The Ultimate Guide to Radio Frequency Shielding Material (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for radio frequency shielding material
Navigating the global market for radio frequency shielding material presents a significant challenge for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As industries increasingly rely on sensitive electronic devices, the need for effective shielding against radio frequency interference (RFI) becomes paramount. However, sourcing the right materials—be it for aerospace applications, medical devices, or secure communication environments—requires a nuanced understanding of various shielding options and their unique properties.
This comprehensive guide delves into the diverse types of RF shielding materials, including metals such as copper, aluminum, and nickel silver, as well as elastomers and conductive foams for gaskets. Buyers will gain insights into the applications and performance characteristics of each material, empowering them to make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs. Additionally, we will explore supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and best practices for procurement.
By equipping international B2B buyers with actionable insights and strategies, this guide aims to simplify the sourcing process, ensuring that organizations can effectively shield their technologies from unwanted interference. Whether you are a buyer in Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, or elsewhere in Europe, understanding the intricacies of RF shielding materials will enhance your competitive edge and protect your investments in technology.
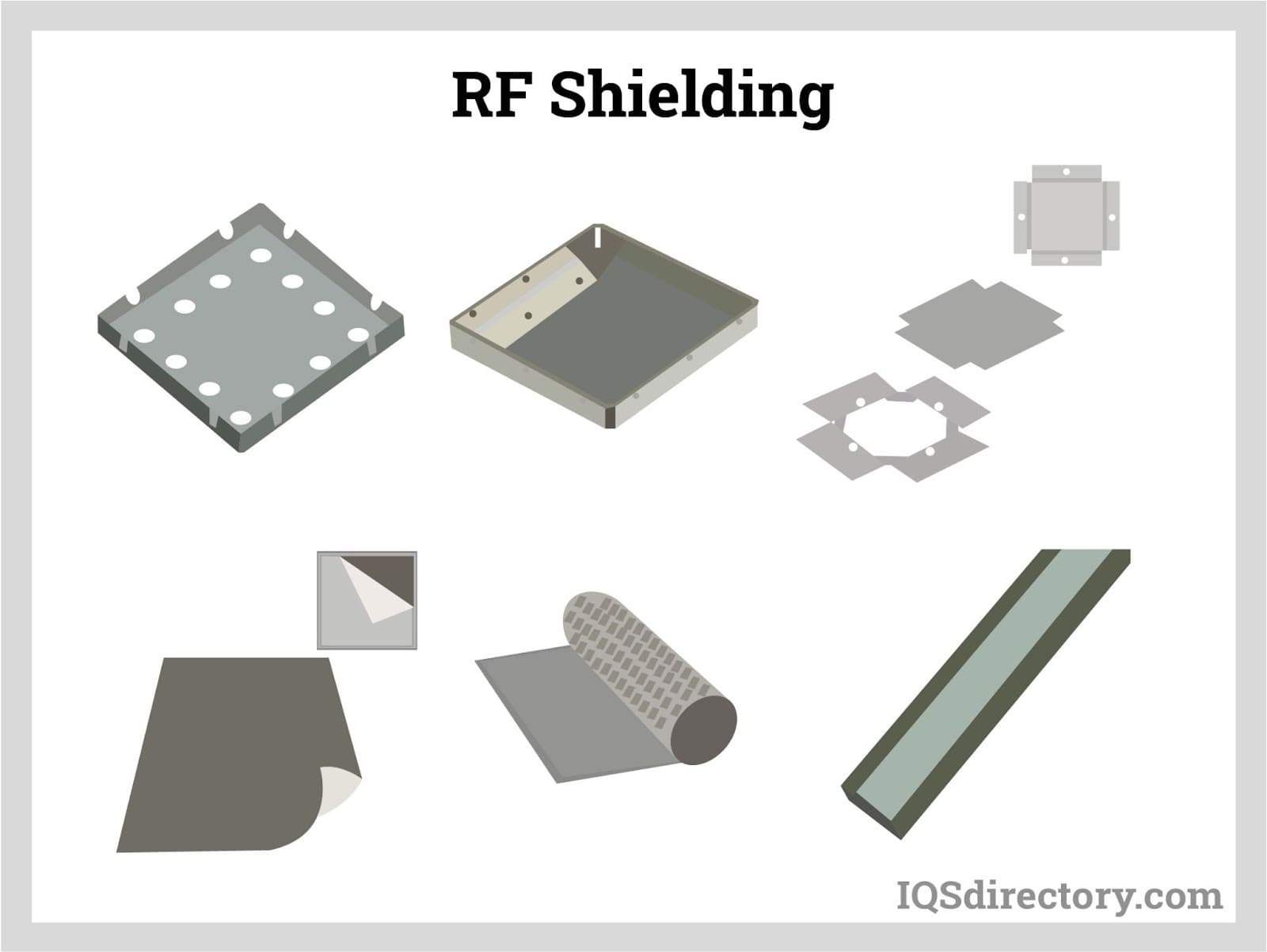
Understanding radio frequency shielding material Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | High conductivity, excellent RF absorption | Aerospace, medical devices, telecommunications | Pros: Superior performance; Cons: Higher cost |
| Aluminum | Lightweight, cost-effective, moderate conductivity | Consumer electronics, automotive, industrial | Pros: Affordable; Cons: Lower conductivity |
| Nickel Silver | Corrosion-resistant, aesthetically pleasing | Military, defense, telecommunications | Pros: Good conductivity; Cons: Higher price |
| Steel | Strong, ferromagnetic properties | Industrial machinery, telecommunications | Pros: Durable and strong; Cons: Heavier |
| Conductive Elastomers | Flexible, filled with conductive particles | Automotive, electronics, aerospace | Pros: Versatile; Cons: Variable performance |
What are the characteristics of Copper RF Shielding Materials?
Copper is one of the most effective materials for radio frequency shielding due to its high conductivity and excellent RF absorption capabilities. It is widely used in applications requiring robust shielding, such as aerospace and medical devices. When considering copper, buyers should evaluate the cost against the required performance. Although it is more expensive than other materials, its superior shielding effectiveness can justify the investment, especially in critical applications.
Why is Aluminum a popular choice for RF Shielding?
Aluminum is favored for its lightweight nature and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for various applications, including consumer electronics and automotive components. While it provides moderate conductivity, buyers should be aware of its susceptibility to galvanic corrosion. When choosing aluminum, consider the balance between cost and performance, especially in environments where weight savings are crucial.
What makes Nickel Silver unique for RF Shielding?
Nickel silver, an alloy of copper, is known for its corrosion resistance and attractive appearance. It is commonly used in military and telecommunications applications where both aesthetic and functional properties are important. Buyers should consider the trade-off between its higher cost and the benefits of durability and performance. Nickel silver can be an excellent choice for applications requiring long-term reliability in challenging environments.
How does Steel perform in RF Shielding applications?
Steel stands out due to its strength and ferromagnetic properties, which enable it to provide effective magnetic shielding. It is often used in industrial machinery and telecommunications equipment. While steel offers durability, its weight can be a drawback in some applications. Buyers should assess whether the strength and magnetic properties meet their specific shielding requirements, especially when weight is a concern.
What are the advantages of using Conductive Elastomers for RF Shielding?
Conductive elastomers are flexible materials filled with conductive particles, making them ideal for applications requiring a tight seal, such as automotive and aerospace components. Their versatility allows them to conform to various shapes, enhancing their effectiveness as gaskets and seals. However, performance can vary based on the specific formulation. Buyers should carefully evaluate the intended application to ensure that the chosen elastomer meets the necessary shielding standards.
Key Industrial Applications of radio frequency shielding material
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Radio Frequency Shielding Material | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | RF shielding for avionics and communication systems | Ensures signal integrity and safety in critical systems | Compliance with aviation regulations and certifications |
| Medical Devices | RF shielding in MRI machines and diagnostic equipment | Protects sensitive data and ensures accurate diagnostics | Material biocompatibility and electromagnetic compatibility |
| Telecommunications | RF shielding in data centers and telecom infrastructure | Reduces interference, enhancing network reliability | Scalability and adaptability to various system designs |
| Defense and Security | RF shielding for secure communication facilities | Prevents unauthorized access to sensitive information | High-performance materials with proven security standards |
| Automotive | RF shielding in electric vehicles and infotainment systems | Protects against electromagnetic interference in systems | Lightweight materials that meet automotive safety standards |
How is Radio Frequency Shielding Material Utilized in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace sector, RF shielding material is critical for ensuring the reliability of avionics and communication systems. These systems must operate without interference to maintain safety and functionality during flight. Shielding materials, such as copper and aluminum, are employed to create enclosures that protect sensitive equipment from external RF signals. Buyers in this sector must consider materials that comply with stringent aviation regulations and certifications, ensuring their products can withstand extreme conditions.
What Role Does RF Shielding Play in Medical Devices?
In medical devices, particularly MRI machines and diagnostic equipment, RF shielding materials are essential to prevent interference that could compromise diagnostic accuracy. These materials help maintain the integrity of sensitive data and protect patient safety. Buyers should prioritize materials that are biocompatible and provide electromagnetic compatibility, ensuring they meet the specific requirements of the medical industry while adhering to health regulations.
How is RF Shielding Important for Telecommunications?
Telecommunications infrastructure relies heavily on RF shielding to minimize interference in data centers and communication networks. Effective shielding enhances network reliability by reducing electromagnetic interference that can disrupt signal transmission. B2B buyers in telecommunications should focus on sourcing scalable and adaptable shielding solutions that fit various system designs, ensuring robust performance in diverse environments across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Why is RF Shielding Critical in Defense and Security?
In defense and security applications, RF shielding is crucial for protecting secure communication facilities from electronic eavesdropping. The use of high-performance shielding materials ensures that sensitive information remains confidential and secure from unauthorized access. Buyers in this sector need to consider materials that meet rigorous security standards and have a proven track record of performance, particularly in high-stakes environments.
How is RF Shielding Applied in Automotive Industries?
The automotive industry increasingly uses RF shielding materials in electric vehicles and infotainment systems to protect against electromagnetic interference. This shielding is vital for maintaining the functionality of electronic systems, ensuring they operate smoothly without disruption. Buyers should seek lightweight materials that comply with automotive safety standards, particularly as the industry shifts towards more technologically advanced vehicles in regions like Europe and the Middle East.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘radio frequency shielding material’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inadequate Shielding Performance in Critical Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter situations where the RF shielding materials they have sourced fail to meet the specific requirements of their applications, especially in critical sectors such as aerospace, medical devices, or military environments. For example, a manufacturer in Nigeria may invest in aluminum RF shielding foils, believing them to be a cost-effective solution. However, the buyer soon realizes that aluminum does not provide the necessary conductivity to adequately protect sensitive electronics from interference, leading to compromised device performance and potential regulatory violations.
The Solution: To avoid inadequate shielding performance, it’s essential to conduct a thorough needs assessment before purchasing RF shielding materials. Buyers should specify the frequency range they need to shield against and consult with manufacturers who offer tailored solutions. Opt for materials with proven performance metrics, such as copper or nickel silver, which are known for their superior conductivity and attenuation properties. Additionally, engaging with a reliable manufacturing partner who can provide engineering support and testing services will help ensure that the selected materials meet industry standards and application-specific requirements. This proactive approach can significantly reduce the risk of product failure and enhance compliance with regulatory standards.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Integration of Shielding Materials
The Problem: Another common pain point is the difficulty in integrating RF shielding materials into existing designs or systems. For instance, a technology firm in Saudi Arabia may find that the gaskets they purchased do not fit the specific enclosures they are using, resulting in gaps that compromise shielding effectiveness. This integration issue can lead to delays in product development and increased costs due to re-engineering and additional sourcing.
The Solution: To facilitate smoother integration, buyers should prioritize working closely with manufacturers during the design phase of their products. This collaboration can help ensure that the shielding materials selected, such as filled elastomers for gaskets, are compatible with the dimensions and specifications of their enclosures. Buyers should also consider opting for customizable solutions that allow for adjustments in size, shape, and material properties. Investing in 3D modeling and prototyping during the design process can also aid in identifying potential integration challenges early on, thereby minimizing costly adjustments later in the manufacturing cycle.
Scenario 3: Cost Overruns Due to Material Selection
The Problem: Cost overruns are a prevalent issue when purchasing RF shielding materials, especially when buyers do not fully understand the implications of their material choices. For example, a South American electronics company might choose a low-cost RF shielding foil without realizing that it lacks the durability and effectiveness of higher-end options. As a result, they may face additional expenses from product failures, recalls, or the need for further shielding solutions.
The Solution: To mitigate the risk of cost overruns, it is crucial for buyers to adopt a long-term perspective when selecting RF shielding materials. Instead of solely focusing on upfront costs, they should evaluate the total cost of ownership, which includes performance, durability, and potential maintenance expenses. Engaging in thorough market research to understand the performance characteristics and lifespan of various materials can inform better purchasing decisions. Additionally, consulting with industry experts or utilizing comparative studies can provide insights into which materials will deliver the best value in the long run. By making informed choices, buyers can achieve a balance between cost and performance, ultimately leading to savings and enhanced product reliability.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for radio frequency shielding material
When selecting materials for radio frequency (RF) shielding, international B2B buyers must consider various factors, including the specific application requirements, regulatory compliance, and cost-effectiveness. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in RF shielding, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for buyers from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Key Properties of Copper in RF Shielding?
Copper is renowned for its excellent conductivity and is often the go-to material for RF shielding. It has a high temperature rating and can withstand various environmental conditions, making it suitable for a range of applications from medical devices to aerospace.
Pros & Cons:
Copper’s primary advantage is its superior shielding effectiveness, which is essential for high-frequency applications. However, its high cost and susceptibility to corrosion can be significant drawbacks. Additionally, manufacturing complexity can increase due to the need for specialized equipment to shape and form copper components.
Impact on Application:
Copper is highly effective in environments where signal integrity is critical. However, buyers must consider its compatibility with other materials to avoid galvanic corrosion, especially in humid climates.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN is crucial. Buyers from regions like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia should also consider local regulations regarding material sourcing and environmental impact.
How Does Aluminum Compare as a Cost-Effective RF Shielding Material?
Aluminum is a lightweight alternative to copper, often used in applications where weight is a concern, such as in mobile devices and lightweight enclosures.
Pros & Cons:
Aluminum is more cost-effective than copper and offers decent shielding effectiveness. However, it has lower conductivity and may suffer from galvanic corrosion when in contact with dissimilar metals. The manufacturing process is generally simpler, which can lead to lower production costs.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is suitable for applications that do not require the highest levels of shielding effectiveness but still need reliable performance. It is commonly used in consumer electronics and automotive applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the varying quality standards for aluminum in different regions. In Europe, for instance, compliance with REACH regulations may be necessary.
What Advantages Does Nickel Silver Offer in RF Shielding?
Nickel silver, an alloy of copper, nickel, and zinc, is often chosen for its corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal, making it suitable for decorative applications as well as functional ones.
Pros & Cons:
The main advantage of nickel silver is its resistance to tarnishing and corrosion, which extends the lifespan of RF shielding applications. However, it is generally more expensive than aluminum and may not provide the same level of conductivity as pure copper.
Impact on Application:
Nickel silver is ideal for applications requiring both shielding and aesthetic considerations, such as in high-end consumer electronics and medical devices.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure that their suppliers meet international standards for nickel silver alloys, as variations can affect performance. Compliance with local regulations in regions like South America may also be necessary.
Why Consider Conductive Elastomers for RF Shielding Gaskets?
Conductive elastomers, often filled with conductive materials like silver or nickel, are crucial for sealing gaps in RF shielding enclosures.
Pros & Cons:
These materials offer flexibility and can conform to various shapes, providing effective sealing. However, their performance can vary significantly based on the type of filler used, and they may have a shorter lifespan compared to metal options.
Impact on Application:
Conductive elastomers are essential for applications where movement or vibration is present, such as in automotive or aerospace settings.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should evaluate the specific filler materials used in elastomers, as this can impact both cost and performance. Compliance with international standards for elastomer materials is also critical.
Summary Table of RF Shielding Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for radio frequency shielding material | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Aerospace, medical devices | Superior conductivity | High cost, prone to corrosion | High |
| Aluminum | Consumer electronics, automotive | Lightweight, cost-effective | Lower conductivity, corrosion issues | Medium |
| Nickel Silver | High-end electronics, medical devices | Corrosion resistance | Higher cost, lower conductivity | Medium |
| Conductive Elastomers | Automotive, aerospace gaskets | Flexible, good sealing properties | Variable performance, shorter lifespan | Low |
This comprehensive analysis provides B2B buyers with actionable insights into material selection for RF shielding, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their specific application needs and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for radio frequency shielding material
The manufacturing of radio frequency (RF) shielding materials is a complex process that involves several stages, each critical to ensuring the final product meets the stringent requirements for RF interference protection. In addition to understanding the manufacturing processes, international B2B buyers must also navigate the quality assurance measures that guarantee product reliability and compliance with relevant standards. This section provides a detailed overview of the manufacturing processes and quality control (QC) practices that are essential for RF shielding materials.
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of RF Shielding Materials?
The manufacturing process for RF shielding materials typically consists of four main stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage plays a pivotal role in determining the quality and effectiveness of the final product.
1. Material Preparation
Material preparation is the first step in the manufacturing process. This stage involves selecting the appropriate conductive materials, such as copper, aluminum, or nickel silver, based on the specific application requirements. The materials are then cleaned and treated to remove any contaminants that could affect conductivity. For gaskets and seals, elastomers filled with conductive particles are prepared, ensuring the fillers are evenly distributed to optimize shielding performance.
2. Forming Techniques
Once the materials are prepared, they undergo various forming techniques. Common methods include:
-
Stamping: Used for creating metal enclosures, stamping shapes the material into desired forms using dies. This method is efficient for high-volume production and ensures precision.
-
Extrusion: Often used for producing gaskets, extrusion involves forcing the elastomer mixture through a die to create continuous shapes that can then be cut to size.
-
Molding: This technique is frequently employed for complex shapes and is particularly useful for elastomeric gaskets. Injection molding allows for precise control over dimensions and material consistency.
3. Assembly
The assembly stage involves bringing together the formed components. For RF shields, this may include fitting metal enclosures with gaskets or O-rings to create a complete shielding solution. Proper alignment and sealing are crucial to maintain the integrity of the shield against RF signals. Advanced techniques, such as ultrasonic welding or adhesive bonding, may be utilized to ensure a robust assembly that can withstand operational stresses.
4. Finishing Processes
Finishing processes enhance the durability and appearance of the RF shielding materials. Common finishing techniques include:
-
Surface Coating: Applying coatings can improve corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. This is particularly important for materials exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
-
Machining: For high-precision components, machining processes such as milling or drilling may be used to achieve specific tolerances.
-
Testing and Inspection: Prior to the final packaging, products undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet performance specifications.
How is Quality Assurance Implemented in the Manufacturing of RF Shielding Materials?
Quality assurance in the manufacturing of RF shielding materials involves adhering to both international standards and industry-specific requirements. Understanding these standards is crucial for B2B buyers seeking reliable suppliers.
Relevant International Standards for Quality Assurance
-
ISO 9001: This widely recognized standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS). Manufacturers of RF shielding materials should comply with ISO 9001 to demonstrate their commitment to quality and continuous improvement.
-
CE Marking: For products sold in the European market, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. This is particularly relevant for RF shielding materials used in sensitive applications like medical devices or telecommunications.
-
API Standards: In industries such as oil and gas, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards can be crucial. These standards ensure that products can withstand demanding environments.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) is a multi-faceted process that typically involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing cycle:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint assesses the quality of raw materials before they enter production. Suppliers must provide certificates of compliance to verify that materials meet specified standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, periodic inspections are conducted to ensure that processes are being followed correctly and that the products are being produced to specification.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before products are shipped, a final inspection is performed. This may include functional testing, dimensional checks, and visual inspections to ensure that the RF shielding materials meet all performance criteria.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for RF Shielding Materials?
Testing methods are essential for validating the effectiveness of RF shielding materials. Common techniques include:
-
Shielding Effectiveness Testing: This measures the ability of a material to attenuate RF signals, often conducted in a controlled environment using specialized equipment.
-
Environmental Testing: Materials are subjected to various environmental conditions, such as temperature and humidity, to assess their durability and performance over time.
-
Mechanical Testing: This includes tensile strength and flexibility tests to ensure that the materials can withstand physical stresses without failure.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying the quality control processes of suppliers is vital. Here are some effective strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes, quality control practices, and compliance with international standards firsthand.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should ask suppliers for detailed quality reports, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC stages, to ensure transparency in quality assurance.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures and product performance.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
B2B buyers must be aware of specific nuances when dealing with suppliers from different regions. For instance, buyers in Africa may face challenges related to local regulations and standards, while those in Europe must ensure compliance with stringent EU requirements. Understanding these regional differences is critical for successful procurement and supply chain management.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for RF shielding materials are intricate and demand attention to detail. By understanding these processes and implementing robust quality control measures, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that ensure the reliability and performance of their RF shielding solutions.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘radio frequency shielding material’
To effectively procure radio frequency shielding material, it’s essential to follow a structured approach. This guide provides a practical checklist to ensure that international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, can make informed decisions when sourcing these critical materials.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, clearly outline your technical requirements. This includes understanding the frequency ranges you need to shield against and the specific environmental conditions the materials will face.
– Key considerations:
– Determine if you require materials for enclosures or gaskets.
– Identify the necessary conductivity levels and any specific regulatory compliance, particularly for sensitive sectors like aerospace or medical devices.
Step 2: Research Available Materials
Familiarize yourself with the various types of RF shielding materials available on the market. Common options include copper, aluminum, nickel silver, and various elastomers for gaskets.
– Important factors:
– Assess the effectiveness of each material concerning your specifications.
– Compare costs versus performance, especially if budget constraints are a concern.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, thoroughly vet potential suppliers. This step is crucial to ensure reliability and quality in your sourcing process.
– Action items:
– Request detailed company profiles, including years in operation and areas of expertise.
– Look for case studies or references from clients in similar industries or geographical regions to gauge their performance.
Step 4: Verify Certifications and Standards Compliance
Ensure that your suppliers meet the necessary industry standards and certifications for RF shielding materials. Compliance can significantly impact the effectiveness and reliability of the materials.
– Checklist:
– Look for certifications such as ISO 9001 or specific industry-related standards.
– Confirm that materials comply with relevant local and international regulations, especially if you are importing.
Step 5: Request Samples for Testing
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request samples of the materials you are interested in. Testing these samples will help you assess their performance in real-world conditions.
– Testing criteria:
– Evaluate the shielding effectiveness in your specific application.
– Check for durability and resistance to environmental factors relevant to your operation.
Step 6: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Engage in discussions regarding pricing, minimum order quantities, and payment terms. This step is essential to ensure that you are getting the best value for your investment.
– Tips for negotiation:
– Consider long-term partnerships for better pricing and terms.
– Be clear about your budget constraints while exploring options for bulk discounts.
Step 7: Finalize the Order and Monitor Delivery
After selecting a supplier and agreeing on terms, place your order and establish a timeline for delivery. It’s crucial to maintain communication with the supplier to monitor the progress of your order.
– Delivery considerations:
– Confirm shipping methods and expected delivery times.
– Ensure there are contingency plans for delays or quality issues upon receipt.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can systematically approach the procurement of radio frequency shielding materials, minimizing risks and maximizing efficiency in their sourcing strategy.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for radio frequency shielding material Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Radio Frequency Shielding Material Sourcing?
When sourcing radio frequency (RF) shielding materials, understanding the cost structure is critical for international B2B buyers. The overall cost can be broken down into several key components:
-
Materials: The choice of materials, such as copper, aluminum, nickel silver, or elastomers filled with conductive particles, significantly impacts cost. High-performance materials typically command higher prices but offer better shielding effectiveness.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary significantly based on geographic location, skill level, and manufacturing practices. In regions like Europe and North America, labor costs are generally higher compared to Africa and South America.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturers can optimize these costs, which can reflect in pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific RF shielding designs can be a significant initial investment. Buyers should consider whether the tooling costs are amortized over large production runs or borne entirely by smaller orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that RF shielding materials meet industry standards and certifications is crucial. QC processes can add to the overall cost but are essential for ensuring product reliability.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary based on the supplier’s location, shipping method, and distance to the buyer. Incoterms also play a role in determining who bears these costs.
-
Margin: Supplier profit margins will vary based on market conditions, competition, and the perceived value of the product. Understanding the competitive landscape can help buyers gauge if they are getting a fair price.
How Do Price Influencers Affect RF Shielding Material Costs?
Several factors influence the price of RF shielding materials, which international B2B buyers must consider:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their needs while benefiting from lower prices.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specific material requirements can drive up costs. Buyers should clearly define their needs to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials or those with specific certifications (e.g., military-grade) may come at a premium. Buyers should weigh the importance of these factors against their budget.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers with a proven track record may charge more, but they often provide better service and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms (e.g., FOB, CIF) can significantly affect the total cost of ownership. Buyers should clarify responsibilities to avoid hidden costs.
What Are Essential Tips for Buyers to Optimize RF Shielding Material Costs?
International B2B buyers should adopt strategies to enhance cost-efficiency in sourcing RF shielding materials:
-
Negotiation Strategies: Build long-term relationships with suppliers to leverage better pricing and terms. Consider negotiating on volume, payment terms, and delivery schedules.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Assess not just the purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with installation, maintenance, and potential failures. Investing in higher-quality materials may reduce TCO in the long run.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and trade regulations that may affect pricing. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should research local market conditions.
-
Comparative Analysis: Conduct a thorough analysis of multiple suppliers to understand market pricing and identify the best value. Consider both direct costs and qualitative factors like service and support.
-
Seek Expert Guidance: Engage with industry experts or consultants who can provide insights into material selection and sourcing strategies tailored to specific regions and applications.
Disclaimer on Pricing Information
Prices for RF shielding materials can vary widely based on numerous factors, including material type, quantity, and supplier. The prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and should be confirmed with suppliers for accurate quotations. Always consider the total cost of ownership when evaluating offers.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing radio frequency shielding material With Other Solutions
When evaluating solutions for protecting sensitive electronic components from radio frequency interference (RFI), it’s crucial for international B2B buyers to consider various alternatives to traditional radio frequency shielding materials. Each option comes with its own strengths and limitations, making it essential to analyze these alternatives in the context of specific applications and environments.
Comparison Table of RF Shielding Solutions
| Comparison Aspect | Radio Frequency Shielding Material | Conductive Coatings | Faraday Cages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High effectiveness in blocking RFI | Moderate; depends on thickness | Excellent for broad-spectrum interference |
| Cost | Varies; generally higher upfront | Lower initial cost | Moderate; dependent on size and material |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires precise manufacturing | Easy application; spray or brush | Installation can be complex |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; durable materials | Needs reapplication over time | Low; typically a permanent solution |
| Best Use Case | Aerospace, medical, defense | Consumer electronics, automotive | Secure facilities, military applications |
What Are Conductive Coatings and Their Advantages?
Conductive coatings are a viable alternative to traditional shielding materials, particularly for applications in consumer electronics and automotive industries. These coatings can be applied as a spray, paint, or adhesive and provide a layer of conductivity that blocks RF signals.
Pros:
– Cost-Effective: Lower initial investment compared to bulk shielding materials.
– Ease of Application: Simple to apply in various shapes and sizes, making it suitable for complex geometries.
Cons:
– Performance Limitations: Their effectiveness can vary significantly based on thickness and application technique.
– Maintenance Needs: Conductive coatings may require reapplication over time, especially in high-wear environments.
How Do Faraday Cages Provide Effective RF Shielding?
Faraday cages are structures designed to block external static and non-static electric fields. They are typically made from conductive materials that redirect and dissipate incoming RF signals, making them excellent for secure facilities and military applications.
Pros:
– Broad-Spectrum Protection: Highly effective across a wide range of frequencies, providing comprehensive shielding.
– Durability: Once installed, Faraday cages require minimal maintenance.
Cons:
– Complex Installation: Building a Faraday cage can be complicated and costly, especially for large or irregularly shaped areas.
– Space Requirements: They require a significant amount of physical space, which may not be feasible in all environments.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right RF Shielding Solution?
When selecting the appropriate RF shielding solution, B2B buyers should consider factors such as the specific application requirements, budget constraints, and long-term maintenance capabilities. Radio frequency shielding materials offer high performance and durability, making them suitable for critical applications in sectors like aerospace and defense. On the other hand, conductive coatings provide a flexible and cost-effective option for less critical applications, while Faraday cages excel in providing comprehensive protection in secure environments. Ultimately, understanding the unique needs of your application will guide you in choosing the most effective solution for your RF shielding requirements.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for radio frequency shielding material
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Radio Frequency Shielding Material?
Understanding the technical properties of radio frequency (RF) shielding materials is critical for B2B buyers, especially in sectors where signal integrity is paramount. Here are some key specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific composition and purity level of the RF shielding material. For example, copper grades like C11000 are widely used for their excellent conductivity. Buyers must select the appropriate grade based on the application’s requirements, as higher-grade materials often provide better shielding effectiveness and durability.
2. Shielding Effectiveness (SE)
Shielding effectiveness is a measure of how well a material can block RF signals, typically expressed in decibels (dB). It is crucial for determining whether a material will adequately protect sensitive electronic components from interference. A higher SE value indicates better performance, which is essential for applications in aerospace and defense sectors.
3. Thickness
The thickness of the shielding material directly impacts its effectiveness and weight. Thicker materials generally provide superior shielding but may increase the overall weight of the assembly. For instance, a common thickness for aluminum shielding is between 0.5 mm to 2 mm. Buyers should balance the need for protection with practical considerations like weight and space.
4. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in the dimensions of the shielding material. In RF shielding applications, precise tolerances are essential to ensure effective sealing and minimize gaps that could compromise shielding performance. Tight tolerances (e.g., ±0.1 mm) may be necessary in high-stakes environments like medical devices.
5. Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance is vital for maintaining the longevity and effectiveness of RF shielding materials, especially in humid or corrosive environments. Materials like nickel silver or specially coated aluminum can offer enhanced resistance. Buyers in regions with harsh climates should prioritize materials with high corrosion resistance to avoid premature failure.
6. Temperature Range
The operational temperature range specifies the extremes within which the RF shielding material can function effectively. This is especially critical for applications that may experience high heat or cold, such as automotive or aerospace components. Knowing the temperature limits helps prevent material degradation that could lead to reduced shielding performance.
What Common Trade Terminology Should B2B Buyers Know for RF Shielding?
Familiarizing yourself with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the RF shielding market. Here are some common terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for buyers seeking customized RF shielding solutions tailored to specific applications.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is vital for budget planning, especially for businesses in emerging markets that may have limited capital to invest upfront.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document used to request pricing and terms from suppliers. Crafting a clear RFQ can streamline the procurement process and ensure that you receive competitive bids from multiple suppliers.
4. Incoterms
Incoterms are international commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in the shipping process. Familiarity with Incoterms can help B2B buyers navigate shipping logistics and avoid unexpected costs, particularly when sourcing materials from overseas suppliers.
5. EMI (Electromagnetic Interference)
EMI refers to the disruption of electronic signals caused by electromagnetic fields. Understanding EMI is crucial for buyers as it influences the design and selection of RF shielding materials to ensure they meet the necessary performance standards.
6. Faraday Cage
A Faraday cage is a structure made of conductive material that blocks external static and non-static electric fields. Buyers should consider this concept when designing enclosures for sensitive equipment to enhance shielding effectiveness.
By grasping these essential properties and terminologies, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing RF shielding materials, ensuring that they meet both technical requirements and budget constraints.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the radio frequency shielding material Sector
What Are the Key Market Trends Influencing RF Shielding Material Sourcing?
The global market for radio frequency (RF) shielding materials is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for electronic devices across various sectors, including telecommunications, healthcare, and aerospace. As businesses become more reliant on wireless technology, the need for effective shielding against electromagnetic interference (EMI) and RF signals has surged. This trend is particularly notable in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where rapid urbanization and technological advancements are propelling the demand for RF shielding solutions.
Emerging technologies such as 5G, IoT, and automotive electronics are reshaping the landscape of RF shielding materials. For international B2B buyers, this means staying informed about advanced materials like conductive polymers and composite materials that offer a balance of weight, cost, and shielding effectiveness. The shift towards miniaturization of devices also necessitates innovative shielding solutions, making it crucial for buyers to work closely with manufacturers who can provide tailored designs.
Moreover, the market dynamics are shifting due to increased competition and the rise of local manufacturers in emerging markets. Buyers should consider diversifying their supplier base to include regional players, which can offer competitive pricing and reduced lead times. This approach not only enhances supply chain resilience but also fosters collaboration in product development, ensuring that businesses remain at the forefront of RF shielding technology.
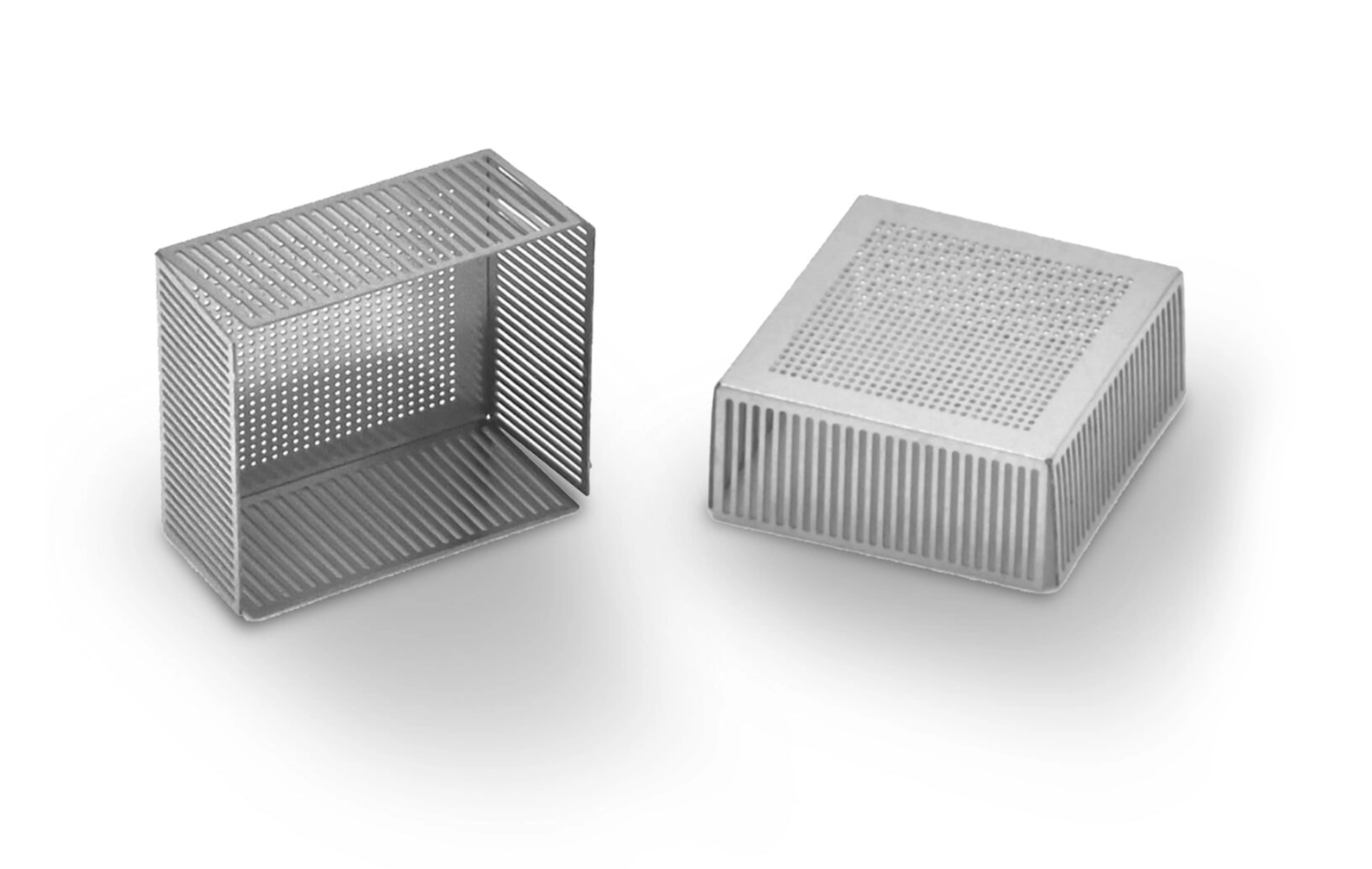
A stock image related to radio frequency shielding material.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact RF Shielding Material Selection?
Sustainability has become a critical factor in the sourcing of RF shielding materials. Buyers are increasingly aware of the environmental impact associated with the production and disposal of shielding materials. The industry is witnessing a shift towards ‘green’ materials, such as recycled metals and eco-friendly elastomers, which not only meet performance standards but also reduce carbon footprints.
Ethical sourcing practices are gaining traction, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, where supply chains often involve complex socio-economic factors. B2B buyers are encouraged to engage with suppliers who prioritize transparency and ethical labor practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and Fair Trade certifications can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainable practices.
Additionally, utilizing materials with lower environmental impact, such as conductive foams and fabrics that require less energy in their production processes, can enhance a company’s sustainability profile. By prioritizing ethical and sustainable sourcing, businesses can not only comply with regulatory requirements but also enhance their brand reputation among increasingly eco-conscious consumers and partners.
What Is the Historical Context of RF Shielding Materials in B2B Markets?
The evolution of RF shielding materials dates back to the early 20th century with the advent of radio technology. Initially, simple metal enclosures, often referred to as Faraday cages, were employed to block external electromagnetic fields. As technology progressed, the demand for more sophisticated solutions led to the development of various conductive materials, including copper and aluminum, which offered enhanced shielding properties.
In the latter half of the 20th century, the proliferation of electronic devices necessitated further innovation in RF shielding. The introduction of elastomeric materials filled with conductive particles marked a significant advancement, providing flexible and effective shielding options. Today, the focus has shifted towards creating lightweight, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly materials that can meet the diverse needs of modern applications.
Understanding this historical context allows B2B buyers to appreciate the advancements in material science and the importance of selecting the right RF shielding solutions that align with their technological needs and sustainability goals. As the sector continues to evolve, staying abreast of historical trends can provide valuable insights for future sourcing decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of radio frequency shielding material
-
How do I solve RF interference issues in my facility?
To address RF interference, begin by conducting a thorough assessment of your facility to identify sources of interference. Utilize RF shielding materials, such as conductive metals or filled elastomers, to create barriers around sensitive equipment. Consider designing enclosures that reflect or absorb RF signals effectively. Collaborating with a knowledgeable supplier who specializes in RF shielding can also provide tailored solutions to your specific needs, ensuring optimal shielding performance. -
What is the best material for RF shielding in industrial applications?
Copper is often regarded as the best material for RF shielding due to its excellent conductivity and effectiveness in absorbing and redirecting RF signals. However, for applications requiring lighter materials, aluminum can be a cost-effective alternative, although it may be less conductive. Nickel silver and steel are also suitable options depending on the required durability and magnetic shielding properties. Always consider the specific requirements of your application, including frequency range and environmental conditions, when selecting a material. -
What factors should I consider when sourcing RF shielding materials internationally?
When sourcing RF shielding materials internationally, consider factors such as supplier reputation, material certification, compliance with local regulations, and the ability to meet your specific requirements. Evaluate the supplier’s manufacturing capabilities and experience in producing RF shielding materials tailored to your needs. Additionally, assess logistics, shipping costs, and delivery times to ensure a smooth procurement process. Establishing strong communication with suppliers can help clarify expectations and ensure quality. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for RF shielding materials?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for RF shielding materials can vary significantly between suppliers and depend on the type of material and its intended use. Some suppliers may offer flexible MOQs for standard materials, while custom-designed products may require higher quantities. It’s advisable to discuss your project requirements with potential suppliers to understand their MOQ policies and negotiate terms that align with your procurement strategy. -
How can I vet suppliers for RF shielding materials effectively?
To vet suppliers for RF shielding materials, begin by researching their background and industry reputation. Look for customer reviews, case studies, and certifications that demonstrate their expertise in RF shielding. Request samples to evaluate the quality of their materials and inquire about their manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures. Establishing a direct line of communication can provide insights into their responsiveness and reliability, helping you make informed decisions. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing RF shielding materials?
Payment terms for RF shielding materials can vary by supplier and region. Common options include upfront payment, partial payment upon order confirmation, and balance upon delivery. International buyers should clarify payment methods, such as wire transfers or letters of credit, and ensure they comply with local regulations. It’s beneficial to negotiate terms that provide security and flexibility while maintaining a positive relationship with your supplier. -
How do I ensure quality assurance in my RF shielding materials?
Ensuring quality assurance in RF shielding materials involves collaborating closely with your supplier to establish clear specifications and performance standards. Request documentation of material certifications and compliance with industry standards, such as ISO certifications. Implementing a quality control process that includes regular inspections and testing of materials during production can help identify potential issues early. Consider visiting the supplier’s facility if feasible to gain firsthand insight into their manufacturing practices.
A stock image related to radio frequency shielding material.
- What logistical considerations should I keep in mind for international shipping of RF shielding materials?
When shipping RF shielding materials internationally, consider the logistics of transportation, including shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs or duties. Ensure that your supplier is experienced in international shipping and can provide necessary documentation for customs clearance. Plan for possible delays and communicate with your supplier about shipping timelines. Additionally, consider insurance options to protect your investment during transit.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for radio frequency shielding material

A stock image related to radio frequency shielding material.
As the demand for effective radio frequency (RF) shielding materials continues to grow across various industries, strategic sourcing becomes increasingly critical for international B2B buyers. Understanding the diverse range of materials—such as copper, aluminum, and elastomer-filled gaskets—enables businesses to make informed decisions that enhance shielding effectiveness while balancing cost and performance.
Investing in high-quality RF shielding materials is not just about compliance; it’s about ensuring the integrity of sensitive electronic components across sectors like aerospace, healthcare, and telecommunications. Buyers must prioritize partnerships with manufacturers that not only offer top-tier materials but also possess the engineering expertise to tailor solutions to specific applications.
Looking ahead, the evolving technological landscape will likely introduce new challenges in RF interference, particularly in emerging markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This presents a unique opportunity for B2B buyers to leverage strategic sourcing to enhance their competitive edge.
To navigate this dynamic market, connect with suppliers that provide innovative solutions and exceptional support. By doing so, you can ensure your organization is well-equipped to meet future RF shielding needs effectively.