Master AC Plug Standards: The Complete Buying Guide (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for ac plug standards
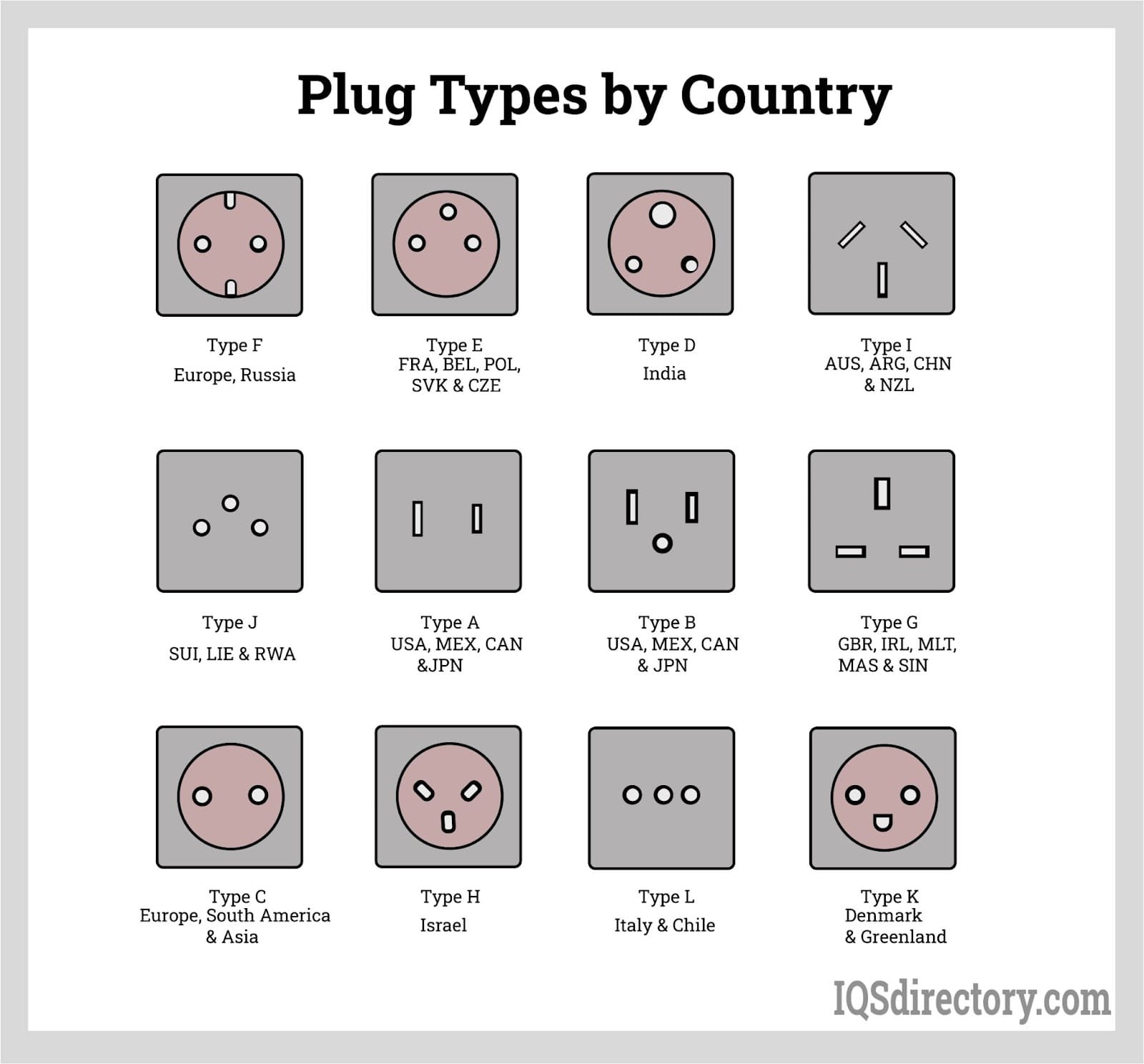
In today’s interconnected world, navigating the diverse landscape of AC plug standards can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers. With various plug types, voltages, and safety regulations in different regions, sourcing compatible electrical components becomes crucial for seamless operations. This comprehensive guide delves into the complexities of AC plug standards, offering insights into the 15 types currently in use worldwide, including those prevalent in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, such as types C, M, and G.
Understanding the specific applications of each plug type, alongside their voltage and current ratings, equips B2B buyers with the knowledge to make informed decisions. We will also explore the importance of supplier vetting to ensure compliance with local regulations and safety standards, as well as strategies for cost management in procurement processes.
By addressing these critical elements, this guide empowers buyers to not only select the right AC plug standards for their needs but also to mitigate risks associated with electrical compatibility and safety. Whether you are sourcing for manufacturing, construction, or any other industrial application, understanding AC plug standards is essential for maintaining operational efficiency and compliance across borders.
Understanding ac plug standards Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type C | 2 pins, not grounded, 2.5 A, 220-240 V | Common in Europe, Africa, South America | Pros: Widely used, compatible with many devices. Cons: Not grounded, which may pose safety risks. |
| Type G | 3 pins, grounded, 13 A, 220-250 V | Predominantly used in the UK and Middle East | Pros: High safety standard due to grounding. Cons: Bulkier design may limit compatibility with some devices. |
| Type M | 3 pins, grounded, 16 A, 220-240 V | Used in South Africa and India | Pros: Suitable for high-power devices. Cons: Less common, may require adapters in other regions. |
| Type E | 2 pins, grounded, 16 A, 220-240 V | Common in France, Belgium, and parts of Europe | Pros: Grounding enhances safety; versatile in usage. Cons: Compatibility issues with non-grounded devices. |
| Type I | 2 or 3 pins, grounded options, 10 A, 220-240 V | Used in Australia, New Zealand, and Argentina | Pros: Versatile plug design; suitable for various applications. Cons: Potential for confusion with different pin configurations. |
What are the Characteristics of Type C AC Plugs?
Type C plugs are characterized by their two non-grounded pins and are commonly used across Europe, Africa, and South America. They support voltages ranging from 220-240 V and current ratings of 2.5 A. B2B buyers should consider Type C plugs for their widespread acceptance and compatibility with a variety of devices, especially in regions where these plugs are standard. However, the lack of grounding can pose a safety risk for sensitive equipment.
Why Choose Type G Plugs for Your Business Needs?
Type G plugs are distinguished by their three grounded pins, providing enhanced safety for electrical connections. They are primarily utilized in the UK and the Middle East, operating at 220-250 V with a current rating of 13 A. Businesses looking for reliable and safe power connections should consider Type G plugs, especially for high-power applications. However, their bulkier design may require additional considerations for space and compatibility with devices that use smaller plugs.
What Makes Type M Plugs Suitable for High-Power Applications?
Type M plugs feature three grounded pins and are rated for 16 A at 220-240 V, making them suitable for high-power devices. Predominantly used in South Africa and India, these plugs are ideal for businesses that require robust power solutions. However, Type M plugs are less common outside their primary regions, which could necessitate the use of adapters for international operations, potentially complicating logistics.
How Do Type E Plugs Enhance Safety for European Businesses?
Type E plugs are easily recognizable by their two grounded pins and are widely used in France, Belgium, and parts of Europe. With a current rating of 16 A and a voltage range of 220-240 V, these plugs provide a safe and versatile connection for various devices. B2B buyers should consider Type E plugs for their grounding feature, which enhances electrical safety, although compatibility with non-grounded devices may pose challenges.
Why Consider Type I Plugs for Versatile Applications?
Type I plugs are unique for their ability to accommodate both 2 and 3-pin configurations, making them versatile for various applications. Used primarily in Australia, New Zealand, and Argentina, they support 10 A and operate at 220-240 V. Businesses should consider Type I plugs for their flexibility; however, the differing pin configurations can create confusion, necessitating careful selection based on specific device requirements.
Key Industrial Applications of ac plug standards
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of ac plug standards | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Powering machinery and equipment | Enhanced operational efficiency and safety | Compatibility with local voltage and plug types, quality standards |
| Construction | Temporary power supply for construction sites | Cost-effective power solutions during projects | Robustness of plugs, weather resistance, and compliance with local regulations |
| IT and Telecommunications | Connecting servers and networking equipment | Reliable uptime and data integrity | Adequate grounding, surge protection, and standardization across equipment |
| Healthcare | Medical equipment connectivity | Ensured safety and compliance with health standards | Specific plug types for medical devices, grounding requirements, and certifications |
| Hospitality | Powering appliances in hotels and restaurants | Improved customer experience and operational reliability | Flexibility in plug types to accommodate diverse international guests |
How Are AC Plug Standards Applied in Manufacturing?
In the manufacturing sector, AC plug standards are crucial for powering various machinery and equipment. Businesses rely on standardized plugs to ensure compatibility with local electrical systems, which enhances operational efficiency and safety. For international buyers, particularly in regions like South Africa and Brazil, understanding the local voltage and plug types is vital. This knowledge helps prevent equipment damage and operational downtime, which can be costly.
Why Are AC Plug Standards Important in Construction?
In construction, AC plug standards facilitate the temporary power supply necessary for tools and equipment on job sites. Using standardized plugs ensures that workers can safely connect various devices without compatibility issues. For buyers in the Middle East and Africa, sourcing robust plugs that withstand harsh environmental conditions is essential. Additionally, compliance with local electrical regulations ensures safety and reduces liability risks.
How Do AC Plug Standards Benefit IT and Telecommunications?
In the IT and telecommunications industry, AC plug standards ensure reliable connectivity for servers and networking equipment. Standardized plugs facilitate seamless integration and help maintain uptime, which is critical for data integrity. International B2B buyers must consider grounding requirements and surge protection when sourcing plugs for sensitive equipment. This attention to detail mitigates risks associated with power fluctuations, particularly in regions with unstable electrical grids.

A stock image related to ac plug standards.
What Role Do AC Plug Standards Play in Healthcare?
In healthcare, proper connectivity of medical equipment is paramount. AC plug standards ensure that devices meet safety and compliance standards, which is crucial for patient care. Buyers must be aware of specific plug types for medical devices, particularly in regions like Europe and South America, where regulations may vary. Ensuring adequate grounding and adherence to certifications can significantly impact patient safety and operational efficiency.
How Are AC Plug Standards Used in the Hospitality Sector?
In the hospitality industry, AC plug standards are vital for powering appliances in hotels and restaurants. Standardized plugs enhance the customer experience by accommodating a diverse range of international guests with various electrical devices. For businesses in Europe and Africa, sourcing flexible plug types that can adapt to different guest needs is essential. This adaptability not only improves service quality but also minimizes operational disruptions related to electrical compatibility.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘ac plug standards’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Diverse AC Plug Standards in International Markets
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face significant challenges when dealing with the diverse AC plug standards across different countries. For instance, a company in South Africa looking to expand its operations to Europe may encounter compatibility issues with the local plug types. This can lead to delays in equipment deployment, increased shipping costs for additional adapters, and potential electrical hazards if incompatible plugs are used. The lack of a universal standard creates confusion and complicates the procurement process, making it essential for buyers to understand the specific requirements of each target market.
The Solution:
To effectively navigate the diverse AC plug standards, buyers should start by creating a comprehensive compatibility checklist based on their target markets. This checklist should include the specific plug types, voltage requirements, and frequency specifications for each country. For instance, while South Africa primarily uses Type M plugs, European countries often utilize Type C and Type F plugs. By collaborating with local distributors or electrical engineers familiar with the regional standards, buyers can ensure that their equipment is compatible and safe for use. Additionally, investing in multi-standard power strips or adapters can provide a temporary solution while transitioning to localized equipment.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Compliance with Local Electrical Safety Regulations
The Problem:
Another common pain point for B2B buyers is the need to comply with local electrical safety regulations when sourcing equipment that utilizes AC plug standards. For example, a manufacturer in Brazil may import machinery that doesn’t meet the country’s electrical safety norms, resulting in legal penalties or the need for costly modifications. This situation can arise when buyers are unaware of the specific grounding requirements or voltage ratings mandated by local authorities, leading to potential safety hazards and operational disruptions.
The Solution:
To ensure compliance with local electrical safety regulations, buyers should conduct thorough research into the applicable standards before making procurement decisions. Engaging with a local compliance consultant can provide valuable insights into the specific requirements for electrical equipment in the target market. Buyers should also prioritize sourcing equipment from manufacturers who provide clear documentation of compliance with local standards, such as certifications from recognized bodies. This proactive approach not only mitigates the risk of penalties but also enhances the overall safety and reliability of the equipment being used.
Scenario 3: Managing the Costs of Adapting Equipment for Different Markets
The Problem:
Cost management becomes a critical concern when B2B buyers need to adapt their existing equipment to fit various AC plug standards. For instance, a company operating in multiple countries may find that retrofitting machinery to accommodate different plug types incurs significant costs, both in terms of labor and materials. Additionally, the need for continuous investment in adapters or converters can erode profit margins and complicate inventory management.
The Solution:
To manage these costs effectively, buyers should consider a dual or multi-plug system when designing or purchasing new equipment. This approach allows for flexibility across different markets without the need for extensive modifications. Furthermore, buyers can evaluate suppliers who offer customizable solutions that can be tailored to specific regional requirements, potentially reducing the need for additional adaptations later on. Establishing strong relationships with manufacturers that understand international standards can lead to more cost-effective procurement strategies, ensuring that equipment is not only compliant but also financially viable for operation in diverse markets.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for ac plug standards
What Are the Key Materials Used in AC Plug Standards?
When selecting materials for AC plugs, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that affect performance, durability, and compliance with regional standards. Below, we analyze four common materials used in AC plug manufacturing, highlighting their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Properties of Thermoplastic Materials in AC Plugs?
Key Properties:
Thermoplastics, such as polycarbonate and nylon, are widely used due to their excellent electrical insulation properties and resistance to impact and chemicals. They typically have a temperature rating of up to 85°C and can withstand moderate mechanical stress.
Pros & Cons:
Thermoplastics are lightweight and cost-effective, making them suitable for mass production. However, they may not offer the same level of durability as metals and can be prone to wear under extreme conditions.
Impact on Application:
These materials are ideal for plugs used in residential and light commercial applications where high mechanical stress is not a concern.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Thermoplastics must comply with standards like UL (Underwriters Laboratories) and IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission). Buyers should ensure that the materials meet local regulations, especially in regions like South Africa and Egypt, where safety standards are stringent.
How Do Metal Components Enhance AC Plug Performance?
Key Properties:
Metals such as brass and copper are often used for the pins and contacts in AC plugs. They have excellent conductivity and can handle high temperatures (up to 200°C) and current loads.
Pros & Cons:
Metal components provide superior durability and reliability, ensuring long-term performance. However, they are heavier and more expensive than plastic alternatives, which can increase manufacturing costs.
Impact on Application:
Metal components are essential for plugs that need to handle high power loads, such as industrial applications or heavy-duty consumer electronics.
Considerations for International Buyers:
B2B buyers should verify that metal components meet corrosion resistance standards, especially in humid or coastal environments common in Africa and South America. Compliance with ASTM standards is crucial for ensuring product quality.
What Role Do Rubber and Silicone Play in AC Plug Design?
Key Properties:
Rubber and silicone are often used for insulation and sealing in AC plugs. They provide excellent flexibility, temperature resistance (up to 200°C), and water resistance.
Pros & Cons:
These materials enhance safety by preventing electrical shocks and are durable against environmental factors. However, they can be more expensive and may complicate the manufacturing process.
Impact on Application:
Rubber and silicone are particularly beneficial for outdoor plugs or those used in wet environments, where moisture and physical stress are concerns.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure that rubber and silicone materials comply with local safety standards, such as those set by the European Union (CE marking) and South African Bureau of Standards (SABS).
Why Is the Selection of Composite Materials Important for AC Plugs?
Key Properties:
Composite materials, often a blend of plastics and metals, offer a balance of strength, weight, and cost. They can withstand high temperatures and provide good electrical insulation.
Pros & Cons:
Composites can be designed to meet specific performance criteria, making them versatile. However, they may be more expensive to produce and require specialized manufacturing techniques.
Impact on Application:
These materials are suitable for high-performance applications where both mechanical strength and electrical insulation are critical, such as in industrial machinery.
Considerations for International Buyers:
B2B buyers should assess the manufacturing capabilities of suppliers to ensure they can meet the required composite specifications and certifications, particularly in regions with strict compliance requirements.
Summary Table of Material Selection for AC Plug Standards
| Material | Typical Use Case for AC Plug Standards | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermoplastic | Residential and light commercial plugs | Lightweight and cost-effective | Less durable under extreme conditions | Low |
| Metal | Heavy-duty and industrial plugs | Superior durability and reliability | Heavier and more expensive | High |
| Rubber/Silicone | Outdoor and moisture-prone plugs | Excellent insulation and flexibility | More expensive and manufacturing complexity | Medium |
| Composite | High-performance industrial plugs | Balance of strength and weight | Higher production costs | High |
This comprehensive analysis of materials for AC plug standards provides B2B buyers with actionable insights to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for ac plug standards
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of AC Plugs?
The manufacturing process for AC plugs involves several critical stages, each essential for ensuring the final product meets international standards. Below are the main stages of the manufacturing process:
-
Material Preparation
The first step involves selecting and preparing raw materials. Common materials include high-quality plastics for the casing, copper or brass for the pins, and rubber or silicone for insulation. Suppliers should ensure that materials comply with relevant standards, such as RoHS for hazardous substances. -
Forming
This stage involves shaping the raw materials into the desired components. Techniques like injection molding are commonly used for plastic casings, while stamping or machining is employed for metal pins. Precision in this stage is crucial to ensure compatibility with international plug standards. -
Assembly
During assembly, various components are joined together. Automated assembly lines are typically used, where the components are fitted into the casing and secured. This stage may also include the integration of safety features like earthing pins, which are essential for grounding purposes. -
Finishing
The final manufacturing stage involves finishing processes such as surface treatment, coating, or printing. These processes not only enhance the aesthetic appeal but also improve durability and resistance to environmental factors. Quality checks are often integrated into this stage to ensure that all products meet specified standards.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in AC Plug Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in the manufacturing of AC plugs to ensure safety, reliability, and compliance with international standards. Here’s an overview of how QA is typically implemented:
-
What Are the Relevant International Standards for AC Plugs?
Compliance with standards such as ISO 9001 is essential for quality management systems. Additionally, region-specific certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) for European markets and UL (Underwriters Laboratories) for North America ensure that products meet safety requirements. Buyers should verify that suppliers have the necessary certifications to mitigate risks. -
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints?
Quality Control (QC) checkpoints include:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspection of raw materials before production to ensure compliance with specifications.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process to catch defects early.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing of finished products to confirm they meet all standards and specifications. -
What Common Testing Methods Are Used?
Various testing methods are employed to verify the quality and safety of AC plugs, including:
– Electrical Testing: Checking for short circuits, insulation resistance, and grounding effectiveness.
– Mechanical Testing: Assessing durability through impact resistance and tensile strength tests.
– Environmental Testing: Evaluating performance under extreme conditions such as temperature and humidity variations.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of potential suppliers:
-
Conduct Supplier Audits
Regular audits can provide insights into a supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality control measures. These audits should assess compliance with international standards and the effectiveness of their quality management systems. -
Request Quality Reports
Suppliers should provide comprehensive quality reports detailing their testing procedures, results, and any corrective actions taken for non-compliance. This transparency is vital for building trust. -
Engage Third-Party Inspection Services
Utilizing third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes. This is especially important for international buyers who may not have the resources to conduct on-site evaluations.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers need to be aware of specific nuances related to quality control and certification when sourcing AC plugs:
-
Understanding Regional Standards
Different regions have unique standards and regulations governing electrical safety. For instance, buyers in Europe must ensure that products meet CE marking requirements, while those in the Middle East may need to comply with Gulf Conformity Mark (G Mark) standards. Understanding these requirements is crucial for market access. -
Awareness of Local Testing Laboratories
Familiarity with local testing laboratories that are accredited to conduct safety and performance testing can streamline the certification process. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers use recognized laboratories to validate compliance. -
Navigating Import Regulations
Each country has distinct import regulations that can affect the acceptance of electrical products. Buyers should be informed about the documentation required for customs clearance, including certificates of compliance and safety testing reports.
Conclusion
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for AC plugs, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing products. Ensuring compliance with international standards and implementing robust quality control practices will not only enhance product reliability but also foster trust between buyers and suppliers. As the global market continues to expand, prioritizing quality will be key to successful international trade in electrical components.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘ac plug standards’
To ensure a successful procurement process for AC plug standards, it is essential to follow a systematic approach. This checklist provides actionable steps for B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, to navigate the complexities of sourcing electrical plugs and sockets effectively.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the cornerstone of your sourcing process. Consider the type of plugs required based on the regions you are targeting, as different countries use various plug types and voltage standards. For example, Type C plugs are commonly used across Europe and Africa, while Type G is prevalent in the UK and Ireland.
- Voltage and Current Ratings: Ensure that the plugs meet the voltage (e.g., 220-240V) and current ratings (e.g., 10A, 16A) suitable for your equipment.
- Compatibility Requirements: Determine if the plugs need to be compatible with existing infrastructure or if you require unique configurations for specific devices.
Step 2: Research Global Standards and Compliance
Understanding international standards is vital to ensure safety and compatibility. Familiarize yourself with the relevant IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) standards that apply to the AC plugs and sockets in your target markets.
- Safety Certifications: Verify that products comply with safety standards such as CE marking in Europe or UL certification in the United States.
- Country-Specific Regulations: Research any additional regulations specific to countries where the plugs will be used, as non-compliance can lead to costly delays or rejections.
Step 3: Identify Reliable Suppliers
Finding trustworthy suppliers is critical to securing quality products. Look for manufacturers with a proven track record in producing AC plugs that meet international standards.
- Supplier Verification: Request documentation that proves the supplier’s compliance with relevant certifications and standards.
- Industry Reputation: Consider reviews and testimonials from other businesses in your region to assess the supplier’s reliability.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Before making bulk purchases, always request samples to evaluate the quality and functionality of the plugs. This step helps identify potential issues early in the procurement process.
- Testing Compatibility: Ensure that the samples work seamlessly with your equipment and existing sockets.
- Quality Assurance: Assess the materials used and the overall build quality to avoid future failures or safety hazards.
Step 5: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you have identified a suitable supplier and tested their products, the next step is to negotiate pricing and terms. This includes discussing payment methods, delivery schedules, and warranty conditions.
- Bulk Order Discounts: Inquire about discounts for large orders, which can significantly reduce your overall costs.
- Clear Terms of Service: Ensure that all agreements are documented, including return policies and service guarantees.
Step 6: Plan for Logistics and Import Regulations
Effective logistics planning is essential to ensure timely delivery and compliance with import regulations. Understand the shipping methods available and any tariffs that may apply.
- Shipping Options: Evaluate different shipping options based on cost, speed, and reliability.
- Customs Clearance: Familiarize yourself with customs procedures in your country to avoid delays or unexpected fees.
Step 7: Implement a Quality Control Process
After receiving the products, establish a quality control process to ensure that all items meet your specifications and standards.
- Inspection Procedures: Develop a checklist for inspecting plugs and sockets upon arrival.
- Feedback Loop: Create a system for providing feedback to suppliers on product quality, which can help improve future orders.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing AC plug standards effectively, ensuring compliance, safety, and compatibility in their operations.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for ac plug standards Sourcing
What are the Key Cost Components in AC Plug Standards Sourcing?
When sourcing AC plug standards, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The main cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly influences the overall cost. High-quality plastics and metals that comply with international safety standards tend to be more expensive but are essential for durability and safety.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region. For instance, manufacturing in countries with lower labor costs may seem appealing, but the trade-off could be lower quality. Skilled labor is essential for ensuring the plugs meet safety and performance specifications.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations such as utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead costs.
-
Tooling: The initial setup costs for molds and machinery can be significant, especially for customized plugs. These costs are amortized over the production volume, making higher volumes more cost-effective.
-
Quality Control (QC): Investing in robust QC processes ensures compliance with international standards, which is critical for safety. This can add to the overall cost but can prevent costly recalls or compliance issues later.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, including freight and insurance, can vary widely based on distance, weight, and mode of transport. Incoterms can also affect costs, as they define responsibilities between the buyer and seller regarding shipping and logistics.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding the market conditions and competitive landscape can help buyers negotiate better terms.
How Do Price Influencers Affect AC Plug Standards?
Several factors influence the pricing of AC plugs, including:
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders typically attract lower unit prices due to economies of scale. Establishing a minimum order quantity (MOQ) can also help negotiate better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs and unique specifications can increase costs. Buyers should assess whether the additional expense aligns with their needs.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (like CE or UL) can elevate costs but are essential for ensuring safety and compliance, especially in regulated markets.
-
Supplier Factors: The reliability and reputation of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but can offer better quality assurance and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the Incoterms chosen can influence total costs. For example, “CIF” (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) means the supplier covers shipping costs, which can lead to higher upfront prices but lower risk for the buyer.
What are Effective Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in AC Plug Sourcing?
To maximize cost-efficiency when sourcing AC plugs, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Build relationships with suppliers to negotiate better prices. Long-term contracts can often yield discounts.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but also maintenance, energy consumption, and potential failure costs. Opting for higher-quality plugs may involve a higher upfront cost but can result in savings over time.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of import duties, taxes, and currency fluctuations that can affect overall costs. Understanding local regulations and compliance requirements is also critical.
-
Market Research: Stay informed about market trends, competitor pricing, and emerging technologies. This knowledge can empower buyers to make informed decisions and potentially leverage better pricing.
Disclaimer on Pricing
It’s important to note that pricing can fluctuate based on market conditions, raw material availability, and geopolitical factors. Buyers should always conduct thorough research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure they are receiving competitive pricing tailored to their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing ac plug standards With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to AC Plug Standards
In the global marketplace, businesses often face challenges when selecting the right electrical connections for their operations. While AC plug standards provide a reliable method for connecting devices to power sources, alternative solutions may offer specific advantages depending on the context of use. This section examines two viable alternatives to traditional AC plug standards, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | AC Plug Standards | Universal Power Adapters | Wireless Power Transfer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Reliable for standard voltage needs | Versatile for multiple plug types | Eliminates the need for plugs |
| Cost | Generally low initial investment | Moderate cost, varies by brand | Higher initial cost for technology |
| Ease of Implementation | Straightforward installation | Requires user knowledge of compatibility | Requires specific equipment and setup |
| Maintenance | Minimal maintenance required | Occasional replacements needed | Limited maintenance, but tech-dependent |
| Best Use Case | Standardized environments (e.g., offices) | Travel and multi-country use | Modern setups where cabling is impractical |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Universal Power Adapters?
Universal power adapters are designed to accommodate various plug types, making them an excellent alternative for businesses operating in multiple regions. The primary advantage is their versatility; they can adapt to different plug standards, which is beneficial for international operations. However, these adapters may have a moderate cost and require users to be knowledgeable about compatibility issues. In environments with frequent plug changes, they can be a practical solution, albeit with the potential downside of needing replacement if damaged.
How Does Wireless Power Transfer Compare to AC Plug Standards?
Wireless power transfer, or inductive charging, is an innovative technology that allows devices to charge without physical connections. This method is particularly advantageous in environments where traditional cabling may be cumbersome or hazardous. It eliminates wear and tear on plugs and sockets, reducing maintenance needs. However, the technology comes with a higher initial investment and requires specific setups to implement effectively. This solution is best suited for modern workplaces that prioritize aesthetics and safety over traditional wiring methods.
Making the Right Choice: How Should B2B Buyers Decide?

A stock image related to ac plug standards.
When evaluating whether to use AC plug standards, universal power adapters, or wireless power transfer, B2B buyers should consider their specific operational needs. Factors such as the geographical location of operations, the nature of the equipment being powered, and budget constraints will play significant roles in the decision-making process. For businesses with standardized equipment in stable regions, traditional AC plug standards may suffice. Conversely, those with diverse international needs or modern workspace designs may find universal adapters or wireless solutions to be more advantageous. Ultimately, understanding the unique requirements of your business will guide you to the most suitable power connection solution.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for ac plug standards
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of AC Plug Standards?
Understanding the technical properties of AC plug standards is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when sourcing electrical components for international markets. Here are some key specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
The material grade of plugs is vital for ensuring durability and electrical safety. Common materials include thermoplastics for the housing and copper for the pins. The choice of materials affects not only the product’s longevity but also its resistance to heat and corrosion. For buyers, selecting plugs with high-quality materials can prevent costly failures and ensure compliance with safety standards.
2. Current Rating
The current rating, usually measured in amperes (A), indicates the maximum amount of electrical current the plug can safely carry. For example, plugs may be rated for 10A, 16A, or even higher. This specification is critical for matching plugs to the equipment they will serve. B2B buyers must ensure that the plugs selected can handle the power requirements of their devices to prevent overheating and potential hazards.
3. Voltage Rating
Voltage rating denotes the maximum voltage the plug can withstand, typically ranging from 100V to 250V. In regions like Europe and Africa, where 220-240V is common, understanding the voltage compatibility of plugs is essential. This specification is particularly important for international trade, as mismatched voltage ratings can lead to equipment failure and safety risks.
4. Pin Configuration and Size
Different countries have various plug types, each with unique pin configurations and sizes. For instance, the Type C plug features two round pins, while Type G has three rectangular pins. Understanding these differences is crucial for buyers looking to import or export electrical equipment across regions. Selecting the wrong configuration can lead to incompatibility issues, resulting in additional costs and delays.
5. Grounding (Earthing)
Grounding refers to the inclusion of a third pin for electrical safety, providing a path for fault currents. This feature is especially critical in regions where electrical safety standards are stringent. Buyers should prioritize plugs with grounding capabilities to mitigate risks of electrical shocks and equipment damage.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to AC Plug Standards?
Familiarity with industry terminology helps streamline procurement processes and enhances negotiation capabilities. Here are some essential terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. For buyers, partnering with OEMs can ensure high-quality components that meet specific technical standards, facilitating smoother integration into their products.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for B2B buyers to manage inventory costs effectively. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their production needs while minimizing excess stock.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by buyers to suppliers to request pricing and availability for specific products. Crafting an effective RFQ can lead to better pricing and terms, making it an essential step in the procurement process.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined international trade terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers. Knowledge of Incoterms helps B2B buyers understand shipping responsibilities, insurance, and risk management, which is essential for international transactions.
5. Certification Compliance
This term refers to adherence to specific safety and quality standards set by regulatory bodies. Ensuring that plugs meet certification requirements can safeguard against legal issues and enhance product marketability.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing AC plugs, ensuring compliance and safety in their electrical systems.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the ac plug standards Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in AC Plug Standards?
The global market for AC plug standards is being shaped by several key drivers, including increasing international trade, the rise of smart technologies, and the urgent need for standardization in electrical equipment. As international B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe navigate these complexities, understanding the specific plug types relevant to their regions becomes critical. For instance, Type C plugs are widely used across Europe, Africa, and South America, while Type M is prevalent in South Africa.
Emerging trends in sourcing include a shift towards integrated solutions that accommodate multiple plug types to meet diverse market needs. Companies are increasingly seeking suppliers who can provide a range of plug types, such as Types E, F, and G, which are essential for compatibility across various countries. This demand for versatility is amplified by the growing trend of e-commerce and direct-to-consumer models, requiring businesses to ensure their products are compatible with local standards. Furthermore, the rise of e-mobility and the push for electric vehicles are propelling the development of advanced plug designs, making it essential for B2B buyers to stay informed about technological advancements.
How Can B2B Buyers Prioritize Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in AC Plug Standards?
Sustainability is becoming a non-negotiable aspect of procurement strategies in the AC plug standards sector. The environmental impact of electrical components, from production to disposal, necessitates a focus on ethical sourcing practices. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through the use of eco-friendly materials and responsible manufacturing processes.
Certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management and adherence to RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) standards can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. Additionally, the adoption of ‘green’ certifications for products ensures that they meet environmental standards and regulations, making them more attractive in a market increasingly concerned with sustainability. By choosing suppliers that prioritize ethical sourcing, international buyers not only contribute to environmental protection but also enhance their brand reputation and compliance with global regulations.
What Is the Brief Evolution of AC Plug Standards and Its Importance for B2B Buyers?
The evolution of AC plug standards has been driven by the need for safety, compatibility, and efficiency in electrical systems. Initially, electrical outlets were designed based on local requirements, leading to a proliferation of plug types globally. Over time, organizations like the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) have sought to standardize these components to facilitate international trade and improve safety.
Today, the importance of understanding these standards is paramount for B2B buyers. With global supply chains and diverse markets, knowledge of the specific plug types and their compatibility ensures that products meet local regulations and consumer needs. For example, as businesses in South Africa and Brazil expand their markets, they must navigate the different plug types and voltage standards to avoid costly compliance issues. Understanding the historical context of these standards not only aids in sourcing but also informs strategic decisions for market entry and expansion.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of ac plug standards
-
How do I ensure compatibility with international ac plug standards when sourcing?
To ensure compatibility with international AC plug standards, start by identifying the specific plug types used in your target markets. Research the voltage and frequency requirements for the region, as these vary significantly. Utilize resources like the World Standards website to cross-reference plug types with countries. Additionally, consult with suppliers to verify their products meet the necessary certifications and standards for your intended market. This proactive approach minimizes installation issues and enhances customer satisfaction. -
What is the best ac plug type for use in South Africa?
In South Africa, the most commonly used ac plug type is Type M, which features three grounded pins and operates at 220-240V. When sourcing plugs for the South African market, consider the current ratings (typically 16 A) and ensure compliance with local regulations. If your products will be exported to South Africa, it’s crucial to partner with manufacturers who are familiar with these standards to avoid costly compliance issues and ensure reliable performance. -
What are the common challenges faced when sourcing ac plugs for international markets?
Common challenges when sourcing ac plugs for international markets include differing regulations and standards, variations in voltage and frequency, and ensuring product safety and compatibility. Language barriers and cultural differences may also complicate supplier negotiations and communications. To overcome these challenges, conduct thorough market research, utilize experienced local partners, and establish clear communication channels with suppliers. This will help you navigate the complexities of international sourcing effectively. -
How can I vet suppliers for ac plug standards compliance?
Vetting suppliers for ac plug standards compliance involves checking their certifications, quality control processes, and production capabilities. Request samples to assess product quality and ensure they meet the required international standards. Additionally, review customer testimonials and case studies to gauge their reputation in the market. Using third-party inspection services can also provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s compliance with safety and quality standards. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for ac plugs, and how do they affect sourcing decisions?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for ac plugs can vary significantly depending on the supplier and product specifications. Smaller suppliers may have lower MOQs, while larger manufacturers might require higher volumes to justify production runs. Consider your market demand and budget when evaluating MOQs. Negotiating terms with suppliers can help secure a more favorable MOQ, but be cautious of overcommitting to stock that may not sell quickly, leading to increased holding costs. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing ac plugs internationally?
Payment terms for sourcing ac plugs internationally typically range from upfront payment to net 30, 60, or even 90 days, depending on the supplier’s policies and the buyer’s relationship with them. It’s common to negotiate a deposit (often 30%) before production, with the balance due upon shipment or delivery. Always clarify payment methods accepted (e.g., bank transfer, letters of credit) and ensure that terms are documented in the purchase agreement to avoid disputes later.
A stock image related to ac plug standards.
-
How can I ensure quality assurance for ac plugs sourced internationally?
To ensure quality assurance for internationally sourced ac plugs, implement a robust QA process that includes pre-shipment inspections, product testing, and compliance checks with relevant standards. Establish clear quality criteria with your suppliers and consider utilizing third-party inspection services for unbiased assessments. Maintaining open communication with suppliers about quality expectations and conducting regular audits can also help uphold product quality throughout the sourcing process. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing ac plugs?
When importing ac plugs, key logistics considerations include shipping methods, customs regulations, and lead times. Choose a reliable freight forwarder who understands the intricacies of international shipping and can assist with documentation and customs clearance. Be aware of import duties and taxes that may apply to your products, and factor these costs into your pricing strategy. Planning for potential delays and maintaining flexibility in your supply chain can also mitigate disruptions in product availability.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for ac plug standards
In navigating the complexities of AC plug standards, international B2B buyers must prioritize strategic sourcing to ensure compatibility and safety across diverse markets. Understanding the various plug types—ranging from Type C prevalent in Europe and Africa, to Type G used in the UK—enables businesses to make informed purchasing decisions. This knowledge not only mitigates the risk of equipment malfunction but also aligns with local regulations, enhancing operational efficiency.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Benefit Your Business?
Implementing a strategic sourcing approach allows buyers to leverage supplier relationships, negotiate better terms, and gain access to high-quality products tailored to specific regional standards. By focusing on reliable suppliers with expertise in AC plug standards, businesses can streamline their supply chain and reduce costs associated with compliance failures.
What’s Next for International Buyers?
As global demand for electrical compatibility increases, staying ahead of evolving standards will be crucial. Buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should actively seek partnerships with manufacturers who prioritize innovation and safety in their product offerings. Embrace the opportunity to enhance your supply chain resilience and ensure your business remains competitive in the international market. Start evaluating your sourcing strategy today to secure a reliable future.