Enhance Quality: The Ultimate RF Shielding Guide (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for rf shielding
In an increasingly interconnected world, the challenge of sourcing effective RF shielding solutions has become a top priority for businesses across diverse industries. As radiofrequency interference (RFI) proliferates due to the rise of wireless technologies and devices, international B2B buyers—especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—must navigate a complex landscape of materials and manufacturing techniques to protect their electronic systems. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, covering various types of RF shielding, their applications, manufacturing methods, and key considerations for supplier selection.
By delving into the intricacies of RF shielding, this guide empowers decision-makers to make informed purchasing choices that align with their unique operational needs. Whether you are looking for solutions for sensitive electronic equipment, telecommunications, or medical devices, understanding the nuances of RF shielding can significantly impact your product’s performance and compliance with international standards.
Furthermore, we provide insights into cost considerations and best practices for vetting suppliers, ensuring that you partner with manufacturers who can deliver high-quality solutions tailored to your requirements. Equip yourself with the knowledge necessary to tackle the challenges of RF interference and enhance the reliability of your electronic systems in the global market.
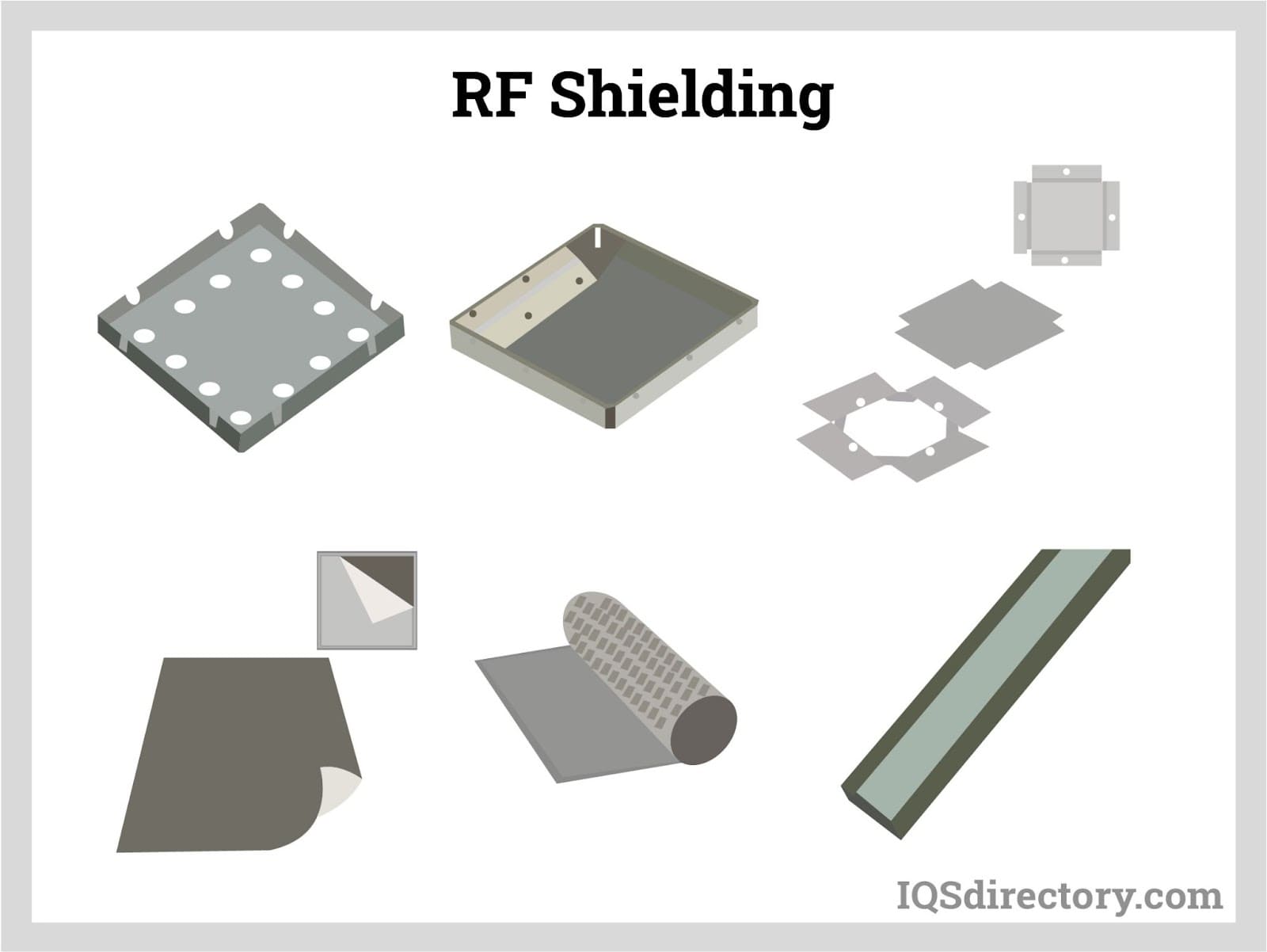
Understanding rf shielding Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conductive Enclosures | Made from metals like aluminum or copper; high RF attenuation. | Electronics, telecommunications, defense. | Pros: Effective at blocking RF signals; durable. Cons: Can be heavier and more expensive. |
| RF Shielding Foils | Thin, flexible layers of conductive materials; easy to apply. | Consumer electronics, automotive. | Pros: Lightweight and versatile; cost-effective. Cons: Lower durability compared to rigid options. |
| EMI/RF Absorbers | Materials that absorb RF energy rather than reflect it. | Aerospace, medical devices. | Pros: Reduces interference without reflection; compact. Cons: Limited effectiveness at certain frequencies. |
| Faraday Cages | Enclosures that completely surround sensitive equipment. | Secure facilities, military applications. | Pros: Highly effective shielding; customizable size. Cons: Requires precise design and installation. |
| Multi-Layer Shielding | Combinations of different materials for enhanced performance. | High-security environments, SCIFs. | Pros: Excellent performance across a range of frequencies; adaptable. Cons: Complex manufacturing processes may increase costs. |
What Are Conductive Enclosures and Their Suitability for B2B Buyers?
Conductive enclosures are typically constructed from metals such as aluminum or copper, providing high levels of RF attenuation. They are particularly suitable for industries like telecommunications, electronics, and defense, where protecting sensitive devices from RF interference is critical. When considering a purchase, B2B buyers should evaluate the enclosure’s weight, durability, and installation requirements, as these factors can significantly impact their operational efficiency and costs.
How Do RF Shielding Foils Benefit B2B Applications?
RF shielding foils are thin layers made from conductive materials, designed for flexibility and ease of application. They are commonly used in consumer electronics and automotive industries due to their lightweight nature and cost-effectiveness. Buyers should consider the foil’s adhesion properties, thickness, and compatibility with the surfaces they intend to shield, ensuring optimal performance without compromising the integrity of the devices.
What Are EMI/RF Absorbers and Their Key Considerations?
EMI/RF absorbers are specialized materials that absorb radio frequency energy rather than reflecting it. They are often used in aerospace and medical device applications where minimizing interference is crucial. For B2B buyers, it’s essential to assess the absorber’s frequency range and installation requirements to ensure it meets the specific shielding needs of their applications, as effectiveness can vary significantly across different frequencies.
Why Choose Faraday Cages for High-Security Applications?
Faraday cages are enclosures designed to completely surround sensitive equipment, providing exceptional shielding effectiveness. They are often employed in secure facilities and military applications where data protection is paramount. Buyers should consider the design specifications, including size and material choices, as these factors will influence both the cage’s performance and installation complexity.
What Are the Advantages of Multi-Layer Shielding for B2B Buyers?
Multi-layer shielding combines various materials to achieve enhanced RF shielding performance across a wide frequency range. This type of shielding is ideal for high-security environments like Sensitive Compartmented Information Facilities (SCIFs). B2B buyers must evaluate the manufacturing processes involved, as the complexity can lead to higher costs. However, the adaptability and superior performance of multi-layer shielding often justify the investment in critical applications.
Key Industrial Applications of rf shielding
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of RF Shielding | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Telecommunications | Enclosures for cellular base stations | Prevents RF interference, ensuring reliable signal transmission | Compliance with international standards, durability in various climates |
| Healthcare | MRI machine shielding | Protects sensitive equipment from external RF interference | Material certifications, ease of installation, maintenance requirements |
| Aerospace & Defense | Sensitive Compartmented Information Facilities (SCIFs) | Secures classified information from unauthorized RF access | Military-grade materials, third-party testing, and certification |
| Consumer Electronics | Mobile device casings | Enhances performance by reducing interference and improving user experience | Cost-effectiveness, design flexibility, and compatibility with existing products |
| Automotive | RF shielding in electric vehicles | Minimizes interference in critical communication systems | Lightweight materials, thermal resistance, and environmental compliance |
How is RF Shielding Used in Telecommunications?
In the telecommunications sector, RF shielding is crucial for cellular base stations, which are exposed to various RF signals that can disrupt communication. By employing RF shielding materials, these enclosures effectively mitigate interference, ensuring that signals remain clear and reliable. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America where infrastructure is rapidly evolving, sourcing materials that comply with international standards is vital. Additionally, these materials must withstand diverse environmental conditions, making durability a key consideration.
What Role Does RF Shielding Play in Healthcare?
In the healthcare industry, RF shielding is predominantly utilized in MRI machines to protect them from external radio frequency interference. Such interference can distort imaging results, leading to inaccurate diagnoses. Buyers in this sector must prioritize materials that are certified for medical use, ensuring safety and compliance with health regulations. The ease of installation and maintenance of these shielding solutions is also critical, as healthcare facilities operate under stringent operational timelines.
Why is RF Shielding Essential in Aerospace & Defense?
The aerospace and defense sectors rely heavily on RF shielding for Sensitive Compartmented Information Facilities (SCIFs), which safeguard classified information from unauthorized access. The shielding materials used must meet military-grade specifications and undergo rigorous third-party testing to ensure effectiveness. For international buyers, particularly in the Middle East and Europe, understanding the certification processes and sourcing from reputable manufacturers is essential to maintain security and compliance with defense regulations.
How Does RF Shielding Enhance Consumer Electronics?
In consumer electronics, RF shielding is integrated into mobile device casings to minimize interference, thereby enhancing performance and user experience. As the demand for high-quality electronic devices grows globally, manufacturers must focus on sourcing cost-effective shielding solutions that do not compromise on quality. Design flexibility is also crucial, allowing for seamless integration into various products while ensuring compatibility with existing technologies.
What Benefits Does RF Shielding Offer in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, particularly with the rise of electric vehicles, RF shielding is employed to reduce interference in critical communication systems, such as those used for navigation and safety. Sourcing lightweight yet effective shielding materials is essential to maintain vehicle performance and compliance with environmental standards. Buyers must consider factors like thermal resistance and the ability to withstand harsh automotive environments when selecting RF shielding solutions.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘rf shielding’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inadequate RF Shielding for Medical Devices
The Problem: B2B buyers in the medical equipment sector often face challenges with RF interference that can compromise the functionality and safety of sensitive devices. For instance, MRI machines are particularly susceptible to RF signals, which can lead to distorted imaging and inaccurate diagnostics. A medical device manufacturer might find that their product is receiving interference from nearby electronic equipment, risking both patient safety and compliance with stringent regulatory standards. This not only threatens the reliability of the device but also the manufacturer’s reputation.
The Solution: To effectively combat RF interference, it is crucial to implement comprehensive RF shielding strategies right from the design phase. Start by conducting a thorough RF analysis of the intended environment, identifying potential sources of interference. Collaborate with an experienced RF shielding manufacturer who can provide tailored solutions. Use materials like conductive metals or specialized RF shielding films that can be integrated into the device’s casing. Ensure that the RF shielding is tested for effectiveness, ideally using third-party validation to meet industry standards. Furthermore, consider designing a Faraday cage around critical components to provide an additional layer of protection against unwanted RF signals.
Scenario 2: High Costs Due to RF Shielding Failures
The Problem: Many B2B buyers are frustrated by the high costs associated with RF shielding failures, which can stem from poorly designed shielding solutions. For example, a telecommunications company may invest heavily in RF shielding for their base stations, only to find that the shielding does not meet required performance standards, leading to signal loss and the need for costly redesigns. This not only incurs additional expenses but can also delay project timelines and affect service delivery.
The Solution: To mitigate the risk of RF shielding failures, it is essential to engage in detailed planning and testing. Begin by selecting a reputable RF shielding partner with a proven track record in your industry. Prioritize materials that have been tested for RF attenuation across a broad spectrum of frequencies. Before full-scale manufacturing, employ prototyping to test the effectiveness of the shielding design under real-world conditions. This allows for adjustments before significant investments are made. Furthermore, adopting a phased approach to deployment can help identify potential issues early on, reducing the risk of costly failures down the line.
Scenario 3: Compliance with International RF Shielding Standards
The Problem: B2B buyers exporting electronic devices face the challenge of ensuring their products comply with various international RF shielding standards. For instance, a European manufacturer may wish to penetrate the African or South American markets but find that their existing RF shielding solutions do not meet the local regulatory requirements, leading to delays in product launch and increased compliance costs.
The Solution: To navigate the complex landscape of international RF compliance, it is essential to stay informed about the specific regulations in each target market. Engage with local experts or regulatory consultants who can provide insights into the applicable standards. Design products with adaptable RF shielding solutions that can be easily modified to meet diverse requirements. This may involve using modular shielding components that can be tailored to specific regulations without a complete redesign. Additionally, consider obtaining certifications from recognized international bodies to enhance credibility and facilitate smoother market entry. By proactively addressing compliance issues, you can not only expedite the product launch process but also build trust with international partners and customers.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for rf shielding
What Are the Common Materials Used for RF Shielding?
When selecting materials for RF shielding, it’s essential to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations. Below, we analyze four common materials used in RF shielding applications, focusing on their performance characteristics and implications for international B2B buyers.
How Does Copper Perform in RF Shielding Applications?
Copper is widely recognized for its excellent electrical conductivity and is a popular choice for RF shielding. It typically offers high attenuation rates, making it effective in blocking a broad spectrum of RF signals.
Key Properties: Copper has a high thermal and electrical conductivity, with a melting point around 1,984°F (1,085°C). It exhibits good corrosion resistance, especially when coated or treated.
Pros & Cons: While copper is highly effective, it can be expensive compared to other materials. Its manufacturing process can be complex due to the need for precise machining and joining techniques. However, it is suitable for high-performance applications, such as telecommunications and aerospace.
Impact on Application: Copper is compatible with various media and can be used in environments where high-frequency signals are present.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of compliance with standards such as ASTM B187 for copper products. In regions like Europe and the Middle East, sourcing high-purity copper may be essential for specific applications.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in RF Shielding?
Aluminum is another common material for RF shielding, favored for its lightweight and cost-effective properties. It provides good shielding effectiveness, particularly when used in thicker gauges.
Key Properties: Aluminum has a melting point of about 1,221°F (660.3°C) and is resistant to corrosion due to the formation of a protective oxide layer.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its low cost and ease of fabrication, making it suitable for mass production. However, its shielding effectiveness is generally lower than that of copper, especially at higher frequencies.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is often used in consumer electronics and automotive applications where weight and cost are critical factors.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM B209 is crucial. In regions such as South America, where cost sensitivity is high, aluminum may be the preferred choice.
How Effective is Steel for RF Shielding?
Steel, particularly stainless steel, is used in RF shielding for its durability and strength. It provides good shielding effectiveness and is often used in industrial applications.
Key Properties: Stainless steel has a melting point of approximately 2,500°F (1,370°C) and offers excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for harsh environments.
Pros & Cons: Steel is robust and can withstand mechanical stress, but it is heavier and more expensive than aluminum. Its manufacturing process can also be more complex, requiring specialized welding techniques.
Impact on Application: Steel is commonly used in applications where structural integrity is as important as RF shielding, such as in military and aerospace settings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards like ASTM A240. In regions like Africa, sourcing local suppliers for stainless steel can reduce costs.
What Advantages Does Conductive Fabric Offer for RF Shielding?
Conductive fabric is an innovative material for RF shielding, often used in flexible applications. It combines textile properties with conductive elements, making it versatile.
Key Properties: Conductive fabrics can be made from various fibers coated with conductive metals, providing good flexibility and moderate shielding effectiveness.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage is its lightweight and flexible nature, making it ideal for wearable technology and portable devices. However, its shielding effectiveness is generally lower than that of metals, and it may not be suitable for high-frequency applications.
Impact on Application: Conductive fabric is often used in consumer electronics and military applications where flexibility is required.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM D4935 is important. In Europe, there is a growing demand for sustainable materials, which may influence sourcing decisions.
Summary Table of RF Shielding Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for RF Shielding | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Telecommunications, aerospace | High attenuation and conductivity | Expensive and complex manufacturing | High |
| Aluminum | Consumer electronics, automotive | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower shielding effectiveness | Medium |
| Steel (Stainless) | Industrial, military applications | Durability and mechanical strength | Heavier and more expensive | Medium to High |
| Conductive Fabric | Wearable tech, portable devices | Flexibility and lightweight | Lower shielding effectiveness | Medium |
This comprehensive analysis provides a clear understanding of the various materials available for RF shielding, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for rf shielding
What Are the Main Stages of the RF Shielding Manufacturing Process?
The manufacturing of RF shielding involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the required specifications for performance and durability. Understanding these processes can aid B2B buyers in selecting the right manufacturing partner.
Material Preparation: How Are RF Shielding Materials Selected and Processed?
The first stage in RF shielding manufacturing is material preparation. Common materials used include aluminum, copper, and specialized conductive polymers. The choice of material depends on factors like frequency range, environmental conditions, and specific application requirements.
-
Material Sourcing: It’s essential to procure high-quality materials that meet international standards. Buyers should verify suppliers’ certifications and quality of raw materials.
-
Material Testing: Conduct tests such as tensile strength and conductivity to ensure the materials meet required specifications.
-
Cutting and Shaping: Materials are cut into specific dimensions using precision tools to minimize waste and ensure uniformity.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape RF Shielding Components?
Once the materials are prepared, they undergo forming processes to create the desired shapes for RF shielding components.
-
Stamping and Die-Cutting: This technique is commonly used to create flat components like panels and enclosures. It allows for high-volume production with consistent quality.
-
Bending and Forming: For more complex shapes, processes like bending or extrusion may be employed. Buyers should inquire about the machinery used and the expertise of the workforce.
-
Molding: In cases where polymers are used, injection molding can create intricate designs that enhance shielding effectiveness.
Assembly: How Are RF Shielding Components Joined Together?
Assembly is a crucial step in ensuring the functionality of RF shielding products. This stage typically involves the following techniques:
-
Welding: For metal components, welding ensures a strong bond that maintains the integrity of the shield. Different welding techniques like TIG or MIG may be used based on material compatibility.
-
Adhesives and Sealants: In some cases, non-metallic components may require adhesives. It’s vital to choose adhesives that can withstand environmental factors without degrading.
-
Fasteners and Hardware: The use of screws, bolts, and other fasteners ensures that components remain securely in place.
Finishing: What Treatments Enhance RF Shielding Performance?
The finishing stage involves surface treatments that enhance both performance and aesthetics. Common techniques include:
-
Coating: Applying conductive or non-conductive coatings can improve durability and resistance to environmental factors. For example, a nickel coating can enhance corrosion resistance.
-
Surface Treatment: Processes like anodizing can be employed to increase surface hardness and reduce wear.
-
Quality Checks: Final inspections during this stage ensure that the shielding meets all specifications before shipment.
What Are the Key Quality Control Measures in RF Shielding Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of RF shielding, as even minor defects can lead to significant performance issues. Understanding these measures can help B2B buyers evaluate potential suppliers.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
International standards provide a framework for quality assurance in manufacturing processes. Buyers should be familiar with the following:
-
ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system and is essential for ensuring consistent quality in manufacturing processes.
-
CE Marking: For products sold in Europe, CE marking indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
-
API Standards: In industries such as oil and gas, adherence to API standards can be critical for ensuring the reliability and safety of RF shielding products.
What Are the Common Quality Control Checkpoints in RF Shielding?
Quality control checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to catch defects early and ensure compliance with specifications:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials are inspected for quality and compliance with specifications before they enter the production line.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, random inspections are conducted to monitor the production process and identify any deviations from quality standards.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipment, the final product undergoes a comprehensive inspection to ensure it meets all specifications and passes required tests.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is critical to ensuring product reliability and compliance.
What Methods Are Effective for Supplier Audits?
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can provide insights into a supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality control measures. Buyers should prepare a checklist based on relevant standards to assess compliance.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can help buyers understand the supplier’s quality control history, including any past issues and resolutions.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control processes. This step is particularly valuable for buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where local compliance may differ.
What Nuances Should International Buyers Consider?
International buyers should be aware of the following nuances when evaluating suppliers:
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding cultural approaches to quality assurance can provide insights into a supplier’s practices. For instance, some regions may prioritize speed over quality, which can impact RF shielding performance.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that suppliers are compliant with both local and international regulations, as this can affect product acceptance in various markets.
-
Communication Barriers: Language differences can lead to misunderstandings regarding quality specifications. Establishing clear communication channels is essential.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for RF shielding is vital for B2B buyers looking to procure reliable products. By focusing on material selection, manufacturing techniques, and stringent quality control practices, buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers, ensuring that their RF shielding needs are met effectively and efficiently.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘rf shielding’
Introduction
In the rapidly evolving landscape of technology, sourcing effective RF shielding solutions has become essential for businesses across various sectors. This guide offers a practical checklist for international B2B buyers—especially from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—looking to procure RF shielding materials and services. The following steps will help you navigate the complexities of sourcing, ensuring you select the right products and partners to meet your specific needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outlining your technical requirements is crucial for successful RF shielding procurement. Consider the frequency range you need to shield against, the environment in which the shielding will be used, and specific performance metrics like attenuation levels.
A stock image related to rf shielding.
- Key considerations: Identify if you require solid or perforated shielding, and understand the potential impact of thermal and acoustic insulation on your application.
Step 2: Research Available Materials and Solutions
Understanding the various materials available for RF shielding is essential in making an informed decision. Different materials such as aluminum, copper, and specialized composites offer varying levels of effectiveness, durability, and cost.
- Material properties: Investigate attributes such as conductivity, weight, and flammability ratings to ensure compatibility with your application requirements.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, it’s vital to conduct thorough evaluations of potential suppliers. Look for established manufacturers with proven track records in RF shielding.
- What to check: Request case studies, company profiles, and references from similar industries. Ensure that the supplier adheres to industry standards and certifications, such as IEEE or ASTM compliance.
Step 4: Request Samples and Conduct Testing
Once you’ve shortlisted suppliers, request samples to evaluate their products in real-world conditions. Testing the samples will help you assess their effectiveness in shielding against RF interference.
- Testing criteria: Focus on key performance indicators such as RF attenuation, durability under stress, and compliance with your technical specifications.
Step 5: Understand Pricing Structures and Terms
Pricing can vary significantly based on materials, manufacturing processes, and supplier reputation. Understanding the pricing structures will enable you to make cost-effective decisions.
- Cost factors: Consider not only the initial purchase price but also potential long-term savings associated with durability and maintenance. Look for transparent pricing models that outline all costs involved.
Step 6: Check for Post-Purchase Support and Services
Reliable post-purchase support can significantly enhance your RF shielding implementation. Ensure the supplier offers comprehensive support, including installation guidance, maintenance services, and troubleshooting assistance.
- Support considerations: Inquire about warranty options, availability of technical support, and whether they provide training for your team on proper installation and usage.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Finalize the Agreement
A stock image related to rf shielding.
Once you’ve chosen a supplier, it’s time to negotiate terms that align with your business needs. Ensure that the contract covers all aspects, including delivery schedules, payment terms, and quality assurance measures.
- Contract essentials: Pay special attention to clauses related to performance guarantees and penalties for non-compliance, which can protect your investment and ensure accountability.
By following this step-by-step checklist, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the sourcing process for RF shielding, ensuring that they select the right materials and partners for their specific needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for rf shielding Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in RF Shielding Sourcing?
When sourcing RF shielding solutions, understanding the cost structure is essential for effective budgeting and negotiation. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly influences the overall cost. Common materials like aluminum, copper, and specialized composites vary in price based on quality and availability. Higher quality materials that meet military standards or specific certifications often come at a premium.
-
Labor: Labor costs can fluctuate based on the complexity of the RF shielding design and manufacturing process. Custom solutions requiring skilled labor for precision work will increase costs. In regions with higher labor costs, such as Europe, this can be a significant factor.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead costs, which is critical for maintaining competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs for custom RF shielding can be substantial, particularly for unique designs. These costs are amortized over production runs, so higher volume orders typically yield lower per-unit tooling costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring compliance with industry standards, such as ASTM or IEEE, requires rigorous QC processes. This adds to the cost but is crucial for ensuring reliability and performance, especially in sensitive applications.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary widely depending on the size, weight, and destination of the RF shielding products. International shipping can introduce additional complexities and expenses, such as customs duties and taxes.
-
Margin: Supplier margins will vary based on market conditions and competitive landscape. Understanding the typical margin range for RF shielding products can aid in evaluating supplier pricing.
How Do Price Influencers Affect RF Shielding Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of RF shielding solutions, especially for international buyers:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Suppliers often provide discounts for larger orders. Understanding the MOQ can help buyers negotiate better pricing, particularly for bulk purchases.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized solutions that meet specific technical requirements generally incur higher costs. Buyers should clearly define their needs to avoid unexpected expenses later in the process.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials that comply with stringent certifications (e.g., military-grade standards) will command a higher price. Buyers should weigh the importance of these certifications against their budget.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers with proven track records may charge more but offer better quality assurance and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the shipping terms (Incoterms) is crucial for calculating total landed costs. Different terms can shift responsibilities for shipping costs, customs duties, and risks between the buyer and supplier.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in RF Shielding Procurement?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, consider the following actionable tips:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Leverage your understanding of cost components and price influencers during negotiations. Don’t hesitate to seek volume discounts or flexible payment terms.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial purchase price. Consider factors like maintenance, performance longevity, and potential downtime costs related to RF shielding failures.
-
Explore Local Suppliers: Sourcing from local manufacturers can reduce shipping costs and lead times. It also allows for easier communication and potential support for local regulations.
-
Stay Informed About Market Trends: Prices for raw materials fluctuate based on global demand and supply chains. Keep abreast of market trends to time your purchases effectively.
-
Request Samples: Before committing to large orders, request samples to evaluate the quality of materials and craftsmanship. This can prevent costly mistakes down the line.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Pricing for RF shielding solutions can vary widely based on the factors outlined above. It is advisable for buyers to obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing and to factor in all associated costs for accurate budgeting.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing rf shielding With Other Solutions
When considering solutions to combat radio frequency interference (RFI), it’s essential for B2B buyers to explore a range of alternatives to RF shielding. While RF shielding is a widely recognized solution, various other methods can also mitigate RFI. Understanding these alternatives can help buyers make informed decisions based on their specific requirements, such as performance, cost, and ease of implementation.
Comparison Table of RF Shielding and Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | RF Shielding | Conductive Coatings | EMI Filters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High RF attenuation (up to 73 dB) | Moderate attenuation; varies by type | Effective for certain frequency ranges |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Generally lower than RF shielding | Varies; generally moderate |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires precise design and installation | Easy application; typically spray or brush-on | Requires integration into circuit design |
| Maintenance | Low; durable materials | May require periodic reapplication | Low; passive components |
| Best Use Case | Sensitive electronics, military applications | General electronics, consumer devices | Power supplies, communication devices |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Conductive Coatings?
Conductive coatings serve as a practical alternative to RF shielding by providing a layer of conductive material that can reflect or absorb RF signals. These coatings are typically applied as a spray or paint, making them easy to implement on various surfaces.
Pros:
– Cost-effective compared to traditional RF shielding.
– Simple application process that doesn’t require complex engineering designs.
– Versatile; can be used on a variety of surfaces.
Cons:
– Performance is generally lower than dedicated RF shielding, with attenuation effectiveness depending on the coating’s thickness and material.
– May need reapplication over time, especially in environments with wear and tear.
How Do EMI Filters Function as an Alternative to RF Shielding?
EMI filters are another option for mitigating electromagnetic interference, including RFI. These filters are designed to block unwanted frequencies while allowing desired signals to pass through, commonly used in power supplies and communication devices.
Pros:
– Effective for filtering out specific frequency ranges, enhancing signal integrity in electronics.
– Passive devices require minimal maintenance.
– Can be integrated into existing designs without extensive modifications.
Cons:
– Limited to specific frequencies; may not provide comprehensive protection across all RF spectrums.
– Integration into designs may require additional engineering resources and expertise.
How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for RF Interference?
For international B2B buyers, selecting the appropriate solution for RF interference involves assessing several factors. Start by evaluating the specific application requirements, including the level of RF attenuation needed and the types of devices involved. Consider the budget constraints, as RF shielding tends to be more expensive than alternatives like conductive coatings or EMI filters.
Additionally, ease of implementation and maintenance should influence the decision; for example, if frequent access to the device is required, a solution that allows for easier application and reapplication may be advantageous. Ultimately, a thorough understanding of the operational environment and the potential sources of interference will enable buyers to select the most effective method for their unique needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for rf shielding

A stock image related to rf shielding.
What Are the Key Technical Properties of RF Shielding?
Understanding the essential technical properties of RF shielding is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when selecting materials that will effectively mitigate radio frequency interference (RFI). Here are some of the most critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
– The grade of the material used in RF shielding directly influences its effectiveness. Common materials include copper, aluminum, and specialized alloys. Higher-grade materials often provide better attenuation and durability. For international buyers, understanding the grade can help in assessing quality and compliance with industry standards. -
Shielding Effectiveness (SE)
– Shielding effectiveness is measured in decibels (dB) and indicates how well a material can block RFI. For instance, a material with an SE of 60 dB can reduce RFI signals by a factor of 1,000, making it vital for sensitive electronic applications. Buyers should look for materials that meet or exceed industry standards to ensure optimal performance. -
Tolerance and Thickness
– Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in the dimensions of the shielding material. This is particularly important in applications where precise fit and form are necessary. Thickness also plays a role; thicker materials can provide better shielding but may also increase weight and costs. It’s essential for buyers to balance these factors according to their application requirements. -
Frequency Range
– Different RF shielding materials are effective across varying frequency ranges. Buyers should specify the frequency ranges relevant to their applications to ensure the chosen material provides adequate protection. Understanding frequency performance is crucial for applications in telecommunications, medical devices, and military equipment. -
Environmental Resistance
– The ability of RF shielding materials to withstand environmental factors such as humidity, temperature fluctuations, and chemical exposure is vital. Materials that are resistant to corrosion and have a long lifespan will reduce maintenance costs and enhance the reliability of the equipment. Buyers must inquire about environmental ratings for materials used in their specific regions. -
Flammability Ratings
– Flammability ratings indicate how a material behaves in the presence of fire. Materials with a Class A rating are less likely to ignite and contribute to fire hazards, making them safer for use in sensitive environments. Understanding these ratings is crucial for buyers in sectors like defense and aerospace.
What Are Common Trade Terminologies in RF Shielding?
Familiarity with industry jargon can greatly aid B2B buyers in navigating the RF shielding landscape. Here are several key terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– An OEM is a company that produces components that are used in another company’s end products. Buyers should look for reputable OEMs who can provide high-quality RF shielding solutions tailored to their specifications. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for international buyers to manage inventory costs effectively, especially when entering new markets or testing new products. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a price quotation for specific products or services. It is an essential tool for buyers to compare costs, ensuring they get the best deal for their RF shielding needs. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. For international transactions, understanding these terms can help buyers navigate logistics and reduce the risk of unexpected costs. -
TEMPEST
– TEMPEST refers to a U.S. government standard for protecting sensitive electronic equipment from eavesdropping through unintentional emissions. Buyers in the defense sector should ensure that their RF shielding meets TEMPEST standards for enhanced security. -
RFI (Radio Frequency Interference)
– RFI is the disruption of electronic devices due to unwanted RF signals. Recognizing the sources and implications of RFI is critical for buyers looking to implement effective shielding solutions in their products.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting RF shielding solutions that meet their specific needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the rf shielding Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in RF Shielding?
The RF shielding market is experiencing robust growth due to an increasing demand for electronic devices in various industries, including telecommunications, healthcare, and defense. The proliferation of wireless technologies and the resultant rise in radio frequency interference (RFI) have made RF shielding a critical component in device design. International B2B buyers, especially from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must understand several key trends shaping the market.
First, there is a marked shift towards advanced materials that offer better shielding effectiveness while being lightweight and cost-efficient. For instance, multi-layered shielding solutions, such as those incorporating aluminum and polyethylene, are gaining traction. This trend is particularly relevant for buyers in sectors like aerospace and defense, where stringent standards for electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) are paramount.
Second, the integration of smart technologies in RF shielding is on the rise. Manufacturers are increasingly utilizing IoT-enabled solutions to monitor and manage RF performance dynamically. This development enables companies to respond swiftly to interference issues, ensuring operational continuity. Buyers should seek partnerships with suppliers who are at the forefront of technological innovation in RF shielding materials and systems.
Lastly, the ongoing global push for energy efficiency and sustainability is influencing sourcing decisions. Companies are now prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to environmentally friendly practices and materials. Understanding these market dynamics will empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with both their operational needs and corporate social responsibility goals.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact RF Shielding?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming critical considerations for B2B buyers in the RF shielding sector. The environmental impact of materials used in RF shielding, particularly metals and plastics, raises concerns regarding resource depletion and waste. Buyers are increasingly demanding transparency in supply chains, prompting suppliers to adopt responsible sourcing practices.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers should look for manufacturers who adhere to international standards, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety. This not only ensures compliance but also enhances brand reputation and consumer trust.
Moreover, the market is seeing a rise in ‘green’ certifications for RF shielding materials. For instance, materials that are recyclable or made from recycled content are gaining popularity. These options not only reduce environmental footprints but also meet the growing regulatory requirements in regions such as Europe, where the Circular Economy Action Plan emphasizes resource efficiency.
By prioritizing sustainability and ethical sourcing, international B2B buyers can mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions and enhance their competitive edge in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of RF Shielding?
The concept of RF shielding has evolved significantly since its inception. Initially used primarily in military applications during World War II, RF shielding technology was developed to protect sensitive communication devices from enemy interference. As electronic devices became more complex and widespread, the need for effective RF shielding expanded into commercial sectors, including consumer electronics, automotive, and telecommunications.
In the late 20th century, advancements in materials science led to the development of more efficient shielding solutions, enabling manufacturers to create thinner, lighter, and more effective shields. The introduction of multi-layered composites and smart materials in the 21st century has further revolutionized the industry, allowing for better performance and integration into compact electronic devices.
Today, RF shielding is a vital aspect of product design across various industries, driven by the increasing prevalence of wireless technology and the need to safeguard sensitive information from RFI. Understanding this historical context is crucial for B2B buyers as they navigate the complexities of sourcing and integrating RF shielding solutions into their products.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of rf shielding
-
How do I solve RF interference issues in my electronic devices?
To effectively solve RF interference (RFI) problems, start by identifying the sources of interference and the frequencies involved. Utilize RF shielding materials like metal enclosures or specialized fabrics to create barriers that block unwanted signals. Conduct thorough testing to ensure your shielding solution meets the required attenuation levels. Collaborating with an experienced RF shielding manufacturer can provide you with tailored solutions that align with your specific device requirements and operational environment. -
What is the best material for RF shielding in sensitive environments?
The best material for RF shielding in sensitive environments typically includes metals like aluminum and copper due to their excellent conductivity and attenuation properties. Multi-layered materials, such as those combining aluminum foil with reinforcing fabrics, offer enhanced performance by addressing both RF and thermal insulation needs. When selecting materials, consider the specific frequencies you need to block and ensure compliance with industry standards for shielding effectiveness. -
How can I vet suppliers for RF shielding materials internationally?
Vetting suppliers for RF shielding materials requires a multi-faceted approach. Start by checking their certifications, such as ISO standards or military specifications, which indicate quality and compliance. Request samples to assess material performance and durability. Additionally, look for customer testimonials or case studies that demonstrate successful partnerships. Engaging in direct communication to discuss your specific needs and timelines can also provide insight into their reliability and responsiveness. -
What customization options are available for RF shielding solutions?
Many manufacturers offer extensive customization options for RF shielding solutions. This can include tailoring the size, shape, and thickness of materials to fit specific applications. You can also choose between solid or perforated designs, depending on the balance between shielding effectiveness and ventilation needs. Discussing your requirements upfront with the manufacturer can help ensure that the final product meets your exact specifications. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for RF shielding products?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for RF shielding products can vary widely among suppliers, often depending on the complexity of the materials and manufacturing processes involved. Some manufacturers may require a MOQ of several hundred units, while others may offer flexibility for smaller orders, especially for customized solutions. It’s advisable to clarify these terms during initial discussions to ensure that they align with your project needs and budget. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing RF shielding internationally?
Payment terms for international RF shielding purchases often include options like advance payment, net 30/60 days, or letter of credit. It’s common for suppliers to require a deposit upfront, especially for custom orders. Always clarify the payment terms in your contract and consider the implications of currency fluctuations when dealing with international transactions. Ensure that the terms are mutually agreeable to avoid complications during the fulfillment process. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for RF shielding products?
Ensuring quality assurance (QA) for RF shielding products involves several steps. First, verify that the supplier has a robust QA process in place, including material inspections and performance testing. Request documentation of compliance with relevant industry standards, such as IEEE 299 for shielding effectiveness. Regular audits or third-party testing can further ensure that the products meet your specifications and performance requirements before they reach your facility. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing RF shielding materials?
When importing RF shielding materials, consider factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs or duties. Choose reliable logistics partners who understand the specific requirements for handling and transporting technical materials. Timely communication regarding shipment tracking and delivery schedules is crucial to avoid project delays. Additionally, assess whether the supplier can provide documentation necessary for customs clearance to streamline the import process.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for rf shielding
Why Is Strategic Sourcing Critical for RF Shielding?
In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, the importance of effective RF shielding cannot be overstated. International B2B buyers, especially those operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must prioritize strategic sourcing to mitigate the risks associated with radio frequency interference (RFI). By understanding the diverse materials and manufacturing methods available, businesses can select the most suitable RF shielding solutions tailored to their specific applications.
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers?
Investing in high-quality RF shielding not only protects sensitive equipment but also enhances operational efficiency and compliance with industry regulations. Collaborating with expert manufacturers can streamline the design and production processes, ensuring that your RF shields meet stringent performance standards. Additionally, considering the geographical and regulatory differences across regions will help in selecting the right partners and materials.
What’s Next for International B2B Buyers?
As the demand for RF shielding continues to rise, driven by advancements in communication technologies and increased regulatory scrutiny, now is the time for international buyers to act. Evaluate your sourcing strategies and engage with trusted manufacturers who can provide innovative RF solutions. By doing so, you position your business at the forefront of technological resilience, ensuring long-term success in an increasingly interconnected world.