Top 2 Gate Valve Manufacturers List and Guide: How To Solve Scena…
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for Gate Valve Manufacturers
The global market for gate valve manufacturers presents a unique set of challenges for international B2B buyers, particularly when it comes to sourcing reliable, high-quality products that meet stringent industry standards. With a diverse range of valve types—including resilient seated, metal seated, and knife gate valves—buyers must navigate various specifications, applications, and compliance requirements. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, detailing the different types of gate valves, their applications across industries such as oil and gas, water treatment, and pharmaceuticals, and essential criteria for vetting suppliers.
In addition to exploring the technical aspects of gate valve design and performance, we delve into cost considerations and procurement strategies tailored for markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including Nigeria and Brazil. By addressing the critical factors that influence purchasing decisions, this guide empowers B2B buyers to make informed choices, ensuring they procure the right gate valves for their specific needs. With insights from leading manufacturers and industry experts, readers will gain a nuanced understanding of the global gate valve landscape, ultimately enhancing their supply chain efficiency and operational effectiveness.
Top 10 Gate Valve Manufacturers Manufacturers & Suppliers List
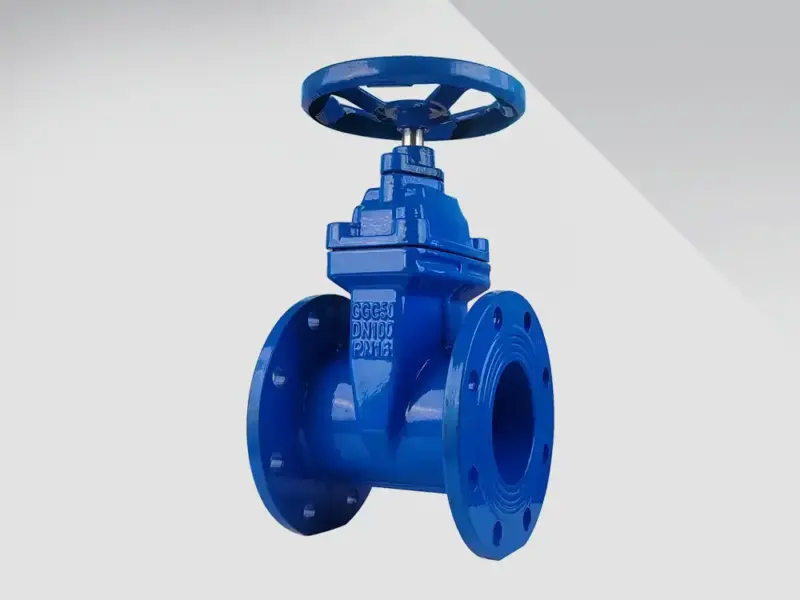
1. Henry Pratt – Gate Valves
Domain: henrypratt.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Pratt® gate valves are designed for wastewater and sewage applications, available in Non-Rising Stem (NRS) and Outside Screw & Yoke (OS&Y) versions. Sizes range from 2″ to 96″. Metal Seated Solid Wedge Valves comply with AWWA C500, ANSI, and ASTM standards. Valves 14″ and larger feature bronze body and wedge guides. Equipped with hand wheels, non-operating nuts, and integrally cast mounting pads f…
2. Valveman – Gate Valves
Domain: valveman.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Gate valves are designed to operate in fully open or closed positions, providing minimum pressure drop with straight-through flow. They utilize a gate mechanism that slides to create a tight seal, making them suitable for water, oil, gas, and steam applications. Available in various materials, sizes, and pressure classes, gate valves are resilient and effective in both commercial and industrial se…
Understanding Gate Valve Manufacturers Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metal Seated Solid Wedge | Designed for high pressure; minimal flow restriction; robust metal seating surfaces. | Oil & gas, water treatment, industrial processes. | Pros: High durability and reliability. Cons: Less effective for throttling. |
| Resilient Seated | EPDM or similar material for sealing; non-rising stem design; fusion bonded epoxy coating. | Fire protection, municipal waterworks, sewage systems. | Pros: Good sealing performance; suitable for various pressures. Cons: Limited temperature range. |
| Outside Screw & Yoke (OS&Y) | Features a stem that is exposed; allows for easy visibility of valve position. | Water distribution, HVAC systems, irrigation. | Pros: Easy maintenance; clear indication of valve status. Cons: Vulnerable to environmental factors. |
| Bolted Bonnet | Male-female joint with spiral wound gasket; available in various materials. | Chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, manufacturing. | Pros: Strong construction; customizable. Cons: More complex installation. |
| Knife Gate | Slim profile; designed for on/off service in slurry applications; customizable materials. | Pulp and paper, mining, wastewater treatment. | Pros: Effective in handling thick fluids; space-saving design. Cons: Not suitable for high-pressure applications. |
What Are the Characteristics of Metal Seated Solid Wedge Gate Valves?
Metal seated solid wedge gate valves are renowned for their durability and high-pressure handling capabilities. These valves utilize robust metal seating surfaces to provide a reliable seal, making them ideal for applications in oil and gas, water treatment, and various industrial processes. When purchasing, consider the valve’s pressure rating and compatibility with the fluid being controlled, as they are not suitable for throttling but excel in on/off service.
How Do Resilient Seated Gate Valves Perform in Various Applications?
Resilient seated gate valves feature a seal made from EPDM or similar materials, making them particularly effective in applications requiring excellent sealing performance. They are commonly used in fire protection systems and municipal waterworks due to their ability to handle varying pressures and provide a reliable shut-off. Buyers should assess temperature limits and the chemical compatibility of the sealing material to ensure optimal performance.
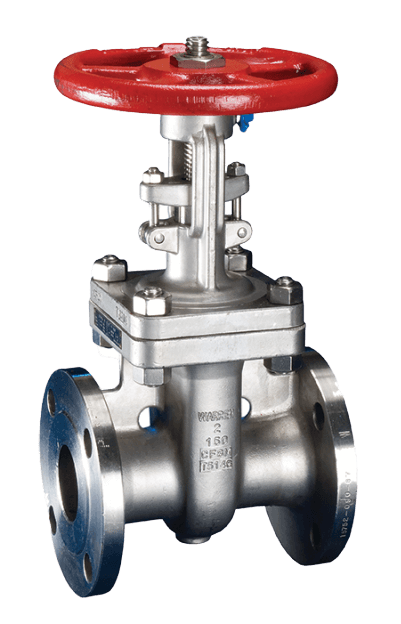
What Are the Benefits of Outside Screw & Yoke (OS&Y) Gate Valves?
OS&Y gate valves are characterized by their exposed stem, which allows for easy visibility of the valve’s open or closed position. This feature is beneficial in water distribution and HVAC systems where maintenance and operational clarity are crucial. When considering an OS&Y valve, evaluate its environmental exposure, as the exposed components may require additional protection against corrosion and wear.
Why Choose Bolted Bonnet Gate Valves for Chemical Processing?
Bolted bonnet gate valves are designed with a male-female joint and a spiral wound gasket, providing a robust and customizable solution for demanding applications such as chemical processing and pharmaceuticals. Their strong construction ensures durability, but buyers should be prepared for potentially more complex installation processes. Consider the specific material requirements based on the chemicals being handled to avoid compatibility issues.
In What Situations Are Knife Gate Valves Most Effective?
Knife gate valves are uniquely designed for on/off service in applications involving slurries or thick fluids, such as in the pulp and paper or mining industries. Their slim profile allows for installation in tight spaces, making them a practical choice for wastewater treatment facilities. When purchasing knife gate valves, it is essential to evaluate their pressure ratings and compatibility with the media to ensure they meet the demands of the application effectively.
Key Industrial Applications of Gate Valve Manufacturers
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Gate Valve Manufacturers | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water and Wastewater | Use in municipal water supply and sewage treatment systems | Ensures reliable flow control, reducing downtime | Compliance with AWWA and NSF standards; corrosion resistance |
| Oil and Gas | Control of fluid flow in pipelines and refineries | Minimizes leakage and enhances operational efficiency | High pressure ratings; materials suitable for harsh environments |
| Pharmaceuticals | Regulation of fluid transfer in production processes | Maintains purity and prevents contamination | FDA compliance; low-emission designs; precise flow control |
| Fire Protection | Integration in fire suppression systems | Ensures immediate response and reliability in emergencies | UL/FM certification; compatibility with existing systems |
| Manufacturing and Heavy Industry | Management of steam and coolant flow in production lines | Improves energy efficiency and reduces maintenance costs | Customization options; durability under high temperatures |
How Are Gate Valve Manufacturers Used in Water and Wastewater Applications?
Gate valves are critical in municipal water supply and sewage treatment systems, enabling precise control over water flow. By ensuring minimal pressure drop and efficient operation, these valves help municipalities manage resources effectively. Buyers in this sector must prioritize compliance with AWWA and NSF standards, as well as seek materials that resist corrosion to extend the lifespan of the equipment, especially in challenging environments typical of African and South American regions.
What Role Do Gate Valves Play in the Oil and Gas Industry?
In the oil and gas sector, gate valves are essential for controlling the flow of crude oil and natural gas through pipelines and refineries. Their design minimizes leakage and pressure drops, enhancing overall operational efficiency. For international buyers, especially in the Middle East, sourcing valves with high pressure ratings and materials that withstand harsh conditions is crucial to ensure safety and reliability in their operations.
How Are Gate Valves Critical in Pharmaceuticals?
Gate valves are used extensively in the pharmaceutical industry to regulate fluid transfer during production processes. Their precise operation is vital to maintaining product purity and preventing contamination. Buyers must consider FDA compliance and opt for low-emission designs to meet stringent health regulations. Given the global nature of pharmaceutical supply chains, manufacturers should be able to provide detailed certifications and quality assurances.
Why Are Gate Valves Important for Fire Protection Systems?
In fire protection systems, gate valves ensure immediate water flow during emergencies, making them essential for effective fire suppression. The reliability of these valves can be a matter of life and property protection. Buyers should seek UL/FM certified products that integrate seamlessly with existing fire safety systems. Compatibility and ease of installation are key considerations for international buyers, particularly in rapidly urbanizing regions.
How Do Gate Valves Benefit Manufacturing and Heavy Industry?
In manufacturing and heavy industry, gate valves manage steam and coolant flow in production lines, significantly impacting energy efficiency and maintenance costs. Their robust construction and low operational torque make them ideal for high-temperature applications. Buyers should look for customization options to fit specific operational needs and ensure durability under demanding conditions, especially in sectors prevalent in Europe and South America.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘Gate Valve Manufacturers’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Compliance and Certification Challenges
The Problem: B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, often face hurdles related to compliance with local regulations and international standards when sourcing gate valves. For example, they may struggle to ensure that the products meet essential certifications like ANSI/NSF for drinking water applications or AWWA standards for wastewater management. This challenge can lead to project delays, increased costs, and potential legal repercussions if non-compliant products are used.
The Solution: To overcome compliance challenges, buyers should prioritize sourcing gate valves from manufacturers who provide clear documentation of certifications and compliance with local and international standards. When evaluating suppliers, ask for proof of certifications and specifications for each valve type. Additionally, consider engaging with manufacturers who have a local presence or partnerships in your region, as they are often more familiar with local regulations. Building a strong relationship with a reliable manufacturer can facilitate access to updated regulatory information, ensuring that you remain compliant while sourcing high-quality products.
Scenario 2: Handling Performance and Reliability Concerns
The Problem: Many B2B buyers experience concerns regarding the performance and reliability of gate valves, particularly in high-stakes industries such as oil and gas or water treatment. Buyers may receive valves that do not perform as promised, leading to leaks, maintenance issues, or even catastrophic failures. This not only impacts operational efficiency but can also result in significant financial losses and damage to reputation.
The Solution: To mitigate performance concerns, buyers should conduct thorough due diligence on manufacturers before making a purchase. This includes reviewing product specifications, testing results, and user testimonials. Look for manufacturers that offer performance guarantees or warranties on their products. Additionally, consider requesting samples or conducting on-site inspections of valves to assess their quality firsthand. Engaging with a manufacturer that specializes in custom solutions can also ensure that the specific requirements of your application are met, thereby enhancing reliability.
Scenario 3: Managing Supply Chain and Lead Time Issues
The Problem: Supply chain disruptions are increasingly common in global markets, and buyers often face long lead times for gate valve orders. This can be particularly challenging in regions with less developed logistics networks, where delays can stall entire projects. Buyers may find themselves caught in a cycle of urgent needs and extended waiting periods, which can lead to increased costs and project overruns.
The Solution: To effectively manage supply chain challenges, buyers should establish strong relationships with multiple manufacturers to create a diversified supply chain. This strategy allows for flexibility and reduces dependency on a single supplier. Additionally, consider implementing a Just-In-Time (JIT) inventory strategy, which can help align orders with project schedules and reduce the need for large inventory holdings. Engage in proactive communication with manufacturers regarding lead times and potential delays, and explore options for expedited shipping when necessary. Leveraging local suppliers for smaller, urgent orders can also help mitigate long lead times for critical projects.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for Gate Valve Manufacturers
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Gate Valve Manufacturing?
Gate valves are critical components in various industrial applications, and the choice of material significantly impacts their performance, durability, and suitability for specific environments. Below, we analyze four common materials used in gate valve manufacturing: ductile iron, stainless steel, carbon steel, and brass.
Ductile Iron: A Versatile Choice for Many Applications
Ductile iron is known for its excellent strength and ductility, making it a popular choice for gate valves, especially in waterworks and sewage applications. It offers high corrosion resistance when properly coated, typically with fusion-bonded epoxy. Ductile iron valves can handle pressures up to 300 psi and temperatures ranging from -20°F to 180°F.
Pros: Ductile iron is relatively cost-effective and provides good impact resistance, making it suitable for high-stress environments. Its manufacturing process is well-established, leading to lower production costs.
Cons: While ductile iron is durable, it can be susceptible to corrosion if not properly coated, especially in aggressive environments. Additionally, it may not be suitable for high-temperature applications above 180°F.
Impact on Application: Ductile iron gate valves are ideal for water distribution systems and sewage treatment plants. However, international buyers should ensure compliance with AWWA and NSF standards, especially in regions like Africa and South America, where water quality is a concern.
Stainless Steel: Superior Corrosion Resistance for Harsh Environments
Stainless steel is often chosen for its outstanding corrosion resistance and high-temperature capabilities. It can withstand pressures up to 4500 psi and temperatures exceeding 1000°F, making it suitable for a variety of industrial applications, including oil and gas, pharmaceuticals, and food processing.
Pros: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its durability and resistance to corrosion, which extends the lifespan of the valve. It also requires minimal maintenance, reducing long-term operational costs.
Cons: Stainless steel is generally more expensive than ductile iron and requires more complex manufacturing processes, which can lead to higher costs.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel gate valves are essential in industries where media compatibility is critical, such as chemical processing. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should be aware of compliance with standards like ASTM and ASME, ensuring the valves meet local regulations.
Carbon Steel: Strength and Cost-Effectiveness
Carbon steel is a strong and cost-effective material, making it a common choice for gate valves in various industrial applications. It can handle high pressures and is often used in oil and gas pipelines.
Pros: Carbon steel offers high tensile strength and is relatively inexpensive compared to stainless steel. Its manufacturing processes are straightforward, making it accessible for many manufacturers.
Cons: Carbon steel is prone to corrosion, especially in humid or saline environments, and typically requires protective coatings or linings to enhance its durability.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel gate valves are suitable for oil and gas applications but may not be ideal for water applications without proper treatment. International buyers should consider the need for coatings and compliance with relevant standards like API and ASME.
Brass: A Compact Option for Smaller Valves
Brass is often used for smaller gate valves, particularly in plumbing and HVAC applications. It offers good corrosion resistance and is easy to machine.
Pros: Brass valves are lightweight and compact, making them suitable for residential and commercial applications. They also have good thermal conductivity.
Cons: Brass is not suitable for high-pressure applications and can be more expensive than other materials like ductile iron.
Impact on Application: Brass gate valves are commonly used in water supply systems and heating applications. Buyers should ensure compliance with local standards, especially in Europe where lead-free regulations are stringent.
Summary of Material Selection for Gate Valve Manufacturers
| Material | Typical Use Case for Gate Valve Manufacturers | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ductile Iron | Waterworks, sewage applications | Good strength and impact resistance | Susceptible to corrosion without coating | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Oil & gas, pharmaceuticals, food processing | Superior corrosion resistance | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Carbon Steel | Oil & gas pipelines | High tensile strength | Prone to corrosion | Medium |
| Brass | Plumbing, HVAC applications | Lightweight and easy to machine | Not suitable for high pressure | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions based on the specific requirements of their projects and the regulatory landscape in their regions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for Gate Valve Manufacturers
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Gate Valves?
The manufacturing process for gate valves is intricate, comprising several essential stages that ensure the final product meets industry standards and customer expectations. Below are the main stages involved:
Material Preparation
The first step in gate valve manufacturing is material selection and preparation. High-quality materials such as ductile iron, stainless steel, and carbon steel are commonly used. These materials undergo rigorous testing to verify their mechanical properties and suitability for the intended application. For instance, ductile iron valves often require heat treatment to enhance strength and ductility. Once the materials are approved, they are cut to size and prepared for the next stage.
Forming
The forming stage involves shaping the raw materials into the valve components. Techniques such as casting, forging, and machining are employed to create various parts like the body, bonnet, and gate. For example, the casting process allows for the creation of complex shapes and is often used for larger valves. In contrast, forging is utilized for smaller, high-pressure valves to ensure structural integrity. Precision machining is then applied to achieve the required tolerances and surface finishes, crucial for optimal sealing and performance.
Assembly
During assembly, the formed components are brought together to create the complete valve. This stage typically involves several sub-assemblies, such as the gate, stem, and bonnet. Manufacturers often utilize fixtures and jigs to ensure accurate alignment and fitment. The assembly process may also include the installation of gaskets and seals to prevent leaks. It is crucial to follow standardized assembly protocols to ensure consistency across batches, particularly for valves intended for critical applications such as oil and gas or waterworks.
Finishing
Finishing processes enhance the valve’s durability and resistance to corrosion. Common finishing techniques include surface treatment, painting, and coating. For instance, fusion bonded epoxy coating is frequently applied to both the interior and exterior surfaces of the valve to protect against environmental factors. This step not only improves aesthetics but also extends the valve’s lifespan, which is especially important for applications in harsh conditions.
How Is Quality Assurance Integrated into Gate Valve Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the manufacturing of gate valves, ensuring that each product meets or exceeds international standards. Key elements of QA include the following:
What International Standards Guide Gate Valve Quality Assurance?
Manufacturers often adhere to various international standards to ensure quality and safety. ISO 9001 is a widely recognized quality management standard that provides a framework for consistent product quality. In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking, API 598, and AWWA standards are crucial, particularly for valves used in waterworks and oil and gas applications. Compliance with these standards assures buyers that the products have been rigorously tested and certified for safety and performance.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are established throughout the manufacturing process to monitor quality at every stage. These checkpoints typically include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Regular checks during the manufacturing process identify any deviations from quality standards.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The completed valves undergo comprehensive testing and inspection before shipment. This can include pressure testing, leak testing, and dimensional verification.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Gate Valve Manufacturing?
Various testing methods are employed to ensure the performance and reliability of gate valves. Common methods include:
- Hydrostatic Testing: This test involves filling the valve with water and applying pressure to check for leaks. It simulates operating conditions and is critical for pressure-rated valves.
- Visual Inspection: A thorough examination of the valve’s surface for defects, cracks, or irregularities is conducted. This is often the first line of defense in quality assurance.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing and radiography are used to detect internal flaws without damaging the valve. This is particularly important for high-stakes applications in oil and gas.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers looking to ensure the quality of gate valves from manufacturers can take several proactive steps:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can reveal their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. Buyers can assess compliance with international standards and certifications.
-
Request Quality Assurance Reports: Buyers should request documentation related to quality control processes, including inspection and testing reports. These reports provide insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased evaluation of the manufacturing process and the final product. This is particularly beneficial for international transactions where trust is paramount.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control and certification. Different regions may have varying standards, so it is essential to understand local regulations and compliance requirements.
-
Regional Standards: Buyers should familiarize themselves with local standards that may differ from international ones. For example, certain African countries may have specific requirements for valves used in municipal water systems.
-
Certification Recognition: Not all certifications are recognized universally. It is vital for buyers to ensure that the certifications held by manufacturers are acknowledged in their respective countries.
By comprehensively understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing gate valves, ensuring they select suppliers that prioritize quality and compliance.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘Gate Valve Manufacturers’
Introduction
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers looking to source gate valves from manufacturers. Understanding the intricacies of gate valve procurement is essential for ensuring quality, performance, and compliance with industry standards. This checklist will help you navigate the complexities of selecting the right manufacturer to meet your specific needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, clearly outline the technical specifications required for your gate valves. Consider factors such as size, pressure ratings, materials (such as ductile iron or stainless steel), and the specific standards (like AWWA, ANSI, or API) that the valves must meet. This clarity will not only streamline the selection process but also help in communicating effectively with potential suppliers.
Step 2: Research Potential Manufacturers
Conduct thorough research to identify manufacturers with a strong reputation in the gate valve market. Look for companies that specialize in the types of valves you need, such as resilient seated or metal seated options. Utilize industry directories, trade shows, and online resources to compile a list of potential candidates.
Step 3: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that the manufacturers you are considering hold the necessary certifications and comply with relevant industry standards. This includes certifications like NSF/ANSI for drinking water safety and AWWA standards for durability and performance. Verified certifications reflect a commitment to quality and can prevent future compliance issues.
Step 4: Evaluate Supplier Experience and Expertise
Assess the experience and expertise of potential suppliers in your specific industry. Inquire about their history, projects completed, and any specialized knowledge they may possess regarding gate valves. A manufacturer with extensive experience is more likely to understand your needs and provide tailored solutions.
Step 5: Request Samples and Technical Documentation
Before making a final decision, request samples of the gate valves along with detailed technical documentation. This should include data sheets, installation guidelines, and maintenance instructions. Evaluating physical samples and documentation helps you assess quality and compatibility with your existing systems.
Step 6: Consider After-Sales Support and Warranty Terms
Evaluate the after-sales support offered by manufacturers, including warranty terms and maintenance services. A robust support system can significantly impact the long-term reliability and performance of your gate valves. Look for manufacturers who provide comprehensive warranties and readily available customer service.
Step 7: Compare Pricing and Terms of Sale
Finally, compare pricing structures and terms of sale from different manufacturers. While cost is an important factor, ensure that you are also considering value, including the quality of materials and level of service. Transparent pricing and favorable terms can lead to a more beneficial long-term relationship.
By following this step-by-step checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing gate valve manufacturers, ensuring they select partners that align with their operational requirements and industry standards.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for Gate Valve Manufacturers Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Gate Valve Manufacturing?
Understanding the cost structure of gate valve manufacturing is essential for B2B buyers aiming to make informed sourcing decisions. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the cost. Common materials include ductile iron, stainless steel, and bronze, each varying in price based on market conditions. Specialty materials for high-performance applications can elevate costs further.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass wages for skilled workers involved in manufacturing, assembly, and quality control. Regions with lower labor costs can offer competitive pricing, but the trade-off may be quality and reliability.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize overhead, leading to better pricing for buyers.
-
Tooling: Initial investment in tooling is crucial, especially for custom gate valves. Tooling costs can be amortized over large production runs, making high-volume orders more cost-effective.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that gate valves meet industry standards requires investment in quality control processes. Certifications such as ANSI/NSF 61 and AWWA standards add to the production cost but are necessary for compliance and safety.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary widely based on the destination, order volume, and chosen Incoterms. Buyers must consider these costs when evaluating total pricing.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically apply a profit margin based on market conditions, competition, and perceived value. Buyers should be aware that margins can vary significantly between suppliers.
How Do Pricing Influencers Affect Gate Valve Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of gate valves, making it essential for buyers to understand these dynamics:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Higher order volumes generally lead to lower unit prices. Manufacturers often have MOQs that can impact pricing structures, so negotiating larger orders may yield better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs and specific material requirements can significantly increase costs. Standard products are usually more competitively priced due to reduced production complexity.
-
Quality and Certifications: Valves that meet stringent international quality standards or are certified for specific applications (like drinking water) typically command higher prices. Buyers should balance the need for certification against budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and service levels can influence pricing. Established manufacturers with a track record of quality may charge a premium, but this can be justified by reduced risk and improved service.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) affects the total landed cost. Buyers must consider how these terms influence shipping responsibilities and costs.
What Are the Best Tips for Negotiating Gate Valve Pricing?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation and strategic sourcing can lead to substantial savings:
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond just the purchase price, consider installation, maintenance, and operational costs over the valve’s lifecycle. A higher upfront cost may lead to lower TCO if the valve has superior durability and performance.
-
Leverage Market Insights: Stay informed about market trends and material prices. Understanding fluctuations can provide leverage during negotiations, especially if you can demonstrate knowledge of current market conditions.
-
Negotiate Terms: Don’t hesitate to negotiate payment terms, delivery schedules, and warranty conditions. Flexible terms can enhance the overall value of the deal.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms over time. Suppliers are often willing to offer discounts or better service to repeat customers.
-
Explore Alternative Suppliers: While it’s essential to consider established manufacturers, exploring smaller or emerging suppliers can yield competitive pricing and innovative solutions.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Pricing for gate valves can vary widely based on the factors mentioned above. Buyers should seek quotations tailored to their specific needs and conduct thorough due diligence to ensure they receive fair and competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing Gate Valve Manufacturers With Other Solutions
Understanding the Alternatives to Gate Valve Manufacturers
When evaluating gate valve manufacturers, it’s essential to consider alternative solutions that may offer similar functionalities. This analysis will compare gate valves against two viable alternatives: Butterfly Valves and Ball Valves. Each of these options has unique features that may appeal to different operational needs and environmental conditions.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Gate Valve Manufacturers | Butterfly Valves | Ball Valves |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent for on-off flow control; minimal pressure drop | Good for throttling; moderate pressure drop | Excellent sealing, suitable for on-off control |
| Cost | Generally higher initial investment | Moderate cost, often more affordable | Varies widely, generally mid-range |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires more space and specific alignment | Easier to install in tight spaces | Simple installation; versatile design |
| Maintenance | Requires regular inspection and maintenance | Low maintenance; less frequent checks needed | Low maintenance; durable and reliable |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for high-pressure applications in industrial settings | Suitable for HVAC systems, water distribution | Best for quick shut-off in gas and liquid applications |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Butterfly Valves
Butterfly valves utilize a rotating disc to regulate flow and can be used for both on-off control and throttling. Their design allows for quick operation and they are generally more compact than gate valves, making them easier to install in constrained spaces. However, they may not provide the same level of sealing as gate valves, which can lead to pressure drops in high-stakes applications. They are often chosen for water distribution and HVAC systems due to their affordability and ease of maintenance.
Ball Valves
Ball valves feature a spherical closure element that allows for a quick and effective shut-off. They are renowned for their tight sealing capabilities, making them ideal for applications requiring a reliable stop in flow. While they are versatile and easy to install, their cost can vary significantly depending on the material and size. Ball valves are frequently employed in both gas and liquid applications where quick operation is essential. However, they are less effective in throttling applications compared to gate valves.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate valve solution hinges on understanding your specific operational requirements. Gate valves are ideal for high-pressure environments and applications requiring minimal flow resistance, making them a strong choice for industrial settings. Conversely, if budget constraints are a priority or if space is limited, butterfly or ball valves may present more economical and space-efficient alternatives. Assessing your operational parameters, maintenance capabilities, and budget will guide you in making an informed decision that aligns with your business objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for Gate Valve Manufacturers
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Gate Valves?
Gate valves are crucial components in various industrial applications, and understanding their technical properties is essential for B2B buyers. Here are several critical specifications that manufacturers and buyers should consider:
-
Material Grade
– Gate valves are commonly made from various materials such as ductile iron, stainless steel, and carbon steel. The choice of material affects the valve’s strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion. For example, stainless steel valves are preferred in chemical processing due to their high corrosion resistance, while ductile iron is often used in waterworks applications due to its strength and cost-effectiveness. -
Pressure Rating
– This specification indicates the maximum pressure the valve can withstand, typically expressed in psi (pounds per square inch). Understanding the pressure rating is vital for ensuring the valve is suitable for the intended application, particularly in high-pressure environments like oil and gas sectors. Common pressure classes include ANSI Class 150 to Class 4500. -
End Connections
– Gate valves can have various end connections, including flanged, threaded, and welded. The type of connection impacts installation methods and compatibility with existing piping systems. Flanged connections are often preferred for larger valves, while threaded connections are suitable for smaller sizes. -
Seat Design
– The seating surface of a valve is critical for achieving a proper seal. Common seat designs include metal-seated and resilient-seated options. Metal-seated valves are durable and suitable for high-temperature applications, while resilient-seated valves offer better sealing performance in lower pressure applications. The choice between these designs can affect maintenance costs and operational efficiency. -
Bonnet Type
– The bonnet design of a gate valve influences its maintenance and repair requirements. Common types include bolted and welded bonnets. Bolted bonnets allow for easier access for maintenance, while welded bonnets provide a more robust seal but complicate repairs. Understanding these differences can help buyers choose valves that align with their operational capabilities. -
Operating Mechanism
– Gate valves can be operated manually or automatically, depending on the application. Manual gate valves typically feature hand wheels or operating nuts, while automated valves may include electric or pneumatic actuators. This specification is crucial for operational efficiency, especially in large-scale industrial settings.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the Gate Valve Industry?
Navigating the terminology in the gate valve market can be daunting. Here are several key trade terms that B2B buyers should be familiar with:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– An OEM refers to companies that manufacture products that are sold under another company’s brand. In the gate valve industry, this term is significant when considering partnerships for custom valve solutions, as it often entails adherence to specific quality and design standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQs is essential for buyers, as it can impact procurement strategies, especially for smaller operations or one-time projects. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a formal document requesting price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. This term is vital for buyers to understand when seeking competitive pricing and evaluating multiple suppliers for their gate valve needs. -
Incoterms
– Incoterms are international commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. They clarify aspects such as shipping costs, risk of loss, and delivery points, which are crucial for B2B buyers involved in global sourcing of gate valves. -
Fugitive Emissions
– This term refers to unintentional leaks of gases or vapors from pressurized equipment. For gate valve manufacturers, understanding and mitigating fugitive emissions is essential for compliance with environmental regulations and ensuring product integrity. -
AWWA (American Water Works Association) Standards
– AWWA standards provide guidelines for the design and manufacture of waterworks products, including gate valves. Familiarity with these standards is important for buyers in the water utility sector to ensure compliance and reliability in their applications.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms will empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions when sourcing gate valves, ensuring that they select the right products for their specific applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Gate Valve Manufacturers Sector
What Are the Key Trends Shaping the Gate Valve Manufacturers Market?
The gate valve market is experiencing significant transformations driven by several global factors. A surge in infrastructure development across emerging markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe is a primary driver. Countries such as Nigeria and Brazil are investing heavily in water management and energy projects, which increases demand for high-quality gate valves. Additionally, the rise of automation and Industry 4.0 is influencing the way manufacturers produce and market their products. Advanced technologies, including IoT and AI, are facilitating predictive maintenance and smarter supply chain management, enabling manufacturers to respond swiftly to changing market needs.
Moreover, sustainability has become a critical focus area, with manufacturers adopting eco-friendly practices and materials. This trend is particularly pertinent for international buyers looking for suppliers that align with global sustainability standards. The push for compliance with regulations, such as ANSI/NSF standards for drinking water applications, is shaping product development and certification processes. As manufacturers innovate, they are also exploring hybrid designs that combine metal and resilient seating to enhance performance while minimizing environmental impact.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Decisions for Gate Valve Manufacturers?
Sustainability is no longer just a buzzword; it has become a cornerstone of procurement strategies for B2B buyers in the gate valve sector. Manufacturers are increasingly held accountable for their environmental impact, prompting a shift toward ethical sourcing and sustainable manufacturing practices. This involves utilizing materials that are recyclable or have a lower carbon footprint, such as ductile iron and stainless steel, which are favored for their durability and longevity.
Moreover, certifications like LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) and ISO 14001 are becoming essential for manufacturers aiming to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability. Buyers are keen to partner with suppliers who can provide transparency in their supply chain practices, ensuring that materials are sourced ethically and responsibly. This focus on ethical sourcing not only meets regulatory requirements but also resonates with end-users who prioritize sustainability in their purchasing decisions.
What Is the Historical Context of Gate Valve Manufacturing?
The evolution of gate valve manufacturing can be traced back to the early industrial era when the need for reliable fluid control systems became paramount. Initially, gate valves were crafted from simple materials and designed primarily for on-off control in water and steam applications. Over the decades, advancements in metallurgy and manufacturing processes have led to the development of more sophisticated valve designs, including resilient seated and metal seated options.
The introduction of strict industry standards, such as those from the American Water Works Association (AWWA) and the American National Standards Institute (ANSI), has further refined the design and manufacturing processes. These standards ensure that gate valves meet the rigorous demands of various industries, including oil and gas, pharmaceuticals, and water treatment. Today, the market is characterized by innovation, with manufacturers continually seeking to enhance performance, sustainability, and compliance to meet the evolving needs of international B2B buyers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of Gate Valve Manufacturers
-
How do I choose the right gate valve for my application?
Selecting the appropriate gate valve involves considering factors such as the type of fluid, pressure requirements, and the specific application. For instance, if you are working with wastewater, opt for a valve with corrosion-resistant materials and a robust design. Additionally, consider the valve’s size and whether it meets industry standards such as ANSI or AWWA. Consult with manufacturers for technical specifications and ensure the valve’s design aligns with your operational needs. -
What materials are commonly used in gate valve manufacturing?
Gate valves are typically made from a variety of materials, including ductile iron, stainless steel, and bronze. Ductile iron is favored for its strength and durability, making it suitable for waterworks and fire protection applications. Stainless steel is often used in corrosive environments, while bronze is preferred for applications involving drinking water. Each material has distinct properties, so choose based on your specific environmental conditions and the fluid being transported. -
What customization options are available for gate valves?
Many gate valve manufacturers offer customization options to suit specific industrial needs. Customization can include variations in size, materials, and valve designs such as bolted or welded bonnets. Additionally, options for coatings, such as fusion-bonded epoxy, can enhance durability and resistance to corrosion. When approaching suppliers, clearly outline your requirements to ensure the final product meets your operational demands. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for gate valves?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for gate valves can vary significantly among manufacturers and depend on factors such as product type and customization requirements. Generally, MOQs can range from a few pieces for standard valves to larger quantities for custom or specialized products. It is advisable to discuss your needs with potential suppliers to negotiate MOQs that align with your purchasing capabilities and project timelines. -
What payment terms should I expect from gate valve suppliers?
Payment terms can differ widely based on the supplier’s policies and the nature of your business relationship. Common arrangements include upfront payments, net 30 or net 60 terms, and letters of credit for international transactions. It’s essential to clarify payment structures upfront to avoid misunderstandings. Additionally, consider discussing discounts for bulk orders or early payments, which can provide financial benefits. -
How do I assess the quality assurance (QA) processes of gate valve manufacturers?
To evaluate the quality assurance processes of gate valve manufacturers, request documentation regarding their manufacturing standards and certifications (e.g., ISO 9001). A reputable manufacturer should have robust QA protocols, including material inspections, testing for pressure and leak integrity, and compliance with international standards such as API or AWWA. Additionally, inquire about their warranty policies and customer feedback mechanisms to gauge overall product reliability. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing gate valves internationally?
When sourcing gate valves internationally, consider shipping times, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Collaborate with suppliers who have experience in international logistics to ensure smooth delivery. It’s vital to establish clear communication regarding lead times and shipping methods. Additionally, factor in local infrastructure and distribution capabilities to minimize delays upon arrival at your location. -
How can I ensure reliable after-sales support from gate valve manufacturers?
To ensure reliable after-sales support, select manufacturers known for their customer service reputation. Inquire about their technical support services, warranty policies, and availability of spare parts. It’s beneficial to establish a clear line of communication for troubleshooting and maintenance inquiries. Additionally, consider suppliers that provide training or resources to help your team effectively operate and maintain the gate valves.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for Gate Valve Manufacturers
What Are the Key Insights for Sourcing Gate Valves?
In the competitive landscape of gate valve manufacturing, strategic sourcing emerges as a vital component for international B2B buyers. Key takeaways include the importance of selecting suppliers who meet industry standards such as AWWA, ANSI, and NSF certifications. This ensures that the valves not only perform efficiently but also comply with safety and quality regulations essential for projects across various sectors, including oil and gas, waterworks, and industrial applications.
Moreover, understanding the diverse designs and materials available—ranging from ductile iron to stainless steel—enables buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their specific operational needs. As manufacturers innovate with features like low operation torque and enhanced sealing capabilities, buyers can leverage these advancements to optimize performance and reduce long-term costs.
How Can Buyers Prepare for Future Trends in Gate Valve Manufacturing?
Looking ahead, the demand for high-quality, reliable gate valves is expected to rise, particularly in emerging markets in Africa, South America, and the Middle East. International buyers should proactively engage with manufacturers to explore customized solutions that address unique challenges in their regions. By establishing strong relationships with reputable suppliers, buyers can ensure a steady supply of cutting-edge products that meet evolving market demands.
In conclusion, strategic sourcing in the gate valve sector not only enhances operational efficiency but also positions businesses for future growth. Take the initiative to evaluate your sourcing strategies today and connect with leading manufacturers to secure a competitive advantage in your industry.