Master GCode CNC: The Complete Guide to Boost Productivity (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for gcode cnc
Navigating the complexities of sourcing G-code CNC machines can be a daunting task for international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The challenge lies not only in understanding the various types of CNC machinery available but also in identifying reliable suppliers who can meet specific production needs. This guide aims to demystify the global market for G-code CNC, providing a comprehensive overview of the different machine types, applications across industries, and essential supplier vetting processes.
By exploring key factors such as operational costs, machine capabilities, and programming standards, this guide equips buyers with the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions. Whether you’re a manufacturer in Kenya looking to enhance your machining capabilities or a business in Argentina seeking to optimize production efficiency, understanding G-code CNC technology is crucial.
In the coming sections, we will delve into the intricacies of G-code commands, the benefits of various CNC applications, and the critical considerations for selecting the right supplier. This resource not only serves as a roadmap for navigating the G-code CNC landscape but also empowers you to leverage these insights for competitive advantage in your market.
Understanding gcode cnc Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| G-Code for CNC Milling | Utilizes G00, G01, G02, G03 for linear and circular movements | Precision component manufacturing | Pros: High precision, versatile for various materials. Cons: Requires skilled operators to program effectively. |
| G-Code for CNC Lathes | Focuses on turning operations, often using G-code commands for tool control | Automotive and aerospace parts | Pros: Efficient for cylindrical parts, reduces waste. Cons: Limited to rotational shapes; not ideal for complex geometries. |
| G-Code for 3D Printing | Adapts G-Code for additive manufacturing processes | Prototyping and custom designs | Pros: Allows for complex shapes, material savings. Cons: Slower than traditional machining methods. |
| G-Code for 5-Axis Machining | Enables complex geometries with simultaneous movement on five axes | Aerospace, medical device production | Pros: High precision and efficiency for intricate designs. Cons: Higher initial investment and maintenance costs. |
| M-Code for CNC Operations | Controls auxiliary functions such as tool changes and coolant | Broad range of CNC applications | Pros: Enhances machine functionality and efficiency. Cons: Requires understanding of both G-Code and M-Code for optimal use. |
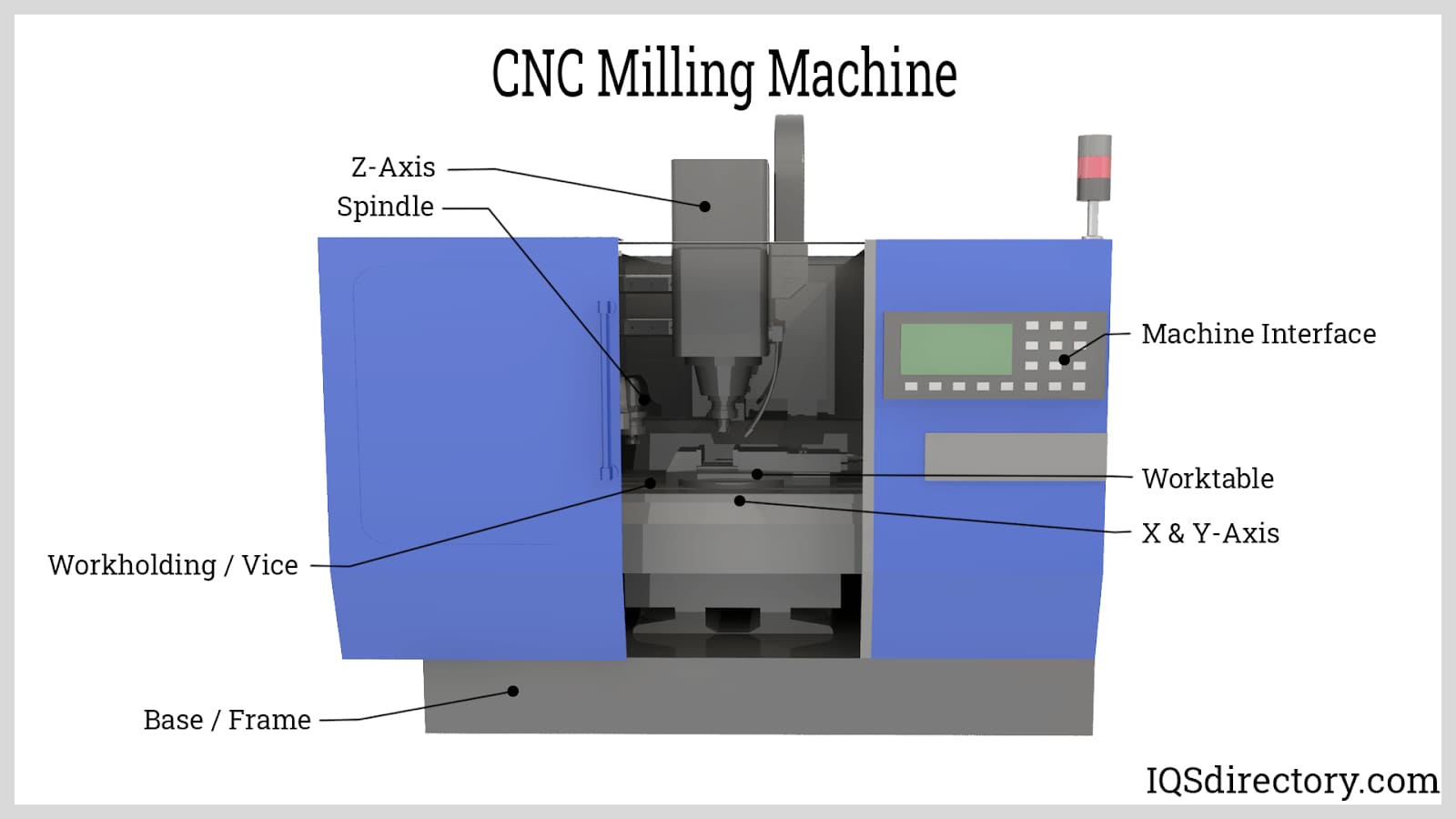
What are the Key Characteristics of G-Code for CNC Milling?
G-Code for CNC milling is the most common type of G-Code, primarily used in the manufacturing of precision components. It employs commands such as G00 for rapid positioning, G01 for linear interpolation, and G02/G03 for circular interpolation. This type is suitable for various materials, making it versatile for different industries. When considering a purchase, buyers should assess the machine’s compatibility with their existing software and the skill level of their operators to maximize efficiency.
How Does G-Code for CNC Lathes Differ from Other Types?
G-Code for CNC lathes specializes in operations that involve turning materials to produce cylindrical parts. This variation is particularly advantageous in industries such as automotive and aerospace, where precision and material reduction are crucial. Buyers should consider the machine’s capabilities in terms of speed and accuracy, as well as the availability of skilled operators who can effectively program and manage lathe operations.
Why is G-Code for 3D Printing Important for Modern Manufacturing?
G-Code for 3D printing is a variation that has adapted traditional G-Code commands for additive manufacturing processes. This type allows for the creation of complex shapes that are often impossible to achieve with subtractive methods. It is particularly beneficial for prototyping and custom designs. Buyers should evaluate the compatibility of their 3D printers with various materials and the software’s ability to generate efficient G-Code for optimal production speeds.
What Advantages Does G-Code for 5-Axis Machining Offer?
G-Code for 5-axis machining enables simultaneous movement across five axes, allowing for the production of intricate geometries with high precision. This type is especially relevant in industries like aerospace and medical device manufacturing, where complex shapes are often required. While it offers significant advantages in terms of efficiency and accuracy, buyers should be prepared for a higher initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs associated with advanced machinery.
How Does M-Code Enhance CNC Operations?
M-Code complements G-Code by controlling auxiliary functions such as tool changes, spindle speed, and coolant flow. This type is essential for the efficient operation of CNC machines across various applications. Buyers should ensure that their operators are trained in both G-Code and M-Code programming to fully utilize the machine’s capabilities and enhance overall productivity. Understanding the integration of both codes will enable better workflow management in manufacturing processes.
Key Industrial Applications of gcode cnc
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of gcode cnc | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Precision component manufacturing | High accuracy and reduced waste in complex parts production | Certification of suppliers, compliance with international standards |
| Automotive | Tooling and fixture production | Enhanced production efficiency and lower lead times | Machine compatibility, materials used, and after-sales support |
| Electronics | PCB fabrication and assembly | Increased precision and scalability in production | Supplier reliability, technology integration, and cost-effectiveness |
| Medical Devices | Custom implants and surgical instruments | Tailored solutions that meet strict regulatory standards | Regulatory compliance, quality assurance, and material sourcing |
| Construction | Custom machinery and component manufacturing | Increased versatility and reduced time-to-market | Local availability of materials, machine adaptability, and training |
How is G-Code CNC Used in Aerospace Manufacturing?
In the aerospace industry, G-Code CNC is essential for manufacturing precision components such as turbine blades and structural parts. The high accuracy required in this sector minimizes material waste and ensures compliance with stringent safety standards. International buyers, especially from regions like Africa and South America, must prioritize suppliers who possess the necessary certifications and can demonstrate compliance with international aerospace manufacturing standards. Additionally, the ability to handle complex geometries with multi-axis machines is crucial.
What Are the Applications of G-Code CNC in Automotive Tooling?
Automotive companies leverage G-Code CNC for producing tooling and fixtures that support assembly lines. The efficiency gained from CNC machining reduces lead times and enhances production capabilities, allowing manufacturers to meet market demands swiftly. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should consider machine compatibility and the quality of materials used in tooling to ensure longevity and performance. After-sales support is also vital, as it helps maintain production efficiency.
How Does G-Code CNC Enhance Electronics Manufacturing?
In electronics manufacturing, G-Code CNC plays a pivotal role in the fabrication of printed circuit boards (PCBs) and assembly processes. The precision offered by CNC machines allows for intricate designs that are crucial for modern electronics. For international B2B buyers, especially from Europe and South America, it is essential to evaluate supplier reliability and their ability to integrate advanced technologies into their processes. Cost-effectiveness is another critical factor, as it impacts the overall production budget.
What Are the Key Benefits of G-Code CNC in Medical Device Production?
The medical device sector utilizes G-Code CNC for creating custom implants and surgical instruments tailored to specific patient needs. This customization is vital for complying with strict regulatory standards while delivering high-quality products. International buyers must ensure that their suppliers adhere to regulatory compliance and quality assurance protocols, especially when sourcing from regions like Africa and the Middle East. Material sourcing is also a key consideration, as biocompatibility is often required for medical applications.
How is G-Code CNC Applied in Construction Machinery Manufacturing?
In the construction industry, G-Code CNC is employed for manufacturing custom machinery and components that enhance operational versatility. This application allows companies to reduce time-to-market for new products, which is crucial in a competitive landscape. Buyers from South America and Africa should focus on the local availability of materials, the adaptability of machines to various projects, and the availability of training for their workforce to maximize the benefits of CNC technology.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘gcode cnc’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Understanding G-Code Syntax and Commands
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, particularly those new to CNC machining or transitioning from manual to automated processes, struggle with the complexity of G-Code syntax. This can lead to errors in programming, resulting in production delays and costly mistakes. For instance, a manufacturer in Kenya may find it challenging to ensure precision when using commands like G01 for linear interpolation or G02 for circular interpolation. Misunderstandings about feed rates or measurement units can further exacerbate these issues, causing frustration and potential financial loss.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, international buyers should invest in comprehensive training programs focused on G-Code programming. Engaging with local CNC training centers or online courses specifically tailored for G-Code can equip staff with the necessary skills. Additionally, utilizing simulation software that allows users to visualize and practice G-Code commands in a controlled environment can significantly enhance understanding. Encouraging a culture of continuous learning within the organization will also help keep team members updated on the latest techniques and best practices, ensuring they are confident and proficient in programming CNC machines.
Scenario 2: Inconsistent Results Due to Machine Calibration Issues
The Problem: Buyers often face challenges with inconsistent machining results, which can be traced back to improper machine calibration. For example, a manufacturing firm in Argentina might experience variations in part dimensions due to the CNC machine’s settings not being correctly aligned with the specified G-Code commands. This inconsistency can lead to increased scrap rates and rework, negatively impacting profitability and customer satisfaction.
The Solution: To address calibration issues, it is essential to establish a routine maintenance and calibration schedule for CNC machines. Buyers should consider partnering with reputable service providers or equipment manufacturers who offer calibration services and support. Furthermore, adopting a standardized checklist for machine setup can ensure that all parameters, including those related to G-Code commands, are verified before starting a job. Leveraging technology, such as CNC monitoring software, can also help detect anomalies in real-time, allowing for quick adjustments and maintaining high-quality production standards.
Scenario 3: Challenges in Integrating G-Code with CAD/CAM Systems
The Problem: Another common pain point for B2B buyers is the difficulty in integrating G-Code with CAD (Computer-Aided Design) and CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) systems. Companies in the Middle East, for instance, may struggle to convert complex designs into G-Code efficiently, leading to delays and increased labor costs. This integration gap can hinder a company’s ability to scale production and meet customer demands promptly.
The Solution: To streamline the integration process, buyers should invest in high-quality CAD/CAM software that supports seamless G-Code generation. Researching software options that include features for easy import/export of designs and automatic G-Code generation can significantly reduce the time and effort required to transition from design to machining. Additionally, implementing a feedback loop between design and production teams can ensure that any challenges in G-Code generation are addressed early in the process. Regular training sessions on utilizing these software tools effectively will empower employees to maximize the capabilities of their systems, enhancing overall operational efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for gcode cnc
What Are the Key Properties of Aluminum for G-Code CNC Machining?
Aluminum is one of the most commonly used materials in CNC machining due to its excellent machinability and lightweight properties. It typically exhibits a temperature rating of up to 400°F and is resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for various applications, including aerospace and automotive components. The alloying of aluminum can enhance its strength, allowing it to withstand higher pressures without compromising its integrity.
Pros and Cons of Using Aluminum in CNC Machining
The primary advantage of aluminum is its durability combined with a relatively low cost, making it an attractive option for manufacturers. It is easy to machine, which reduces manufacturing complexity and time. However, aluminum can be less durable than other metals like steel under extreme conditions, which may limit its use in high-stress applications. Additionally, while the initial cost is low, the long-term performance may require consideration of the specific application.
Impact on Application and Considerations for International Buyers
Aluminum’s compatibility with various media, including air and water, makes it a versatile choice. However, international buyers, especially from regions like Africa and South America, should be aware of local standards such as ASTM or DIN for quality assurance. Compliance with these standards ensures that the material meets the necessary performance criteria, especially in industries like automotive and aerospace.
How Does Steel Compare as a Material for G-Code CNC Machining?
Steel is another widely utilized material in CNC machining, known for its high strength and durability. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications. Different grades of steel, such as stainless or tool steel, offer varying levels of corrosion resistance and hardness.
Pros and Cons of Using Steel in CNC Machining
The key advantage of steel is its exceptional strength and durability, which allows it to be used in high-stress environments. However, steel is generally more expensive than aluminum, and its machining can be more complex due to its hardness, leading to longer production times. This increased complexity can also result in higher tool wear, which may add to operational costs.
Impact on Application and Considerations for International Buyers
Steel’s compatibility with various media, including oils and chemicals, makes it suitable for industrial applications. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should consider the specific grade of steel needed for their applications, ensuring compliance with relevant standards such as JIS or EN. Understanding these standards is crucial for ensuring the material’s performance in demanding environments.
What Are the Benefits of Using Plastics in CNC Machining?
Plastics, particularly engineering plastics like nylon and polycarbonate, are increasingly popular in CNC machining. They offer excellent chemical resistance and can operate effectively at moderate temperatures, typically up to 180°F.
Pros and Cons of Using Plastics in CNC Machining
The main advantage of plastics is their lightweight nature and cost-effectiveness, making them suitable for a wide range of applications, including consumer products and automotive parts. However, plastics can be less durable than metals and may not perform well under high temperatures or mechanical stress. This limitation can restrict their use in heavy-duty applications.
Impact on Application and Considerations for International Buyers
Plastics are compatible with a variety of media, including water and mild chemicals, but may not be suitable for high-temperature applications. Buyers from Africa and South America should ensure that the selected plastic meets local standards for safety and performance, as well as consider the environmental impact of plastic use in their industries.
How Do Composites Enhance G-Code CNC Machining Applications?
Composites, such as carbon fiber reinforced plastics, are gaining traction in CNC machining due to their high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent stiffness. They can withstand temperatures up to 300°F and offer good chemical resistance.
Pros and Cons of Using Composites in CNC Machining
The key advantage of composites is their lightweight nature combined with high strength, making them ideal for aerospace and automotive applications. However, they can be more expensive than traditional materials and may require specialized machining techniques, which can complicate the manufacturing process.
Impact on Application and Considerations for International Buyers
Composites are compatible with various media but may require careful handling during machining to avoid delamination. International buyers, particularly in Europe, should be aware of specific standards governing composite materials to ensure compliance and performance.
Summary Table of Material Selection for G-Code CNC
| Material | Typical Use Case for gcode cnc | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Aerospace components | Lightweight and easy to machine | Less durable under extreme stress | Low |
| Steel | Heavy machinery parts | Exceptional strength and durability | Higher cost and complex machining | High |
| Plastics | Consumer products | Cost-effective and lightweight | Less durable under high stress | Med |
| Composites | Aerospace and automotive parts | High strength-to-weight ratio | More expensive and complex to machine | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides international B2B buyers with critical insights into material properties, advantages, and considerations, ensuring informed decision-making in their CNC machining applications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for gcode cnc
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing G-Code CNC Components?
Manufacturing components for G-code CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines involves several critical stages, each ensuring that the final product meets specific performance and quality standards. Understanding these stages is essential for international B2B buyers looking to source CNC machinery or components, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
1. Material Preparation: How Is Raw Material Selected and Processed?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. Common materials used for CNC machining include metals (aluminum, steel, titanium), plastics, and composites. The choice of material depends on the intended application, required strength, and durability.
- Material Selection: Suppliers should provide documentation on material specifications, including mechanical properties and certifications (e.g., ASTM, EN standards).
- Cutting and Shaping: Raw materials are typically cut to size using saws or lasers, followed by surface treatments to remove impurities and ensure a smooth finish. This step is crucial for achieving the desired tolerances in later machining processes.
2. Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape CNC Components?
Once the material is prepared, the forming stage begins. This involves the use of various machining techniques to shape the components accurately.
- CNC Machining: This process uses G-code to control machine tools for cutting, drilling, and milling operations. The precision of CNC machining allows for complex shapes and tight tolerances, making it ideal for producing intricate parts.
- Additive Manufacturing: For certain applications, 3D printing may be utilized to create parts directly from CAD models, especially for prototypes or low-volume production runs.
3. Assembly: How Are CNC Components Assembled and Integrated?
After forming, components may need to be assembled into larger systems or machines.
- Component Integration: This could involve the assembly of motors, controllers, and other electronic components into the CNC machine frame. Suppliers should provide clear assembly documentation and verification of component compatibility.
- Testing During Assembly: It’s common to conduct preliminary tests on components during assembly to ensure they meet functional requirements before final assembly.
4. Finishing: What Processes Ensure Surface Quality and Performance?
The finishing stage enhances the aesthetic and functional properties of the CNC components.
- Surface Treatment: Techniques such as anodizing, powder coating, or polishing are applied to improve corrosion resistance and surface finish. These treatments are particularly relevant for applications in harsh environments, common in regions like Africa and the Middle East.
- Quality Control Checks: Final inspections are performed to ensure that the components meet all specifications before they are shipped.
What Quality Assurance Standards Should B2B Buyers Look For?
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of G-code CNC components, ensuring that products are reliable and meet international standards. International B2B buyers should be familiar with relevant quality assurance standards to verify supplier capabilities.
1. International Standards: What Certifications Should Be Considered?
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the criteria for a quality management system (QMS). Suppliers with ISO 9001 certification demonstrate their commitment to consistent quality and customer satisfaction.
- CE Marking: For products sold in Europe, CE marking indicates compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards. This is particularly important for buyers in Europe.
- API Standards: For suppliers in the oil and gas sector, API (American Petroleum Institute) standards ensure that products meet specific performance and safety requirements.
2. Industry-Specific Quality Checks: What Are the Key Quality Control Points?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integral to the manufacturing process. Buyers should inquire about the specific QC measures implemented by suppliers.
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to verify that they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during manufacturing ensures that any deviations from specifications are caught early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A thorough inspection of finished products ensures that they meet all performance and quality standards before shipment.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For B2B buyers, especially those from regions with varying quality standards, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial.
1. What Methods Are Available for Supplier Audits?
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes and quality control systems firsthand. This can provide insights into the supplier’s capabilities and adherence to standards.
- Documentation Review: Requesting access to quality control documentation, such as inspection reports and quality management system manuals, can provide additional assurance of the supplier’s commitment to quality.
2. How Can Third-Party Inspections Enhance Confidence?
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspection services can provide unbiased verification of the supplier’s quality control processes and product quality. This is particularly beneficial for buyers unfamiliar with local suppliers’ practices.
What Are the Unique Quality Control Considerations for International Buyers?
International B2B buyers should be aware of specific nuances in quality control that may arise when sourcing from different regions.
- Cultural Differences: Understanding cultural attitudes towards quality and manufacturing practices can help buyers navigate potential challenges. For instance, buyers from Africa and South America may encounter different production capabilities compared to those in Europe.
- Regulatory Compliance: Buyers must ensure that suppliers comply with both local and international regulations, which can vary significantly between regions.
By focusing on these manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing G-code CNC machinery and components, ensuring they receive high-quality products that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘gcode cnc’
In the fast-evolving landscape of CNC machining, understanding G-code is essential for international B2B buyers. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist to streamline your sourcing process for G-code CNC solutions, ensuring you make informed decisions that align with your operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding your specific requirements is the first step in sourcing G-code CNC machines. Determine the types of materials you will be machining, the complexity of the designs, and the expected production volume. This clarity will enable you to select a machine that meets your technical needs effectively.
- Considerations:
- What axes do you need? (e.g., 3-axis vs. 5-axis)
- What is the maximum size of the workpiece?
- What tolerance levels must be achieved?
Step 2: Research Global Suppliers
Conduct thorough research on suppliers from regions known for CNC manufacturing, such as Europe and Asia. Look for companies that have a proven track record in producing G-code CNC machines that suit your specifications.
- Key Actions:
- Utilize online directories and trade platforms to find reputable suppliers.
- Review customer testimonials and ratings for insights into reliability and service quality.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Don’t just rely on their website; consider visiting their facilities if possible.
- What to Check:
- Supplier’s experience with G-code CNC machines.
- Customer support and after-sales service offered.
- Availability of spare parts and maintenance services.
Step 4: Assess Compliance and Certifications
Ensure that the suppliers comply with international standards and possess relevant certifications. This step is vital for ensuring quality and safety, particularly in industries with stringent regulations.
- Focus Areas:
- ISO certifications related to manufacturing processes.
- Compliance with local regulations in your target market (e.g., CE marking for Europe).
Step 5: Request Samples and Demonstrations
Before finalizing your decision, request samples or demonstrations of the G-code CNC machines. This will give you firsthand insight into the machine’s capabilities and how well it performs with your specific applications.
- What to Look For:
- Precision and accuracy during operation.
- Ease of use of the software interface for G-code programming.
- Reliability and speed of the machining process.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have identified a suitable supplier, it’s time to negotiate terms. Ensure that you discuss pricing, delivery timelines, warranty, and service agreements to avoid any surprises later.
- Key Negotiation Points:
- Payment terms and financing options.
- Lead times for production and delivery.
- Support during installation and initial training for your team.
Step 7: Finalize the Purchase Agreement
After negotiations, review and finalize the purchase agreement. Ensure that all terms are clearly outlined and that both parties have a mutual understanding of the expectations.
- Final Checks:
- Review the warranty and return policy.
- Confirm that the contract includes service level agreements for support.
- Ensure clarity on intellectual property rights, especially if custom modifications are involved.
By following this checklist, international B2B buyers can effectively source G-code CNC solutions that meet their operational needs while ensuring quality and reliability in their manufacturing processes.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for gcode cnc Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in G-Code CNC Sourcing?
When sourcing G-Code CNC machinery, international B2B buyers should understand the various cost components that influence the overall pricing structure. The main cost components include:
-
Materials: The quality and type of materials used in the manufacturing of CNC machines directly affect costs. For instance, high-grade steel or aluminum can increase material costs but improve durability and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly by region. In countries such as Kenya and Argentina, labor might be less expensive than in Europe or the Middle East, impacting the overall production cost. Additionally, skilled labor for programming and machine operation may command higher wages.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facilities, utilities, and administrative expenses. Understanding a supplier’s overhead can provide insights into their pricing strategy.
-
Tooling: The cost of tooling required for CNC operations can be substantial. Buyers should consider whether the supplier includes tooling in their pricing or if it is an additional cost.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that the machines meet specified standards. Suppliers who invest in quality assurance may have higher upfront costs, but they can save buyers money in the long run by reducing defects and increasing reliability.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs can vary based on the distance between the supplier and the buyer. Understanding Incoterms is crucial as they dictate who is responsible for costs at various stages of shipping.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can vary based on their market position, brand reputation, and the exclusivity of the machinery they provide. Buyers should seek transparency regarding margins during negotiations.
How Do Price Influencers Affect G-Code CNC Sourcing Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of G-Code CNC machinery, including:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Ordering in bulk can significantly lower the per-unit cost. Suppliers often provide discounts for larger orders, making it advantageous for businesses that require multiple units.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features or modifications can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses during production.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials and the presence of quality certifications (ISO, CE, etc.) can affect prices. Machines that meet higher quality standards may come at a premium but can provide better long-term value.
-
Supplier Factors: Established suppliers with a good reputation may charge more than lesser-known companies. However, the reliability and service offered by reputable suppliers often justify the higher cost.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the implications of different Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) can help buyers manage logistics costs effectively. These terms determine who bears the risk and cost at various stages of shipping.
What Are Some Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in G-Code CNC Sourcing?
International buyers should consider the following strategies to enhance cost-efficiency in their sourcing process:
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing and terms. Leverage your purchasing power, especially when ordering in bulk, to negotiate better deals.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial purchase price. Consider ongoing costs such as maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential downtime. A slightly higher upfront cost may result in lower TCO over time.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations and international trade tariffs that can impact overall costs. Building relationships with suppliers in your region can also mitigate some of these risks.
-
Research and Due Diligence: Investigate potential suppliers thoroughly. Request quotes from multiple vendors and compare not only prices but also service offerings, delivery times, and warranty conditions.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
It’s essential to recognize that prices for G-Code CNC machinery can fluctuate based on market conditions, supplier capabilities, and specific buyer requirements. Always seek up-to-date quotes and clarify all terms before finalizing any purchase.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing gcode cnc With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Solutions for CNC Machining
In the competitive landscape of CNC machining, businesses often seek alternatives to G-code CNC systems. While G-code is the standard for controlling CNC machines, alternatives may offer unique advantages depending on specific operational needs, production volumes, and technological capabilities. This analysis will explore two prominent alternatives: Parametric CAD/CAM Software and Conversational Programming. Each alternative has distinct features and benefits that can influence the decision-making process for international B2B buyers.

A stock image related to gcode cnc.
Comparison Table of G-Code CNC and Alternative Solutions
| Comparison Aspect | G-Code CNC | Parametric CAD/CAM Software | Conversational Programming |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision with extensive control | Moderate precision; depends on CAD capabilities | Good for simple tasks; less control |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; ongoing training costs | Higher initial investment; software licenses can be costly | Lower initial investment; often included with machines |
| Ease of Implementation | Steep learning curve; requires programming knowledge | Requires CAD knowledge; can be complex | User-friendly; designed for operators with minimal programming experience |
| Maintenance | Regular updates required; skilled technicians needed | Software updates; requires periodic training | Minimal maintenance; less complexity |
| Best Use Case | Complex parts requiring high precision | Custom designs and intricate parts | Short-run jobs with straightforward designs |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Parametric CAD/CAM Software?
Parametric CAD/CAM software allows users to design complex parts with intricate geometries. This software can automate the generation of toolpaths based on design changes, making it particularly beneficial for industries that require rapid prototyping and customization, such as aerospace and automotive sectors. However, the initial investment can be substantial, and ongoing costs for licenses and updates can add to the financial burden. Additionally, a solid understanding of CAD principles is necessary, which may require dedicated training for staff.
How Does Conversational Programming Compare to G-Code CNC?
Conversational programming provides an intuitive interface for operators, enabling them to input commands through a simplified format rather than traditional G-code. This method is especially advantageous for less complex machining tasks or for businesses that prioritize quick setup times and user-friendliness. While this approach can significantly reduce the learning curve for operators, it might lack the precision and flexibility offered by G-code systems, making it less suitable for intricate machining operations. Moreover, it may not support as wide a range of machine types as G-code.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When selecting the right CNC machining solution, B2B buyers should evaluate their specific needs, including the complexity of parts, production volumes, and available expertise. G-code CNC remains a robust choice for high-precision applications, while parametric CAD/CAM software excels in custom design and rapid prototyping scenarios. Conversely, conversational programming may be ideal for businesses seeking ease of use and quick turnaround for simpler tasks. By carefully assessing these factors, buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and budget constraints.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for gcode cnc
What Are the Key Technical Properties of G-Code CNC Machines?
When engaging in the procurement of CNC machinery and services, understanding specific technical properties is critical for making informed decisions. Here are some essential specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the quality and type of materials that can be machined using CNC technology. Common materials include aluminum, stainless steel, and plastics, each with different machinability characteristics. For B2B buyers, selecting the right material grade is crucial as it impacts the durability, performance, and cost-effectiveness of the final products.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance is the allowable deviation in dimensions from the specified measurement. It plays a significant role in quality control, especially in industries like aerospace and automotive where precision is paramount. Understanding tolerance levels can help buyers ensure that the parts produced meet their exact specifications, minimizing waste and rework.
3. Feed Rate
Feed rate is the speed at which the CNC machine moves the cutting tool across the workpiece, typically measured in millimeters per minute (mm/min). A higher feed rate can lead to faster production times but may affect the surface finish and dimensional accuracy. Buyers should assess their production needs to find an optimal balance between speed and quality.
4. Axis Configuration
The axis configuration of CNC machines (e.g., 3-axis, 5-axis) determines their capability in handling complex shapes and designs. A 5-axis machine offers greater flexibility and precision for intricate parts, which can be a significant advantage in competitive markets. Buyers should evaluate their design requirements to select the appropriate configuration.
5. Spindle Speed
Spindle speed indicates how fast the cutting tool rotates, typically expressed in revolutions per minute (RPM). Higher spindle speeds can enhance the machining process for certain materials but may require more advanced tooling. Buyers need to consider the types of materials they will be machining to ensure compatibility with the spindle speed of the CNC machine.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to G-Code CNC?
In the world of CNC machining, several trade terms are frequently used. Understanding these terms can help B2B buyers navigate contracts and negotiations more effectively.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM produces components or products that are sold by another company under its brand. For B2B buyers, working with OEMs can provide access to high-quality parts designed specifically for their machines, ensuring compatibility and performance.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers to understand as it affects inventory management and production costs. Buyers must assess their demand to negotiate favorable MOQs with suppliers.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products or services. This is an essential step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare offers and make informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms can help B2B buyers avoid disputes over shipping, insurance, and customs duties, making it easier to manage cross-border transactions.
5. CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing)
CAM refers to the use of software to control machine tools in the manufacturing process. This technology streamlines production and enhances precision. B2B buyers should consider investing in CAM systems to improve their manufacturing efficiency and quality.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of the CNC machining market more effectively, ensuring they make strategic decisions that align with their operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the gcode cnc Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the G-Code CNC Sector?
The G-Code CNC sector is experiencing significant transformation driven by technological advancements and shifting global economic conditions. A major trend is the increasing adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies, which enhance connectivity and automation in manufacturing processes. This includes the integration of IoT devices, enabling real-time data collection and analysis, which helps international B2B buyers optimize production efficiency and reduce downtime.
A stock image related to gcode cnc.
In regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there’s a growing demand for precision manufacturing solutions, particularly for industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who offer advanced CNC machines that can handle complex geometries and multi-axis operations. Furthermore, the rise of digital twins and advanced simulation software allows manufacturers to test and refine their machining processes virtually, reducing material waste and production costs.
Another key trend is the focus on customization and rapid prototyping. B2B buyers are seeking CNC solutions that can quickly adapt to changing design specifications, which is crucial in industries where time-to-market is a competitive advantage. As a result, suppliers who can provide flexible and scalable G-Code CNC solutions are likely to gain a competitive edge.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact G-Code CNC Purchasing Decisions?
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal consideration for B2B buyers in the G-Code CNC sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is under scrutiny, prompting companies to seek suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly practices. This includes adopting energy-efficient machinery and utilizing sustainable materials, which not only minimizes waste but also reduces the carbon footprint of the production process.
Moreover, ethical sourcing is gaining traction as buyers demand transparency in their supply chains. Suppliers who can demonstrate compliance with ethical standards and possess certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management or ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety, are more likely to attract business. Companies in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are increasingly favoring partnerships with manufacturers that commit to sustainable practices, thus enhancing their own brand reputation.
Investing in ‘green’ materials and technologies, such as biodegradable lubricants or recyclable components, not only aligns with global sustainability goals but also meets the expectations of environmentally conscious consumers. As such, B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who are proactively working towards sustainability in their operations, as this will be a significant differentiator in the competitive landscape.
What Is the Brief Evolution of G-Code CNC Technology?
The evolution of G-Code CNC technology has been remarkable since its inception in the 1950s. Initially developed for controlling machine tools, G-Code has transformed into a universal language for CNC programming, enabling precision and automation in manufacturing. The introduction of computer numerical control (CNC) in the 1980s revolutionized the industry, allowing for more complex and accurate machining tasks.
As technology advanced, so did the capabilities of CNC machines. The introduction of multi-axis machining in the late 1990s provided manufacturers with the ability to create intricate parts with greater efficiency. Today, G-Code CNC technology continues to evolve with the integration of AI and machine learning, further enhancing automation and predictive maintenance capabilities. This evolution not only improves operational efficiency but also allows for greater customization, meeting the diverse needs of international B2B buyers in various sectors.
Overall, understanding these market dynamics, sustainability considerations, and the historical context of G-Code CNC technology will empower B2B buyers to make informed sourcing decisions that align with their operational goals and ethical standards.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of gcode cnc
-
How do I solve common issues when programming G-Code for CNC machines?
Common issues in G-Code programming include incorrect commands and syntax errors. To resolve these, thoroughly review the G-Code for mistakes and ensure that the commands align with the machine’s specifications. Utilize simulation software to test the code virtually before actual machining. Additionally, consult the machine’s user manual for specific G-Code commands and parameters, as variations can exist between different manufacturers. Regular training for operators can also mitigate these issues by enhancing their understanding of G-Code intricacies. -
What is the best CNC machine for producing intricate designs with G-Code?
For producing intricate designs, a 5-axis CNC machine is the best option. These machines can manipulate tools along five axes, allowing for more complex shapes and angles, which are essential for detailed work. Look for machines that support advanced G-Code commands for precision. Brands like Haas and DMG Mori offer models specifically designed for intricate machining. When sourcing, ensure that the machine’s capabilities align with your specific production needs and material types. -
How do I vet suppliers for G-Code CNC machines internationally?
To vet international suppliers for G-Code CNC machines, start by checking their certifications, such as ISO 9001, which indicates quality management practices. Request references from previous customers and assess their experience with similar machines. Conduct virtual meetings to discuss technical specifications and after-sales support. It’s also beneficial to visit their facilities if possible or utilize third-party inspection services to ensure they meet your quality standards before making a purchase. -
What customization options should I consider when sourcing CNC machines?
When sourcing CNC machines, consider customization options such as software compatibility, additional axes, and tool changers. Verify if the machine can be tailored to handle specific materials or if it can integrate with your existing production systems. Additionally, inquire about the possibility of customizing G-Code programming features to suit your operational requirements. This will enhance the machine’s adaptability and optimize production efficiency. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for CNC machines and G-Code software?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for CNC machines can vary significantly based on the manufacturer and machine type. Typically, MOQs can range from one machine for high-end models to several units for more standardized models. For G-Code software, it often depends on licensing agreements; some suppliers may offer single licenses while others may require bulk purchases. Always clarify MOQs before proceeding to avoid unexpected costs and ensure your order aligns with your production scale. -
What payment terms should I negotiate when purchasing CNC machines internationally?
When purchasing CNC machines internationally, negotiate payment terms that protect your investment. Common practices include a deposit upfront (usually 30-50%) with the balance due upon delivery or after installation. Consider using letters of credit for larger transactions to secure both parties. Additionally, inquire about payment methods that offer buyer protection, such as PayPal or escrow services, especially if dealing with new suppliers. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) in my CNC machine procurement?
To ensure quality assurance (QA) in CNC machine procurement, establish clear quality standards and specifications in your contract. Request detailed documentation, including machine calibration certificates and quality control reports. Consider implementing a pre-shipment inspection to verify that the machine meets your requirements before it leaves the supplier’s facility. Additionally, confirm that the supplier offers a warranty and after-sales support for any potential issues post-purchase. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing CNC machines?
When importing CNC machines, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and delivery timelines. Choose a reliable freight forwarder experienced in handling heavy machinery. Ensure you have all necessary documentation, including bills of lading and customs declarations, to avoid delays. Also, factor in local transportation from the port to your facility and potential installation costs. Planning these logistics in advance will facilitate a smoother import process.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
A stock image related to gcode cnc.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for gcode cnc
As the global landscape for CNC machining continues to evolve, the importance of strategic sourcing in acquiring G-Code CNC solutions cannot be overstated. International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, stand to benefit immensely from a thorough understanding of G-Code programming and its applications. Knowledge of commands such as G00 for rapid travel and G01 for linear interpolation can drastically enhance operational efficiency and precision in manufacturing processes.
Investing in the right CNC technologies not only streamlines production but also fosters competitiveness in an increasingly interconnected market. Strategic sourcing allows businesses to identify reliable suppliers, ensuring access to cutting-edge machinery and support services that are crucial for maintaining high standards of quality and efficiency.
Looking ahead, the demand for advanced CNC machining capabilities will likely surge as industries strive for greater customization and reduced lead times. International B2B buyers are encouraged to leverage this moment to forge partnerships that will pave the way for innovation and growth. By prioritizing strategic sourcing, businesses can position themselves advantageously for the future, ready to meet the challenges and opportunities of a dynamic manufacturing environment.