier handling. However, it may not be the best choice for high-impact areas.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should look for aluminum that meets international standards, such as EN 573 for aluminum alloy specifications. In regions like South America, where humidity is high, ensuring proper coating is essential to prevent corrosion.
What Role Does PVC Play in Cold Room Construction?
Key Properties: PVC is a versatile plastic known for its excellent chemical resistance and low thermal conductivity. It is lightweight and can be easily molded into various shapes.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of PVC is its affordability and ease of installation. However, it may not withstand extreme temperatures as effectively as other materials, limiting its use in very low-temperature environments.
Impact on Application: PVC is suitable for cold rooms that require frequent cleaning and maintenance, as it is resistant to many chemicals. However, its thermal insulation properties may not be sufficient for all applications, particularly those requiring ultra-low temperatures.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with local regulations regarding plastic materials is crucial, especially in the Middle East and Europe, where certain PVC formulations may be restricted. Buyers should also consider the environmental impact of PVC disposal.
Summary of Material Selection for Cold Rooms
| Material | Typical Use Case for Cold Room | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyurethane Foam | Insulation panels for temperature control | High thermal efficiency | Susceptible to moisture absorption | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Walls and shelving in high-traffic areas | Durability and corrosion resistance | High cost and weight | High |
| Aluminum | Framework and access doors | Lightweight and cost-effective | Less durable than stainless steel | Medium |
| PVC | Wall coverings and shelving | Affordable and easy to install | Limited low-temperature performance | Low |
By carefully considering these materials and their properties, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cold room
What Are the Main Stages of Cold Room Manufacturing Processes?
The manufacturing process for cold rooms involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the required specifications for performance, safety, and longevity. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How is Material Prepared for Cold Room Production?
Material preparation is the first step in the cold room manufacturing process. This involves sourcing high-quality materials such as insulated panels, flooring systems, and refrigeration components. Insulated panels are typically made from materials like polyurethane or polystyrene, which provide excellent thermal insulation. The thickness and density of these panels are crucial, as they directly affect the cold room’s efficiency and energy consumption.
Moreover, suppliers should ensure that all materials comply with international standards to guarantee safety and quality. This is particularly important for B2B buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where local manufacturing standards may vary. Buyers should inquire about the origin of materials and whether they meet relevant certifications.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Cold Room Components?
Once materials are prepared, the next stage is forming. This stage involves cutting, shaping, and assembling the insulated panels and other structural components. Advanced techniques, such as CNC machining, are often used to ensure precision and consistency in the dimensions of the panels.
The forming process also includes the creation of door systems, which are essential for maintaining the thermal envelope of the cold room. Different door types, including swinging, sliding, or even vinyl strip doors, can be manufactured based on the specific needs of the business. Buyers should consider the type of door that minimizes cold air loss while providing easy access for staff.
How is Cold Room Assembly Conducted?
The assembly stage involves putting together all the components, including the insulated panels, flooring, refrigeration systems, and controls. This process often requires skilled labor to ensure that all parts fit together correctly, creating a robust structure that can withstand the operational demands of a cold room.
Quality assurance at this stage is critical. Manufacturers should implement a series of checks to ensure that all components function as intended. Buyers can ask for documentation regarding assembly methods and the qualifications of the assembly team, as this can impact the cold room’s performance.
What Finishing Touches Are Added to Cold Rooms?
Finishing processes typically include painting, sealing, and installing any additional features such as lighting and emergency systems. The goal is to create a cold room that is not only functional but also aesthetically pleasing and safe for users.
Finishing touches often include the installation of automatic defrost systems and internal panic buttons, which enhance user safety and operational efficiency. Buyers should verify that these features meet the specific safety regulations and standards of their respective regions.
What Are the Key Quality Assurance Standards for Cold Rooms?
Quality assurance (QA) is a vital aspect of the cold room manufacturing process, ensuring that products meet both international and industry-specific standards.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
ISO 9001 is a widely recognized international standard that outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS). Manufacturers that comply with ISO 9001 demonstrate their commitment to quality and customer satisfaction. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers with ISO certification, as this indicates a structured approach to quality management.
In addition, CE marking is essential for products sold in the European Economic Area (EEA), ensuring that they meet safety, health, and environmental protection standards. For buyers in the Middle East, understanding the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) standards can also be beneficial.
What Are the Industry-Specific Quality Control Checkpoints?
During the manufacturing process, several quality control checkpoints are implemented. These typically include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial check verifies the quality of raw materials before they are used in production.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Conducted during various stages of production, IPQC ensures that the assembly and installation meet the required standards.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): This last stage involves comprehensive testing of the completed cold room to ensure it operates correctly and meets all specifications.
Common testing methods include thermal performance testing, pressure tests, and safety inspections. B2B buyers should request detailed reports of these tests to verify compliance with quality standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers can take several steps to ensure their suppliers maintain high-quality standards throughout the manufacturing process.
What Steps Can Buyers Take for Supplier Audits?
Conducting supplier audits is one of the most effective ways to verify quality control processes. Buyers should schedule regular audits to evaluate the supplier’s manufacturing practices, quality assurance measures, and adherence to international standards. During these audits, buyers can assess the supplier’s compliance with ISO standards, review documentation, and even inspect the manufacturing facilities.
How Important Are Reports and Third-Party Inspections?
Requesting detailed quality control reports is essential for transparency. These reports should outline the results of IQC, IPQC, and FQC processes. Additionally, engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide unbiased assessments of the supplier’s quality management practices. This is especially relevant for international buyers who may be unfamiliar with local manufacturing standards.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate various quality control nuances when sourcing cold rooms.
How Do Regional Regulations Affect Quality Standards?
Different regions may have specific regulations that affect quality assurance processes. For instance, buyers in Europe may need to consider GDPR compliance when dealing with suppliers, while those in Africa might face different local regulations. Understanding these nuances is critical for ensuring that the cold room complies with all necessary legal requirements.
Why Is Understanding the Supply Chain Important?
Buyers should also consider the entire supply chain, from material sourcing to final delivery. Disruptions in the supply chain can impact quality, so it is vital to work with suppliers who maintain robust quality control practices throughout their operations.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in cold room production is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on these aspects, buyers can make informed decisions that ensure they receive high-quality, reliable cold storage solutions tailored to their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cold room’
To effectively procure a cold room for your business, a systematic approach is essential. This checklist provides international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, with actionable steps to ensure they make informed decisions when sourcing cold room solutions.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical requirements is the foundation of your cold room procurement process. Consider factors such as temperature range, size, and capacity based on your storage needs. For example, if you require both refrigeration and freezing capabilities, specify that in your requirements.
- Temperature Needs: Identify whether you need a standard cold room or a specialized freezer.
- Storage Capacity: Calculate the volume of goods you intend to store to determine the appropriate size.
Step 2: Assess Your Location and Site Conditions
Understanding the physical space where the cold room will be installed is crucial. Evaluate the ambient temperature, ventilation, and accessibility of the installation site. Proper site conditions will significantly impact the efficiency and functionality of the cold room.
- Ventilation Requirements: Ensure there is adequate airflow to maintain temperature stability.
- Physical Space: Measure the area to confirm that the cold room will fit without obstructing operations.
Step 3: Research and Shortlist Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers of cold rooms. Look for companies with a proven track record in your region and industry. This step is vital for finding reliable partners who can meet your specific needs.
- Supplier Experience: Consider the supplier’s years in business and their specialization in cold room technology.
- Client Testimonials: Seek reviews or case studies from previous clients to gauge customer satisfaction.
Step 4: Evaluate Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Before finalizing a supplier, verify their certifications and compliance with industry standards. This ensures that the cold room meets safety and performance regulations, which is especially important in regions with strict health codes.
- Quality Certifications: Look for ISO certifications or similar standards that demonstrate a commitment to quality.
- Local Compliance: Check if the supplier adheres to local regulations regarding refrigeration and food safety.
Step 5: Request Detailed Proposals and Quotes
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request detailed proposals that outline the specifications, installation timelines, and pricing. A comprehensive quote will help you compare offerings and make an informed decision.
- Breakdown of Costs: Ensure the proposal includes a detailed cost breakdown covering materials, installation, and maintenance.
- Warranty and Support: Inquire about warranty terms and after-sales support to safeguard your investment.
Step 6: Plan for Installation and Maintenance
Discuss the installation process with your chosen supplier. Proper installation is crucial for the longevity and efficiency of your cold room. Additionally, consider scheduling regular maintenance checks to prevent unexpected failures.
- Installation Timeline: Confirm how long the installation will take and any potential disruptions to your operations.
- Maintenance Plans: Explore options for ongoing maintenance services to ensure optimal performance.
Step 7: Finalize the Purchase Agreement
After evaluating all factors and selecting a supplier, finalize the purchase agreement. Ensure that all terms, including delivery timelines, payment terms, and warranty conditions, are clearly outlined.
- Contract Clarity: Review the contract to ensure that it accurately reflects your agreements.
- Legal Review: Consider having a legal expert review the contract to protect your interests.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing a cold room effectively, ensuring they select a solution that meets their operational needs and adheres to industry standards.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cold room Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Cold Room Sourcing?
When sourcing cold rooms, understanding the breakdown of costs is essential for effective budgeting and financial planning. The major components include:
-
Materials: The cost of high-quality insulated panels, refrigeration units, and flooring materials are significant. Materials need to be durable and efficient to ensure optimal thermal performance.
-
Labor: Installation labor can vary greatly depending on the complexity of the cold room design and local labor rates. Skilled technicians are required to ensure proper installation and functionality.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs related to the production of cold rooms, such as utilities, equipment depreciation, and facility maintenance.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in specialized tools for the assembly and installation of cold rooms can be substantial, particularly for custom designs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the cold room meets specified standards and certifications incurs costs in testing and quality assurance processes.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, including freight charges and potential customs duties, can significantly impact the overall price, especially for international buyers.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to their costs, which can vary based on market conditions and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Cold Room Costs?
Several factors can influence the final price of cold rooms:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger volumes often leads to discounts. Understanding Minimum Order Quantities (MOQ) can help buyers negotiate better deals.
-
Specifications and Customization: Tailored solutions that meet specific business requirements generally cost more than standard models. Buyers should weigh the need for customization against budget constraints.
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly affects costs. For example, opting for high-performance insulation will increase the upfront cost but can lead to energy savings over time.
-
Quality and Certifications: Cold rooms that meet international standards and certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) may have a higher price tag but offer peace of mind regarding safety and efficiency.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation and experience can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their reliability and service quality.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms (e.g., FOB, CIF) is crucial for international buyers, as they dictate who bears the shipping costs and risks, influencing the total cost.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficient Cold Room Sourcing?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Be prepared to negotiate prices and terms with suppliers. Leverage competitive offers from multiple vendors to secure the best deal.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price, but also the operational costs over the cold room’s lifecycle. Energy efficiency, maintenance, and potential downtime should all be factored into the decision.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of currency fluctuations and tariffs that could affect overall costs. Establishing relationships with local suppliers may mitigate some of these risks.
-
Research and Comparison: Conduct thorough market research to compare prices, features, and service offerings from different suppliers. This can help identify the best value proposition.
-
Consider After-Sales Support: A supplier that offers robust after-sales support, including maintenance and repairs, can save costs in the long run.
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices
Prices for cold rooms can vary widely based on the factors outlined above. It is advisable for buyers to obtain customized quotes tailored to their specific requirements and to account for any potential additional costs that may arise during sourcing and installation.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cold room With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Cold Rooms for B2B Buyers
When considering refrigeration solutions for commercial needs, cold rooms are often a top choice due to their efficiency and capacity. However, several alternatives can also meet the demands of various businesses. Understanding these options can help international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe make informed decisions.
Comparison Table of Refrigeration Solutions
| Comparison Aspect | Cold Room | Walk-In Freezer | Refrigerated Shipping Container |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent temperature control; ideal for large stock | Superior freezing capabilities; maintains temperatures below 0°C | Good for transport; temperature can vary based on external conditions |
| Cost | Higher initial investment; lower operating costs due to energy efficiency | Higher upfront costs; long-term savings on bulk freezing | Moderate costs; potential for high transport costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires professional installation; site-specific | Needs specialized installation; space planning required | Easier to deploy in various locations; no permanent installation needed |
| Maintenance | Requires regular maintenance checks; more durable | Regular checks necessary; potential for mechanical failures | Limited maintenance; needs inspection before transport |
| Best Use Case | Large-scale food storage in restaurants or warehouses | Food distribution centers or businesses requiring bulk freezing | Temporary storage and transportation of goods across regions |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Walk-In Freezers?
Walk-in freezers offer similar benefits to cold rooms but are specifically designed for freezing perishable goods. They maintain lower temperatures, making them ideal for businesses with high-volume freezing needs, such as meat processing or ice cream production. However, they come with higher initial costs and require careful planning for installation. Maintenance can also be more frequent due to the complexity of the freezing systems.
How Do Refrigerated Shipping Containers Compare?
Refrigerated shipping containers provide an effective solution for transporting perishable items over long distances. They are versatile and can be used for both storage and transport, making them a valuable asset for businesses in logistics. However, their performance can be affected by external temperatures, which may lead to fluctuations in internal conditions. While they have moderate costs, shipping can become expensive if not managed properly.
Conclusion: How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Refrigeration Solution?
Selecting the right refrigeration solution depends on various factors, including the specific needs of your business, budget, and operational efficiency. Cold rooms are ideal for businesses that require consistent and large-scale storage, while walk-in freezers cater to those focused on freezing capabilities. Refrigerated shipping containers offer flexibility for transport needs. Assessing your business’s unique requirements will help you make a well-informed decision that maximizes efficiency and cost-effectiveness in your operations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cold room
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Cold Rooms?
Understanding the critical specifications of cold rooms is vital for international B2B buyers, especially when making informed purchasing decisions. Below are some key technical properties that influence performance and suitability for various applications.
What is the Importance of Material Grade in Cold Rooms?
Material Grade: Cold rooms are typically constructed using insulated wall panels made from materials like polyurethane or polystyrene. The grade of these materials affects thermal efficiency, durability, and maintenance. High-grade materials minimize energy loss, which is crucial for cost-effective operations.
B2B Importance: Selecting the right material grade ensures longevity and compliance with local health and safety regulations, particularly in regions with high ambient temperatures like Africa and the Middle East.
How Does Temperature Tolerance Affect Cold Room Efficiency?
Temperature Tolerance: This specification defines the range within which a cold room can maintain its set temperature, typically between -2°C and 10°C for refrigeration, and down to -50°C for freezing applications.
B2B Importance: Knowing the temperature tolerance is essential for businesses that handle perishable goods, as improper temperature management can lead to spoilage and financial loss.
Why is Insulation Thickness Critical for Cold Room Performance?
Insulation Thickness: The thickness of insulation in the walls, ceiling, and flooring impacts the cold room’s thermal envelope. Thicker insulation generally provides better temperature retention and energy efficiency.
B2B Importance: Buyers should consider insulation thickness to ensure optimal energy consumption, especially in colder climates or for businesses with high refrigeration demands.
What Role Does Humidity Control Play in Cold Room Operations?
Humidity Control: Cold rooms often require specific relative humidity (RH) levels to preserve products effectively. Humidity controls are vital for preventing spoilage, especially for fresh produce and certain pharmaceuticals.
B2B Importance: For buyers in the food and pharmaceutical sectors, understanding humidity control can directly affect product quality and shelf life.
Common Trade Terms in the Cold Room Industry
Familiarity with industry jargon is crucial for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Below are some common trade terms associated with cold rooms.
What is an OEM in the Cold Room Sector?
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): This term refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the cold room context, OEMs often supply essential components like compressors and condensers.
B2B Importance: Partnering with reputable OEMs ensures that the cold room equipment is of high quality and reliability, which is crucial for maintaining temperature control.
How Does MOQ Affect Cold Room Purchases?
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): This term indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For cold room components, MOQs can vary widely based on the supplier and the complexity of the equipment.
B2B Importance: Understanding MOQs helps buyers plan their procurement strategies, especially when dealing with multiple suppliers in different regions.
What is an RFQ and Why is it Important?
RFQ (Request for Quotation): An RFQ is a document that a buyer sends to potential suppliers to request pricing and availability for specific products or services.
B2B Importance: Submitting an RFQ allows buyers to compare offers from various suppliers, helping them make cost-effective decisions while ensuring quality and compliance with specifications.
How Do Incoterms Influence Cold Room Shipping and Delivery?
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms): These are standardized terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. They clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs.
B2B Importance: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international buyers to manage risks and costs associated with shipping cold room equipment across borders, particularly for businesses in Africa and South America.
By grasping these essential technical properties and industry terminology, international B2B buyers can make well-informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and product quality.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cold room Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in the Cold Room Sector?
The cold room sector is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for food safety and quality, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. One of the main global drivers is the rising consumer preference for fresh and frozen foods, which necessitates robust cold storage solutions. Additionally, the expansion of e-commerce and online grocery shopping is creating new challenges for logistics and supply chain management, pushing businesses to invest in more efficient cold storage systems.
Emerging technologies such as IoT (Internet of Things) and AI (Artificial Intelligence) are transforming the cold room landscape. These technologies enable real-time monitoring of temperature and humidity levels, ensuring optimal conditions for stored goods and minimizing spoilage. As a result, B2B buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers that offer smart cold room systems with integrated monitoring capabilities.
Another trend is the move towards modular and customizable cold room solutions. Businesses are seeking flexible options that can adapt to changing storage needs without requiring extensive renovations. This trend is especially relevant for companies in fast-growing markets, where demand can fluctuate rapidly. International buyers should also be aware of regional regulations and compliance standards that may impact sourcing decisions, particularly in terms of energy efficiency and environmental impact.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact Your Cold Room Solutions?
Sustainability is becoming a crucial factor in the decision-making process for B2B buyers in the cold room sector. The environmental impact of refrigeration systems is significant, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption. As a result, many companies are prioritizing sustainable practices and seeking cold room solutions that minimize their carbon footprint.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining importance. Buyers are increasingly demanding transparency in the supply chain, favoring suppliers who adhere to ethical practices and use environmentally friendly materials. Certifications such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) and ISO 14001 are becoming essential for suppliers aiming to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability.
In addition, the use of eco-friendly insulation materials and energy-efficient refrigeration systems can significantly reduce energy costs and improve overall operational efficiency. By investing in sustainable cold room solutions, businesses not only enhance their corporate social responsibility (CSR) profile but also position themselves competitively in a market that increasingly values environmental stewardship.
What is the Historical Context of Cold Rooms in B2B?
The evolution of cold rooms can be traced back to the early 20th century when refrigeration technology began to gain traction in commercial applications. Initially, cold storage solutions were limited and often required significant space and resources. However, advancements in insulation materials and refrigeration technology have transformed cold rooms into efficient, space-saving solutions.
Over the decades, the cold room industry has shifted from simple walk-in freezers to sophisticated systems capable of maintaining precise temperature and humidity levels. The integration of technology has further enhanced cold room capabilities, allowing for better monitoring and control of storage conditions. This evolution has been particularly beneficial for businesses in sectors such as food service, pharmaceuticals, and logistics, where temperature-sensitive products are commonplace.
Today, international B2B buyers have access to a diverse range of cold room solutions tailored to meet specific industry needs, making it easier to ensure product quality and compliance with safety regulations. Understanding this historical context can help buyers appreciate the advancements in technology and design that continue to shape the cold room sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cold room
-
How do I choose the right cold room for my business needs?
Choosing the right cold room requires a clear understanding of your specific storage requirements. Consider factors like the types of products you will store (e.g., food, pharmaceuticals), the volume of stock, and the desired temperature range. It’s essential to assess the available space, ambient temperatures, and the potential need for additional features like shelving, security systems, or specialized controls. Consulting with a supplier who can conduct a site survey and offer tailored solutions can also help ensure you make the right decision. -
What are the key features to look for in a cold room?
Key features of a cold room include energy efficiency, adequate insulation, and effective temperature control systems. Look for automatic defrosting capabilities, emergency escape options, and robust door systems to minimize cold air loss. Additionally, consider the construction materials for durability, especially in harsh environments. Customizable shelving and racking options can enhance organization, while advanced control systems can provide real-time monitoring of temperature and humidity levels. -
What is the average lead time for cold room delivery and installation?
Lead times for cold room delivery and installation can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of your order. Generally, expect a timeframe of 4 to 12 weeks from order confirmation to installation. Custom-designed cold rooms may take longer due to the need for specific engineering and manufacturing. It’s advisable to discuss timelines upfront with your supplier and factor in additional time for site preparation and any necessary permits. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing a cold room?
Payment terms for purchasing a cold room can vary by supplier and may include options like upfront payment, installments, or financing. Typical arrangements may require a deposit upon order confirmation, followed by the balance due before installation. International buyers should be aware of any currency exchange implications and additional costs associated with shipping and customs duties. Always clarify terms in writing to avoid misunderstandings and ensure smooth transactions. -
How can I vet suppliers for cold room systems?
Vetting suppliers involves researching their reputation, experience, and customer reviews. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in your industry and those who offer comprehensive after-sales support. Request case studies or references from similar projects to assess their capability. It’s also beneficial to inquire about their compliance with international standards and certifications relevant to cold storage solutions. Engaging in preliminary discussions can provide insights into their responsiveness and professionalism.

A stock image related to cold room.
-
Are there minimum order quantities (MOQ) for cold room purchases?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can depend on the supplier and the specific cold room configuration. Some suppliers may have an MOQ for custom-built units, while others may accommodate smaller orders for standard models. For international buyers, it’s essential to discuss MOQs upfront, as they can affect shipping costs and overall project feasibility. If you require multiple units, negotiating bulk pricing may also be an option worth exploring. -
What are the logistics considerations for importing a cold room?
Logistics considerations for importing a cold room include shipping methods, customs clearance, and local regulations. Ensure you understand the shipping costs and potential delays associated with transporting large, heavy equipment. It’s critical to work with a logistics partner experienced in handling cold storage equipment to navigate import duties and ensure compliance with local standards. Planning for installation logistics at your facility is also crucial to minimize downtime and facilitate efficient setup. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from cold room suppliers?
Quality assurance measures from cold room suppliers should include adherence to industry standards and certifications for refrigeration systems. Suppliers should provide documentation for performance testing and validation of the cold room’s temperature and humidity control capabilities. Additionally, inquire about warranty terms and the availability of preventive maintenance plans. A reputable supplier will also offer support for troubleshooting and repairs, ensuring the longevity and reliability of your cold room system.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
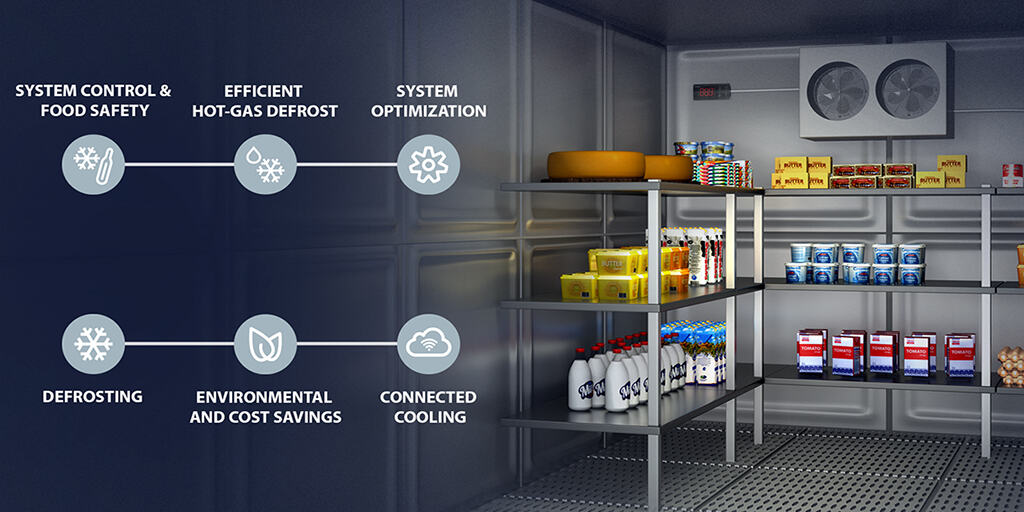
A stock image related to cold room.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cold room
In the competitive landscape of international trade, the strategic sourcing of cold rooms presents significant advantages for businesses across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Key takeaways include the importance of selecting the right size and temperature control systems tailored to your specific needs, understanding the mechanical and insulation requirements, and ensuring proper installation for optimal performance.
Investing in a cold room not only enhances food safety and storage efficiency but also leads to long-term cost savings through energy efficiency and reduced operational complexity. As the demand for reliable cold storage solutions continues to rise, especially in sectors like food service and pharmaceuticals, the need for strategic sourcing becomes even more critical.
Looking ahead, international B2B buyers are encouraged to leverage local expertise and global suppliers to optimize their cold storage solutions. By doing so, businesses can ensure they remain competitive in a rapidly evolving market. Now is the time to act—evaluate your cold room needs, explore potential partnerships, and position your company for success in the global marketplace.