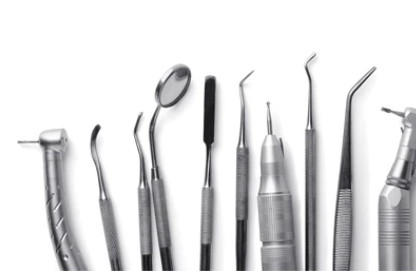
Top 5 Dental Instruments Manufacturers List and Guide: How To Sol…
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for dental instruments manufacturers
In an increasingly competitive landscape, international B2B buyers face the crucial challenge of sourcing high-quality dental instruments that meet the diverse needs of their practices while ensuring cost-effectiveness. The global market for dental instruments manufacturers is vast and varied, encompassing a wide range of products from surgical tools to preventive care instruments. Understanding the nuances of this market is essential for making informed purchasing decisions, particularly for buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key markets like Saudi Arabia and Brazil.
This comprehensive guide is designed to equip B2B buyers with critical insights into the dental instruments manufacturing sector. It covers essential aspects such as the types of instruments available, their applications in various dental practices, and the importance of thorough supplier vetting. Additionally, the guide delves into cost considerations and strategies for negotiating favorable terms with manufacturers. By leveraging this information, buyers can streamline their procurement processes, mitigate risks, and enhance the efficiency of their operations.
Ultimately, this guide empowers international buyers to navigate the complexities of sourcing dental instruments, ensuring they can confidently select suppliers that align with their quality standards and business goals. Whether you are looking to expand your product offerings or optimize your existing inventory, the insights contained herein will be invaluable in driving successful purchasing decisions.
Top 10 Dental Instruments Manufacturers Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Henry Schein – Dental Instruments & Tools
Domain: henryschein.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Henry Schein Dental offers a wide selection of dental instruments and tools, including:
– Hand instruments and surgical instruments manufactured by reputable companies such as Hu-Friedy, GC America, Integra Miltex, A. Titan, and Premier Dental.
– Products under the Henry Schein private label brand, including scalers, curettes, serrated cotton pliers, dental mirrors, and surgical instrument cleaner…
2. TBSDental – Empower Surgical Kit
Domain: tbsdental.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: [{‘product_name’: ‘Empower Surgical Kit’, ‘pack_size’: ’11 Pack’, ‘price’: ‘$1,595.00’}, {‘product_name’: ‘Ridge Preservation Kit’, ‘pack_size’: ’10 Pack’, ‘price’: ‘$1,195.00’}, {‘product_name’: ‘elvatome® 2.0 Kit’, ‘pack_size’: ‘5 Pack’, ‘price’: ‘$995.00’}, {‘product_name’: ‘BTG Basic Extraction Kit’, ‘pack_size’: ’10 Pack’, ‘price’: ‘$1,595.00’}, {‘product_name’: ‘BTG Micro FRINGS®’, ‘type’: ‘…
3. LM-Dental – Periodontal Microsurgery Instruments
Domain: lm-dental.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: LM-Dental offers a range of high-quality dental instruments designed for safety, efficiency, and patient comfort. Key products include: 1. LM™ Periodontal Microsurgery Instruments – Developed for versatility in surgical techniques, enhancing microsurgery with a focus on patient care and efficiency. 2. LM™ Prepare and Build-up Kit – A restorative instrument kit designed to optimize workflow for ind…
4. Safco Dental – Comprehensive Dental Supplies
Domain: safcodental.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Dental Supplies, Dental Products & Equipment, Free Shipping Over $250, Categories: Acrylics and reline, Anesthetics, Burs and Diamonds, CAD-CAM, Crown and Bridge, Dental Disposables, Dental Instruments, Evacuation Products, Finishing and polishing, Gloves, Hemostatics & retraction, Impression materials, Infection Control, Pharmaceuticals and OTC, Preventives, Restorative and Cosmetic Dentistry, Su…
5. Karl Schumacher – Sharpened Spade Proximator®
Domain: karlschumacher.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Surgical dental instruments are critical to the success of dental procedures. Karl Schumacher manufactures high-quality surgical dental instruments designed for comfort during prolonged use, reducing strain on the hand and wrist. Featured products include:
1. **Sharpened Spade Proximator®** – Yellow, Original price: $185.50, Current price: $185.50.
– Quote: “Every single tooth I extract, I us…
Understanding dental instruments manufacturers Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surgical Instruments Manufacturers | Focus on precision and functionality; often handcrafted. | Oral surgeries, periodontal procedures. | Pros: High precision, durability. Cons: Higher cost due to craftsmanship. |
| General Dental Instruments | Wide variety, including hand instruments and tools. | Routine dental examinations and treatments. | Pros: Cost-effective, versatile. Cons: May lack specialized features. |
| Custom Instrument Manufacturers | Tailored solutions to meet specific needs; innovative designs. | Specialty practices, unique procedures. | Pros: Personalized to requirements. Cons: Longer lead times and potential higher costs. |
| Disposable Dental Instruments | Single-use items, promoting hygiene and convenience. | General dentistry, emergency services. | Pros: Reduces risk of cross-contamination. Cons: Ongoing costs for continuous supply. |
| Digital Dental Instrument Makers | Integration of digital technology for enhanced diagnostics. | Advanced diagnostics, orthodontics. | Pros: Improved accuracy and efficiency. Cons: Higher initial investment and training required. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Surgical Instruments Manufacturers?
Surgical instruments manufacturers focus on providing high-quality tools designed for precision and functionality, often handcrafted by skilled technicians. These instruments are essential for oral surgeries and periodontal procedures, where accuracy is crucial. B2B buyers should consider the durability and performance of these instruments, understanding that the craftsmanship may come at a higher price point. When sourcing, it’s important to evaluate the manufacturer’s reputation and the specific instruments available to ensure they meet clinical needs.
How Do General Dental Instruments Differ from Specialized Tools?
General dental instruments encompass a wide range of tools, including hand instruments, mirrors, and explorers, suitable for routine dental examinations and treatments. Their versatility makes them a staple in dental practices, providing cost-effective solutions for common procedures. However, B2B buyers should assess the quality and material of these instruments to ensure they are not compromising on performance for the sake of cost. Additionally, understanding the specific needs of the practice will help in selecting the most appropriate tools.
Why Consider Custom Instrument Manufacturers for Unique Needs?
Custom instrument manufacturers offer tailored solutions that cater to the specific needs of dental practices. This includes innovative designs that can enhance the efficiency of unique procedures. While these bespoke instruments can significantly improve practice workflows, B2B buyers should be aware of longer lead times and potentially higher costs associated with custom orders. It’s crucial to communicate detailed requirements to ensure that the final product meets expectations.
What Are the Advantages of Disposable Dental Instruments?
Disposable dental instruments are designed for single-use, promoting hygiene and convenience in dental practices. They are particularly beneficial in general dentistry and emergency services, where the risk of cross-contamination needs to be minimized. While they provide significant advantages in infection control, B2B buyers should factor in the ongoing costs associated with maintaining a continuous supply of these instruments. Evaluating the balance between convenience and cost will be vital for decision-making.
How Are Digital Dental Instrument Makers Revolutionizing Dentistry?
Digital dental instrument manufacturers are at the forefront of integrating technology into dental practices, enhancing diagnostics and treatment precision. Instruments such as digital scanners and imaging devices are becoming essential in advanced diagnostics and orthodontics. While these tools can significantly improve the accuracy and efficiency of procedures, B2B buyers should consider the higher initial investment and the potential need for staff training to effectively utilize these advanced technologies. Choosing the right digital solutions can lead to better patient outcomes and streamlined practice operations.
Key Industrial Applications of dental instruments manufacturers
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of dental instruments manufacturers | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dental Clinics | Surgical instruments for extractions and periodontal surgery | Enhanced patient outcomes and increased operational efficiency | Quality assurance, sterilization compliance, and delivery timelines |
| Dental Laboratories | Custom instrument fabrication and precision tools | Improved accuracy in dental prosthetics and restorations | Material specifications, customization options, and certification standards |
| Educational Institutions | Teaching and demonstration tools for dental training | Better training outcomes for dental students | Availability of training kits, durability, and cost-effectiveness |
| Dental Supply Distributors | Comprehensive instrument catalogs for resale | Diverse product offerings to meet varied customer needs | Supplier reliability, product variety, and pricing strategies |
| Research Institutions | Advanced dental research instruments | Contribution to innovation and improved dental practices | Access to cutting-edge technology, research partnerships, and regulatory compliance |
How Are Dental Instruments Manufacturers Applied in Dental Clinics?
In dental clinics, manufacturers provide a wide range of surgical instruments, including forceps, scalers, and curettes, essential for various procedures like extractions and periodontal surgeries. These instruments enhance patient outcomes through precision and reliability, which are crucial in delicate procedures. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing high-quality, sterilizable instruments that comply with local health regulations is imperative. Additionally, understanding the delivery timelines is vital to maintain a steady supply in busy clinical environments.
What Role Do Dental Instruments Manufacturers Play in Dental Laboratories?
Dental laboratories rely on manufacturers for custom instrument fabrication and precision tools that are critical for creating dental prosthetics and restorations. The quality of these instruments directly impacts the accuracy and longevity of dental products, thereby improving patient satisfaction. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should prioritize suppliers who offer a range of materials and customization options, ensuring that the instruments meet specific laboratory requirements. Certification standards also play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of the laboratory’s output.
How Are Dental Instruments Used in Educational Institutions?
Educational institutions utilize dental instruments manufacturers to provide teaching and demonstration tools that facilitate the training of dental students. Instruments such as dental mirrors, explorers, and models are crucial for hands-on learning experiences. For institutions in emerging markets, securing durable and cost-effective training kits can significantly enhance educational outcomes. Buyers must consider the availability of these kits and the long-term durability of the instruments, ensuring they withstand extensive use in training environments.
What Benefits Do Dental Supply Distributors Gain from Dental Instruments Manufacturers?
Dental supply distributors benefit from partnering with manufacturers by offering a comprehensive catalog of instruments for resale. This diversity allows them to meet varied customer needs, from small practices to large clinics. For distributors in regions like Brazil and Saudi Arabia, supplier reliability and product variety are crucial factors in maintaining competitive advantage. Additionally, understanding pricing strategies can help distributors effectively position themselves in the market, ensuring they meet the demands of diverse clientele.
How Do Research Institutions Leverage Dental Instruments Manufacturers?
Research institutions leverage dental instruments manufacturers to obtain advanced instruments that facilitate innovative dental research. The ability to access cutting-edge technology enables researchers to contribute to advancements in dental practices and patient care. For international buyers, especially those in Europe, establishing research partnerships with manufacturers can provide insights into the latest developments and compliance with regulatory standards. This collaboration can lead to improved methodologies and groundbreaking findings in dental health.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘dental instruments manufacturers’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Product Quality Across Suppliers
The Problem: B2B buyers often face the challenge of sourcing dental instruments from multiple manufacturers, leading to inconsistent product quality. This inconsistency can impact the performance of dental procedures, resulting in dissatisfaction among practitioners and patients alike. Buyers may find that instruments from one supplier perform exceptionally well, while those from another fail to meet the required standards, leading to increased frustration and potential harm to their business reputation.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, B2B buyers should focus on establishing long-term relationships with a select few reputable manufacturers known for their high-quality standards. Conduct thorough research by reviewing online reviews, seeking recommendations from industry peers, and requesting product samples before making large purchases. Additionally, buyers should prioritize manufacturers that offer guarantees or warranties on their products, ensuring that any defective items can be replaced or refunded. By creating a list of preferred suppliers and conducting regular performance evaluations based on instrument reliability and user feedback, buyers can ensure consistent quality and enhance their operational efficiency.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Customization of Dental Instruments
The Problem: Many dental practices require specialized instruments tailored to specific procedures or patient needs. However, finding manufacturers willing to accommodate customization requests can be a frustrating endeavor. This can lead to delays in treatment, as practitioners might have to rely on generic instruments that do not meet their precise requirements, ultimately affecting patient care and satisfaction.
The Solution: B2B buyers should proactively engage with manufacturers that offer customization services. When discussing potential orders, clearly articulate the specific requirements and intended use of the instruments. It’s advisable to inquire about the manufacturer’s experience with custom orders and their capacity to deliver on such requests. Additionally, buyers should consider collaborating with manufacturers during the design phase to ensure that the instruments are developed according to their specifications. Establishing a feedback loop post-delivery can also help manufacturers refine their offerings and better serve the buyer’s needs in future orders.
Scenario 3: Navigating Regulatory Compliance and Certification Challenges
The Problem: With varying regulations and compliance standards across regions, B2B buyers often struggle to ensure that the dental instruments they procure meet all necessary certifications and quality standards. This complexity can lead to delays in procurement, unexpected costs, and, in some cases, the inability to use certain instruments in practice, which can disrupt service delivery and patient care.
The Solution: Buyers should prioritize working with manufacturers who provide clear documentation regarding their products’ compliance with local and international standards. Before finalizing any orders, it is crucial to verify that the instruments are certified by relevant authorities, such as the FDA in the United States or CE marking in Europe. To simplify this process, buyers can create a checklist of required certifications for their region and ask manufacturers to provide this information upfront. Additionally, staying informed about changes in regulations and maintaining communication with industry associations can help buyers navigate compliance issues effectively, ensuring a smooth procurement process.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for dental instruments manufacturers
When selecting materials for dental instruments, manufacturers must consider various factors that affect performance, durability, and compliance with international standards. Here, we analyze four common materials used in dental instruments, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of Stainless Steel in Dental Instruments?
Stainless steel is the most widely used material in dental instruments due to its excellent mechanical properties. It exhibits high corrosion resistance, which is critical for instruments that come into contact with bodily fluids. Stainless steel can withstand high temperatures, making it suitable for sterilization processes. Its strength and durability ensure that instruments maintain their shape and function over time.
Pros: Stainless steel is durable, relatively inexpensive, and easy to manufacture. It can be polished to a high finish, which is essential for aesthetic appeal and hygiene.
Cons: While stainless steel is resistant to corrosion, it can still be susceptible to pitting and crevice corrosion in certain environments. Additionally, it may not be suitable for all specialized applications, such as those requiring extreme flexibility.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel instruments are compatible with a wide range of dental procedures, making them versatile. However, they may not perform well in highly acidic or alkaline environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure that the stainless steel used complies with international standards such as ASTM or DIN. Understanding local regulations regarding material safety and sterilization practices is also essential.
How Does Titanium Compare as a Material for Dental Instruments?
Titanium is increasingly popular in dental applications due to its superior strength-to-weight ratio and excellent biocompatibility. It is highly resistant to corrosion, particularly in saline environments, making it ideal for surgical tools.
Pros: Titanium’s lightweight nature reduces fatigue during prolonged use. Its biocompatibility minimizes the risk of allergic reactions in patients.
Cons: Titanium is generally more expensive than stainless steel and can be more challenging to manufacture due to its hardness. This can lead to higher production costs.
Impact on Application: Titanium is particularly well-suited for implants and surgical instruments that require high strength and corrosion resistance. However, it may not be the best choice for instruments that require extensive sharpness, as it can be more difficult to sharpen.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that titanium instruments meet international standards for medical devices. Additionally, understanding the local market’s acceptance of titanium instruments is crucial, especially in regions with budget constraints.
What Are the Advantages of Plastic Materials in Dental Instruments?
Plastic materials, such as thermoplastics, are used in disposable dental instruments due to their lightweight nature and cost-effectiveness. They are often used for items that require single-use applications, such as syringes or trays.
Pros: Plastics are inexpensive to produce and can be molded into complex shapes, allowing for innovative designs. They are also lightweight, making them easy to handle.
Cons: Plastic instruments are generally less durable than metal counterparts and may not withstand high temperatures, limiting their use in sterilization processes.
Impact on Application: Plastic instruments are ideal for single-use applications, reducing the risk of cross-contamination. However, their limited lifespan may not suit all dental practices.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that plastic materials comply with safety standards, such as those set by the FDA or EU regulations. Understanding local preferences for disposable versus reusable instruments is also important.
Why Is Glass Important for Certain Dental Instruments?
Glass is used in specific dental instruments, particularly for those requiring high precision, such as dental mirrors and certain types of syringes. It offers excellent clarity and is easy to sterilize.
Pros: Glass is chemically inert and does not react with dental materials, ensuring accurate results. Its smooth surface facilitates easy cleaning and sterilization.
Cons: Glass is fragile and can break easily, posing a safety risk. It is also heavier than plastic alternatives, which may affect usability.
Impact on Application: Glass instruments are ideal for precise applications but may not be suitable for environments where durability is a concern.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the fragility of glass instruments and consider local regulations regarding their use. Understanding the market demand for glass versus plastic or metal instruments is also essential.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Dental Instruments
| Material | Typical Use Case for dental instruments manufacturers | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | General dental instruments | High durability and corrosion resistance | Susceptible to pitting in harsh environments | Medium |
| Titanium | Surgical instruments and implants | Lightweight and biocompatible | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Plastic | Disposable instruments | Cost-effective and easy to mold | Less durable and limited sterilization | Low |
| Glass | Dental mirrors and precise syringes | Chemically inert and easy to sterilize | Fragile and heavier than plastic alternatives | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers in the dental instruments market, helping them make informed decisions based on material properties, applications, and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for dental instruments manufacturers
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Dental Instruments?
The manufacturing process for dental instruments involves several critical stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage is designed to ensure that the final products meet the rigorous standards expected in the dental industry.
Material Preparation
The process begins with the selection of high-quality raw materials, often stainless steel or titanium, chosen for their durability and resistance to corrosion. These materials are subjected to rigorous inspections to confirm their compliance with industry specifications. Suppliers typically provide certificates of compliance to ensure that materials meet international standards.
Forming
In the forming stage, raw materials are shaped into the desired instrument forms. Techniques such as forging, casting, and machining are commonly employed. Advanced CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are utilized to achieve precise dimensions and ensure uniformity across batches. This level of precision is essential, as even minor deviations can affect the instrument’s performance.
Assembly
Once formed, the components of the dental instruments are assembled. This stage often requires skilled labor to ensure that each part fits perfectly and functions effectively. For complex instruments, this may involve multiple components, each requiring careful alignment and secure fastening.
Finishing
The finishing stage involves polishing and coating the instruments to enhance their aesthetic appeal and functional performance. Techniques such as electro-polishing not only improve the surface finish but also help in reducing the risk of bacterial adhesion. Quality assurance checks are performed throughout this stage to ensure that the instruments are free from defects and ready for sterilization.
How Is Quality Control Implemented in Dental Instrument Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is paramount in the manufacturing of dental instruments, as they must meet strict health and safety regulations. Manufacturers adhere to both international standards like ISO 9001 and industry-specific certifications, such as CE marking and FDA approval.
International Standards and Certifications
ISO 9001 is a widely recognized quality management standard that ensures manufacturers have a systematic approach to managing their processes and improving customer satisfaction. CE marking indicates that a product meets EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards, while FDA approval is crucial for products entering the United States market. Suppliers must demonstrate compliance with these standards to gain access to various international markets.
Quality Control Checkpoints
A robust QC system typically involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet the required specifications before they enter production.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process helps identify and rectify any issues that may arise, ensuring that deviations are addressed promptly.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the instruments are fully assembled, they undergo a final inspection, which includes functional testing and visual checks to ensure they meet both aesthetic and functional standards.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Dental Instruments?
Various testing methods are employed to validate the quality and safety of dental instruments. These methods ensure that the instruments can withstand the rigors of clinical use.
- Functional Testing: This involves simulating the instrument’s intended use to verify that it performs as expected. For example, scalers and curettes are tested for their cutting efficiency.
- Sterilization Validation: Instruments must be tested to ensure they can withstand sterilization processes without losing their integrity. This may involve subjecting instruments to high temperatures or chemical sterilants.
- Corrosion Resistance Testing: Given that dental instruments are often exposed to moisture and chemicals, manufacturers conduct tests to ensure their resistance to corrosion over time.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s QC processes is essential for ensuring product quality and compliance with local regulations.
Audits and Inspections
One effective way to verify QC is through on-site audits. Conducting audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes, QC systems, and overall compliance with industry standards. Buyers should request to see documentation of past audits and certifications.
Quality Reports
Requesting quality reports from suppliers can provide insights into their QC processes. These reports often include data on defect rates, testing results, and compliance with international standards. Buyers should look for transparency in these reports, as they indicate the manufacturer’s commitment to quality.
Third-Party Inspections
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s manufacturing practices. These inspections can help verify that the supplier adheres to the necessary quality standards and regulations.
What Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Consider in Quality Control?
International buyers should be aware of specific nuances related to quality control that can vary by region. For instance, regulations in Europe are typically stricter than those in other regions, necessitating compliance with CE marking requirements. In contrast, suppliers targeting markets in Africa and South America may face different regulatory frameworks, which could influence the types of certifications they pursue.
Additionally, buyers should consider cultural differences in business practices and communication styles. Establishing clear expectations regarding quality standards and compliance from the outset can help mitigate misunderstandings and ensure a smoother procurement process.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance mechanisms in dental instrument production is crucial for B2B buyers. By engaging with suppliers who adhere to stringent quality standards and maintaining open lines of communication, buyers can secure high-quality instruments that meet their clinical needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘dental instruments manufacturers’
To effectively source dental instruments from manufacturers, this guide provides a comprehensive checklist tailored for international B2B buyers. Whether you are seeking suppliers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe, following these steps will help ensure a successful procurement process.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging with suppliers, clearly outline the technical specifications for the dental instruments you require. This includes material quality, dimensions, and any specific features relevant to your practice. Having detailed specifications will streamline communication and help you identify manufacturers that can meet your needs effectively.
Step 2: Conduct Market Research
Research the dental instruments market to identify potential manufacturers. Look for companies with a strong reputation and positive reviews from existing clients. Utilize online platforms, industry publications, and trade shows to gather information about various suppliers and their product offerings.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers before committing to a partnership. Request company profiles, product catalogs, and customer testimonials to gauge their credibility and experience in the industry. Consider the following:
– Certifications: Ensure that the manufacturers comply with international quality standards (e.g., ISO certifications).
– Product Range: Check if they offer a wide variety of instruments to meet your diverse needs.
Step 4: Request Samples
Always ask for product samples before placing a bulk order. Testing samples allows you to assess the quality, durability, and usability of the instruments firsthand. This step is crucial to avoid costly mistakes and ensures that the products align with your expectations.
Step 5: Review Pricing and Payment Terms
Once you have shortlisted a few suppliers, request detailed pricing information and payment terms. Compare costs while considering factors such as shipping fees and potential tariffs. Additionally, inquire about volume discounts or payment plans that may be available for larger orders.
Step 6: Verify Manufacturing Capabilities
Understanding the manufacturing capabilities of your selected suppliers is vital. Inquire about their production processes, lead times, and capacity to scale as your needs grow. This will help ensure they can fulfill your orders promptly and maintain consistent quality.
Step 7: Establish Clear Communication Channels
Effective communication is key to a successful partnership. Ensure that you establish clear communication channels with your suppliers, including preferred methods of contact and response times. Regular updates on order status and any potential issues will foster a strong working relationship and facilitate smoother transactions.
By following this step-by-step checklist, you can make informed decisions when sourcing dental instruments from manufacturers, ultimately enhancing your procurement efficiency and ensuring quality products for your practice.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for dental instruments manufacturers Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Dental Instruments Manufacturing?
When sourcing dental instruments, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The selection of high-quality raw materials significantly impacts the cost. Stainless steel, titanium, and specialized alloys are commonly used, with prices fluctuating based on market demand and availability.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for the precision required in dental instruments. Labor costs vary by region, with countries offering lower wages potentially providing cost advantages.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient production processes can help minimize these overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Initial investment in tooling can be substantial, particularly for custom instruments. However, these costs can be amortized over high production volumes.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that instruments meet regulatory standards requires investment in quality control processes. This is especially critical for markets with stringent certification requirements.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary significantly based on shipping methods, distances, and chosen Incoterms. Proper logistics planning can mitigate these costs.
-
Margin: Manufacturers set their margins based on the competitive landscape, perceived value, and production costs. Understanding the margin expectations can help buyers negotiate better prices.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Dental Instruments Pricing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of dental instruments:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often attract discounts, making it financially advantageous for buyers to consolidate their purchases.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom instruments tailored to specific needs may incur additional costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the potential price increase.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Instruments made from premium materials or those with certifications (like ISO or CE) typically command higher prices due to their superior quality and assurance.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established manufacturers with a track record of quality may charge a premium.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms determine the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping costs and risks. Understanding these terms can lead to more favorable pricing arrangements.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency in Sourcing Dental Instruments?
International buyers can leverage several strategies to optimize their sourcing process:
-
Negotiation: Engage in discussions with suppliers to explore pricing flexibility. Highlighting potential for repeat business can incentivize suppliers to offer better terms.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial purchase price. Consider factors such as maintenance costs, durability, and potential downtime, which can significantly impact long-term value.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and trade regulations that may affect pricing. Building relationships with local distributors can help navigate these complexities.
-
Quality vs. Cost: While it may be tempting to opt for the lowest-priced instruments, prioritize quality and reliability to avoid costly replacements or legal issues arising from substandard products.
By understanding these cost components, price influencers, and strategic tips, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they source high-quality dental instruments while optimizing their budgets.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing dental instruments manufacturers With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Dental Instruments Manufacturers
In the dental industry, choosing the right tools is crucial for ensuring quality patient care and operational efficiency. While traditional dental instruments manufacturers provide a wide range of tools, there are alternative solutions available that may better suit specific needs. This analysis aims to compare the offerings of dental instruments manufacturers with two viable alternatives: digital dentistry technology and outsourcing dental instrument supply.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Dental Instruments Manufacturers | Digital Dentistry Technology | Outsourcing Dental Instrument Supply |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision, durability | Advanced accuracy, efficiency | Variable, dependent on supplier |
| Cost | Moderate to high | High initial investment | Potentially lower, depending on volume |
| Ease of Implementation | Straightforward | Requires training and software | Simple, depends on supplier’s processes |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed | Minimal maintenance | Supplier handles maintenance |
| Best Use Case | Traditional practices | Tech-savvy practices | Cost-sensitive operations |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Digital Dentistry Technology?
Digital dentistry technology, which includes CAD/CAM systems and 3D printing, offers a modern approach to dental practices. Pros include enhanced accuracy in creating dental restorations, reduced material waste, and quicker turnaround times. However, the cons are significant, as these technologies often require substantial upfront investments and ongoing costs for software updates and training. Additionally, practices must adapt their workflows to integrate these systems effectively, which can be a barrier for some.
How Does Outsourcing Dental Instrument Supply Compare?
Outsourcing dental instrument supply involves partnering with a third-party provider who manages the procurement and supply of dental tools. This can be a cost-effective solution for practices looking to reduce overhead and focus on patient care. The pros include lower costs, as suppliers may offer bulk pricing and take care of logistics. However, the cons include potential variability in the quality of instruments and reliance on the supplier for timely delivery, which can impact patient care if not managed properly.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When evaluating options, B2B buyers in the dental sector must consider their specific needs, budget constraints, and operational workflows. If precision and traditional methods are paramount, sticking with established dental instruments manufacturers may be the best choice. For practices aiming to leverage technology for enhanced efficiency, digital dentistry could be the future. Alternatively, outsourcing can provide significant cost savings but requires careful vetting of suppliers to ensure quality and reliability. Ultimately, a thorough assessment of each option against the unique demands of the practice will guide buyers to the optimal solution.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for dental instruments manufacturers
What Are the Key Technical Properties for Dental Instruments Manufacturers?
Understanding the technical properties of dental instruments is crucial for manufacturers and B2B buyers alike. Here are some essential specifications that impact product quality and performance:
1. Material Grade
The material grade refers to the type of metal or alloy used in the manufacturing of dental instruments. Common materials include stainless steel, titanium, and specialty alloys. The choice of material affects durability, corrosion resistance, and overall performance. High-grade stainless steel is often preferred for its resistance to rust and ability to withstand sterilization processes, which is critical for maintaining hygiene in dental practices.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance indicates the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension of the instrument. For example, surgical instruments like scalpels and forceps require precise tolerances to ensure proper functionality and safety during procedures. Inaccurate tolerances can lead to instrument failure, impacting patient safety and causing delays in dental treatments.
3. Finish
The finish of dental instruments refers to the surface treatment applied to enhance durability and aesthetics. Common finishes include satin, mirror, and anodized coatings. A good finish not only improves the visual appeal but also increases resistance to wear and tear, making the instruments easier to clean and sterilize, thereby ensuring compliance with health regulations.
4. Ergonomics
Ergonomics refers to the design features of an instrument that enhance comfort and usability for the dental professional. Instruments designed with ergonomic principles can reduce hand fatigue and improve precision during procedures. This is particularly important in a dental setting, where practitioners may be using instruments for extended periods.
5. Sterilization Compatibility
This property indicates whether the instruments can withstand various sterilization methods, such as autoclaving or chemical sterilization. Instruments that are not compatible with standard sterilization processes can pose significant health risks to patients and practitioners. Ensuring sterilization compatibility is vital for compliance with health and safety standards.
6. Weight
The weight of dental instruments can affect their handling and usability. Lightweight instruments are generally preferred for their ease of use, especially during prolonged procedures. However, the material used can influence weight without compromising strength or durability.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the Dental Instruments Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the dental instruments market. Here are several common terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the dental industry, an OEM might manufacture instruments that are branded and sold by a dental supply company. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for buyers looking for quality assurance and reliability.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. In the dental instruments market, MOQs can vary significantly based on the manufacturer and the type of instrument. Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their inventory and budget effectively.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit pricing and terms for specific products or services. For dental instruments manufacturers, issuing an RFQ is a common practice to compare costs and terms from multiple suppliers before making a purchasing decision.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms used in international transactions to clarify responsibilities between buyers and sellers. They define who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers to avoid potential disputes and ensure smooth logistics in cross-border transactions.
5. CE Marking
CE marking indicates that a product complies with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards. For dental instruments exported to Europe, CE marking is often a requirement. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers have the necessary certifications to facilitate market entry.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing dental instruments, ultimately leading to better procurement strategies and enhanced operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the dental instruments manufacturers Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Influencing Dental Instruments Manufacturing?
The dental instruments manufacturing sector is experiencing a transformative phase driven by several global factors. A significant driver is the increasing demand for advanced dental care solutions, particularly in emerging markets such as Africa and South America. With a growing population and rising disposable incomes, these regions are witnessing enhanced investment in healthcare infrastructure, leading to a surge in demand for high-quality dental instruments. Additionally, the rise of dental tourism in countries like Brazil and Turkey is further propelling the market, as international patients seek affordable yet quality dental services.
Technological advancements are also reshaping the industry landscape. The integration of digital technologies in dental practices is becoming commonplace, with tools like 3D printing and CAD/CAM systems enhancing precision and efficiency in instrument manufacturing. As a result, manufacturers are increasingly focused on developing innovative products that cater to the evolving needs of dental practitioners. Moreover, the advent of e-commerce platforms is simplifying the procurement process for international buyers, allowing them to easily compare products and prices from various manufacturers.
Additionally, the growing emphasis on patient safety and regulatory compliance is pushing manufacturers to adopt higher quality standards. International B2B buyers are more discerning than ever, seeking suppliers who can guarantee product reliability and compliance with global health regulations. This trend underscores the importance of transparency in sourcing and manufacturing processes, particularly for buyers in regions with stringent regulatory frameworks.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Changing the Dental Instruments Landscape?
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal consideration for dental instruments manufacturers as global awareness of environmental issues rises. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly in terms of waste generation and resource depletion, has prompted buyers to prioritize suppliers who adopt eco-friendly practices. International B2B buyers are increasingly looking for manufacturers that utilize sustainable materials and production methods, which not only reduce the ecological footprint but also align with corporate social responsibility goals.
Ethical sourcing is another critical aspect influencing purchasing decisions. Buyers are now demanding transparency in the supply chain, ensuring that materials are sourced responsibly and that labor practices adhere to ethical standards. Manufacturers who can demonstrate compliance with sustainability certifications, such as ISO 14001 or other green certifications, are gaining a competitive edge in the market. This trend is particularly relevant for buyers from Europe and the Middle East, where regulatory pressures and consumer expectations are driving the demand for ethically produced dental instruments.
Furthermore, the use of biodegradable and recyclable materials in the production of dental instruments is gaining traction. By investing in green technologies and materials, manufacturers can not only meet buyer demands but also contribute positively to the environment, enhancing their brand reputation in the process.
How Has the Dental Instruments Manufacturing Sector Evolved Over Time?
The dental instruments manufacturing sector has undergone significant evolution over the decades. Initially characterized by rudimentary tools crafted from basic materials, the industry has transformed with advancements in technology and materials science. The introduction of stainless steel and titanium has revolutionized instrument durability and performance, while innovations in ergonomics have enhanced user comfort and efficiency.
Over the years, the sector has also seen a shift from a focus on mass production to a more customized approach. Manufacturers now offer bespoke solutions tailored to the specific needs of dental practitioners, reflecting a broader trend towards personalization in healthcare. This evolution has not only improved the quality of dental care but has also positioned dental instrument manufacturers as essential partners in the broader healthcare ecosystem.
In conclusion, understanding these market dynamics and trends is crucial for international B2B buyers in the dental instruments sector. By recognizing the importance of sustainability, ethical sourcing, and technological advancements, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and values.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of dental instruments manufacturers
-
How do I choose the right dental instruments manufacturer for my practice?
Choosing the right dental instruments manufacturer involves assessing several key factors. Start by evaluating the manufacturer’s reputation and experience in the industry. Look for certifications and compliance with international standards to ensure quality. Additionally, consider their product range and whether they offer custom solutions tailored to your specific needs. Request samples to assess the quality firsthand and read reviews from other B2B buyers. Finally, consider their responsiveness and customer service, as this can significantly impact your purchasing experience. -
What types of dental instruments can I source from manufacturers?
Dental instruments manufacturers typically offer a wide range of products, including surgical instruments, hand tools, diagnostic tools, and specialized equipment. Common items include forceps, scalers, curettes, and surgical kits. Many manufacturers also provide custom instruments designed to meet specific procedural requirements. When sourcing, check the catalog or inquire directly to ensure the manufacturer can meet your comprehensive needs, whether for general dentistry or specialized practices. -
What are the common minimum order quantities (MOQ) for dental instruments?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can vary significantly among dental instruments manufacturers. Typically, MOQs range from as low as 10 to 100 units, depending on the type of instrument and the manufacturer’s policies. Some manufacturers may offer flexibility on MOQs for first-time orders or when building a long-term relationship. It’s essential to discuss these terms upfront to align your purchasing strategy with the manufacturer’s capabilities, especially if you are sourcing for a larger practice or multiple locations. -
How can I ensure the quality of dental instruments from manufacturers?
To ensure quality, request certifications such as ISO or CE marking, which indicate compliance with international quality standards. It’s beneficial to review the manufacturer’s quality assurance processes, including material sourcing, production methods, and testing protocols. Consider visiting their facility if possible or ask for references from other clients. Additionally, testing samples before placing a bulk order can provide insight into the instruments’ durability and performance. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing dental instruments internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely among manufacturers, but typical options include upfront payment, 30% deposit with the balance due before shipping, or net 30/60 days after receipt of goods. It’s crucial to clarify these terms during negotiations to avoid any misunderstandings. Some manufacturers may offer financing options or discounts for early payment. Ensure that payment methods align with your financial practices, and consider using secure payment platforms to mitigate risks in international transactions. -
What factors should I consider regarding logistics when sourcing dental instruments?
Logistics is a critical aspect of sourcing dental instruments internationally. Consider the shipping methods offered by the manufacturer, such as air freight for quicker delivery or sea freight for cost savings. Assess the manufacturer’s ability to handle customs clearance and documentation, as this can impact delivery timelines. Additionally, inquire about their return policy and warranty terms for defective instruments, ensuring you have a plan in place for any issues that may arise during shipping. -
Can manufacturers provide custom dental instruments tailored to my specifications?
Many dental instruments manufacturers offer customization services to create instruments tailored to specific procedural needs. This often involves collaboration between your practice and the manufacturer to design and develop instruments that meet your exact requirements. Be prepared to provide detailed specifications and possibly prototypes. Custom instruments can enhance efficiency and effectiveness in your practice, so consider this option if standard instruments do not fully meet your needs. -
What should I look for in terms of customer support from dental instruments manufacturers?
Effective customer support is essential when partnering with dental instruments manufacturers. Look for manufacturers that offer dedicated account management, responsive communication channels, and after-sales support. Ensure they provide assistance with product inquiries, troubleshooting, and claims for defective items. A manufacturer that prioritizes customer service can greatly enhance your sourcing experience and foster a long-term business relationship. Regular follow-ups and feedback opportunities are also indicators of good support.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for dental instruments manufacturers
In the competitive landscape of dental instruments manufacturing, strategic sourcing emerges as a vital component for international B2B buyers. By leveraging partnerships with reputable manufacturers, buyers can ensure access to high-quality instruments that enhance operational efficiency and patient care. The importance of assessing product ranges, such as surgical kits and specialized tools, cannot be overstated; it directly impacts the quality of dental procedures and practice outcomes.
Moreover, considering factors such as customization capabilities and local market needs can lead to significant cost savings and improved product relevance. Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should actively engage with manufacturers that demonstrate a commitment to innovation and quality assurance, such as those offering handcrafted products or patented technologies.
As the dental industry continues to evolve, the demand for advanced, reliable instruments will only grow. Embrace the opportunity to source strategically, aligning with manufacturers that not only meet your immediate needs but also support your long-term goals. Reach out today to explore partnerships that will elevate your practice and enhance patient satisfaction.