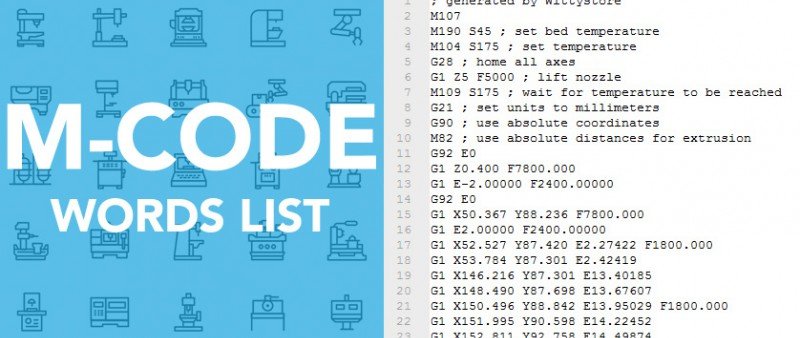
Master Fanuc M Codes: The Complete Guide for Buyers (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for fanuc m codes
In the intricate world of CNC machining, understanding Fanuc M codes is crucial for optimizing manufacturing processes and enhancing productivity. For international B2B buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, sourcing the right M codes can be a daunting task. This guide aims to simplify that challenge by providing a comprehensive overview of Fanuc M codes, their types, applications, and the nuances of supplier vetting.
Navigating through the various M codes—each tailored for specific machine operations—can significantly impact operational efficiency and product quality. From controlling spindle speeds to managing coolant systems, knowing the right codes can streamline workflows and reduce downtime. Furthermore, this guide will delve into cost considerations, helping buyers make informed financial decisions while sourcing these essential components.
By equipping B2B buyers with actionable insights and practical knowledge, this resource empowers them to engage confidently with suppliers and ensure their manufacturing processes run smoothly. Whether you are a manufacturer in Turkey looking to enhance your machining capabilities or a factory owner in Nigeria aiming to optimize production, understanding Fanuc M codes is the first step toward achieving operational excellence.
Understanding fanuc m codes Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| General M Codes | Basic commands for machine control (e.g., M00, M02) | General CNC operations | Pros: Easy to understand; essential for all CNC users. Cons: Limited functionality for complex tasks. |
| Tool Change M Codes | Commands for changing tools (e.g., M06) | Multi-tool machining setups | Pros: Automates tool changes; increases efficiency. Cons: May require additional setup and calibration. |
| Spindle Control M Codes | Commands for spindle operation (e.g., M03, M05) | Milling and drilling applications | Pros: Direct control over spindle speed; enhances machining precision. Cons: Incorrect settings can lead to equipment wear. |
| Coolant Control M Codes | Commands for managing coolant flow (e.g., M08, M09) | Metalworking and machining processes | Pros: Improves tool life and part finish; essential for high-speed machining. Cons: Requires maintenance of coolant systems. |
| Subprogram M Codes | Commands for calling subprograms (e.g., M98, M99) | Complex machining tasks requiring modularity | Pros: Streamlines programming for complex tasks; reduces errors. Cons: Can complicate the programming process. |
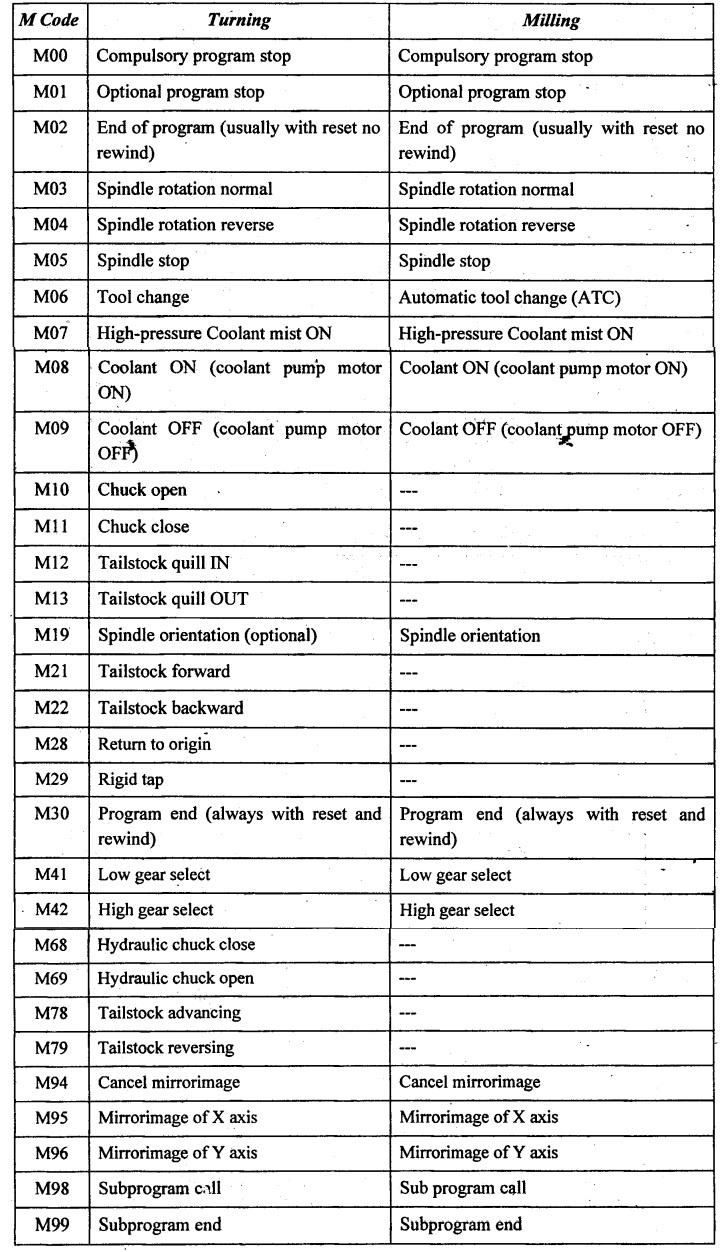
What Are General M Codes and Their B2B Relevance?
General M codes, such as M00 (program stop) and M02 (end of program), serve as foundational commands that control the basic operations of CNC machines. These codes are essential for any CNC operator, providing straightforward instructions that facilitate the execution of machining tasks. For B2B buyers, understanding these codes is critical as they form the basis of machine programming, ensuring that operators can efficiently manage machine operations with minimal risk of error.
How Do Tool Change M Codes Enhance Production Efficiency?
Tool change M codes, particularly M06, are vital for operations involving multiple tools. These codes automate the process of switching tools during machining, significantly enhancing production efficiency and reducing downtime. For businesses engaged in high-volume manufacturing, the ability to quickly change tools can lead to improved throughput and productivity. Buyers should consider machines with robust tool change capabilities to maximize operational efficiency.
Why Are Spindle Control M Codes Important in Machining?
Spindle control M codes, such as M03 (spindle on clockwise) and M05 (spindle stop), allow operators to manage spindle speed and direction. This control is crucial for achieving precise machining results, especially in milling and drilling applications. For B2B buyers, investing in machines with advanced spindle control features can lead to enhanced machining accuracy and improved quality of finished products. However, it is essential to ensure that operators are trained to set the correct parameters to avoid excessive wear on the equipment.
What Role Do Coolant Control M Codes Play in Machining Processes?
Coolant control M codes, including M08 (coolant on) and M09 (coolant off), are essential for maintaining optimal machining conditions. These codes help manage coolant flow, which is critical for cooling tools, preventing overheating, and improving surface finishes. For international B2B buyers, particularly in metalworking industries, selecting machines equipped with effective coolant management systems can lead to longer tool life and better product quality, although they require regular maintenance.
How Do Subprogram M Codes Contribute to Programming Efficiency?
Subprogram M codes, such as M98 (call subprogram) and M99 (end subprogram), enable operators to call and execute pre-written programs within a main program. This modular approach simplifies complex machining tasks and reduces programming errors. B2B buyers should consider the availability of subprogramming features when selecting CNC machines, as they allow for greater flexibility in manufacturing processes, although they can add complexity to initial programming efforts.
Key Industrial Applications of fanuc m codes
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of fanuc m codes | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Tool Change Automation (M06) | Increased efficiency and reduced downtime | Compatibility with existing CNC machines; supplier reliability |
| Automotive Manufacturing | Spindle Control (M03, M04) | Enhanced precision in machining components | Access to technical support; availability of spare parts |
| Oil & Gas | Coolant Management (M08, M09) | Improved tool life and machining accuracy | Local regulations on coolant disposal; supplier certifications |
| Metal Fabrication | Program Stops and Subprograms (M00, M98) | Streamlined operations and flexibility in production | Ease of integration with existing systems; training availability |
| Electronics Assembly | Rigid Tapping (M29) | Higher quality threads and reduced cycle times | Understanding of specific electronic component needs; support for automation |
How Are Fanuc M Codes Applied in Aerospace Manufacturing?
In the aerospace sector, tool change automation using M06 is critical for maintaining high efficiency during production. Given the complexity of aerospace components, the ability to quickly switch tools minimizes downtime and enhances productivity. International buyers, particularly those from Africa and South America, should ensure that the M codes are compatible with their existing CNC machines and that their suppliers can provide reliable support and maintenance.
What Role Do Fanuc M Codes Play in Automotive Manufacturing?
In automotive manufacturing, spindle control (M03 and M04) is vital for achieving precision when machining engine components and other critical parts. The ability to control spindle speed accurately leads to better surface finishes and dimensional accuracy. B2B buyers in regions like Turkey and Nigeria should focus on suppliers that offer robust technical support and a steady supply of spare parts to maintain operational efficiency.
How Is Coolant Management Utilized in the Oil & Gas Industry?
For the oil and gas industry, effective coolant management through M08 and M09 commands is essential for extending tool life and ensuring machining accuracy in harsh environments. The use of coolants helps manage the heat generated during machining, which is critical for maintaining equipment integrity. Buyers must consider local regulations regarding coolant disposal and ensure that suppliers have the necessary certifications to comply with environmental standards.
In What Ways Are Fanuc M Codes Beneficial for Metal Fabrication?
In metal fabrication, program stops and subprograms (M00 and M98) facilitate streamlined operations by allowing for complex machining tasks to be divided into manageable segments. This flexibility enables manufacturers to adapt quickly to changing production demands. Buyers should evaluate the ease of integration of these codes into their existing systems and ensure that training resources are available for their workforce.
How Do Fanuc M Codes Enhance Electronics Assembly?
In electronics assembly, rigid tapping (M29) significantly improves the quality of threaded holes in circuit boards and other components. This capability reduces cycle times while ensuring high-quality threads, which is critical for the reliability of electronic devices. International buyers should be aware of the specific needs of electronic components and seek suppliers that provide automation support to enhance their production processes.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘fanuc m codes’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Understanding M-Code Variations Across Machines
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa and South America, face significant challenges due to the lack of standardized M-codes across different CNC machine manufacturers. For instance, an M-code that operates a spindle on one machine may not correspond to the same function on another brand. This discrepancy can lead to errors during programming, resulting in production delays, increased costs, and even damage to machinery. Buyers often find themselves confused and frustrated as they attempt to adapt their existing knowledge to new machines.
The Solution: To effectively navigate M-code variations, buyers should invest in comprehensive training and resources tailored to their specific machine models. Start by obtaining the official M-code documentation from the machine manufacturer, which outlines the codes used for that specific model. Additionally, consider enrolling in workshops or online courses that focus on CNC programming and Fanuc systems. Collaborating with local training centers or industry experts can also provide valuable insights. Establishing a network with other users of similar machinery can facilitate knowledge sharing and best practices, ultimately reducing programming errors and enhancing operational efficiency.
Scenario 2: Challenges with M-Code Implementation in Complex Operations
The Problem: In industries requiring intricate machining operations, such as aerospace or automotive, the implementation of M-codes becomes increasingly complex. Buyers may struggle with executing multi-step processes that involve numerous M-codes, leading to confusion and potential errors. For example, integrating tool changes, coolant control, and spindle speed adjustments can overwhelm operators, especially if they lack hands-on experience with Fanuc M-codes.
The Solution: To address these complexities, buyers should utilize simulation software that allows operators to visualize and practice their M-code sequences in a risk-free environment. Software solutions like CAD/CAM programs often come equipped with simulation capabilities, helping users test their M-code sequences before executing them on the actual machine. Moreover, create a detailed checklist or flowchart that outlines each step in the machining process, associating the relevant M-codes with the corresponding actions. This structured approach minimizes the likelihood of errors and enhances overall productivity. Implementing a mentorship program where experienced operators guide newer staff can also build competency in handling complex M-code operations.
Scenario 3: Inefficient Troubleshooting of M-Code Related Errors
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face significant downtime due to M-code errors that arise during machine operation. Errors can manifest as unexpected stops, incorrect tool functions, or coolant issues, leading to costly delays in production. The lack of immediate troubleshooting resources or knowledge can exacerbate these issues, causing frustration among operators and management alike.
The Solution: To improve troubleshooting efficiency, buyers should establish a comprehensive M-code error handling guide that includes common error codes and their solutions. This guide should be readily accessible to all operators and maintenance staff. Additionally, investing in real-time monitoring tools can help identify issues before they escalate. Technologies such as IoT-enabled sensors can provide alerts when a machine is not operating as intended, allowing for immediate intervention. Regular maintenance and proactive training on common error scenarios will further enhance the team’s ability to quickly resolve issues. Establishing a feedback loop where operators can report M-code related issues can also inform ongoing training and process improvements, ultimately fostering a culture of continuous learning and operational excellence.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for fanuc m codes
When selecting materials for Fanuc M codes in CNC machining, it is essential to understand the properties, advantages, and limitations of various materials. This knowledge will help international B2B buyers make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements, especially in diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Key Properties of Aluminum in CNC Machining?
Aluminum is a popular choice for CNC machining due to its lightweight nature and excellent machinability. It has a high strength-to-weight ratio, making it suitable for applications where weight reduction is critical. Additionally, aluminum has good corrosion resistance, particularly when anodized. However, it has a lower melting point compared to other metals, which can lead to deformation under high temperatures.
Pros: Aluminum is durable, cost-effective, and easy to machine, which makes it ideal for intricate designs. Its lightweight nature enhances the performance of components in applications like aerospace and automotive.
Cons: While aluminum is strong, it may not be suitable for high-pressure applications. Its thermal expansion can also lead to dimensional changes in precision components.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with various media, including water and some chemicals, but care must be taken with strong acids or bases.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN for aluminum grades. In regions like Turkey and Nigeria, understanding local regulations regarding aluminum sourcing and processing is crucial.
How Does Stainless Steel Perform in CNC Applications?
Stainless steel is renowned for its exceptional corrosion resistance and strength, making it a preferred material for high-stress applications. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, which is essential in industries like oil and gas, where durability is paramount.
A stock image related to fanuc m codes.
Pros: Stainless steel offers high durability and longevity, making it suitable for components exposed to harsh environments. Its aesthetic appeal also makes it a popular choice in consumer products.
Cons: The machining process for stainless steel can be more complex and costly due to its hardness. This can lead to longer production times and increased wear on tools.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including corrosive substances, making it ideal for chemical processing applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must consider the specific grade of stainless steel required for their applications, ensuring compliance with relevant standards. In Europe, for instance, adherence to EN standards is crucial.
What Are the Advantages of Using Titanium in CNC Machining?
Titanium is increasingly used in CNC machining due to its high strength-to-weight ratio and exceptional corrosion resistance. It is particularly valuable in aerospace and medical applications where performance and biocompatibility are critical.
Pros: Titanium is lightweight yet incredibly strong, making it ideal for demanding applications. Its resistance to corrosion and oxidation extends the lifespan of components.
Cons: The cost of titanium is relatively high, and its machining can be challenging due to its toughness, leading to increased tool wear and production costs.
Impact on Application: Titanium is compatible with various media, including seawater and aggressive chemicals, making it suitable for marine and chemical processing applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific titanium grades required for their applications and ensure compliance with international standards. In regions like South America, understanding local sourcing and processing capabilities is essential.
How Does Plastic Compare in CNC Machining Applications?
Plastics, such as polycarbonate and nylon, are often used in CNC machining for parts that require lightweight and cost-effective solutions. They offer good machinability and can be produced in various colors and finishes.
Pros: Plastics are generally less expensive than metals and can be machined quickly. They are also resistant to corrosion and can be designed for specific applications.
Cons: Plastics may not have the same strength or durability as metals, making them unsuitable for high-stress applications. They can also be sensitive to temperature changes.
Impact on Application: Plastics are compatible with various media, but they may degrade in the presence of strong solvents or high temperatures.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the specific type of plastic required for their applications and ensure compliance with relevant standards. In Africa and the Middle East, understanding the local market for plastic materials is vital for sourcing.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for fanuc m codes | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Aerospace, automotive components | Lightweight and easy to machine | Lower melting point | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Oil and gas, chemical processing | High durability and corrosion resistance | More complex machining process | High |
| Titanium | Aerospace, medical applications | High strength-to-weight ratio | High cost and challenging machining | High |
| Plastic | Consumer products, housings | Cost-effective and versatile | Lower strength compared to metals | Low |
This comprehensive analysis provides international B2B buyers with actionable insights into material selection for Fanuc M codes, helping them navigate the complexities of CNC machining in their respective markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for fanuc m codes
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Processes for Fanuc M Codes?
The manufacturing processes for components that utilize Fanuc M codes encompass several critical stages, including material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage is integral to ensuring the quality and functionality of the final product.
How Is Material Prepared for CNC Machining?
Material preparation involves selecting the appropriate raw materials, which can include metals, plastics, or composites, depending on the final application. The materials are then cut to size and shaped into manageable pieces, often using techniques such as sawing, shearing, or laser cutting. It is essential that the material meets specific standards to ensure compatibility with the CNC machining process.
What Forming Techniques Are Commonly Used in CNC Machining?
Forming is primarily achieved through CNC machining, which employs Fanuc M codes to guide the machine tools. Key techniques include:
- CNC Milling: Involves the use of rotating cutting tools to remove material, creating complex shapes and designs.
- CNC Turning: Utilizes a lathe to produce cylindrical parts by rotating the workpiece against a cutting tool.
- Drilling and Tapping: M codes facilitate operations such as drilling holes and creating threads in various materials.
The precision of these techniques is crucial for producing components that meet strict tolerances.
How Is Assembly Conducted in the Manufacturing Process?
Assembly involves integrating the machined components into larger systems or products. This may require additional processes such as welding, fastening, or adhesive bonding. During assembly, it is vital to follow the specifications outlined in the M code programs to ensure that each part fits correctly and functions as intended.
What Finishing Techniques Are Essential for CNC Machined Parts?
Finishing processes enhance the aesthetic and functional qualities of the manufactured components. Common techniques include:
- Surface Treatment: Processes such as anodizing, plating, or coating improve corrosion resistance and surface finish.
- Deburring and Polishing: These techniques remove sharp edges and enhance the surface smoothness, which is critical for parts that will be in contact with other components.
Implementing these finishing techniques ensures that the final products meet industry standards and customer expectations.
What International Standards and Quality Assurance Measures Are Relevant?
Quality assurance is crucial in the manufacturing of components that utilize Fanuc M codes. Adhering to international standards such as ISO 9001 ensures that manufacturers maintain a consistent quality management system. Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) or API (American Petroleum Institute) may be required depending on the application and market.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial phase checks the quality of raw materials before they are used in production. Suppliers should provide certification and inspection reports to ensure compliance with specifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, periodic inspections are conducted to verify that processes align with quality standards. This may include measuring dimensions and tolerances using specialized tools.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the components are complete, a thorough inspection is carried out. This includes functional testing, visual inspections, and compliance checks against international standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For international B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential to ensure product reliability. Here are some actionable steps:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of the manufacturing facility can provide insights into the supplier’s adherence to quality standards and practices. Consider using third-party auditors for impartial assessments.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide detailed quality reports, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC phases. These documents should outline inspection methods, findings, and corrective actions taken if necessary.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Hiring third-party inspection services can further validate the quality of the products before shipment. This step is especially important for buyers in regions with less stringent local regulations.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Quality Assurance?
Common testing methods employed during the QC process include:
- Dimensional Inspection: Using calipers and gauges to ensure that the dimensions of machined parts meet specified tolerances.
- Functional Testing: Assessing the performance of components under simulated operating conditions to verify their functionality.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing or X-ray inspection are employed to detect internal flaws without damaging the components.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
Navigating the complexities of quality control and certification can be challenging for international B2B buyers. It is essential to understand the specific requirements of each market, as they can vary significantly. For instance, European buyers may require CE certification for certain products, while those in the Middle East might look for compliance with GSO (Gulf Standards Organization) standards.
Furthermore, establishing strong communication with suppliers regarding quality expectations and certification requirements is crucial. It fosters transparency and ensures that both parties are aligned on quality standards, ultimately leading to successful partnerships.
Conclusion
For international B2B buyers, particularly from diverse regions, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures associated with Fanuc M codes is vital. By focusing on the stages of manufacturing, relevant international standards, and effective quality control practices, buyers can ensure that they source high-quality components that meet their needs and standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘fanuc m codes’
In the competitive landscape of manufacturing, procuring Fanuc M codes is a critical step for businesses looking to enhance their CNC machining capabilities. This guide offers a structured checklist to help B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, navigate the sourcing process effectively.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is vital for ensuring that the M codes you procure align with your operational needs. Consider the types of CNC machines you are using and the specific operations you intend to perform. This will help in identifying which M codes are necessary, such as spindle control, coolant management, and tool changes.
- Key Considerations:
- Identify your machine model and its compatible M codes.
- Document specific machining processes that will utilize these codes.
Step 2: Research Reliable Suppliers
Finding reputable suppliers is essential for ensuring the quality and reliability of the M codes you acquire. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in providing CNC programming solutions. Utilize industry networks and online platforms to gather information on potential suppliers.
- Key Considerations:
- Check for customer reviews and case studies related to the suppliers.
- Ensure they have experience with your specific machine type.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct a thorough evaluation. Request detailed company profiles, references, and examples of past work, particularly from businesses in your region or industry. This helps in assessing their capabilities and reliability.
- Key Considerations:
- Inquire about their technical support and after-sales services.
- Assess their response times and customer service quality.
Step 4: Verify Compliance and Certifications
Ensure that your chosen suppliers comply with international standards and possess relevant certifications. This is especially important for B2B buyers in regions with strict manufacturing regulations. Compliance guarantees that the M codes meet quality and safety requirements.
- Key Considerations:
- Look for ISO certifications or industry-specific standards.
- Confirm that their M codes are compatible with your specific CNC machinery.
Step 5: Request Samples and Demonstrations
Before finalizing your purchase, ask for samples or demonstrations of the M codes in action. This allows you to evaluate their functionality and compatibility with your machines. It’s an opportunity to test how well they integrate into your existing processes.
- Key Considerations:
- Conduct trials to assess performance and ease of use.
- Evaluate the support provided during the demonstration phase.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you have identified a suitable supplier, engage in negotiations to finalize terms and pricing. Ensure that the agreement covers not just the cost, but also warranties, support, and delivery timelines. Negotiating favorable terms can enhance your operational efficiency and reduce costs.
- Key Considerations:
- Discuss bulk purchase discounts or loyalty agreements.
- Clarify payment terms and conditions.
Step 7: Establish a Relationship for Future Needs
Building a long-term relationship with your supplier can lead to better service and pricing in the future. Regular communication can help you stay updated on new M codes, technologies, and trends in CNC machining. A reliable partner can be invaluable as your business grows.
- Key Considerations:
- Schedule regular check-ins to discuss performance and new offerings.
- Consider joint training sessions to ensure staff are well-versed in using the M codes effectively.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline the sourcing process for Fanuc M codes, ensuring they acquire the right tools for enhanced machining capabilities.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for fanuc m codes Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Fanuc M Codes?
When sourcing Fanuc M codes, international B2B buyers must consider several cost components that contribute to the overall pricing structure. These include:
-
Materials: The quality and type of materials used in the manufacturing process play a crucial role in determining costs. High-quality raw materials may increase initial expenditures but can lead to better performance and durability, which are vital for long-term operations.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary significantly based on the region of production. For example, countries with lower labor costs may offer more competitive pricing but could also result in variations in quality. Skilled labor is often required for programming and operating CNC machines, affecting the overall labor expense.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses all indirect costs related to production, such as utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. A clear understanding of these overheads is essential to gauge the total cost of sourcing Fanuc M codes.
-
Tooling: Specialized tools and equipment are necessary for producing M codes, which can be a substantial cost factor. Depending on the complexity of the codes, tooling costs can vary, impacting the final price.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing robust QC measures is crucial for ensuring the reliability of M codes. This can add to the cost, but it is an investment in quality that mitigates risks of faulty production, especially in high-stakes industries.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs are vital considerations, especially for international shipments. Understanding logistics costs, including tariffs and duties, can significantly impact the overall pricing structure.
-
Margin: Suppliers will factor in their desired profit margin, which can vary based on market conditions and competition. Buyers should be aware of the typical margins in their region to negotiate effectively.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Sourcing Costs for Fanuc M Codes?
Several factors can influence the pricing of Fanuc M codes, making it essential for buyers to navigate these elements carefully:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Higher order volumes can lead to economies of scale, resulting in lower per-unit costs. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to benefit from bulk pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized M codes tailored to specific machinery or processes can incur additional costs. Buyers should clearly define their specifications to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Premium materials and compliance with industry certifications can increase costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of investing in higher-quality materials against budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reliability and reputation of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their expertise and assurance of quality, while newer entrants may offer lower prices but with potential risks.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping and logistics costs. Understanding these terms can help buyers negotiate better deals and avoid hidden charges.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Sourcing Fanuc M Codes?
To achieve cost-efficiency while sourcing Fanuc M codes, international B2B buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Leverage your position as a buyer by negotiating terms that can lead to cost savings. Understanding market rates and being prepared to walk away can strengthen your negotiation stance.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial purchase price. Consider long-term costs associated with maintenance, reliability, and performance to make informed purchasing decisions.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations and their impact on pricing. Additionally, familiarize yourself with local market conditions in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to better navigate sourcing challenges.
-
Request Detailed Quotes: Ensure that suppliers provide comprehensive quotes that break down costs. This transparency allows buyers to identify areas for potential savings.
-
Stay Informed About Market Trends: Keeping abreast of developments in CNC machining and M code technology can help buyers anticipate changes in pricing and adjust their sourcing strategies accordingly.
Disclaimer
The prices and cost structures discussed in this analysis are indicative and may vary based on specific supplier negotiations, market conditions, and regional factors. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough market research and supplier evaluations to determine accurate pricing for their unique sourcing needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing fanuc m codes With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives to Fanuc M Codes
In the realm of CNC machining, Fanuc M codes are a widely recognized standard for controlling machine functions such as spindle speed and coolant flow. However, as international B2B buyers explore their options, it’s crucial to consider viable alternatives that may offer unique advantages in specific contexts. This analysis will compare Fanuc M codes with alternative solutions, focusing on performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases.
Comparison Table of Fanuc M Codes and Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Fanuc M Codes | Siemens Sinumerik Codes | Haas M Codes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and speed | Comparable precision, versatile | Reliable for general machining |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment | Slightly higher due to advanced features | Lower, but limited functionality |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized training | Steeper learning curve, but well-documented | User-friendly, less training needed |
| Maintenance | Regular updates needed | Requires technical support | Minimal maintenance required |
| Best Use Case | Complex, high-volume production | Advanced applications, multi-axis machining | Small to medium-scale operations |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Siemens Sinumerik Codes: A Flexible Alternative
Siemens Sinumerik offers a robust set of G and M codes that rival Fanuc’s capabilities. These codes provide advanced functionality for complex machining tasks, particularly in industries demanding high precision and versatility. The main advantage of Sinumerik is its adaptability to different types of CNC machinery, making it ideal for businesses looking to diversify their production capabilities. However, this flexibility comes with a steeper learning curve and potentially higher initial costs, as users may require more extensive training and support.
Haas M Codes: A Cost-Effective Solution for General Machining
Haas Automation provides its own set of M codes that are particularly user-friendly and accessible for beginners in CNC machining. The simplicity of Haas M codes allows for quick implementation and minimal training, making it a cost-effective choice for small to medium-sized enterprises. While Haas codes may not offer the advanced features seen in Fanuc or Sinumerik, they are reliable for general machining operations. Companies focused on straightforward machining tasks may find Haas M codes to be a practical solution, though they may need to consider limitations in versatility and complexity.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting a CNC control solution, B2B buyers must evaluate their specific operational needs, production scale, and budget constraints. Fanuc M codes excel in high-precision environments requiring complex programming, making them suitable for industries like aerospace and automotive. Conversely, Siemens Sinumerik codes provide flexibility for advanced applications, while Haas M codes are ideal for those seeking a straightforward, cost-effective approach. Ultimately, understanding the unique advantages and limitations of each option will empower buyers to make informed decisions that align with their business objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for fanuc m codes
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Fanuc M Codes?
Understanding the critical specifications of Fanuc M codes is vital for international B2B buyers involved in CNC machining. Here are some key properties that can influence purchasing decisions and operational efficiency:
1. Compatibility with Machine Models
Compatibility is crucial when selecting M codes for CNC machines. Different Fanuc models may have unique M codes, particularly those above M79. Buyers must verify compatibility with their specific machines to avoid operational errors, ensuring seamless integration into existing workflows.
2. Precision and Tolerance Levels
Precision is a non-negotiable aspect of CNC machining. Fanuc M codes play a significant role in achieving the desired tolerances during manufacturing processes. A clear understanding of the acceptable tolerance levels for components can help buyers choose the right M codes, ultimately impacting the quality and reliability of the final product.
3. Cycle Time Optimization
The selection of appropriate M codes can significantly influence cycle times. For instance, using M codes for specific cycles (e.g., M08 for coolant on) can enhance machining efficiency. Buyers should prioritize M codes that streamline processes and reduce cycle time to improve productivity, especially in high-volume manufacturing scenarios.
4. Error Handling and Program Control
Certain M codes are designed for error handling and program control, such as M00 (program stop) and M02 (end of program). Understanding these codes allows buyers to implement robust error management strategies, which is essential for maintaining operational continuity and minimizing downtime.
5. Tool Management
M codes related to tool management, such as M06 (tool change), are essential for maintaining machining efficiency. Proper tool management can reduce setup times and ensure that the right tools are used for each operation, which is particularly important for buyers managing complex machining tasks.
6. Safety Features
Safety is paramount in CNC machining. M codes can control safety features such as spindle stops (M05) and coolant operations (M08). Buyers should prioritize M codes that enhance safety protocols, reducing risks associated with machine operation, which is particularly critical in manufacturing environments.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Fanuc M Codes?
Familiarity with industry jargon can greatly enhance communication and negotiation effectiveness in B2B transactions. Here are essential terms that buyers should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of Fanuc M codes, understanding the OEM can help buyers ensure they are purchasing compatible parts and software that meet their specific requirements.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ for Fanuc M code-related products can help buyers plan their purchases effectively, ensuring they meet supplier requirements while optimizing inventory levels.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit pricing and terms for specific products or services. For buyers interested in Fanuc M codes, issuing an RFQ can lead to competitive pricing and better understanding of available options, fostering informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in global trade. Familiarity with these terms helps buyers navigate shipping and logistics related to M code products, ensuring clarity in terms of delivery and risk management.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order until it is fulfilled. Understanding lead times for Fanuc M code products is essential for buyers to manage production schedules effectively, especially when working with tight deadlines.
6. Technical Support
Technical support refers to assistance provided by manufacturers or suppliers regarding product use and troubleshooting. Buyers should seek suppliers that offer robust technical support for Fanuc M codes, ensuring they can resolve issues quickly and maintain operational efficiency.
A stock image related to fanuc m codes.
These technical properties and trade terms not only facilitate informed decision-making but also enhance operational efficiency, especially for international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the fanuc m codes Sector
What Are the Current Market Trends Influencing the Fanuc M Codes Sector?
The Fanuc M Codes sector is witnessing significant transformations driven by advancements in technology and shifts in global manufacturing dynamics. One of the primary drivers is the increasing automation of production processes. International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are integrating CNC machines with sophisticated M Codes to enhance precision and reduce operational costs. The demand for multi-axis CNC machines, especially those that utilize Fanuc M Codes for various machining operations, is on the rise. This is particularly relevant for buyers in emerging markets, where the need for complex part production is growing due to industrialization.
Another key trend is the adoption of Industry 4.0 principles, which emphasize connectivity and data exchange in manufacturing technologies. Companies are now focusing on smart manufacturing solutions, which allow for better monitoring and control of machining processes through M Codes. This trend is essential for international buyers looking to optimize their supply chains and improve production efficiency. As a result, sourcing partners who can offer advanced CNC machines with integrated M Code functionalities are becoming increasingly valuable.
Furthermore, the shift towards customization and on-demand manufacturing is reshaping sourcing strategies. B2B buyers are looking for suppliers who can provide flexible solutions that utilize Fanuc M Codes for tailored production runs. This trend highlights the importance of building relationships with suppliers who can adapt to changing market demands while maintaining high-quality standards.
How Is Sustainability Impacting Sourcing Decisions for Fanuc M Codes?
Sustainability is increasingly becoming a pivotal factor in sourcing decisions within the Fanuc M Codes sector. International buyers are now more aware of the environmental impacts of their manufacturing processes, prompting a shift towards sustainable practices. This encompasses the selection of materials, the efficiency of production methods, and the overall lifecycle of the machinery involved.
Buyers are seeking suppliers who prioritize ethical sourcing and can demonstrate compliance with environmental standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and adherence to REACH regulations for chemical safety are becoming essential for suppliers in this space. Additionally, the use of ‘green’ materials in the production of components that utilize Fanuc M Codes can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of manufacturing processes.
The demand for energy-efficient CNC machines is also on the rise. Buyers are increasingly interested in sourcing machinery that not only meets their production needs but also minimizes energy consumption. This trend aligns with global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and highlights the importance of partnering with suppliers who are committed to sustainability.
What Is the Historical Context Behind Fanuc M Codes?
The evolution of Fanuc M Codes dates back to the development of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology in the mid-20th century. Initially, CNC machines operated on rudimentary programming languages that required extensive manual input. As technology advanced, the introduction of G-Code and M-Code languages allowed for more sophisticated control of machining processes. M Codes, specifically, are critical for managing non-motion functions such as tool changes and coolant control, which are essential for effective machining operations.
The 1980s saw significant improvements in CNC technology, driven by the rise of computerization. This era marked the beginning of widespread adoption of Fanuc controls in various industries, enhancing precision and efficiency in manufacturing. Today, Fanuc M Codes continue to evolve, incorporating features that support modern manufacturing demands, such as automation and real-time data exchange, making them indispensable for international B2B buyers seeking competitive advantages in their production processes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of fanuc m codes
-
How do I solve issues with Fanuc M Codes in CNC programming?
To resolve problems with Fanuc M Codes, start by checking the compatibility of your CNC machine with the specific M Codes you are using. Refer to the machine’s user manual or the manufacturer’s guidelines for a complete list of supported codes. Ensure that your code syntax is correct, and consider running a simulation to identify any errors before executing on the actual machine. Additionally, collaborating with experienced CNC programmers can provide insights into troubleshooting specific M Code-related issues. -
What is the best way to select a supplier for Fanuc M Codes?
When selecting a supplier for Fanuc M Codes, prioritize those with a strong reputation in the CNC machining industry. Check for certifications, customer testimonials, and case studies that demonstrate their expertise. It’s also beneficial to assess their technical support capabilities, as reliable post-purchase assistance can be crucial. Consider suppliers who offer customization options for M Codes, ensuring that they can meet your specific machining needs while maintaining quality. -
How can I customize Fanuc M Codes for my specific machining needs?
Customizing Fanuc M Codes typically involves programming specific sequences that align with your machining operations. Work closely with a knowledgeable CNC programmer or a supplier who specializes in custom M Code solutions. Provide detailed specifications about your machining processes, and request a prototype or sample program to evaluate functionality. It’s essential to test any customized codes in a controlled environment before full implementation to ensure they perform as expected. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for Fanuc M Codes?
Minimum order quantities for Fanuc M Codes can vary significantly based on the supplier and the nature of the codes required. Generally, suppliers may have a MOQ ranging from a few hundred to several thousand lines of code. It’s advisable to communicate your specific needs with potential suppliers to negotiate favorable terms. Some suppliers may offer lower MOQs for initial orders or for long-term partnerships, so don’t hesitate to discuss your requirements.
A stock image related to fanuc m codes.
-
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing Fanuc M Codes internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of Fanuc M Codes typically vary by supplier but can include options such as upfront payment, net 30, or net 60 terms. Many suppliers may request a deposit before commencing work, particularly for customized solutions. It’s crucial to clarify these terms before finalizing any agreements and to ensure that they align with your budget and cash flow. Consider utilizing secure payment platforms that offer buyer protection to mitigate risks. -
How do I ensure quality assurance (QA) when sourcing Fanuc M Codes?
To ensure quality assurance when sourcing Fanuc M Codes, establish clear criteria for code performance and accuracy before engaging suppliers. Request samples or trial runs to evaluate the quality of the M Codes produced. Consider implementing a QA process that includes regular audits of the supplied codes and feedback loops with your CNC operators. Collaborating with suppliers who adhere to ISO standards can also enhance confidence in their QA practices. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing Fanuc M Codes from international suppliers?
When sourcing Fanuc M Codes internationally, consider logistics factors such as shipping times, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Establish a reliable communication channel with your supplier to track shipments and resolve any issues promptly. It may also be beneficial to engage a logistics partner familiar with international shipping to streamline the process. Ensure that all documentation is accurate and complete to avoid delays at customs. -
How can I stay updated on changes to Fanuc M Codes and programming techniques?
Staying updated on changes to Fanuc M Codes and programming techniques can be achieved through regular engagement with industry publications, forums, and professional networks. Participate in workshops, webinars, and trade shows focused on CNC machining and Fanuc technologies. Joining online communities or user groups specific to Fanuc programming can also provide valuable insights and updates from fellow professionals in the field.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for fanuc m codes
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, understanding and effectively implementing Fanuc M codes is crucial for optimizing CNC operations. By strategically sourcing the right technology and expertise, international B2B buyers can enhance production efficiency, reduce downtime, and ensure precision in machining processes. The seamless integration of these codes not only streamlines operations but also fosters innovation, enabling businesses to meet the increasing demands of global markets.
What are the benefits of leveraging Fanuc M codes for your operations? Companies that prioritize strategic sourcing of CNC resources can achieve significant cost savings while maintaining high-quality standards. This is particularly relevant for businesses in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where competitive manufacturing is essential for growth.
As the industry continues to evolve with advancements in technology and automation, now is the time for B2B buyers to invest in comprehensive training and resources related to Fanuc M codes. By doing so, they will position themselves as leaders in their respective markets. Embrace this opportunity to enhance your machining capabilities and drive your business forward in the global economy.