Master M Codes for CNC: The Complete Programming Guide (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for m codes for cnc
In the fast-evolving landscape of manufacturing, understanding M codes for CNC machines is paramount for international B2B buyers seeking to enhance their operational efficiency. The challenge of sourcing the right M codes can be daunting, especially for businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where the diversity of CNC machinery and applications can lead to confusion and inefficiencies. This comprehensive guide demystifies M codes, covering their types, applications, and the critical factors to consider when vetting suppliers and assessing costs.
Our objective is to empower B2B buyers with the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions. By exploring the various functionalities of M codes, such as tool changes, coolant control, and spindle operations, this guide provides actionable insights into how these codes can optimize machining processes. Additionally, we will address the importance of understanding manufacturer-specific M codes, which can vary significantly across different CNC machines.
This resource serves as a strategic tool for businesses looking to streamline their operations and improve productivity. Whether you are a manufacturer in Saudi Arabia or a machining service provider in the UK, this guide equips you with the necessary information to navigate the complexities of M codes effectively, ensuring that your procurement strategies align with your operational goals.
Understanding m codes for cnc Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| M00 – Program Stop | Halts the CNC program execution completely. | Quality control checks and tool changes. | Pros: Easy to use for manual checks. Cons: Can disrupt workflow if used excessively. |
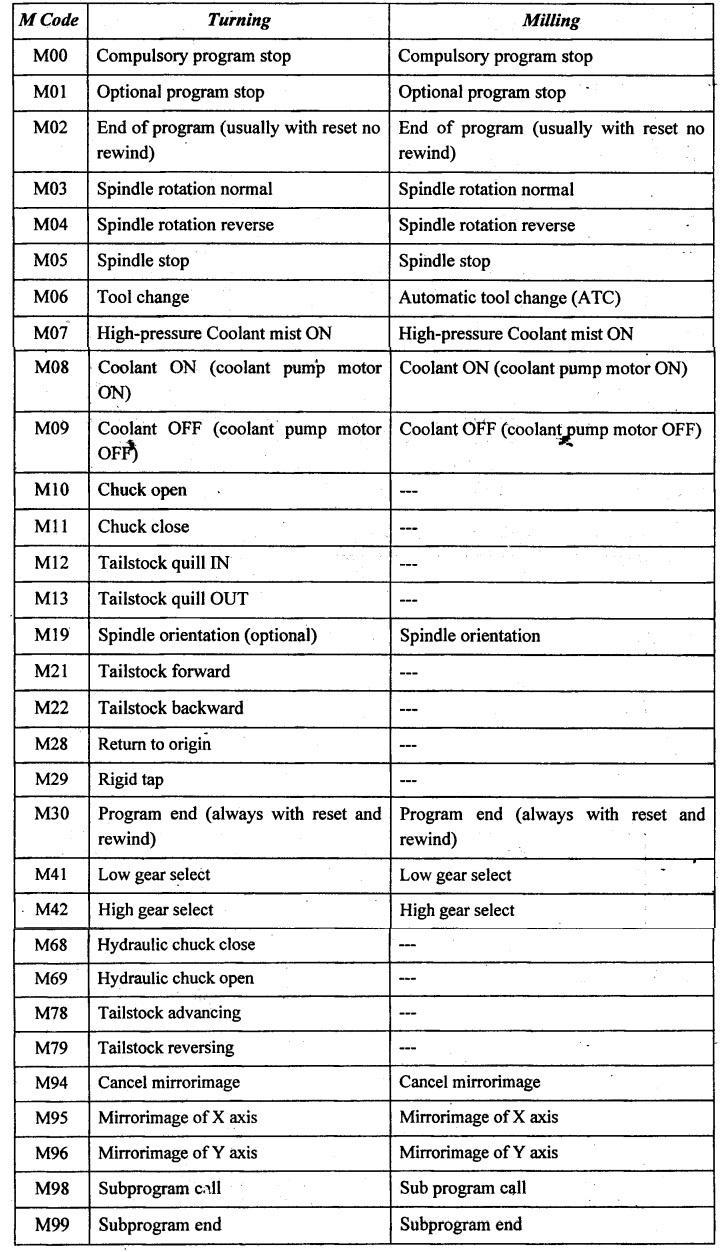
| M03/M04 – Spindle Control | Controls spindle direction (clockwise/counter-clockwise). | Essential for milling and drilling operations. | Pros: Increases versatility in machining. Cons: Incorrect usage can damage tools. |
| M06 – Tool Change | Initiates the automatic tool change process. | Used in complex machining operations. | Pros: Enhances efficiency and reduces downtime. Cons: Requires compatible tool holders. |
| M08/M09 – Coolant Control | Activates or deactivates coolant systems. | Crucial for heat management in machining. | Pros: Prevents tool wear and overheating. Cons: Improper management can lead to contamination. |
| M30 – Program End | Ends the CNC program and resets the machine. | Finalizing production runs and resetting machines. | Pros: Simple and effective for program management. Cons: May require manual intervention for restarts. |
What Are the Characteristics of M00 – Program Stop?
M00 is a fundamental M-code that halts the CNC machine’s operation entirely. It is typically used for quality control checks or tool changes, allowing operators to inspect workpieces or replace tools without the risk of accidental movement. This code is suitable for operations where precision is paramount, ensuring that no unintended machining occurs during critical checks. B2B buyers should consider the implications of using M00, as excessive halting can lead to inefficiencies and increased cycle times.
How Do M03 and M04 – Spindle Control Enhance Machining Flexibility?
M03 and M04 are essential M-codes that control the spindle’s rotational direction, either clockwise or counter-clockwise. This capability is crucial for various machining operations, particularly in milling and drilling, where the direction can affect the cutting process and tool life. For B2B buyers, understanding the specific spindle requirements of their CNC machines is vital, as improper use of these codes can result in tool damage or subpar machining quality.
Why Is M06 – Tool Change Important for Complex Operations?
M06 facilitates automatic tool changes, a critical function in CNC machining, especially for complex operations requiring multiple tools. This M-code enhances efficiency by reducing manual intervention and downtime during production runs. Buyers should evaluate the compatibility of their CNC machines with various tool holders and the range of tools available, ensuring that they can fully leverage the benefits of M06 in their operations.
What Role Do M08 and M09 – Coolant Control Play in CNC Machining?
M08 and M09 are used to manage coolant systems, activating and deactivating coolant flow during machining processes. This function is vital for maintaining optimal temperatures and preventing overheating, which can lead to tool wear and compromised workpiece integrity. B2B buyers must consider the coolant management systems of their CNC machines, as effective coolant application can significantly enhance machining performance and extend tool life.
How Does M30 – Program End Contribute to Workflow Management?
M30 signals the end of a CNC program and resets the machine for the next operation. This M-code is integral to managing production runs, ensuring that machines are prepared for subsequent tasks. Buyers should assess how M30 integrates with their operational workflows, as a smooth transition between programs can lead to increased productivity and reduced downtime in manufacturing environments.
Key Industrial Applications of m codes for cnc
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of m codes for cnc | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Automated Tool Changes for Complex Components | Reduces downtime and improves production efficiency | Compatibility with existing systems, ease of programming |
| Automotive | Precision Machining of Engine Parts | Enhances accuracy and quality of critical components | Supplier reliability, technical support availability |
| Medical Devices | CNC Machining of Surgical Instruments | Ensures high precision and compliance with regulations | Certification standards, material sourcing options |
| Electronics | PCB Manufacturing and Assembly | Streamlines production processes, reduces waste | Lead times, cost-effectiveness, and scalability |
| Energy | Machining of Turbine Components | Increases operational efficiency and reliability | Material specifications, energy efficiency compliance |
How Are M Codes for CNC Used in Aerospace Manufacturing?
In the aerospace industry, M codes facilitate automated tool changes for complex components, significantly reducing machine downtime. This is crucial for maintaining high production efficiency, especially given the stringent quality standards required in aerospace manufacturing. International buyers need to ensure that the CNC machines they source are compatible with their existing systems and that they have access to robust programming support for M code implementation.
What Role Do M Codes Play in Automotive Precision Machining?
Automotive manufacturers use M codes to control the machining of engine parts with precision. M codes enable functionalities such as spindle control and coolant management, which enhance the accuracy and quality of critical components. For international buyers, especially in regions like South America and Europe, sourcing machines with proven reliability and excellent technical support is vital to avoid production delays and maintain competitive advantage.
How Are M Codes Essential in Medical Device Manufacturing?
In the medical devices sector, M codes are employed in the CNC machining of surgical instruments, where precision is paramount. These codes help in managing operations that ensure compliance with stringent regulatory standards. Buyers from the Middle East and Africa should prioritize suppliers who can provide machinery that meets certification standards and offer material sourcing options that comply with medical regulations.
How Do M Codes Streamline Electronics Production?
M codes are integral to the manufacturing and assembly of printed circuit boards (PCBs) in the electronics industry. They streamline production processes by enabling automated tasks, which reduces material waste and enhances overall efficiency. For B2B buyers, especially in Europe, considerations such as lead times, cost-effectiveness, and the ability to scale production are crucial when selecting CNC machinery that utilizes M codes.
What Are the Benefits of M Codes in Energy Sector Applications?
In the energy sector, M codes are utilized for the precise machining of turbine components, contributing to increased operational efficiency and reliability. The correct application of M codes can lead to significant improvements in the performance of energy systems. International buyers must focus on material specifications and ensure that the CNC equipment meets energy efficiency compliance standards to maximize their investment.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘m codes for cnc’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Understanding M-Code Variability Across Different CNC Machines
The Problem:
B2B buyers often encounter the issue of M-code variability when integrating CNC machines from different manufacturers. Each manufacturer may implement M-codes differently or use unique codes for similar functions. This inconsistency can lead to confusion, errors in programming, and ultimately, wasted resources during production. For example, a company in Saudi Arabia might purchase machines from both European and Asian suppliers, only to find that the M-codes for basic operations like coolant control or spindle start differ significantly, causing delays in manufacturing and training.
The Solution:
To overcome this challenge, buyers should prioritize thorough research on M-code compatibility before making any purchasing decisions. This includes obtaining detailed M-code documentation from manufacturers and understanding the specific codes used for their machines. It’s advisable to create a comprehensive M-code reference guide that consolidates the different codes and their functions across the machines in use. Furthermore, investing in training programs for machine operators that cover M-code functions and variations can enhance operational efficiency. Utilize simulation software that allows for testing various M-codes in a controlled environment to identify potential issues before they arise on the shop floor. By establishing a standardized approach to M-code usage, companies can significantly reduce the risk of errors and streamline their CNC operations.
Scenario 2: Inadequate Training on M-Codes for CNC Operations
The Problem:
A common pain point for B2B buyers is the lack of proper training for operators on M-codes specific to their CNC machines. New employees or those transitioning from manual to CNC operations may struggle to understand how to utilize M-codes effectively, leading to inefficient programming, increased cycle times, and even machine damage. In regions like South America, where there may be fewer resources for advanced CNC training, this gap can become a significant obstacle to maximizing machine potential.
The Solution:
To address this issue, companies should invest in comprehensive training programs tailored to their specific CNC setups. Partnering with CNC machine manufacturers or local training institutions can provide valuable resources. Develop a structured onboarding process that includes hands-on workshops focusing on M-code operations, simulations, and troubleshooting common errors. Create easy-to-follow training manuals that outline M-codes and their applications, supplemented with visual aids and real-world scenarios. Additionally, encourage a mentorship program where experienced operators guide newcomers, fostering a culture of continuous learning. By prioritizing M-code training, businesses can enhance their workforce’s skills, leading to higher productivity and reduced operational risks.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Troubleshooting M-Code Related Issues
The Problem:
International B2B buyers frequently face difficulties in troubleshooting M-code related issues that arise during CNC operations. Problems such as unexpected machine stops or incorrect tool changes can stem from programming errors or miscommunications between the operator and the machine’s control system. In the Middle East, where companies might operate multiple machines in varying conditions, diagnosing these problems quickly is crucial to maintain production schedules.
The Solution:
To mitigate troubleshooting challenges, companies should implement a systematic approach to diagnosing M-code issues. First, maintain a detailed log of M-code commands used in production, noting any anomalies or errors encountered. This log serves as a valuable resource for identifying patterns that may indicate persistent issues. Establish a troubleshooting framework that includes step-by-step guidelines for common M-code problems, integrating visual aids and flowcharts to simplify the process. Regular maintenance checks on CNC machines should also be conducted to ensure that all components are functioning correctly and that software updates are applied consistently. Furthermore, consider utilizing CNC diagnostic software that can analyze machine performance and provide real-time feedback on M-code execution. This proactive approach not only helps in resolving issues promptly but also enhances overall operational reliability, ultimately leading to increased productivity.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for m codes for cnc
What Are the Key Properties of Aluminum for M Codes in CNC?
Aluminum is a popular choice for CNC machining due to its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and ease of fabrication. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 400°F (204°C) and exhibits good machinability, allowing for faster production rates. Aluminum’s low density makes it ideal for applications where weight is a critical factor, such as in aerospace and automotive components.
Pros: Aluminum is lightweight, durable, and resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for outdoor applications. Its low cost relative to other metals and ease of machining reduce manufacturing complexity.
Cons: While it is strong, aluminum can be less durable than steel in high-stress applications. It also has lower heat resistance, which can limit its use in high-temperature environments.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with various media, including water and oils, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. However, it may not be ideal for environments with high chemical exposure.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN. In countries like Saudi Arabia, where heat can be extreme, selecting the right aluminum alloy is crucial to maintain performance.
How Does Steel Perform in CNC Machining Applications?
Steel is renowned for its strength, durability, and versatility, making it a staple in CNC machining. It has a high-temperature rating, often exceeding 1,000°F (538°C), and offers excellent wear resistance. Various steel grades, such as stainless and tool steel, provide different properties suitable for specific applications.
Pros: Steel’s high tensile strength and resistance to deformation make it ideal for heavy-duty applications. It can withstand higher temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for high-performance environments.
Cons: Steel is generally more expensive than aluminum and can be more challenging to machine due to its hardness. This may lead to increased manufacturing complexity and longer lead times.
Impact on Application: Steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including fuels and chemicals, making it versatile for industrial applications. However, its susceptibility to rust and corrosion may necessitate protective coatings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards like ASTM and JIS is vital, especially for buyers in Africa and South America. Understanding local regulations regarding steel grades and treatments can also impact procurement decisions.
What Are the Benefits of Using Plastics in CNC Machining?
Plastics, such as polycarbonate and nylon, are increasingly used in CNC machining due to their lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion and chemicals. They typically have lower temperature ratings, around 200°F (93°C), but offer excellent machinability and flexibility.
A stock image related to m codes for cnc.
Pros: Plastics are cost-effective and can be produced in various colors and finishes. Their lightweight nature makes them ideal for applications where weight savings are essential.
Cons: Plastics can have lower strength and durability compared to metals, making them unsuitable for high-stress applications. They may also deform under high temperatures.
Impact on Application: Plastics are compatible with various media, including water and certain chemicals, making them suitable for a wide range of applications, from consumer products to industrial components.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of local regulations regarding plastic materials, especially in Europe, where compliance with REACH and RoHS standards is mandatory. Understanding the specific properties of different plastics can help in selecting the right material for the intended application.
How Do Composites Enhance CNC Machining Applications?
Composite materials, such as carbon fiber and fiberglass, are gaining traction in CNC machining due to their high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent corrosion resistance. They typically have a temperature rating of around 300°F (149°C) and can be tailored for specific applications.
Pros: Composites offer exceptional strength and durability while remaining lightweight. They are also resistant to chemical corrosion, making them suitable for harsh environments.
Cons: Composites can be more expensive than traditional materials and may require specialized machining techniques, increasing manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Composites are compatible with various media and are often used in aerospace, automotive, and marine applications where weight reduction is critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like South America and Africa should consider the availability of composite materials and the necessary expertise for machining them. Compliance with international standards for composites can also vary, so understanding local regulations is essential.
Summary Table of Material Selection for M Codes in CNC
| Material | Typical Use Case for m codes for cnc | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Aerospace components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower heat resistance | Medium |
| Steel | Heavy machinery parts | High strength and durability | More expensive and harder to machine | High |
| Plastics | Consumer products | Cost-effective and versatile | Lower strength and durability | Low |
| Composites | Aerospace and automotive applications | High strength-to-weight ratio | More expensive and complex to machine | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides international B2B buyers with essential insights into the properties, advantages, and limitations of various materials used in CNC machining. Understanding these factors can significantly enhance decision-making processes in sourcing and procurement.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for m codes for cnc
What Are the Key Stages of the Manufacturing Process for M Codes in CNC Machining?
The manufacturing process for M codes in CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining involves several critical stages, each playing a pivotal role in ensuring the precision and quality of the final product. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers, especially those engaged in international procurement.
1. Material Preparation: How Is the Right Material Chosen and Prepared?
Material preparation is the foundational step in CNC machining. It involves selecting the appropriate material—typically metals like aluminum, steel, or plastics—based on the specifications of the parts to be produced.
- Material Selection: Buyers should consider factors such as material strength, machinability, and cost-effectiveness. Suppliers should provide a detailed material specification sheet.
- Cutting and Shaping: Materials are cut to size, often using saws or lasers, to ensure they fit the machining requirements. This step must be executed with precision to minimize waste and ensure efficient machining.
How Are Parts Formed Using CNC Machinery and M Codes?
The forming stage is where the material undergoes significant transformation into the desired shape. This stage utilizes CNC machines programmed with M codes to control various functions.
- CNC Programming: M codes are integrated into the G-code that instructs the CNC machine on operations like spindle control and coolant management. Understanding the specific M codes for different machines is crucial for optimal performance.
- Machining Techniques: Common techniques include milling, turning, and drilling. Each technique may require different M codes to manage tool changes, spindle speeds, and other parameters. For instance, M06 is used for tool change, while M03 activates the spindle in a clockwise direction.
What Are the Assembly and Finishing Processes Involved?
After forming, parts may require assembly and finishing to meet the final product specifications.
- Assembly: This may involve combining multiple components into a single unit. It’s essential for buyers to verify that the assembly process adheres to quality standards to ensure functionality.
- Finishing Processes: Techniques such as sanding, polishing, and coating are employed to enhance the surface quality and aesthetic appeal of the parts. These processes can significantly affect the final product’s performance and longevity.
What Quality Control Measures Are Essential for CNC Machining?
Quality assurance is a crucial aspect of the CNC machining process. Implementing effective QC measures ensures that the final products meet international standards and buyer specifications.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
Adhering to recognized international standards is vital for ensuring product quality. ISO 9001 is a widely accepted quality management standard that outlines requirements for a quality management system (QMS). Other relevant standards may include:
- CE Marking: Essential for products sold within the European Union, ensuring compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: Particularly relevant for buyers in the oil and gas sector, these standards ensure that products meet industry-specific requirements.
How Are Quality Control Checkpoints Structured?
Quality control checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to catch defects early. The typical checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage involves inspecting raw materials and components before they enter the production process.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections during machining ensure that parts are being produced to the required specifications.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The final inspection before parts are shipped, ensuring that all specifications and standards have been met.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in CNC Machining?
Various testing methods are employed to ensure the quality and functionality of CNC machined parts:
- Dimensional Inspection: Using tools like calipers and micrometers to measure dimensions and tolerances.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic and magnetic particle testing check for internal and surface defects without damaging the parts.
- Functional Testing: Ensuring that the final product operates as intended under real-world conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, verifying supplier quality control practices is essential for mitigating risks associated with procurement.
- Supplier Audits: Conducting audits of suppliers can provide insights into their quality management systems and adherence to international standards. Buyers should look for certifications like ISO 9001 or specific industry-related certifications.
- Quality Reports: Requesting regular quality reports from suppliers can help in tracking their performance over time.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality assurance processes, ensuring that products meet the required standards before shipment.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers must also consider the regional differences in quality control standards and regulations. This is particularly important for buyers from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
- Cultural and Regulatory Differences: Buyers should be aware of the local regulations that may affect quality standards, especially when dealing with suppliers from different countries.
- Language Barriers: Communication is crucial; hence, buyers should ensure that specifications and quality requirements are clearly understood by all parties involved.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures specific to M codes in CNC machining, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they procure high-quality products that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘m codes for cnc’
In this section, we will explore a practical sourcing guide tailored for B2B buyers interested in procuring M codes for CNC machines. This checklist will help you navigate the complexities of sourcing these critical components, ensuring that you make informed decisions that meet your operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before you begin your search, clearly outline your technical requirements for the M codes. This includes understanding which CNC machines you will be using and the specific operations you need the M codes to perform.
- Considerations: Different machines may require unique M codes, and knowing your machine’s specifications will help you select the appropriate codes that ensure compatibility and efficiency.
Step 2: Research Available M Codes
Compile a comprehensive list of common M codes relevant to your industry and specific machines. This involves studying various manufacturers’ manuals and resources to understand the standard codes and their functionalities.
- Action Items: Create a reference document that includes descriptions of each M code, focusing on those that are most applicable to your operations, such as M00 for program stop or M08 for coolant on.
Step 3: Identify Reliable Suppliers
Finding trustworthy suppliers is crucial. Look for manufacturers or distributors that specialize in CNC components and have a proven track record in your region, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe.
- Tips: Check online reviews, industry forums, and request recommendations from peers in your field to gauge the reliability and reputation of potential suppliers.
Step 4: Request Samples and Documentation
Before making a purchase, request samples of the M codes or related products. Additionally, obtain technical documentation that details the compatibility and usage of the M codes with your CNC machines.
- Importance: This step allows you to assess the quality and functionality of the M codes in real-world applications, reducing the risk of operational disruptions later.
Step 5: Evaluate Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that your suppliers adhere to industry standards and possess the necessary certifications for manufacturing CNC components. This is particularly important in regions with strict regulatory frameworks.
- Key Certifications: Look for ISO certifications or other relevant quality management systems that demonstrate the supplier’s commitment to quality and safety.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, engage in negotiations regarding pricing, delivery timelines, and after-sales support. Clear agreements on these terms can prevent misunderstandings and ensure smooth transactions.
- Best Practices: Be transparent about your expectations and requirements, and ensure that all terms are documented to avoid future disputes.
Step 7: Establish a Support Plan
After procurement, set up a support plan with your supplier for ongoing assistance with M codes. This includes training for your staff on how to implement and troubleshoot the codes effectively.
- Why It Matters: Having a support plan in place will enhance your operational efficiency and ensure that your team can effectively utilize the M codes in your CNC machines.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can make well-informed decisions when sourcing M codes for CNC applications, ensuring compatibility and enhancing manufacturing efficiency across various industries.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for m codes for cnc Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for M Codes in CNC Sourcing?
When analyzing the cost structure for M codes in CNC sourcing, several components must be taken into account:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly influences the overall cost. High-quality materials often lead to higher expenses but can enhance the durability and performance of the finished product.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is necessary for programming and operating CNC machines effectively. Labor costs can vary widely based on the region, with higher costs typically found in developed nations compared to emerging markets in Africa or South America.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, and depreciation of machinery. Efficient management of overhead can lead to cost savings, particularly for companies with high production volumes.
-
Tooling: Specific tooling requirements for different M codes can incur additional expenses. Custom tooling, although more costly upfront, may result in better efficiency and lower per-unit costs over time.
-
Quality Control (QC): Investing in robust QC processes ensures that the final products meet required specifications, which can prevent costly rework or returns in the long run.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary significantly depending on the destination. International buyers need to consider customs duties and potential delays that can impact the supply chain.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their costs and ensure profitability. Understanding the typical margins in your industry can help in negotiating better prices.
How Do Price Influencers Affect M Code Costs for CNC Machines?
Several factors can influence the pricing of M codes in the CNC industry:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Suppliers often provide better pricing for larger orders. Buyers should assess their production needs and negotiate MOQs that align with their purchasing strategy.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can lead to higher costs due to the need for tailored solutions. It’s essential to balance customization with cost-effectiveness.
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly impacts pricing. Buyers should weigh the benefits of premium materials against budget constraints.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that meet specific industry standards or certifications may come at a premium. Buyers should ensure that the quality justifies the cost.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers might charge more due to their experience and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the Incoterms used in international trade can significantly affect total costs. Buyers should negotiate terms that minimize risk and ensure clarity in shipping responsibilities.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Negotiating M Code Costs?
To optimize costs when sourcing M codes for CNC machines, international buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Approach negotiations with a clear understanding of your requirements and market pricing. Leverage your purchasing volume to negotiate discounts.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Analyze the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the purchase price. Consider factors such as maintenance, durability, and lifecycle costs to make informed decisions.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Different regions have unique pricing structures influenced by local labor costs, material availability, and market demand. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should research these factors to ensure competitive pricing.
-
Be Aware of Indicative Prices: Prices can fluctuate based on market conditions, so it’s crucial to request up-to-date quotes. Always seek clarity on what is included in the price to avoid unexpected costs.
By understanding these cost components, price influencers, and negotiation strategies, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing M codes for CNC machining, ultimately leading to more efficient operations and improved profitability.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing m codes for cnc With Other Solutions
When evaluating the efficiency of CNC machining processes, particularly regarding the use of M codes, it is essential to explore viable alternatives that can achieve similar operational goals. This section delves into a comparative analysis of M codes against two alternative solutions: PLC (Programmable Logic Controllers) and Robotics Automation. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of these alternatives, B2B buyers can make informed decisions tailored to their specific operational requirements.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | M Codes for CNC | PLC (Programmable Logic Controllers) | Robotics Automation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision in machining tasks | Reliable for simple control tasks | Excellent for complex operations |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment | Generally lower cost | Higher initial investment |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires programming knowledge | User-friendly with graphical interfaces | Requires advanced programming skills |
| Maintenance | Low to moderate | Low maintenance | High maintenance |
| Best Use Case | Complex machining operations | Simple automation tasks | High-volume, repetitive tasks |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of M Codes for CNC?
M codes, or miscellaneous codes, are integral to CNC machining, providing precise control over various functions such as tool changes and spindle operations. The primary advantages of M codes include their high level of precision and compatibility with complex machining tasks. However, they require a solid understanding of programming, which can be a barrier for some users. Additionally, while the initial investment is moderate, the ongoing costs associated with training and potential programming errors can add up.
How Do PLCs Serve as an Alternative to M Codes?
PLC technology is a popular alternative for automating machinery and processes. PLCs are known for their reliability and ease of use, especially for straightforward tasks. They typically feature user-friendly graphical interfaces that make programming accessible even to those with limited technical expertise. While PLCs can handle various control functions efficiently, they may not offer the same level of precision required for intricate machining operations. Furthermore, while the initial costs are lower, the applications for PLCs may be limited in scope compared to the capabilities of CNC systems.
What Role Does Robotics Automation Play in CNC Machining?
Robotics automation represents a cutting-edge alternative to M codes, particularly for manufacturers requiring high-volume production and efficiency. Robots can perform complex tasks with exceptional speed and accuracy, making them ideal for repetitive machining operations. However, the initial investment for robotics can be significantly higher, and their maintenance can be more demanding. Despite these challenges, robotics automation excels in environments where flexibility and adaptability are paramount, allowing manufacturers to respond quickly to changing production demands.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
A stock image related to m codes for cnc.
For B2B buyers, the decision between M codes for CNC, PLCs, and robotics automation hinges on several factors, including the specific manufacturing needs, budget constraints, and the level of technical expertise available within the organization. Buyers should conduct a thorough needs assessment, considering aspects such as production volume, complexity of tasks, and the potential for future growth. By aligning their operational goals with the strengths of each solution, buyers can select the most suitable technology to enhance their manufacturing processes effectively.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for m codes for cnc
A stock image related to m codes for cnc.
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of M Codes for CNC?
Understanding the technical specifications of M codes is crucial for international B2B buyers involved in CNC machining. Here are some key properties that should be noted:
1. M-Code Definitions and Functions
M codes, or miscellaneous codes, serve specific functions within CNC programming. Each M code corresponds to an action that the machine must execute, such as stopping the spindle or turning on coolant. Familiarity with these codes allows buyers to ensure they select machines compatible with their production needs, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency.
2. Compatibility and Customization
Different CNC machines may utilize varying sets of M codes, often tailored to specific manufacturers. Buyers should consider the compatibility of M codes with their existing machinery or the machines they plan to acquire. This knowledge is vital for avoiding costly errors and ensuring seamless integration into the production line.
3. Precision and Tolerance Levels
M codes play a pivotal role in controlling machining processes that require high precision and specific tolerances. Buyers must understand the implications of M codes on the final product quality, as improper code execution can lead to defects, increased waste, and reduced profitability. Knowing the required tolerances for the products being manufactured is essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
4. Machine Control and Automation
M codes facilitate automation in CNC machining. Features such as automatic tool changes or coolant management, controlled via M codes, can significantly streamline operations. Buyers should evaluate the level of automation provided by different CNC machines, as this can enhance productivity and reduce labor costs.
5. Error Handling and Program Control
M codes also include commands for error handling and program control, such as stopping the machine in case of a malfunction. Understanding these commands can help buyers ensure that they are investing in machines that prioritize safety and reliability, which is particularly important in high-stakes production environments.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to M Codes for CNC?
Familiarity with industry terminology can facilitate smoother communication and transactions. Here are several key terms that B2B buyers should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of CNC machinery, understanding the OEM can help buyers identify the quality and reliability of the machines they are considering.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For CNC machines and components, knowing the MOQ can impact purchasing decisions, especially for smaller businesses looking to manage costs without overcommitting resources.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and other key details for a specific quantity of goods. B2B buyers should prepare comprehensive RFQs that detail their requirements, as this can lead to more accurate quotes and better negotiation outcomes.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized international trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, risk, and insurance. Familiarity with Incoterms can help buyers navigate international transactions more effectively, ensuring clarity in terms of shipping and delivery responsibilities.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the goods. Understanding lead times is crucial for B2B buyers in planning production schedules and ensuring that materials are available when needed.
6. Tool Life Management
This refers to the tracking and management of the lifespan of cutting tools used in CNC machining. Effective tool life management can reduce costs and improve efficiency, making it an important consideration for buyers looking to optimize their operations.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and market demands.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the m codes for cnc Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the M Codes for CNC Sector?
The global CNC market, particularly regarding M codes, is experiencing notable growth driven by several factors. The increasing demand for precision machining across industries, including aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing, is propelling the adoption of advanced CNC technologies. International B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (notably Saudi Arabia and the UK), are witnessing a shift towards more automated and efficient production processes. Key trends include the integration of Industry 4.0 principles, which emphasize smart manufacturing, real-time data analytics, and machine-to-machine communication.
Additionally, the rise of 5-axis CNC machining is enabling manufacturers to produce complex geometries that were previously difficult or impossible to achieve. This trend is particularly relevant for buyers looking for high precision and flexibility in manufacturing processes. The growing influence of additive manufacturing and hybrid machining technologies is also reshaping sourcing strategies, encouraging buyers to explore suppliers that offer comprehensive solutions, including both traditional and cutting-edge technologies.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact Your Business in the CNC Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration for international B2B buyers in the CNC sector. As environmental regulations tighten and corporate social responsibility gains prominence, the demand for sustainable practices in sourcing is rising. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who adhere to ethical sourcing standards and offer ‘green’ certifications for their materials and processes. This includes the use of eco-friendly lubricants, recyclable tooling, and energy-efficient machinery.
Incorporating sustainability into sourcing decisions not only enhances a company’s reputation but also leads to cost savings over time through reduced waste and energy consumption. Moreover, aligning with suppliers that prioritize sustainability can open up access to new markets and customer segments that value eco-conscious practices. For buyers from regions such as Africa and South America, where sustainable development is a key focus, these practices can significantly enhance competitiveness.
What Is the Evolution and Historical Context of M Codes in CNC Technology?
The evolution of M codes in CNC technology dates back to the early days of computer numerical control in the 1950s. Initially, M codes were developed to manage auxiliary functions of CNC machines, such as tool changes and spindle control. Over the decades, as CNC technology advanced, the complexity and functionality of M codes expanded significantly.
In the 1980s, the integration of computerization into CNC processes marked a turning point, leading to the widespread adoption of M codes across various machine types. This evolution has enabled manufacturers to streamline operations and improve efficiency, making it crucial for B2B buyers to understand the specific M codes relevant to their machinery. Today, M codes play a vital role in ensuring precision and flexibility in modern manufacturing processes, making knowledge of these codes essential for effective sourcing and operational success.
By recognizing the historical significance and current trends associated with M codes, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with technological advancements and market demands.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of m codes for cnc
-
How do I troubleshoot issues with M codes in CNC machines?
Troubleshooting M code issues typically involves checking the machine’s manual for specific M code functions and ensuring the correct codes are being used. Verify that the machine is properly set up for the intended operation, and examine the control system for any errors or alarms. Regular maintenance checks and keeping the machine’s software updated can also help prevent issues. If problems persist, consult with the manufacturer’s technical support for detailed assistance. -
What is the best way to choose M codes for specific CNC applications?
Selecting the best M codes depends on the type of CNC operation you are performing. For instance, M codes for spindle control, coolant management, and tool changes are crucial for milling applications. Review the machine’s manual to identify the M codes that align with your operational needs. Additionally, consider the specific materials you are machining and the intricacies of your designs to ensure optimal performance. -
How do I ensure the compatibility of M codes across different CNC machines?
M code compatibility can vary significantly between different CNC machine brands and models. To ensure compatibility, always refer to the specific machine’s manual for its designated M codes. It may be beneficial to standardize your operations by using machines from the same manufacturer or models known for similar programming structures. Conducting thorough testing of M codes in a controlled environment before full-scale production is also advisable. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) when sourcing M codes from suppliers?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for M code programming services or related CNC software can vary based on the supplier and the complexity of the codes required. Typically, suppliers may set MOQs based on production costs and the level of customization needed. It’s crucial to discuss your specific requirements with potential suppliers to negotiate favorable terms, especially if you are a small or medium-sized enterprise. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing M code services internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases can vary widely depending on the supplier’s policies and the buyer’s negotiation. Common terms include upfront payments, partial payments before delivery, or payment upon receipt. For international transactions, consider using secure payment methods like letters of credit or escrow services to mitigate risks. Always clarify payment terms in the contract to avoid misunderstandings. -
How do I verify the quality assurance processes of suppliers for M code programming?
To verify a supplier’s quality assurance processes, request documentation of their certifications and quality control measures. Inquire about their experience in CNC programming and ask for references from previous clients. Conducting site visits or audits can also provide insights into their operational standards. Look for suppliers that have established quality benchmarks and regularly conduct tests to ensure the accuracy of their M codes. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing M codes from international suppliers?
When sourcing M codes internationally, consider logistics factors such as shipping times, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Establish clear communication with your supplier regarding delivery timelines and tracking options. Additionally, factor in any risks related to international shipping, such as delays or damages, and consider using logistics partners experienced in handling CNC equipment and software. -
How can I customize M codes to better suit my CNC machining needs?
Customizing M codes requires a clear understanding of your specific machining processes and goals. Work closely with your CNC programmer or supplier to define the necessary modifications. Many suppliers offer customization services, allowing you to tailor M codes for unique operations or machines. Ensure that any custom codes are thoroughly tested to maintain machine safety and operational efficiency before implementing them in production.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for m codes for cnc
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers in M Codes for CNC?
In summary, understanding M codes is essential for optimizing CNC machining operations. These miscellaneous codes control various machine functions, allowing for enhanced precision and efficiency in manufacturing processes. By strategically sourcing CNC machines and components that utilize M codes effectively, international buyers can significantly improve their production capabilities while reducing operational costs.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Operational Efficiency?
Strategic sourcing not only streamlines procurement but also ensures that businesses acquire high-quality machines and tools tailored to their specific needs. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, investing in the right CNC technology, complemented by a deep understanding of M codes, can lead to increased competitiveness in the global market.
What Should International B2B Buyers Do Next?
As the industry evolves, staying informed about advancements in CNC technology and M code applications is crucial. We encourage buyers to engage with suppliers, participate in industry forums, and explore training opportunities to deepen their knowledge. By proactively seeking partnerships and resources, you can position your business for future growth and success in the dynamic landscape of CNC machining.