Top 8 Overhead Crane Manufacturers,Overhead Crane List and Guide: …
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for overhead crane manufacturers,overhead crane
In the intricate landscape of global manufacturing, sourcing the right overhead crane can significantly influence operational efficiency and safety. For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the challenge lies not only in selecting a reliable overhead crane manufacturer but also in understanding the diverse types, applications, and technologies available. This guide aims to demystify the complexities of the overhead crane market, offering insights into various crane types—from bridge and gantry cranes to hoists and automated systems—alongside their specific applications across industries such as construction, automotive, and manufacturing.
By navigating through the essential criteria for supplier vetting, buyers will be equipped to assess quality, reliability, and service capabilities of potential partners. Furthermore, we will delve into cost considerations, financing options, and maintenance requirements, ensuring that decision-makers are fully informed and confident in their purchasing choices. This comprehensive resource empowers B2B buyers to make strategic investments that not only enhance productivity but also ensure compliance with safety standards and operational requirements. With a focus on actionable insights and expert recommendations, this guide serves as a vital tool for businesses looking to optimize their material handling processes and drive growth in a competitive global market.
Top 10 Overhead Crane Manufacturers,Overhead Crane Manufacturers & Suppliers List
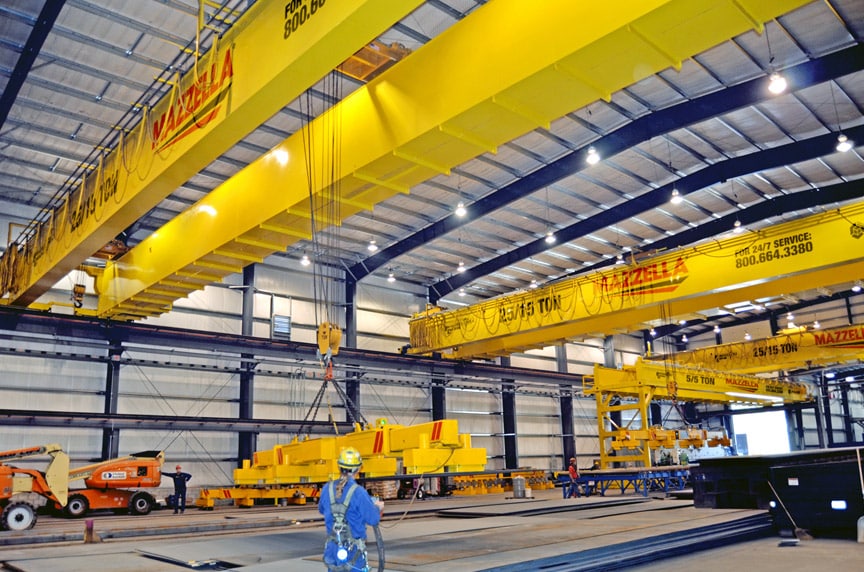
1. American Equipment – Overhead Bridge Cranes
Domain: amquipinc.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: American Equipment offers a range of overhead bridge cranes designed for heavy lifting and material handling. Key features include:
– Types of Cranes: Patented Track Cranes, Top-Running Double Girder, Top-Running Trolley, Top-Running Single Girder, Under-Running Single Girder, and Under-Running Trolley.
– Capacities: Ranging from 3 to 300 tons depending on the crane type.
– Span: Up to 200 feet…
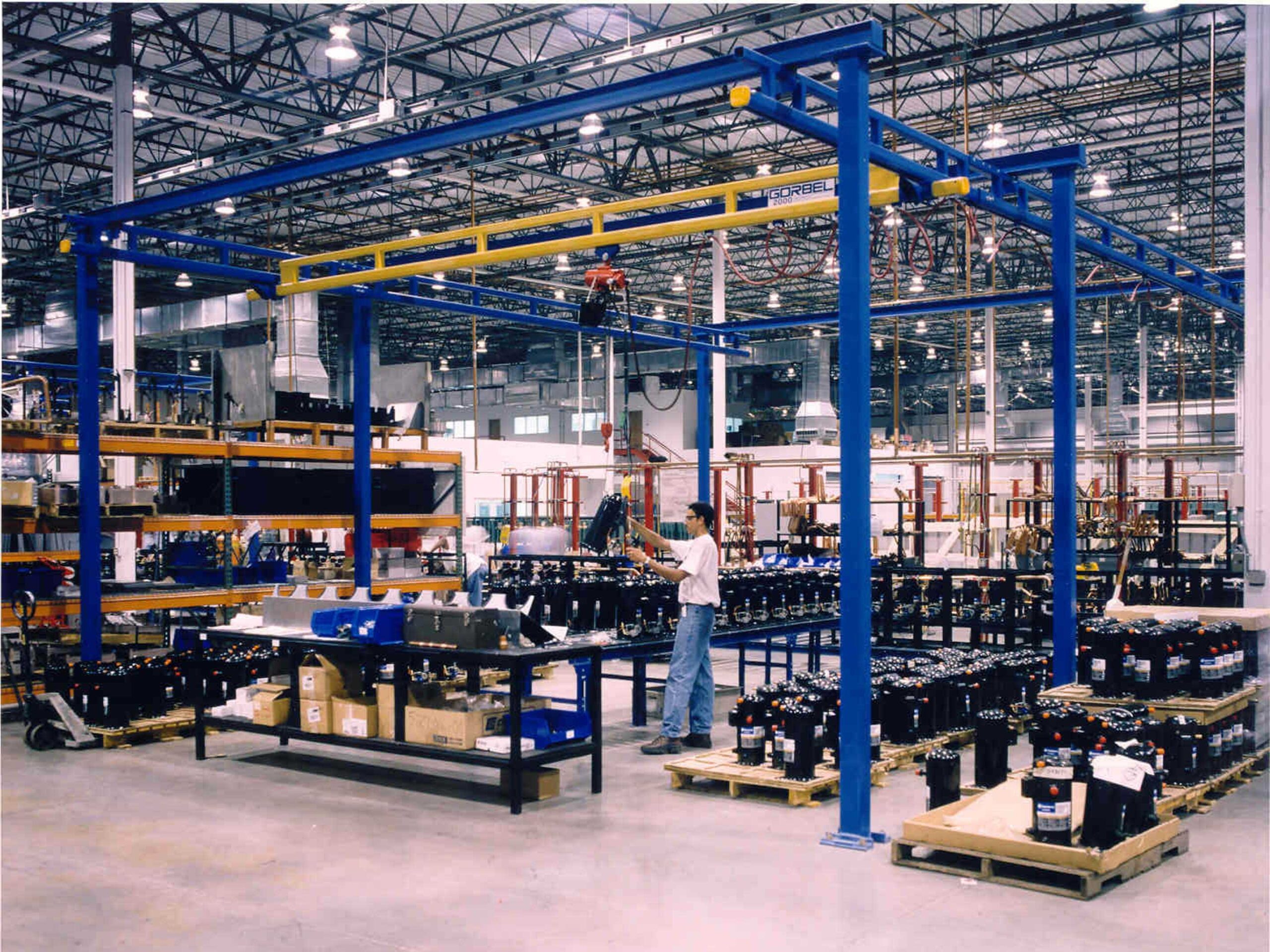
2. Mazzella Companies – Overhead Bridge Cranes & Gantry Cranes
Domain: mazzellacompanies.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: The text provides an overview of various manufacturers of overhead bridge cranes and gantry cranes, detailing their founding years, U.S. headquarters locations, insights into their operations, and the industries they serve. Key manufacturers mentioned include: 1. Demag Cranes & Components Corp. – Founded in 1965, headquartered in Solon, Ohio, specializes in crane technology and serves industries l…
3. Wazee Crane – Overhead Bridge Cranes
Domain: wazeecrane.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Wazee Crane specializes in the manufacture and supply of overhead bridge cranes and hoists. They have a complete manufacturing facility in Broomfield, Colorado, capable of fabricating cranes of various complexities, including welded plate box girders with spans exceeding 100 feet. Wazee Crane designs and builds cranes in compliance with CMAA, NEC, OSHA, MSHA, and ASME standards. They offer a range…
4. Konecranes – Reliable Overhead Cranes
Domain: konecranes.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Reliable Overhead Cranes for Safe, Efficient Lifting. Types of cranes include: C-series electric chain hoist cranes, rope hoist cranes, gantry cranes, portable cranes, wall-mounted console cranes, built-up cranes, and custom cranes. Features include smart features for overhead cranes, remote operating stations, and crane advisor tools. Specialized cranes for hazardous environments include EX elect…
5. Demag – Overhead Crane Sets
Domain: demagcranes.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Demag offers a range of crane sets for overhead cranes, including single- and double-girder overhead traveling cranes and suspension cranes. The crane sets are designed for optimal performance and cost-effectiveness, featuring mechanical, electrical, and structural elements necessary for safe and efficient operation. Key benefits include safety features like limit switches and overload protection,…
6. TS Overhead Crane – Overhead Cranes & Hoists
Domain: tsoverheadcrane.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Overhead Cranes: Overhead Bridge Cranes, Overhead Crane Kits, Patented Track Cranes; Hoists: Electric Chain Hoists, Wire Rope Hoists, Manual Chain Hoists, Air Chain Hoists; Jib Cranes: Foundationless Jib Cranes, Light Duty Jib Cranes, I-Beam Jib Cranes, Wall or Column Mounted Jib Cranes, Work Station Jib Cranes, Articulating Jib Cranes, Portable Jib Cranes; Gantry Cranes: Portable Aluminum Gantry …
7. EMH Inc. – Overhead Cranes & Components
Domain: emhcranes.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: EMH Inc. is a one-source manufacturer of overhead cranes and components, offering a complete line of overhead material handling equipment designed for loads ranging from 35 lbs. to 300 tons. Key products include: Overhead Bridge Cranes, Gantry Cranes, AL SYSTEMS™ Aluminum Workstation Cranes, NOMAD® Free Standing Bridge Cranes, Standard Wire Rope Hoists, Engineered Hoists, End Trucks (Top Running S…
8. Konecranes – Industrial Cranes
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Konecranes, EMH, Whiting, Virginia Crane, Demag, Mazzella, OMI Cranes, DeShazo, Coffing, Harrington, Zenar, Morgan Engineering, Ace Cranes, Simmers, ABUS Kransysteme, P&H, R&M, Shepard Niles, Franco, Landel, Verlinde, SWF, Donati, Stahl, CMCO, Proserv, Kranbau Köthen, Omis S.p.a.
Understanding overhead crane manufacturers,overhead crane Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Overhead Bridge Cranes | High load capacity, spans long distances, can be top or under-running | Manufacturing, Warehousing, Construction | Pros: Versatile, efficient space utilization. Cons: High initial cost, requires overhead space. |
| Gantry Cranes | Supported by legs, movable, often more affordable than bridge cranes | Shipping yards, outdoor construction sites | Pros: Cost-effective, flexible placement. Cons: Limited load capacity compared to bridge cranes. |
| Jib Cranes | Rotating arm, ideal for localized lifting, compact design | Workshops, assembly lines | Pros: Space-saving, easy to operate. Cons: Limited lifting range, lower capacity. |
| Workstation Cranes | Designed for manual lifting tasks, often operated by hand | Assembly lines, maintenance areas | Pros: Ergonomic design, promotes worker safety. Cons: Slower than automated systems, limited capacity. |
| Patented Track Cranes | Unique track design for smoother operation, customizable | Heavy-duty applications, factories | Pros: Efficient movement, can handle heavier loads. Cons: More complex installation, higher maintenance. |
What Are the Characteristics of Overhead Bridge Cranes?
Overhead bridge cranes are robust systems designed for heavy lifting across large spans, making them ideal for manufacturing and warehousing environments. They can be configured as either top-running or under-running systems, with the former offering greater hook height. Buyers should consider the initial investment and the need for adequate overhead space, as well as the crane’s load capacity and span requirements tailored to their specific operational needs.
How Do Gantry Cranes Differ from Other Types?
Gantry cranes are distinguished by their ability to operate independently of building structures, supported by legs. This makes them particularly useful in outdoor applications, such as shipping yards and construction sites. While they are generally more affordable than overhead bridge cranes, buyers must assess their lifting capacity and the potential for mobility, as gantry cranes often need a flat surface for optimal operation.
What Makes Jib Cranes Suitable for Specific Applications?
Jib cranes are compact and offer a rotating arm that allows for localized lifting, making them perfect for workshops and assembly lines. Their design saves floor space while facilitating easy operation. However, businesses should be aware of their limited lifting range and capacity, which may not meet the needs of larger-scale operations.
Why Choose Workstation Cranes for Manual Lifting Tasks?
Workstation cranes are specifically designed for manual lifting tasks, often operated by hand. They enhance ergonomics and worker safety in assembly lines and maintenance areas. While they promote efficiency and safety, buyers must consider the trade-off in speed and lifting capacity compared to automated systems, which may be necessary for high-volume operations.
What Are the Benefits of Patented Track Cranes?
Patented track cranes feature a unique track design that allows for smoother operation and greater customization. These cranes are particularly suited for heavy-duty applications in factories where efficiency is critical. However, potential buyers should factor in the complexity of installation and the higher maintenance requirements associated with these systems, which can affect long-term operational costs.
Key Industrial Applications of overhead crane manufacturers,overhead crane
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of overhead crane manufacturers,overhead crane | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Heavy lifting for assembly lines | Increases efficiency and reduces labor costs | Ensure compatibility with existing systems; consider load capacity needs |
| Construction | Moving construction materials on-site | Enhances productivity and safety on job sites | Evaluate terrain and space constraints; check for mobile options |
| Mining | Transporting heavy equipment and materials | Improves operational efficiency and reduces downtime | Assess harsh environmental conditions; ensure compliance with safety standards |
| Energy & Utilities | Handling heavy components for power plants | Streamlines maintenance and installation processes | Look for cranes with specialized features for energy sector requirements |
| Aerospace & Defense | Lifting and transporting aircraft components | Ensures precision and safety in handling sensitive materials | Source manufacturers with experience in aerospace standards and certifications |
How Do Overhead Cranes Benefit the Manufacturing Sector?
In manufacturing, overhead cranes are integral for lifting heavy components during assembly processes. These cranes facilitate the movement of materials along assembly lines, significantly enhancing operational efficiency and reducing labor costs. Buyers should consider the load capacities and compatibility with existing systems to ensure seamless integration. Additionally, manufacturers must be aware of the specific safety and operational standards applicable in their region, particularly in diverse markets like Africa and Europe.
What Role Do Overhead Cranes Play in Construction Applications?
In the construction industry, overhead cranes are essential for moving heavy materials such as steel beams and concrete blocks on job sites. Their ability to operate in tight spaces enhances productivity while promoting safety by minimizing manual lifting. Buyers should evaluate the terrain and spatial constraints of their construction sites and consider mobile options if flexibility is required. Understanding local regulations and construction standards is also crucial for international buyers.
How Are Overhead Cranes Used in Mining Operations?
Mining operations utilize overhead cranes to transport heavy equipment and materials, which is vital for maintaining efficiency and minimizing downtime. These cranes can handle significant loads and are designed to operate in harsh environments. Buyers in the mining sector must assess the specific environmental conditions and ensure that the cranes comply with industry safety standards. Selecting manufacturers with experience in mining applications can provide additional peace of mind.
What Benefits Do Overhead Cranes Offer in Energy & Utilities?
In the energy and utilities sector, overhead cranes are crucial for handling heavy components during installation and maintenance of power plants. These cranes streamline processes, ensuring that operations run smoothly and efficiently. Buyers should look for cranes with specialized features that meet the unique requirements of the energy sector, such as explosion-proof designs or high load capacities. Understanding the operational challenges specific to this industry is essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
Why Are Overhead Cranes Important in Aerospace & Defense?
In the aerospace and defense industries, overhead cranes are used for lifting and transporting sensitive components, ensuring precision and safety during handling. The unique requirements of this sector necessitate sourcing cranes from manufacturers with proven expertise in aerospace standards and certifications. Buyers must prioritize manufacturers that can provide tailored solutions while adhering to strict safety regulations, especially in international markets where compliance can vary significantly.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘overhead crane manufacturers,overhead crane’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Delays in Crane Delivery and Installation
The Problem:
One of the significant pain points for B2B buyers in the overhead crane market is the lengthy lead times associated with the delivery and installation of their new equipment. This can result from several factors, including manufacturing delays, supply chain issues, and the complexity of installation in specific facilities. For buyers, these delays can halt production lines, lead to loss of revenue, and compromise project timelines, causing frustration and uncertainty.
The Solution:
To mitigate this issue, buyers should establish clear communication with potential overhead crane manufacturers from the outset. Request detailed timelines for production and installation, and ensure that the manufacturer provides a comprehensive project plan. It’s advisable to seek out manufacturers with a proven track record of timely deliveries and those who maintain robust supply chain management practices. Additionally, consider implementing a phased approach to crane procurement, where smaller, less critical cranes are installed first. This can help maintain some level of operational efficiency while waiting for larger equipment. Lastly, always have a contingency plan in place, including alternative suppliers or rental options, to cover any unexpected delays.
Scenario 2: Inadequate Training for Crane Operators
The Problem:
Another common challenge faced by companies investing in overhead cranes is insufficient training for operators. Many organizations assume that once the crane is installed, their workforce can operate it without specialized training. This misconception can lead to improper usage, increasing the risk of accidents and equipment damage, which can have dire consequences for workplace safety and operational efficiency.
The Solution:
To address this challenge, it is crucial for buyers to prioritize comprehensive training programs as part of their procurement process. Before finalizing any purchase, inquire about the manufacturer’s training offerings. Reputable manufacturers often provide operator training, including hands-on instruction and safety protocols. Furthermore, consider implementing an ongoing training program that includes refresher courses and updates on new equipment features. Engaging with third-party training organizations can also enhance operator knowledge and safety awareness. By investing in proper training, businesses can improve the operational competency of their workforce, reduce the risk of accidents, and maximize the lifespan of their overhead cranes.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Customizing Crane Solutions
The Problem:
Buyers often encounter challenges when trying to customize overhead cranes to fit specific operational needs. Many manufacturers offer standard solutions, which may not align with the unique requirements of every facility. This can lead to inefficiencies, reduced productivity, and increased operational costs if the equipment does not integrate well with existing systems or workflows.
The Solution:
To successfully navigate customization challenges, buyers should engage with manufacturers that specialize in tailored solutions. Start by conducting a thorough assessment of your facility’s needs, including load capacity, workspace dimensions, and specific lifting tasks. Communicate these requirements clearly to potential manufacturers and ask for case studies or references from similar projects they have completed. A collaborative approach can help in co-designing a solution that meets your specific needs. Additionally, consider manufacturers that utilize advanced design software to simulate crane operations within your facility before final production. This proactive strategy not only ensures a better fit but also reduces the likelihood of costly modifications after installation.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for overhead crane manufacturers,overhead crane
What Are the Key Materials Used in Overhead Crane Manufacturing?
When selecting materials for overhead cranes, manufacturers must consider factors such as strength, weight, cost, and environmental conditions. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of overhead cranes, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
Steel: The Backbone of Overhead Cranes
Key Properties: Steel is renowned for its high tensile strength, durability, and ability to withstand high loads. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 500°F (260°C) and can be treated for enhanced corrosion resistance.
Pros & Cons: Steel’s primary advantage is its robustness, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. However, it is susceptible to corrosion unless treated, which can increase maintenance costs. Manufacturing complexity is moderate, as steel can be easily shaped and welded.
Impact on Application: Steel is ideal for environments where heavy lifting is required, such as manufacturing plants and construction sites. It is compatible with various media, including water and chemicals, depending on the treatment.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East must ensure compliance with standards such as EN 1090 for structural steelwork. In Africa and South America, local regulations regarding material sourcing and environmental impact may also apply.
Aluminum: The Lightweight Alternative
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight yet strong, with excellent corrosion resistance. It can withstand temperatures up to 400°F (204°C) and has a low density, making it easier to handle.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of aluminum is its weight, which reduces energy costs during operation. However, it has lower tensile strength compared to steel, making it less suitable for extremely heavy loads. The manufacturing process can be more complex due to the need for specialized welding techniques.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is ideal for applications requiring mobility and ease of installation, such as portable cranes. Its corrosion resistance makes it suitable for environments with high humidity or exposure to chemicals.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of standards like ASTM B221 for aluminum extrusions. In regions like Germany, where stringent regulations exist, ensuring compliance with local standards is crucial.
Composite Materials: The Future of Crane Manufacturing?
Key Properties: Composite materials, such as fiberglass reinforced plastic (FRP), offer excellent strength-to-weight ratios and corrosion resistance. They can withstand temperatures up to 300°F (149°C) and are non-conductive.
Pros & Cons: Composites are lightweight and resistant to corrosion, making them suitable for harsh environments. However, they can be more expensive than traditional materials and may require specialized manufacturing techniques.
Impact on Application: Composites are ideal for applications in corrosive environments, such as chemical plants or marine settings. They are not suitable for extremely heavy loads but excel in applications where weight savings are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should check for compliance with industry-specific standards, such as ASTM D638 for tensile properties of plastics. Understanding local market acceptance of composites is also important, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, where traditional materials are more common.
High-Strength Steel Alloys: Enhanced Performance
Key Properties: High-strength steel alloys are designed to provide superior performance under extreme conditions. They can withstand temperatures exceeding 600°F (315°C) and offer enhanced fatigue resistance.
Pros & Cons: These alloys provide significant advantages in terms of load capacity and durability, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications. However, they can be more expensive and require advanced manufacturing techniques.
Impact on Application: High-strength alloys are suitable for cranes used in heavy industries like mining and construction. They are compatible with various media but may require specific coatings for corrosion resistance.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM A992 for structural steel is essential. Buyers in Europe, particularly Germany, should also consider DIN standards to ensure quality and safety.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Overhead Cranes
| Material | Typical Use Case for overhead crane manufacturers,overhead crane | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy-duty lifting applications | High tensile strength | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Portable and lightweight cranes | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower tensile strength | Medium |
| Composite Materials | Corrosive environments | Excellent strength-to-weight ratio | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| High-Strength Steel Alloys | Heavy industries like mining and construction | Superior load capacity | Higher cost and advanced processing | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides insights for international B2B buyers, enabling them to make informed decisions tailored to their specific operational needs and regulatory environments.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for overhead crane manufacturers,overhead crane
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Overhead Cranes?
The manufacturing process for overhead cranes involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure that the final product meets stringent quality and performance standards.
-
Material Preparation: The process begins with the selection of high-quality raw materials, typically structural steel, which is essential for the strength and durability of the crane. This stage includes cutting, bending, and treating the materials to ensure they meet specific load and safety requirements. Advanced technologies such as laser cutting and CNC machining are often employed to achieve precise dimensions.
-
Forming: Once the materials are prepared, they undergo various forming processes. Techniques such as welding, forging, and machining are utilized to shape components like girders, trolleys, and hoists. This stage is critical as it determines the structural integrity of the crane. Manufacturers may also use robotic welding systems to enhance consistency and reduce human error.
-
Assembly: After forming, the individual components are assembled into the crane structure. This stage requires skilled labor to ensure proper alignment and fit. Assembly may take place in a controlled environment to minimize exposure to contaminants. Manufacturers often employ modular designs, allowing for easier transportation and installation at the client’s site.
-
Finishing: The final stage involves applying protective coatings, such as paint or galvanization, to enhance corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. This process is vital, especially for cranes operating in harsh environments. Additionally, quality checks are conducted to ensure that all components meet the required specifications.
How Do Overhead Crane Manufacturers Ensure Quality Assurance?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in the overhead crane manufacturing process. Manufacturers adhere to international and industry-specific standards to guarantee product reliability and safety.
-
International Standards: Compliance with standards such as ISO 9001 is fundamental. ISO 9001 outlines requirements for a quality management system, ensuring that manufacturers maintain consistent quality in their processes. This certification can reassure B2B buyers that the manufacturer is committed to quality.
-
Industry-Specific Standards: In addition to ISO standards, overhead crane manufacturers often comply with industry-specific certifications such as CE marking, which indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area. Other relevant standards may include API (American Petroleum Institute) for cranes used in the oil and gas sector.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Overhead Crane Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are strategically integrated throughout the manufacturing process to identify and rectify defects before they reach the final product stage.
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials upon delivery to ensure they meet specified standards. This step is crucial in preventing defects that could compromise the crane’s integrity.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, periodic inspections are conducted at various stages, such as after forming and assembly. This ongoing QC ensures that any issues are detected early, allowing for immediate corrections.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once assembly is complete, the crane undergoes a comprehensive inspection and testing phase. This includes load testing, functional testing, and safety checks to verify that the crane operates as intended and meets all performance criteria.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Overhead Cranes?
Testing methods are essential for validating the performance and safety of overhead cranes. Common practices include:
-
Load Testing: This involves applying a load that exceeds the crane’s rated capacity to ensure it can handle stress without failure. Load testing is typically conducted in a controlled environment, often with the presence of third-party inspectors to guarantee impartiality.
-
Functional Testing: This series of tests assesses the crane’s operational capabilities, including hoisting, lowering, and lateral movements. It ensures that all controls function correctly and that safety features, such as emergency stops, are operational.
-
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing and magnetic particle inspection are used to detect internal defects in materials without causing damage. These methods are crucial for ensuring the structural integrity of critical components.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify the Quality Control Processes of Overhead Crane Manufacturers?
B2B buyers, especially those in international markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of overhead crane manufacturers.
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting audits of the manufacturer’s facilities can provide insights into their quality management systems and production capabilities. Buyers should look for manufacturers with robust QA processes that comply with international standards.
-
Review of Quality Reports: Requesting access to quality control documentation, including inspection reports, testing certifications, and compliance records, can help buyers assess the manufacturer’s commitment to quality.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can add an additional layer of verification. These independent inspectors can assess the quality of both the materials and the final product, providing an unbiased evaluation.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For B2B buyers from diverse regions, understanding the nuances of quality control and certification is essential.
-
Regional Standards Compliance: Buyers should be aware of the specific regulations and standards that apply in their regions. For instance, cranes sold in the EU must comply with CE marking, while products in the U.S. may need to meet OSHA regulations.
-
Import and Export Regulations: Different countries may have varying import/export standards that could affect the certification and compliance of overhead cranes. Buyers must ensure that their selected manufacturers can navigate these regulations effectively.
-
Cultural and Communication Considerations: When dealing with international suppliers, it is vital to establish clear communication channels. Language barriers and cultural differences can impact the understanding of quality standards, making it important to engage with manufacturers that prioritize transparency and clarity in their processes.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in place, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they select reliable overhead crane manufacturers that align with their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘overhead crane manufacturers,overhead crane’
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers in search of overhead crane manufacturers and crane systems. The procurement of overhead cranes is a significant investment that can enhance operational efficiency. Following this step-by-step checklist will help you make informed decisions throughout the sourcing process.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating your search, clearly outline the technical specifications of the overhead crane you need. This includes the required lifting capacity, span, and height, as well as the specific operational environment (e.g., indoor or outdoor use). Knowing your requirements ensures that you focus on manufacturers capable of meeting your unique needs.
- Lifting Capacity: Determine the maximum load the crane must handle.
- Span and Height: Measure the space available for installation to avoid future complications.
Step 2: Research Potential Manufacturers
Compile a list of potential overhead crane manufacturers by conducting thorough research. Look for companies with a strong reputation in the industry, as well as those that cater to your specific geographical region. This step is vital to ensure you are considering suppliers who understand local regulations and market conditions.
- Industry Experience: Focus on manufacturers with a proven track record in your industry.
- Global Presence: Consider companies that have experience in international markets, especially if you are sourcing from Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verify the certifications and compliance of potential suppliers with relevant industry standards. Certifications like ISO 9001 or CE marking indicate that the manufacturer adheres to high-quality management and safety standards. This step is crucial to ensuring the reliability and safety of the equipment.
- Quality Management Systems: Check for ISO certifications that reflect the manufacturer’s commitment to quality.
- Safety Standards Compliance: Ensure the supplier meets local and international safety regulations.
Step 4: Request Detailed Proposals
Once you have narrowed down your list, request detailed proposals from the manufacturers. These proposals should include technical specifications, pricing, delivery timelines, and service offerings. A comprehensive proposal allows you to compare options effectively and understand the total cost of ownership.
- Cost Breakdown: Look for transparency in pricing, including installation and maintenance services.
- Service Offerings: Assess the level of after-sales support and training provided by the manufacturer.
Step 5: Conduct Site Visits and Inspections
If possible, visit the manufacturing facilities or inspect existing installations of the cranes. This step provides insights into the production processes and the quality of the equipment. It also allows you to assess the manufacturer’s commitment to quality control.
- Production Facilities: Observe the technology and processes used in manufacturing.
- Installed Systems: Speak to current users about their experiences with the cranes.
Step 6: Check Customer References and Case Studies
Request references from past clients and case studies that demonstrate the manufacturer’s capability and reliability. Engaging with other customers can provide valuable insights into the manufacturer’s service quality and the performance of their cranes in real-world applications.
- Industry-Specific References: Seek feedback from companies in your sector for relevant insights.
- Performance Metrics: Inquire about the operational efficiency and uptime of the cranes.
Step 7: Finalize Contractual Agreements
After thorough evaluation and discussions, finalize your agreements with the chosen manufacturer. Ensure that the contract clearly outlines all terms, including warranties, service agreements, and delivery schedules. This step is essential to protect your investment and ensure accountability.
- Warranties and Guarantees: Ensure warranty terms are clear and comprehensive.
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs): Define expectations for maintenance and support services.
By following this structured approach, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the procurement process for overhead cranes, ensuring they select a manufacturer that aligns with their operational needs and business goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for overhead crane manufacturers,overhead crane Sourcing
What are the Key Cost Components for Overhead Crane Manufacturers?
When analyzing the cost structure of overhead crane manufacturing, several critical components come into play:
-
Materials: The primary materials used in overhead cranes include steel, aluminum, and various alloys. The choice of materials significantly impacts cost, especially for cranes designed for heavy-duty applications. Advanced materials that offer higher durability or corrosion resistance typically come at a premium.
-
Labor: Labor costs include wages for skilled workers involved in design, manufacturing, and assembly. The complexity of the crane design directly influences labor intensity and cost. Manufacturers that invest in skilled labor often produce higher-quality products, which can justify a higher price point.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and machinery depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce these overhead costs, ultimately influencing the pricing strategy.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specialized crane designs can add to initial costs. For manufacturers offering standard models, tooling expenses may be lower, but customization often results in higher per-unit costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes are essential in ensuring safety and compliance with industry standards. Implementing these measures incurs additional costs, but they are vital for maintaining product reliability, especially in high-stakes industries like aerospace and construction.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs for delivering cranes to international buyers can be substantial. Factors such as shipping method, distance, and local regulations play a significant role in logistics expenses.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically apply a markup to cover operational costs and profit. The margin can vary based on market demand, competition, and the perceived value of the product.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Overhead Crane Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of overhead cranes, particularly for international buyers:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often attract discounts, making it crucial for buyers to evaluate their needs and potential for bulk purchasing. Understanding MOQ requirements can help in negotiating better terms.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom cranes tailored to specific operational needs typically cost more than standard models. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against budget constraints.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (like ISO standards) can lead to increased costs but may also enhance safety and operational efficiency, contributing to a lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the manufacturer can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a history of quality and service may charge more but offer peace of mind through warranties and support.
-
Incoterms: Understanding international commercial terms is essential for buyers involved in global procurement. Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, impacting the final pricing.
What Buyer Tips Can Help in Negotiating Overhead Crane Prices?
-
Negotiation: Engage multiple suppliers to obtain quotes and leverage competition to negotiate better pricing. Building a relationship with manufacturers can also lead to more favorable terms over time.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Assess the Total Cost of Ownership, which includes initial purchase price, installation, maintenance, and operational costs. A slightly higher upfront cost may lead to lower long-term expenses.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of the fluctuations in currency exchange rates, tariffs, and import duties that can affect the final cost. Engaging local representatives or consultants familiar with the regional market can provide valuable insights.
-
Research and Due Diligence: Investigate manufacturer backgrounds, customer reviews, and case studies to ensure that you choose a reputable supplier. Understanding the market landscape can enhance your negotiation strategy.
-
Documentation and Contracts: Ensure that all terms, including warranties and service agreements, are clearly documented in contracts. This protects against unforeseen costs and provides clarity on responsibilities.
Disclaimer
Prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and can vary based on market conditions, regional factors, and specific supplier negotiations. Always consult directly with manufacturers for accurate and up-to-date pricing information.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing overhead crane manufacturers,overhead crane With Other Solutions
When evaluating material handling solutions, businesses often face the challenge of choosing the right equipment to meet their operational needs. Overhead cranes are a popular choice due to their efficiency and versatility; however, there are alternative technologies and methods that can also achieve similar results. This analysis provides a comparative overview of overhead crane systems against two viable alternatives: Forklifts and Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs).
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Overhead Crane Manufacturers, Overhead Crane | Forklifts | Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High lifting capacity; ideal for heavy loads | Versatile but limited by capacity | High efficiency; automated routing |
| Cost | High initial investment; long-term savings | Lower upfront cost; higher operating costs | Moderate investment; ROI through efficiency |
| Ease of Implementation | Complex installation; requires structural support | Easy to deploy; flexible operation | Requires significant planning and integration |
| Maintenance | Regular inspections needed; specialized service | Routine maintenance; easy repairs | Low maintenance; software updates required |
| Best Use Case | Heavy manufacturing, assembly lines | Warehouses, construction sites | Warehousing, repetitive tasks |
Understanding the Alternatives: Forklifts
Forklifts are a widely used alternative for material handling, especially in warehouses and construction sites. They offer flexibility in maneuvering loads in tight spaces and can be operated by a trained operator. The upfront costs for forklifts tend to be lower than those of overhead cranes, making them an attractive option for businesses with limited budgets. However, their lifting capacity is often lower compared to overhead cranes, which may limit their effectiveness in heavy-duty applications. Additionally, they require more floor space and can pose safety risks if not operated properly.
Exploring Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
Automated Guided Vehicles represent a modern approach to material handling, utilizing robotics and software for efficient transport of goods. AGVs can navigate through predefined paths, reducing the need for manual labor and increasing operational efficiency. They are particularly effective in environments where repetitive tasks are common, such as warehousing. The initial investment for AGVs can be moderate, but they often lead to significant cost savings over time due to reduced labor needs and increased productivity. However, implementing AGVs requires careful planning and integration with existing systems, which can complicate deployment.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Business
Selecting the right material handling solution requires a thorough understanding of your operational requirements, budget constraints, and future growth plans. Overhead cranes excel in heavy lifting and are ideal for manufacturing environments, while forklifts offer flexibility for lighter loads and varied applications. AGVs, on the other hand, provide automation and efficiency but require a more significant upfront investment and integration effort. By carefully evaluating these options against your specific needs, you can make an informed decision that enhances productivity and drives operational success.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for overhead crane manufacturers,overhead crane
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Overhead Cranes?
Understanding the technical specifications of overhead cranes is crucial for B2B buyers looking to make informed purchasing decisions. Here are some essential properties that influence performance, safety, and operational efficiency:
1. Load Capacity
Load capacity refers to the maximum weight an overhead crane can safely lift. This is typically expressed in tons and varies widely among different crane types. Buyers must assess their specific lifting needs to ensure the crane can handle the intended loads, which directly impacts operational safety and efficiency.
2. Span Length
Span length is the distance between the crane’s support structures, such as columns or walls. This measurement determines how much area the crane can cover while lifting and moving loads. Selecting the correct span is vital for maximizing workspace efficiency and ensuring the crane fits within the operational layout of a facility.
3. Hoisting Speed
Hoisting speed is the rate at which the crane can raise or lower loads, usually measured in feet per minute (FPM). Higher speeds can improve productivity but may require more robust safety features. Buyers should balance speed with safety considerations, especially in environments with heavy or hazardous materials.
4. Travel Speed
Travel speed indicates how quickly the crane can move horizontally along its runway. Similar to hoisting speed, this metric influences operational efficiency. Understanding travel speed helps businesses optimize workflows and minimize downtime, essential for competitive operations in sectors such as manufacturing and logistics.
5. Duty Cycle
The duty cycle defines how frequently a crane can be used over a specific period without overheating or experiencing wear. It is typically classified from light to heavy duty. Selecting a crane with the appropriate duty cycle ensures that it meets the demands of the intended application while prolonging its lifespan.
6. Control Systems
Control systems can include pendant controls, radio remote controls, or automated systems. The choice of control system affects operator efficiency and safety. Advanced controls can enhance precision and reduce the risk of accidents, making it essential for buyers to consider the training and operational needs of their staff.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Overhead Crane Industry?
Familiarity with industry terminology is vital for effective communication and negotiation with overhead crane manufacturers. Below are key trade terms that every buyer should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of overhead cranes, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify quality standards and warranty coverage, ensuring they receive reliable equipment.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is particularly relevant for buyers looking to purchase multiple cranes or components. Knowing the MOQ helps in budgeting and can influence purchasing decisions, especially for smaller operations.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that solicits price and delivery information from suppliers for specific goods or services. For buyers, submitting an RFQ to multiple manufacturers can facilitate competitive pricing and help identify the best fit for their material handling needs.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers, as they clarify who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and liability during transport, which can significantly impact total cost calculations.
5. Certification Standards
Certification standards refer to the guidelines and regulations that equipment must meet to ensure safety and reliability. Familiarity with these standards can help buyers ensure that their cranes comply with local and international safety regulations, minimizing risk and liability.
6. Lead Time
Lead time is the period between placing an order and receiving the product. Understanding lead times is essential for project planning and inventory management, especially in industries where timing is critical for operational efficiency.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the complex landscape of overhead crane manufacturing with greater confidence, ensuring they select the right equipment for their operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the overhead crane manufacturers,overhead crane Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in Overhead Crane Manufacturing?
The overhead crane market is experiencing significant growth driven by several global factors. The increasing demand for automation in material handling, particularly in sectors such as manufacturing, construction, and logistics, is propelling the need for advanced crane systems. In regions like Africa and South America, burgeoning industrial sectors are investing in modern infrastructure, while the Middle East sees substantial projects requiring robust lifting solutions. In Europe, particularly Germany, there is a push towards integrating smart technologies and IoT in overhead cranes, enhancing efficiency and safety.
Emerging technologies such as data analytics and machine learning are reshaping sourcing trends in the overhead crane sector. Buyers are increasingly seeking manufacturers that offer integrated solutions with predictive maintenance capabilities, which can minimize downtime and improve operational efficiency. The trend of modular and customizable crane systems is also gaining traction, allowing businesses to tailor solutions to their specific needs and maximize return on investment. Furthermore, as businesses focus on digital transformation, the demand for manufacturers who provide comprehensive digital platforms for crane management is on the rise.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Overhead Crane Industry?
Sustainability is becoming a central pillar in the overhead crane manufacturing sector. Companies are increasingly recognizing the environmental impact of their operations, prompting a shift towards sustainable practices. This includes the use of eco-friendly materials and processes in crane production, as well as the implementation of energy-efficient systems in crane operations. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Europe and the Middle East, sourcing from manufacturers with green certifications, such as ISO 14001, is becoming a critical criterion in the procurement process.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as stakeholders demand transparency in supply chains. Manufacturers that prioritize responsible sourcing and labor practices not only comply with regulatory standards but also enhance their brand reputation. Buyers are encouraged to engage with suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials or reducing emissions in their manufacturing processes. By opting for cranes that are designed for longevity and lower energy consumption, businesses can not only meet regulatory requirements but also contribute to a more sustainable future.
What Is the Historical Context of Overhead Crane Development?
The evolution of overhead crane technology can be traced back to the industrial revolution, where the need for efficient material handling became paramount. Initially, cranes were operated manually, but as industries expanded, so did the complexity and size of lifting equipment. The introduction of electric power in the early 20th century marked a significant turning point, allowing for greater lifting capacities and operational efficiencies.
Over the decades, advancements in engineering and materials science have led to the development of sophisticated overhead crane systems, including automated solutions that enhance safety and productivity. Today, manufacturers are integrating smart technology and IoT into crane systems, allowing for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, which are essential for modern industrial operations. Understanding this evolution helps buyers appreciate the continuous innovation in the sector and the importance of selecting manufacturers that are at the forefront of these advancements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of overhead crane manufacturers,overhead crane
-
How do I select the right overhead crane for my facility?
Selecting the right overhead crane involves evaluating several factors including load capacity, span requirements, and the type of materials you will be handling. Consider whether you need a top-running or under-running crane based on your facility’s ceiling height and layout. Additionally, assess your operational needs—such as frequency of use and lifting speeds. Collaborating with an experienced manufacturer can provide you with tailored recommendations, ensuring the chosen crane aligns with your workflow and productivity goals. -
What are the key features to look for in an overhead crane?
When sourcing an overhead crane, key features to consider include load capacity, span length, and control options (e.g., pendant or radio control). Look for cranes with safety features like overload protection, anti-collision systems, and robust materials that meet your operational requirements. Additionally, consider the availability of automation options and integrated systems for enhanced efficiency. A manufacturer that offers comprehensive support for installation and maintenance can also be a crucial factor in your decision-making process. -
What is the typical lead time for ordering an overhead crane?
Lead times for overhead crane orders can vary significantly based on customization, complexity, and the manufacturer’s production schedule. Generally, standard models may take anywhere from 8 to 12 weeks, while custom-designed cranes can extend this timeline to 16 weeks or more. It is advisable to discuss timelines with the manufacturer upfront and factor in additional time for installation and training, ensuring your project remains on schedule. -
How do I vet potential overhead crane manufacturers?
Vetting overhead crane manufacturers is crucial for ensuring quality and reliability. Start by checking their industry reputation through customer reviews and case studies. Look for manufacturers with extensive experience in your specific industry and a portfolio of successful installations. Verify their certifications and compliance with international safety standards. Additionally, assess their service offerings, including maintenance and support, to ensure you have a reliable partner for the long term. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for overhead cranes?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for overhead cranes can vary by manufacturer and the specifics of your order. Some manufacturers may have a MOQ of one unit, especially for custom designs, while others may require larger orders for standard models to optimize production. It’s essential to discuss your needs directly with potential suppliers to understand their MOQ policies and explore options that fit your budget and operational requirements. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing an overhead crane?
Payment terms for overhead crane purchases can vary widely among manufacturers. Common arrangements include a deposit upon order confirmation, followed by progress payments during manufacturing, with the final balance due upon delivery or installation. Some suppliers may offer financing options, especially for larger orders. Always clarify payment terms upfront and ensure they align with your financial planning to avoid any disruptions during the procurement process. -
How can I ensure quality assurance for my overhead crane?
To ensure quality assurance for your overhead crane, choose a manufacturer that follows stringent quality control processes throughout production. Look for ISO certifications or other relevant industry standards that demonstrate commitment to quality. Inquire about their testing procedures, including load testing and safety inspections, before delivery. Additionally, consider requesting documentation of compliance with international safety regulations to ensure the crane meets your operational safety requirements. -
What are the logistics considerations for shipping overhead cranes internationally?
Shipping overhead cranes internationally involves several logistics considerations, including freight costs, customs regulations, and delivery timelines. Collaborate with your manufacturer to understand packaging and shipping requirements to prevent damage during transit. Ensure all necessary documentation, such as import/export permits and certifications, is in order to avoid customs delays. Additionally, consider engaging a logistics partner with experience in heavy equipment transport to navigate these complexities effectively.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for overhead crane manufacturers,overhead crane
In today’s competitive landscape, strategic sourcing for overhead cranes is not merely a procurement activity; it is a critical investment in operational efficiency and productivity. By carefully selecting manufacturers that align with your specific needs—whether for heavy-duty applications or specialized industrial environments—you can optimize your material handling processes. Key considerations include evaluating the supplier’s industry experience, the technological sophistication of their offerings, and their commitment to service and support.
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should prioritize partnerships with manufacturers who not only provide high-quality products but also offer comprehensive services, including maintenance and training. This holistic approach ensures longevity and reliability of the equipment, ultimately translating to cost savings and enhanced operational capabilities.
As we look ahead, the demand for innovative and adaptable crane solutions will only grow. Now is the time to engage with reputable overhead crane manufacturers and leverage their expertise to propel your business forward. Embrace this opportunity to enhance your operations and secure a competitive edge in your market.