The Ultimate Guide to Alternating Current Supply (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for alternating current supply
As international B2B buyers explore the complexities of sourcing alternating current (AC) supply, a key challenge often arises: how to identify reliable suppliers that meet diverse operational needs while ensuring cost-effectiveness. The global market for AC supply is vast, encompassing a wide range of products, from generators and transformers to motors and other essential components. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the AC supply landscape, addressing crucial aspects such as product types, applications across various industries, effective supplier vetting strategies, and cost considerations.
By navigating this guide, B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including countries like Argentina and Egypt—will gain valuable insights into making informed purchasing decisions. Understanding the nuances of AC supply not only enhances operational efficiency but also mitigates risks associated with unreliable products and suppliers.
Moreover, this resource empowers buyers with actionable strategies to evaluate and select the best AC solutions tailored to their specific requirements. As we delve into the intricacies of AC supply, we will illuminate the pathways to optimizing procurement processes, ensuring that businesses can harness the full potential of alternating current technology in their operations.
Understanding alternating current supply Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Phase AC | Utilizes one alternating voltage waveform; simple design | Residential, small businesses, light loads | Pros: Cost-effective, easy installation; Cons: Limited capacity for heavy machinery. |
| Three-Phase AC | Consists of three interconnected alternating waveforms; more efficient | Industrial machinery, large facilities | Pros: Higher efficiency, better load distribution; Cons: More complex installation. |
| High Voltage AC | Transmission at voltages above 100 kV; minimizes losses over long distances | Power distribution networks | Pros: Reduced transmission losses; Cons: Requires specialized equipment and safety measures. |
| Low Voltage AC | Operates at voltages below 1 kV; commonly used in small applications | Commercial buildings, small machinery | Pros: Safer for low-power applications; Cons: Limited range and capacity. |
| Variable Frequency AC | Allows for adjustable frequency; enhances motor control | HVAC systems, variable speed drives | Pros: Energy savings, improved performance; Cons: Higher initial investment. |
What Are the Characteristics of Single-Phase AC?
Single-phase AC is characterized by its use of a single alternating voltage waveform, making it a straightforward and cost-effective solution for residential and light commercial applications. It is commonly found in homes and small businesses, where the power demand is relatively low. For B2B buyers, the simplicity of installation and lower upfront costs make single-phase AC an attractive option, although it may not support heavy machinery effectively.
How Does Three-Phase AC Differ from Other Types?
Three-phase AC consists of three separate alternating waveforms that work together to provide a more stable and efficient power supply. This type is essential for industrial applications, where large machinery and equipment require consistent power. The benefits of three-phase AC include better load distribution and increased efficiency, which can lead to lower operating costs over time. However, the complexity of installation and the need for specialized equipment can be drawbacks for some buyers.
What Are the Advantages of High Voltage AC?
High voltage AC systems are designed to transmit electricity at voltages exceeding 100 kV, which significantly reduces transmission losses over long distances. This type is primarily used in power distribution networks, where efficient energy transfer is critical. While high voltage AC systems can lead to substantial cost savings in energy transmission, they require specialized equipment and stringent safety measures, making them a more complex investment for B2B buyers.
In What Scenarios is Low Voltage AC Suitable?
Low voltage AC operates at voltages below 1 kV and is commonly used in commercial buildings and small machinery. This type of power supply is ideal for applications that do not require high energy levels, making it safer for low-power operations. For B2B buyers, the lower risk associated with low voltage AC can be appealing; however, the limited range and capacity may restrict its applicability in more demanding industrial settings.
Why Consider Variable Frequency AC for Your Business?
Variable frequency AC systems allow for adjustable frequency settings, which enhance motor control and energy efficiency. This feature is particularly beneficial in HVAC systems and variable speed drives, where precise control over motor speed can lead to significant energy savings. Although the initial investment in variable frequency AC technology can be higher, the long-term operational savings and performance improvements often justify the cost for businesses looking to optimize their energy consumption.
A stock image related to alternating current supply.
Key Industrial Applications of alternating current supply
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Alternating Current Supply | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Electric Motors for Production Equipment | Enhanced efficiency and reduced operational costs | Reliability of AC motors, maintenance support, and energy efficiency ratings |
| Construction | Power Tools and Heavy Machinery | Improved productivity and operational reliability | Voltage compatibility, safety certifications, and local supply chain logistics |
| Telecommunications | Data Centers and Network Infrastructure | High uptime and energy efficiency | Scalability of power supply, cooling systems, and redundancy features |
| Agriculture | Irrigation Systems and Pumps | Increased crop yield and resource efficiency | Power source stability, weather resistance, and energy consumption analysis |
| Transportation | Electric Trains and Public Transit Systems | Lower emissions and operational cost savings | Infrastructure compatibility, energy tariffs, and long-term maintenance agreements |
How Is Alternating Current Supply Used in Manufacturing?
In the manufacturing sector, alternating current (AC) is primarily utilized to power electric motors that drive production equipment, such as conveyor belts, assembly lines, and robotic systems. The use of AC motors enhances efficiency due to their simplicity and reliability, which are crucial for high-volume production. For international buyers, particularly those in Africa and South America, sourcing AC motors requires careful consideration of voltage specifications and energy efficiency ratings to ensure compatibility with local power grids and to minimize operational costs.
What Role Does Alternating Current Supply Play in Construction?
In the construction industry, alternating current is essential for operating power tools and heavy machinery, including drills, saws, and cranes. The reliability of AC power allows for continuous operation, which is vital for meeting project deadlines. Buyers should focus on sourcing equipment that meets local voltage standards and safety certifications, especially in the Middle East and Europe, where regulations may vary significantly. Additionally, understanding local supply chain logistics can help ensure timely delivery and support.
How Is Alternating Current Supply Essential for Telecommunications?
Telecommunications infrastructure, particularly data centers, relies heavily on alternating current for powering servers and network equipment. The efficiency of AC systems contributes to high uptime and energy savings, which are critical for maintaining service levels in a competitive market. International buyers must consider the scalability of power supply solutions and the integration of cooling systems to manage heat generated by equipment. Redundancy features are also crucial to ensure uninterrupted service.
In What Ways Does Alternating Current Supply Benefit Agriculture?
In the agricultural sector, alternating current is used to power irrigation systems and pumps, enabling efficient water management and enhancing crop yields. AC power allows for the automation of irrigation processes, which can lead to significant resource savings. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should evaluate the stability of the power source, the weather resistance of equipment, and energy consumption to optimize operational efficiency.
How Does Alternating Current Supply Impact Transportation?
Transportation systems, particularly electric trains and public transit, utilize alternating current to operate efficiently and reduce emissions. The adoption of AC power in these systems leads to lower operational costs and supports sustainable urban development. For international buyers, key considerations include the compatibility of infrastructure with AC systems, understanding local energy tariffs, and establishing long-term maintenance agreements to ensure the longevity of the transportation assets.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘alternating current supply’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Voltage Fluctuations Affecting Equipment Performance
The Problem: B2B buyers in sectors such as manufacturing or data centers often face the issue of voltage fluctuations in their alternating current (AC) supply. These fluctuations can cause equipment to malfunction, leading to production downtime and increased operational costs. For instance, in an industrial setting, sensitive machinery might require a consistent voltage to operate efficiently. When the voltage fluctuates, it can lead to overheating, reduced lifespan of electrical components, and even total failure of the equipment.
The Solution: To mitigate voltage fluctuations, buyers should invest in voltage regulation systems such as Automatic Voltage Regulators (AVRs) or Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS) that provide stable AC output. When sourcing these systems, it’s essential to analyze the specific voltage requirements of your equipment and choose a regulator that can handle peak loads effectively. Additionally, regular maintenance and monitoring of the power supply system can help identify potential issues before they escalate. Integrating power quality monitoring tools will also provide real-time data on voltage stability, enabling proactive adjustments.
Scenario 2: Incompatibility with DC Equipment
The Problem: Many companies are now integrating more DC-powered devices into their operations, particularly in renewable energy sectors or for energy-efficient technologies. A common pain point arises when attempting to connect these devices to an existing AC supply. This incompatibility can lead to inefficiencies, increased energy costs, and the need for additional infrastructure investments.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, B2B buyers should consider implementing AC to DC converters or using hybrid systems that can seamlessly switch between AC and DC supplies. When specifying these systems, it’s vital to assess the total load requirements of all connected devices to ensure the converters can handle the combined output. Additionally, engaging with suppliers who offer customizable solutions can allow for future scalability. It’s also prudent to conduct a cost-benefit analysis to determine if the investment in hybrid systems will yield long-term savings and efficiency improvements.
Scenario 3: Safety Hazards Due to Improper Wiring
The Problem: In regions with varying electrical standards, improper wiring of AC supplies can pose significant safety hazards. For B2B buyers, especially in construction or facility management, this can lead to electrical fires, equipment damage, and potentially serious injuries to personnel. The lack of adherence to local codes and regulations often results in installations that are not only unsafe but also non-compliant.
The Solution: To address this issue, B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing services from certified electrical contractors who are well-versed in both local and international wiring standards. During the procurement process, ensure that contractors provide detailed project plans that outline compliance with safety regulations. Additionally, implementing regular electrical audits and training for staff on safety standards can help mitigate risks associated with improper installations. Buyers should also consider investing in circuit protection devices, such as circuit breakers and fuses, to enhance safety further. Keeping abreast of the latest safety regulations and technology will also equip buyers to make informed decisions regarding their AC supply systems.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for alternating current supply
What Are the Key Materials for Alternating Current Supply?
Selecting the right materials for alternating current (AC) supply systems is crucial for ensuring efficiency, reliability, and compliance with international standards. Below is an analysis of several common materials used in AC applications, focusing on their properties, pros and cons, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Do Copper Conductors Perform in AC Applications?
Copper is one of the most widely used materials for electrical conductors in AC systems. Its excellent electrical conductivity (approximately 60% better than aluminum) allows for efficient energy transmission with minimal losses. Additionally, copper has a high melting point (around 1,984°F or 1,085°C), making it suitable for high-temperature applications.
Pros: Copper’s durability and resistance to corrosion make it a long-lasting choice for electrical wiring. It is also relatively easy to work with, allowing for complex manufacturing processes without significant complications.
Cons: The primary drawback is its cost; copper is significantly more expensive than alternatives like aluminum. Furthermore, its weight can be a limiting factor in certain applications where lightweight materials are preferred.
Impact on Application: Copper conductors are compatible with a wide range of media, making them suitable for various AC applications, including power distribution and industrial machinery.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should be aware of local regulations regarding copper sourcing and recycling. Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and IEC is essential for ensuring product quality.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Alternating Current Supply?
Aluminum is often chosen as a cost-effective alternative to copper for AC applications. It has good conductivity (about 60% that of copper) and is significantly lighter, which can be advantageous in overhead power lines.
Pros: The lower cost and lightweight nature of aluminum make it an attractive option for large-scale installations. Its corrosion resistance is also beneficial, especially in humid or coastal environments.
Cons: Aluminum has a lower thermal conductivity and can be more prone to mechanical failure under stress compared to copper. Additionally, its electrical connections require more careful management to avoid issues like oxidation.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is widely used in power transmission lines and busbars, but its lower conductivity means that larger cross-sections are needed to carry the same current as copper.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that aluminum products meet local and international standards, such as JIS in Japan or DIN in Germany. Proper certification can help avoid complications during installation and operation.
How Do Insulating Materials Affect AC Systems?
Insulating materials, such as PVC (polyvinyl chloride) and XLPE (cross-linked polyethylene), are essential in AC systems to prevent electrical leakage and ensure safety.
Pros: PVC is cost-effective and provides good insulation properties, making it a popular choice for low-voltage applications. XLPE offers superior thermal and chemical resistance, making it suitable for high-voltage applications.
Cons: PVC can degrade under UV exposure, while XLPE is more expensive and may require specialized manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application: The choice of insulating material can significantly influence the safety and longevity of AC systems, particularly in harsh environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with safety standards, such as IEC 60332 for fire resistance, is critical. Buyers in the Middle East and Europe should also consider environmental regulations regarding material disposal.
What Are the Benefits of Using Steel in AC Applications?
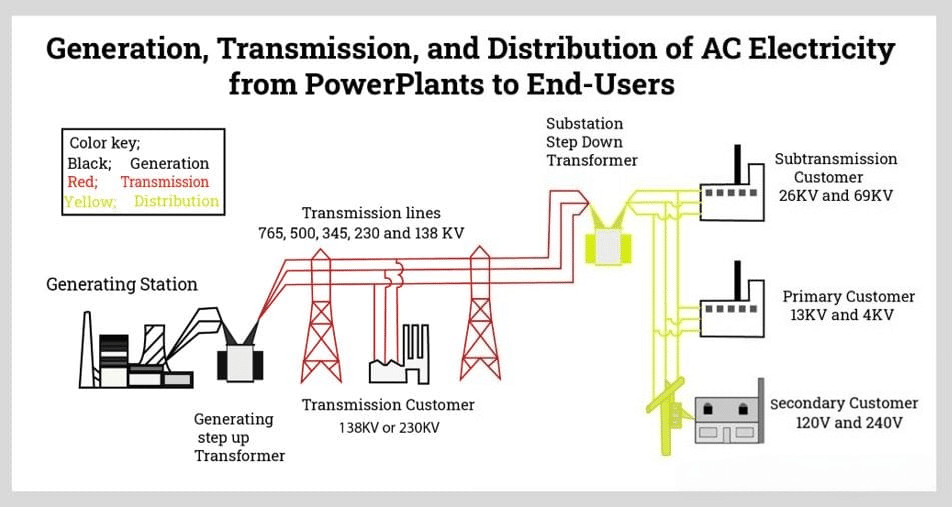
A stock image related to alternating current supply.
Steel is often used in structural components of AC systems, such as towers and support structures. Its high tensile strength and durability make it an ideal choice for supporting heavy electrical equipment.
Pros: Steel’s strength allows for the construction of robust structures that can withstand harsh weather conditions. It is also recyclable, making it an environmentally friendly option.
Cons: The primary disadvantage of steel is its susceptibility to corrosion, which can be mitigated through galvanization but adds to manufacturing costs.
Impact on Application: Steel structures provide stability and support for overhead power lines and substations, ensuring the integrity of the entire AC supply system.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider local availability and the cost of galvanization processes to ensure compliance with structural standards and regulations.
Summary Table of Materials for Alternating Current Supply
| Material | Typical Use Case for alternating current supply | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Electrical wiring, power distribution | Excellent conductivity | High cost | High |
| Aluminum | Overhead power lines, busbars | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower conductivity | Medium |
| PVC | Insulation for low-voltage cables | Cost-effective and good insulation | Degrades under UV exposure | Low |
| Steel | Structural supports for power systems | High tensile strength | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for alternating current supply
What Are the Typical Manufacturing Processes for Alternating Current Supply?
The manufacturing of alternating current (AC) supply equipment involves several critical stages, each requiring precision and adherence to quality standards. Understanding these processes can help B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe ensure they are sourcing reliable products.
What Are the Main Stages in AC Supply Manufacturing?
-
Material Preparation
– The first stage involves selecting and preparing raw materials, such as copper, aluminum, and insulating materials. These materials are crucial for the efficiency and safety of AC equipment.
– Suppliers should ensure that raw materials meet international standards, such as ASTM or ISO specifications, to guarantee quality and performance. -
Forming
– This stage includes shaping the materials into the required components. Techniques such as stamping, forging, and casting are commonly employed to create parts like stators, rotors, and transformer cores.
– Advanced technologies like CNC machining can enhance precision and reduce waste, which is particularly important for maintaining cost-effectiveness. -
Assembly
– The assembly process involves bringing together various components to create a functional AC supply unit. This often includes the integration of electrical wiring, circuit boards, and mechanical parts.
– Automated assembly lines can improve efficiency and consistency, reducing the potential for human error. -
Finishing
– Once assembled, products undergo finishing processes such as painting, coating, and insulation to protect against environmental factors and ensure durability.
– Quality checks during this phase are crucial to prevent defects from affecting performance.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in AC Supply Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in ensuring the reliability and safety of AC supply products. Implementing a robust QA system involves adhering to international and industry-specific standards.
What Are the Relevant International Standards for AC Supply Manufacturing?
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system and is essential for manufacturers looking to demonstrate their commitment to quality.
- CE Marking: For products sold in Europe, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: Relevant for manufacturers involved in oil and gas sectors, ensuring that products meet the specific requirements of these industries.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in AC Supply Production?
To maintain high-quality standards, manufacturers typically establish several quality control checkpoints throughout the production process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
– In this phase, raw materials are inspected for quality before production begins. This includes checking for compliance with specifications and standards. -
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
– During the manufacturing process, ongoing inspections ensure that components meet quality standards at each stage. This helps identify issues early and reduces the risk of defects in the final product. -
Final Quality Control (FQC)
– After assembly, a comprehensive inspection is conducted to ensure that the finished product meets all specifications and regulatory requirements. Testing often includes electrical safety tests, performance evaluations, and environmental simulations.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for AC Supply Products?
Manufacturers employ various testing methods to validate the performance and safety of AC supply products:
- Electrical Testing: This includes tests for voltage, current, and insulation resistance to ensure the product operates within specified limits.
- Thermal Testing: Evaluating how products perform under high temperatures helps identify potential failure points.
- Vibration and Shock Testing: Assessing the durability of equipment under physical stress ensures reliability in real-world applications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control is essential for mitigating risks:
- Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and adherence to quality standards.
- Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide documentation of their quality assurance processes, including test results and compliance certificates.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can offer an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality management practices.
What QC and Certification Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Consider?
Understanding the nuances of quality control and certification is crucial for B2B buyers:
- Regional Certifications: Different regions may have specific certification requirements. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations to ensure compliance.
- Cultural Differences: Quality expectations may vary across cultures. Open communication with suppliers regarding quality standards and expectations can help bridge these gaps.
- Documentation and Traceability: Ensure that suppliers maintain accurate records of their manufacturing and quality processes. This transparency is vital for accountability and traceability.
Conclusion
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for alternating current supply are intricate and require a comprehensive understanding from B2B buyers. By familiarizing themselves with the stages of manufacturing, relevant standards, and verification methods, buyers can make informed decisions and forge successful partnerships with reliable suppliers. This knowledge is particularly crucial for international buyers navigating diverse markets and regulatory landscapes.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘alternating current supply’
Introduction
Navigating the procurement of alternating current (AC) supply can be complex, especially for international B2B buyers. This checklist aims to provide a structured approach to sourcing AC supply effectively, ensuring that you meet your technical requirements, maintain compliance, and secure reliable suppliers. By following these steps, you can streamline your purchasing process while minimizing risks associated with sourcing from different regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging with suppliers, it is essential to outline your technical requirements for AC supply. This includes voltage levels, frequency specifications, and load characteristics.
- Voltage and Frequency: Ensure you understand the standard voltage and frequency requirements in your region (e.g., 220V/50Hz in Europe and many parts of Africa).
- Load Requirements: Determine the expected load capacity to ensure the AC supply can meet operational demands without risk of overload.
Step 2: Research Regulatory Standards
Compliance with local and international regulations is critical when sourcing AC supply.
- Identify Applicable Standards: Familiarize yourself with standards such as IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) or local standards specific to your country.
- Certification Verification: Ensure that suppliers possess the necessary certifications, which can include ISO standards, to guarantee product safety and reliability.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to any supplier, conduct thorough evaluations to ensure they meet your needs.
- Supplier Profiles: Request detailed company profiles, including their experience in the AC supply market and any relevant case studies.
- References and Reviews: Ask for references from other businesses in your industry or region to gain insights into the supplier’s reliability and service quality.
Step 4: Assess Quality Assurance Processes
Quality assurance is vital for ensuring the longevity and safety of AC supply systems.
- Quality Control Measures: Inquire about the supplier’s quality control processes, including testing procedures and product warranties.
- Production Certifications: Look for suppliers with certifications like ISO 9001, which indicate a commitment to quality management systems.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, the next step is to negotiate favorable terms.
- Pricing Transparency: Ensure that pricing is clear and includes all potential costs, such as shipping, tariffs, and taxes.
- Payment Terms: Discuss payment options and terms, including any required deposits or payment upon delivery.
Step 6: Plan for Logistics and Delivery
Logistics play a crucial role in the timely delivery of AC supplies.
- Shipping Arrangements: Confirm the supplier’s shipping methods and timelines to avoid delays in your project.
- Customs and Import Regulations: Understand the customs requirements in your country to prevent any legal issues that may arise during importation.
Step 7: Implement a Post-Purchase Review Process
After the procurement process is complete, establish a review process to assess supplier performance.
- Supplier Evaluation: Regularly evaluate the supplier based on quality, delivery times, and service responsiveness.
- Feedback Mechanism: Implement a feedback system to communicate any issues or improvements needed for future transactions.
By following this practical sourcing guide, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the complexities of procuring alternating current supply, ensuring both compliance and operational efficiency.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for alternating current supply Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Alternating Current Supply Sourcing?
When sourcing alternating current (AC) supply, international B2B buyers must consider various cost components that contribute to the overall pricing structure. The main cost factors include:
-
Materials: The quality and type of materials used in manufacturing AC equipment significantly affect the cost. For instance, copper for wiring and high-grade steel for transformers can be more expensive but offer better conductivity and durability.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary widely by region. In Africa and South America, labor can be less expensive compared to Europe or the Middle East. Understanding local labor rates can provide opportunities for cost savings.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with factory operations, maintenance, and utilities. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce these overheads, impacting the final price.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling can be substantial, especially for custom AC products. Buyers should inquire about tooling costs when negotiating with suppliers.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC measures ensures product reliability and compliance with international standards. While this may increase costs, it ultimately reduces the risk of product failure and warranty claims.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs can vary based on distance, mode of transport, and Incoterms used. Buyers should analyze these costs carefully to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding industry standards for margins can help buyers negotiate better deals.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Alternating Current Supply Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of AC supply, impacting how buyers approach their sourcing strategies:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) can significantly affect pricing. Bulk orders often lead to discounts, so buyers should assess their needs against supplier requirements.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom solutions tailored to specific applications often come at a premium. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unnecessary costs.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (such as ISO or CE) can increase costs but may be necessary for compliance and reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and financial stability of a supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer better reliability and service.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms affects the cost structure, including who bears the risk and shipping costs. Understanding these terms is crucial for accurate budgeting.
What Are the Best Practices for Negotiating AC Supply Prices?
International B2B buyers can enhance their sourcing strategies through effective negotiation and a keen understanding of the total cost of ownership (TCO):
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: Buyers should consolidate orders to meet MOQs and negotiate better pricing based on volume.
-
Assess Total Cost of Ownership: Beyond initial pricing, consider factors such as maintenance, energy efficiency, and lifespan. A lower upfront cost may lead to higher TCO if the product is less reliable.
-
Stay Informed About Pricing Trends: Keeping abreast of market trends, material costs, and geopolitical factors can provide leverage during negotiations.
-
Utilize Multiple Suppliers: Engaging with multiple suppliers can create competition, leading to better pricing and terms.
-
Understand Local Market Conditions: For buyers in regions like Africa and South America, understanding local economic conditions can help in negotiating favorable terms.
What Should International Buyers Keep in Mind Regarding Pricing Nuances?
International B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of the following nuances:
-
Currency Fluctuations: Exchange rates can affect pricing. Buyers should factor in currency risks when negotiating contracts.
-
Cultural Differences: Approaches to negotiation can vary culturally. Understanding local business practices can enhance relationship-building and negotiation outcomes.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that all products meet local regulations and standards, as non-compliance can lead to additional costs and delays.
-
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices: Prices can fluctuate based on market conditions, and buyers should seek updated quotes and assess multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing.
By considering these insights and employing strategic sourcing practices, international B2B buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of alternating current supply sourcing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing alternating current supply With Other Solutions
Introduction: What Are the Alternatives to Alternating Current Supply?
In the realm of electrical power systems, alternating current (AC) has long been the standard for transmission and distribution due to its efficiency and ease of voltage transformation. However, as technology evolves, various alternatives emerge, each with unique advantages and challenges. This analysis compares AC supply with direct current (DC) and renewable energy systems, providing B2B buyers with insights to make informed decisions about their electrical infrastructure.
Comparison Table of Alternating Current Supply and Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Alternating Current Supply | Direct Current (DC) | Renewable Energy Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency for long distances; suitable for heavy loads | Limited range; best for low-power applications | Variable output; efficiency depends on technology used |
| Cost | Lower initial infrastructure costs; high maintenance over time | Higher installation costs; low maintenance | Initial investment can be high; potential long-term savings |
| Ease of Implementation | Well-established technology; widely available | More complex installation; requires specialized equipment | Requires integration with existing systems; regulatory challenges |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed; transformers and generators require servicing | Generally low maintenance; fewer moving parts | Varies by technology; can be high for solar and wind |
| Best Use Case | Industrial applications; urban distribution networks | Battery storage, electronics, and electric vehicles | Off-grid solutions, remote areas, and sustainable development |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Direct Current (DC)?
Direct current (DC) is characterized by a constant flow of electricity in one direction, making it particularly suitable for battery-operated devices and applications requiring stable voltage. Pros include ease of energy storage and minimal energy loss in short-distance transmission. However, cons include difficulty in voltage transformation, making it less efficient for long-distance applications compared to AC. For B2B buyers in industries such as electronics and electric vehicles, DC provides reliable performance but may require more sophisticated infrastructure for broader applications.
How Do Renewable Energy Systems Compare to AC Supply?
Renewable energy systems, including solar and wind power, offer a sustainable alternative to traditional AC supply. The advantages include reduced reliance on fossil fuels and potential cost savings over time due to lower operational expenses. However, the disadvantages encompass variable energy output and significant initial investment costs. B2B buyers looking to invest in renewable technologies must consider the integration challenges with existing AC infrastructure and regulatory compliance, particularly in regions like Europe where sustainability is a priority.
Conclusion: How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
Choosing the right electrical supply solution depends on various factors, including the specific application, budget constraints, and long-term operational goals. B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should assess their unique energy needs, regulatory environments, and infrastructure capabilities. While alternating current remains a reliable choice for many applications, alternatives like direct current and renewable energy systems can offer specialized benefits that may align better with specific projects or sustainability objectives. A thorough analysis of these factors will empower buyers to make informed decisions that best suit their operational requirements.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for alternating current supply
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Alternating Current Supply?
Understanding the technical properties of alternating current (AC) supply is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly those involved in industrial applications. Here are some essential specifications that can guide decision-making:
1. Voltage Rating: Why Is It Critical for AC Supply?
The voltage rating of an AC supply indicates the maximum voltage the system can handle. Common ratings include 110V, 220V, and 380V. For international buyers, knowing the voltage rating is essential to ensure compatibility with local electrical systems and equipment. This helps prevent costly equipment damage and ensures compliance with regional standards.
2. Frequency: How Does It Affect Performance?
Frequency, measured in Hertz (Hz), refers to how often the current alternates direction per second. Common frequencies are 50Hz and 60Hz, depending on the region. Understanding the frequency is vital for ensuring that motors and other equipment operate efficiently and without overheating. Mismatched frequencies can lead to operational inefficiencies and equipment failure.
3. Power Factor: What Is Its Significance?
The power factor indicates the efficiency with which electrical power is converted into useful work output. It is a ratio of real power (used for work) to apparent power (total power supplied). A power factor closer to 1 signifies better efficiency. For B2B buyers, understanding power factor is essential for optimizing energy costs and ensuring that equipment runs efficiently.
4. Phase Configuration: Why Does It Matter?
AC supply can be single-phase or three-phase. Three-phase systems are commonly used in industrial settings for their efficiency in power distribution and ability to support heavier loads. Knowing the phase configuration helps buyers choose the right system for their operational needs, impacting overall productivity and energy costs.
5. Material Grade: How Does It Impact Longevity?
Material grade pertains to the quality of conductors and insulators used in AC supply systems. Higher-grade materials can withstand higher temperatures and corrosive environments, which is crucial for durability and safety. For international buyers, investing in higher-grade materials can lead to reduced maintenance costs and longer service life.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Alternating Current Supply?
Familiarity with industry terminology can streamline the procurement process for B2B buyers. Here are several key terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): What Does It Mean?
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers source quality components that meet specific technical requirements without compromising on standards.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Why Is It Important?
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For international buyers, knowing the MOQ can help in budgeting and inventory management. It’s crucial to negotiate terms that align with operational needs and storage capabilities.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation): How Should It Be Used?
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for a specific quantity of goods. This is essential for B2B buyers looking to compare prices and terms from multiple suppliers, ensuring they secure the best deal.
4. Incoterms: What Are They and Why Do They Matter?
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is vital for buyers to manage shipping costs, risks, and liabilities effectively, ensuring smooth cross-border transactions.
5. Lead Time: How Does It Affect Planning?
Lead time is the period between placing an order and receiving it. For B2B buyers, understanding lead times is essential for effective project planning and inventory management. Longer lead times may necessitate adjustments in scheduling and resource allocation.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions regarding their alternating current supply needs, ultimately leading to more efficient operations and cost savings.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the alternating current supply Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Alternating Current Supply Sector?
The alternating current (AC) supply sector is witnessing transformative changes driven by technological advancements, regulatory frameworks, and increasing demand for energy efficiency. Global drivers such as urbanization, industrialization, and the need for reliable electricity supply are compelling B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets like Africa and South America, to explore innovative AC solutions. The rise of smart grids and the Internet of Things (IoT) is creating opportunities for enhanced monitoring and management of AC systems, enabling businesses to optimize energy consumption and reduce operational costs.
In Europe and the Middle East, regulatory pressures are pushing industries toward adopting more efficient AC technologies. For instance, the European Union’s Green Deal aims to make Europe climate-neutral by 2050, prompting investments in energy-efficient AC systems and renewable integration. This trend is mirrored in South America, where countries like Argentina are investing in modernizing their power infrastructure to support sustainable development goals.
Furthermore, there is a noticeable shift towards digital transformation in sourcing processes. B2B buyers are increasingly leveraging data analytics and AI tools to assess supplier capabilities, track market trends, and manage risks associated with AC supply chains. This data-driven approach enhances decision-making, allowing businesses to identify the best sourcing options while ensuring compliance with international standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Ensure Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in the Alternating Current Supply Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing have become pivotal in the AC supply sector as businesses recognize their role in environmental stewardship. The environmental impact of AC production, including carbon emissions and resource depletion, underscores the need for responsible sourcing practices. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate commitment to sustainability through eco-friendly manufacturing processes and the use of renewable materials.
Obtaining certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems can signal a supplier’s dedication to sustainable practices. Additionally, exploring ‘green’ certifications for products—like Energy Star or EPEAT—can help buyers select AC equipment that meets stringent energy efficiency criteria. These certifications not only enhance the credibility of suppliers but also align with the growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible products.
Incorporating ethical sourcing practices also extends to ensuring fair labor practices within the supply chain. Buyers should conduct thorough audits and engage with suppliers who adhere to ethical labor standards, particularly in regions where such regulations may be less stringent. By prioritizing sustainability and ethical sourcing, B2B buyers can strengthen their brand reputation and foster long-term relationships with environmentally conscious partners.
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of the Alternating Current Supply Sector?
The journey of alternating current supply began in the late 19th century, driven by the need for efficient long-distance electricity transmission. Nikola Tesla’s development of AC induction motors and transformers laid the foundation for widespread AC adoption, eclipsing direct current (DC) systems. The “War of Currents,” primarily between Tesla and Thomas Edison, highlighted AC’s advantages in power distribution, leading to its dominance in electrical grids globally.
Over the decades, advancements in AC technology have continued to evolve. The introduction of high-voltage AC transmission systems significantly improved energy distribution capabilities, facilitating the growth of urban centers and industrial hubs. In recent years, the integration of renewable energy sources and smart technologies has transformed the AC landscape, paving the way for sustainable practices and innovative solutions tailored to the needs of modern B2B buyers.
Understanding this historical context enables international buyers to appreciate the advancements that have shaped the current AC supply market, guiding their strategic decisions in sourcing and investment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of alternating current supply
-
How do I solve issues related to alternating current supply voltage fluctuations?
Voltage fluctuations in alternating current supply can lead to equipment malfunctions and inefficiencies. To address this, consider investing in voltage stabilizers or transformers that can regulate the voltage levels to the desired specifications. Collaborate with your supplier to understand the voltage requirements of your equipment and ensure that the AC supply can consistently meet these needs. Additionally, conducting regular maintenance checks and monitoring the electrical system can preemptively identify and rectify voltage issues. -
What is the best type of alternating current for industrial applications?
For industrial applications, three-phase alternating current (AC) is often the best choice due to its efficiency and ability to power heavy machinery. Three-phase AC provides a constant power supply and is more efficient for large loads compared to single-phase AC. When sourcing, ensure your suppliers can provide three-phase systems that meet local standards and regulations. Additionally, inquire about the compatibility of the AC supply with your existing machinery to avoid operational disruptions. -
How can I vet suppliers of alternating current systems for my business?
Vetting suppliers is crucial for ensuring quality and reliability in your AC systems. Start by checking their certifications, such as ISO standards, which indicate adherence to quality management practices. Request references from previous clients, and consider conducting site visits to assess their manufacturing capabilities. Additionally, evaluate their customer support and after-sales service, as these can be critical in case of technical issues or maintenance needs. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for alternating current supply systems?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly among suppliers based on the type of AC systems and components required. For larger industrial systems, MOQs may be higher due to the complexity of the equipment and the costs involved in production. Always clarify MOQs during initial discussions with potential suppliers and consider negotiating terms that align with your purchasing capabilities. If you’re a smaller business, look for suppliers that cater to smaller orders or offer flexible purchasing options. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing alternating current supply?
Payment terms can differ by supplier and region. Common arrangements include upfront payments, partial payments upon order confirmation, and balance payments upon delivery. It’s essential to negotiate terms that are favorable to your cash flow while ensuring the supplier feels secure in their transaction. For international transactions, consider using secure payment methods like letters of credit or escrow services to mitigate risks associated with cross-border payments.
A stock image related to alternating current supply.
-
How do I ensure quality assurance for my alternating current systems?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed specifications and certifications from your suppliers. Most reputable manufacturers will conduct routine testing and quality checks on their products before shipment. Consider establishing a quality assurance protocol that includes inspection upon arrival, followed by regular performance evaluations of the AC systems in operation. Collaborating with suppliers who have a strong reputation for quality can significantly reduce the risk of receiving subpar products. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing alternating current supply?
Logistics play a vital role in the timely and safe delivery of AC supply systems. Evaluate the shipping methods available, considering both cost and transit time. Ensure that your supplier has experience with international shipping and can handle customs clearance processes efficiently. Additionally, consider the need for insurance during transit to protect against potential damages or losses. Establish a clear communication channel with your supplier and freight forwarder to track shipments and address any issues promptly. -
What are the common customization options available for alternating current systems?
Customization options for alternating current systems can include voltage ratings, frequency adjustments, and integration with existing electrical systems. Many suppliers offer tailored solutions to meet specific industry needs or regulatory requirements. Engage in discussions with potential suppliers to understand the extent of their customization capabilities, including the design process and lead times. Custom solutions can enhance the efficiency and compatibility of your AC supply with your operational needs.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for alternating current supply
In navigating the complexities of alternating current (AC) supply, strategic sourcing emerges as a vital approach for international B2B buyers. By understanding the distinct advantages of AC over direct current (DC), particularly in terms of efficiency, reliability, and cost-effectiveness, businesses in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can make informed procurement decisions. Leveraging AC’s capability to power high-demand applications and its compatibility with transformers and motors allows for scalable solutions tailored to diverse operational needs.
What are the key benefits of strategic sourcing in AC supply?
Strategic sourcing not only enhances supply chain efficiency but also fosters long-term partnerships with reliable vendors, ensuring access to high-quality components and technologies. As global energy demands continue to rise, the importance of a robust AC infrastructure cannot be overstated.
What’s next for international buyers in the AC market?
Looking ahead, B2B buyers should actively seek out innovative solutions and local partnerships to optimize their AC supply chains. By embracing advancements in AC technologies and sustainable practices, companies can position themselves competitively in an evolving market landscape. Take the next step towards a more efficient future—evaluate your AC sourcing strategy today and unlock new opportunities for growth and sustainability.