Maximize Efficiency: The Complete Gear Drive Guide (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for gear drive
Navigating the global market for gear drive systems can be daunting for international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in dynamic markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The challenge lies in not only sourcing high-quality gear drives but also ensuring they meet the specific requirements of various applications, from automotive to industrial machinery. This guide addresses these complexities by providing a comprehensive overview of gear drive types, applications, and key considerations for supplier vetting and cost analysis.
In this guide, buyers will explore the diverse landscape of gear drives, including enclosed gear units, gear motors, and shaft-mounted speed changers, each with unique characteristics and benefits. We will delve into the critical factors influencing the selection process, such as performance reliability, maintenance requirements, and compliance with international standards. Additionally, we will offer insights into effective supplier evaluation strategies, helping buyers identify reputable manufacturers that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
By equipping B2B buyers with actionable insights and practical tools, this guide empowers them to make informed purchasing decisions that enhance operational efficiency and competitiveness. Whether you are sourcing gear drives for a new project or optimizing existing systems, understanding the nuances of the global gear drive market is essential for success in today’s interconnected business landscape.
Understanding gear drive Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enclosed Gear Unit | Compact design; integrated with supporting structure | Heavy machinery, manufacturing equipment | Pros: Space-efficient, durable. Cons: Limited customization options. |
| Gear Motor | Combines motor and gear unit; compact integration | Robotics, conveyor systems | Pros: Simplified installation, reduced footprint. Cons: Potential overheating issues. |
| Shaft Mounted Speed Changer | Directly mounted on input shaft; minimal space usage | Agricultural machinery, construction vehicles | Pros: Easy installation, high efficiency. Cons: May require frequent maintenance. |
| Planetary Gear System | Multiple gears rotate around a central gear | Automotive, aerospace applications | Pros: High torque density, compact design. Cons: Complex design may lead to higher costs. |
| Bevel Gear Drive | Allows for change in axis direction; angular motion | Marine applications, automotive differentials | Pros: Versatile design, effective in tight spaces. Cons: Requires precise alignment for optimal performance. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of Enclosed Gear Units?
Enclosed gear units are designed for compactness and durability, making them ideal for heavy machinery and manufacturing equipment. These units integrate the driver and gears within a protective casing, which enhances their longevity and reduces the risk of contamination. B2B buyers should consider the unit’s size, weight capacity, and the potential for customization based on specific operational needs.
How Do Gear Motors Benefit Robotics and Conveyor Systems?
Gear motors combine a motor and gear unit into a single compact assembly, making them highly suitable for applications in robotics and conveyor systems. Their integration simplifies installation and reduces the overall footprint of machinery. When purchasing, buyers should evaluate the motor’s power output, efficiency ratings, and heat dissipation capabilities, as these factors directly impact operational performance.
What Should Buyers Know About Shaft Mounted Speed Changers?
Shaft mounted speed changers are designed to be directly attached to the input shaft of a driven machine, minimizing space requirements. Commonly used in agricultural machinery and construction vehicles, these units are valued for their ease of installation and high efficiency. Buyers should assess the maintenance requirements and the expected lifecycle of the speed changer to ensure long-term reliability.
Why Choose Planetary Gear Systems for Automotive and Aerospace Applications?
Planetary gear systems feature a central gear (the sun gear) surrounded by multiple gears (planet gears), providing high torque density in a compact design. This makes them particularly advantageous for automotive and aerospace applications where space is at a premium. B2B buyers should consider the complexity of the design, which can lead to higher costs, but also offers superior performance and durability.
What are the Advantages of Bevel Gear Drives in Marine Applications?
Bevel gear drives are designed to change the direction of motion between shafts that are at an angle to each other, making them particularly effective in marine applications and automotive differentials. Their versatility allows them to fit into tight spaces while maintaining efficient power transmission. Buyers should focus on alignment precision and material quality to ensure optimal performance and longevity in demanding environments.
Key Industrial Applications of gear drive
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of gear drive | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Transmission systems in vehicles | Enhances performance and efficiency in power transmission | Compatibility with existing systems; durability; supplier reliability |
| Manufacturing | Conveyor systems for material handling | Increases production efficiency and reduces downtime | Load capacity; speed requirements; maintenance support |
| Mining | Drive systems for heavy machinery | Improves operational reliability and extends equipment life | Environmental conditions; torque specifications; service availability |
| Agriculture | Gear drives in tractors and harvesters | Boosts productivity and operational efficiency | Adaptability to different terrains; power requirements; local support |
| Renewable Energy | Wind turbine gearboxes | Maximizes energy conversion and operational lifespan | Efficiency ratings; material quality; compliance with local standards |
How is Gear Drive Used in the Automotive Sector?
In the automotive industry, gear drives are integral to transmission systems, enabling efficient power transfer from the engine to the wheels. They solve problems related to torque management and speed variation, which are critical for vehicle performance. Buyers in this sector, especially from regions like Europe and South America, should focus on compatibility with existing vehicle systems and the durability of materials used in gear construction. Additionally, understanding local regulations regarding emissions and efficiency can influence sourcing decisions.
What Role Does Gear Drive Play in Manufacturing?
In manufacturing, gear drives are crucial for conveyor systems that transport materials and products. They increase production efficiency by ensuring smooth and controlled movement, thereby reducing downtime caused by mechanical failures. International buyers, particularly in Africa and the Middle East, must consider load capacity and speed requirements when sourcing gear drives. Furthermore, maintenance support and the availability of spare parts are essential factors to ensure uninterrupted operations.

A stock image related to gear drive.
How is Gear Drive Essential in the Mining Industry?
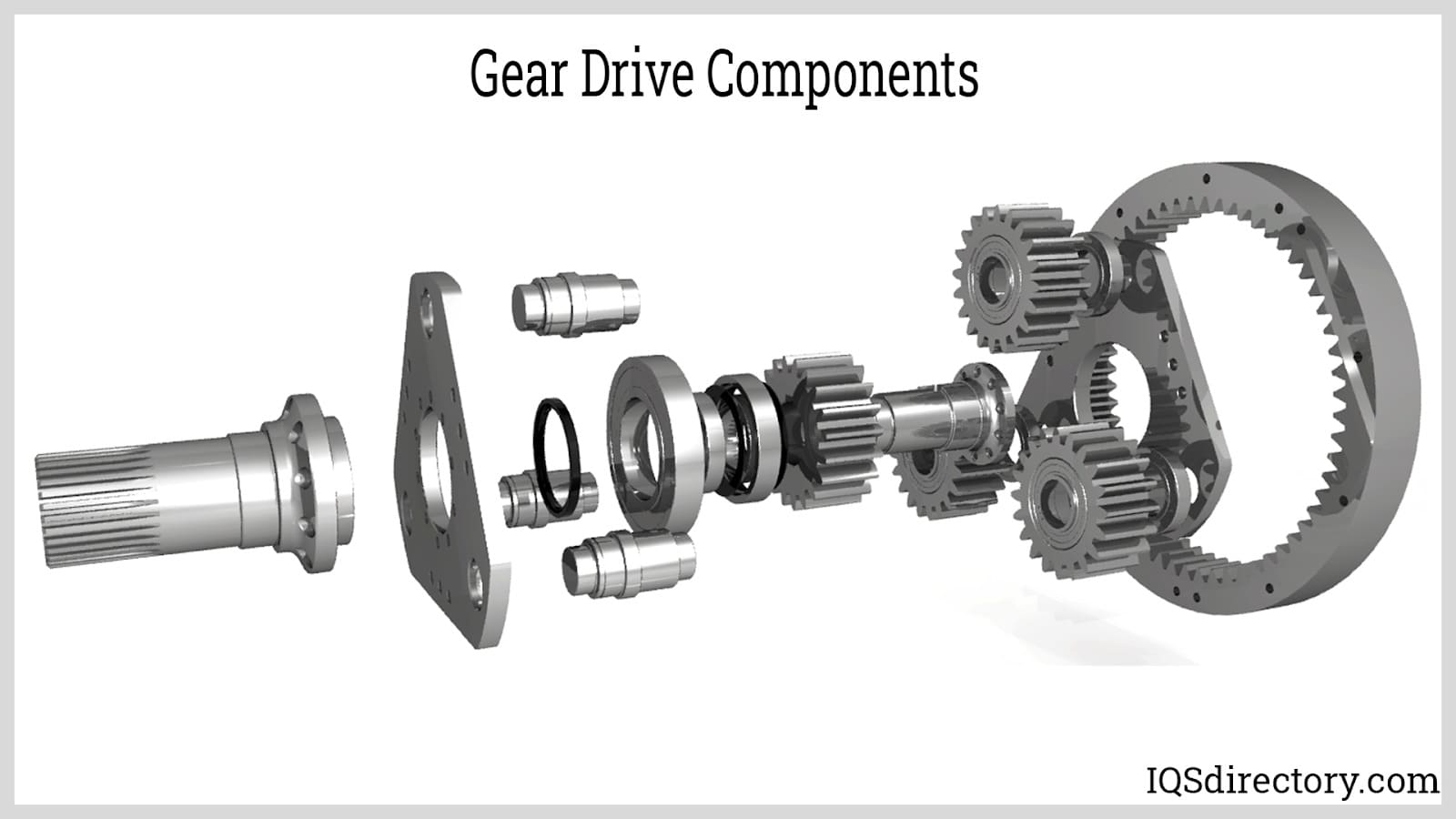
A stock image related to gear drive.
In the mining sector, gear drives are utilized in heavy machinery, such as excavators and haul trucks, to enhance operational reliability. They address challenges related to high torque and harsh environmental conditions, ensuring that equipment remains functional under extreme loads. Buyers from mining operations in South America and Africa should prioritize specifications that cater to their specific environmental conditions and torque requirements. Additionally, sourcing from suppliers who offer robust service and support in remote locations can significantly impact operational success.
Why are Gear Drives Important for Agriculture?
In agriculture, gear drives are used in tractors and harvesters to improve productivity and efficiency. They facilitate the transfer of power to various attachments, enhancing the operational capabilities of farming equipment. Buyers in regions like Europe and Africa should consider the adaptability of gear drives to different terrains and the specific power requirements of their machinery. Local support and service availability are also critical to minimize downtime during peak agricultural seasons.
How Do Gear Drives Enhance Renewable Energy Solutions?
In the renewable energy sector, particularly in wind turbines, gear drives play a vital role in converting kinetic energy into electrical energy. They maximize energy conversion efficiency and extend the operational lifespan of turbines. Buyers from Europe, which is heavily invested in renewable energy, should focus on efficiency ratings and the quality of materials used in gear construction. Compliance with local environmental standards and regulations is also a significant consideration when sourcing gear drives for this application.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘gear drive’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Ensuring Compatibility with Existing Machinery
The Problem: One of the most significant challenges for B2B buyers in sectors such as manufacturing and construction is ensuring that new gear drive systems are compatible with existing machinery. Incompatibilities can lead to costly downtimes and necessitate expensive retrofitting, which can disrupt production schedules and inflate operational costs. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America, where machinery might be older or custom-made, often face heightened risks of mismatch, leading to frustration and financial losses.
The Solution: To mitigate compatibility issues, B2B buyers should conduct a thorough compatibility assessment before purchasing gear drives. This involves gathering detailed specifications of existing machinery, including shaft dimensions, load capacities, and operational speeds. Engaging with suppliers who offer customization options can be beneficial, as they can tailor gear drives to specific requirements. Additionally, utilizing advanced modeling software can help visualize the integration of new gear systems into existing setups, ensuring that all operational parameters are met without the need for significant modifications. Regular communication with manufacturers about specific needs and expected performance can also lead to better-tailored solutions.
Scenario 2: Addressing Noise and Vibration Concerns
The Problem: Noise and vibration issues are prevalent with gear drive systems, particularly in heavy machinery used in sectors like mining and construction. Excessive noise not only affects operator comfort but can also lead to regulatory compliance issues in countries with strict environmental standards. B2B buyers from Europe and the Middle East may find that their existing gear drive systems produce disruptive noise levels, leading to potential penalties or operational restrictions.
The Solution: To address noise and vibration concerns, buyers should prioritize the selection of gear drives that are designed with sound-dampening features. Considerations such as gear material, tooth design, and lubrication methods can significantly impact noise levels. For instance, opting for helical gears instead of spur gears can reduce operational noise. Furthermore, implementing vibration isolation mounts and ensuring proper alignment during installation can minimize vibration transmission. Buyers should also consult with manufacturers about noise ratings and seek gear drives that have been tested in similar applications to ensure they meet performance expectations. Regular maintenance and monitoring can help identify potential noise issues before they escalate.
Scenario 3: Managing Maintenance and Downtime
The Problem: Another critical pain point for B2B buyers is the maintenance of gear drive systems. Many companies experience unexpected downtime due to gear failures or inadequate maintenance practices, resulting in lost revenue and delayed project timelines. This issue is particularly pressing for buyers in South America and Africa, where access to skilled technicians and replacement parts may be limited, leading to extended periods of inactivity.
The Solution: To effectively manage maintenance and minimize downtime, B2B buyers should invest in a proactive maintenance strategy that includes regular inspections and predictive maintenance technologies. Utilizing condition monitoring systems can help detect early signs of wear and tear, allowing for timely interventions before a complete failure occurs. Additionally, partnering with suppliers who offer comprehensive service agreements can ensure access to expert support and genuine replacement parts when needed. Implementing a training program for in-house maintenance staff on the specific requirements of gear drives can also enhance operational efficiency. Finally, documenting maintenance activities and performance history can help buyers identify patterns and optimize their maintenance schedules, thus reducing the likelihood of unexpected failures.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for gear drive
What Are the Key Materials Used in Gear Drive Manufacturing?
When selecting materials for gear drives, it is crucial to consider the specific requirements of the application, including performance, cost, and compliance with international standards. Below are analyses of four common materials used in gear drive manufacturing, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
Steel: The Most Common Choice for Gear Drives
Key Properties: Steel is known for its high tensile strength, durability, and ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures. It typically has good fatigue resistance and can be treated to enhance its properties further.
Pros & Cons: Steel’s advantages include its robustness and ability to handle heavy loads, making it suitable for various industrial applications. However, it can be prone to corrosion if not properly treated or coated, which can affect its longevity. Additionally, the manufacturing process can be complex, leading to higher costs.
Impact on Application: Steel gears are compatible with a wide range of media, including oils and lubricants, which helps maintain performance under various conditions. However, in environments with high humidity or corrosive substances, additional protective coatings may be necessary.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM A572 or DIN 17200 for steel quality. In Africa and South America, sourcing steel that meets these standards can be challenging, so local availability and supplier reliability are critical.
Aluminum: Lightweight and Corrosion-Resistant
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, has good corrosion resistance, and offers decent strength-to-weight ratios. It is also non-magnetic and has excellent thermal conductivity.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its lightweight nature, which can lead to reduced energy consumption in applications where weight is a critical factor. However, aluminum is generally less durable than steel and may not perform well under extreme loads or high temperatures.
Impact on Application: Aluminum gears are particularly suitable for applications in automotive and aerospace industries where reducing weight is essential. However, they may not be suitable for heavy-duty applications requiring high torque.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should look for compliance with standards such as ASTM B221 or JIS H4000. In regions like South America, where aluminum may be less common, ensuring that suppliers can provide certified materials is essential.
Cast Iron: A Strong Contender for Heavy-Duty Applications
Key Properties: Cast iron is known for its excellent wear resistance, good machinability, and ability to dampen vibrations. It can withstand high loads and has a high compressive strength.
Pros & Cons: The durability of cast iron makes it ideal for heavy-duty applications, but it is relatively brittle compared to steel. This brittleness can lead to fractures under sudden impacts. Additionally, cast iron is heavier, which may not be suitable for all applications.
Impact on Application: Cast iron gears are often used in applications such as construction machinery and heavy industrial equipment. They perform well in environments where high loads and vibrations are present.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM A48 is crucial for ensuring quality. Buyers in Africa and the Middle East should consider local sourcing options to reduce costs and ensure material availability.
Plastic: The Emerging Material for Lightweight Applications
Key Properties: Modern engineering plastics, such as Nylon and PEEK, offer good strength, low weight, and excellent corrosion resistance. They can also operate effectively in a wide temperature range.
Pros & Cons: The lightweight nature of plastic gears can lead to significant energy savings. They are also quieter in operation compared to metal gears. However, plastics may not handle high loads as effectively as metals, leading to potential wear issues over time.
Impact on Application: Plastic gears are often used in consumer products, robotics, and applications where noise reduction is important. They are generally not suitable for high-stress environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the plastics used meet relevant standards, such as ASTM D638 or ISO 1043. In Europe, compliance with REACH regulations for chemical safety is also essential.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Gear Drives
| Material | Typical Use Case for gear drive | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy industrial applications | High strength and durability | Prone to corrosion | High |
| Aluminum | Automotive and aerospace | Lightweight | Less durable under heavy loads | Medium |
| Cast Iron | Construction machinery | Excellent wear resistance | Brittle under impact | Medium |
| Plastic | Consumer products and robotics | Lightweight and quiet operation | Limited load capacity | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions based on performance requirements, cost considerations, and compliance with regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for gear drive
What Are the Main Manufacturing Processes for Gear Drives?
Manufacturing gear drives involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets performance and quality standards. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each of these stages employs specific techniques to create durable and efficient gear drives that can withstand demanding industrial applications.
How Is Material Prepared for Gear Drive Manufacturing?
Material preparation begins with selecting high-quality raw materials, typically alloy steels or specialized composites, which offer the necessary strength and wear resistance. The materials undergo processes such as heat treatment to enhance their properties. This stage also includes cutting the materials into precise dimensions, ensuring that they meet design specifications.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Gear Drive Manufacturing?
The forming stage employs various techniques, including:
- Hobbing: This process uses a hob cutter to create gear teeth profiles. It’s efficient for producing large quantities of gears with high precision.
- Shaping and Broaching: These methods are used for producing internal gears and specialized shapes. They ensure accuracy in tooth geometry.
- Forging: Often used for high-strength applications, forging can produce complex shapes while enhancing the material’s grain structure.
Each of these techniques is chosen based on the design requirements and the intended application of the gear drive.
How Is Gear Drive Assembly Conducted?
The assembly stage is crucial, as it brings together all individual components—gears, shafts, bearings, and housings. It involves:
- Alignment: Ensuring that all components are correctly aligned to prevent premature wear and failure.
- Lubrication: Applying appropriate lubricants to minimize friction and heat generation during operation.
- Securing: Using fasteners, welding, or adhesive bonding to ensure that all parts are securely held together.
Attention to detail in this stage is vital for achieving optimal performance in the final product.
What Finishing Techniques Are Applied to Gear Drives?
Finishing techniques enhance the surface quality and performance of gear drives. Common methods include:
- Grinding: This process refines the surface finish and improves the dimensional accuracy of gear teeth.
- Coating: Applying surface treatments such as hardening or anti-corrosion coatings to improve durability and resistance to wear.
- Polishing: A final step to ensure smooth surfaces, reducing friction and enhancing the operational lifespan.
These finishing processes contribute significantly to the overall reliability and efficiency of gear drives.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Implemented in Gear Drive Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is essential in gear drive manufacturing to ensure that products meet international standards and client specifications. Key QA measures include adherence to relevant standards, implementation of inspection checkpoints, and rigorous testing methods.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for Gear Drive Quality Assurance?
International standards such as ISO 9001 are critical for ensuring consistent quality management practices. Additionally, industry-specific standards like API (American Petroleum Institute) and CE (Conformité Européenne) certification are crucial for specific applications, particularly in the oil and gas sector and European markets, respectively. Compliance with these standards ensures that gear drives are safe, reliable, and suitable for international markets.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Gear Drive Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial inspection checks raw materials for compliance with specifications before they enter production.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process ensures that any deviations from standards are identified and corrected promptly.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive inspection of the finished product, including dimensional checks and performance testing, guarantees that the gear drives meet all required specifications.
These checkpoints are vital for maintaining high standards throughout the manufacturing process.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Gear Drives?
Testing methods vary based on the application but typically include:
- Load Testing: Assessing the gear drive’s performance under simulated operating conditions to ensure it can handle the required loads.
- Vibration Analysis: Monitoring vibrations during operation to identify potential failures before they occur.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing and magnetic particle inspection help identify internal flaws without damaging the component.
These methods not only confirm the quality of the gear drives but also provide valuable insights into their operational reliability.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control practices is crucial. Here are several strategies to ensure supplier compliance:
What Audit Processes Should Be Conducted?
Conducting regular audits of suppliers can reveal their adherence to quality standards. Buyers should look for:
- Documentation: Requesting quality management system documentation, including certifications and quality manuals.
- On-Site Audits: Visiting the manufacturing facility to observe processes firsthand and assess compliance with quality standards.
- Supplier Performance Reviews: Regularly reviewing supplier performance metrics to ensure they meet agreed-upon standards.
How Can Buyers Access Quality Reports and Third-Party Inspections?
Buyers should request quality reports from suppliers that detail their QA processes and results. Additionally, engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures, offering peace of mind regarding the product’s reliability.
What Nuances Should International Buyers Consider Regarding Quality Control?
International buyers must be aware of the nuances in quality control that can vary by region. For instance, regulatory requirements and standards may differ significantly between Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding these differences is essential for ensuring compliance and minimizing risks associated with cross-border transactions.
By focusing on these detailed manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they select reliable gear drive suppliers that meet their operational needs and quality expectations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘gear drive’
To assist international B2B buyers in sourcing gear drives effectively, this guide provides a structured checklist that outlines essential steps to ensure informed procurement. Whether you are a buyer from Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe, following these steps will help you make a well-informed decision.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is crucial for identifying the right gear drive for your needs. Consider factors such as load capacity, gear ratio, and environmental conditions where the gear drive will operate. This clarity helps in narrowing down options and ensures compatibility with existing systems.
- Load Capacity: Assess the maximum load the gear drive will need to handle.
- Gear Ratio: Determine the required speed reduction or increase based on your application.
Step 2: Research Industry Standards and Certifications
Understanding the relevant industry standards is essential for ensuring quality and reliability. Look for suppliers that comply with standards such as the American Gear Manufacturers Association (AGMA) or ISO certifications.
- Quality Assurance: Compliance with recognized standards indicates adherence to quality assurance processes.
- Safety Regulations: Verify that the gear drives meet local safety and performance regulations applicable in your region.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Don’t just rely on their website; engage directly with their customer service and sales teams to gauge their responsiveness and knowledge.
- Supplier History: Look for suppliers with a proven track record in gear drive manufacturing and customer satisfaction.
- Customer Reviews: Seek feedback from other B2B buyers regarding their experiences with the supplier.
Step 4: Request and Compare Quotes
Once you’ve identified potential suppliers, request detailed quotes that include pricing, lead times, and terms of service. Comparing quotes allows you to assess not just the cost, but also the value offered.
- Cost Transparency: Ensure that the quotes break down costs for materials, labor, and additional services.
- Lead Times: Consider the delivery schedules and how they align with your project timelines.
Step 5: Assess After-Sales Support and Warranty
A reliable after-sales support system and warranty are essential for long-term satisfaction. Inquire about the warranty duration and what it covers, as well as the availability of technical support.
- Technical Assistance: Confirm that the supplier offers ongoing support for installation and maintenance.
- Warranty Terms: Understand the warranty specifics to ensure protection against manufacturing defects.
Step 6: Consider Customization Options
If your application has unique requirements, explore customization options with suppliers. Custom gear drives may be necessary to meet specific operational demands or constraints.
- Tailored Solutions: Discuss your needs and see if the supplier can offer bespoke designs that align with your specifications.
- Cost Implications: Understand how customization may affect pricing and lead times.
Step 7: Finalize Your Purchase Agreement
Before finalizing your purchase, ensure that all terms and conditions are clearly outlined in a formal agreement. This should include payment terms, delivery schedules, and any contingencies for potential issues.
- Legal Considerations: Ensure compliance with international trade regulations applicable to your transaction.
- Documentation: Keep all correspondence and documents for future reference.
By following this structured checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the sourcing process for gear drives with confidence, ensuring they select the best product for their specific needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for gear drive Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Gear Drive Sourcing?
When sourcing gear drives, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The selection of materials significantly impacts the price. High-quality steel or specialty alloys used in gear manufacturing can increase costs but improve durability and performance. Consider sourcing from regions known for specific materials to optimize costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can affect the overall price. In areas with higher labor costs, such as Europe, manufacturers may pass these costs onto buyers. Conversely, sourcing from regions with lower labor costs might provide savings.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations, utilities, and maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead and thus lower prices for buyers.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific gear designs can be a significant upfront cost. Buyers should consider whether they require custom designs or if standard products will suffice, as this can influence total costs.
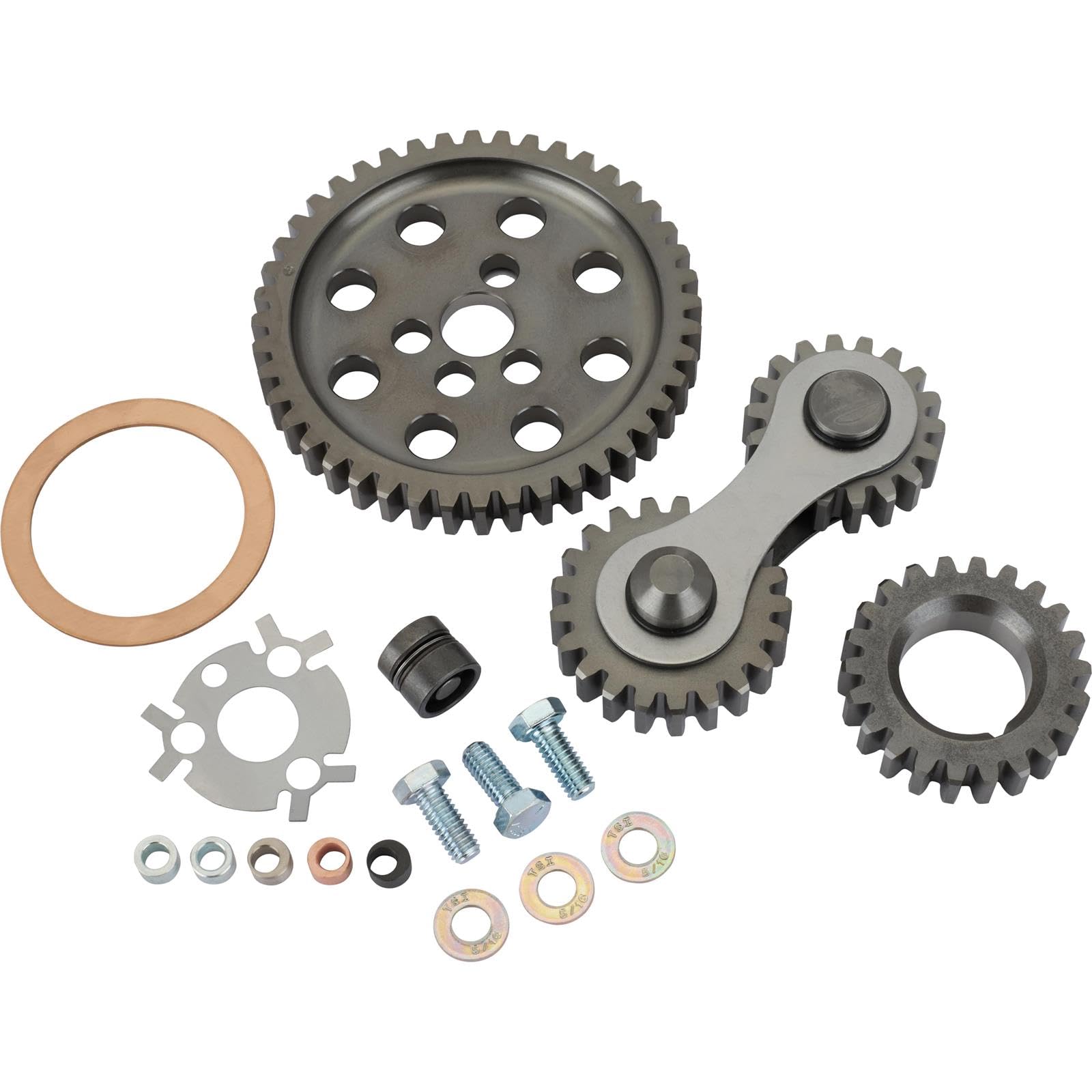

A stock image related to gear drive.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC processes ensures product reliability but adds to manufacturing costs. Buyers should evaluate the importance of certifications (e.g., ISO standards) when assessing potential suppliers.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary greatly depending on the supplier’s location and the chosen Incoterms. Understanding the implications of freight, insurance, and delivery terms can help buyers manage logistics expenses effectively.
-
Margin: Suppliers will apply a profit margin on top of their costs. This margin can fluctuate based on demand, competition, and supplier relationships.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Gear Drive Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of gear drives:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Purchasing in bulk can lead to significant discounts. Buyers should negotiate MOQs with suppliers to optimize pricing based on their projected needs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized gear drives tailored to specific applications will typically cost more than standard products. Buyers must assess the necessity of customization against budget constraints.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-grade materials and industry certifications often lead to increased costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of enhanced performance against the additional expense.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while newer entrants might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms can significantly impact the total cost. Understanding responsibilities regarding shipping, customs, and insurance can prevent unexpected expenses.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Gear Drive Sourcing?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the following tips can enhance cost efficiency:
-
Negotiate Terms: Always engage in negotiations with suppliers. This includes discussing pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Strong negotiation skills can lead to better deals.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond initial purchase prices, consider maintenance, operational efficiency, and longevity of gear drives. A higher upfront cost may be justified by lower long-term expenses.
-
Research Suppliers Thoroughly: Investigate potential suppliers’ backgrounds, reviews, and product quality. Building relationships with reliable suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms over time.
-
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Prices can fluctuate based on market conditions, including supply chain disruptions or material shortages. Keeping abreast of industry news can help buyers make informed purchasing decisions.
-
Utilize Local Expertise: For buyers in regions like Africa or South America, leveraging local agents or consultants can provide insights into best practices and potential cost savings in sourcing gear drives.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
While indicative prices can provide a baseline for understanding costs, they are subject to change based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific project requirements. Buyers should conduct thorough due diligence and request formal quotes to obtain accurate pricing tailored to their needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing gear drive With Other Solutions
When evaluating power transmission solutions, it’s essential to consider alternatives to gear drives that can achieve similar objectives. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of various technologies enables B2B buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their specific applications and operational requirements.
| Comparison Aspect | Gear Drive | Chain Drive | Belt Drive |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency and precision | Moderate efficiency, prone to stretching | Good efficiency, but can slip |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, low lifetime cost | Lower initial cost, high maintenance cost | Moderate initial cost, moderate maintenance |
| Ease of Implementation | Complex installation requiring expertise | Simple installation, less technical knowledge required | Moderate installation complexity |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, long lifespan | High maintenance due to wear | Moderate maintenance, periodic replacement needed |
| Best Use Case | Heavy-duty applications requiring precision | Light to moderate load applications | General-purpose, low to moderate load applications |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Chain Drive Compared to Gear Drive?
Chain drives are a popular alternative to gear drives, especially in applications where cost is a significant factor. They excel in light to moderate load applications and are easier to install and maintain. However, chain drives can stretch over time, leading to reduced efficiency and requiring more frequent adjustments or replacements. They also typically have lower performance compared to gear drives, making them less suitable for heavy-duty applications where precision is crucial.
How Does Belt Drive Compare to Gear Drive?
Belt drives offer a versatile solution suitable for a range of applications. They are less complex to install than gear drives and can be more cost-effective in certain scenarios. However, they may not deliver the same level of efficiency and precision, especially under heavy loads, as they are prone to slipping. Maintenance requirements are moderate, and while belts may have a longer lifespan than chains, they will still need periodic replacement. Belt drives are most effective in general-purpose applications where high precision is not as critical.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Power Transmission Solution?
Selecting the appropriate power transmission solution depends on various factors, including application demands, budget constraints, and maintenance capabilities. Gear drives are ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring high efficiency and precision, but they come with a higher initial investment. Chain drives can be a cost-effective alternative for lighter loads, albeit with higher maintenance needs. Belt drives offer a middle ground, suitable for general-purpose applications but lacking the performance of gear drives. By assessing these factors, B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and financial constraints.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for gear drive
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Gear Drives?
Understanding the technical specifications of gear drives is crucial for international B2B buyers looking to optimize their machinery’s performance. Here are several essential properties that should guide your purchasing decisions:
-
Material Grade
– Gear drives are typically made from materials such as carbon steel, stainless steel, or aluminum alloys. The choice of material affects durability, weight, and corrosion resistance. For buyers from Africa and South America, where environmental conditions can vary, selecting the right material is essential to enhance longevity and reduce maintenance costs. -
Tolerances
– Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension. In gear drives, tighter tolerances generally lead to smoother operation and reduced wear. Buyers should assess the tolerances specified by manufacturers to ensure compatibility with existing systems, especially in high-precision applications common in Europe and the Middle East. -
Reduction Ratio
– This specification indicates the ratio of the input speed to the output speed. A higher reduction ratio means more torque and less speed, which is crucial for applications requiring significant force. Understanding the desired reduction ratio helps buyers select gear drives that meet operational requirements without compromising efficiency. -
Horsepower Rating
– The horsepower rating defines the amount of power a gear drive can transmit. This rating is vital for ensuring that the gear drive can handle the operational demands of your machinery. B2B buyers must match the horsepower rating with their application’s requirements to avoid premature failure. -
Efficiency
– Efficiency measures how much input power is converted into output power. High-efficiency gear drives minimize energy losses, which is particularly beneficial for buyers in energy-sensitive industries. Evaluating the efficiency ratings from suppliers can lead to significant cost savings in the long run. -
Operating Temperature Range
– The specified operating temperature range indicates the conditions under which the gear drive can function optimally. This is particularly important for buyers in regions with extreme climates, such as parts of Africa and the Middle East. Ensuring that the gear drive can operate effectively within the local temperature conditions is critical for reliability.
What Are Common Terms Used in Gear Drive Trade?
Familiarizing yourself with industry jargon can streamline communication with suppliers and enhance your purchasing strategy. Here are some essential terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for ensuring that you are purchasing authentic and compatible parts. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management, particularly for international buyers who may face shipping constraints. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document that a buyer sends to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products. Crafting a clear RFQ can help buyers receive accurate quotes and streamline the procurement process. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with these terms can prevent misunderstandings and ensure smooth logistics. -
Lead Time
– Lead time refers to the duration from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times can help B2B buyers plan their operations more effectively, especially when sourcing from international suppliers. -
After-Sales Support
– This term encompasses the services provided by suppliers after a sale, including installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting. Evaluating after-sales support options can significantly impact the long-term performance of gear drives and the overall satisfaction of your procurement decision.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and enhance their competitive edge in the global market.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the gear drive Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Gear Drive Sector?
The gear drive market is experiencing notable growth driven by increased demand across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. Key trends influencing this market include the integration of advanced technologies such as IoT and AI, which enhance predictive maintenance capabilities and operational efficiencies. International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of the ongoing shift towards customization and modular designs, allowing for more tailored solutions that meet specific operational needs.
Emerging markets are also witnessing a surge in infrastructure development, spurring demand for gear drives in construction and heavy machinery. In Europe, particularly in Spain, there is a strong emphasis on energy-efficient gear drive solutions, aligning with the EU’s sustainability goals. Buyers should consider local suppliers who can provide not only competitive pricing but also compliance with regional standards and certifications. Additionally, the trend towards digitalization is shaping sourcing strategies, as companies increasingly prefer suppliers who can offer comprehensive digital platforms for product tracking and order management.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact Gear Drive Procurement?
Sustainability is becoming a central theme in the gear drive sector, with a growing recognition of the environmental impacts associated with manufacturing and sourcing. B2B buyers are now prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate commitment to sustainability through ethical supply chains and eco-friendly practices. This includes sourcing materials from certified suppliers that utilize renewable resources and have low carbon footprints.
Additionally, ‘green’ certifications such as ISO 14001 can provide assurance to buyers regarding the supplier’s environmental management systems. Buyers from Africa and South America should seek out manufacturers who are investing in sustainable technologies and practices, as these can not only reduce environmental impact but also enhance brand reputation and customer loyalty. Emphasizing sustainability in procurement decisions can lead to long-term cost savings through improved efficiencies and reduced waste.
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of Gear Drives in the B2B Context?
The evolution of gear drives dates back to ancient civilizations, where simple gear mechanisms were used in basic machinery. Over time, advancements in materials and engineering principles have led to the development of complex gear drive systems that are integral to modern machinery. In the early 20th century, the automotive and aerospace industries began to adopt gear drives extensively, recognizing their ability to efficiently transmit power and improve performance.
Today, gear drives are critical components across various applications, from small precision instruments to large industrial machines. The introduction of computer-aided design (CAD) and simulation tools has revolutionized the design and manufacturing processes, allowing for greater precision and customization. As international B2B buyers navigate this dynamic landscape, understanding the historical context can provide valuable insights into current innovations and future trends in gear drive technology.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of gear drive
-
How do I choose the right gear drive for my application?
Selecting the right gear drive involves assessing your specific application requirements, including load capacity, speed, and environmental conditions. Consider the type of gearing (e.g., spur, helical, bevel), the arrangement of shafts, and the desired reduction ratio. It’s also essential to evaluate the operating conditions, such as temperature and humidity, especially if you’re sourcing from diverse regions like Africa or Europe. Consult with suppliers about their product specifications and ensure they align with your operational needs. -
What are the advantages of using gear drives over chain drives?
Gear drives offer several benefits over chain drives, including higher efficiency, durability, and precise timing. Unlike chains, gears do not stretch over time, which means they provide consistent performance without the need for frequent adjustments. Additionally, gear drives can transmit more power in a smaller space, making them ideal for compact machinery. However, consider factors like noise levels and potential harmonics when making your choice, as these can vary by design and application. -
What should I consider when vetting international suppliers of gear drives?
When vetting international suppliers, focus on their industry experience, certifications, and customer reviews. It’s crucial to assess their quality assurance processes and whether they comply with international standards (e.g., ISO certifications). Request samples to evaluate product quality and inquire about their manufacturing capabilities and lead times. Establish clear communication channels to ensure transparency regarding any potential challenges related to logistics and customs. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for gear drives?
Minimum order quantities for gear drives can vary significantly between manufacturers. Some suppliers may allow small orders for standard products, while custom gear drives often come with higher MOQs due to specialized manufacturing processes. It’s advisable to discuss your needs upfront with potential suppliers to negotiate favorable terms, especially if you’re looking to test products in smaller batches before committing to larger orders. -
How can I ensure quality assurance when purchasing gear drives internationally?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed product specifications and certifications from your supplier. Consider conducting third-party inspections during production and before shipment. Additionally, establish a clear return policy and warranty terms to protect your investment. Collaborating with suppliers that have a robust quality management system in place can further enhance your confidence in the products you receive. -
What payment terms should I negotiate with my gear drive supplier?
Payment terms can vary, but it’s essential to negotiate conditions that suit your cash flow and risk tolerance. Common options include payment in advance, letters of credit, or net payment terms (e.g., 30, 60, or 90 days). Discuss the possibility of partial payments upon order confirmation and the balance upon delivery. Ensure that the agreed terms are documented in the purchase contract to avoid future disputes. -
What logistical considerations should I keep in mind when importing gear drives?
When importing gear drives, consider shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations specific to your country. Understand the total landed cost, including tariffs, taxes, and shipping fees, to avoid unexpected expenses. Collaborate with a reliable logistics partner who can navigate customs clearance and ensure timely delivery. It’s also wise to have contingency plans for potential delays, particularly in regions with fluctuating supply chain dynamics. -
How can I customize gear drives to fit my specific needs?
Customization of gear drives typically involves discussing your requirements directly with the manufacturer. This can include adjustments in size, gearing ratios, materials, or mounting configurations. Many suppliers offer engineering support to help design a solution tailored to your application. Be prepared to provide detailed specifications and operational parameters to facilitate the design process and ensure the final product meets your expectations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for gear drive
The landscape of gear drive sourcing is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements and global market dynamics. For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, strategic sourcing has become paramount. By understanding the intricate design considerations and the performance metrics of gear drives, businesses can make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs.
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers in Gear Drive Sourcing?
B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to quality and innovation. Understanding the pros and cons of various gear drive configurations—such as enclosed gear units versus gear motors—can lead to more efficient and reliable machinery. Additionally, leveraging local suppliers can mitigate risks associated with logistics and supply chain disruptions, particularly in diverse regions like Africa and South America.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Gear Drive Procurement?
Strategic sourcing not only streamlines procurement processes but also fosters long-term partnerships with manufacturers who can provide ongoing support and customization. As you explore options, consider engaging with manufacturers that utilize advanced modeling techniques to optimize gear design, ensuring durability and performance.
What’s Next for Gear Drive Buyers?
Looking ahead, the demand for high-quality gear drives will continue to grow as industries seek reliable solutions to enhance productivity. Now is the time to evaluate your sourcing strategies and engage with trusted suppliers. By doing so, you can secure competitive advantages in your operations and contribute to the overall resilience of your supply chain. Act now to position your business for success in the evolving gear drive market.