Top 6 Heat Sink Manufacturers List and Guide: How To Solve Scenar…
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for Heat Sink Manufacturers
In the rapidly evolving landscape of technology, sourcing high-quality heat sink manufacturers is a critical challenge for B2B buyers aiming to enhance their product performance and reliability. As electronic devices become increasingly complex, the need for efficient thermal management solutions has never been more paramount. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the global heat sink manufacturing market, addressing key factors such as types of heat sinks, their applications across various industries, and essential supplier vetting processes.
International buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—countries like Vietnam and Brazil—will find actionable insights tailored to their unique market dynamics. The guide will delve into cost considerations, customization options, and the importance of certifications like ISO and ITAR compliance, enabling informed purchasing decisions that align with quality standards and operational needs.
By navigating this intricate landscape with clarity and confidence, B2B buyers can forge successful partnerships with manufacturers who not only meet their thermal management requirements but also contribute to their long-term strategic goals. Whether you are looking for standard or custom solutions, this guide equips you with the knowledge necessary to make sound investment choices in heat sink technology.
Top 10 Heat Sink Manufacturers Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. HeatsinkUSA – Aluminum Heatsinks
Domain: heatsinkusa.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: HeatsinkUSA supplies aluminum heatsinks that are extruded in Belding, Michigan, USA. The heatsinks are available for various applications including commercial LED lighting, audio, electronics, industrial, medical, aerospace, and defense. There is no minimum order requirement. The company charges a flat fee of $5.00 for handling, which covers any number of horizontal cuts needed. Vertical cuts are …
2. Mouser – Heat Sink Distribution
3. Celsia – Custom Heat Sink Solutions
Domain: celsiainc.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Celsia specializes in custom heat sink solutions, including custom heat pipe and vapor chamber heat sinks. Key offerings include:
– **Heat Sink Types**: 1-Piece Vapor Chambers, 2-Piece Vapor Chambers, Specialty Two-Phase designs, Extruded Heat Sinks, Zipper Fin Heat Sinks, Machined Heat Sinks, Skived Heat Sinks, and Full Heat Sink Assemblies.
– **Technologies**: Heat Pipe, Vapor Chamber, Thermosi…
4. Wakefield Thermal – Air Cooled Board Level Heatsinks
Domain: wakefieldthermal.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Wakefield Thermal Air Cooled Board Level Heatsinks are designed with stamping or extrusion for common package sizes to enhance thermal performance. They are typically attached to both the device and the PCB. Key features include:
– Common package sizes: T0220, T0247, D2pak.
– Stamped heat sinks with features that clip onto the device, eliminating the need for screws or secondary clips.
– Bent/twis…
5. Metoree – Heat Sinks
Domain: us.metoree.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Heat sinks are components used for cooling electronic devices, primarily to prevent excessive temperature rise in electronic equipment. They are simple in structure and do not require physical operation, making them reliable. Heat sinks are typically used in conjunction with electronic components that generate heat, such as CPUs in personal computers. The performance of heat sinks is measured by t…
6. QATS – Custom Heat Sinks and Cooling Solutions
Domain: qats.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: ATS Custom Heat Sinks for Liquid and Air Cooling Solutions. Thousands of heat sinks designed for BGA, ASIC, CPU, GPU, Power Brick, LED, LGA, DSP, TSOP, and DIP applications. Innovative solutions integrating heat sinks, heat pipes, heat exchangers, fans, and cold plates. Rapid prototyping available from US-based manufacturing facility for quick turn-around time. Custom Heat Sink Design Services off…
Understanding Heat Sink Manufacturers Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Extruded Aluminum Heat Sinks | Lightweight, cost-effective, high thermal conductivity | Consumer electronics, industrial machinery | Pros: Affordable, customizable; Cons: Limited to specific shapes. |
| Custom Machined Heat Sinks | High precision, tailored designs for specific needs | Aerospace, medical, defense | Pros: Exact specifications; Cons: Higher cost, longer lead times. |
| Skived Heat Sinks | High fin density, excellent for forced convection | High-performance computing, telecom | Pros: Superior thermal performance; Cons: More complex manufacturing. |
| Vapor Chamber Heat Sinks | Two-phase cooling technology, effective for compact designs | High-end electronics, LED lighting | Pros: Efficient thermal management; Cons: More expensive, requires precise design. |
| Zipper Fin Heat Sinks | High fin density for enhanced airflow | Consumer electronics, automotive | Pros: Optimized for forced convection; Cons: Limited to specific applications. |
What Are the Characteristics of Extruded Aluminum Heat Sinks?
Extruded aluminum heat sinks are among the most common types available, known for their lightweight nature and cost-effectiveness. They are produced through a process where aluminum is forced through a die, resulting in a variety of shapes. These heat sinks are ideal for consumer electronics and industrial machinery, providing excellent thermal conductivity to dissipate heat efficiently. When purchasing, buyers should consider the specific shape and size required for their application, as customization options may be limited compared to other types.
How Do Custom Machined Heat Sinks Meet Specific Needs?
Custom machined heat sinks are designed for applications requiring high precision and tailored specifications. These heat sinks are often used in aerospace, medical, and defense industries where exact thermal management is critical. The manufacturing process allows for intricate designs that can accommodate unique cooling requirements. Buyers should weigh the benefits of precision against the higher costs and longer lead times associated with custom machining, ensuring that their specific needs justify the investment.
Why Choose Skived Heat Sinks for Performance?
Skived heat sinks are characterized by their high fin density, making them particularly effective in forced convection environments. They are suitable for applications in high-performance computing and telecom sectors, where efficient heat dissipation is crucial. While they offer superior thermal performance, the manufacturing process is more complex, which can lead to higher costs. Buyers should consider the thermal demands of their application and whether the investment in skived heat sinks aligns with their performance goals.
What Advantages Do Vapor Chamber Heat Sinks Provide?
Vapor chamber heat sinks utilize two-phase cooling technology to manage heat effectively, making them ideal for compact electronic devices and high-performance applications like LED lighting. Their ability to spread heat over a larger area enhances thermal management, which is vital for maintaining device performance. However, the complexity of their design can lead to higher costs. Buyers must assess whether the efficiency gains justify the investment, especially in applications where space and thermal performance are at a premium.
How Do Zipper Fin Heat Sinks Optimize Airflow?
Zipper fin heat sinks are designed with high fin density to maximize airflow, making them suitable for consumer electronics and automotive applications. They are particularly effective in scenarios where forced convection is used to improve cooling efficiency. While they offer optimized performance, their application may be limited to specific designs that can accommodate their unique structure. Buyers should evaluate the compatibility of zipper fin heat sinks with their existing systems and the potential benefits they can bring to overall thermal management.
Key Industrial Applications of Heat Sink Manufacturers
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Heat Sink Manufacturers | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electronics | Cooling systems for consumer electronics | Prolongs device lifespan and enhances performance | Customization capabilities, quick lead times, and material quality |
| Telecommunications | Thermal management in telecom infrastructure | Ensures reliability and efficiency of communication systems | Compliance with industry standards, durability in harsh environments |
| Medical Devices | Heat sinks in imaging and diagnostic equipment | Improves accuracy and performance of critical medical devices | Regulatory compliance (ISO, ITAR), precision engineering capabilities |
| Aerospace & Defense | Thermal management in avionics and military equipment | Enhances reliability and safety in critical applications | ITAR compliance, rapid prototyping, and stringent quality controls |
| Industrial Machinery | Heat dissipation in motors and industrial equipment | Increases operational efficiency and reduces downtime | Material selection, customization options, and environmental resistance |
How Are Heat Sink Manufacturers Used in Electronics?
In the electronics sector, heat sinks are vital for cooling systems in consumer devices like smartphones and laptops. These components dissipate heat generated by processors, preventing overheating and ensuring optimal performance. International buyers must consider customization options, as electronic designs vary significantly. Quick lead times are essential to meet production schedules, and the choice of materials, such as aluminum for its thermal conductivity, plays a crucial role in product effectiveness.
What Role Do Heat Sink Manufacturers Play in Telecommunications?
Telecommunications infrastructure relies on effective thermal management to maintain the performance of servers and communication devices. Heat sinks help manage the heat produced by high-performance components, ensuring reliable data transmission. For buyers in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing heat sinks that comply with industry standards and can withstand environmental challenges is crucial. Durability and resistance to extreme temperatures are key factors when selecting a supplier.
How Are Heat Sink Manufacturers Essential for Medical Devices?
In the medical sector, heat sinks are critical for devices such as MRI machines and ultrasound equipment. They help maintain optimal operating temperatures, which is vital for accurate imaging and diagnostics. Buyers need to ensure that manufacturers comply with regulatory standards like ISO and ITAR, as safety and precision are paramount. Additionally, the ability to produce high-quality, custom-engineered solutions quickly can be a significant advantage in this rapidly evolving field.
Why Are Heat Sink Manufacturers Important in Aerospace and Defense?
Heat sinks are essential in aerospace and defense applications, where they manage heat in avionics and military electronics. These components enhance system reliability, which is crucial for safety and mission success. Buyers in this sector must prioritize suppliers that comply with ITAR regulations and can provide rapid prototyping services. Stringent quality controls are necessary to ensure that the heat sinks can withstand extreme conditions and maintain performance under pressure.
How Do Heat Sink Manufacturers Benefit Industrial Machinery?
In industrial machinery, heat sinks dissipate heat from motors and other equipment, increasing operational efficiency and minimizing downtime. Effective thermal management is essential for maintaining productivity in manufacturing processes. Buyers should focus on sourcing heat sinks that offer excellent material properties, such as corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity. Customization options that cater to specific machinery needs can further enhance performance and longevity.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘Heat Sink Manufacturers’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Customization for Unique Applications
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter challenges when seeking heat sinks tailored to specific applications. For instance, a telecommunications company may require a heat sink that fits a unique shape or size to effectively manage heat dissipation in their latest product. Standard offerings often do not meet the performance criteria or spatial constraints, leading to prolonged development timelines and potential product delays. This situation can be frustrating, particularly for companies under pressure to innovate and maintain competitive advantages.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, B2B buyers should seek heat sink manufacturers that specialize in custom solutions. Initiating a conversation with the engineering team of a manufacturer can provide insights into available customization options. It’s crucial to provide detailed application data, such as thermal loads, available space, and environmental conditions. Engaging in collaborative design discussions can lead to the creation of a heat sink that is not only tailored to specific requirements but also optimized for performance. Manufacturers like Celsia, known for their agile organizations and collaborative design philosophy, can often expedite the prototyping process, enabling quicker time-to-market for new products.
Scenario 2: Supply Chain Delays and Lead Time Concerns
The Problem: Another common pain point is the unpredictability of supply chain logistics, which can lead to extended lead times for critical components like heat sinks. B2B buyers in regions such as Africa or South America may face additional challenges due to shipping delays, customs issues, or limited local supplier options. This situation can disrupt production schedules and impact project timelines, ultimately affecting customer satisfaction and revenue.
The Solution: To mitigate supply chain risks, buyers should prioritize manufacturers that offer transparent lead time commitments and flexible shipping options. Conducting thorough research to identify suppliers with a proven track record of reliability is essential. Inquire about their inventory management practices and whether they hold stock of popular heat sink designs to fulfill orders quickly. Additionally, consider forming strategic partnerships with manufacturers who have a global presence, like Radian Thermal Products, which can leverage their multiple manufacturing locations to ensure timely delivery regardless of geographical challenges. Establishing a reliable communication channel with the supplier can also facilitate proactive updates on order status and potential delays.
Scenario 3: Quality Assurance and Compliance Challenges
The Problem: For buyers in highly regulated industries, such as medical or aerospace, ensuring that heat sinks meet specific quality and compliance standards can be a significant concern. The failure to adhere to standards like ISO, RoHS, or ITAR can lead to costly recalls, project delays, or even legal repercussions. Buyers may find it challenging to navigate the certification process and verify that their suppliers comply with these stringent requirements.
The Solution: To address these quality assurance challenges, B2B buyers should prioritize partnering with heat sink manufacturers that are certified and have a robust quality management system in place. Request documentation that verifies compliance with relevant standards and inquire about their quality assurance processes, such as testing protocols for raw materials and finished products. Manufacturers like PSI Industries, with ISO 9001:2015 certification, provide reassurances of their commitment to quality. Additionally, buyers should consider conducting audits or site visits to assess the manufacturer’s capabilities firsthand. Building a strong relationship with the supplier can also facilitate ongoing discussions around quality improvements and compliance updates, ensuring that the products meet the necessary standards consistently.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for Heat Sink Manufacturers
What Are the Key Properties of Aluminum for Heat Sink Applications?
Aluminum is the most widely used material for heat sinks due to its excellent thermal conductivity, which typically ranges from 205 to 250 W/mK. This property allows for efficient heat dissipation, essential for maintaining optimal operating temperatures in electronic devices. Additionally, aluminum is lightweight, making it easier to handle and integrate into various applications. It also exhibits good corrosion resistance, particularly when anodized, which enhances its durability in harsh environments.
However, while aluminum is highly effective, it does have some limitations. Its relatively lower melting point (around 660°C) compared to other metals can be a concern in high-temperature applications. Moreover, the manufacturing complexity can increase when intricate designs are required, potentially leading to higher costs. For international buyers, understanding local compliance standards (such as ASTM or DIN) is crucial, especially when dealing with industries that have stringent requirements.
How Does Copper Compare as a Heat Sink Material?
Copper is another popular choice for heat sinks, known for its superior thermal conductivity, which can reach up to 400 W/mK. This makes copper an excellent option for applications requiring rapid heat dissipation. Additionally, copper has a higher melting point (around 1,085°C) than aluminum, making it suitable for high-temperature environments.
On the downside, copper is significantly heavier and more expensive than aluminum, which can impact shipping costs and overall project budgets. Its susceptibility to corrosion can also be a concern unless protective coatings are applied. For B2B buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where environmental conditions may vary, it is essential to consider the long-term durability of copper heat sinks and their maintenance requirements.
What Role Does Stainless Steel Play in Heat Sink Manufacturing?
Stainless steel is less common but still relevant in specific applications, particularly where corrosion resistance is paramount. Its thermal conductivity is lower than that of aluminum and copper, typically around 15-25 W/mK, which may limit its effectiveness as a heat sink. However, stainless steel’s exceptional durability and resistance to oxidation make it ideal for environments exposed to moisture or chemicals.
The primary drawback of stainless steel is its higher cost and weight, which can complicate manufacturing and installation processes. For international buyers, it’s crucial to ensure that the chosen stainless steel grade meets local standards, such as JIS or ASTM, to avoid compliance issues.
Why is Graphite Emerging as a Material for Heat Sinks?
Graphite is gaining traction as a heat sink material due to its excellent thermal conductivity (around 200-400 W/mK) and lightweight nature. It is particularly effective in applications where space is limited, as it can be molded into complex shapes. Additionally, graphite is resistant to corrosion and can operate effectively at high temperatures.
However, the cost of graphite can be a significant barrier, and its brittleness may pose challenges during manufacturing and installation. For buyers in Europe and the Middle East, understanding the material’s compatibility with specific media and ensuring compliance with local standards is essential for successful application.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Heat Sink Manufacturers
| Material | Typical Use Case for Heat Sink Manufacturers | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Consumer electronics, industrial machinery | Lightweight, excellent thermal conductivity | Lower melting point, manufacturing complexity | Medium |
| Copper | High-performance computing, automotive | Superior thermal conductivity | Heavier, more expensive, corrosion risk | High |
| Stainless Steel | Harsh environments, marine applications | Excellent corrosion resistance | Lower thermal conductivity, higher cost | Medium to High |
| Graphite | Space-constrained applications, aerospace | Lightweight, high thermal conductivity | Brittle, higher cost | High |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for Heat Sink Manufacturers
What Are the Main Manufacturing Processes for Heat Sink Manufacturers?
Heat sink manufacturing involves a series of systematic processes that transform raw materials into effective thermal management solutions. Understanding these processes is crucial for B2B buyers looking for reliable suppliers.
Material Preparation: How Are Raw Materials Processed?
The initial stage of heat sink manufacturing involves selecting high-quality raw materials, predominantly aluminum due to its excellent thermal conductivity, lightweight nature, and corrosion resistance. Manufacturers typically begin with aluminum billets or sheets, which are then cleaned and treated to remove any impurities. This step ensures that the end product maintains high thermal performance and durability.
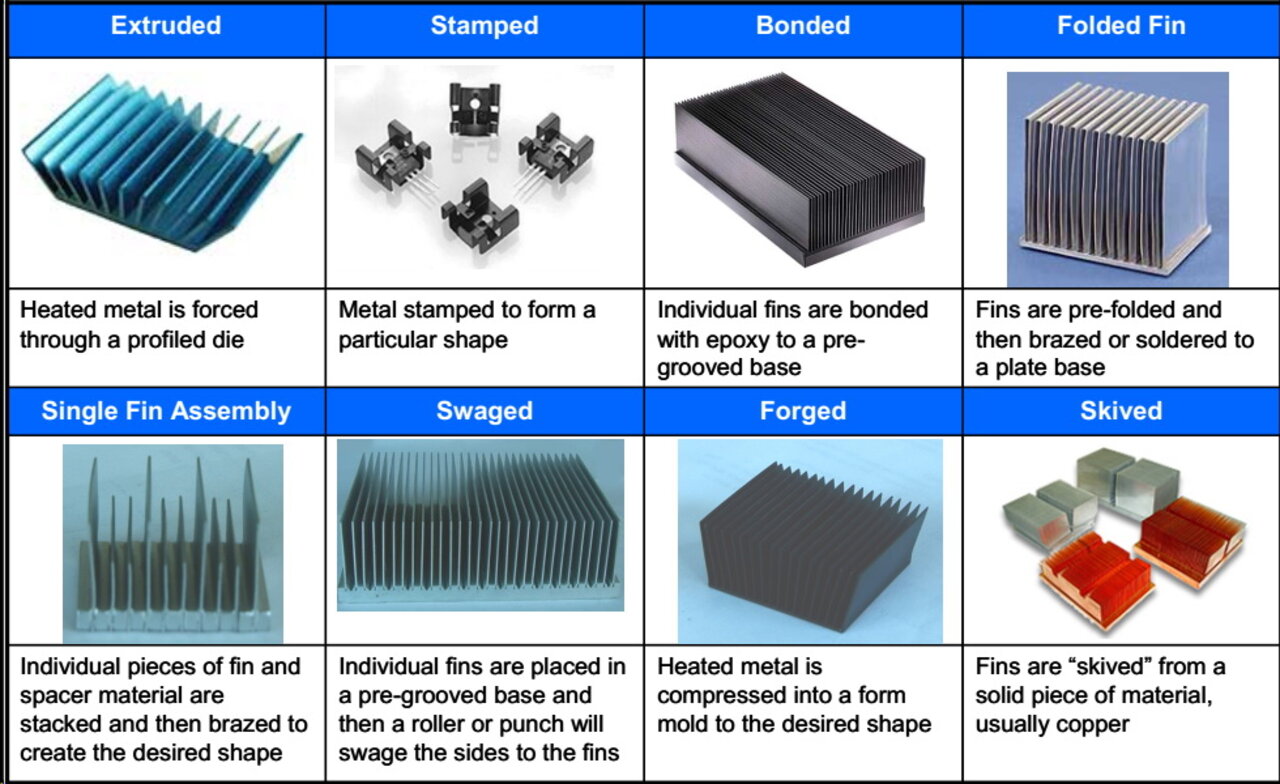
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape Heat Sinks?
After preparation, the forming process begins. This stage can involve several techniques, including:
-
Extrusion: A common method where heated aluminum is forced through a die to create a specific profile. This technique allows for complex shapes with high precision and is ideal for mass production.
-
CNC Machining: For custom designs or specific dimensions, CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is employed. This process offers flexibility and precision, allowing manufacturers to create intricate designs that meet unique specifications.
-
Skiving and Stamping: These methods are often used for creating high-performance heat sinks with increased surface area. Skiving involves shaving off material to form fins, while stamping uses dies to cut and shape the aluminum.
Assembly: How Are Components Integrated?
Once the individual components are formed, the next step is assembly. This stage may involve welding, soldering, or mechanical fastening, depending on the design requirements. Heat sink assembly must ensure that all parts fit together securely to facilitate optimal thermal performance.
What Finishing Processes Are Essential for Heat Sink Quality?
Finishing is crucial in enhancing the aesthetic appeal and functional performance of heat sinks. Common finishing processes include:
-
Anodizing: This electrochemical process increases corrosion resistance and surface hardness while improving thermal performance by enhancing the surface area.
-
Powder Coating: This method adds a protective layer to the heat sink, which is particularly useful for applications in harsh environments.
-
Surface Treatment: Techniques such as bead blasting or chemical etching can improve the heat sink’s thermal properties by increasing surface roughness.
What Quality Assurance Standards Should Heat Sink Manufacturers Adhere To?
Quality assurance is paramount in ensuring that heat sinks meet international and industry-specific standards. B2B buyers should look for manufacturers that comply with the following standards:
-
ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems, ensuring that manufacturers consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements.
-
CE Certification: In Europe, this certification indicates that the product meets health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
-
ITAR Compliance: For manufacturers involved in defense and aerospace, adherence to International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) ensures that products meet strict security protocols.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Heat Sink Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are essential throughout the manufacturing process to maintain high standards. Common QC practices include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, regular inspections are conducted to monitor processes and identify any deviations from quality standards.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once manufacturing is complete, a comprehensive inspection is performed to verify that the heat sinks meet all specifications and quality standards before shipping.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Heat Sink Quality Assurance?
Various testing methods are employed to evaluate the thermal performance and durability of heat sinks. Common tests include:
-
Thermal Conductivity Tests: These assess the efficiency of heat transfer, ensuring that the heat sink performs adequately under operational conditions.
-
Mechanical Stress Tests: These tests determine the structural integrity of heat sinks under load, simulating real-world conditions.
-
Corrosion Resistance Tests: Ensuring that the heat sink can withstand environmental challenges is vital, especially in industries such as medical and aerospace.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For international buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control processes is crucial. Here are actionable steps:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturer’s capabilities and adherence to quality standards firsthand.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Manufacturers should provide detailed QC reports, including results from testing and compliance certifications.
-
Third-party Inspections: Engaging independent inspectors can offer an unbiased evaluation of the manufacturer’s quality processes and product integrity.
What Are the Specific Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers face unique challenges regarding quality control. Here are some nuances to consider:
-
Understanding Local Standards: Different regions may have varying standards and certifications. Buyers should ensure that the manufacturer complies with both local and international regulations.
-
Logistics and Supply Chain: Quality can be affected by the logistics involved in shipping. Buyers should consider how transportation conditions may impact the integrity of the heat sinks.
-
Cultural and Communication Differences: Establishing clear communication and understanding between buyers and manufacturers can mitigate misunderstandings regarding quality expectations.
Conclusion
In summary, a comprehensive understanding of manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures is essential for B2B buyers in the heat sink industry. By prioritizing manufacturers that adhere to international quality standards and employing robust QC practices, buyers can ensure that they receive reliable and high-performing thermal management solutions for their applications.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘Heat Sink Manufacturers’
Introduction
Sourcing heat sinks is a critical process for businesses that rely on thermal management solutions. This checklist is designed to guide B2B buyers through the essential steps of identifying and selecting the right heat sink manufacturers. By following this practical guide, you can ensure that your procurement process is efficient, cost-effective, and aligned with your technical needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the foundation of your sourcing process. Consider the requirements of your application, such as size, material (e.g., aluminum or copper), thermal performance, and any specific design features. This clarity will help you communicate your needs effectively to potential suppliers, ensuring they can meet your expectations.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential heat sink manufacturers. Look for companies with a proven track record in your industry, paying attention to their experience, capabilities, and product range. Utilize online resources, industry directories, and trade shows to gather information about suppliers, including their manufacturing processes and technology.
Step 3: Verify Supplier Certifications
Before engaging with any supplier, it’s crucial to verify their certifications. Look for ISO certifications, ITAR compliance, and other relevant quality standards that demonstrate their commitment to quality and safety. Certifications ensure that the manufacturer adheres to industry best practices, reducing risks associated with product defects.
Step 4: Evaluate Customization Capabilities
Customization is often necessary to meet specific thermal management needs. Assess whether the manufacturers can provide tailored solutions such as custom sizes, shapes, and materials. Evaluate their engineering support, including their ability to produce prototypes and engage in collaborative design processes, which is essential for meeting unique application requirements.
Step 5: Request Samples and Prototypes
Once you have narrowed down your list of suppliers, request samples or prototypes of their heat sinks. This step allows you to evaluate the quality and performance of their products firsthand. Testing samples in your application will provide insight into their thermal efficiency and overall fit for your needs.
Step 6: Compare Pricing and Lead Times
Gather quotes from multiple suppliers and compare their pricing structures and lead times. Understand the factors influencing their costs, such as material choices, customization options, and order volumes. Ensure that you factor in shipping costs and timelines, as these can significantly impact your overall budget and project deadlines.
Step 7: Establish Clear Communication Channels
Effective communication is vital throughout the sourcing process. Establish clear lines of communication with your chosen supplier to discuss technical specifications, project timelines, and any potential challenges. A responsive and communicative supplier can significantly enhance the efficiency of your procurement process and ensure successful project execution.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their sourcing process, leading to informed decisions and successful partnerships with heat sink manufacturers.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for Heat Sink Manufacturers Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Heat Sink Manufacturing?
When sourcing heat sinks, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts pricing. Aluminum is commonly used due to its excellent thermal conductivity and cost-effectiveness, while specialized materials like copper may incur higher costs due to their superior performance in specific applications.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary widely based on the region and the complexity of the manufacturing process. Skilled labor is essential for custom designs and intricate machining processes, which can drive up costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Manufacturers often pass these costs onto buyers, making it important to evaluate potential suppliers’ operational efficiencies.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling is often required for specific designs, which can represent a significant upfront investment. Buyers should inquire about tooling costs and whether they are included in the quoted price.
-
Quality Control (QC): Quality assurance processes are essential to ensure product reliability, especially in high-stakes industries like aerospace and medical applications. The costs associated with QC can affect the final price, but investing in quality can reduce long-term risks.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling fees can vary greatly depending on the location of the supplier and the buyer. International logistics can add complexity, including customs duties and tariffs, which should be factored into the total cost.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding the typical margins for the industry can help buyers assess whether a quoted price is competitive.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Heat Sink Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of heat sinks, particularly for international buyers:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often attract lower unit prices. Negotiating MOQs can lead to significant savings, especially for businesses that anticipate steady demand.
-
Specifications and Customization: Highly customized products generally cost more due to the additional engineering and production efforts involved. Buyers should clarify their specifications upfront to receive accurate quotes.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Heat sinks used in regulated industries (e.g., medical, aerospace) may require specific certifications (ISO, RoHS, ITAR). Suppliers often charge a premium for certified products, which can affect overall pricing.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and experience of the supplier can influence pricing. Established manufacturers may command higher prices due to their track record, while newer entrants might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of shipment and delivery (Incoterms) can affect the total landed cost. Buyers should be clear about who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and customs duties.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Negotiating Heat Sink Prices?
B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Firmly: Always seek to negotiate pricing, especially for larger orders or long-term contracts. Suppliers may offer discounts based on volume or commitment.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider the TCO, which includes maintenance, efficiency, and lifespan of the heat sinks. A higher upfront cost may be justified if the product delivers better performance and longevity.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Sourcing: International buyers should be aware of additional costs such as tariffs, shipping fees, and potential currency fluctuations. It’s beneficial to work with suppliers experienced in international trade to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Request Detailed Quotes: Ensure quotes include all cost components to facilitate a clear comparison between suppliers. This transparency aids in identifying the most cost-effective options.
-
Build Relationships: Developing strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, priority service, and more favorable terms in the long run.
Disclaimer
Prices for heat sinks can fluctuate based on market conditions, material availability, and supplier policies. The information provided is indicative and should be verified through direct supplier engagement for accurate pricing relevant to specific requirements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing Heat Sink Manufacturers With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Heat Sink Manufacturers
In the realm of thermal management, heat sinks are critical components for dissipating heat generated by electronic devices. However, there are viable alternatives to traditional heat sink manufacturers that also serve to address thermal challenges. This section delves into these alternatives, comparing them against conventional heat sink solutions.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Heat Sink Manufacturers | Phase Change Materials (PCMs) | Liquid Cooling Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency in heat dissipation | Excellent for managing transient thermal spikes | Superior heat transfer, especially in high-load scenarios |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; varies by customizability | High upfront cost, but savings on energy bills | Higher installation and maintenance costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Straightforward installation with custom options | Requires specialized knowledge for integration | Complex setup requiring professional installation |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, occasional cleaning | Minimal maintenance, depending on application | Regular maintenance required for pumps and fluid |
| Best Use Case | Electronics, LED lighting, industrial applications | Electronics with fluctuating heat loads | High-performance computing, gaming, and industrial machinery |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Phase Change Materials (PCMs)
Phase Change Materials are substances that absorb or release thermal energy during phase transitions, such as from solid to liquid. They are particularly effective in applications where heat loads fluctuate significantly, providing a buffer against thermal spikes. The main advantage of PCMs is their ability to maintain temperature stability, which can enhance the longevity of sensitive electronic components. However, the initial investment can be high, and their integration into existing systems may require specialized knowledge and engineering expertise.
Liquid Cooling Systems
Liquid cooling systems utilize liquids, typically water or specialized coolants, to transfer heat away from electronic components. These systems are renowned for their superior heat transfer capabilities, making them ideal for high-performance environments such as data centers and gaming rigs. While they offer excellent cooling efficiency, the complexity of installation and the need for regular maintenance can be significant drawbacks. Additionally, the higher upfront costs associated with liquid cooling systems may deter some businesses from adopting this technology.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Thermal Management Solution
When evaluating thermal management solutions, B2B buyers must consider specific operational needs, budget constraints, and the technical capabilities of their teams. Heat sink manufacturers offer a reliable and cost-effective solution for many applications, particularly where space and simplicity are critical. However, for environments with high thermal loads or where temperature fluctuations are common, alternatives like Phase Change Materials or liquid cooling systems may provide superior performance. Ultimately, the choice will depend on the unique requirements of each project, emphasizing the importance of thorough analysis and consultation with thermal management experts.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for Heat Sink Manufacturers
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Heat Sinks That Manufacturers Should Consider?
When engaging with heat sink manufacturers, understanding the critical technical properties is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some of the most important specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
– Heat sinks are predominantly made from aluminum due to its excellent thermal conductivity, lightweight nature, and corrosion resistance. Manufacturers often specify material grades, such as 6061 or 6063, which indicate the specific alloy composition and mechanical properties. For B2B buyers, selecting the right material grade ensures optimal heat dissipation and durability for the intended application, whether in consumer electronics or industrial machinery. -
Thermal Conductivity
– This property measures a material’s ability to transfer heat. High thermal conductivity is crucial for effective heat sink performance, as it dictates how quickly heat can be dissipated away from sensitive components. In the B2B context, understanding thermal conductivity helps buyers evaluate which heat sink will best suit their product’s thermal management needs, ultimately enhancing reliability and longevity. -
Tolerance
– Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension. In heat sink manufacturing, precision is vital to ensure proper fit and function within electronic assemblies. A tighter tolerance often results in higher manufacturing costs but is necessary for applications that require exact specifications. B2B buyers should consider the required tolerances based on their product’s design to avoid issues during assembly or operation. -
Fin Design and Density
– The design and density of fins on a heat sink play a crucial role in its cooling efficiency. Fins increase the surface area for heat exchange, and various designs (like serrated or Zipper fins) are optimized for specific airflow conditions. Understanding these designs helps B2B buyers select heat sinks that align with their cooling requirements, especially in high-performance applications. -
Size and Configuration
– Heat sinks come in various shapes and sizes, which must match the dimensions and thermal profiles of the electronic components they cool. Customization options can include extrusions, skived designs, or even machined heat sinks for unique applications. For B2B buyers, clarity on size and configuration is critical to ensure compatibility with existing designs and to avoid costly modifications.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the Heat Sink Manufacturing Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon can enhance communication and negotiation with heat sink suppliers. Here are several key terms that B2B buyers should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of heat sinks, an OEM may require custom designs for specific products, necessitating collaboration with manufacturers for tailored thermal solutions. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– This term defines the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQs is essential for B2B buyers, as it impacts inventory management and cost-effectiveness. Suppliers with no MOQ can be advantageous for companies needing smaller quantities or prototyping. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products. It’s a critical step in the procurement process, allowing B2B buyers to gather competitive offers and assess their options based on technical specifications and pricing. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– These terms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade, particularly concerning shipping and delivery. Familiarity with Incoterms, such as FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight), is crucial for B2B buyers to understand their obligations and costs associated with shipping heat sinks from manufacturers. -
Lead Time
– Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving it. For B2B buyers, understanding lead times is vital for project planning and inventory management, especially in industries where timely delivery is critical for maintaining production schedules.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing heat sinks, ensuring they choose the right products for their thermal management needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Heat Sink Manufacturers Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Affecting Heat Sink Manufacturers?
The global heat sink manufacturing sector is experiencing a transformative phase driven by technological advancements and evolving market demands. A primary driver is the increasing emphasis on thermal management in electronics, particularly in industries such as telecommunications, automotive, and consumer electronics. As devices become more compact and powerful, the need for efficient heat dissipation solutions has surged. Additionally, the rise of renewable energy technologies and electric vehicles is propelling demand for innovative thermal management solutions, thus broadening the market scope for heat sink manufacturers.
Emerging B2B tech trends, such as the integration of AI and IoT in manufacturing processes, are enhancing product design and operational efficiencies. Manufacturers are leveraging advanced simulation tools and automation to optimize heat sink designs tailored to specific applications, which is particularly appealing to international buyers seeking customized solutions. Furthermore, the adoption of 3D printing technology is revolutionizing the prototyping phase, allowing for quicker turnaround times and reduced costs.
For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding regional market dynamics is crucial. Factors such as local regulations, supply chain logistics, and economic conditions can significantly impact sourcing decisions. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that demonstrate agility in adapting to these dynamics, ensuring timely delivery and compliance with regional standards.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Reshaping the Heat Sink Manufacturing Sector?
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of procurement strategies in the heat sink manufacturing sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is under scrutiny, prompting buyers to seek suppliers committed to reducing their carbon footprints. Heat sink manufacturers are increasingly adopting eco-friendly materials and practices, such as using aluminum, which boasts excellent thermal conductivity, is lightweight, and is highly recyclable. This not only enhances product performance but also aligns with global sustainability goals.
Moreover, ethical sourcing is gaining importance among international buyers. Companies are expected to maintain transparency in their supply chains, ensuring that materials are sourced responsibly and that labor practices comply with international standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and RoHS for hazardous substances are becoming essential criteria for evaluating potential suppliers. Buyers should prioritize partnerships with manufacturers who can demonstrate their commitment to sustainability and ethical practices, as this not only mitigates risk but also enhances brand reputation.
How Has the Heat Sink Manufacturing Sector Evolved Over Time?
The heat sink manufacturing sector has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Initially dominated by basic aluminum extrusions, the market has shifted towards more sophisticated designs that incorporate advanced materials and technologies. The introduction of custom heat sink solutions, including vapor chambers and heat pipes, has enabled manufacturers to meet the increasing thermal management demands of modern electronics.
Technological advancements, such as the adoption of computer-aided design (CAD) and computational fluid dynamics (CFD), have further refined product development processes. These innovations allow manufacturers to simulate and optimize designs before production, ensuring higher performance and efficiency. As the industry continues to grow, the focus on sustainability and ethical sourcing will likely shape its future trajectory, making it essential for buyers to stay informed about the latest trends and practices within the sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of Heat Sink Manufacturers
-
How do I determine the right heat sink for my application?
To find the right heat sink, start by assessing the thermal requirements of your device, including the heat generated (in watts) and the acceptable operating temperature range. Consider factors like airflow, available space, and environmental conditions. Collaborate with your heat sink manufacturer to discuss your specific needs; many offer thermal simulation tools and engineering support to optimize design. Custom solutions might be necessary for unique applications, so inquire about available options. -
What materials are most commonly used for heat sinks, and why?
Aluminum is the most popular material for heat sinks due to its excellent thermal conductivity, lightweight nature, and resistance to corrosion. It is also cost-effective and highly recyclable, making it an environmentally friendly choice. Other materials like copper may be used for higher thermal performance, but they are heavier and more expensive. When selecting a material, consider your application’s thermal performance needs, weight constraints, and budget. -
What customization options are available for heat sinks?
Heat sinks can be customized in various ways to meet specific requirements, including size, shape, and fin design. Manufacturers often offer options for material thickness, surface treatments, and integrated features like mounting holes or thermal interface materials. Collaborating with the supplier’s engineering team can help ensure that your heat sink is tailored to your device’s cooling needs and enhances overall performance. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for heat sinks?
Minimum order quantities vary by manufacturer and depend on the complexity of the design and materials used. Some suppliers may have no minimum order requirement for standard products, while custom solutions might require larger quantities to be cost-effective. When discussing your order, clarify the MOQ with the manufacturer to align your production needs and budget accordingly. -
What should I consider when vetting a heat sink manufacturer?
When vetting a heat sink manufacturer, assess their certifications (such as ISO), production capabilities, and experience in your industry. Request samples to evaluate quality and performance. Additionally, check customer reviews and testimonials to gauge reliability and service. Establish clear communication channels to discuss your needs and ensure they can meet deadlines and provide ongoing support. -
What payment terms are typically offered by heat sink manufacturers?
Payment terms can vary significantly among manufacturers. Common practices include upfront payment, 30-day terms, or a deposit followed by the balance upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer credit terms based on your business history. Ensure you understand the payment structure before placing an order, and inquire about any potential discounts for larger orders or early payments. -
How do logistics and shipping impact the procurement of heat sinks?
Logistics and shipping are crucial in the procurement process, particularly for international buyers. Consider the lead times for production, as well as the shipping methods available (air freight vs. sea freight) and associated costs. Ensure the manufacturer has experience with international shipping regulations and can provide necessary documentation for customs clearance. Discuss delivery timelines to avoid production delays and ensure timely project completion. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from heat sink manufacturers?
Quality assurance measures typically include rigorous testing protocols throughout the production process. Expect manufacturers to conduct thermal performance tests, dimensional inspections, and material quality checks. Certifications such as ISO 9001 indicate a commitment to quality standards. Inquire about their testing methodologies and whether they provide documentation or reports that validate the heat sink’s performance and reliability.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for Heat Sink Manufacturers
In today’s competitive landscape, strategic sourcing is paramount for heat sink manufacturers aiming to enhance operational efficiency and product quality. By forging strong partnerships with reliable suppliers, businesses can access innovative materials and technologies that improve thermal management solutions. The diverse offerings from global manufacturers allow buyers to find customized solutions tailored to specific industry needs, whether in telecommunications, defense, or medical applications.
Moreover, the emphasis on sustainability—particularly with aluminum heat sinks—positions manufacturers to meet growing environmental standards while reducing costs. As international markets evolve, buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should leverage the expertise of seasoned suppliers to ensure they remain ahead of technological advancements.
Looking forward, the demand for high-performance heat sinks will continue to grow, driven by advancements in electronics and the need for effective thermal management. Now is the time for international B2B buyers to evaluate their sourcing strategies and engage with manufacturers that can provide not only quality products but also innovative solutions for their specific applications. Embrace the future of thermal management by exploring partnerships that drive success and sustainability in your operations.