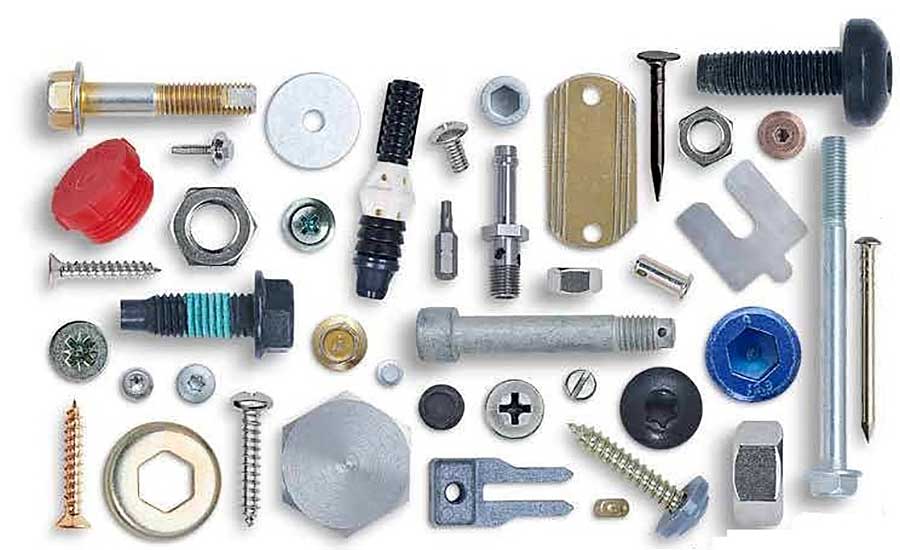
Top 10 Fastener Manufacturers List and Guide: How To Solve Scenar…
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for Fastener Manufacturers
In the fast-paced world of manufacturing, sourcing high-quality fasteners can pose a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. Fasteners, essential components in various industries including automotive, aerospace, and construction, serve as the backbone for countless applications. This comprehensive guide delves into the nuances of the global market for fastener manufacturers, offering insights into different types of fasteners, their applications, and best practices for supplier vetting.
Understanding the landscape of fastener manufacturing is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—like Brazil and Saudi Arabia—will benefit from our expert analysis on cost factors, quality standards, and customization options available in the market. This guide not only outlines the critical considerations for sourcing fasteners but also equips buyers with actionable strategies to navigate supplier relationships effectively.
By addressing key challenges and providing clarity on the fastener supply chain, we empower B2B buyers to streamline their procurement processes, minimize risks, and ultimately enhance their operational efficiency. Whether you’re seeking bulk orders or specialized fasteners, this guide is designed to be your go-to resource for navigating the complex global fastener market.
Top 10 Fastener Manufacturers Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. National Bolt & Nut Corporation – Custom Non-Standard Fasteners
Domain: powertelcom.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: The text provides information about various fastener manufacturers in the USA, highlighting their main products. Key product details include:
– National Bolt & Nut Corporation: Large-diameter custom non-standard fasteners, including bolts, nuts, studs, washers, bend bolts, U-bolts, long length rods, hex cap screws, clevis pins, dowel pins, cotter pins, spring pins, custom nuts, spacers, and washe…
2. Midwest Fastener – Complete Line of Fasteners
Domain: fastenerconnection.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Midwest Fastener offers a complete line of fasteners, including branded products such as TorqueMaster, HangMaster, and SaberDrive. These products are designed to increase visibility and boost sales, while also focusing on customer retention, simplifying stocking, reducing merchandising costs, and increasing profits. The company emphasizes reliable, rugged, and secure construction fasteners.
3. Birmingham Fastener – Fasteners & Custom Manufacturing
Domain: bhamfast.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Birmingham Fastener offers a variety of fasteners including Structural Bolts, Bent Bolts, Headed Bolts, Flange Bolts, T-Head Bolts, Mechanical Joint Gasket Packs, Bracing Hardware, Metal Building Screws, Sealants, and Pipe Flashing. They also provide value-added services such as Custom Manufacturing, Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI), Lab/Testing Services, and Packaging and Assembly. The company serv…
4. Fasteners Clearinghouse – Comprehensive Fastener Directory
Domain: fastenersclearinghouse.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Fastener Distributor Directory; 1,835,906 fasteners as of 07/11/2025; Categories include: General Industrial Hardware, Rivets, Bolts & Cap Screws, Screws, Nuts, Washers, Electronic Components & Hardware; Specializations: Metric Fasteners, Military Fasteners, Stainless Fasteners, Secondary Processing, Kitting & Assembly Services; End Markets: Aerospace, Automotive, Construction, Electronics, Health…
5. TFG USA – High-Quality Fasteners
Domain: tfgusa.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: High-Quality Fasteners Manufacturer | TFG USA QMS 9001:2015 Certified. Types of fasteners include threaded (anchors, bolts, nuts, studs, screws, socket products, self-tapping screws, self-threading screws, self-drilling screws, sheet metal screws, machine screws, special screws, automotive fasteners, roofing screws, drywall screws, acoustic ceiling screws, insert-molded knobs) and threadless (pins…
6. Jet-Tek – Aerospace Fasteners
Domain: jet-tek.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Jet-tek is a stocking distributor of aerospace and aircraft fasteners from top manufacturers. They have over 30 years of experience and can locate and deliver any type of aerospace fastener. Key manufacturers include Air Industries, Airdrome, Airfasco Industries, Alcoa Fasteners, Avdel, Boeing, Bristol Industries, California Screw Products, Camloc Fasteners, Fairchild Fastener Technology, Hi-lok F…
7. Vegas Fastener – Specialty Fasteners
Domain: vegasfastener.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Vegas Fastener specializes in manufacturing specialty fasteners that conform to Industrial Fasteners Institute (IFI) standards. Their product offerings include sockets, studs, bolts, machined components, and nuts. They utilize a variety of unique materials, including non-ferrous alloys such as Inconel, Monel, K-Monel, and Super Alloys, as well as nickel alloys, Hastelloy, and stainless steels. The…
8. IQS Directory – Fasteners & Industrial Products
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Fastener manufacturers and suppliers provide a wide range of products including bolts, metric fasteners, stainless steel fasteners, cold headed parts, self tapping screws, latches, industrial fasteners, rivets, and screw machine products. They offer services such as design, engineering, and manufacturing of fasteners to meet specific company requirements. Key companies mentioned include Ford Faste…
9. Bay Supply – Fasteners & Tools
Domain: baysupply.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Fastener Manufacturers | Shop By Manufacturer of Rivets, Bolts, Tools, & More – Bay Supply. Key product categories include: Rivets (Blind, Open End, Hard Metric, Multi Grip, Structural, Lock, Bulbing, Grooved, Solid, Mate, Semi Tubular), Lockbolts (with and without break-pins, collars, break-pins, reinforced panel), Bolts (Blind, Carriage, Eye, Flange, Heavy Hex, Self-Sealing Hex, U-Bolts, Vibrati…
10. Cardinal Fastener – Large Diameter Hot Forged Bolts
Domain: cardinalfastener.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Cardinal Fastener Inc. is a leading manufacturer of large diameter, hot forged bolts in America. Key product details include:
– Manufacturing capabilities for head styles and diameters up to 4-1/2″ or M72.
– Materials forged include carbon steels, alloys, high nickel alloys, and stainless steels.
– Product offerings include:
– Hex Head Bolts
– Hex Cap Screws
– Heavy Hex Bolts
– Heav…
Understanding Fastener Manufacturers Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Fasteners | Mass-produced, widely used, and available in various sizes | Automotive, Construction, Manufacturing | Pros: Cost-effective, readily available. Cons: Limited customization options. |
| Custom Fasteners | Tailored to specific requirements, often made to order | Aerospace, Energy, Heavy Equipment | Pros: Exact specifications, high performance. Cons: Longer lead times, higher cost. |
| Specialty Fasteners | Unique designs for specific applications | Military, Medical, High-Tech Industries | Pros: Enhanced functionality, meets niche needs. Cons: Can be expensive and hard to source. |
| High-Strength Fasteners | Made from advanced materials, designed for durability | Construction, Aerospace, Automotive | Pros: Increased load-bearing capacity, longevity. Cons: Higher cost, potential over-engineering. |
| Fastener Distributors | Suppliers of a wide range of fasteners from various manufacturers | Retail, Wholesale, Industrial Supply | Pros: Comprehensive inventory, quick delivery. Cons: Quality can vary among brands. |
What Are Standard Fasteners and Their Key Characteristics?
Standard fasteners are the backbone of many industries, characterized by their mass production and uniform sizes. These fasteners, including screws, nuts, and bolts, are readily available and suitable for general applications in automotive and construction sectors. B2B buyers appreciate the cost-effectiveness and immediate availability of standard fasteners, but they may face limitations in customization, which can be a drawback for specialized projects.
How Do Custom Fasteners Meet Unique Requirements?
Custom fasteners are manufactured to meet specific design and performance criteria, making them ideal for industries like aerospace and heavy equipment. These fasteners are made to order, allowing for precise specifications that align with unique project demands. While the benefits of custom fasteners include enhanced performance and tailored solutions, buyers must consider longer lead times and potentially higher costs associated with these products.
What Makes Specialty Fasteners Different from Others?
Specialty fasteners are designed for unique applications, often found in military, medical, and high-tech industries. Their distinctive designs and materials cater to specific needs, providing enhanced functionality that standard fasteners cannot offer. While these fasteners can fulfill niche requirements effectively, they may come at a premium price and can be harder to source, requiring careful consideration for B2B buyers.
Why Choose High-Strength Fasteners for Durability?
High-strength fasteners are engineered from advanced materials to withstand demanding conditions, making them suitable for construction and aerospace applications. Their ability to bear heavy loads and resist wear makes them a preferred choice for critical applications. However, the increased cost and potential for over-engineering can be a concern for buyers, necessitating a thorough evaluation of project requirements.
How Do Fastener Distributors Enhance Supply Chain Efficiency?
Fastener distributors serve as intermediaries, providing a wide array of fasteners from multiple manufacturers. They simplify the procurement process for businesses in retail, wholesale, and industrial supply sectors by ensuring a comprehensive inventory and quick delivery options. However, the quality of fasteners can vary among brands, so buyers should conduct due diligence to ensure they select reliable products that meet their standards.
Key Industrial Applications of Fastener Manufacturers
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Fastener Manufacturers | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Assembly of vehicles and components (e.g., engines, chassis) | Enhanced safety and performance, reduced assembly time | Compliance with industry standards, customization options, lead times |
| Aerospace | Production of high-strength fasteners for aircraft structures | Increased reliability, compliance with strict safety regulations | Material certifications, tolerance specifications, delivery reliability |
| Construction | Use in building frameworks, bridges, and infrastructure projects | Structural integrity, durability under load, cost-effectiveness | Local regulations, material availability, bulk purchasing options |
| Energy | Fasteners for wind turbines, oil rigs, and solar installations | Improved operational efficiency, resistance to environmental factors | Corrosion resistance, specialized coatings, international shipping |
| Military & Defense | Secure assembly of military vehicles and equipment | Mission-critical reliability, adherence to defense standards | Compliance with military specifications, sourcing from certified vendors |
How Are Fastener Manufacturers Used in the Automotive Industry?
Fastener manufacturers play a crucial role in the automotive sector by providing essential components for vehicle assembly. These fasteners are used in various applications, including securing engines, chassis, and body panels. Buyers in this industry require fasteners that meet stringent safety and performance standards, as any failure can lead to catastrophic results. Additionally, automotive manufacturers often seek customized solutions to fit specific design needs, making it essential for suppliers to offer flexibility in production and quick turnaround times.
What Are the Applications of Fasteners in Aerospace Manufacturing?
In aerospace manufacturing, fasteners are critical for assembling aircraft structures and components, where high strength and precision are paramount. Fastener manufacturers supply specialized products that meet rigorous industry standards, ensuring reliability and safety during flight. International buyers must consider certifications such as AS9100 and ISO:9001, which guarantee that fasteners meet the necessary quality and performance criteria. Additionally, tolerance specifications and delivery reliability are crucial, as delays can significantly impact production schedules.
How Are Fasteners Used in Construction Projects?
Fasteners are integral to the construction industry, where they are employed in building frameworks, bridges, and various infrastructure projects. The durability and structural integrity provided by high-quality fasteners contribute to the longevity and safety of these constructions. Buyers in this sector need to be aware of local regulations and standards that govern fastener specifications. Furthermore, sourcing from local manufacturers can reduce lead times and shipping costs, which is particularly beneficial for large-scale projects.
What Role Do Fasteners Play in the Energy Sector?
In the energy sector, fasteners are used in applications such as wind turbines, oil rigs, and solar panel installations. These fasteners must withstand harsh environmental conditions, including extreme temperatures and corrosive elements. Fastener manufacturers provide specialized coatings and materials to enhance corrosion resistance and overall durability. International buyers should focus on suppliers that offer comprehensive solutions tailored to their specific environmental challenges, ensuring that fasteners contribute to improved operational efficiency.
How Are Fasteners Essential in Military and Defense Applications?
Fasteners are vital in the military and defense sectors, where they secure assembly in vehicles and equipment that must perform reliably under extreme conditions. Fastener manufacturers supply products that meet military specifications, ensuring mission-critical reliability. Buyers in this sector must prioritize sourcing from certified vendors who can guarantee compliance with defense standards. Additionally, understanding the unique requirements of military applications, such as weight considerations and material strength, is essential for effective procurement.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘Fastener Manufacturers’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Quality Assurance Challenges in Fastener Sourcing
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with ensuring the quality and compliance of fasteners sourced from manufacturers, especially when dealing with international suppliers. Issues such as inconsistent quality standards, lack of certifications, and subpar manufacturing processes can lead to significant risks, including product failures, costly recalls, and damage to brand reputation. Buyers may find it difficult to verify the quality assurance processes of potential suppliers, especially when they are located in regions with varying industrial standards.
The Solution: To mitigate these risks, buyers should prioritize sourcing fasteners from manufacturers with robust quality assurance systems in place. Start by requesting documentation that outlines the manufacturer’s quality control processes, certifications (such as ISO 9001 or AS9100), and compliance with industry-specific standards like ASTM or DIN. Additionally, conducting supplier audits—either remotely or on-site—can provide deeper insights into their manufacturing practices. Engaging third-party quality inspection services can further ensure that the fasteners meet the required specifications before they are shipped. By establishing a clear quality checklist and maintaining open communication with suppliers about quality expectations, buyers can significantly reduce the likelihood of quality-related issues.
Scenario 2: Managing Lead Times and Delivery Reliability
The Problem: Fastener procurement often involves tight project timelines, and delays in delivery can halt production lines or construction projects, leading to financial losses. Buyers frequently encounter challenges related to lead times, especially when sourcing custom or specialty fasteners from overseas manufacturers, where shipping delays and customs clearance can add uncertainty to delivery schedules. The inability to predict when the required fasteners will arrive can disrupt project planning and execution.
The Solution: To address lead time issues, buyers should develop a strategic partnership with their fastener suppliers. This includes discussing and agreeing on realistic lead times before placing orders, taking into account production schedules, shipping times, and potential bottlenecks. Implementing a just-in-time (JIT) inventory system can also help minimize stock shortages. For critical components, consider maintaining a safety stock or working with manufacturers that offer expedited shipping options. Establishing clear communication channels and regular check-ins with suppliers can help buyers stay informed about any potential delays, allowing them to adjust project timelines proactively.
Scenario 3: Overcoming Customization and Specification Complexities
The Problem: Fasteners often need to be customized to meet specific project requirements, which can lead to confusion and errors in specifications. Buyers may struggle with conveying their exact needs to manufacturers, resulting in miscommunications that can lead to receiving incorrect products. This scenario is particularly common when working with specialized fasteners for unique applications, where standard options are insufficient.
The Solution: To effectively navigate customization challenges, buyers should invest time in developing detailed specifications for their fasteners. This includes providing clear drawings, material requirements, and performance standards to the manufacturer. Utilizing digital tools, such as CAD software, can facilitate the sharing of precise design specifications. Additionally, engaging in early discussions with manufacturers can help identify feasible customization options and potential limitations. Buyers should also consider requesting prototypes or samples before placing large orders to ensure that the final products meet their specifications. By fostering a collaborative relationship with manufacturers and leveraging technology for precise communication, buyers can streamline the customization process and reduce the risk of errors.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for Fastener Manufacturers
What Are the Key Properties of Steel Fasteners for Manufacturers?
Steel is the most common material used in fastener manufacturing due to its excellent mechanical properties. It typically offers high tensile strength, making it suitable for a variety of applications, including automotive and construction. Steel fasteners can withstand high temperatures and pressures, ensuring durability in demanding environments. Additionally, different grades of steel, such as stainless steel or carbon steel, can be selected based on specific requirements for corrosion resistance.
Pros & Cons of Steel Fasteners
While steel fasteners are known for their strength, they can be susceptible to rust if not properly treated or coated. The manufacturing process can be complex, especially for custom designs, which may increase costs. However, their widespread availability and versatility often make them a cost-effective choice for many applications.
Impact on Application
Steel fasteners are compatible with a wide range of media, including water, oil, and various chemicals, depending on the specific grade used. For international buyers, understanding the local environmental conditions is crucial, as humidity and exposure to corrosive elements can significantly impact performance.
How Do Aluminum Fasteners Compare in Terms of Performance?
Aluminum fasteners are increasingly popular due to their lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion. They are particularly advantageous in applications where weight reduction is critical, such as in the aerospace and automotive industries. Aluminum also has good thermal and electrical conductivity, making it suitable for specific electronic applications.
Pros & Cons of Aluminum Fasteners
The primary advantage of aluminum fasteners is their lightweight, which can lead to lower shipping costs and easier handling. However, they generally have lower tensile strength compared to steel, which may limit their use in high-stress applications. Additionally, aluminum fasteners can be more expensive than their steel counterparts, impacting overall project budgets.
Impact on Application
Aluminum fasteners are ideal for applications exposed to moisture and corrosive environments, as they naturally form a protective oxide layer. International buyers should consider local standards and regulations regarding aluminum use, especially in industries like aerospace, where compliance with specific certifications is mandatory.
What Are the Benefits of Using Plastic Fasteners in Manufacturing?
Plastic fasteners are gaining traction due to their lightweight and non-corrosive properties. They are often used in applications where metal fasteners may not be suitable, such as in electrical or electronic devices, where conductivity must be minimized.
Pros & Cons of Plastic Fasteners
The main advantage of plastic fasteners is their resistance to corrosion and chemical exposure, making them ideal for diverse environments. However, they generally have lower load-bearing capabilities and may not be suitable for high-stress applications. The manufacturing process for plastic fasteners can be simpler and more cost-effective, but their performance under extreme temperatures may be limited.
Impact on Application
Plastic fasteners are compatible with various media, but their use should be evaluated based on the specific application requirements. For international buyers, understanding the local market’s acceptance of plastic fasteners and compliance with relevant standards is essential.
What Role Does Titanium Play in Fastener Manufacturing?
Titanium fasteners are renowned for their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance. They are often used in high-performance applications, including aerospace, medical devices, and marine environments.
Pros & Cons of Titanium Fasteners
Titanium fasteners are incredibly durable and can withstand extreme conditions, making them suitable for specialized applications. However, they are significantly more expensive than steel or aluminum fasteners, which can be a limiting factor for many projects. The manufacturing process is also more complex, requiring specialized equipment and expertise.
Impact on Application
Titanium fasteners are particularly valuable in applications where weight reduction and corrosion resistance are critical. International buyers should be aware of the specific standards and certifications required for titanium fasteners in their respective industries, as compliance can vary significantly.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Fastener Manufacturers
| Material | Typical Use Case for Fastener Manufacturers | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Automotive, construction | High tensile strength | Susceptible to rust | Medium |
| Aluminum | Aerospace, automotive | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower tensile strength | High |
| Plastic | Electrical devices, consumer products | Non-corrosive and lightweight | Limited load-bearing capacity | Low |
| Titanium | Aerospace, medical devices | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio | High cost and complex manufacturing | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, aiding in the decision-making process when sourcing fasteners tailored to specific applications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for Fastener Manufacturers
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process for Fasteners?
The manufacturing of fasteners is a complex process that typically encompasses several key stages, including material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation: This initial stage involves selecting high-quality raw materials, often steel or other alloys, based on the specific requirements of the fasteners to be produced. The materials are subjected to processes such as annealing or heat treatment to enhance their mechanical properties. Proper material preparation ensures that the final fasteners exhibit the necessary strength and durability.
-
Forming: During this stage, the raw materials are shaped into the desired fastener forms using various techniques. Common forming methods include cold heading, forging, and machining. Cold heading is particularly prevalent for producing screws and bolts, as it allows for the efficient shaping of metal at room temperature, maintaining material integrity while minimizing waste.
-
Assembly: Some fasteners require additional components to be assembled, such as washers or nuts. This stage ensures that all parts fit together correctly, adhering to the specified tolerances. Automated assembly lines are often utilized to enhance precision and efficiency, especially for high-volume production.
-
Finishing: The final manufacturing stage involves applying surface treatments to improve corrosion resistance, aesthetics, and performance. Techniques such as plating, coating, or anodizing are employed to provide the necessary protective layers. Proper finishing not only enhances the durability of the fasteners but also meets specific industry standards.
Which Key Techniques Are Used in Fastener Manufacturing?
Fastener manufacturers leverage various techniques to ensure efficiency and quality. Techniques such as cold forming and hot forging are fundamental to producing strong and reliable fasteners.
-
Cold Forming: This method uses high-pressure to shape metal at room temperature. It is efficient for producing large quantities of fasteners with minimal waste. Cold forming enhances the mechanical properties of the metal, resulting in stronger finished products.
-
Hot Forging: In contrast to cold forming, hot forging involves heating the metal above its recrystallization temperature before shaping it. This technique allows for the production of larger and more complex fastener designs, providing better control over the material properties.
-
Machining: For precision fasteners, machining is often necessary. This process involves removing material from a workpiece to achieve the desired dimensions and surface finish. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are commonly used to ensure high precision and repeatability.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Fastener Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in fastener manufacturing, ensuring that products meet international and industry-specific standards. Fastener manufacturers typically adhere to quality management systems such as ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for an effective quality management system.
What International Standards Are Relevant for Fastener Quality Assurance?
-
ISO 9001: This standard provides a framework for quality management systems and is applicable across industries. Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that a manufacturer has a systematic approach to managing quality, thereby enhancing customer satisfaction.
-
CE Marking: For fasteners sold within the European Economic Area, CE marking indicates compliance with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards. Manufacturers must ensure their products meet specific directives to obtain this certification.
-
API Standards: In sectors like oil and gas, API (American Petroleum Institute) standards apply to fasteners used in critical applications. Compliance with these standards ensures that fasteners can withstand the demanding conditions present in these industries.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Fastener Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integral to maintaining product integrity throughout the manufacturing process. Common QC checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival at the manufacturing facility. The aim is to verify that the materials meet specified standards before production begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, IPQC is conducted to monitor production parameters and ensure that the fasteners are being produced according to specifications. This includes regular measurements and testing at various stages.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the fasteners are produced, FQC involves comprehensive testing to verify that the final products meet all quality standards and specifications. This may include dimensional checks, tensile strength tests, and surface finish evaluations.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a fastener manufacturer’s quality control processes is crucial. Here are several strategies buyers can employ:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can provide insights into a manufacturer’s quality management practices, production processes, and compliance with standards. Audits allow buyers to assess the manufacturer’s capabilities firsthand.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting quality assurance reports and documentation from the supplier can help buyers understand the manufacturer’s adherence to quality standards. These documents often include inspection results, certifications, and compliance records.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the manufacturer’s quality control processes. These services can verify compliance with international standards and evaluate product quality before shipment.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate various certifications and quality control nuances when sourcing fasteners. Understanding these nuances can facilitate smoother transactions and reduce risks associated with product quality.
-
Regional Standards: Different regions may have specific standards and certifications. For instance, the requirements for fasteners in Europe may differ from those in the Middle East. Buyers should be aware of these regional differences to ensure compliance.
-
Traceability and Documentation: Buyers should prioritize suppliers that provide detailed documentation regarding the sourcing and testing of raw materials. Traceability is crucial for quality assurance, especially for applications in critical industries.
-
Language and Communication: Language barriers can complicate quality assurance processes. Buyers should ensure that they can communicate effectively with suppliers regarding quality expectations and standards.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices of fastener manufacturers, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they source high-quality fasteners that meet their specific needs and industry standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘Fastener Manufacturers’
The following practical sourcing guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in effectively procuring fasteners from manufacturers. Whether you are sourcing for construction, automotive, aerospace, or other industries, this checklist will help streamline your decision-making process.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to suppliers, clearly outline your technical requirements. This includes the type of fasteners needed (screws, bolts, nuts, washers), material specifications (steel, stainless steel, plastic), and any industry standards (ASTM, ISO) that must be met. Having these specifications helps ensure that the suppliers understand your needs and can provide suitable products.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential fastener manufacturers. Look for companies with a solid reputation in your industry and verify their experience and capabilities. Utilize online directories, trade shows, and industry publications to gather a list of potential suppliers.
Step 3: Verify Supplier Certifications
Confirm that the suppliers possess the necessary certifications to ensure quality and compliance. Look for ISO certifications, industry-specific standards, and other relevant quality assurances. These certifications indicate that the manufacturer adheres to recognized quality management systems and can produce reliable fasteners.
Step 4: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities
Assess the manufacturing capabilities of each supplier to ensure they can meet your volume and customization needs. Inquire about their production processes, lead times, and the technology they use. A manufacturer with advanced technology may offer better precision and faster turnaround times.
Step 5: Request Samples and Conduct Testing
Before finalizing your supplier, request samples of the fasteners you intend to purchase. Conduct quality testing to verify that the samples meet your specifications and industry standards. This step is crucial to avoid costly mistakes later in the procurement process.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you’ve narrowed down your options, negotiate pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Be sure to discuss any additional costs that may arise, such as shipping or customizations. A clear agreement upfront can prevent misunderstandings later in the transaction.
Step 7: Establish Communication Channels
Maintain open lines of communication with your chosen supplier. Regular updates on production status, shipping information, and any potential issues can help ensure a smooth procurement process. Establishing a strong relationship with your supplier fosters trust and can lead to better service and support in the future.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing fasteners, ultimately enhancing their project’s success and ensuring high-quality outcomes.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for Fastener Manufacturers Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Fastener Manufacturing?
Understanding the cost structure of fastener manufacturing is essential for B2B buyers looking to optimize their sourcing strategies. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of raw materials significantly influences costs. Common materials such as steel, aluminum, and specialty alloys vary in price depending on market fluctuations and availability. High-performance materials typically incur higher costs but can enhance product durability and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass direct wages for manufacturing personnel as well as indirect costs associated with training and benefits. Regions with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but it’s crucial to assess the skill level and experience of the workforce to ensure quality.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead costs, allowing manufacturers to offer more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling, including molds and dies, can be substantial, particularly for custom fasteners. However, once the tooling is established, the cost per unit decreases significantly with higher production volumes.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC measures is vital for maintaining product standards and certifications. While these processes add to costs, they can prevent costly recalls and enhance brand reputation.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs are influenced by the distance between the supplier and the buyer, as well as the mode of transportation. Import duties and tariffs can further complicate logistics costs for international buyers.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically add a markup to cover their operational costs and profit. Margins can vary based on market competition and the perceived value of the product.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Fastener Sourcing?
Several factors can influence pricing in fastener sourcing, which B2B buyers should consider:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Purchasing in bulk often results in lower prices per unit. Manufacturers may set MOQs that can affect overall sourcing costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom fasteners tailored to specific applications can lead to increased costs due to additional engineering and production requirements. However, these may be necessary for specialized projects.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Fasteners that meet international standards (like ISO or ASTM) may command higher prices but offer assurance of quality and reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of a supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers with a proven track record may charge more for their products due to perceived quality and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is critical for international buyers. Different Incoterms can shift costs and responsibilities between buyers and sellers, affecting the total landed cost of fasteners.
What Tips Can Help International Buyers Optimize Fastener Sourcing Costs?
For B2B buyers, especially those from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can enhance cost efficiency:
-
Negotiate Terms: Engage in discussions with suppliers to negotiate pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Leveraging long-term relationships can also yield better pricing.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond initial costs to assess the long-term implications of your sourcing decisions. Consider factors like durability, maintenance, and potential failure rates, which can impact overall project costs.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be mindful of currency fluctuations, local taxes, and tariffs that can affect the final cost of fasteners. Establishing contracts in stable currencies can mitigate some risks.
-
Consider Local Suppliers: In some cases, sourcing from local manufacturers can reduce shipping costs and lead times. Additionally, local suppliers may be more familiar with regional standards and requirements.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for fasteners can fluctuate based on market conditions, material availability, and geopolitical factors. Buyers are encouraged to obtain quotes directly from manufacturers to get the most accurate and up-to-date pricing information tailored to their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing Fastener Manufacturers With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Fastener Manufacturers
In the fasteners industry, sourcing the right components is critical for project success. While fastener manufacturers are the traditional go-to for securing parts, buyers should consider alternative solutions that may offer comparable performance and cost-effectiveness. This analysis compares fastener manufacturers with two viable alternatives: adhesive bonding and welding. Each method has unique characteristics that may suit different applications and project requirements.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Fastener Manufacturers | Adhesive Bonding | Welding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High tensile strength; reliable connections | Good for stress distribution; flexibility | Extremely strong; permanent bonds |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depending on custom specs | Generally lower, especially for bulk use | Can be higher due to equipment and skill needs |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple; requires tools for installation | Requires surface preparation; curing time needed | Requires skilled labor and safety precautions |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; durable in harsh conditions | May require periodic inspection | Low, but may need rework if not done correctly |
| Best Use Case | Mechanical assemblies in various industries | Lightweight materials; non-structural uses | Heavy-duty applications; structural integrity |
Pros and Cons of Adhesive Bonding
Adhesive bonding involves using specialized adhesives to join materials, offering unique advantages. One of the primary benefits is its ability to bond dissimilar materials, such as metal to plastic, which fasteners cannot do. Adhesives also distribute stress across a larger surface area, reducing the risk of failure under load. However, they may require careful surface preparation and can be sensitive to temperature and humidity during the curing process. This method is ideal for applications where weight savings are crucial, such as in aerospace or automotive industries.
Pros and Cons of Welding
Welding is a method that uses high heat to melt and fuse materials, creating a very strong bond. It is particularly effective for heavy-duty applications, such as in construction and shipbuilding, where the structural integrity is paramount. The primary drawback is the need for skilled labor and specialized equipment, which can increase costs and implementation time. Additionally, welding may not be suitable for all materials and can introduce heat-related distortions. It is best used in situations where permanent, load-bearing joints are required.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting between fastener manufacturers and alternative methods like adhesive bonding or welding, B2B buyers should carefully evaluate their specific project requirements. Factors such as material types, load conditions, environmental exposure, and cost constraints play a significant role in the decision-making process. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each option allows buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and project specifications. By considering all available solutions, buyers can optimize their sourcing strategy and enhance the overall efficiency of their projects.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for Fastener Manufacturers
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Fasteners That Buyers Should Know?
Understanding the technical specifications of fasteners is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure they select the appropriate products for their applications. Here are some essential properties:
-
Material Grade: Fasteners are manufactured from various materials, including carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloys. Material grade indicates the strength, corrosion resistance, and suitability for specific environments. For instance, stainless steel fasteners are preferred in corrosive environments, such as marine applications, due to their resistance to rust and corrosion.
-
Tensile Strength: This property measures the maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking. It is vital for determining the fastener’s load-bearing capacity in applications, such as structural engineering or automotive manufacturing. A higher tensile strength generally indicates a more robust fastener.
-
Thread Pitch: This refers to the distance between threads on a screw or bolt. Thread pitch is essential for ensuring compatibility with corresponding nuts or tapped holes. Buyers must understand whether they need fine or coarse threads, as this affects the assembly’s strength and ease of installation.
-
Tolerance: Tolerance specifies the allowable variation in a fastener’s dimensions. Tight tolerances are critical in high-precision applications, such as aerospace or medical devices, where even minor deviations can lead to failures. Understanding the required tolerances helps buyers select fasteners that meet their precise specifications.
-
Coating and Finish: Fasteners often come with various coatings, such as zinc plating or black oxide, to enhance their corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. The choice of coating can significantly impact the fastener’s performance and lifespan, especially in harsh environments.
-
Heat Treatment: Some fasteners undergo heat treatment processes to improve their mechanical properties, such as hardness and tensile strength. This is particularly important in high-stress applications, where enhanced durability is required.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in Fastener Manufacturing?
Familiarizing yourself with industry jargon can facilitate better communication and decision-making when sourcing fasteners. Here are some common terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that are used in another company’s end product. For fastener manufacturers, being an OEM means providing components that meet specific standards required by the end-user’s product.
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for buyers to manage inventory and cash flow effectively. It can impact pricing, especially for smaller businesses looking to purchase specialty fasteners.
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation): An RFQ is a document that potential buyers send to suppliers to request pricing and availability for specific products. Providing detailed RFQs helps suppliers understand the buyer’s needs, leading to more accurate quotes and reducing the back-and-forth during the procurement process.
-
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms): These are standardized terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms can help buyers navigate shipping, risk, and costs associated with fastener procurement from overseas manufacturers.
-
Lead Time: This term refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the product. For fastener manufacturers, shorter lead times can be a competitive advantage, especially in industries with tight production schedules.
-
Certification Standards: Fasteners often need to meet specific certification standards, such as ISO, ASTM, or DIN. These certifications ensure that the products comply with international quality and safety standards. Buyers should verify certifications to mitigate risks associated with product failures.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terminology, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing fasteners for their projects, ensuring quality and compatibility with their applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Fastener Manufacturers Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends: What Are the Current Dynamics in the Fastener Manufacturing Sector?
The fastener manufacturing sector is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for durable, high-quality fastening solutions across diverse industries such as automotive, aerospace, construction, and energy. The global market is expected to reach USD 100 billion by 2025, fueled by the expansion of infrastructure projects in emerging markets and the rising trend of automation. International B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should pay attention to key trends shaping the market.
One notable trend is the integration of advanced technologies like IoT and AI into manufacturing processes, enhancing efficiency and allowing for real-time tracking of supply chains. Additionally, the shift towards just-in-time (JIT) inventory management is prompting fastener manufacturers to improve their logistics and distribution capabilities. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who can offer quick turnaround times and flexible sourcing options to adapt to changing market demands.
Moreover, sustainability is becoming a focal point for manufacturers. As global regulations tighten around environmental impact, fastener manufacturers are adopting eco-friendly materials and practices. This shift not only addresses regulatory requirements but also aligns with the growing consumer preference for sustainable products. For international buyers, understanding these dynamics is crucial for making informed sourcing decisions and ensuring alignment with industry best practices.
How Is Sustainability Shaping Ethical Sourcing in the Fastener Industry?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing have become paramount in the fastener manufacturing sector, reflecting a broader commitment to environmental responsibility and social accountability. The production of fasteners often involves significant resource consumption and waste generation, which underscores the importance of adopting sustainable practices. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to reducing their environmental footprint through the use of renewable energy, efficient manufacturing processes, and waste minimization strategies.
The demand for “green” certifications, such as ISO 14001, is on the rise, as buyers seek assurance that their suppliers adhere to environmental management standards. Additionally, manufacturers are exploring the use of recycled materials in their fasteners, which not only reduces resource consumption but also appeals to eco-conscious clients. This transition toward sustainable practices is not merely a trend but a fundamental shift that can influence brand loyalty and market positioning.
For international buyers, partnering with fastener manufacturers that prioritize sustainability can enhance their own corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives and improve their brand image. Establishing ethical supply chains can lead to stronger relationships with customers, as businesses increasingly favor suppliers who align with their values and demonstrate a commitment to sustainability.
What Is the Historical Context of Fastener Manufacturing for B2B Buyers?
The fastener manufacturing industry has evolved significantly over the past century, transitioning from traditional, manual production methods to advanced, automated processes. Initially, fasteners were produced primarily by blacksmiths and small workshops, focusing on basic designs and materials. However, the industrial revolution in the late 19th century marked a turning point, introducing mass production techniques that allowed for the rapid creation of standardized fasteners.
As industries expanded, the demand for more specialized and high-strength fasteners grew, leading to innovations in materials and manufacturing processes. By the mid-20th century, the introduction of new alloys and coatings enhanced the performance and durability of fasteners, making them suitable for a wider range of applications. Today, fastener manufacturers leverage cutting-edge technology, such as computer-aided design (CAD) and automated assembly lines, to meet the complex requirements of modern industries.
Understanding this evolution is essential for B2B buyers seeking reliable suppliers. Knowledge of the historical context allows buyers to appreciate the advancements in quality and technology that differentiate leading manufacturers in the fastener sector, enabling them to make informed sourcing decisions that align with their operational needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of Fastener Manufacturers
-
How do I choose the right fastener manufacturer for my needs?
Selecting the right fastener manufacturer involves assessing several factors, including product quality, manufacturing capabilities, and industry experience. Start by identifying your specific fastener requirements, such as material type, size, and application. Research potential suppliers by looking at their certifications (like ISO), customer reviews, and case studies. Additionally, consider their ability to offer customization and their responsiveness to inquiries, as these can indicate their commitment to customer service and flexibility. -
What types of fasteners are available for different industries?
Fasteners come in various forms, including screws, bolts, nuts, washers, and specialized components tailored for specific industries. For instance, automotive applications often require high-strength fasteners, while construction may utilize anchors and U-bolts. Aerospace industries demand precision-engineered components, whereas agricultural sectors might need corrosion-resistant fasteners. Understanding your industry’s unique requirements will help you select the appropriate fastener type and ensure optimal performance. -
What should I know about minimum order quantities (MOQ) when sourcing fasteners?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can vary significantly among fastener manufacturers. Some suppliers may require large MOQs for custom products, while others offer flexibility with smaller orders for standard items. It’s essential to communicate your needs upfront and inquire about MOQs during the negotiation process. If your order volume is low, look for manufacturers that provide smaller batch production or are willing to accommodate your needs without compromising on quality. -
How can I ensure the quality of fasteners from international suppliers?
To ensure quality when sourcing fasteners internationally, request samples for testing before placing a bulk order. Verify that the manufacturer adheres to international quality standards, such as ISO 9001, and ask for relevant certifications. Consider conducting a factory audit or utilizing third-party inspection services to assess manufacturing processes and quality control measures. Maintaining open communication with the supplier throughout the process can also help address any concerns regarding quality. -
What are the common payment terms in international fastener trade?
Payment terms can vary based on the manufacturer and the buyer’s location. Common terms include advance payment, letter of credit, and net 30 or 60 days after delivery. It’s crucial to clarify payment methods accepted by the supplier, such as bank transfers or credit cards, and to establish terms that protect both parties. Be aware of currency exchange rates and potential fees, as these can impact the total cost of your order. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing fasteners?
When importing fasteners, consider factors such as shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations. Choose a reliable logistics partner experienced in handling international shipments to ensure timely delivery. Familiarize yourself with import duties and taxes applicable to fasteners in your country, as these can significantly affect overall costs. Additionally, ensure proper packaging to prevent damage during transit and avoid any potential delays in customs clearance. -
How can I customize fasteners to meet specific project requirements?
Customization options for fasteners often include variations in size, shape, material, and surface treatments. Many manufacturers offer design assistance to help you develop a fastener that meets your project specifications. When discussing customization, provide detailed drawings or specifications to ensure clarity. Be prepared for potential lead times associated with custom manufacturing, and confirm the supplier’s ability to deliver within your project timeline. -
What are the best practices for supplier vetting in the fastener industry?
To effectively vet fastener suppliers, start by checking their industry experience and customer references. Review their certifications and compliance with international standards. Conduct background research, including financial stability and market reputation, to assess reliability. Additionally, engage in direct communication with potential suppliers to gauge their responsiveness and willingness to collaborate. Establishing a good relationship with your supplier can lead to better service and more favorable terms over time.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for Fastener Manufacturers
In the ever-evolving landscape of fastener manufacturing, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical component for success. By leveraging the diverse offerings from leading manufacturers across the globe, businesses can ensure they obtain high-quality fasteners tailored to their specific needs. Key takeaways highlight the importance of selecting suppliers with a proven track record, robust quality assurance processes, and a commitment to customer service excellence.
As international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek to optimize their supply chains, establishing partnerships with reliable fastener manufacturers can yield significant cost savings and enhance project efficiency. The growing demand for customized solutions further emphasizes the need for collaboration between buyers and manufacturers to meet unique specifications.
Looking ahead, the fastener industry is poised for growth, driven by advancements in technology and increasing global connectivity. Now is the time for B2B buyers to take action—evaluate your sourcing strategies, explore new partnerships, and invest in quality fasteners that will propel your projects forward. Engage with manufacturers who understand your market dynamics and can provide innovative solutions tailored to your business needs.