Optimize Operations: The Ultimate Guide to Linear Rails (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for linear rails
Navigating the complexities of sourcing linear rails can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers, especially in emerging markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the nuances of linear rails—ranging from V-Slot and C-Beam systems to heavy-duty options—requires not only technical knowledge but also a strategic approach to procurement. This guide delves deep into the various types of linear rails available, their diverse applications across industries, and essential factors to consider when vetting suppliers.
In today’s competitive landscape, informed purchasing decisions hinge on a thorough understanding of product specifications, cost structures, and supplier reliability. Buyers will find actionable insights on how to assess quality, negotiate pricing, and ensure compliance with regional standards. This resource is particularly tailored to meet the unique needs of businesses in regions such as Saudi Arabia and Vietnam, where the demand for reliable motion systems is steadily increasing.
By the end of this guide, B2B buyers will be empowered to make strategic decisions that not only enhance operational efficiency but also position their companies for growth in the global market. With the right knowledge and tools at hand, navigating the world of linear rails becomes a streamlined process that drives success.
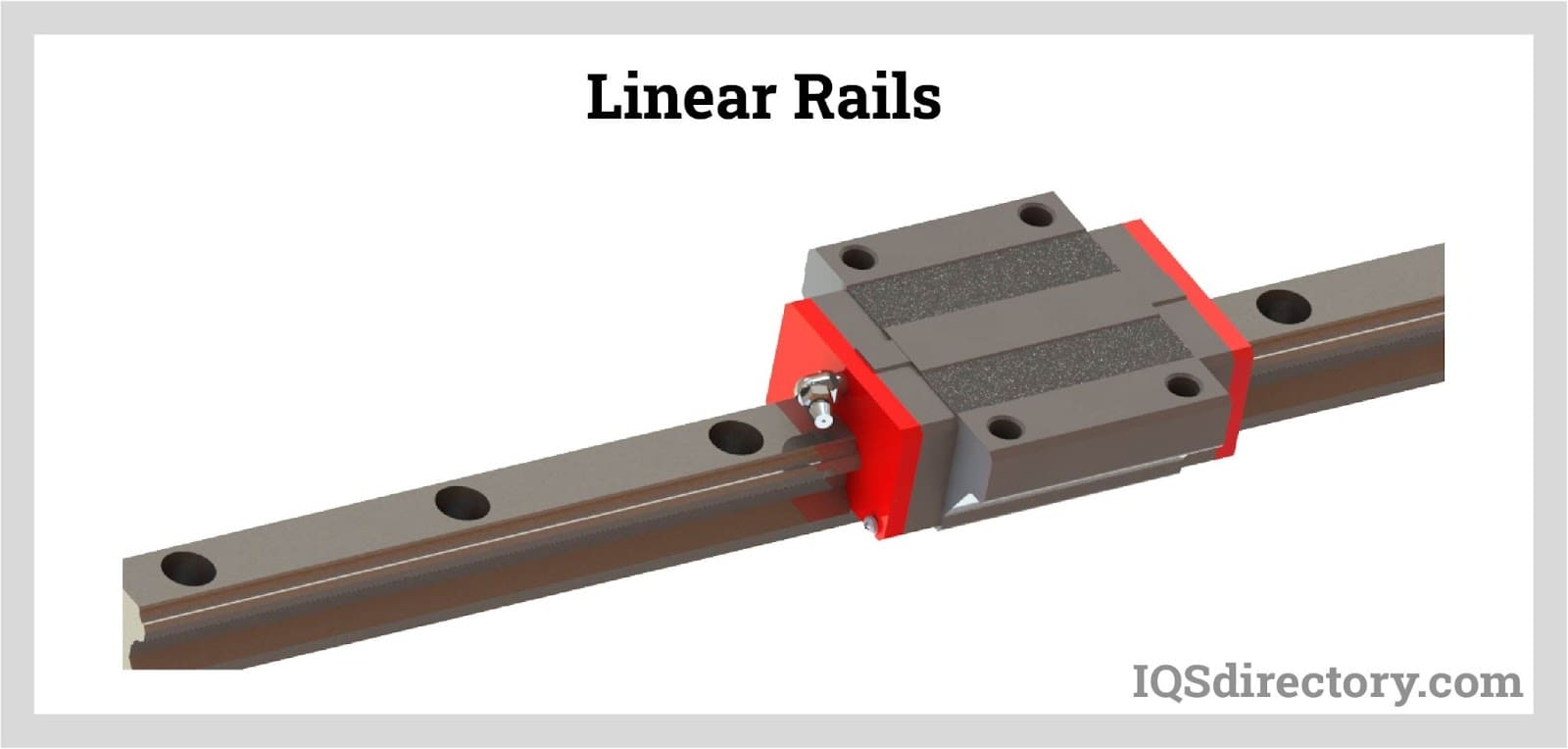
Understanding linear rails Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| V-Slot | Aluminum extrusion with a V-shaped groove for easy assembly | CNC machines, robotics, DIY projects | Pros: Lightweight, easy to customize; Cons: May not handle heavy loads well. |
| Linear Guide (MGN) | Compact design with low profile and high precision | Automation, medical devices, packaging | Pros: High accuracy, smooth motion; Cons: Limited load capacity compared to larger options. |
| Heavy Duty Rails | Robust construction with hardened raceways for high loads | Industrial machinery, automotive | Pros: High load capacity, durable; Cons: Heavier and more expensive. |
| Telescopic Rails | Extendable design for space-saving applications | Warehouse automation, material handling | Pros: Efficient use of space; Cons: More complex installation and maintenance. |
| C-Beam | Versatile beam with integrated linear motion capabilities | 3D printers, CNC applications | Pros: Multi-functional, good for custom setups; Cons: Requires precise alignment. |
What are the characteristics of V-Slot linear rails?
V-Slot linear rails are characterized by their aluminum extrusion design featuring a V-shaped groove. This design facilitates easy assembly and customization, making them ideal for applications in CNC machines, robotics, and various DIY projects. When considering V-Slot for purchase, buyers should note that while they are lightweight and versatile, they may not support heavy loads as effectively as other types.
How do MGN linear guides differ in terms of performance?
MGN linear guides are known for their compact and low-profile design, which allows for high precision and smooth motion. They are commonly used in automation, medical devices, and packaging applications where accuracy is crucial. Buyers should evaluate the load capacity, as MGN guides may have limitations compared to larger linear rail systems, but they excel in applications requiring high accuracy and reduced friction.
What makes heavy-duty rails suitable for industrial applications?
Heavy-duty rails are built with robust materials and hardened raceways, allowing them to handle high loads and dynamic forces. They are primarily used in industrial machinery and automotive applications where durability is essential. While their high load capacity is a significant advantage, buyers must also consider the increased weight and cost associated with these rails, which may affect installation and operational costs.
Why are telescopic rails important for space efficiency?
Telescopic rails offer an extendable design that maximizes space efficiency, making them ideal for warehouse automation and material handling applications. Their ability to retract and expand allows for better organization and accessibility in tight spaces. However, buyers should be aware that the installation and maintenance of telescopic rails can be more complex compared to standard linear rails, which could lead to increased operational overhead.
What benefits do C-Beam linear rails provide for custom setups?
C-Beam linear rails are versatile components that integrate linear motion capabilities into a beam structure, making them suitable for 3D printers and CNC applications. Their design allows for flexibility in custom setups, enabling buyers to create tailored solutions for specific needs. While they offer excellent functionality, precise alignment during installation is crucial to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
Key Industrial Applications of linear rails
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Linear Rails | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | CNC Machining and Automation | Enhances precision and speed in machining processes | Load capacity, dimensional accuracy, and environmental resistance |
| Healthcare | Medical Device Assembly | Improves assembly efficiency and product consistency | Compliance with health regulations and ease of cleaning |
| Logistics | Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems | Increases storage efficiency and reduces operational costs | Custom lengths, load ratings, and integration capabilities |
| Aerospace | Component Testing and Assembly | Ensures precision in testing and assembly operations | High load capacity, vibration resistance, and material durability |
| Packaging | Automated Packaging Lines | Enhances throughput and reduces labor costs | Speed ratings, compatibility with existing systems, and maintenance needs |
How Are Linear Rails Used in Manufacturing?
In the manufacturing sector, linear rails are integral to CNC machining and automation. They provide smooth, precise movement for cutting tools, enabling high-speed operations with minimal friction. This results in improved accuracy and consistency in the production of components. International buyers should consider load capacity and dimensional accuracy, especially in regions like Africa and South America, where operational challenges may arise from varying infrastructure conditions.
What Role Do Linear Rails Play in Healthcare Applications?
Linear rails are crucial in the healthcare industry, particularly in the assembly of medical devices. They facilitate the precise movement required for assembling complex devices, ensuring that products meet stringent quality and safety standards. For international buyers, sourcing rails that comply with health regulations and are easy to clean is essential, especially in markets like the Middle East where hygiene is paramount.
How Are Linear Rails Beneficial in Logistics?
In logistics, linear rails are employed in automated storage and retrieval systems (ASRS) to streamline operations. They allow for rapid movement of goods, enhancing storage efficiency and reducing operational costs. Buyers in regions such as Europe should prioritize custom lengths and load ratings to fit specific warehouse configurations, ensuring that the systems can handle the demands of their logistics operations.
What Are the Applications of Linear Rails in Aerospace?
In the aerospace sector, linear rails are utilized for component testing and assembly, where precision is critical. They ensure that components are tested under exact conditions, leading to reliable and safe aerospace products. Buyers need to focus on high load capacities and vibration resistance, particularly in regions with stringent aerospace regulations, such as Europe and the Middle East.
How Do Linear Rails Enhance Packaging Operations?
Linear rails are vital in automated packaging lines, where they improve throughput and reduce labor costs by facilitating quick and efficient movement of products through the packaging process. Buyers should consider speed ratings and the compatibility of linear rails with existing systems to ensure seamless integration into their packaging operations, particularly in fast-growing markets like South America.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘linear rails’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Misalignment Issues in Precision Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter challenges with misalignment in linear rail systems, especially in precision applications such as CNC machines or robotic arms. Misalignment can lead to increased wear on components, reduced accuracy, and ultimately, product failure. This issue is particularly prevalent when operating in environments with temperature fluctuations or heavy vibration, which can cause rails to shift or bend, compromising their performance. Buyers may feel frustrated when they realize that misalignment can result in significant downtime and maintenance costs.
The Solution: To address misalignment, it is crucial to select linear rails with self-aligning features or to use linear guide systems specifically designed for high-load applications. Buyers should thoroughly assess the environmental conditions and operational requirements before sourcing their linear rails. When specifying rails, opting for hardened raceways can enhance durability and resistance to deformation. Additionally, regular maintenance, including periodic alignment checks and lubrication, can help prevent misalignment issues. Investing in a reliable installation process, possibly utilizing professional technicians, ensures that the linear rails are mounted correctly from the outset, significantly reducing the risk of future misalignment.
Scenario 2: Insufficient Load Capacity for Heavy Applications
The Problem: Many businesses in sectors such as manufacturing or logistics require linear rails capable of handling heavy loads. However, buyers frequently underestimate the load requirements for their applications, leading to the selection of inadequate linear rails. This oversight can result in failure during operation, which not only affects productivity but can also pose safety hazards. Buyers may find themselves in a bind when their chosen system cannot support the weight of the equipment or materials being moved, leading to costly replacements and project delays.
The Solution: To prevent this problem, buyers should conduct a thorough analysis of their operational needs, including the maximum load requirements, frequency of use, and any dynamic forces that may occur during operation. Consulting with manufacturers or suppliers who specialize in heavy-duty linear rails can provide valuable insights into which products are best suited for specific applications. It’s advisable to opt for linear rails designed with reinforced structures or higher load capacities. Additionally, incorporating safety factors into the load calculations can provide extra assurance that the selected rails will perform reliably under demanding conditions.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Sourcing Replacement Parts
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges in sourcing replacement parts for linear rail systems, especially when dealing with older or less common models. This can lead to extended downtime and disruptions in production, as businesses may not have immediate access to necessary components. The frustration mounts when buyers realize that certain parts are either obsolete or have long lead times, jeopardizing their operational efficiency.
The Solution: To alleviate sourcing difficulties, buyers should prioritize working with manufacturers that offer a comprehensive range of replacement parts and support for their linear rail systems. Establishing relationships with multiple suppliers can also provide flexibility and options when sourcing components. Additionally, investing in modular systems that allow for easy upgrades and replacements can help ensure compatibility with future parts. Implementing an inventory management system that tracks the lifespan and replacement schedules of critical components can further mitigate downtime, allowing businesses to anticipate needs and order replacements proactively. By taking these proactive steps, buyers can ensure that they are not left scrambling for parts when they are most needed.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for linear rails
What Are the Common Materials Used for Linear Rails?
When selecting linear rails for international B2B applications, the choice of material plays a crucial role in performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Here, we analyze four common materials used in linear rail manufacturing: aluminum, stainless steel, carbon steel, and plastic composites. Each material has unique properties that cater to different operational environments and application requirements.
How Does Aluminum Perform in Linear Rail Applications?
Aluminum is a popular choice for linear rails due to its lightweight nature and excellent corrosion resistance. It typically has a temperature rating up to 100°C and can handle moderate loads effectively.
Pros:
– Lightweight, making it easy to handle and install.
– Excellent corrosion resistance, suitable for humid or wet environments.
– Good machinability allows for complex designs.
Cons:
– Lower load-bearing capacity compared to steel, which may limit its application in heavy-duty scenarios.
– More expensive than carbon steel, impacting overall project budgets.
Impact on Application: Aluminum rails are ideal for applications in industries like automation and robotics, where weight reduction is crucial. However, they may not be suitable for high-load environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN is essential. Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure that the aluminum used meets these specifications to avoid issues with quality and performance.
What Are the Benefits of Stainless Steel in Linear Rails?
Stainless steel is renowned for its strength and durability, making it suitable for demanding applications. It offers high corrosion resistance and can withstand temperatures up to 300°C.
Pros:
– Exceptional strength and durability, ideal for heavy-duty applications.
– High corrosion resistance, making it suitable for harsh environments.
– Long lifespan, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
Cons:
– Heavier than aluminum, which can complicate installation.
– Higher cost compared to both aluminum and carbon steel.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel rails are commonly used in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and other industries where hygiene is paramount. Their robustness allows them to handle heavy loads and harsh conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific grades of stainless steel (e.g., 304, 316) that may be required for their applications, particularly in compliance with local regulations in regions like Africa and South America.
Why Choose Carbon Steel for Linear Rails?
Carbon steel is often favored for its strength and affordability. It can handle high loads and is suitable for applications where cost is a significant factor.

A stock image related to linear rails.
Pros:
– High strength-to-weight ratio, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications.
– Generally lower cost compared to aluminum and stainless steel.
– Good wear resistance.
Cons:
– Susceptible to corrosion, requiring protective coatings or treatments.
– Limited temperature resistance, typically up to 200°C.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel rails are ideal for industrial machinery and equipment where cost-effectiveness is critical. However, they may not be suitable for environments exposed to moisture without proper treatment.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that carbon steel rails are treated or coated to prevent rust, especially in humid regions like Southeast Asia and parts of Africa.
What Role Do Plastic Composites Play in Linear Rail Applications?
Plastic composites are becoming increasingly popular for specific applications due to their lightweight and non-corrosive properties. They typically have a lower load capacity but excel in environments where corrosion is a concern.
Pros:
– Lightweight and easy to install.
– Excellent corrosion resistance, suitable for chemical exposure.
– Low friction properties reduce wear.
Cons:
– Limited load-bearing capacity compared to metals.
– Lower temperature resistance, typically under 100°C.
Impact on Application: Plastic composite rails are often used in medical devices and food processing equipment where hygiene and corrosion resistance are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with food safety standards is crucial for buyers in the food industry, particularly in regions like Europe and the Middle East.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Linear Rails
| Material | Typical Use Case for Linear Rails | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Automation, robotics | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower load capacity | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, pharmaceuticals | Exceptional strength | Heavier and more expensive | High |
| Carbon Steel | Industrial machinery | High strength-to-weight ratio | Susceptible to corrosion | Low |
| Plastic Composites | Medical devices, food processing | Corrosion-resistant | Limited load capacity | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides essential insights for international B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions based on specific application needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for linear rails
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Linear Rails?
The manufacturing process of linear rails involves several critical stages, each contributing to the overall performance and reliability of the final product. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers, especially when sourcing from international suppliers.
-
Material Preparation
– The process begins with selecting high-quality materials, often steel or aluminum, that meet specific performance requirements. The chosen materials undergo rigorous testing to ensure they are free from defects and suitable for the intended application.
– Material is then cut into the desired dimensions using precision cutting methods, such as laser cutting or water jet cutting, to ensure accuracy and reduce waste. -
Forming
– After material preparation, the next step is forming. Techniques such as extrusion or machining are employed to create the desired shapes and profiles of the rails.
– For instance, extruded aluminum rails are shaped under high pressure, resulting in strong, lightweight components ideal for various applications. Machining processes, including milling and grinding, are used to achieve precise dimensions and tolerances. -
Assembly
– In this stage, various components, such as bearings and carriages, are assembled with the linear rails. This assembly may involve manual labor or automated systems, depending on the complexity and volume of production.
– Quality checks are integrated into this stage to ensure that all parts fit correctly and function smoothly together. Assembly processes may also include the application of lubricants to enhance the operational efficiency of the rails. -
Finishing
– The final stage is finishing, which may include surface treatments like anodizing, plating, or painting. These processes not only improve aesthetics but also enhance corrosion resistance and wear properties.
– Final inspections are conducted to assess surface quality and dimensional accuracy before the products are packaged for shipment.
How Is Quality Assurance Integrated into Linear Rail Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is crucial in the manufacturing of linear rails, as it directly affects performance, safety, and customer satisfaction. Understanding QA processes can empower international B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions.
-
What Are the Relevant International Standards for Linear Rails?
– The most recognized international standard is ISO 9001, which outlines criteria for a quality management system. Compliance with this standard ensures that manufacturers consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
– In addition to ISO certifications, industry-specific certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) and API (American Petroleum Institute) may apply, depending on the intended application of the linear rails. -
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
– Quality control begins with Incoming Quality Control (IQC), where raw materials are inspected upon arrival. This step helps identify any issues before production starts.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC) involves ongoing inspections during the manufacturing process. This may include checks on dimensions, surface finishes, and assembly accuracy.
– Final Quality Control (FQC) is performed on finished products to verify that they meet all specified standards before they are shipped. This stage often includes functional testing, load testing, and dimensional verification. -
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Quality Assurance?
– Various testing methods are employed to ensure the performance and durability of linear rails. Common tests include:- Dimensional Inspection: Using coordinate measuring machines (CMM) to verify dimensions against specifications.
- Functional Testing: Assessing the operational performance under load conditions to ensure smooth movement and stability.
- Corrosion Resistance Testing: Conducting salt spray tests or other methods to evaluate the durability of surface treatments.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, ensuring the quality of linear rails sourced from suppliers can be challenging. Here are actionable steps to verify supplier QC processes:
-
Conduct Supplier Audits
– Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control systems. Buyers should request to see the supplier’s quality management system documentation, including ISO certifications and quality manuals. -
Request Quality Control Reports
– Suppliers should provide detailed QC reports, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC stages. Reviewing these reports can help buyers gauge the supplier’s commitment to maintaining high-quality standards. -
Engage Third-Party Inspection Services
– Consider hiring third-party inspection services to conduct independent quality checks at various stages of production. These services can offer an unbiased assessment and provide additional assurance regarding product quality.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
When dealing with suppliers from different regions, international B2B buyers should be aware of specific nuances in quality control:
-
Cultural and Regulatory Differences
– Different countries may have varying standards and regulations concerning manufacturing and quality assurance. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local practices and ensure that their suppliers comply with both international and local standards. -
Communication Barriers
– Language differences can lead to misunderstandings regarding quality expectations. Establishing clear communication channels and possibly involving local representatives can mitigate this issue. -
Time Zone Challenges
– Coordinating quality checks and audits across time zones can be complex. Buyers should plan accordingly to ensure timely communication and follow-ups with suppliers.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in linear rail production, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ultimately leading to better product performance and customer satisfaction.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘linear rails’
In the dynamic world of manufacturing and automation, sourcing the right linear rails is essential for ensuring operational efficiency and product quality. This guide provides a structured checklist for international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, to facilitate a successful procurement process.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding the specific requirements for linear rails is the first critical step. Determine the load capacity, dimensions, and material specifications needed for your application. Additionally, consider the environment in which the rails will operate—will they be exposed to dust, moisture, or extreme temperatures? This clarity will guide you in selecting the appropriate type of linear rail, such as V-slot or C-beam rails.
Step 2: Research Supplier Options
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers. Utilize industry directories, trade shows, and online platforms to compile a list of manufacturers and distributors. Pay attention to their reputation within the industry, especially among buyers in your region. A well-established supplier is more likely to provide reliable products and customer service.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to any supplier, it’s crucial to vet them thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Inquire about their experience in exporting to your area, as this can affect shipping times and customs processes. Look for suppliers that have positive reviews and a proven track record in delivering high-quality linear rails.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that the suppliers you are considering hold relevant certifications. This may include ISO certifications, which indicate adherence to international quality management standards. Additionally, check if they have specific certifications related to linear motion products. These certifications are a good indicator of the supplier’s commitment to quality and compliance with industry standards.
Step 5: Request Samples and Test Products
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request samples of their linear rails. Testing samples allows you to assess the quality and compatibility of the rails with your existing systems. Pay attention to the precision of the machining, the smoothness of motion, and any other functional requirements specific to your application. This step is vital to avoid costly mistakes later in the procurement process.
Step 6: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Engage in negotiations to secure favorable pricing and terms. Consider not just the unit price but also shipping costs, payment terms, and warranty conditions. It’s essential to clarify the total cost of ownership, which includes installation and maintenance costs. Ensure that the terms align with your budget and operational needs.
Step 7: Establish a Long-term Relationship
After selecting a supplier, focus on building a long-term relationship. Effective communication and collaboration can lead to better pricing, priority service, and support for future projects. Regularly review the performance of the supplier and provide feedback, as this can enhance the partnership and ensure ongoing quality and service improvements.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their procurement process for linear rails, ensuring they choose the right products and suppliers to meet their operational requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for linear rails Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Linear Rails Sourcing?
When sourcing linear rails, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting and decision-making. Key components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts cost. Common materials include aluminum and steel, each with varying price points based on quality and sourcing location. High-grade materials may incur higher initial costs but offer better durability and longevity.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages of workers involved in the manufacturing process. Regions with lower labor costs, such as parts of Africa and South America, may provide competitive pricing but could compromise on quality unless proper training and processes are in place.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs related to production, such as utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing practices can help minimize these overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be significant, especially for custom designs. Buyers should consider whether the supplier has the necessary tooling capabilities to meet their specifications without incurring excessive costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous quality control measures can add to the overall cost. However, investing in QC is essential for ensuring product reliability, especially in applications that require precision.
A stock image related to linear rails.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs vary greatly based on the destination and shipping method. International buyers should factor in tariffs, customs duties, and transport logistics when calculating total expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. This can vary based on market conditions, supplier reputation, and competitive landscape.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Linear Rails Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of linear rails, impacting the final cost for international buyers:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Purchasing in bulk often leads to significant discounts. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to optimize costs, especially when sourcing from suppliers in Europe or the Middle East.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specific materials can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses during production.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (like ISO or CE) can raise costs but ensure compliance with industry standards. Buyers should assess whether these certifications are necessary for their applications.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and location of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their reliability and service, while emerging suppliers might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the agreed-upon Incoterms is essential, as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. This understanding can help avoid unexpected costs.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency in Linear Rails Sourcing?
For international B2B buyers, especially from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can enhance cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiation: Engage in negotiations with suppliers to secure better pricing or terms. Highlighting long-term partnership potential can encourage suppliers to offer competitive rates.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Instead of focusing solely on the purchase price, consider the TCO, which includes maintenance, operational efficiency, and lifespan. Investing in higher-quality linear rails may yield savings over time.
-
Market Research: Conduct thorough research on suppliers and pricing trends in different regions. This knowledge can empower buyers to make informed decisions and negotiate effectively.
-
Leverage Technology: Utilize online platforms and sourcing tools to compare prices and specifications from various suppliers, ensuring the best deal is secured.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of seasonal fluctuations and market dynamics that may affect pricing. For example, demand spikes during certain times of the year can lead to increased costs.
Conclusion
Sourcing linear rails requires a comprehensive understanding of the cost structure and pricing influencers. By considering key components, negotiating effectively, and focusing on the total cost of ownership, international buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their procurement strategies. Always remember that prices can fluctuate based on market conditions, and it’s advisable to seek multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing linear rails With Other Solutions
Introduction: What Are the Alternatives to Linear Rails?
In the realm of linear motion systems, linear rails are widely recognized for their precision and reliability. However, B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, may find themselves considering alternative solutions that can better meet their unique operational needs. This section will delve into viable alternatives to linear rails, comparing their performance, costs, ease of implementation, maintenance requirements, and best use cases.
Comparison Table of Linear Rails and Alternative Solutions
| Comparison Aspect | Linear Rails | Linear Guides | Smooth Rods |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and rigidity | Varying load capacities; good for moderate precision | Low precision; suitable for simple applications |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Low to moderate | Low |
| Ease of Implementation | Moderate complexity | Easy to install | Very easy; minimal setup |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance | Moderate maintenance needs | Low maintenance |
| Best Use Case | CNC machines, robotics | Industrial automation, conveyors | Simple linear motion systems |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternative Solutions
1. Linear Guides: Are They a Suitable Replacement for Linear Rails?
Linear guides are designed for various load capacities and often feature self-aligning properties. This makes them an excellent choice for applications where misalignment may occur. The primary advantage of linear guides is their affordability and ease of installation, making them ideal for smaller operations or those with budget constraints. However, they may not offer the same level of precision as linear rails, particularly in high-speed applications.
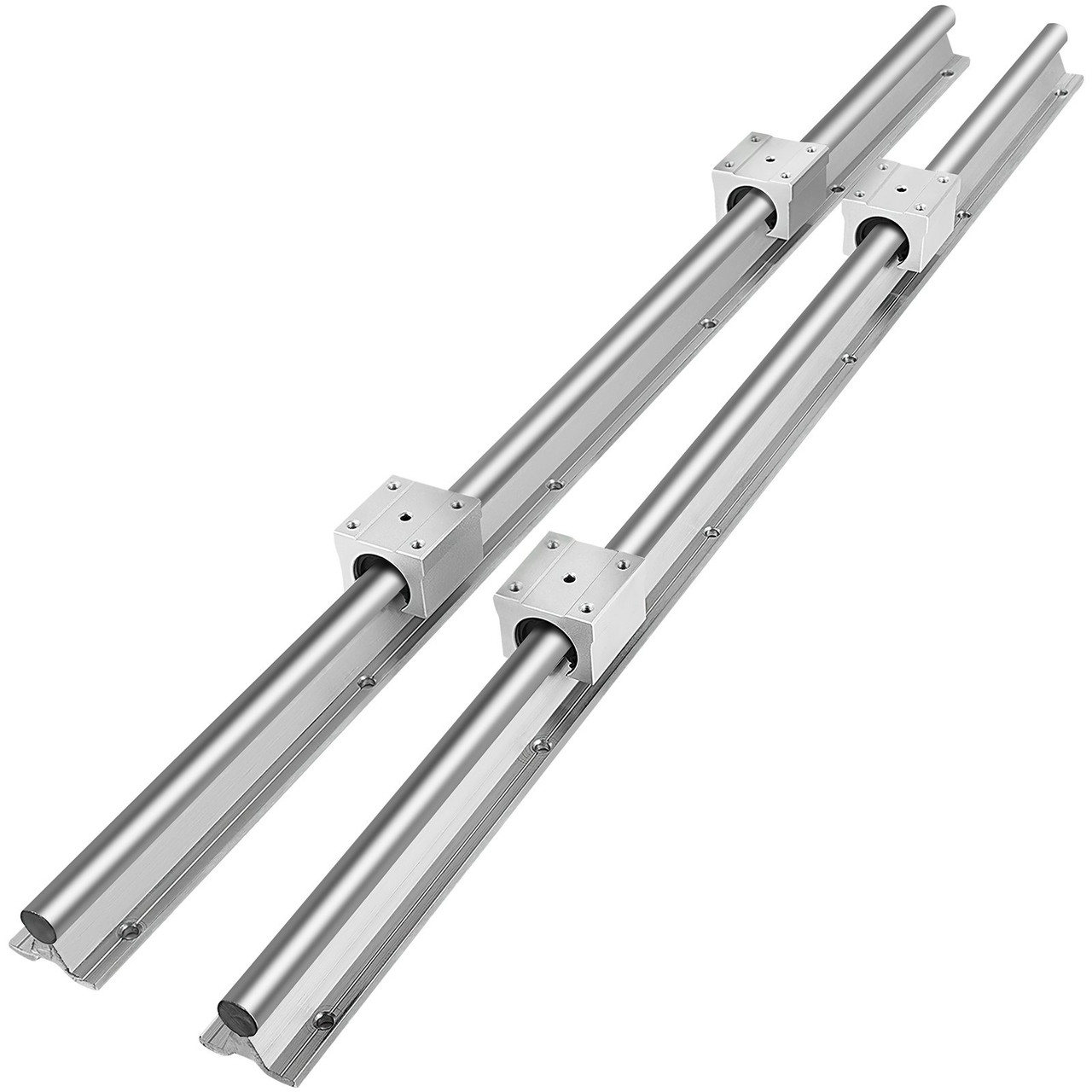

A stock image related to linear rails.
2. Smooth Rods: When to Choose Them Over Linear Rails?
Smooth rods are another alternative that can be a cost-effective solution for specific applications. They are primarily used in simpler linear motion systems, such as those found in 3D printers and basic CNC machines. Their installation is straightforward, requiring minimal effort and tools. However, smooth rods provide lower precision and are not suitable for high-load or high-speed applications, which may limit their use in more demanding environments.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When evaluating alternatives to linear rails, it is crucial for B2B buyers to carefully consider their specific operational requirements. Factors such as load capacity, precision needs, budget constraints, and the complexity of implementation play a significant role in determining the most suitable solution. Linear rails excel in precision and rigidity, making them ideal for high-tech applications, while linear guides and smooth rods offer cost-effective alternatives for less demanding tasks. Ultimately, the right choice will align with both the technical demands of the application and the financial objectives of the organization.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for linear rails
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Linear Rails?
Understanding the essential technical properties of linear rails is crucial for B2B buyers. Here are several critical specifications:
-
Material Grade
– Linear rails are typically made from materials like carbon steel, stainless steel, or aluminum. The choice of material affects the rail’s strength, corrosion resistance, and weight. For instance, stainless steel is ideal for environments prone to moisture, while aluminum is often chosen for lightweight applications. -
Load Capacity
– This specification indicates the maximum weight a linear rail can support without failing. It is essential for ensuring that the rail can handle the intended application, whether in automation systems or CNC machines. Understanding load capacity helps buyers select the right rail for their operational needs. -
Tolerance
– Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation in the dimensions of the rail. High precision is critical in applications requiring accurate motion control. A tighter tolerance means better performance and longevity, making it a vital consideration for buyers focused on quality. -
Length and Profile
– Linear rails come in various lengths and profiles (e.g., square, round, or V-shaped). The choice of length must align with the specific application, while the profile can affect the rail’s ability to handle load and motion direction. Buyers need to evaluate these dimensions based on their machinery requirements. -
Lubrication Type
– The lubrication type influences the rail’s maintenance needs and operational efficiency. Some rails require manual lubrication, while others may come with self-lubricating features. Understanding lubrication requirements is essential for long-term operational planning and cost management. -
Operating Temperature Range
– This specification indicates the temperatures within which the rail can operate effectively. Selecting a rail that can withstand the operating conditions of the intended environment is vital for ensuring reliability and performance.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know?
Familiarity with industry terminology can enhance communication and negotiation in the procurement process. Here are some common terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– An OEM produces components that are used in another company’s end product. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and quality assurance processes. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ refers to the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory planning, especially for smaller businesses or startups. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers to request price quotes for specific products. This process helps buyers compare costs and negotiate better deals. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms helps buyers understand shipping, risk, and cost responsibilities. -
Lead Time
– Lead time is the period between placing an order and receiving it. Understanding lead time is crucial for project planning and ensuring that production schedules are met. -
Certification Standards
– Certification standards indicate whether a product meets specific quality or safety benchmarks (e.g., ISO, CE). Buyers should verify that linear rails meet applicable certification standards to ensure compliance and performance.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, enhance their procurement strategies, and ensure successful project outcomes.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the linear rails Sector
What Are the Key Trends and Market Dynamics in the Linear Rails Sector?
The global linear rails market is experiencing notable growth, driven by increasing automation across various industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, and robotics. The rising demand for precision machinery and equipment is pushing the need for high-quality linear guide systems. For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding current and emerging sourcing trends is crucial.
One significant trend is the adoption of advanced technologies such as Industry 4.0, which emphasizes smart manufacturing and IoT-enabled devices. This shift is prompting companies to seek linear rails that integrate seamlessly with automated systems and offer enhanced performance metrics. Moreover, the supply chain is becoming increasingly globalized, allowing buyers access to a wider range of suppliers and products. However, this also necessitates a keen awareness of supply chain risks, including geopolitical tensions and fluctuating tariffs, which can impact pricing and availability.
Sourcing strategies are also evolving, with a growing focus on local suppliers to minimize lead times and enhance reliability. For instance, buyers in regions like Saudi Arabia and Vietnam are increasingly prioritizing local manufacturers to reduce dependency on imports and mitigate potential disruptions. Additionally, sustainability considerations are becoming paramount, as businesses strive to align with global environmental standards and consumer expectations.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Affect Linear Rails?
Sustainability in the linear rails sector is not merely a trend but a necessity in today’s business landscape. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including energy consumption and waste production, is under scrutiny. B2B buyers are increasingly required to ensure that their supply chains adhere to ethical practices, which encompass sourcing raw materials responsibly and maintaining transparency throughout the production process.
Ethical sourcing includes selecting suppliers who prioritize environmentally friendly practices, such as using recyclable materials and minimizing carbon footprints. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) are becoming essential criteria for buyers looking to evaluate their suppliers. These certifications not only demonstrate compliance with environmental regulations but also enhance brand reputation and customer trust.
Furthermore, the trend towards ‘green’ materials in linear rail manufacturing is gaining traction. Companies are exploring alternatives like aluminum and other sustainable composites that reduce environmental impact without compromising performance. Buyers who prioritize these materials can position themselves as leaders in sustainability, appealing to a growing segment of eco-conscious consumers.
What Is the Historical Context of Linear Rails in B2B Applications?
The evolution of linear rails dates back to the early industrial era when the need for precise motion control in machinery became apparent. Initially crafted from wood and metal, linear guides have significantly advanced with the introduction of advanced materials and manufacturing techniques.
By the late 20th century, the development of ball bearing technology revolutionized linear motion systems, enhancing load capacities and operational efficiency. This evolution has allowed for the integration of linear rails in various applications, from simple conveyor systems to complex robotics and CNC machines. Today, the linear rails sector is characterized by continuous innovation, with manufacturers constantly refining designs to meet the ever-increasing demands for precision, speed, and sustainability.
For international B2B buyers, understanding this historical context is vital as it informs the current market dynamics and the potential for future developments in linear rail technology.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of linear rails
-
How do I choose the right linear rails for my application?
Selecting the appropriate linear rails depends on several factors, including load capacity, operating environment, and the required precision. Start by assessing the weight and dimensions of the components that will move along the rails. Next, consider the environment: if it’s prone to dust or moisture, opt for rails with protective features. Lastly, evaluate the desired speed and accuracy; for high-speed applications, look for rails with low friction and high rigidity. Consulting with suppliers can also provide tailored recommendations based on your specific needs. -
What is the best type of linear rail for high-load applications?
For high-load applications, heavy-duty linear rails such as the Rollon Heavy Line or C-Beam systems are recommended. These rails are designed with hardened raceways and robust bearings that can handle significant weight while maintaining stability and precision. Additionally, look for rails that feature self-aligning capabilities to mitigate installation errors. It’s crucial to analyze the load distribution and ensure that the selected rail can accommodate peak loads without compromising performance. -
What are the common materials used in linear rails, and how do they affect performance?
Linear rails are typically made from materials such as carbon steel, aluminum, and stainless steel. Carbon steel offers high strength and load-bearing capacity, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications, while aluminum is lightweight and corrosion-resistant, suitable for mobile applications. Stainless steel rails provide excellent resistance to rust and wear, making them perfect for environments with moisture. The choice of material directly impacts durability, maintenance needs, and overall performance, so select based on your specific application requirements. -
What should I consider when vetting international suppliers for linear rails?
When vetting international suppliers, prioritize their reputation, experience, and quality certifications. Check for customer reviews and case studies that demonstrate their capability to deliver high-quality products consistently. Ensure that they have robust quality assurance processes in place, such as ISO certifications. Additionally, inquire about their ability to provide technical support and after-sales service. This due diligence helps mitigate risks associated with sourcing from overseas suppliers. -
Are there minimum order quantities (MOQs) for linear rails, and how do they vary by supplier?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for linear rails can vary significantly by supplier, often depending on the material, customization, and manufacturing processes. Some suppliers may have MOQs as low as 10 units for standard products, while others may require larger orders for custom sizes or materials. It’s advisable to communicate directly with suppliers to understand their specific MOQs and negotiate terms that align with your purchasing needs, especially if you are looking to minimize initial investment costs. -
What payment terms are typically offered for international B2B transactions involving linear rails?
Payment terms for international transactions can vary widely but commonly include options like advance payment, partial upfront deposits, and net terms (e.g., net 30 or net 60). It’s essential to establish clear payment agreements before placing orders to avoid misunderstandings. Some suppliers may also offer trade financing options or letters of credit, which can provide additional security for both parties. Always ensure that payment terms are documented in the purchase agreement. -
How can I ensure quality assurance for linear rails sourced internationally?
To ensure quality assurance for internationally sourced linear rails, request detailed product specifications and quality certifications from suppliers. Implement an inspection process where samples are tested for compliance with your required standards prior to full-scale production. Collaborate with third-party inspection services to conduct quality checks during manufacturing and prior to shipment. This proactive approach helps identify potential issues early and ensures that the final products meet your quality expectations. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing linear rails?
When importing linear rails, consider factors such as shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations. Choose a reliable logistics partner familiar with international shipping to manage the transport of goods efficiently. Be aware of potential tariffs and duties that may apply to your shipments, and ensure all documentation is accurate to prevent delays at customs. Additionally, factor in the cost of insurance to protect your investment during transit, especially for high-value or fragile components.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for linear rails
In conclusion, effective strategic sourcing of linear rails is essential for international B2B buyers seeking to optimize their operations. The diverse range of linear rail systems—from standard options to heavy-duty solutions—offers flexibility to meet specific application needs across various industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, and robotics. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that provide not only high-quality products but also robust support services, including customization, technical advice, and timely delivery.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Procurement Process?
By leveraging strategic sourcing, businesses can achieve significant cost savings, ensure consistent quality, and improve supply chain resilience. It’s imperative to establish long-term partnerships with reputable manufacturers and distributors, particularly those that understand the unique challenges faced by markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Does the Future Hold for Linear Rails?
Looking ahead, the demand for advanced linear motion solutions will continue to rise as automation and precision engineering become increasingly vital in global markets. Now is the time for international buyers to assess their sourcing strategies and align with innovative suppliers that can provide the latest technologies and trends in linear rail systems. Engage with suppliers today to future-proof your operations and drive competitive advantage in your industry.