Improve Performance: The Complete Guide to EMI Filters (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for emi filters
Navigating the complexities of sourcing EMI filters can be a daunting task for international B2B buyers, especially in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With the growing reliance on electronic devices across various industries, the need for effective electromagnetic interference (EMI) solutions has never been more critical. EMI filters are essential components that protect sensitive equipment from damaging electrical noise, ensuring reliability and performance in applications ranging from medical devices to industrial machinery.
This comprehensive guide delves into the diverse types of EMI filters available, their applications across multiple sectors, and essential supplier vetting strategies. By exploring the nuances of active versus passive filters, the guide equips buyers with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions tailored to their specific operational requirements. Additionally, we will provide insights into cost considerations and compliance with international regulations, which are crucial for companies operating in multiple markets.
By the end of this guide, B2B buyers will have a clear understanding of how to navigate the global market for EMI filters effectively, empowering them to select the right solutions that not only meet their technical needs but also align with their strategic goals. Whether you are in Italy, Vietnam, or anywhere in between, this resource is designed to streamline your purchasing process and enhance your operational efficiency.
Understanding emi filters Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Passive EMI Filters | Composed of passive components (capacitors, inductors, resistors) to absorb unwanted noise. | Industrial machinery, consumer electronics, medical devices. | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to integrate. Cons: Limited to specific frequency ranges. |
| Active EMI Filters | Utilize an internal power supply to generate counteracting currents to eliminate noise. | Aerospace, telecommunications, and high-frequency applications. | Pros: Effective across a wider frequency range. Cons: More complex and costly. |
| Common Mode Chokes | Designed to suppress common-mode noise in differential signals. | Networking equipment, audio devices, and power supplies. | Pros: Highly effective for differential signals. Cons: May not address all types of EMI. |
| Differential Mode Filters | Target differential noise between conductors, ideal for reducing crosstalk. | Data transmission, telecommunications, and audio equipment. | Pros: Enhances signal integrity. Cons: Requires careful design for optimal performance. |
| Filtered Power Entry Modules | Integrate filtering and power entry in one unit, simplifying design. | Power supplies, industrial control systems, and medical devices. | Pros: Space-saving, reduces assembly time. Cons: Potentially higher upfront cost. |
What Are Passive EMI Filters and When Should They Be Used?
Passive EMI filters are made up of components such as capacitors, inductors, and resistors. They function by absorbing unwanted electromagnetic noise without requiring an external power source. These filters are particularly suitable for applications where cost-effectiveness is crucial, such as in consumer electronics and industrial machinery. Buyers should consider the frequency ranges they need to suppress, as passive filters typically operate effectively within specific bands.
How Do Active EMI Filters Work and What Are Their Advantages?
Active EMI filters leverage an internal power supply to generate currents that counteract electromagnetic interference. This type of filter is ideal for high-frequency applications such as aerospace and telecommunications, where the need for robust EMI suppression is paramount. While they offer broader frequency coverage and superior noise reduction, buyers should weigh the benefits against the higher complexity and cost associated with their design and implementation.
What Are Common Mode Chokes and Their Best Applications?
Common mode chokes are specialized passive filters designed to suppress common-mode noise in differential signals. They are widely used in networking equipment, audio devices, and power supplies to enhance performance and reliability. When considering common mode chokes, B2B buyers should evaluate the specific applications and the types of noise they need to mitigate, as these filters are highly effective but may not address all EMI concerns.
Why Choose Differential Mode Filters for Your Signal Integrity Needs?
Differential mode filters are engineered to target noise that occurs between conductors, making them essential for applications like data transmission and telecommunications. These filters improve signal integrity by reducing crosstalk and enhancing overall performance. Buyers should focus on the filter design to ensure compatibility with their systems, as optimal performance often requires careful consideration of the specific circuit characteristics.
How Do Filtered Power Entry Modules Simplify Design?
Filtered Power Entry Modules combine EMI filtering with power entry, offering a space-saving solution that simplifies design and assembly processes. These modules are particularly beneficial in power supplies and industrial control systems, where integrating multiple functions into a single component can lead to efficiency gains. However, B2B buyers must consider the potential for higher initial costs versus the long-term benefits of reduced assembly time and improved reliability.
Key Industrial Applications of emi filters
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of EMI Filters | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Medical Imaging Equipment | Ensures accurate imaging and device reliability | Compliance with medical standards and certifications |
| Aerospace & Defense | Communication Systems in Aircraft | Prevents signal disruption, enhancing operational safety | Rugged designs suitable for harsh environments |
| Industrial Automation | Robotics and Control Systems | Increases efficiency and reduces downtime | Compatibility with existing systems and scalability |
| Telecommunications | Base Stations and Network Infrastructure | Enhances signal clarity and communication reliability | Compliance with regional EMC regulations |
| Consumer Electronics | Smart Devices and Wearables | Protects device functionality and user experience | Cost-effectiveness and miniaturization for compact designs |
How Are EMI Filters Used in Healthcare Applications?
In the healthcare sector, EMI filters are crucial for medical imaging equipment, such as MRI and CT scanners. These devices require uninterrupted power and minimal interference to ensure accurate imaging results. EMI filters help mitigate electromagnetic noise that can distort images, thereby protecting patient safety and ensuring reliable diagnostics. For international buyers, it’s essential to source filters that comply with regional medical standards, such as ISO 13485, ensuring both safety and quality.
What Role Do EMI Filters Play in Aerospace & Defense?
In aerospace and defense, EMI filters are integral to communication systems used in aircraft. These systems must operate flawlessly under challenging conditions, where electromagnetic interference can lead to catastrophic failures. Filters protect sensitive electronic components from both conducted and radiated EMI, ensuring that communication remains clear and reliable. Buyers in this sector should prioritize rugged designs that meet military specifications, such as MIL-STD-461, to withstand extreme environments.
How Are EMI Filters Applied in Industrial Automation?
In industrial automation, EMI filters are vital for robotics and control systems that drive production efficiency. These filters reduce noise in power supplies and control circuits, minimizing downtime caused by equipment malfunctions. By ensuring that robots and automated systems function smoothly, businesses can significantly enhance productivity. Buyers should consider compatibility with existing automation frameworks and the ability to scale as production needs evolve.
Why Are EMI Filters Important in Telecommunications?
EMI filters are essential in telecommunications, particularly in base stations and network infrastructure. They enhance signal clarity by filtering out unwanted noise, which is crucial for maintaining reliable communication networks. As the demand for high-speed data transmission increases, the need for effective EMI filtering becomes even more critical. International buyers should be aware of regional EMC regulations to ensure compliance, as well as the need for robust filters that can handle varying environmental conditions.
How Do EMI Filters Benefit Consumer Electronics?
In the consumer electronics sector, EMI filters are used in smart devices and wearables to protect functionality and enhance user experience. These filters help to eliminate interference from other electronic devices, ensuring that smart technology operates seamlessly. For B2B buyers, sourcing cost-effective EMI filters that allow for miniaturization without compromising performance is essential, particularly as the trend towards smaller, more integrated devices continues to grow.
3 Common User Pain Points for ’emi filters’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Unreliable Equipment Performance Due to EMI
The Problem:
International B2B buyers often face the challenge of ensuring their sensitive electronic equipment operates reliably in environments with high electromagnetic interference (EMI). For instance, manufacturers in sectors such as healthcare and industrial automation may find that their devices malfunction or degrade in performance due to EMI generated by nearby machinery or communication devices. This can lead to costly downtimes, production delays, and can compromise safety in critical applications. Additionally, navigating the varying EMI regulations across different countries can add another layer of complexity.
The Solution:
To mitigate these issues, B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing EMI filters that are specifically designed to handle the expected levels of interference in their operational environments. When selecting an EMI filter, consider the type of EMI prevalent in your industry—conducted or radiated—and the specific frequency ranges that your equipment operates within. For example, using a passive EMI filter can help absorb unwanted energy and stabilize the power supply for sensitive devices.
Buyers should also consult with manufacturers to customize filters that meet their specific needs, ensuring compliance with local electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standards. Furthermore, conducting thorough EMI testing during the design phase of equipment can identify potential issues before deployment, allowing for adjustments to be made early in the development process.
Scenario 2: High Costs Due to Non-Compliance with EMC Regulations
The Problem:
B2B buyers frequently encounter financial repercussions stemming from non-compliance with electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) regulations. This is particularly relevant for companies operating in Europe, where regulations like EN55011 and EN55022 are stringent. Failure to comply can result in hefty fines, product recalls, and damage to reputation, creating a significant financial burden. Additionally, the need for re-engineering products to meet these standards can lead to unexpected costs and delays in time-to-market.
The Solution:
To avoid these pitfalls, it is essential for buyers to integrate EMI filters into their product designs from the very beginning. Engaging with EMI filter suppliers who understand local and international regulations can provide invaluable guidance in selecting the right filter types and specifications that align with compliance requirements.
Conducting pre-compliance testing with the help of specialized third-party laboratories can also help identify potential compliance issues before the official testing phase. This proactive approach not only reduces the risk of financial penalties but also enhances the overall reliability and marketability of the products. Additionally, investing in quality EMI filtering solutions can ultimately lead to reduced maintenance costs and improved customer satisfaction.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Selecting the Right EMI Filter for Applications
The Problem:
Choosing the appropriate EMI filter can be a daunting task for B2B buyers, especially when faced with a myriad of options and technical specifications. Many buyers struggle with understanding the differences between active and passive filters, as well as how to select the right type based on their specific applications. This confusion can lead to suboptimal choices that do not adequately protect their equipment, resulting in performance issues and increased operational risks.
The Solution:
To simplify the selection process, buyers should start by clearly defining their application requirements, including the nature of the EMI present and the operational frequencies of their devices. It is beneficial to work closely with filter manufacturers who can provide expertise on the types of filters suitable for specific applications.
Additionally, buyers should consider investing in EMI filter evaluation kits, which allow them to test different filters in their specific environments before making a large purchase. Leveraging technical support from manufacturers for installation and configuration can also enhance the effectiveness of the EMI filters. By taking a systematic approach to filter selection and seeking expert guidance, buyers can ensure that they invest in solutions that provide the necessary protection and improve the longevity of their electronic devices.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for emi filters
What Materials Are Commonly Used in EMI Filters?
When selecting materials for EMI filters, it’s crucial to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and how they align with the specific needs of international B2B buyers. Below are analyses of four common materials used in EMI filter construction.
A stock image related to emi filters.
1. Ferrite Materials
Key Properties: Ferrite materials are characterized by their high magnetic permeability and low electrical conductivity. They can effectively absorb high-frequency noise and are typically rated for temperatures up to 200°C.
Pros & Cons: Ferrites are durable and lightweight, making them suitable for a variety of applications, including consumer electronics and automotive components. However, they can be brittle and may require careful handling during manufacturing, which can increase costs.
Impact on Application: Ferrite materials are particularly effective in applications that involve high-frequency signals, such as RF communications. Their ability to suppress unwanted signals makes them ideal for devices operating in environments with high electromagnetic interference.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as IEC 61000-3-2 is essential. Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure that ferrite materials meet local regulations regarding electromagnetic compatibility (EMC).
2. Capacitor-Based Materials
Key Properties: Capacitor-based EMI filters typically use ceramic or tantalum capacitors, which offer high capacitance values and excellent frequency response. They can function effectively at high temperatures, often exceeding 125°C.
Pros & Cons: These materials provide efficient noise filtering and are widely available. However, they can be expensive, particularly tantalum capacitors, and may require complex manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application: Capacitor-based materials are ideal for applications requiring high-frequency noise suppression, such as in medical devices and industrial automation. Their reliability under varying conditions makes them suitable for critical applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the need for compliance with standards like EN55022 for IT equipment. Additionally, sourcing materials from reputable suppliers is crucial to ensure quality and reliability.
3. Metal-Based Filters
Key Properties: Metal-based EMI filters, often made from aluminum or copper, provide excellent conductivity and are highly effective in shielding against electromagnetic interference. They can withstand high temperatures and are resistant to corrosion.
Pros & Cons: These materials are highly durable and can be manufactured in various shapes and sizes. However, they can be heavier and more expensive than other materials, which may limit their use in lightweight applications.
Impact on Application: Metal-based filters are particularly beneficial in industrial environments where durability and resistance to harsh conditions are required. They are commonly used in military and aerospace applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with military and aerospace standards such as MIL-STD-461 is critical for buyers in these sectors. Additionally, understanding local manufacturing capabilities can help in sourcing suitable metal materials.
4. Polymer-Based Materials
Key Properties: Polymer materials, such as conductive polymers, offer flexibility and lightweight characteristics. They can operate effectively at moderate temperatures, typically up to 85°C, and provide good electrical insulation.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of polymer-based EMI filters is their cost-effectiveness and ease of manufacturing. However, their lower thermal and electrical performance compared to metals or ceramics can be a limitation in high-demand environments.
Impact on Application: These materials are suitable for consumer electronics and automotive applications where weight and cost are critical factors. Their ability to be molded into complex shapes allows for versatile designs.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that polymer materials comply with relevant standards, such as RoHS and REACH in Europe. Understanding the local market’s preferences for material types can also influence purchasing decisions.
Summary Table of Material Selection for EMI Filters
| Material | Typical Use Case for EMI Filters | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ferrite Materials | RF communications, automotive components | Lightweight and effective at high frequencies | Brittle, requires careful handling | Medium |
| Capacitor-Based Materials | Medical devices, industrial automation | High capacitance and reliable performance | Expensive and complex manufacturing | High |
| Metal-Based Filters | Military, aerospace applications | Highly durable and effective shielding | Heavier and more costly | High |
| Polymer-Based Materials | Consumer electronics, automotive | Cost-effective and easy to manufacture | Lower thermal and electrical performance | Low |

A stock image related to emi filters.
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers looking to optimize their EMI filter choices based on application needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for emi filters
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of EMI Filters?
The manufacturing of EMI filters involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure that the final product meets the stringent requirements for performance and reliability. Understanding these stages can help international B2B buyers assess potential suppliers more effectively.
1. Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in EMI Filter Manufacturing?
The manufacturing process begins with material selection. Common materials for EMI filters include:
- Capacitors: These components are crucial for filtering out unwanted frequencies.
- Inductors: Used for energy storage and creating a magnetic field, inductors are essential for passive EMI filters.
- Resistors: Often used to control the amount of current passing through the circuit.
- Ferrite Cores: These are often used in inductors and transformers to improve efficiency by providing a low reluctance path for magnetic fields.
Quality control begins at this stage, with suppliers often required to provide certification of material properties, such as dielectric strength and thermal stability.
2. Forming: How Are EMI Filters Shaped and Assembled?
Once materials are prepared, the next step is forming. This can involve several techniques:
- Winding: Inductors are created by winding wire around a core. The precision of this winding affects the inductance and, consequently, the filter’s performance.
- Molding: Some components, like capacitors, may be molded into specific shapes for integration into circuits.
- Soldering: For assemblies that require multiple components, soldering techniques are employed, such as wave soldering or surface mount technology (SMT).
During this phase, manufacturers must adhere to specific tolerances to ensure that each component fits together correctly, which is vital for the filter’s overall performance.
3. Assembly: What Are the Key Steps in Assembling EMI Filters?
The assembly stage combines the individual components into a complete EMI filter. Key techniques include:
- Manual Assembly: Skilled technicians may assemble complex filters by hand, ensuring that each connection is secure.
- Automated Assembly: For high-volume production, automated systems can be used to improve efficiency and consistency.
- Integration: Filters may be integrated into printed circuit boards (PCBs) or housed in protective enclosures, depending on the end-use application.
Quality assurance checks are often performed at this stage to ensure that the assembly meets design specifications.
4. Finishing: How Is the Final Product Prepared for Market?
The final stage involves finishing processes, which may include:
- Testing: Each filter undergoes rigorous testing to ensure it meets performance standards.
- Coating: Protective coatings may be applied to enhance durability and resistance to environmental factors.
- Labeling and Packaging: Proper labeling is essential for compliance with international standards, and packaging must protect the product during shipping.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for EMI Filters?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in the manufacturing of EMI filters, ensuring compliance with both international and industry-specific standards. Key standards include:
- ISO 9001: This globally recognized quality management standard ensures consistent quality in production processes. Manufacturers should provide documentation demonstrating adherence to ISO 9001.
- IEC 61000-3-2: This standard focuses on limits for harmonic current emissions and is critical for EMI filter compliance.
- CE Marking: For products sold in Europe, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: In sectors like oil and gas, API standards may apply to EMI filters used in critical applications.
What Are the Quality Control Checkpoints During Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are essential for identifying defects and ensuring that each EMI filter meets the required specifications. Common checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial step involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified criteria.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During production, samples may be tested at various stages to catch defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipping, a comprehensive test of the finished product ensures it meets all performance and safety standards.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for EMI Filters?
Several testing methods are employed to evaluate the performance and reliability of EMI filters:
- Insertion Loss Testing: This measures the reduction in signal power when the filter is inserted into the circuit, helping to determine its effectiveness.
- Impedance Testing: This assesses the filter’s impedance characteristics across different frequencies.
- Environmental Testing: Filters are subjected to temperature, humidity, and vibration tests to ensure they can withstand real-world conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
International B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality control processes of potential suppliers:
- Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to evaluate a manufacturer’s processes and quality assurance measures firsthand.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can provide insights into a manufacturer’s quality metrics and historical performance.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the manufacturing processes and product quality.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances when dealing with quality control:
- Cultural Differences: Understanding the cultural context of suppliers can enhance communication and expectations around quality.
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have unique regulatory requirements that impact product specifications and quality assurance processes.
- Logistics and Supply Chain Considerations: The complexity of international logistics can affect product quality during transit. Buyers should consider suppliers’ capabilities in packaging and shipping to minimize damage.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for EMI filters is vital for international B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing stages, as well as the relevant standards and quality control measures, buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ’emi filters’
When sourcing EMI filters, having a structured approach can ensure you select the right product for your needs while minimizing risks. This guide provides actionable steps to help B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, navigate the procurement process effectively.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, it’s essential to identify your specific technical requirements. Consider factors such as the type of EMI (conducted vs. radiated), the frequency range (typically between 10 kHz to 10 GHz), and the application environment (industrial, medical, military, etc.). A clear specification will streamline your search and ensure that the filters you consider can adequately protect your electronic devices.
Step 2: Research Regulatory Compliance Standards
Understanding the compliance standards that apply to your industry and region is critical. Familiarize yourself with local and international regulations regarding EMI and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC). For instance, in Europe, filters must adhere to EN55011 or EN55022 standards. Ensuring that your selected filters meet these standards can prevent future legal issues and enhance product reliability.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct thorough due diligence. Look for suppliers with proven experience in manufacturing EMI filters tailored to your specific industry needs. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from other businesses in your sector. This step is vital for assessing the supplier’s reputation and reliability, ensuring you partner with a trustworthy manufacturer.
Step 4: Assess Product Performance and Specifications
Request detailed specifications and performance data for the EMI filters you are considering. Evaluate parameters such as insertion loss, energy coupling, and signal conditioning capabilities. These metrics will help you determine how effectively the filters can mitigate interference and protect your devices, ultimately influencing your product’s overall performance.
Step 5: Verify Supplier Certifications
Check for relevant certifications that indicate quality and compliance with industry standards. Certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems or specific EMC compliance certifications are indicators of a reputable supplier. This verification helps ensure that you are sourcing from manufacturers that adhere to high-quality standards, reducing the risk of receiving subpar products.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have narrowed down your list of potential suppliers, initiate discussions regarding pricing, lead times, and warranty conditions. Be clear about your expectations and seek favorable terms that protect your interests. Effective negotiation can lead to better pricing, improved service levels, and enhanced support, making it a crucial step in the sourcing process.
Step 7: Conduct a Pilot Order
Before placing a large order, consider conducting a pilot purchase of EMI filters. This trial allows you to assess the product’s performance in real-world applications and evaluate the supplier’s responsiveness and service quality. It’s an opportunity to identify any potential issues before committing to a larger investment, ensuring that your final choice aligns with your operational needs.
By following this practical checklist, B2B buyers can enhance their sourcing strategy for EMI filters, ensuring that they select the right products while minimizing risks associated with electromagnetic interference.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for emi filters Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in EMI Filter Sourcing?
When sourcing EMI filters, understanding the cost structure is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. The total cost typically comprises several components:
-
Materials: The primary materials used in EMI filters include capacitors, inductors, resistors, and sometimes transformers. The quality and specifications of these materials directly impact the performance and cost of the filters. For instance, high-quality materials that meet stringent certifications can significantly increase costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs are associated with the assembly and testing of EMI filters. Skilled technicians are often required to ensure that filters meet quality standards and performance specifications. In regions with higher labor costs, such as Europe, these expenses can be a significant portion of the total cost.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead costs, but initial investments in technology may be necessary.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific EMI filter designs can be a substantial upfront cost. While it can lead to long-term savings in production, buyers must consider these costs when evaluating potential suppliers.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous quality control measures ensures that EMI filters meet required standards. The costs associated with QC processes, including testing and certification, should be factored into the overall price.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs can vary significantly based on the supplier’s location and the buyer’s destination. For international buyers, understanding the logistics costs associated with shipping EMI filters is essential.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically apply a profit margin to cover their operational costs and to ensure a return on investment. This margin can vary widely based on the supplier’s market position and the uniqueness of the product.
How Do Price Influencers Affect EMI Filter Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of EMI filters, and being aware of these can help buyers negotiate better deals:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Suppliers often offer discounts for larger orders. Understanding the MOQ can help buyers optimize their purchasing strategy to achieve better unit prices.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom-designed EMI filters that meet specific application requirements usually come at a premium. Buyers should weigh the need for customization against the potential cost benefits of standard products.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly affects pricing. High-performance materials may be necessary for mission-critical applications, but they can drive up costs.
-
Quality and Certifications: Filters that comply with international standards (like IEC or UL certifications) may cost more due to the rigorous testing and quality assurance processes involved. However, these certifications can provide peace of mind and assurance of product reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and location can impact pricing. Established suppliers with a proven track record may charge higher prices but offer better service and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for international buyers. They dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in terms of shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly affect total costs.
What Are the Best Tips for B2B Buyers in EMI Filter Sourcing?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, here are actionable tips to enhance cost efficiency:
-
Negotiate: Don’t hesitate to negotiate prices, especially for bulk orders. Suppliers may be willing to adjust their pricing structures based on order volume and payment terms.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with maintenance, durability, and energy efficiency of the EMI filters. A cheaper filter may result in higher costs over time due to frequent replacements or inefficiencies.
-
Research Market Prices: Understanding the market price range for EMI filters can empower buyers during negotiations. This includes benchmarking against similar products in different regions.
-
Local Sourcing: Whenever possible, consider sourcing from local manufacturers to minimize logistics costs and simplify the supply chain. Local suppliers may also be more adaptable to specific needs.
-
Stay Informed on Regulations: Be aware of the regulatory landscape in your region, as compliance can affect both pricing and sourcing strategies.
Disclaimer on Pricing
Prices for EMI filters can fluctuate based on market conditions, material availability, and changes in manufacturing processes. It is advisable for buyers to request quotes from multiple suppliers and conduct thorough due diligence to ensure they are obtaining the best value for their investment.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing emi filters With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to EMI Filters: What Are Your Options?
As international B2B buyers seek effective solutions to mitigate electromagnetic interference (EMI), understanding the alternatives to EMI filters is essential. While EMI filters are widely used for their effectiveness in blocking unwanted electrical noise, other technologies and methods can also provide protection for sensitive electronic devices. This section compares EMI filters with two alternative solutions: Shielding and Isolation Transformers.
Comparison Table of EMI Filters and Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | EMI Filters | Shielding | Isolation Transformers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency in noise reduction; effective against both conducted and radiated EMI. | Effective against radiated EMI; may require careful design for complete effectiveness. | Excellent for reducing conducted EMI; can isolate devices from power surges. |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depending on complexity and specifications. | Varies widely; can be low-cost for simple materials but high for advanced designs. | Generally moderate; initial investment may be higher due to installation requirements. |
| Ease of Implementation | Generally straightforward; can be integrated into devices or used standalone. | Requires careful design and placement; may complicate manufacturing processes. | Installation can be complex; needs careful planning of electrical systems. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; occasional testing recommended to ensure effectiveness. | Minimal maintenance; however, physical damage can reduce effectiveness. | Low maintenance; regular checks recommended for electrical integrity. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for consumer electronics, medical devices, and military applications. | Best for environments with high radiated EMI, such as industrial settings. | Suitable for sensitive electronic equipment needing isolation from power sources. |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Shielding?
Shielding involves enclosing sensitive electronic components in materials that block electromagnetic fields. Common materials include metal enclosures or conductive coatings.
Pros:
– Effective at reducing radiated EMI, especially in environments with high levels of interference.
– Can be tailored to specific frequencies, providing targeted protection.
Cons:
– Requires careful design and placement to ensure effectiveness; improper shielding can lead to “leakage” of EMI.
– Can increase manufacturing complexity and costs, particularly for advanced shielding solutions.
How Do Isolation Transformers Work and What Are Their Benefits?
Isolation transformers are electrical devices that transfer power between two circuits while isolating them from each other. They are particularly effective at reducing conducted EMI and protecting sensitive equipment from voltage spikes.
Pros:
– Excellent at isolating devices from electrical noise and surges, providing clean power to sensitive equipment.
– Simple in operation and can be used in various applications, from industrial machinery to consumer electronics.
Cons:
– Installation can be complex and requires skilled labor; improper installation may negate benefits.
– They do not provide protection against radiated EMI, so additional solutions may be necessary.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
When selecting between EMI filters, shielding, and isolation transformers, B2B buyers should consider their specific applications and environments. Factors such as the type of EMI (conducted vs. radiated), the level of sensitivity of the electronic devices, budget constraints, and installation capabilities all play crucial roles in determining the best solution. Conducting a thorough needs assessment and consulting with experts in EMI protection can help ensure the chosen method effectively meets the requirements while optimizing costs and implementation efforts.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for emi filters
What Are the Key Technical Properties of EMI Filters That B2B Buyers Should Know?
Understanding the essential technical properties of EMI filters is crucial for international B2B buyers, particularly those engaged in sectors like telecommunications, medical devices, and industrial automation. Here are some critical specifications that should be considered:
1. Insertion Loss
Insertion loss refers to the reduction in signal power that occurs when an EMI filter is introduced into a circuit. It is typically expressed in decibels (dB). For B2B buyers, a low insertion loss value is essential, as it indicates that the filter will not significantly degrade the signal quality of the devices being used. This property is particularly important in applications requiring high signal integrity, such as data communications.
2. Common Mode Rejection Ratio (CMRR)
CMRR measures the effectiveness of an EMI filter in rejecting unwanted signals that are common to both the input and output. It is expressed in decibels and indicates the filter’s ability to minimize interference. A high CMRR is crucial for maintaining the performance of sensitive electronic equipment, especially in environments with high electromagnetic noise, such as industrial settings.
3. Rated Voltage and Current
The rated voltage and current define the maximum electrical load that an EMI filter can handle without failure. This specification is vital for buyers as it determines the filter’s suitability for different applications. Ensuring that the rated voltage and current align with the operating conditions of the equipment will help prevent potential damage and operational failures.
4. Frequency Range
The frequency range specifies the spectrum of frequencies over which the EMI filter operates effectively. For B2B buyers, it is important to select filters that cover the frequency ranges pertinent to their applications. Filters designed for specific frequency bands can significantly improve performance by targeting the specific types of EMI that are most relevant to the equipment being used.
5. Temperature Range
The operational temperature range indicates the environmental conditions in which the EMI filter can function reliably. This specification is particularly important for buyers in regions with extreme temperatures or for applications in harsh environments. Selecting a filter that can withstand the anticipated temperature variations will ensure longevity and reliability.
What Are Common Trade Terminologies Related to EMI Filters?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms that buyers should be aware of:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is vital for B2B buyers, as they often rely on OEMs for the design and production of EMI filters that meet specific industry standards.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest order that a supplier is willing to accept. For buyers, knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management. It can also impact the overall cost per unit, making it a critical factor in procurement decisions.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process where buyers request pricing and terms from suppliers. Understanding how to properly create and submit an RFQ can streamline the purchasing process and ensure that buyers receive competitive offers that meet their technical specifications.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding the delivery of goods. Familiarity with these terms is crucial for international B2B buyers, as they dictate shipping responsibilities, risk management, and cost allocations.
5. EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility)
EMC refers to the ability of electronic devices to operate without causing or being affected by electromagnetic interference. For B2B buyers, ensuring that products comply with EMC regulations is essential for market access and operational reliability.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, international B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing EMI filters, ultimately leading to enhanced product performance and compliance with industry standards.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the emi filters Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the EMI Filters Sector?
The global EMI filters market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing reliance on electronic devices across various sectors, including telecommunications, automotive, and healthcare. As industries become more interconnected, the demand for reliable electronic performance and compliance with stringent electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) regulations is paramount. International buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must be aware of emerging trends such as the integration of advanced technologies like IoT and AI, which necessitate sophisticated EMI filtering solutions to mitigate interference.
Another key trend is the shift towards miniaturization and customization of EMI filters. As electronic devices become smaller and more complex, manufacturers are increasingly focused on producing compact filters that do not compromise performance. This trend is particularly notable in regions like Europe and South America, where innovation in consumer electronics is rapidly evolving. Moreover, the rise of electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy systems has spurred demand for high-performance EMI filters that can withstand challenging operational environments.
International buyers should also consider the growing emphasis on local sourcing and partnerships with manufacturers who understand regional compliance requirements. In Africa and the Middle East, establishing relationships with local suppliers can facilitate quicker access to tailored EMI solutions, enhancing supply chain efficiency.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Be Integrated into EMI Filter Procurement?
The environmental impact of manufacturing electronic components, including EMI filters, is a critical consideration for B2B buyers today. Sourcing from suppliers who prioritize sustainability not only aligns with global environmental goals but also enhances brand reputation. Buyers should seek manufacturers that utilize eco-friendly materials and processes, ensuring that their sourcing practices contribute to a more sustainable future.
Ethical sourcing is also vital in the EMI filters sector, particularly in emerging markets. Ensuring that suppliers adhere to fair labor practices and transparent supply chains can mitigate risks associated with unethical production methods. International buyers should look for certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 26000 for social responsibility, which demonstrate a commitment to sustainable and ethical practices.
Green certifications and materials, such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) compliance, are essential when evaluating potential suppliers. By prioritizing these factors, B2B buyers can not only reduce their environmental footprint but also position themselves as leaders in corporate responsibility within their respective industries.
What Is the Evolution of EMI Filters and Its Relevance to Today’s B2B Landscape?
The evolution of EMI filters has been marked by significant technological advancements since their inception in the mid-20th century. Initially developed to address radio frequency interference in military applications, EMI filters have since expanded their applications across various industries, including telecommunications, automotive, and medical devices.
Today, the focus is on enhancing performance while meeting stringent regulatory standards. As electronic devices have become more prevalent, the need for effective EMI protection has intensified, leading to innovations in filter design and materials. This historical perspective is crucial for B2B buyers, as understanding the evolution of EMI filters can inform their purchasing decisions and highlight the importance of selecting reliable suppliers that can adapt to changing market needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of emi filters
-
How do I solve electromagnetic interference issues in my electronic devices?
To mitigate electromagnetic interference (EMI) issues, start by implementing EMI filters tailored to your specific application. Evaluate the sources of EMI—whether conducted or radiated—and select filters that address these types. Consider passive filters for general noise suppression or active filters for more complex environments. Additionally, ensure proper grounding and shielding in your device design. Regular testing during the design phase can help identify potential interference before full-scale production. -
What is the best EMI filter for my industrial application?
The best EMI filter for industrial applications depends on the specific requirements of your equipment, including frequency range, power capacity, and environmental conditions. Passive filters are often suitable for general applications, while active filters may be necessary for sensitive equipment requiring precise noise cancellation. Consult with manufacturers to understand the performance characteristics and compliance with relevant standards, such as IEC or EN regulations, to ensure the filter meets your operational needs. -
What should I consider when selecting an EMI filter supplier?
When choosing an EMI filter supplier, evaluate their experience and expertise in your industry. Look for suppliers with a proven track record of delivering quality products that comply with international standards. Request samples to assess product performance and reliability. Additionally, consider their capacity for customization, lead times, and after-sales support. Supplier certifications, such as ISO, can also indicate a commitment to quality and continuous improvement. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for EMI filters?
Minimum order quantities for EMI filters can vary widely among suppliers, often ranging from 50 to several hundred units. Factors influencing MOQ include the complexity of the filter design, production capabilities, and material costs. For small businesses or startups, some suppliers may offer flexibility in MOQs to foster relationships. It’s advisable to discuss your needs directly with suppliers to negotiate terms that work for both parties. -
What payment terms are common in international B2B transactions for EMI filters?
Common payment terms in international B2B transactions include net 30, net 60, or payment in advance, depending on the supplier’s policies and your business relationship. Many suppliers also accept letters of credit, which provide security for both parties in international trade. It’s crucial to establish clear payment terms before finalizing orders to avoid any misunderstandings. Always ensure that payment methods are secure and reliable, especially when dealing with cross-border transactions. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) when sourcing EMI filters?
To ensure quality assurance when sourcing EMI filters, request detailed documentation on the manufacturing process, including compliance with relevant industry standards. Ask for test reports or certifications that validate the performance of the filters. Implement a quality control protocol that includes random sampling and testing upon receipt of goods. Building a strong relationship with your supplier can also enhance trust in their QA processes. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing EMI filters?
Logistics for importing EMI filters involve several key considerations, including shipping methods, customs regulations, and lead times. Evaluate the most cost-effective shipping options, whether by air or sea, based on urgency and budget. Familiarize yourself with import duties and taxes in your country to avoid unexpected costs. Additionally, ensure that your supplier provides all necessary documentation for smooth customs clearance, including certificates of origin and compliance. -
How can I customize EMI filters to meet specific application needs?
Customizing EMI filters involves working closely with your supplier to define your specific requirements, such as frequency range, size, and power ratings. Provide detailed specifications regarding the intended application, including any environmental factors that may affect performance. Many manufacturers offer design services that can help create filters tailored to your needs. Collaborate on prototypes and conduct testing to ensure the customized filter meets your performance expectations before full-scale production.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for emi filters
In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, strategic sourcing of EMI filters is paramount for international B2B buyers. Understanding the fundamental role of EMI filters in safeguarding electronic devices from electromagnetic interference can significantly enhance operational reliability across diverse industries, including healthcare, manufacturing, and defense.
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers in Emerging Markets?
For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, particularly in countries like Italy and Vietnam, the emphasis should be on selecting high-quality EMI filters that comply with international standards. This not only ensures regulatory compliance but also enhances product performance and longevity. Additionally, leveraging partnerships with reliable suppliers can provide access to innovative technologies and cost-effective solutions tailored to specific industry needs.
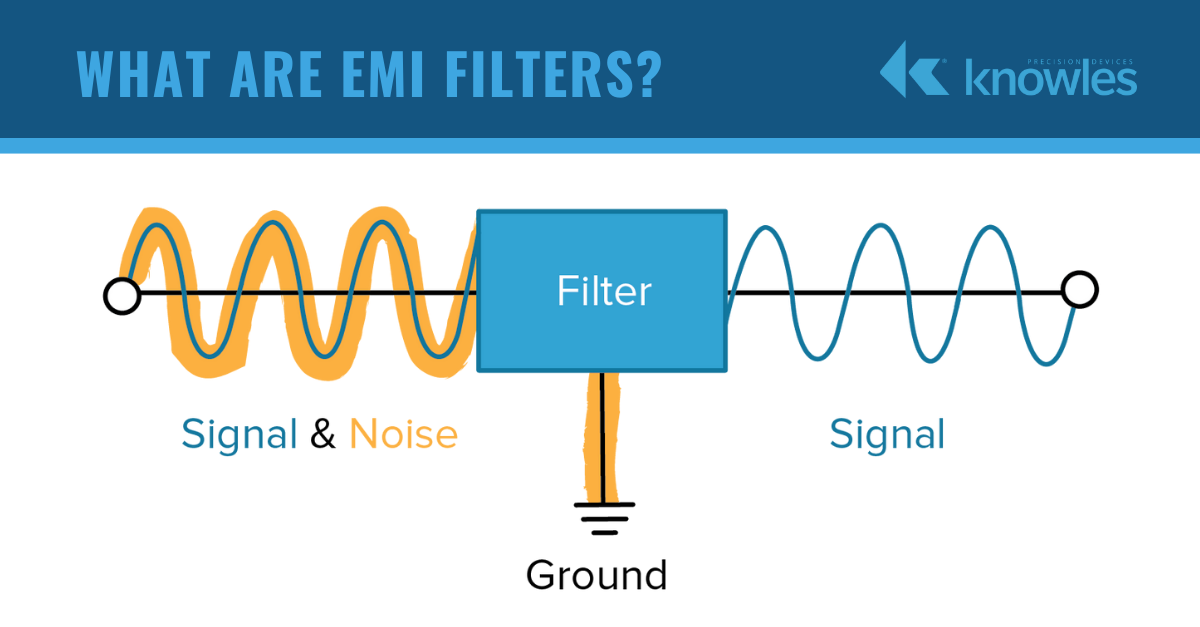
A stock image related to emi filters.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Competitive Edge?
Investing in strategic sourcing practices allows businesses to optimize their supply chain, reduce costs, and improve product quality. As electronic devices become increasingly interconnected, the demand for effective EMI solutions will only rise. Buyers are encouraged to stay ahead of market trends and invest in advanced EMI filtering technologies that promise greater efficiency and noise reduction.
In conclusion, as the global market for EMI filters continues to expand, international B2B buyers should prioritize strategic sourcing to enhance their operational capabilities. Embrace the future of electronics with confidence, and ensure that your products are protected against EMI—your success in the market depends on it.