Master the Art of Sourcing High-Quality CNC Machine Parts
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cnc machine parts
In today’s fast-paced industrial landscape, the demand for high-quality CNC machine parts is surging across global markets. These components are vital for precision manufacturing, enabling businesses to produce intricate designs with minimal waste and maximum efficiency. As international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek to enhance their manufacturing capabilities, understanding the nuances of sourcing CNC machine parts becomes paramount.
This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, covering essential topics including types of CNC machine parts, materials used, manufacturing and quality control processes, and key suppliers. We delve into the cost considerations and market dynamics that influence procurement decisions, ensuring that buyers are well-equipped to navigate the complexities of the global supply chain.
Furthermore, the guide addresses frequently asked questions, providing clarity on common concerns that can arise during the sourcing process. By leveraging the insights presented here, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that not only meet their operational needs but also align with their strategic goals.
In an increasingly interconnected world, this resource empowers businesses to optimize their sourcing strategies, ensuring access to the best CNC machine parts while fostering long-term partnerships with reliable suppliers. As you embark on this journey, equip yourself with the knowledge to thrive in the competitive landscape of CNC manufacturing.
Understanding cnc machine parts Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spindle | High-speed rotation, precise control | Machining operations, milling | Pros: Essential for precision; Cons: High maintenance costs. |
| Linear Guides | Smooth motion, minimal friction, high load capacity | CNC routers, milling machines | Pros: Enhances accuracy; Cons: Requires careful installation. |
| Ball Screws | Converts rotary motion to linear motion with minimal backlash | CNC lathes, machining centers | Pros: High efficiency; Cons: Sensitive to contamination. |
| Control Systems | Software-driven, integrates with various CNC components | Automation, real-time monitoring | Pros: Flexibility in operations; Cons: Complexity can require training. |
| Tool Holders | Variety of designs (collet, chuck) for different tools | Tool changes in milling and drilling | Pros: Versatility; Cons: Quality varies significantly. |
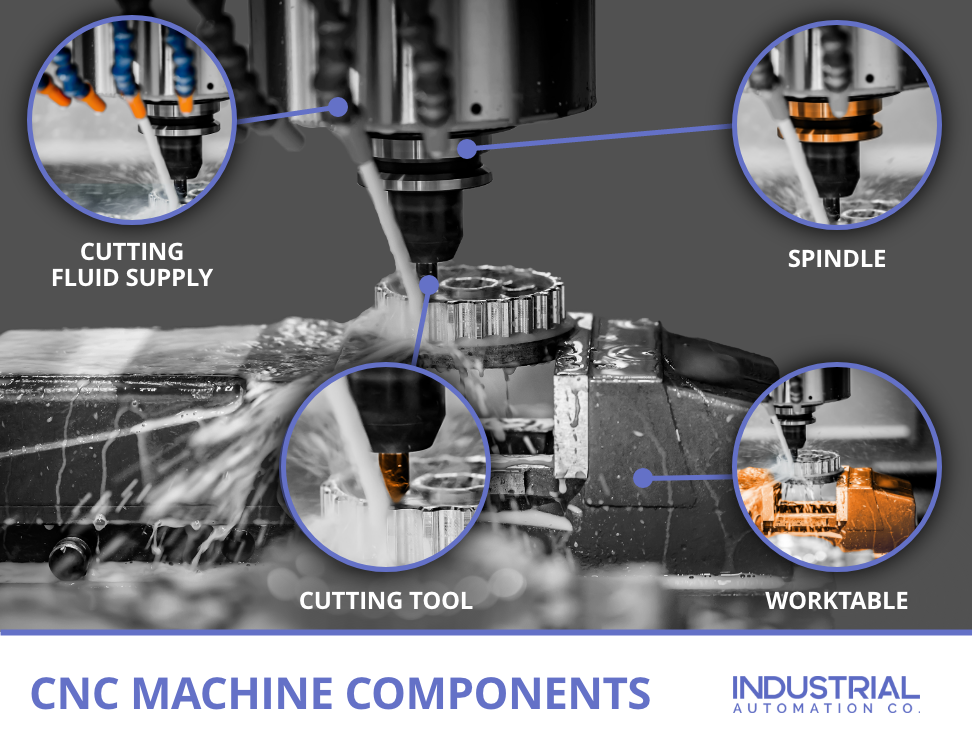
Spindle
The spindle is a critical component in CNC machines, responsible for the high-speed rotation necessary for machining operations. It is characterized by its ability to maintain precise control over speed and torque. For B2B buyers, selecting the right spindle involves considering the machine’s operational requirements and the materials being processed. High-quality spindles can enhance productivity but may come with higher maintenance costs, which should be factored into the total cost of ownership.
Linear Guides
Linear guides provide smooth and precise motion to CNC machines, minimizing friction and allowing for high load capacities. They are essential for applications requiring high accuracy, such as CNC routers and milling machines. When purchasing linear guides, buyers should assess factors like load ratings and installation requirements. While they significantly enhance the accuracy of the machine, the installation process can be complex, necessitating skilled labor to ensure optimal performance.
Ball Screws
Ball screws are vital for converting rotary motion into linear motion with minimal backlash, making them ideal for CNC lathes and machining centers. Their efficiency and precision are key selling points, especially for high-speed applications. Buyers should consider the environment in which ball screws will operate, as they are sensitive to contamination. Proper maintenance and the selection of high-quality ball screws can lead to significant performance improvements, but they may require more rigorous upkeep than other components.
Control Systems
Control systems are the brain of CNC machines, integrating various components and allowing for automation and real-time monitoring. These systems vary in complexity and capability, impacting how operators interact with the machine. B2B buyers need to evaluate the flexibility of the control system based on their specific operational needs. While advanced systems offer greater functionality, they can also introduce a learning curve for operators, which may necessitate training investments.
Tool Holders
Tool holders come in various designs, such as collets and chucks, and are essential for securing tools during machining processes. Their versatility allows for quick tool changes in milling and drilling applications. Buyers should consider the compatibility of tool holders with their existing tools and machines, as the quality can vary widely. Investing in high-quality tool holders can improve machining efficiency, but it’s crucial to ensure they meet specific operational requirements to avoid performance issues.
Related Video: How to Design Parts for CNC Machining
Key Industrial Applications of cnc machine parts
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of CNC Machine Parts | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Precision components for aircraft | Enhanced safety and performance; reduced weight | Certifications (e.g., AS9100), material specifications |
| Automotive | Engine and transmission parts | Improved efficiency and durability; cost savings | Quality assurance, OEM compatibility |
| Medical Devices | Surgical instruments and implants | High precision for patient safety; regulatory compliance | Biocompatibility, traceability |
| Electronics Manufacturing | Enclosures and circuit board supports | Reduced production time; improved product reliability | Tolerance levels, lead times |
| Oil & Gas | Custom fittings and valves | Increased operational efficiency; reduced downtime | Material strength, corrosion resistance |
Aerospace Industry
In the aerospace sector, CNC machine parts are crucial for producing high-precision components such as turbine blades, structural frames, and landing gear parts. These components must adhere to stringent safety and performance standards, making CNC machining ideal due to its ability to create intricate designs with tight tolerances. International buyers should prioritize suppliers with relevant certifications like AS9100, ensuring compliance with aerospace quality management systems. Additionally, material specifications must meet the rigorous demands of weight reduction without compromising strength.
Automotive Industry
CNC machine parts play a vital role in the automotive industry, particularly in manufacturing engine components, transmission parts, and chassis elements. The precision provided by CNC machining enhances the efficiency and durability of automotive parts, leading to improved vehicle performance and cost savings. Buyers should focus on sourcing from manufacturers that offer quality assurance processes and ensure compatibility with OEM specifications. Understanding the supply chain dynamics in various regions, especially in emerging markets, is critical for maintaining production timelines.
Medical Devices
In the medical device industry, CNC machine parts are essential for creating surgical instruments, implants, and diagnostic equipment. The high precision required in these applications ensures patient safety and compliance with regulatory standards. International buyers must pay close attention to the biocompatibility of materials used in production, as well as traceability throughout the manufacturing process. Establishing relationships with suppliers who understand the regulatory landscape in different regions can greatly enhance procurement efficiency.
Electronics Manufacturing
CNC machine parts are widely used in electronics manufacturing for producing enclosures, circuit board supports, and connectors. The ability to produce complex geometries quickly and reliably reduces production time and enhances product reliability. Buyers should consider tolerance levels and lead times when sourcing CNC parts, as these factors can significantly impact the overall production schedule. Additionally, partnering with suppliers who can offer rapid prototyping services can facilitate faster market entry for new electronic products.
Oil & Gas Industry
In the oil and gas sector, CNC machine parts are utilized for custom fittings, valves, and drilling components. These parts must withstand harsh environments, making material strength and corrosion resistance critical factors in the sourcing process. Efficiently manufactured parts can lead to increased operational efficiency and reduced downtime during critical extraction processes. International buyers should evaluate suppliers based on their experience in producing robust components and their ability to meet strict quality standards specific to the oil and gas industry.
Related Video: CNC Machine Working Process 5 Axis Machining Metal & Aluminium Aerospace
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cnc machine parts
When selecting materials for CNC machine parts, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that affect performance, durability, and cost. The following analysis covers four common materials used in CNC machining, highlighting their properties, advantages, and specific considerations for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Aluminum Alloys
Key Properties: Aluminum alloys are lightweight, with excellent corrosion resistance and good thermal conductivity. They typically have a temperature rating up to 150°C, making them suitable for various applications.
Pros & Cons: Aluminum is durable yet lightweight, which can reduce shipping costs. However, it can be more expensive compared to some steel options and may require specialized machining techniques due to its softness.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with a wide range of media, including water and various oils, making it ideal for automotive and aerospace components.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN is crucial. Buyers should also consider local sourcing options to mitigate import duties and shipping delays.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel offers high corrosion resistance and can withstand temperatures up to 800°C. Its mechanical strength makes it suitable for high-stress applications.
Pros & Cons: While stainless steel is highly durable and resistant to wear, it is heavier and more expensive than aluminum. Machining stainless steel can also be more complex, requiring advanced tooling and techniques.
Impact on Application: This material is ideal for parts exposed to harsh environments, such as chemical processing and food production, due to its excellent media compatibility.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards like ASTM A240 and consider the availability of specific grades in their region. Understanding local market conditions can help in negotiating better prices.
Carbon Steel
Key Properties: Carbon steel is known for its high strength and toughness, with a temperature rating that can exceed 500°C. It is less resistant to corrosion compared to stainless steel.
Pros & Cons: Carbon steel is relatively inexpensive and easy to machine, making it a popular choice for many applications. However, its susceptibility to rust and corrosion can limit its use in certain environments.
Impact on Application: Suitable for structural components and parts that do not require high corrosion resistance, carbon steel is often used in construction and heavy machinery.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must be aware of local regulations regarding carbon steel usage, particularly in industries with strict compliance requirements. Familiarity with common standards like JIS G3101 can facilitate smoother transactions.
Plastics (e.g., PEEK, Nylon)
Key Properties: Engineering plastics like PEEK and Nylon offer good chemical resistance, lightweight properties, and can operate in temperatures up to 260°C. They are excellent insulators.
Pros & Cons: Plastics can be less expensive and easier to machine than metals, making them suitable for prototyping and low-volume production. However, they may not offer the same level of durability as metals in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: These materials are well-suited for applications requiring non-conductive properties, such as electrical components and insulators.
Considerations for International Buyers: Ensuring compliance with standards like ASTM D638 for plastics is essential. Buyers should also consider the environmental impact and recycling options for these materials, especially in regions with stringent regulations.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for cnc machine parts | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Alloys | Automotive and aerospace components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost than some steels | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Chemical processing and food production | High strength and corrosion resistance | More complex machining | High |
| Carbon Steel | Structural components in construction | Inexpensive and easy to machine | Susceptible to corrosion | Low |
| Plastics | Electrical components and insulators | Lightweight and easy to machine | Lower durability than metals | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide aims to empower international B2B buyers with the insights needed to make informed decisions regarding CNC machine parts, ensuring optimal performance and compliance with regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cnc machine parts
Understanding the Manufacturing Processes for CNC Machine Parts
The manufacturing of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machine parts is a complex process that requires precision and adherence to industry standards. For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these processes is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions.
Main Stages of Manufacturing
-
Material Preparation
– Selection of Raw Materials: The process begins with the selection of suitable raw materials, often metals like aluminum, steel, or titanium. The choice depends on the desired properties of the final product.
– Cutting and Shaping: Raw materials are cut into manageable sizes using saws or shears. This stage sets the foundation for the subsequent manufacturing steps. -
Forming
– CNC Machining: This stage employs CNC machines to shape the parts according to precise specifications. Techniques include turning, milling, and drilling, allowing for high accuracy and repeatability.
– Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): In some cases, parts may be produced using additive techniques, particularly for complex geometries that traditional methods cannot achieve. -
Assembly
– Component Assembly: If the part consists of multiple components, they are assembled using fasteners, welding, or adhesive bonding. This step is critical for ensuring functionality and durability.
– Sub-assembly Options: For larger projects, components may be pre-assembled into sub-units to streamline the final assembly process. -
Finishing
– Surface Treatment: Finishing processes such as anodizing, painting, or polishing enhance the part’s appearance and resistance to corrosion.
– Quality Checks: After finishing, parts undergo final inspections to ensure they meet the required specifications before being shipped.
Quality Assurance in CNC Manufacturing
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in the CNC manufacturing process, ensuring that parts meet both international and industry-specific standards. For B2B buyers, understanding these QA processes helps in assessing supplier reliability.
Relevant International Standards
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is essential for manufacturers aiming to ensure consistent quality in their products.
- Industry-Specific Certifications: Depending on the application, other certifications may be relevant, such as:
- CE Marking: For products sold in the European Economic Area, indicating compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For parts used in the oil and gas industry, ensuring safety and reliability.
Key Quality Control Checkpoints
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
– Material Inspection: Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications. This includes checking for any defects or inconsistencies. -
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
– Monitoring During Production: Throughout the manufacturing process, regular checks are performed to identify any deviations from specifications. This may involve measuring dimensions, tolerances, and surface finishes. -
Final Quality Control (FQC)
– End-of-Line Testing: Before shipping, products undergo final inspections and tests to verify their quality and compliance with standards.
Common Testing Methods
- Dimensional Inspection: Using calipers, micrometers, and CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machines) to verify the dimensions of machined parts.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing or X-ray inspection are used to detect internal defects without damaging the part.
- Functional Testing: Ensuring that parts perform as expected in real-world applications.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international buyers, particularly those from emerging markets, verifying a supplier’s quality assurance practices is crucial. Here are actionable steps:
-
Conduct Audits
– Supplier Audits: Request to conduct on-site audits of the manufacturing facility to assess their quality management systems and processes.
– Third-Party Audits: Engage third-party inspection firms to evaluate suppliers’ compliance with international standards. -
Review Quality Reports
– Quality Documentation: Request copies of quality control reports, including IQC, IPQC, and FQC findings, to assess the supplier’s historical performance.
– Certification Documentation: Ensure that all relevant certifications (ISO, CE, API) are current and valid. -
Utilize Third-Party Inspection Services
– Independent Inspections: Hire third-party inspection services to perform quality checks on the products before shipment. This adds an additional layer of assurance regarding the quality of the parts.
Navigating Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers
When dealing with suppliers from diverse regions, B2B buyers must be aware of potential differences in quality control practices. Here are several considerations:
- Cultural Differences: Different countries may have varying approaches to quality management. Understanding these cultural nuances can help in setting realistic expectations.
- Regulatory Compliance: Be aware of specific regulations that might affect product quality in different regions, especially when importing goods.
- Communication: Establish clear communication channels with suppliers to ensure that quality expectations are understood and met.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance mechanisms for CNC machine parts is essential for international B2B buyers. By focusing on the stages of production, adhering to international standards, and implementing rigorous quality control measures, buyers can ensure that they receive high-quality products that meet their specific needs. As global markets continue to evolve, staying informed about these processes will enhance procurement strategies and foster successful partnerships.
Related Video: The World’s Largest Bevel Gear CNC Machine- Modern Gear Production Line. Steel Wheel Manufacturing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cnc machine parts Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of CNC machine parts is crucial for international B2B buyers looking to optimize their sourcing strategies. This analysis delves into the key components of costs, the factors influencing pricing, and actionable tips for buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The choice of raw materials significantly affects the overall cost. Common materials used in CNC machining include aluminum, steel, titanium, and plastics. Fluctuations in the prices of these materials due to market demand or geopolitical factors can impact sourcing costs. Buyers should consider long-term contracts with suppliers to mitigate price volatility.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary widely depending on the manufacturing location. Regions with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but this can sometimes lead to compromises in quality. Understanding the local labor market and the skill level of workers is essential for ensuring that parts meet quality standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative expenses associated with production. Overhead can vary based on the efficiency of the manufacturing process and the scale of operations. Buyers should inquire about the supplier’s operational efficiencies to gauge potential cost savings.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs are a significant upfront investment, especially for custom parts. This includes the design and creation of molds, dies, and fixtures needed for production. Buyers should evaluate whether the supplier has the capability to amortize these costs over large production runs, which can lower per-unit costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing robust QC processes adds to the manufacturing cost but is crucial for ensuring the reliability and precision of CNC parts. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who adhere to international quality certifications, as this can mitigate risks associated with defective products.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can be substantial, especially for international shipments. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and customs duties must be considered. Buyers should explore various logistics options and choose Incoterms that minimize their exposure to unexpected costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin on top of their costs to ensure profitability. Understanding the competitive landscape can help buyers negotiate better terms. Researching market rates and establishing relationships with multiple suppliers can create leverage during negotiations.
Price Influencers
Several factors influence the pricing of CNC machine parts:
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk orders often result in lower unit prices due to economies of scale. Buyers should assess their needs and negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQ) that align with their production schedules.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized parts generally incur higher costs due to the additional design and tooling requirements. Buyers should provide clear specifications to avoid miscommunication and potential rework.
-
Materials: The choice of materials not only affects cost but also impacts the performance and durability of the parts. Buyers should balance cost against the functional requirements of the components.
-
Quality/Certifications: Higher-quality parts typically command higher prices. Certifications such as ISO 9001 or AS9100 can be indicators of a supplier’s commitment to quality and consistency.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, location, and production capabilities can significantly influence pricing. Buyers should conduct thorough due diligence to assess supplier reliability.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is vital for managing logistics costs and responsibilities. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can affect the total landed cost.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Leverage volume and long-term contracts during negotiations to achieve better pricing. Establishing a partnership with suppliers can lead to more favorable terms over time.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes not only purchase price but also logistics, maintenance, and potential downtime. This broader view can lead to smarter sourcing decisions.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing variations. Factors such as local economic conditions, tariffs, and trade agreements can influence costs. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should stay informed about these dynamics to make informed purchasing decisions.
Disclaimer
Prices mentioned are indicative and can vary significantly based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific project requirements. Always consult with multiple suppliers to gather accurate quotes tailored to your needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cnc machine parts
Critical Technical Properties of CNC Machine Parts
Understanding the essential technical properties of CNC machine parts is crucial for international B2B buyers. These specifications not only determine the performance and longevity of the parts but also influence purchasing decisions. Here are several key properties to consider:
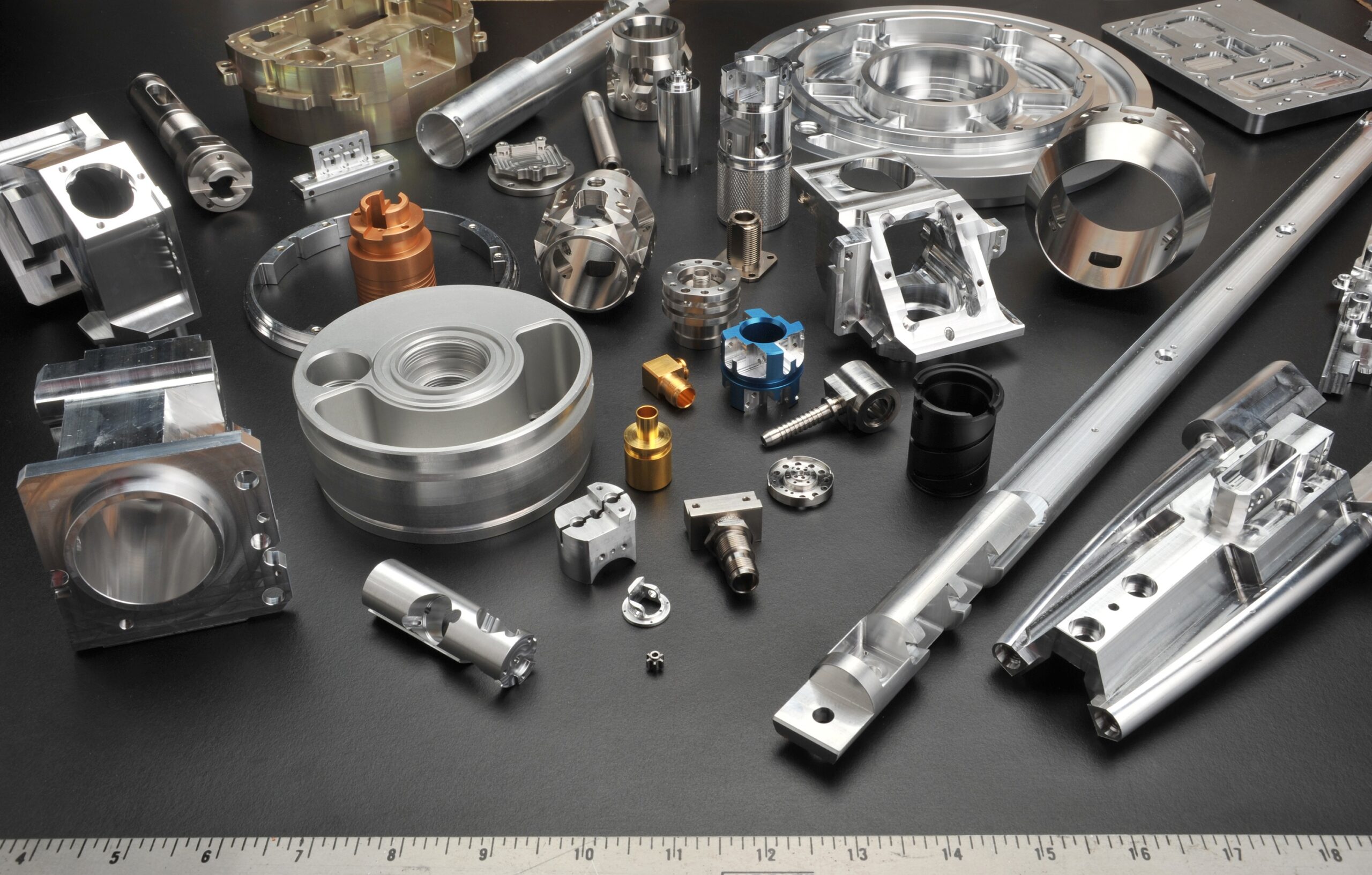

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Material Grade
– Definition: This refers to the specific type of material used in the manufacturing of CNC parts, such as aluminum, steel, or titanium. Each material grade has its unique characteristics, including strength, weight, and corrosion resistance.
– B2B Importance: Selecting the appropriate material grade ensures the part meets the specific demands of the application, such as load capacity and environmental conditions. Buyers must assess material compatibility with their operational requirements to avoid costly failures. -
Tolerance
– Definition: Tolerance indicates the permissible limit or limits of variation in a physical dimension. It is crucial for ensuring that parts fit together correctly during assembly.
– B2B Importance: Tight tolerances can lead to higher production costs, while loose tolerances may result in poor performance. Understanding tolerance requirements helps buyers negotiate effectively with suppliers and ensures quality control in production. -
Surface Finish
– Definition: This refers to the texture and smoothness of the part’s surface, which can affect both aesthetics and functionality.
– B2B Importance: A proper surface finish can enhance a part’s performance by reducing friction and wear. Buyers should specify surface finish requirements to meet both functional and regulatory standards. -
Heat Treatment
– Definition: Heat treatment involves processes like annealing, hardening, or tempering to alter the physical and sometimes chemical properties of a material.
– B2B Importance: Parts that undergo heat treatment can achieve enhanced strength and resistance to wear. Understanding these processes allows buyers to select parts that will perform better under stress. -
Mechanical Properties
– Definition: These include characteristics such as tensile strength, yield strength, and ductility, which define how a material behaves under various types of stress.
– B2B Importance: Knowing the mechanical properties helps buyers assess whether a material will withstand operational demands, thereby preventing unexpected breakdowns and increasing productivity.
Common Trade Terminology in CNC Parts
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the CNC parts market. Here are several common terms to know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– B2B Importance: Understanding the role of OEMs helps buyers identify reliable sources for high-quality parts that are compatible with existing systems. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– B2B Importance: Knowing the MOQ is critical for budgeting and inventory management. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their operational needs without overcommitting financially. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services.
– B2B Importance: Issuing an RFQ helps buyers gather competitive pricing and terms, enabling informed decision-making. A well-structured RFQ can streamline the procurement process. -
Incoterms
– Definition: International Commercial Terms (Incoterms) are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions.
– B2B Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms is vital for understanding shipping costs, insurance, and liability. This knowledge enables buyers to negotiate better terms and avoid misunderstandings in international trade.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Lead Time
– Definition: Lead time is the period between the initiation of an order and its completion.
– B2B Importance: Understanding lead times is crucial for inventory planning and project timelines. Buyers should communicate their timelines clearly to suppliers to ensure timely delivery. -
Certification
– Definition: Certification refers to the validation of a product or supplier against industry standards or regulations.
– B2B Importance: Certifications can provide assurance of quality and compliance, which is essential for maintaining operational standards. Buyers should prioritize suppliers with relevant certifications to mitigate risk.
In summary, a solid grasp of these technical properties and trade terminology will empower international B2B buyers to make informed decisions when sourcing CNC machine parts, ensuring optimal performance and cost-effectiveness in their operations.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the cnc machine parts Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machine parts sector is experiencing significant growth driven by the increasing demand for precision engineering across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and electronics. As international B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it is crucial to understand the key dynamics shaping this market.
Global Drivers:
The rise of automation and Industry 4.0 is a major factor propelling the CNC machine parts market. Enhanced efficiency and productivity through the integration of IoT (Internet of Things) and AI (Artificial Intelligence) technologies are reshaping sourcing strategies. Buyers should leverage these technologies to improve supply chain visibility and reduce lead times.
Current and Emerging Trends:
– Digital Transformation: The adoption of digital tools for procurement, such as e-procurement platforms, is streamlining the sourcing process. Buyers should consider platforms that offer real-time analytics for better decision-making.
– Customization and Additive Manufacturing: There’s a growing trend towards customized machine parts, facilitated by advances in additive manufacturing. Buyers should engage suppliers who can offer tailored solutions to meet specific operational needs.
– Global Supply Chain Resilience: The pandemic highlighted vulnerabilities in global supply chains. Buyers must prioritize suppliers with robust contingency plans and diversified sourcing strategies to mitigate risks.
Understanding these trends will empower B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions, enhancing their competitive edge in their respective markets.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
As global awareness of environmental issues increases, sustainability is becoming a core consideration for B2B buyers in the CNC machine parts sector. The environmental impact of sourcing and manufacturing processes necessitates a shift towards more sustainable practices.
Importance of Ethical Supply Chains:
Implementing ethical sourcing practices is essential not only for compliance with regulations but also for building brand reputation. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate transparency in their supply chains and adhere to ethical labor practices. This includes ensuring that materials are sourced responsibly and that fair labor conditions are maintained.
Green Certifications and Materials:
Investing in suppliers that hold recognized green certifications (such as ISO 14001) can help buyers ensure that they are partnering with environmentally responsible companies. Additionally, sourcing machine parts made from recycled or eco-friendly materials can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of operations. Buyers are encouraged to inquire about the sustainability practices of their suppliers, including the use of renewable energy sources in production processes.
Focusing on sustainability not only meets regulatory requirements but also aligns with the growing consumer demand for environmentally friendly products, thereby enhancing market competitiveness.
Brief Evolution/History
The CNC machine parts sector has evolved significantly since the introduction of CNC technology in the 1940s and 1950s. Initially utilized for basic machining tasks, the technology has advanced to include sophisticated software that integrates with CAD (Computer-Aided Design) systems, allowing for high levels of customization and precision.
Over the decades, the sector has embraced innovations such as multi-axis machining and automation, leading to improved efficiencies and capabilities. As CNC technology continues to evolve, it offers international B2B buyers unprecedented opportunities to enhance their operational efficiency and product quality. Understanding this evolution provides valuable context for making strategic sourcing decisions today.
Related Video: Incoterms for beginners | Global Trade Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cnc machine parts
-
What factors should I consider when vetting suppliers for CNC machine parts?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their industry experience, reputation, and customer reviews. Request references from previous clients, particularly those in your region, to understand their reliability. Evaluate their certifications, such as ISO, which indicate quality management systems. Additionally, assess their production capabilities and technology used in manufacturing. Conducting site visits or virtual inspections can further ensure that the supplier meets your quality expectations. -
Can CNC machine parts be customized, and what are the implications?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for CNC machine parts to meet specific requirements. Discuss your needs early in the negotiation process, including dimensions, materials, and tolerances. Customization may affect the minimum order quantity (MOQ) and lead times, often increasing both. Ensure that the supplier has a robust design and prototyping process to minimize risks during production. Clear communication regarding specifications is crucial to avoid misunderstandings. -
What are the common minimum order quantities (MOQs) for CNC machine parts?
MOQs for CNC machine parts can vary significantly based on the supplier, the complexity of the part, and the materials used. Typically, MOQs range from a few pieces to several hundred. When negotiating, consider your budget and storage capabilities, as ordering more than you need can lead to excess inventory. If you require smaller quantities, look for suppliers that specialize in low-volume production or are open to negotiating MOQs based on your needs. -
How do lead times for CNC machine parts vary, and what should I expect?
Lead times for CNC machine parts depend on factors like part complexity, supplier location, and production capacity. Standard lead times can range from 2 to 12 weeks. When sourcing internationally, account for additional time related to customs clearance and logistics. Always ask for a detailed timeline and be clear about your project deadlines. Establishing a good relationship with your supplier can also help in expediting processes when necessary. -
What payment methods are typically accepted by CNC machine parts suppliers?
Most CNC machine parts suppliers accept various payment methods, including bank transfers, credit cards, and letters of credit. It’s essential to discuss payment terms upfront, including deposits, payment schedules, and final payment upon delivery. Be cautious of suppliers requiring full payment in advance, as this can increase risk. Using secure payment methods can provide additional protection against fraud, especially when dealing with international suppliers. -
What quality assurance (QA) measures should I look for in suppliers?
When assessing suppliers, inquire about their quality assurance processes, including inspection protocols and testing methods. Look for suppliers that adhere to international quality standards, such as ISO 9001. Request documentation of their QA practices, including certifications and test reports for previous orders. Additionally, ensure they have a clear process for handling defects and returns, as this reflects their commitment to quality and customer satisfaction. -
How can I manage logistics effectively when sourcing CNC machine parts internationally?
Effective logistics management involves coordinating with freight forwarders, understanding customs regulations, and selecting reliable shipping methods. Communicate with your supplier about packaging and labeling requirements to ensure compliance with international shipping standards. Consider using a logistics partner experienced in B2B international trade to streamline the process. Additionally, staying informed about potential delays, such as customs inspections, will help you manage expectations and project timelines. -
What steps should I take if a dispute arises with a supplier?
In the event of a dispute, first, attempt to resolve the issue through direct communication with the supplier. Document all correspondence and agreements to reference during discussions. If the issue cannot be resolved amicably, consult the terms outlined in your contract regarding dispute resolution. Consider mediation or arbitration as alternatives to litigation, as they can be more cost-effective and quicker. Engaging legal counsel familiar with international trade can also provide guidance on navigating complex disputes.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cnc machine parts
As the landscape for CNC machine parts continues to evolve, strategic sourcing remains paramount for international buyers. The key takeaways underscore the importance of understanding local market dynamics, supplier reliability, and cost efficiency. By prioritizing these factors, businesses can mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions and quality inconsistencies, ensuring they remain competitive in their respective industries.
Moreover, leveraging technology and data analytics can enhance decision-making processes, allowing buyers to identify optimal sourcing strategies tailored to their specific needs. Collaborating with suppliers who share a commitment to sustainability and innovation can also yield long-term benefits, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, where emerging markets present unique opportunities.
Looking ahead, the demand for high-quality CNC machine parts is set to rise, driven by advancements in manufacturing technologies and increasing automation. International B2B buyers from Europe, the Middle East, and beyond are encouraged to engage proactively with suppliers, fostering partnerships that align with their strategic goals. By doing so, they can not only secure a competitive edge but also contribute to a more resilient and sustainable global supply chain.