The Ultimate Guide to Transformer Parts (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for transformer parts
In today’s interconnected global economy, sourcing high-quality transformer parts poses significant challenges for international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As the demand for reliable electrical infrastructure continues to rise, understanding the intricacies of transformer components—ranging from windings and cores to insulating materials and tap changers—is crucial for ensuring operational efficiency and longevity. This comprehensive guide provides invaluable insights into the various types of transformer parts, their specific applications, and best practices for supplier vetting.
Navigating the complexities of transformer parts sourcing requires informed decision-making. This guide empowers B2B buyers by offering actionable strategies for evaluating suppliers, understanding cost implications, and recognizing the critical role of each component in overall system performance. By delving into industry standards and emerging trends, buyers will be better equipped to make purchases that not only meet immediate operational needs but also align with long-term business goals.
In the following sections, we will explore key considerations that facilitate smarter sourcing decisions, ensuring that businesses can effectively support their electrical infrastructure projects while optimizing costs and enhancing reliability. Whether you are sourcing for a large-scale energy project or seeking components for smaller applications, this guide serves as an essential resource for maximizing your procurement efficiency in the global market for transformer parts.
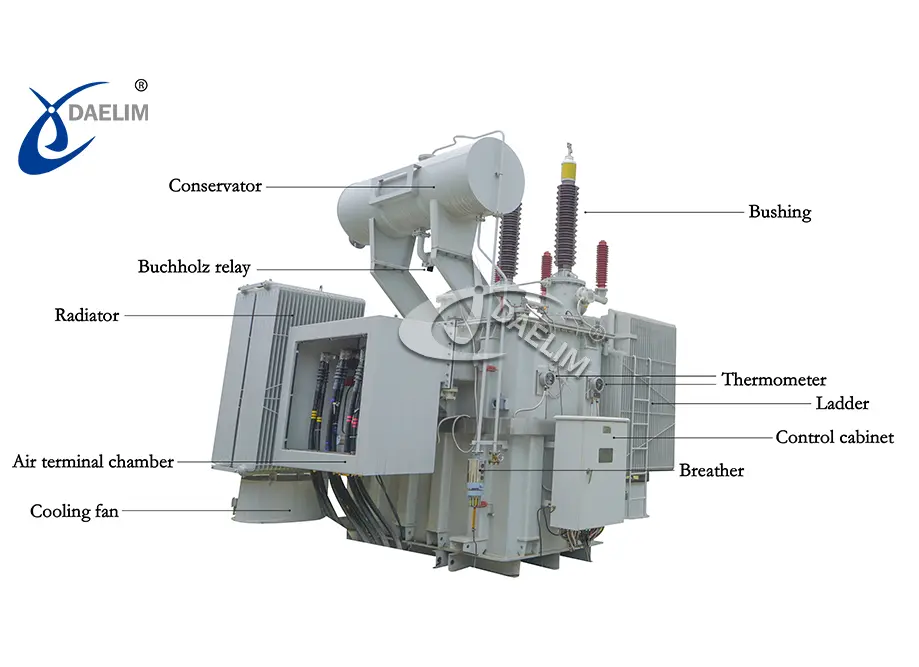
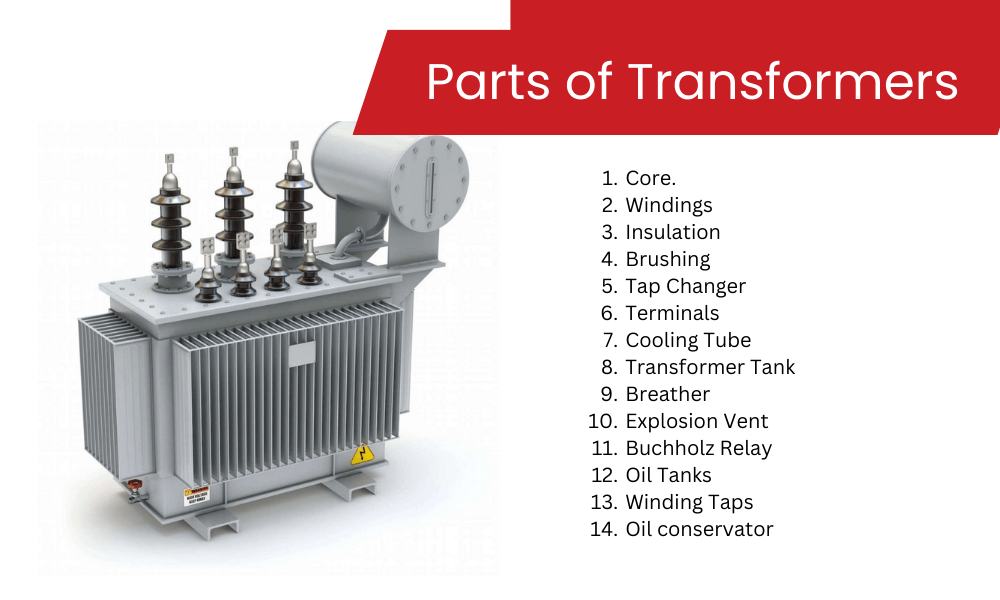
Understanding transformer parts Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windings | Copper or aluminum coils, insulated with paper | Power generation, distribution, and industrial use | Pros: High conductivity; Cons: Difficult to repair |
| Core | Made from high-permeability steel, minimizes losses | High-voltage transmission systems | Pros: Efficient; Cons: Heavy and bulky |
| Tap Changer | Device for voltage variation, connected to windings | Voltage regulation in substations | Pros: Adjustable output; Cons: Maintenance needed |
| Insulating Materials | Mineral oil, pressboard, and paper for insulation | Transformer longevity and performance enhancement | Pros: Effective insulation; Cons: Aging limits life |
| Conservator Tank | Stores insulating oil, regulates transformer oil level | Essential for maintenance and fault detection | Pros: Prevents oil spillage; Cons: Requires monitoring |
What are Transformer Windings and Their Importance in B2B Applications?
Transformer windings are critical components that facilitate the transformation of voltage levels. Typically made from copper or aluminum, these windings are insulated with multiple layers of paper to prevent short circuits and ensure durability. For B2B buyers, selecting the right winding type is essential, as they directly impact the efficiency and performance of the transformer. Considerations include the winding design (core or shell), which affects maintenance and repair options, as rewinding can only be performed in specialized facilities.
How Does the Core Design Affect Transformer Efficiency?
The core of a transformer is composed of thin steel sheets that enhance magnetic permeability while minimizing losses. This component is pivotal for high-voltage transmission systems, as it directly influences the transformer’s efficiency. B2B buyers should evaluate the core’s construction, as a well-designed core can significantly reduce operational costs by lowering energy losses. However, the weight and bulkiness of the core may pose logistical challenges during installation and transport.
What Role Does a Tap Changer Play in Voltage Regulation?
A tap changer is an integral part of transformers, allowing for adjustments in voltage output to meet varying load requirements. This component is particularly crucial in substations where voltage stability is necessary for grid reliability. For B2B buyers, the choice of tap changer can influence operational flexibility; however, it is essential to consider the maintenance requirements and potential operational downtime associated with these devices.
Why are Insulating Materials Critical for Transformer Longevity?
Insulating materials such as mineral oil, paper, and pressboard are essential for maintaining the operational integrity of transformers. They provide electrical insulation and cooling, which are crucial for preventing overheating and electrical failures. B2B buyers must prioritize the selection of high-quality insulating materials, as aging can lead to reduced lifespan and performance issues. Regular monitoring of insulation condition is also necessary to avoid unexpected failures.
How Does a Conservator Tank Contribute to Transformer Maintenance?
The conservator tank is designed to store insulating oil and regulate its level within the transformer. This component plays a vital role in maintenance, as it helps detect potential faults through oil condition monitoring. For B2B buyers, investing in transformers with efficient conservator systems can enhance reliability and reduce maintenance costs. However, it is crucial to ensure that the conservator tank is regularly monitored to prevent oil spillage and associated environmental risks.
Key Industrial Applications of transformer parts
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of transformer parts | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy & Utilities | High-voltage transmission transformers | Ensures efficient power distribution over long distances | Quality of insulating materials and compliance with international standards |
| Manufacturing | Step-down transformers for production equipment | Reduces voltage for machinery operation, enhancing safety and efficiency | Reliability of components and availability of technical support |
| Telecommunications | Transformers in data centers | Stabilizes power supply, preventing equipment damage and downtime | Sourcing from reputable suppliers with proven reliability |
| Mining | Transformers for site power supply | Provides necessary power for heavy machinery and operations | Durability of parts under harsh environmental conditions |
| Agriculture | Transformers for irrigation systems | Powers pumps and systems, improving crop yields and efficiency | Adaptability to local voltage requirements and climate conditions |
How Are Transformer Parts Used in the Energy & Utilities Sector?
In the energy and utilities sector, transformer parts, particularly high-voltage transformers, are critical for efficient power transmission. These transformers adjust voltage levels to minimize energy loss over long distances. For international buyers, sourcing transformers requires attention to the quality of insulating materials and compliance with local and international safety standards. This ensures not only operational efficiency but also the longevity of the equipment in diverse climates.
What Is the Role of Transformer Parts in Manufacturing?
Manufacturing facilities utilize step-down transformers to safely reduce voltage levels for machinery and production equipment. This application enhances operational safety and efficiency, as machinery operates optimally at lower voltages. B2B buyers in this sector should focus on the reliability of transformer parts and the availability of technical support to address any operational issues quickly, especially in regions with fluctuating power supply.
How Do Transformer Parts Benefit Telecommunications?
In telecommunications, transformers are essential in data centers to stabilize power supply, which is crucial for preventing equipment damage and minimizing downtime. The sourcing of transformer parts must prioritize suppliers with a reputation for reliability, as consistent power is vital for maintaining service quality. Buyers should also consider the specifications that meet their localized power requirements.
Why Are Transformer Parts Important in Mining Operations?
Mining operations require robust transformers to supply power to heavy machinery, ensuring that operations run smoothly and efficiently. The rugged nature of mining environments necessitates sourcing durable transformer parts that can withstand extreme conditions. Buyers must evaluate the durability and performance specifications of components to ensure they can handle the demanding operational requirements.
What Is the Significance of Transformer Parts in Agriculture?
In agriculture, transformers are used to power irrigation systems, which are essential for improving crop yields. By ensuring that pumps and other equipment function effectively, transformers directly contribute to agricultural productivity. Buyers in this sector should assess the adaptability of transformer parts to local voltage requirements and environmental conditions, ensuring optimal performance in diverse agricultural settings.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘transformer parts’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Sourcing Quality Transformer Parts for Reliability
The Problem:
For B2B buyers in regions such as Africa and South America, sourcing high-quality transformer parts can be a significant challenge. Many local suppliers may lack the necessary standards or certifications, leading to concerns about the reliability and longevity of components such as windings or insulating materials. A buyer might face delays or failures due to subpar parts, which not only affects project timelines but can also lead to costly repairs and loss of trust among clients.
The Solution:
To mitigate these risks, buyers should adopt a structured approach to sourcing transformer parts. Start by identifying reputable manufacturers with a proven track record in the industry. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems, which can indicate a commitment to quality and consistency. Establish relationships with suppliers that offer detailed product specifications and testing data, particularly for critical components like transformer oil and insulating materials.
Moreover, consider engaging in third-party quality assurance checks before finalizing purchases. This might involve requesting samples or conducting site visits to verify manufacturing practices. By ensuring that all parts meet international standards, buyers can enhance the reliability of their transformer systems and ultimately protect their investments.
Scenario 2: Managing Maintenance and Downtime Effectively
The Problem:
Many B2B buyers, particularly those managing industrial facilities in the Middle East and Europe, experience difficulties in maintaining transformers due to a lack of readily available replacement parts. When transformers fail, the resulting downtime can be devastating, leading to lost production and increased operational costs. The inability to quickly source critical components like tap changers or cooling systems exacerbates these challenges.
The Solution:
To address maintenance issues proactively, buyers should implement a strategic inventory management system that includes critical spare parts for transformers. This entails identifying the most vulnerable components that are prone to failure, such as bushings and insulation materials, and keeping an adequate stock on hand. Establishing a partnership with a reliable supplier for just-in-time delivery can also help ensure that parts are available when needed without incurring high inventory costs.
Additionally, buyers should invest in training for their maintenance teams to conduct regular inspections and predictive maintenance. Utilizing advanced diagnostic tools can help identify potential failures before they lead to breakdowns, allowing for timely interventions. By taking these steps, businesses can significantly reduce downtime and enhance the overall operational efficiency of their transformer systems.
Scenario 3: Understanding Technical Specifications and Compatibility
The Problem:
B2B buyers often struggle with understanding the technical specifications of transformer parts, leading to compatibility issues when integrating new components into existing systems. This problem is particularly prevalent among buyers in developing regions, where access to technical resources may be limited. Mismatches in specifications can result in inefficiencies, increased wear and tear, and even safety hazards.
The Solution:
To overcome these challenges, buyers should prioritize education and training regarding transformer components and their specifications. It’s advisable to engage with technical experts or consultants who can provide guidance on the correct specifications needed for various applications, such as understanding the differences between core and shell transformer designs or the implications of different insulating materials.
Furthermore, buyers should utilize digital tools and resources, such as specification sheets and compatibility checklists, to ensure that every part sourced meets the necessary requirements. Creating a comprehensive database of existing transformer specifications can also help streamline the process when procuring new parts. By investing time and resources into understanding technical specifications, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and safety.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for transformer parts
What Are the Key Materials Used in Transformer Parts?
When selecting materials for transformer parts, it’s crucial to consider the specific properties and performance requirements that will affect the overall efficiency and longevity of the transformer. Below, we analyze four common materials used in transformer construction, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
A stock image related to transformer parts.
How Does Copper Impact Transformer Performance?
Copper is predominantly used in transformer windings due to its excellent electrical conductivity and thermal properties.
- Key Properties: Copper has a high melting point (1,984°F or 1,085°C) and excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for high-temperature applications.
- Pros: Its high conductivity ensures minimal energy loss, enhancing transformer efficiency. Copper is also relatively durable and has a long service life.
- Cons: The primary drawback is its cost, which is generally higher than alternatives like aluminum. Additionally, copper is susceptible to oxidation, which can affect performance if not properly insulated.
- Impact on Application: Copper windings are ideal for high-performance transformers, especially in regions with high electrical demand.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM B170 for copper wire. In regions like Africa and South America, where electrical infrastructure is developing, the reliability of copper components can significantly influence operational efficiency.
What Role Does Steel Play in Transformer Cores?
Steel is a critical material for transformer cores, influencing magnetic properties and efficiency.
- Key Properties: Steel used in transformer cores is typically laminated to reduce eddy current losses. It has a high magnetic permeability and low hysteresis loss, crucial for efficient energy transfer.
- Pros: Laminated steel cores are cost-effective and provide good mechanical strength. They also enhance the transformer’s efficiency by minimizing energy losses.
- Cons: The manufacturing complexity increases with the need for precise lamination. Steel can also be heavy, impacting the overall weight of the transformer.
- Impact on Application: Steel cores are suitable for both step-up and step-down transformers, making them versatile for various applications.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as DIN lamination specifications is essential. Buyers in Europe and the Middle East may prefer high-grade silicon steel for better performance.
How Do Insulating Oils Affect Transformer Longevity?
Insulating oils play a vital role in cooling and insulating transformer components.
- Key Properties: Insulating oils have excellent dielectric strength, thermal stability, and resistance to oxidation, ensuring effective insulation and cooling.
- Pros: They enhance the transformer’s operational efficiency by dissipating heat and preventing electrical breakdown. Insulating oils are also relatively easy to handle and replace.
- Cons: Environmental concerns regarding oil spills can pose significant challenges. Additionally, the aging of oil can lead to reduced performance over time.
- Impact on Application: Proper oil selection is crucial for transformers operating in extreme temperatures, ensuring reliability and safety.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of regulations regarding the disposal and use of insulating oils, particularly in regions with strict environmental laws, such as Europe.
What Are the Benefits of Using Insulating Materials in Transformers?
Insulating materials, including paper and pressboard, are essential for electrical insulation within transformers.
- Key Properties: These materials exhibit high dielectric strength and thermal stability, which are critical for maintaining electrical integrity.
- Pros: They are cost-effective and provide excellent insulation properties, enhancing the safety and reliability of transformers.
- Cons: The aging of organic insulating materials can limit the service life of transformers. They are also less durable compared to synthetic alternatives.
- Impact on Application: Insulating materials are critical in ensuring the safe operation of transformers, especially in high-voltage applications.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should look for compliance with standards like IEC 60216 for thermal endurance. In regions with varying climates, selecting the right insulating materials is vital for performance.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Transformer Parts
| Material | Typical Use Case for transformer parts | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Windings | High electrical conductivity | Higher cost, susceptible to oxidation | High |
| Steel | Cores | Cost-effective, good mechanical strength | Heavy, complex manufacturing | Medium |
| Insulating Oil | Cooling and insulation | Enhances operational efficiency | Environmental concerns, aging issues | Medium |
| Insulating Materials | Electrical insulation | Cost-effective, excellent insulation | Aging limits service life | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the materials that comprise transformer parts, enabling informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and compliance with international standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for transformer parts
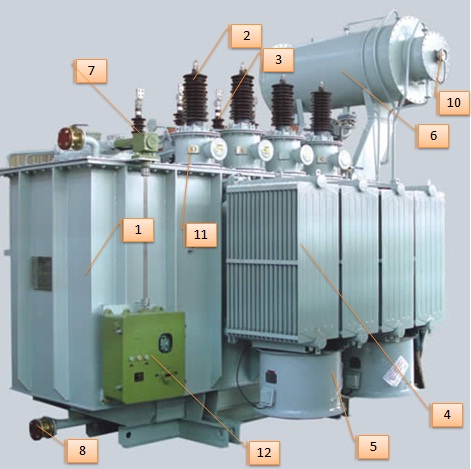
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Transformer Parts?
The manufacturing process for transformer parts is intricate, involving multiple stages that ensure the final product meets stringent quality and performance standards. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation:
– The first step involves sourcing high-quality raw materials such as copper, steel, insulating oil, and specialized insulating materials like paper and pressboard.
– Suppliers should provide certifications for the materials used, ensuring they meet international standards for electrical conductivity, thermal stability, and mechanical strength. -
Forming:
– During the forming stage, materials are shaped into various components. For instance, steel sheets are cut into laminations for the transformer core, which helps reduce energy losses.
– Winding processes involve manual labor where copper or aluminum wires are wound into coils. This stage is critical as it requires skilled labor to ensure proper insulation and winding techniques, which are vital for performance and longevity. -
Assembly:
– The assembly stage combines the individual components into a complete transformer unit. This includes placing the windings around the core, installing the tap changer, and integrating insulating materials.
– Precision is key in this phase to avoid mechanical stresses that could lead to failures during operation. -
Finishing:
– In the finishing stage, transformers undergo treatments such as varnishing for insulation and protective coatings to prevent corrosion.
– The final assembly is inspected for any defects, and components are tested for functionality before moving to quality assurance.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Transformer Parts Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is crucial in ensuring that transformer parts meet both performance and safety standards. International standards such as ISO 9001 provide a framework for maintaining quality throughout the manufacturing process.
-
International Standards:
– Adherence to ISO 9001 ensures a systematic approach to quality management, focusing on customer satisfaction and continual improvement.
– Industry-specific certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) and API (American Petroleum Institute) are also critical, especially for transformers used in specialized applications. -
Quality Control Checkpoints:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to verify they meet specified standards. Any substandard materials are rejected to prevent defects later in the manufacturing process.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing stages, inspections are conducted to ensure that processes are followed correctly and that components meet design specifications.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, each transformer is subjected to rigorous testing to verify its operational capabilities and safety features. This may include electrical testing, insulation resistance testing, and thermal performance assessments.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Transformer Parts Manufacturing?
Testing methods play a pivotal role in validating the quality and reliability of transformer parts. Some common methods include:
- Electrical Testing: Measures parameters such as voltage, current, and impedance to ensure the transformer operates correctly under specified conditions.
- Insulation Resistance Testing: Assesses the integrity of insulation materials to prevent failures due to electrical breakdown.
- Thermal Imaging: Used to identify hotspots that could indicate potential failures in the transformer’s operation.
- Vibration Analysis: Helps in detecting mechanical issues that could lead to premature failure.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Measures?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control measures is essential to ensure product reliability.
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of potential suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes, quality assurance practices, and adherence to international standards.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should ask suppliers for detailed quality assurance reports, including IQC, IPQC, and FQC results. This transparency can help in assessing the supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s manufacturing and quality assurance processes. This is particularly beneficial for buyers who may lack the resources for on-site inspections.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
When sourcing transformer parts internationally, buyers should be aware of several nuances regarding quality control and certification:
- Understanding Regional Standards: Different regions may have varying quality standards and certifications. For example, European buyers may prioritize CE certification, while buyers in the Middle East might focus on GCC standards.
- Cultural and Communication Considerations: Effective communication is vital when discussing quality expectations with suppliers. Buyers should ensure that their specifications are clearly communicated to avoid misunderstandings.
- Logistics and Compliance: Buyers must also consider logistics and compliance with local regulations regarding the import of electrical equipment. Understanding these regulations can prevent delays and additional costs.
Conclusion: Ensuring Quality in Transformer Parts Manufacturing
For B2B buyers, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for transformer parts is critical in making informed purchasing decisions. By focusing on supplier quality control, international standards, and effective communication, buyers can mitigate risks and ensure that they source reliable and high-quality transformer components.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘transformer parts’
In the competitive landscape of international B2B sourcing, particularly for transformer parts, it is essential to follow a structured approach. This checklist will guide you through the critical steps necessary to ensure you procure high-quality components that meet your operational requirements.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical specifications for the transformer parts you need. This includes voltage ratings, materials (such as copper or aluminum for windings), and dimensions. Having a well-defined specification helps avoid misunderstandings with suppliers and ensures that the components are compatible with your existing systems.
Step 2: Research Reliable Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers. Look for manufacturers with a proven track record in producing transformer parts. Utilize online platforms, industry directories, and trade shows to gather information. Ensure that they specialize in the specific components you require, such as tap-changers, cores, or insulating materials.
Step 3: Verify Supplier Certifications and Compliance
It is crucial to verify that your chosen suppliers have the necessary certifications and comply with international standards. Look for ISO certifications or specific industry standards relevant to transformer manufacturing. This step ensures that the parts meet safety, quality, and environmental regulations, reducing the risk of operational failures.
Step 4: Request Samples and Evaluate Quality
Before finalizing your order, request samples of the transformer parts. Evaluate their quality against your technical specifications. Pay attention to details such as the durability of insulation materials, the precision of machining, and overall craftsmanship. This hands-on evaluation can prevent costly mistakes down the line.
Step 5: Assess Lead Times and Delivery Capabilities
Discuss lead times and delivery capabilities with your suppliers. Understanding their production capacity and logistics will help you plan your operations effectively. Ensure that the supplier can meet your timelines, especially if you are working on a project with strict deadlines. Consider potential delays in shipping, particularly for international orders.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you have evaluated the suppliers and their products, negotiate the terms of purchase. This includes pricing, payment terms, and warranties. Be transparent about your budget constraints while ensuring that you do not compromise on quality. A clear agreement helps avoid conflicts later on and ensures a smooth transaction process.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Effective communication is key to a successful supplier relationship. Establish a clear communication plan that outlines how and when you will stay in touch with the supplier. Regular updates on order status, potential issues, and feedback on product performance will foster a collaborative relationship and help address any concerns promptly.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can confidently source transformer parts that meet their specific needs while establishing strong relationships with suppliers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for transformer parts Sourcing
What are the Key Cost Components in Transformer Parts Sourcing?
Understanding the cost structure of transformer parts is essential for international B2B buyers looking to optimize their sourcing strategies. The primary components of cost include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts pricing. Common materials for transformer parts include copper for windings, steel for cores, and insulating oils. The fluctuating prices of these raw materials can affect overall costs, especially in regions where sourcing is limited.
-
Labor: Manufacturing transformer parts often requires skilled labor, particularly for winding and assembly processes. Labor costs vary by region, with countries in Africa and South America typically experiencing lower wage rates compared to Europe. This can be advantageous for buyers seeking cost-effective solutions.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with factory operations, equipment maintenance, and utilities. Efficient production methods and modern technologies can reduce overhead, thus lowering prices for buyers.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling for specialized transformer parts can be substantial. Buyers should consider whether suppliers have the necessary tooling in place, as this can affect lead times and costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that transformer parts meet specified standards. While this can increase costs, it is crucial for preventing defects and ensuring reliability, especially in critical applications.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary widely based on the origin and destination of transformer parts. Factors such as freight rates, customs duties, and handling fees must be considered in the total cost of ownership.
-
Margin: Supplier margins are influenced by market conditions and competition. Buyers should be aware of typical margins in the transformer parts market to assess whether pricing is reasonable.
What Factors Influence the Pricing of Transformer Parts?
Several elements can significantly influence the pricing of transformer parts:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often lead to volume discounts. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their needs to take advantage of cost savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom parts or those with specific performance criteria may incur additional costs. It’s vital to clearly define requirements upfront to avoid unexpected price increases.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (like ISO or IEC standards) can elevate costs. However, investing in certified parts may yield long-term savings through enhanced reliability and performance.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality and service may charge a premium, but they often deliver better value in the long run.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is crucial for pricing negotiations. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, impacting overall costs.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Negotiate Better Prices for Transformer Parts?
To maximize cost-efficiency, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Effective Negotiation: Prepare to negotiate prices by researching market rates and understanding the supplier’s cost structure. Highlighting long-term relationships can also provide leverage.
-
Assess Total Cost of Ownership: Look beyond initial purchase prices. Consider maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential downtime costs associated with lower-quality parts.
-
Explore Multiple Suppliers: Solicit quotes from multiple suppliers to compare prices and terms. This not only helps in identifying competitive pricing but also provides options in case of supply chain disruptions.
-
Leverage Local Suppliers: For buyers in Africa, South America, and the Middle East, engaging local suppliers may reduce shipping costs and lead times, leading to overall savings.
-
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Keeping abreast of market trends and material price fluctuations can help buyers make informed purchasing decisions and time their orders strategically.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for transformer parts can vary widely based on numerous factors, including geographic location, market demand, and specific part requirements. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough research and consult suppliers for the most accurate and current pricing information.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing transformer parts With Other Solutions
The exploration of alternatives to transformer parts can provide B2B buyers with a broader understanding of their options. This can lead to better decision-making when sourcing components for electrical systems. Given the varied applications and requirements across different regions, it’s essential to evaluate alternatives based on performance, cost, and ease of implementation.
Comparison of Transformer Parts with Alternative Solutions
| Comparison Aspect | Transformer Parts | Alternative 1: Static Frequency Converter | Alternative 2: Solid-State Transformer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency for voltage regulation | Moderate efficiency; effective for frequency conversion | High efficiency; handles variable loads well |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment | Higher upfront costs | Higher upfront costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires expertise in installation | More complex setup; requires trained personnel | Requires specialized installation |
| Maintenance | Regular oil checks and insulation replacement | Minimal maintenance; robust design | Minimal maintenance; durable components |
| Best Use Case | High-voltage applications in power grids | Applications needing frequency conversion | Applications requiring size reduction and efficiency |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Static Frequency Converters?
Static frequency converters (SFCs) are used to convert AC power from one frequency to another. This technology is particularly useful in applications where machinery operates on different frequencies.
Pros:
– SFCs provide flexibility in frequency management, which is beneficial in industrial applications.
– They are typically more compact than traditional transformers, making them easier to integrate into existing systems.
Cons:
– The initial investment for SFCs can be significant, especially when compared to traditional transformer parts.
– Their installation is more complex, often requiring skilled technicians, which can increase overall project costs.
How Do Solid-State Transformers Compare to Traditional Transformer Parts?
Solid-state transformers (SSTs) represent a modern approach to voltage regulation and power distribution. They utilize power electronics to manage the conversion of voltage levels.
Pros:
– SSTs offer high efficiency and a smaller footprint compared to traditional transformers, making them ideal for urban settings.
– They can handle varying loads more effectively, providing better performance under dynamic conditions.
Cons:
– The upfront costs for solid-state transformers can be substantially higher than those for conventional transformer parts.
– They require specialized knowledge for installation and maintenance, potentially leading to increased operational costs.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
When selecting between transformer parts and alternative solutions like static frequency converters or solid-state transformers, B2B buyers should consider several factors. Start by assessing the specific requirements of your application, including voltage and frequency needs. Evaluate the total cost of ownership, which includes initial investment, maintenance expenses, and potential downtime. Additionally, consider the availability of skilled personnel for installation and maintenance, as this can impact the long-term feasibility of the chosen solution.
Ultimately, the best choice will depend on balancing performance, cost, and operational requirements in your specific context. By carefully analyzing these alternatives, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and budget constraints.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for transformer parts
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Transformer Parts?
When purchasing transformer parts, understanding their technical specifications is crucial for ensuring compatibility, efficiency, and longevity. Below are some key specifications that international B2B buyers should consider:
What Are the Key Material Grades in Transformer Parts?
-
Material Grade: Transformer components are typically made from materials like copper, aluminum, and various grades of steel. For example, copper is preferred for windings due to its excellent conductivity, while silicon steel is commonly used for cores due to its high magnetic permeability and reduced energy losses. Selecting the right material grade affects not only the efficiency of the transformer but also its overall durability and performance.
-
Thermal Tolerance: This specification refers to a component’s ability to withstand high temperatures without degrading. For example, insulating materials such as paper or resin need to have high thermal tolerance to prevent breakdown during operation. Understanding thermal tolerance is vital for ensuring the transformer operates effectively under varying environmental conditions, especially in regions with extreme temperatures.
-
Dielectric Strength: This property measures a material’s ability to resist electrical breakdown. Insulating materials must have high dielectric strength to prevent short circuits and failures. For B2B buyers, understanding dielectric strength is essential for ensuring safety and reliability in electrical systems.
-
Magnetic Permeability: This is a measure of how easily a material can become magnetized. High magnetic permeability is critical for transformer cores to minimize energy losses. Selecting components with the appropriate magnetic properties is essential for optimizing transformer efficiency.
-
Mechanical Tolerance: This refers to the allowable variation in the dimensions of transformer parts. Tight tolerances are crucial for ensuring proper fit and function. For buyers, understanding mechanical tolerances can help prevent assembly issues and improve the overall reliability of the transformer.
Which Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know?
Navigating the procurement landscape requires familiarity with industry jargon. Here are some essential trade terms that B2B buyers should understand:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): This term refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM specifications is vital for ensuring that replacement parts meet the original quality standards.
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): This indicates the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory management, particularly for international buyers who may face shipping and storage challenges.
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation): An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers asking for price quotes for specific items. B2B buyers should use RFQs to get competitive pricing and ensure they are sourcing high-quality parts at the best value.
-
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms): These are international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping goods. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and logistics, which is particularly important when sourcing from international suppliers.
-
Lead Time: This term refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the goods. Understanding lead times is critical for project planning and inventory management, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, where supply chains may be less predictable.
-
Certification Standards: These are regulatory requirements that transformer parts must meet to ensure safety and reliability. Familiarity with certification standards, such as ISO or IEC, can help buyers avoid compliance issues and ensure that their equipment meets international quality benchmarks.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, streamline their procurement processes, and enhance the efficiency of their electrical systems.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the transformer parts Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Transformer Parts Sector?
The transformer parts sector is experiencing significant shifts influenced by global economic trends, technological advancements, and changing energy policies. International B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate these dynamics to optimize their sourcing strategies. One of the primary drivers is the increasing demand for renewable energy sources, which is prompting investments in power transmission infrastructure. This trend is particularly pronounced in developing regions where energy access is critical for economic growth.
Another important aspect is the adoption of digital technologies in manufacturing and supply chain management. B2B buyers are increasingly leveraging tools like IoT (Internet of Things) for real-time monitoring of transformer performance and predictive maintenance, which enhances operational efficiency. Additionally, automation in manufacturing processes is leading to improved quality control and reduced lead times, allowing buyers to source high-quality transformer parts more reliably.
Emerging markets are also witnessing a surge in demand for customized transformer components tailored to specific operational needs. This trend necessitates closer collaboration between manufacturers and buyers to ensure that the specifications are met efficiently. Furthermore, geopolitical factors and supply chain disruptions have highlighted the need for diversified sourcing strategies, as companies seek to mitigate risks associated with reliance on single-source suppliers.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact Transformer Parts Procurement?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of procurement strategies in the transformer parts sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly in terms of energy consumption and waste generation, is under scrutiny. International buyers must prioritize suppliers that adhere to sustainable practices, such as minimizing carbon footprints and utilizing renewable energy in production.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as it encompasses not only environmental considerations but also social responsibility. Buyers should seek suppliers with transparent supply chains that adhere to fair labor practices and community engagement. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and SA8000 for social accountability can serve as benchmarks for assessing suppliers.
The use of ‘green’ materials, such as recyclable insulating oils and eco-friendly insulating papers, is gaining traction. These materials not only reduce environmental impact but also enhance the overall performance and longevity of transformer parts. By integrating sustainability and ethical sourcing into procurement strategies, B2B buyers can differentiate themselves in a competitive market while contributing to global sustainability goals.
How Has the Transformer Parts Sector Evolved Over Time?
The transformer parts sector has undergone significant evolution since the introduction of electrical transformers in the late 19th century. Initially, transformer components were limited to basic elements like copper windings and iron cores. However, as electrical systems expanded and diversified, the complexity of transformer parts increased. Innovations in materials science led to the development of advanced insulating materials and precision-engineered components, which enhanced efficiency and reliability.
The introduction of digital technologies in recent years has further transformed the landscape, enabling real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance of transformers. This evolution reflects a broader trend towards smarter, more resilient energy systems that can adapt to changing demands. As the sector continues to evolve, international B2B buyers must remain informed and agile to leverage new opportunities and technologies that enhance their sourcing strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of transformer parts
-
How do I solve issues related to transformer oil quality?
To address transformer oil quality issues, it’s essential to conduct regular testing for parameters like acidity, moisture content, and dielectric strength. Working with accredited laboratories can help you understand the oil’s condition and detect contaminants. If problems are identified, consider oil filtration or replacement, ensuring the new oil meets industry standards. Additionally, implementing a routine maintenance program can prevent future issues and extend the life of your transformer. -
What is the best type of transformer winding for high efficiency?
For high efficiency in transformers, the core type winding is often recommended. This design surrounds the core legs, optimizing magnetic flux and minimizing losses. Core type windings, particularly those made from high-conductivity materials like copper, provide better thermal management and electrical performance. When selecting a winding, ensure it aligns with your operational requirements and consider the winding’s insulation material for long-term reliability. -
How can I verify the credibility of a transformer parts supplier?
To verify a supplier’s credibility, start by checking their certifications, such as ISO 9001 or industry-specific standards. Request references from previous clients and review testimonials. Conduct due diligence by visiting their facilities if possible, or use third-party verification services. Additionally, assess their track record in delivering quality parts on time and their responsiveness to inquiries, as this reflects their commitment to customer service. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for transformer parts?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for transformer parts can vary widely depending on the supplier and the specific components. Generally, MOQs range from 50 to 1,000 units. For specialized or custom components, the MOQ might be higher due to manufacturing constraints. When negotiating with suppliers, clarify their MOQ policies, and explore options for reducing the MOQ through consolidated orders or long-term partnerships. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing transformer parts internationally?
International payment terms can vary, but common practices include payment in advance, letters of credit, or net payment terms (e.g., net 30 or net 60). It is advisable to establish clear terms in the contract, including currency, payment methods, and timelines. Be cautious about upfront payments, especially with new suppliers. Using an escrow service can provide added security for both parties in the transaction. -
How do I ensure quality assurance (QA) for transformer parts?
To ensure quality assurance for transformer parts, implement a robust QA process that includes supplier audits, incoming inspection of parts, and final product testing. Request detailed documentation from suppliers, including material certifications and test results. Establish a clear set of quality standards that align with industry regulations, and consider using third-party inspection services for additional verification before accepting shipments. -
What are the logistics considerations when importing transformer parts?
When importing transformer parts, consider factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and duties. Collaborate with logistics partners who specialize in handling electrical components to ensure compliance with international shipping standards. Evaluate the total landed cost, including freight, insurance, and customs fees. Additionally, ensure that your supplier provides proper packaging to prevent damage during transit.
A stock image related to transformer parts.
- How can I customize transformer parts to meet specific requirements?
To customize transformer parts, communicate your specifications clearly to potential suppliers. Discuss aspects like size, materials, and design modifications early in the negotiation process. Many manufacturers are open to custom orders but may have specific MOQs or lead times associated with them. Review prototypes or samples before full-scale production to ensure that the customized parts meet your operational needs and quality standards.

A stock image related to transformer parts.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for transformer parts
In the evolving landscape of transformer parts, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical factor for international B2B buyers. By prioritizing quality components—such as windings, cores, and insulating materials—companies can enhance the reliability and efficiency of their electrical systems. Understanding the complexities of these components and their suppliers enables buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs.
Moreover, the long-term performance of transformers hinges on the quality of materials used, particularly in regions with diverse climatic and operational challenges. By engaging with trusted suppliers and leveraging local market knowledge, buyers can mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions and ensure continuity in their operations.
Looking ahead, the global demand for transformer parts is expected to rise, driven by infrastructural development and renewable energy initiatives. B2B buyers should seize this opportunity to forge strategic partnerships and invest in sustainable sourcing practices. This proactive approach will not only secure a competitive edge but also contribute to a more resilient and responsible energy sector. Embrace the potential of strategic sourcing to empower your business today.