Top 7 Food Processing Machinery Manufacturers List and Guide: How…
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for Food Processing Machinery Manufacturers
In the dynamic landscape of food processing machinery, international B2B buyers face the critical challenge of sourcing reliable and efficient equipment that meets diverse production needs. As markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to expand, the demand for high-quality food processing machinery manufacturers has surged. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, equipping buyers with essential insights into various types of machinery, their applications, and the nuances of supplier vetting.
From innovative cooking systems to advanced packaging solutions, the food processing sector is characterized by rapid technological advancements that directly impact product quality and operational efficiency. Buyers will discover actionable strategies for evaluating suppliers, understanding cost structures, and leveraging market trends to enhance their purchasing decisions.
Moreover, this guide emphasizes the importance of selecting machinery that adheres to stringent safety and sanitation standards, a crucial consideration in today’s food production environment. By navigating the complexities of the global market for food processing machinery, B2B buyers can make informed choices that not only improve their operational outcomes but also ensure compliance with regulatory demands. Empowering businesses with knowledge, this guide is an invaluable tool for those looking to thrive in the competitive food processing industry.
Top 10 Food Processing Machinery Manufacturers Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Heat and Control – Custom Industrial Food Processing Equipment
Domain: heatandcontrol.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Custom Industrial Food Processing Equipment designed for various applications including Bakery Foods, Candy & Confectionery, Cannabis, Cereal, Cheese, Coffee & Tea, Corn Chips, Extruded & Legume Snacks, French Fries & Potato Co-Products, Fruit Snacks, Meat, Poultry & Seafood, Nuts, Pasta, Pellet Snacks, Pet Food & Treats, Pharmaceutical, Plantain & Banana Chips, Potato & Kettle Chips, Prepared Foo…
2. NSK – High-Speed, Low-Noise Ball Screws
Domain: nsk.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: High-Speed, Low-Noise Ball Screws BSS Model: Compact, high-speed screws with noise reduction of up to 6 dB compared to traditional products. Monocarrier™: A compact, lightweight, single-axis actuator that combines a ball screw and linear guide. NSK Linear Guides™: A rich lineup of products for various usage conditions. Megatorque Motor™: Compact, lightweight, highly precise motor without a reducer…
3. Columbia Food Machinery – TOMRA ECO Peeler
Domain: columbiafoodmachinery.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Columbia Food Machinery supplies premium food processing equipment from industry-leading manufacturers. Key products include: TOMRA ECO Peeler, TOMRA Food REYCO ECOMiser™, TOMRA 5B Optical Sorter, PFI PURmotion™ Horizontal Conveyor, Vanmark 2820 Peeler/Scrubber/Washer, A&K Power Husker, SMC Sidewall Return Drag Conveyor, Olney by Tweet/Garot Stone Crib, and MECMESIN TU Tenderometer.
4. Marlen – Industrial Food Processing Equipment
Domain: marlen.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Marlen offers a range of industrial food processing and manufacturing equipment, including: Batch Ovens, Smokehouses, Chillers & Dehydrators, Food Handling & Plant Hygiene solutions, Industrial Filling systems, Industrial Sous Vide Water Cooking & Chilling, Pre-package and Post-package Pasteurization, Searing, Roasting & Grill Marking equipment, Crust Freezers, Slicers, Dicers, and Shredders, Smok…
5. MPD – Food Processing Equipment
Domain: mpd-inc.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Food processing equipment includes Storeveyor – Surge & Storage Bins, Sanitary Flood Fed Crusher, Sanitary Stainless Lump Breaking Crushers, Cordial Sanitary Crumbler, Sanitary Rigimill® Hammermills, Rugged Rigimill® Hammermills, Rugged Industrial Flood Fed Crushers, Industrial Carbon Steel Crushers, Coating, Enrobing & Tumbling Drums, Heavy-Duty Big Block Crushers, Cement Air Slide & Loadout Crus…
6. Neologic Engineers – Food Processing Equipment
Domain: neologicengineers.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
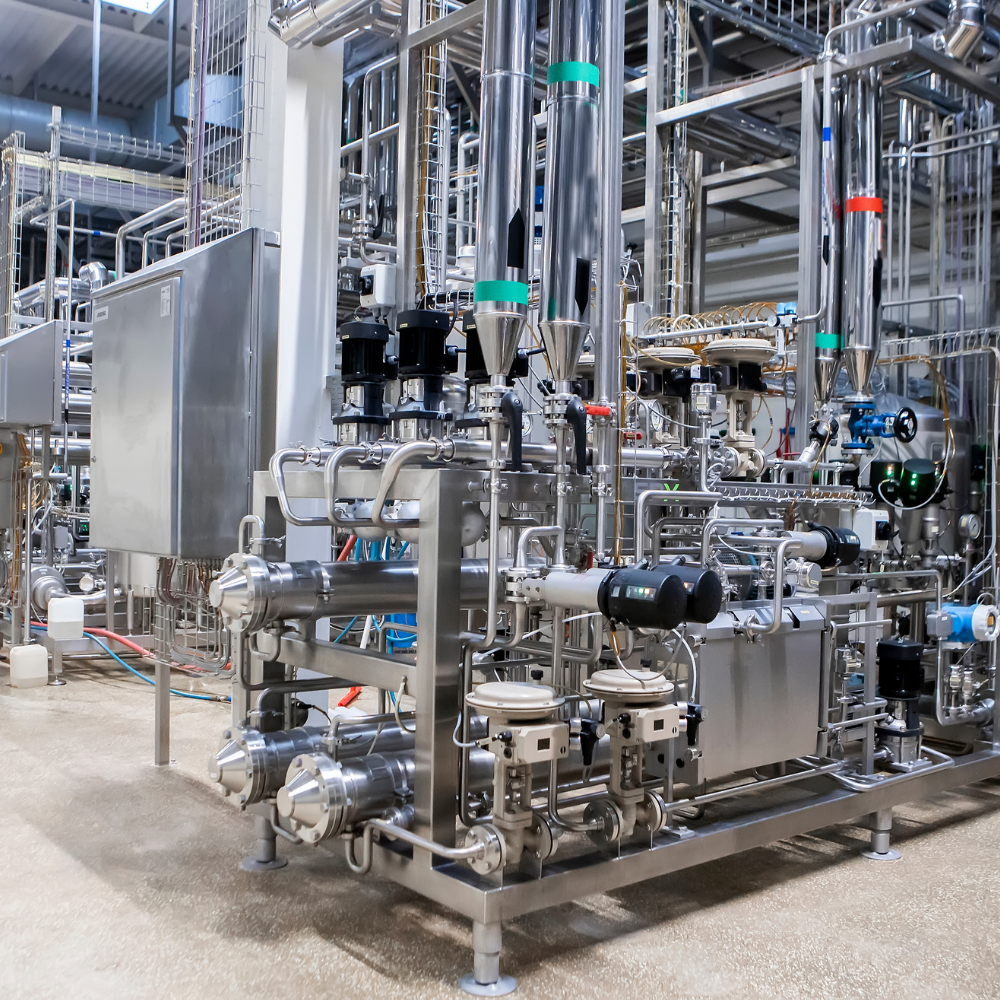
Introduction: Neologic Engineers manufactures a wide range of food processing equipment including Milk Pasteurizer Systems, Juice Pasteurizer Systems, UHT Sterilizer Modules, Aseptic Storage Tanks, Membrane Filtration Systems, Spiral Solutions, IQF Technology, CIP Systems, Dairy Separators, Paneer & Cheese Press, Butter Melting Vats, Milk Reception Modules, Hot Water Modules, Powder Mixing Systems, and Contherm…
7. Spherical Insights – Food Processing Equipment Solutions
Domain: sphericalinsights.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Buhler Group: Milling, baking, and pasta production equipment; energy-efficient milling systems. JBT Corporation: Solutions for thermal processing, freezing, and packaging; innovations for food safety and operational efficiency. Marel: Meat, poultry, and fish processing systems; automated portioning and weighing systems. Tetra Pak: Aseptic processing technology for liquid food; recyclable packagin…
Understanding Food Processing Machinery Manufacturers Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Custom Food Processing Equipment | Tailored solutions for specific processing needs | Meat, dairy, and specialty food sectors | Pros: High efficiency, tailored to needs. Cons: Higher initial costs, longer lead times. |
| Automated Sorting and Grading | Uses advanced technology for precision and speed | Fruit, vegetable, and nut processing | Pros: Reduces labor costs, improves accuracy. Cons: Requires maintenance, tech training needed. |
| Cooking and Heat Treatment Systems | Specialized in cooking processes with energy efficiency | Snack foods, ready-to-eat meals | Pros: High-quality output, energy savings. Cons: Complexity in operation, higher upfront investment. |
| Packaging Machinery | Focus on sealing, labeling, and packing efficiency | All food sectors | Pros: Enhances shelf life, improves presentation. Cons: May require adjustments for different products. |
| Cleaning and Sanitation Equipment | Ensures hygiene and compliance with regulations | All food processing environments | Pros: Essential for safety, reduces contamination risks. Cons: Ongoing costs for cleaning supplies. |
What are the characteristics of Custom Food Processing Equipment?
Custom food processing equipment is designed to meet the unique requirements of specific food products. These machines are built to enhance production efficiency and ensure the quality of the end product. They often involve significant investment in research and development, making them reliable and durable. B2B buyers should consider the initial costs versus the long-term return on investment, as these machines can lead to substantial savings in operational costs over time.
How do Automated Sorting and Grading Systems enhance food processing?
Automated sorting and grading systems leverage cutting-edge technology to accurately sort food products based on size, weight, and quality. This automation significantly reduces labor costs and enhances processing speed, making it an attractive option for businesses dealing with perishable goods. Buyers should assess the technology’s compatibility with their existing systems and the level of maintenance required to ensure optimal performance.
What advantages do Cooking and Heat Treatment Systems offer?
Cooking and heat treatment systems are essential for producing high-quality food products, particularly in the snack and ready-to-eat meal sectors. These systems are designed for energy efficiency, which can lead to reduced operational costs. However, B2B buyers must consider the complexity of these systems and the necessary training for staff to operate them effectively, as well as the upfront investment required.
Why is Packaging Machinery critical in food processing?
Packaging machinery plays a vital role in the food industry by ensuring products are sealed, labeled, and presented attractively for consumers. Efficient packaging enhances shelf life and reduces waste, which is crucial for maintaining profitability. Buyers should evaluate the flexibility of the machinery to accommodate different types of products, as well as the potential need for adjustments or upgrades in the future.
What is the importance of Cleaning and Sanitation Equipment in food processing?
Cleaning and sanitation equipment is fundamental in maintaining hygiene standards in food processing environments. With increasing regulations around food safety, these machines help reduce contamination risks and ensure compliance. Buyers should consider the ongoing costs associated with cleaning supplies and the potential need for regular maintenance to keep these systems functioning effectively.
Key Industrial Applications of Food Processing Machinery Manufacturers
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Food Processing Machinery Manufacturers | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Snack Food Production | Fryers and Ovens for Snack Foods | Enhances product quality and consistency, leading to higher customer satisfaction. | Ensure energy efficiency, ease of maintenance, and compliance with food safety standards. |
| Beverage Processing | Filling and Packaging Machines | Increases production speed and accuracy, reducing waste and labor costs. | Look for machines that offer flexibility for various beverage types and container sizes. |
| Meat and Poultry Processing | Cutting and Deboning Equipment | Improves yield and reduces labor costs while ensuring food safety. | Prioritize equipment that meets hygiene standards and offers easy cleaning features. |
| Bakery and Confectionery | Mixing and Baking Equipment | Ensures uniform mixing and baking, leading to consistent product quality. | Consider the machine’s adaptability to different recipes and production scales. |
| Fruit and Vegetable Processing | Washing, Peeling, and Sorting Machines | Enhances food safety and reduces contamination risks, improving product shelf life. | Verify compliance with local regulations and the machine’s capability to handle various produce types. |
How Do Fryers and Ovens Enhance Snack Food Production?
In the snack food industry, fryers and ovens are crucial for creating high-quality products like chips and pretzels. These machines ensure consistent cooking temperatures, which is vital for flavor and texture. International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and South America, should focus on energy-efficient models that comply with local regulations to reduce operational costs and environmental impact. Additionally, ease of maintenance is essential to minimize downtime and ensure continuous production.
Why Are Filling and Packaging Machines Essential in Beverage Processing?
Filling and packaging machines play a pivotal role in the beverage industry by increasing production speed and accuracy. These machines help reduce waste, ensuring that every drop of product is utilized efficiently. For international buyers, especially in the Middle East and Europe, selecting machinery that can handle various beverage types and container sizes is critical. Flexibility in production lines can lead to a significant competitive advantage, allowing businesses to adapt to changing consumer preferences quickly.
How Do Cutting and Deboning Equipment Improve Meat and Poultry Processing?
In meat and poultry processing, cutting and deboning equipment enhances yield and reduces labor costs while ensuring food safety standards are met. These machines automate labor-intensive tasks, allowing for higher efficiency and consistency in product quality. International buyers should prioritize equipment that meets stringent hygiene standards and can be easily cleaned to prevent contamination. This is particularly important in regions where food safety regulations are becoming increasingly stringent.
What Role Does Mixing and Baking Equipment Play in Bakery and Confectionery?
Mixing and baking equipment is essential in the bakery and confectionery sectors for ensuring uniform mixing and baking processes. This machinery allows for consistent product quality, which is crucial for maintaining brand reputation and customer loyalty. Buyers from diverse regions, including Europe and South America, should consider machines that can adapt to various recipes and production scales, providing flexibility in their operations. This adaptability can significantly enhance a bakery’s ability to meet market demands.
How Do Washing, Peeling, and Sorting Machines Enhance Fruit and Vegetable Processing?
Washing, peeling, and sorting machines are integral to the fruit and vegetable processing industry, enhancing food safety and reducing contamination risks. These machines ensure that produce is clean and ready for packaging, which can significantly improve shelf life and consumer trust. For international buyers, especially in Africa and Asia, verifying that the equipment complies with local regulations is vital. Additionally, the ability to handle various types of produce can optimize processing efficiency and cater to diverse market needs.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘Food Processing Machinery Manufacturers’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Equipment Customization Challenges
The Problem: In a highly competitive food processing landscape, many manufacturers struggle with the need for customized machinery to meet specific production requirements. This often leads to challenges in sourcing equipment that not only fits their unique processes but also adheres to safety and quality standards. B2B buyers may find themselves overwhelmed by options, unsure which manufacturers can deliver the tailored solutions they need, leading to potential production delays and increased costs.
The Solution: To effectively navigate equipment customization challenges, B2B buyers should prioritize manufacturers with a strong track record in custom solutions. Start by requesting case studies or examples of past projects that showcase the manufacturer’s ability to adapt their machinery for different processing needs. Engage in detailed discussions regarding your production goals and seek manufacturers that offer collaborative design processes. This involves working closely with engineers who understand your requirements and can propose tailored machinery solutions that comply with safety standards. Additionally, consider manufacturers that provide post-installation support and training, ensuring that your team is well-equipped to operate the machinery effectively.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Compliance with Food Safety Standards
The Problem: Food processing machinery must adhere to stringent food safety regulations, which can be a daunting task for manufacturers, particularly in regions with evolving compliance requirements. B2B buyers often face the challenge of ensuring that the equipment they procure not only meets local regulations but also aligns with international safety standards. Non-compliance can lead to product recalls, legal issues, and damage to brand reputation.
The Solution: To mitigate compliance risks, B2B buyers should engage manufacturers who prioritize food safety in their machinery design. Look for equipment that has certifications from recognized safety and quality standards, such as NSF or ISO. During the selection process, request documentation that outlines the safety features of the machinery, including materials used, cleaning protocols, and maintenance guidelines. Additionally, manufacturers should provide a clear understanding of how their equipment is tested for safety compliance. Establish a partnership with suppliers who offer ongoing support, including updates on regulatory changes and training for your staff on best practices for maintaining compliance with food safety standards.
Scenario 3: Managing Downtime and Maintenance Costs
The Problem: Unplanned downtime due to machinery failure is a significant pain point for food processing manufacturers, leading to production delays and increased operational costs. B2B buyers often struggle with selecting machinery that is not only reliable but also easy to maintain. This is particularly critical in regions where access to spare parts and technical support may be limited, impacting the overall efficiency of production lines.
The Solution: To effectively manage downtime and maintenance costs, B2B buyers should choose machinery from manufacturers known for their reliability and robust after-sales service. During the procurement process, inquire about the expected lifespan of the equipment and the manufacturer’s track record for durability. Consider suppliers that offer comprehensive maintenance packages, including regular inspections and access to spare parts. Implementing a preventive maintenance schedule can also significantly reduce the risk of unexpected failures. Furthermore, training your operational team on basic troubleshooting and maintenance can empower them to address minor issues before they escalate, ensuring that production remains uninterrupted.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for Food Processing Machinery Manufacturers
What Are the Key Materials Used in Food Processing Machinery?
When selecting materials for food processing machinery, manufacturers must consider various factors, including performance, durability, and compliance with international standards. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in this sector, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
Stainless Steel: The Industry Standard for Food Processing
Key Properties: Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, high-temperature tolerance, and mechanical strength. It typically withstands temperatures up to 800°F (427°C) and pressures exceeding 150 psi, making it suitable for various food processing applications.
Pros & Cons: Its durability and resistance to rust and staining make stainless steel a preferred choice. However, it can be more expensive than other materials, and its manufacturing process can be complex, requiring specialized welding and finishing techniques.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of food products, including acidic and alkaline substances. Its non-reactive nature ensures that food quality is maintained.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local food safety standards, such as those from the FDA or EU regulations. Common grades like 304 and 316 are recognized internationally, but buyers should verify specific requirements in their markets.
Aluminum: Lightweight and Cost-Effective
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, with a density of about one-third that of stainless steel, and offers good corrosion resistance, especially when anodized. It can withstand temperatures up to 400°F (204°C).
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its lower cost and ease of fabrication, which can lead to reduced manufacturing time. However, it is less durable than stainless steel and may not be suitable for high-temperature applications without proper coatings.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is often used in equipment that handles dry or less corrosive food products. Its lightweight nature makes it ideal for portable machinery.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific grades of aluminum that meet food safety standards, such as those outlined in ASTM or JIS. The cost-effectiveness of aluminum may be appealing to manufacturers in emerging markets.
Plastic Composites: Versatile and Lightweight
Key Properties: Plastic composites, including polyethylene and polypropylene, are known for their chemical resistance and lightweight nature. They can operate effectively at temperatures up to 200°F (93°C).
Pros & Cons: These materials are cost-effective and can be molded into complex shapes, making them versatile for various applications. However, they may not withstand high temperatures or pressures, limiting their use in certain food processing environments.
Impact on Application: Plastic composites are ideal for applications involving non-corrosive food products and are often used in conveyor systems and packaging machinery.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with food safety regulations is crucial. Buyers should ensure that the plastics used are FDA-approved or meet equivalent standards in their regions.
Carbon Steel: Strength and Durability
Key Properties: Carbon steel is known for its high strength and durability, with the ability to withstand high pressures and temperatures. However, it is more susceptible to corrosion compared to stainless steel.
Pros & Cons: Its strength makes it suitable for heavy-duty machinery, but it requires protective coatings to prevent rust, which can increase maintenance costs.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is often used in structural components of food processing machinery but may not be suitable for direct food contact without proper treatment.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must be aware of the need for protective coatings and the implications of corrosion in humid climates. Compliance with local standards is essential, particularly in regions with stringent food safety regulations.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Food Processing Machinery
| Material | Typical Use Case for Food Processing Machinery Manufacturers | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Equipment in direct contact with food | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Aluminum | Lightweight machinery for less corrosive products | Cost-effective and easy to fabricate | Limited high-temperature applications | Medium |
| Plastic Composites | Conveyor systems and packaging machinery | Versatile and lightweight | Not suitable for high temperatures | Low |
| Carbon Steel | Structural components of machinery | High strength and durability | Susceptible to corrosion without coatings | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide aims to provide actionable insights for B2B buyers in the food processing machinery sector, facilitating informed decisions based on specific application needs and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for Food Processing Machinery Manufacturers
What Are the Main Stages in Manufacturing Food Processing Machinery?
The manufacturing of food processing machinery involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure that the final product meets the stringent requirements of safety, efficiency, and reliability. The primary stages include:
Material Preparation: How Are Raw Materials Selected and Processed?
The first step in manufacturing food processing machinery is material preparation. This stage involves selecting high-quality materials that can withstand the rigors of food processing. Common materials include stainless steel, which offers corrosion resistance and hygiene, and specialized alloys for components that require high durability.
Once selected, materials undergo processes such as cutting, machining, and surface treatment to achieve the desired specifications. Techniques like laser cutting and CNC machining are prevalent, ensuring precision and uniformity. Additionally, materials are often treated to enhance properties such as strength and resistance to contamination, which are critical in the food industry.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape Components?
The forming stage involves shaping the prepared materials into components. Techniques such as stamping, forging, and molding are commonly used. For example, stamping is often employed for producing flat parts, while forging is useful for creating stronger, more durable components through shaping under heat and pressure.
Innovative techniques, such as additive manufacturing (3D printing), are gaining traction, allowing for the creation of complex geometries that traditional methods may not achieve. This flexibility can lead to enhanced designs that improve the efficiency and performance of food processing equipment.
Assembly: How Are Components Joined Together?
During the assembly stage, individual components are brought together to form the complete machinery. This process can involve welding, bolting, or using adhesive methods, depending on the design and material properties. Precision is crucial here, as misalignment can lead to operational inefficiencies or safety hazards.
Manufacturers often use jigs and fixtures to maintain component alignment during assembly. Advanced technologies, such as robotic automation, are also being integrated into assembly lines to enhance speed and accuracy, ensuring consistent quality across batches.
Finishing: What Processes Ensure Quality and Aesthetics?
The finishing stage focuses on enhancing the machinery’s performance and appearance. Processes such as polishing, anodizing, or applying protective coatings are common. These treatments not only improve the aesthetic appeal but also contribute to the machine’s longevity and resistance to corrosion and wear.
Quality assurance is paramount in this stage, as any imperfections can affect functionality. Manufacturers often employ visual inspections and automated systems to ensure that finishing meets predefined standards.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Food Processing Machinery Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to food processing machinery manufacturing, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer expectations. Key aspects include:
What International and Industry-Specific Standards Should Buyers Know?
To ensure compliance and safety, food processing machinery manufacturers adhere to various international standards, such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems, which emphasizes continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. Additionally, industry-specific standards like CE marking for products sold in Europe and API standards for certain processing equipment are crucial for international trade.
Understanding these standards helps B2B buyers in verifying the credibility of suppliers. Compliance with these certifications often reflects a manufacturer’s commitment to quality and safety.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) involves systematic processes at different checkpoints throughout manufacturing:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards. Any non-compliance can lead to material rejection, preventing downstream issues.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, various inspections are conducted to monitor quality. This may include dimensional checks, functionality tests, and visual inspections. IPQC helps identify defects early, reducing waste and rework.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): At this stage, the completed machinery undergoes rigorous testing to ensure it meets all operational specifications and safety standards. This may include performance testing, stress tests, and hygiene assessments, particularly important for food processing equipment.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Quality Assurance?
Various testing methods are employed during the QC process to ensure machinery reliability:
-
Functional Testing: This assesses whether the machinery operates as intended under normal operating conditions. It verifies that all components function correctly.
-
Stress Testing: Machines are subjected to extreme conditions to evaluate their durability and performance under stress. This helps ensure that the equipment can handle real-world scenarios.
-
Hygiene Testing: Given the nature of food processing, hygiene is critical. Manufacturers often conduct microbiological tests to ensure that equipment is free from contaminants, ensuring food safety.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s QC processes is essential. Here are some actionable steps:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of potential suppliers can reveal their adherence to quality standards. Buyers should request access to audit reports and certifications to assess compliance with international standards.
-
Request Documentation: Manufacturers should provide documentation detailing their QC processes, including inspection reports and testing results. This transparency can help buyers make informed decisions.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control practices. These inspectors can conduct on-site evaluations and testing, ensuring that manufacturers meet the required standards.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers must be aware of the nuances in QC and certification processes across different regions. For instance, standards and regulations may vary significantly between Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding these differences is crucial for compliance and ensuring that equipment meets local regulations.
Furthermore, buyers should consider the logistical aspects of sourcing machinery from different regions, including potential delays in certification processes and the implications for maintenance and support. Collaborating with suppliers who have a deep understanding of these regional differences can streamline the procurement process and enhance overall satisfaction.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices in food processing machinery is vital for B2B buyers. By focusing on these aspects, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and ensure compliance with international standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘Food Processing Machinery Manufacturers’
This guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in efficiently sourcing food processing machinery. By following these steps, you can ensure that your procurement process is streamlined, effective, and aligned with your operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by clearly outlining your requirements for the machinery you need. This includes understanding the types of products you will process, the required production capacity, and specific features like automation levels or compliance with safety standards. A well-defined specification will guide your search and help you communicate effectively with potential suppliers.
Step 2: Conduct Market Research
Investigate the market to identify leading manufacturers and their offerings. Look for industry reports, trade publications, and online resources that detail the latest technologies and trends in food processing machinery. This research will provide insights into available solutions and help you compare capabilities across different suppliers.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, thoroughly vet potential suppliers. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions. Pay special attention to their track record in reliability and customer satisfaction, as well as their ability to provide ongoing support and maintenance.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that the suppliers you consider hold relevant certifications that demonstrate their compliance with industry standards. Certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management or specific food safety certifications (e.g., NSF, HACCP) are crucial. These credentials not only ensure quality but also indicate a commitment to maintaining high standards in food safety.
Step 5: Request and Analyze Quotations
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request detailed quotations that include pricing, delivery timelines, warranty conditions, and terms of service. Analyze these quotes carefully to understand the total cost of ownership, including installation, maintenance, and potential downtime. This analysis will help you make a financially sound decision.
Step 6: Conduct Site Visits or Virtual Tours
If possible, conduct site visits to the manufacturing facilities of your shortlisted suppliers. This will provide you with firsthand insight into their production processes, quality control measures, and overall operational standards. If a physical visit is not feasible, request virtual tours or video demonstrations to assess their capabilities.
Step 7: Finalize the Contract with Clear Terms
After selecting a supplier, finalize the contract with clear terms regarding delivery schedules, payment plans, and service agreements. Ensure that all aspects of the deal are documented to prevent misunderstandings. Consider including performance metrics or service level agreements (SLAs) to hold the supplier accountable for their commitments.
By following this step-by-step checklist, you can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing food processing machinery, ensuring that you make informed decisions that meet your operational needs and enhance your production capabilities.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for Food Processing Machinery Manufacturers Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Food Processing Machinery?
When sourcing food processing machinery, understanding the cost structure is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components typically include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall cost. High-quality, durable materials may incur a higher upfront cost but can lead to lower maintenance and replacement expenses over time.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass both direct and indirect labor associated with manufacturing. Skilled labor for assembly, programming, and testing can increase costs, especially if the machinery requires specialized knowledge.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs such as utilities, rent, and administrative expenses related to the production facility. Effective management of overhead can help reduce the final cost of machinery.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling can be necessary for specialized machinery. While this adds to initial costs, it can enhance production efficiency and product quality.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes are essential in the food processing industry due to safety and compliance standards. The associated costs can be significant but are crucial for ensuring product integrity.
-
Logistics: Costs related to shipping, handling, and storage must be factored in. International shipping can be particularly costly and complex, requiring careful planning to avoid delays and additional charges.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically add a profit margin to their costs. Understanding a supplier’s margin can help in negotiations and finding a competitive price.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Food Processing Machinery Costs?
Several factors influence pricing in food processing machinery, which can vary significantly based on buyer specifications and market conditions:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often lead to discounts due to economies of scale. Buyers should consider their production needs to negotiate favorable terms.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized machinery designed to meet specific processing requirements tends to be more expensive. Buyers should assess the necessity of customization versus off-the-shelf solutions.
-
Materials: The type of materials used can influence both cost and quality. For instance, stainless steel is often preferred for its durability and hygiene but comes at a higher price.
-
Quality Certifications: Machinery that meets international quality standards or certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) might be priced higher due to the assurance of safety and reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, location, and experience of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of reliability may charge premium prices.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms (Incoterms) is crucial for international buyers. These terms define who bears the costs and risks during transportation, impacting the total landed cost.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Costs in Machinery Procurement?
For B2B buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can enhance cost-effectiveness in sourcing:
-
Negotiate: Always negotiate pricing and terms with suppliers. Building a relationship can lead to better deals and potential long-term partnerships.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the long-term costs associated with machinery, including maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime, rather than just the initial purchase price.
-
Research and Benchmark: Conduct market research to benchmark prices and specifications against competitors. This knowledge can empower buyers during negotiations.
-
Evaluate Supplier Stability: Assess the financial health and stability of suppliers. Reliable suppliers are less likely to face disruptions that could affect your production.
-
Understand Local Regulations: Familiarize yourself with import regulations and tariffs that could impact costs when bringing machinery into your country.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for food processing machinery can vary widely based on the factors discussed above. This analysis provides a framework for understanding potential costs, but buyers should seek specific quotes and conduct thorough due diligence to obtain accurate pricing tailored to their needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing Food Processing Machinery Manufacturers With Other Solutions
Introduction: Understanding Alternatives in Food Processing Solutions
In the competitive landscape of food processing, manufacturers often seek optimal solutions that enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and ensure product quality. While food processing machinery manufacturers offer specialized equipment designed for specific tasks, exploring alternative solutions can provide valuable insights. This analysis compares food processing machinery manufacturers with two viable alternatives: automated manual processing systems and outsourcing to third-party processors. Each option presents distinct advantages and considerations that can help B2B buyers make informed decisions.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Food Processing Machinery Manufacturers | Automated Manual Processing Systems | Outsourcing to Third-Party Processors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency with specialized machines | Moderate efficiency, dependent on operator skill | Variable performance, influenced by processor capabilities |
| Cost | Higher initial investment but lower long-term operational costs | Lower initial costs, but higher labor costs | Variable costs based on contract terms and volume |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires significant setup and training | Easier to implement, but needs skilled operators | No setup required, instant processing capabilities |
| Maintenance | Requires regular maintenance and expertise | Lower maintenance, but dependent on manual care | Minimal maintenance; responsibility lies with the processor |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for high-volume production with specific needs | Suitable for small to medium operations needing flexibility | Best for companies wanting to focus on core activities and reduce overhead |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Automated Manual Processing Systems
Automated manual processing systems combine technology with human oversight, allowing for more flexible production lines. These systems can adapt to varying product types and sizes without the need for extensive reconfiguration. However, the reliance on skilled operators can be a double-edged sword. While labor costs may be lower initially, the need for training and potential variability in performance can lead to inconsistent product quality. They are best suited for businesses that require flexibility in production without the capital investment associated with specialized machinery.
Outsourcing to Third-Party Processors
Outsourcing food processing tasks to third-party processors can significantly reduce the operational burden on manufacturers. This approach allows businesses to leverage the expertise and technology of specialized processors without the need for large capital expenditures on machinery. While this can lead to cost savings and a focus on core business activities, the trade-off includes less control over the production process and potential variability in quality and service levels. This solution is ideal for companies looking to scale quickly or those that do not wish to invest in their own processing capabilities.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business Needs
When considering the right food processing solution, B2B buyers must evaluate their specific operational needs, budget constraints, and long-term goals. Food processing machinery manufacturers provide high-performance equipment tailored to specific production needs, making them ideal for high-volume operations. In contrast, automated manual processing systems offer flexibility, while outsourcing provides a cost-effective way to manage production without upfront investment. Ultimately, the choice will depend on factors such as production volume, product variety, and the strategic objectives of the business. By carefully assessing these alternatives, buyers can align their processing solutions with their operational goals, ensuring efficiency and quality in their food production endeavors.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for Food Processing Machinery Manufacturers
What are the Key Technical Properties of Food Processing Machinery?
Understanding the technical specifications of food processing machinery is essential for B2B buyers to ensure they select equipment that meets their operational needs. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
The material grade of machinery components (e.g., stainless steel, aluminum) is crucial for durability, corrosion resistance, and hygiene. In food processing, equipment must withstand harsh cleaning regimes and resist contamination. For example, food-grade stainless steel (like 304 or 316) is commonly used for its resistance to rust and ability to maintain sanitary conditions, ultimately impacting product safety and quality. -
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from a specified dimension in manufacturing. High precision in tolerances is vital, particularly in equipment that involves cutting, mixing, or filling. Tight tolerances ensure consistent product quality and minimize waste, which is critical for maintaining profitability in a competitive market. -
Production Capacity
This specification indicates the maximum output a machine can achieve within a given timeframe. Understanding production capacity helps buyers match equipment to their production demands, ensuring they can meet market needs without over-investing in machinery that exceeds their requirements. -
Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency ratings indicate how much energy machinery consumes during operation. Equipment that operates with lower energy consumption can significantly reduce operational costs over time. Buyers focused on sustainability and cost-effectiveness should prioritize energy-efficient machines to lower their carbon footprint and enhance profitability. -
Maintenance Requirements
Assessing the maintenance needs of food processing machinery is essential for operational longevity and efficiency. Machines with lower maintenance requirements not only save time but also reduce unexpected downtime, allowing for smoother production flows. Features like easy access for cleaning and lubrication can significantly influence operational efficiency. -
Safety Features
Safety is paramount in food processing environments. Equipment should include features like emergency shut-off systems, safety guards, and automatic shut-down capabilities to protect operators and ensure compliance with safety regulations. Buyers should prioritize machinery that meets or exceeds industry safety standards to mitigate risks.
What are Common Trade Terms in the Food Processing Machinery Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation. Here are several common terms you should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In food processing, buying from an OEM often ensures that you receive high-quality, reliable machinery designed specifically for your needs, backed by the manufacturer’s expertise. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for buyers to manage inventory effectively and ensure they are meeting supplier requirements without overcommitting resources. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to request pricing and terms from suppliers. This process is essential for comparing different suppliers’ offerings and securing the best deal for the required machinery. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are standardized terms used in international trade to clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers. Understanding Incoterms helps buyers determine costs related to shipping, insurance, and delivery, thus influencing overall budgeting and logistics planning. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the amount of time from placing an order to receiving the goods. In food processing, understanding lead times is crucial for planning production schedules and ensuring timely delivery of machinery to meet operational needs. -
Turnkey Solutions
This term refers to a complete solution where the supplier provides everything necessary for the machinery to operate. Buyers seeking a streamlined approach to equipment procurement may benefit from turnkey solutions, which can simplify installation and reduce the time to market.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, fostering successful partnerships and optimizing their food processing operations.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Food Processing Machinery Manufacturers Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in Food Processing Machinery?
The food processing machinery sector is experiencing transformative changes driven by several global factors. Rapid urbanization and population growth in regions such as Africa, South America, and the Middle East are increasing the demand for processed foods, compelling manufacturers to invest in advanced machinery that enhances productivity and efficiency. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce is shifting the landscape, leading to a greater emphasis on automated systems that can adapt to fluctuating market demands.
Emerging technologies such as IoT (Internet of Things) and AI (Artificial Intelligence) are reshaping food processing operations. These technologies enable real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, allowing companies to reduce downtime and optimize production processes. Furthermore, there is a growing trend toward customization in machinery to meet specific client needs, enhancing product quality and consistency. International buyers are encouraged to explore suppliers who offer tailored solutions, as this can lead to significant competitive advantages.
The focus on food safety and quality assurance is also paramount. Recent global food safety scares have heightened consumer awareness and regulatory scrutiny, prompting manufacturers to invest in equipment that ensures compliance with stringent safety standards. For international B2B buyers, this means prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to quality and reliability in their machinery offerings.
How Is Sustainability Shaping the Sourcing of Food Processing Machinery?
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of the food processing machinery sector. With increasing awareness of environmental impacts, both manufacturers and buyers are prioritizing sustainable practices. This includes the use of energy-efficient machinery that reduces carbon footprints and operational costs. For instance, equipment designed to minimize waste and utilize renewable resources is gaining traction among forward-thinking companies.
Ethical sourcing is equally critical. Buyers are encouraged to consider suppliers who adhere to ethical labor practices and maintain transparency in their supply chains. This not only fosters trust but also enhances brand reputation in a market that increasingly values corporate social responsibility.
Additionally, certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and NSF for food safety are becoming essential criteria for selecting suppliers. These certifications signal a commitment to sustainability and food safety, providing reassurance to international B2B buyers about the integrity of their sourcing decisions. Investing in ‘green’ machinery not only meets regulatory requirements but also resonates with environmentally conscious consumers, making it a strategic imperative for businesses looking to thrive in today’s market.
What Is the Historical Context of Food Processing Machinery Manufacturing?
The evolution of food processing machinery can be traced back to the industrial revolution, which marked a significant shift from manual to mechanized food production. Early machines were rudimentary, designed primarily for processing staple foods. However, as consumer preferences evolved, so did the technology, leading to the development of specialized equipment that addresses diverse food processing needs.
In the latter half of the 20th century, advancements in automation and electronics revolutionized the industry. Manufacturers began incorporating sophisticated controls and monitoring systems, significantly enhancing production efficiency and product quality. Today, the sector continues to innovate, integrating cutting-edge technologies such as robotics and AI to meet the growing demands of a globalized market. For B2B buyers, understanding this historical context is crucial as it highlights the ongoing evolution and potential future developments in food processing machinery, informing strategic sourcing decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of Food Processing Machinery Manufacturers
-
1. How do I choose the right food processing machinery for my business needs?
Selecting the right food processing machinery involves assessing your production requirements, including capacity, product type, and processing methods. Start by evaluating your current production workflow and identifying bottlenecks. Consult with manufacturers to understand the specifications of various machines and how they can be customized to fit your needs. Additionally, consider factors like energy efficiency, maintenance requirements, and compliance with local food safety regulations to ensure you make an informed decision. -
2. What are the key features to look for in food processing machinery?
When sourcing food processing machinery, prioritize features such as durability, ease of maintenance, and adaptability to different food products. Look for machines that offer energy efficiency and low operating costs, as these can significantly impact your ROI. Additionally, ensure the machinery complies with international safety standards and is designed for easy cleaning to mitigate contamination risks. Integration capabilities with existing systems can also enhance efficiency in your production process. -
3. What is the typical lead time for custom food processing machinery?
Lead times for custom food processing machinery can vary widely based on complexity and manufacturer workload. Generally, expect a timeline of 6 to 12 weeks for production and delivery. Factors influencing this timeframe include design specifications, sourcing of materials, and any necessary certifications. It’s crucial to maintain open communication with your supplier during the manufacturing process to manage expectations and avoid delays. -
4. What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for food processing equipment?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for food processing machinery typically depend on the manufacturer and the type of equipment. Some manufacturers may have no MOQ for standard machinery, while custom machines may require higher quantities. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to negotiate MOQs that align with your production goals. This can help you manage costs and ensure you receive the equipment necessary for your operations. -
5. How can I ensure the quality and reliability of the food processing machinery I purchase?
To ensure quality and reliability, vet potential suppliers by checking their certifications, customer reviews, and track record in the industry. Request detailed documentation about the machinery, including material specifications and safety compliance. Additionally, ask for case studies or references from previous clients who have used the same equipment. Engaging in a trial run or demonstration can also provide insights into the machinery’s performance and reliability. -
6. What payment terms are commonly offered by food processing machinery manufacturers?
Payment terms can vary by supplier, but common options include a percentage upfront (typically 30% to 50%) and the balance upon delivery or installation. Some manufacturers may offer financing options or extended payment plans for larger orders. Always clarify payment terms before finalizing a contract and consider negotiating terms that accommodate your cash flow needs, especially for significant investments in equipment. -
7. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing food processing machinery?
When importing food processing machinery, consider shipping costs, customs duties, and local regulations that may affect delivery. Work with suppliers who can provide detailed shipping schedules and documentation to facilitate a smooth customs process. Additionally, factor in the need for installation and training, as these may require additional logistics planning. Collaborating with a reliable freight forwarder can help streamline the logistics process and ensure timely delivery. -
8. How can I customize food processing machinery to fit my specific production requirements?
Customizing food processing machinery involves collaborating closely with the manufacturer to define your specific production needs. Discuss the types of food products you process, desired output rates, and any unique processing techniques you employ. Many manufacturers offer design consultations to tailor machinery features, such as size, speed, and functionality. Always ensure that any customizations adhere to food safety standards and regulations for your region.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for Food Processing Machinery Manufacturers
In the rapidly evolving landscape of food processing machinery, strategic sourcing remains a cornerstone for manufacturers aiming to enhance efficiency and product quality. By investing in advanced, customizable equipment, businesses can adapt to changing market demands while ensuring operational reliability. The integration of innovative technologies not only minimizes lifecycle costs but also bolsters product safety—critical factors in maintaining consumer trust, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
International buyers should prioritize suppliers that offer comprehensive support, from equipment selection to installation and ongoing maintenance. This holistic approach ensures that the machinery not only meets current processing needs but is also scalable for future growth. As food safety standards continue to rise globally, sourcing partners with a strong commitment to quality and innovation will be invaluable.
Looking ahead, the food processing sector is poised for transformation through technological advancements and sustainability initiatives. We encourage international B2B buyers to engage with manufacturers who are at the forefront of these developments. By doing so, you can position your operations for success in a competitive market, ensuring your products meet the highest standards while capturing consumer interest.