Top 8 Processing Equipment Manufacturers List and Guide: How To S…
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for Processing Equipment Manufacturers
The landscape of processing equipment manufacturing presents a significant challenge for international B2B buyers, particularly when sourcing reliable suppliers for diverse applications. As businesses across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek to enhance their operational efficiency, navigating the global market for processing equipment manufacturers can be daunting. This guide aims to demystify the complexities of sourcing processing equipment, covering a wide array of types, applications, and industries—from food and pharmaceuticals to waste management and mining.
In this comprehensive resource, B2B buyers will gain insights into supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and the latest technological innovations driving the industry. It will highlight the importance of understanding regional market dynamics, regulatory requirements, and sustainability trends that influence purchasing decisions. By equipping buyers with the knowledge to make informed choices, this guide empowers them to identify trustworthy manufacturers who can meet their specific needs and ensure product quality.
Whether you’re a procurement officer in Nigeria or a production manager in Germany, the insights provided here will facilitate strategic purchasing decisions, fostering long-term partnerships with processing equipment manufacturers worldwide. Prepare to streamline your sourcing process and elevate your operational capabilities with the expertise shared in this guide.
Top 10 Processing Equipment Manufacturers Manufacturers & Suppliers List
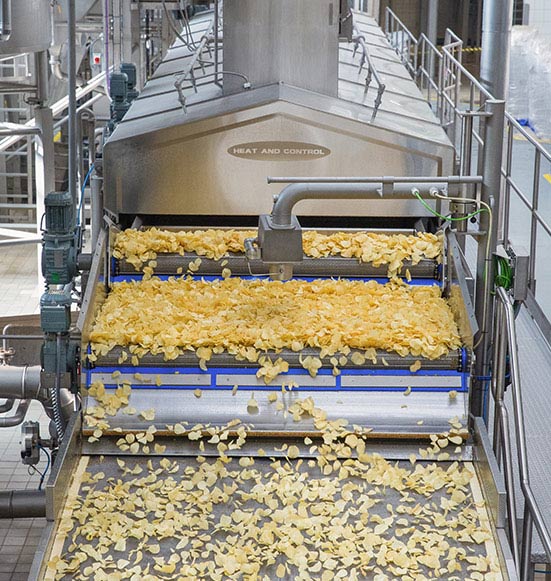
1. Heat and Control – Custom Industrial Food Processing Equipment
Domain: heatandcontrol.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Custom Industrial Food Processing Equipment designed for various applications including Bakery Foods, Candy & Confectionery, Cannabis, Cereal, Cheese, Coffee & Tea, Corn Chips, Extruded & Legume Snacks, French Fries & Potato Co-Products, Fruit Snacks, Meat, Poultry & Seafood, Nuts, Pasta, Pellet Snacks, Pet Food & Treats, Pharmaceutical, Plantain & Banana Chips, Potato & Kettle Chips, Prepared Foo…
2. CM Process Solutions – Industrial Food Processing Equipment
Domain: cmpsol.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: CM Process Solutions specializes in industrial food processing equipment for the food and beverage industry, offering a comprehensive range of products including: Changing Room Equipment, Dump Buggies & Vats, Industrial Washing Systems, Material Handling Equipment, Mixing & Blending solutions, Personal Hygiene Solutions, and Product Sanitizer Tunnels. Key product categories include: 1. Material Ha…
3. Action Stainless – Custom Food Processing Solutions
4. Cedarstone Industry – Food Processing Equipment
Domain: cedarstoneindustry.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Cedarstone Industry offers a wide range of commercial and industrial food processing equipment, including: Mixing Tanks (custom and standard built), Inline High Shear Mixers, High Shear Blenders, CIP Systems, Tube Shell Heat Exchangers, Steam Cookers, Steam Jacket Kettles, Deaerators, Portable Pump Assemblies, Belt Dryers, Bioreactors, Fermenters, Brewing Systems (Nano and Commercial), Alcohol Dis…
5. Kiremko – Potato Processing Lines
Domain: potatopro.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Kiremko Food Processing Equipment: Complete potato processing lines, peelers, blanchers, dryers, fryers. Tummers Food Processing Solutions: Machinery for washing, peeling, drying, cutting, potato processing lines. TOMRA Food: Sensor-based sorting machines, post-harvest solutions. Heat and Control: French Fry Fryer, Potato Chip Fryer, Fastback OMS Batch Fryer. Urschel Laboratories, Inc.: Precision …
6. MPD, Inc. – Food Processing Equipment
Domain: mpd-inc.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Food processing equipment includes: Storeveyor – Surge & Storage Bins, Sanitary Flood Fed Crusher, Sanitary Stainless Lump Breaking Crushers, Cordial Sanitary Crumbler, Sanitary Rigimill® Hammermills, Rugged Rigimill® Hammermills, Rugged Industrial Flood Fed Crushers, Industrial Carbon Steel Crushers, Coating, Enrobing & Tumbling Drums, Heavy-Duty Big Block Crushers, Cement Air Slide & Loadout Cru…
7. IQS Directory – Electric Heaters & Industrial Dryers
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Electric Heaters: Utilities used for heat generation with various configurations including band heaters, strip heaters, cartridge heaters, drum heaters, and tubular heaters. Industrial Dryers: Integrated into final processing stages to remove moisture from bulk materials using air dryers, rotary dryers, or flash dryers. Industrial Mixers: Used to blend multiple bulk or powdered materials, typicall…
8. Westlake Tool & Die – Custom Food-Grade Metal Parts
Domain: westlaketool.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Westlake Tool & Die specializes in custom metal parts for the food processing industry, with over 30 years of experience. They produce high-quality food-grade metal parts, including components for conveyor systems, using materials such as food-grade stainless steel. Their capabilities include metal stamping, robotic welding, and assembly, with a focus on innovation, precision, and cost-effectivene…
Understanding Processing Equipment Manufacturers Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food Processing Equipment | Designed for food safety, hygiene, and efficiency. | Food and beverage manufacturing | Pros: Ensures compliance with safety standards. Cons: Can be costly due to regulatory requirements. |
| Chemical Processing Equipment | Built for handling corrosive materials and precise reactions. | Chemical manufacturing, pharmaceuticals | Pros: High durability and efficiency. Cons: Requires specialized maintenance and training. |
| Packaging Machinery | Automated systems for efficient packing and labeling. | Food, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods | Pros: Increases production speed. Cons: Initial setup can be complex and time-consuming. |
| Waste Treatment Equipment | Systems designed for treating and recycling waste materials. | Environmental management, municipal services | Pros: Supports sustainability initiatives. Cons: May require significant upfront investment. |
| Custom Processing Solutions | Tailored equipment designed to meet specific production needs. | Diverse industries needing unique solutions | Pros: Optimizes production processes. Cons: Longer lead times and potential for higher costs. |
What Are the Characteristics and Suitability of Food Processing Equipment?
Food processing equipment is specifically engineered to meet stringent hygiene and safety standards essential for the food and beverage industry. It includes machinery for mixing, cooking, packaging, and preserving food products. Buyers should consider factors such as compliance with health regulations, the ability to handle various food types, and automation features that enhance operational efficiency. This equipment is ideal for businesses looking to scale production while ensuring product quality and safety.
Why Choose Chemical Processing Equipment for Your Operations?
Chemical processing equipment is characterized by its ability to withstand harsh conditions, including exposure to corrosive substances and extreme temperatures. This equipment is crucial for industries such as pharmaceuticals, petrochemicals, and specialty chemicals. When purchasing, B2B buyers should evaluate the durability, efficiency, and safety features of the equipment. Investing in high-quality chemical processing machinery can lead to increased productivity and reduced downtime, making it a vital consideration for manufacturers.
How Does Packaging Machinery Enhance Production Efficiency?
Packaging machinery plays a critical role in automating the packing and labeling processes for various products, including food, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods. Key features include speed, accuracy, and the ability to handle different packaging formats. Buyers should assess the machinery’s compatibility with their production lines and its capacity to adapt to changing product lines. While packaging machinery can significantly boost production efficiency, buyers should also consider the complexity of installation and training for staff.
What Are the Benefits of Waste Treatment Equipment?
Waste treatment equipment is designed to manage, treat, and recycle waste materials, making it essential for industries focused on sustainability and environmental management. It includes systems for wastewater treatment, solid waste processing, and recycling. When evaluating waste treatment options, B2B buyers should consider the equipment’s efficiency, compliance with environmental regulations, and long-term operational costs. While the initial investment may be high, the long-term benefits include reduced waste disposal costs and enhanced corporate responsibility.
Why Opt for Custom Processing Solutions?
Custom processing solutions provide tailored machinery designed to meet the specific needs of diverse industries, from food production to advanced manufacturing. These solutions are characterized by their flexibility and adaptability to unique production requirements. B2B buyers should focus on the customization options available, the manufacturer’s experience in their industry, and the support offered post-purchase. Although custom solutions can entail longer lead times and higher costs, they often result in optimized production processes and improved product quality, making them a worthwhile investment for many businesses.
Key Industrial Applications of Processing Equipment Manufacturers
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Processing Equipment Manufacturers | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food and Beverage | Automated processing and packaging lines for food products | Enhances efficiency, reduces labor costs, and ensures product safety | Compliance with food safety standards, equipment reliability, and maintenance support |
| Chemical Manufacturing | Custom mixing and blending equipment for chemical formulations | Increases production consistency and product quality | Material compatibility, customization options, and energy efficiency |
| Pharmaceutical | Advanced filling and capping machines for drug production | Ensures precision, minimizes contamination risks, and enhances productivity | Regulatory compliance, scalability, and ease of cleaning/maintenance |
| Wastewater Treatment | Treatment systems for industrial wastewater management | Reduces environmental impact and ensures regulatory compliance | System capacity, technology for specific contaminants, and local regulations |
| Mining and Minerals | Crushing and grinding machinery for ore processing | Improves yield and operational efficiency | Durability in harsh environments, parts availability, and service support |
How is Processing Equipment Used in the Food and Beverage Sector?
Processing equipment manufacturers play a crucial role in the food and beverage industry by providing automated processing and packaging lines. These systems enhance operational efficiency, reduce labor costs, and ensure compliance with food safety regulations. For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, it is essential to consider local compliance with food safety standards, equipment reliability, and the availability of maintenance support when sourcing these solutions.
What Role Does Processing Equipment Play in Chemical Manufacturing?
In the chemical manufacturing sector, processing equipment is vital for custom mixing and blending applications. Manufacturers require equipment that increases production consistency and product quality. International buyers should focus on material compatibility, customization options to fit specific formulations, and energy efficiency to reduce operational costs. Understanding local regulations and environmental considerations is also critical for sourcing decisions.
How is Processing Equipment Essential for Pharmaceutical Production?
In the pharmaceutical industry, precise filling and capping machines are essential for drug production. These machines minimize contamination risks and enhance productivity by ensuring accurate dosages. Buyers from regions such as the Middle East and Europe should prioritize regulatory compliance, scalability for future production needs, and ease of cleaning and maintenance when evaluating suppliers. This ensures that the equipment meets both current and future demands.
What is the Importance of Processing Equipment in Wastewater Treatment?
Processing equipment manufacturers provide critical systems for wastewater treatment, particularly for industries generating significant effluent. These systems help reduce environmental impact and ensure compliance with local regulations. For B2B buyers, sourcing considerations should include system capacity to handle specific wastewater volumes, technology that targets particular contaminants, and adherence to local environmental regulations. This is especially pertinent for companies operating in regions with stringent environmental standards.
How Do Processing Equipment Solutions Benefit the Mining and Minerals Industry?
In the mining and minerals sector, crushing and grinding machinery is essential for ore processing. Processing equipment manufacturers supply machinery that improves yield and enhances operational efficiency. Buyers in regions like Africa, where mining operations are prevalent, should consider the durability of equipment in harsh environments, the availability of parts for maintenance, and the level of service support offered by manufacturers. These factors are critical for minimizing downtime and ensuring consistent production.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘Processing Equipment Manufacturers’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Complex Regulatory Compliance
The Problem: B2B buyers in industries like food processing, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals often face the daunting task of navigating complex regulatory compliance requirements. These regulations can vary significantly between regions, such as in Europe with its stringent EU regulations versus more lenient standards in some African countries. Buyers may struggle to understand which standards apply to their operations, leading to potential fines, production delays, or even product recalls. The risk of investing in processing equipment that does not meet regulatory standards can deter buyers from making necessary purchases or upgrades.
The Solution: To effectively address this pain point, buyers should begin by conducting thorough research on both local and international regulatory requirements applicable to their industry. Engaging with a knowledgeable processing equipment manufacturer who specializes in compliance can provide invaluable insight. Manufacturers often have dedicated compliance teams that can guide buyers through the intricacies of standards such as ISO, FDA, or CE marking. Furthermore, buyers should request documentation that outlines how the equipment meets these regulations before making a purchase. Establishing a partnership with manufacturers that prioritize compliance can not only streamline the procurement process but also provide peace of mind that the equipment will meet required standards.
Scenario 2: Managing Equipment Downtime and Maintenance
The Problem: For many B2B buyers, unexpected equipment downtime is a critical issue that can lead to significant operational losses. This is particularly true in industries where production lines are heavily reliant on processing equipment. Buyers may find themselves dealing with aging machinery that frequently breaks down, causing delays in production and dissatisfaction among customers. Moreover, the costs associated with repairs, lost productivity, and the need for emergency maintenance can quickly escalate, putting pressure on budgets and timelines.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, buyers should adopt a proactive maintenance strategy by partnering with processing equipment manufacturers that offer comprehensive service agreements. These agreements should include regular maintenance checks, predictive analytics to identify potential failures before they occur, and training for in-house staff on basic troubleshooting techniques. Additionally, buyers can invest in modern equipment equipped with IoT (Internet of Things) capabilities that provide real-time data on machine performance and alert operators to potential issues. By prioritizing preventative maintenance and investing in reliable equipment, buyers can significantly reduce downtime, enhance productivity, and ultimately improve their bottom line.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Equipment Scalability and Flexibility
The Problem: As markets evolve, B2B buyers often face the challenge of ensuring their processing equipment can scale and adapt to changing production demands. Many buyers find themselves locked into equipment that cannot accommodate new product lines or increased output without significant modifications or additional investments. This lack of flexibility can hinder a company’s ability to respond to market changes swiftly, potentially causing them to lose competitive advantage.
The Solution: To overcome this hurdle, buyers should prioritize scalability when selecting processing equipment. This involves assessing the modular capabilities of the equipment and ensuring that it can easily adapt to different production requirements. Engaging with manufacturers that offer customizable solutions allows buyers to tailor equipment to their specific needs, providing the necessary flexibility to expand or pivot as required. Furthermore, buyers should consider investing in equipment that integrates advanced technologies, such as automation and smart manufacturing systems. These technologies not only enhance operational efficiency but also allow for easier adjustments in production processes, enabling companies to respond swiftly to market demands. By carefully selecting equipment with scalability in mind, buyers can future-proof their operations and maintain a competitive edge in their industry.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for Processing Equipment Manufacturers
What Are the Key Properties of Stainless Steel for Processing Equipment Manufacturers?
Stainless steel is a widely used material in the processing equipment industry due to its excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and durability. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for various applications, including food processing, pharmaceuticals, and chemical manufacturing. The most common grades used are 304 and 316, with 316 offering superior resistance to chlorides and acids.
Pros of stainless steel include its longevity and low maintenance requirements, which can lead to reduced lifecycle costs. However, cons include higher initial costs compared to other materials and potential manufacturing complexity due to the need for specialized welding techniques. For international buyers, compliance with standards such as ASTM A240 for stainless steel sheets and plates is crucial, especially in regions with stringent food safety regulations.
How Does Carbon Steel Compare as a Material for Processing Equipment?
Carbon steel is another popular choice, particularly for applications where strength and toughness are essential. It offers a good balance of performance and cost, making it suitable for structural components in processing equipment.
Key properties of carbon steel include high tensile strength and the ability to be heat-treated for improved performance. However, it is less resistant to corrosion compared to stainless steel, which can be a significant drawback in harsh environments. The pros of carbon steel include lower material costs and ease of fabrication. The cons are its susceptibility to rust and the need for protective coatings or treatments, which can add to overall costs.
For international buyers, understanding local standards such as DIN 17100 for carbon steel is essential to ensure compliance and suitability for specific applications in their regions.
What Are the Advantages of Using Plastics in Processing Equipment?
Plastics, particularly engineered thermoplastics like polyethylene and polypropylene, are increasingly being used in processing equipment due to their lightweight nature and excellent chemical resistance. These materials are ideal for applications involving corrosive substances, such as in the chemical and food processing industries.
The key properties of plastics include low density, high impact resistance, and the ability to be molded into complex shapes. Pros include lower weight, reduced energy costs during transportation, and corrosion resistance. However, cons include lower temperature and pressure ratings compared to metals, which may limit their use in high-stress applications.
International buyers should consider compliance with standards such as FDA regulations for food contact materials and ISO 9001 for quality management systems, particularly in regions like Europe and North America where regulations are stringent.
How Do Alloys Impact Processing Equipment Performance?
Alloys, such as titanium and nickel-based superalloys, are used in specialized applications where extreme conditions are present, such as high temperatures and corrosive environments. These materials offer exceptional strength-to-weight ratios and resistance to oxidation and corrosion.
Key properties of alloys include high melting points and excellent fatigue resistance. The pros are their ability to perform in extreme environments, making them ideal for aerospace and chemical processing applications. However, the cons include high costs and complex manufacturing processes, which can be a barrier for some manufacturers.
For international buyers, understanding the specific alloy standards such as ASTM B348 for titanium and ASTM B637 for nickel alloys is essential to ensure compliance and performance in their applications.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Processing Equipment Manufacturers
| Material | Typical Use Case for Processing Equipment Manufacturers | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, pharmaceuticals, chemical industries | Excellent corrosion resistance and durability | Higher initial cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Carbon Steel | Structural components in processing equipment | Good strength and lower material costs | Susceptible to rust and requires coatings | Medium |
| Plastics | Chemical processing, food packaging | Lightweight and excellent chemical resistance | Lower temperature/pressure ratings | Low |
| Alloys | Aerospace, high-performance chemical processing | Exceptional strength and oxidation resistance | High costs and complex manufacturing | High |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of material selection considerations for processing equipment manufacturers, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for Processing Equipment Manufacturers
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing for Processing Equipment?
Manufacturing processing equipment involves several key stages that ensure both functionality and reliability. The primary phases include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How is Material Prepared for Processing Equipment Manufacturing?
Material preparation is the initial step where raw materials such as metals, plastics, or composites are sourced and treated. This may involve cutting, shaping, or treating materials to meet specific requirements. For instance, metals often undergo processes such as annealing or hardening to enhance their mechanical properties. The selection of materials is crucial as it directly impacts the durability and efficiency of the equipment.
What Forming Techniques Are Commonly Used in Processing Equipment Manufacturing?
Once the materials are prepared, the next stage is forming. This involves shaping the materials into desired forms using techniques such as machining, welding, casting, or forging. Advanced methods like 3D printing are also gaining traction for creating complex geometries. Each technique has its advantages; for example, casting is beneficial for producing intricate shapes, while machining allows for high precision and tight tolerances.
How Does the Assembly Process Work for Processing Equipment?
After forming, the assembly process begins. This stage is critical as it integrates various components into a functional unit. It may include tasks such as fastening, aligning, and connecting different parts, often requiring skilled labor and specialized tools. Manufacturers may employ lean manufacturing principles during assembly to minimize waste and enhance efficiency. For instance, employing just-in-time (JIT) inventory systems can ensure that components are available when needed, reducing downtime.
What Finishing Processes Are Essential in Manufacturing Processing Equipment?
The final stage is finishing, which enhances the equipment’s appearance and performance. This may involve surface treatments such as painting, coating, or polishing. Finishing processes also serve to protect the equipment from corrosion and wear, which is particularly important in industries like food processing and pharmaceuticals, where hygiene and durability are paramount.
How Do Quality Assurance Standards Impact Processing Equipment Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing process, ensuring that the equipment meets both regulatory and customer standards. International standards like ISO 9001 provide a framework for establishing effective quality management systems. Compliance with these standards not only enhances product quality but also boosts market credibility.
What Are the Key International Quality Standards for Processing Equipment?
In addition to ISO 9001, various industry-specific certifications are crucial for processing equipment manufacturers. For example, CE marking is essential for products sold in the European Economic Area, indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. Similarly, API (American Petroleum Institute) standards are vital for equipment used in the oil and gas industry. Adherence to these standards ensures that manufacturers produce safe and reliable equipment.
What Are the Critical Quality Control Checkpoints in Processing Equipment Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) involves systematic processes to verify that products meet specified requirements. Key checkpoints in QC include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage verifies the quality of raw materials before they enter the manufacturing process.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing stages ensures that any deviations from quality standards are addressed promptly.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before equipment is shipped, it undergoes thorough testing and inspection to confirm compliance with all relevant standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Quality Control in Processing Equipment Suppliers?
B2B buyers play a crucial role in ensuring the reliability of their suppliers. Here are some actionable strategies to verify QC:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes and quality systems in place. This can provide insight into the supplier’s adherence to international standards and their internal quality processes.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide documentation demonstrating compliance with relevant standards and detailing their QC processes. This includes test results, inspection reports, and certifications.
-
Third-party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control practices. This is particularly useful for international buyers who may not have the resources to conduct on-site audits.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, face unique challenges in verifying supplier quality. Understanding local regulations and standards is critical, as these can vary significantly by region.
For example, buyers in Europe must navigate the complexities of CE marking, while those in Africa may need to consider local compliance requirements that differ from international standards. Additionally, language barriers and differences in business practices can complicate communication regarding quality expectations.
Conclusion
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for processing equipment manufacturers are crucial for ensuring product reliability and compliance with international standards. B2B buyers must engage actively in verifying supplier quality through audits, documentation requests, and third-party inspections. By understanding the intricacies of manufacturing and QC, buyers can make informed decisions that will ultimately enhance their operational efficiency and market success.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘Processing Equipment Manufacturers’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in effectively procuring processing equipment from manufacturers. By following this step-by-step checklist, buyers can ensure they select the right suppliers who meet their technical, operational, and budgetary requirements, ultimately leading to successful procurement and enhanced operational efficiency.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by clearly outlining the technical specifications required for your processing equipment. This includes understanding the type of processing needed, capacity requirements, and any specific features such as automation or energy efficiency. A detailed specification helps streamline the sourcing process and ensures that potential suppliers can meet your precise needs.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers in the processing equipment market. Utilize industry directories, trade associations such as PEMA, and platforms like ThomasNet to find reputable manufacturers. Look for suppliers with a strong market presence and positive customer feedback, as these indicators often correlate with reliability and quality.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Before engaging with a supplier, verify their certifications and compliance with relevant industry standards. Important certifications might include ISO 9001 for quality management or specific regulatory approvals related to your industry (e.g., FDA for food processing). Compliance not only ensures product quality but also reduces the risk of legal issues during operations.
Step 4: Request Proposals and Quotes
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request detailed proposals and quotes. This should include pricing, delivery timelines, warranty terms, and service agreements. Comparing multiple proposals will provide insights into market rates and help you identify which supplier offers the best value for your investment.
Step 5: Conduct Site Visits or Virtual Tours
If possible, arrange site visits or virtual tours of the manufacturing facilities of your shortlisted suppliers. This step is crucial for assessing the production capabilities, quality control measures, and overall working conditions. Observing the operation firsthand can provide reassurance about the supplier’s commitment to quality and reliability.
Step 6: Check References and Case Studies
Before finalizing a supplier, request references and case studies from clients within your industry. This will help you gauge their experience and performance in similar projects. Pay close attention to customer feedback regarding the supplier’s responsiveness, support, and equipment reliability to ensure a good fit for your needs.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Finalize the Agreement
Once you have selected a supplier, enter into negotiations to finalize terms of purchase. Discuss payment terms, delivery schedules, and after-sales support. Clear communication during this phase can prevent misunderstandings and set the stage for a positive long-term relationship.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing processing equipment more effectively, ensuring they choose a manufacturer that aligns with their operational goals and quality standards.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for Processing Equipment Manufacturers Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Processing Equipment Manufacturing?
When sourcing processing equipment, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international buyers. The primary components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials significantly affects overall pricing. For instance, high-quality stainless steel or specialized alloys can increase expenses. Buyers should inquire about material certifications to ensure compliance with industry standards.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can impact pricing. In regions with higher labor costs, such as parts of Europe, manufacturers might pass these costs onto buyers. Understanding local labor rates can help buyers assess the fairness of quotes.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Manufacturers with efficient processes may offer lower overhead costs, influencing their pricing strategy.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling can be a significant upfront investment. Buyers should consider whether the tooling costs are included in the quoted price or if they will be billed separately.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure product reliability but can add to costs. Buyers should evaluate the QC measures in place and their impact on pricing.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling can vary greatly, especially for international shipments. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and any tariffs or duties will affect the total cost.
-
Margin: The manufacturer’s profit margin is influenced by competition, market demand, and the value provided through their products and services.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Processing Equipment Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of processing equipment, making it essential for buyers to understand these nuances.
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Purchasing in bulk often leads to discounts. Buyers should assess their needs and negotiate based on volume to secure better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized equipment typically incurs higher costs due to additional engineering and design work. Buyers should clarify their requirements upfront to avoid unexpected costs later.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Equipment made from premium materials or with specific certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) may command higher prices. Buyers should weigh the benefits of these features against their budget.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record and customer service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is vital for international transactions. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can impact overall costs.
What Are the Best Practices for Negotiating Prices in International B2B Equipment Sourcing?
International buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, can leverage several strategies to ensure cost efficiency.
-
Conduct Thorough Research: Before negotiations, gather data on market prices and competitor offerings. This knowledge will empower buyers during discussions.
-
Negotiate Terms: Consider negotiating payment terms, delivery schedules, and warranty conditions in addition to price. Flexible terms can enhance overall value.
-
Assess Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the initial purchase price but the total cost over the equipment’s lifecycle, including maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences and how economic factors may influence costs. For example, currency fluctuations can impact quotes from suppliers in different countries.
-
Request Detailed Quotes: Ask for itemized quotes that break down costs, including materials, labor, and logistics. This transparency allows for more informed comparisons and negotiations.
Conclusion
Navigating the cost and pricing landscape of processing equipment manufacturing requires a keen understanding of the various components that contribute to pricing. By considering the outlined cost structures and price influencers, international buyers can make more informed decisions, ultimately leading to better procurement outcomes. Always remember to seek clarity on costs and negotiate effectively to secure the best value for your investment.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing Processing Equipment Manufacturers With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Solutions for Processing Equipment
When evaluating processing equipment, it’s essential for B2B buyers to consider not only traditional processing equipment manufacturers but also alternative solutions that may offer comparable performance or benefits. These alternatives can provide flexibility, cost savings, or unique advantages depending on the specific needs of your operations. Understanding these options can lead to better decision-making in selecting the most suitable processing solution.
Comparison Table of Processing Equipment Solutions
| Comparison Aspect | Processing Equipment Manufacturers | Automation Software | Modular Processing Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency and reliability | Varies by implementation | Scalable performance |
| Cost | High initial investment | Lower upfront costs | Moderate investment |
| Ease of Implementation | Complex installation process | Quick setup and integration | Moderate complexity |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance required | Minimal maintenance | Flexible maintenance options |
| Best Use Case | Large-scale industrial applications | Small to medium operations | Customizable manufacturing lines |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Automation Software
Automation software serves as an alternative to traditional processing equipment by managing and optimizing production processes through digital means. Its primary advantage is the lower upfront costs compared to purchasing machinery. However, its performance can vary significantly based on how well it integrates with existing systems. While automation software can streamline operations and enhance productivity, it may require ongoing adjustments and training for staff, which can complicate implementation for some organizations. This solution is particularly beneficial for small to medium-sized enterprises looking to improve efficiency without the hefty investment in physical equipment.
Modular Processing Systems
Modular processing systems represent another viable alternative, offering flexibility and scalability in production. These systems can be customized to fit various manufacturing needs, allowing businesses to adapt quickly to changes in demand. While the initial investment may be moderate, the long-term savings can be substantial due to reduced downtime and the ability to expand operations without major overhauls. However, these systems often require a moderate level of complexity in setup and integration with existing processes. Modular systems are ideal for manufacturers looking for a tailored solution that can grow alongside their business.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Processing Solution
For international B2B buyers, selecting the right processing solution involves a careful evaluation of operational needs, budget constraints, and long-term goals. Processing equipment manufacturers provide robust and reliable options for large-scale operations, while automation software and modular processing systems can offer flexibility and cost savings for smaller enterprises or those with dynamic production requirements. By assessing the performance, cost, ease of implementation, and maintenance needs of each alternative, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific operational requirements, ultimately enhancing efficiency and profitability.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for Processing Equipment Manufacturers
What Are the Critical Technical Properties for Processing Equipment Manufacturers?
Understanding the essential technical properties of processing equipment is crucial for international B2B buyers. These specifications not only affect the performance and durability of the equipment but also influence procurement decisions and operational efficiency.
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific classification of the materials used in manufacturing equipment, such as stainless steel, aluminum, or carbon steel. Higher-grade materials typically offer enhanced durability, corrosion resistance, and overall performance. For B2B buyers, selecting the appropriate material grade is vital to ensure that the equipment can withstand the specific conditions of their industry, such as high temperatures or chemical exposure.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance is the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension or measured value. In processing equipment, tight tolerances are often essential for ensuring proper fit and function. For manufacturers, adhering to strict tolerance levels can significantly reduce the risk of malfunction or inefficiency, thus impacting production quality. Buyers should pay close attention to tolerance specifications to ensure compatibility with existing systems.
3. Capacity
Capacity refers to the maximum output or volume that equipment can handle within a given timeframe. This property is crucial for B2B buyers as it directly affects production efficiency and scalability. Understanding capacity ensures that manufacturers can meet demand without overextending resources or compromising quality.
4. Power Requirements
Power requirements specify the energy needed for the equipment to operate effectively. This includes voltage, phase, and frequency specifications. For international buyers, understanding these requirements is essential to ensure compatibility with local power systems and avoid costly modifications or operational delays.
5. Efficiency Ratings
Efficiency ratings indicate how well the equipment converts energy into productive output, often expressed as a percentage. High-efficiency equipment can lead to significant cost savings over time, making it an attractive option for B2B buyers focused on long-term operational costs. Assessing efficiency ratings helps in making informed purchasing decisions that align with sustainability goals.
What Common Trade Terms Should Buyers Know?
Navigating the world of processing equipment can be complex, and familiarity with industry jargon can facilitate smoother transactions and negotiations.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the processing equipment industry, working with OEMs can ensure that buyers receive high-quality, specialized components that are crucial for maintaining operational standards. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is critical for buyers to understand as it can affect inventory costs and cash flow management. Knowing the MOQ helps businesses plan their purchasing strategy and avoid excess stock or under-supply situations.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers to solicit pricing and terms for specific equipment or services. This term is particularly important in B2B transactions, as it allows buyers to compare offers and negotiate terms effectively. A well-prepared RFQ can streamline the procurement process.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping goods. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers, particularly in international transactions, as they clarify aspects such as shipping costs, risks, and delivery responsibilities. Understanding these terms can prevent misunderstandings and disputes during the shipping process.
5. Turnkey Solutions
Turnkey solutions refer to complete systems that are ready for immediate use upon delivery. For buyers, this term signifies a simplified procurement process where the supplier handles all aspects of design, manufacturing, and installation. Choosing turnkey solutions can save time and reduce the complexity of equipment setup.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminology, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and align with their strategic goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Processing Equipment Manufacturers Sector
What Are the Key Trends Shaping the Processing Equipment Manufacturers Market?
The processing equipment manufacturing sector is experiencing significant transformation driven by various global factors. One of the primary drivers is the increasing demand for automation and smart technology, which enhances operational efficiency and reduces labor costs. Advanced manufacturing technologies such as IoT (Internet of Things) and AI (Artificial Intelligence) are being integrated into processing equipment, allowing for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. This trend is particularly relevant for international B2B buyers from regions like Africa and South America, where operational efficiency is crucial for competing in global markets.
Sourcing trends are shifting towards a more collaborative and interconnected supply chain model. Manufacturers are leveraging digital platforms to facilitate better communication and transparency with suppliers and clients, enabling them to respond swiftly to market fluctuations. Additionally, sustainability is becoming a focal point in procurement strategies. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who can demonstrate environmentally friendly practices and compliance with international standards.
Another emerging trend is the localization of supply chains. Many companies are reassessing their sourcing strategies to mitigate risks associated with global disruptions. This shift is particularly relevant for buyers in the Middle East and Europe, where geopolitical factors can influence supply stability. By sourcing closer to home or diversifying supplier bases, companies can enhance their resilience in uncertain times.
How Important Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in the Processing Equipment Manufacturers Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing have become paramount in the processing equipment manufacturing sector, driven by both regulatory requirements and consumer expectations. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is under scrutiny, prompting companies to adopt greener practices. This includes utilizing energy-efficient machinery and reducing waste through innovative recycling techniques. For B2B buyers, partnering with manufacturers that prioritize sustainability can enhance their own brand reputation and align with global sustainability goals.
Moreover, ethical supply chains are critical for maintaining compliance with international regulations. Buyers are increasingly favoring suppliers who can provide transparent sourcing information and demonstrate responsible practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and other green certifications are becoming essential for manufacturers looking to attract international buyers.
The move towards sustainable materials is also gaining momentum. Equipment made from recycled or sustainably sourced materials is not only beneficial for the environment but can also enhance operational efficiency. For B2B buyers, investing in equipment that meets these standards can result in long-term cost savings and improved market positioning.
How Has the Processing Equipment Manufacturing Sector Evolved Over Time?
The processing equipment manufacturing sector has a rich history marked by continuous innovation and adaptation to market needs. Initially, the industry focused on basic mechanical equipment to support various processing industries such as food, chemicals, and pharmaceuticals. Over the decades, technological advancements have led to the development of specialized machinery tailored to specific applications, enhancing productivity and efficiency.
The advent of automation in the late 20th century marked a significant turning point, allowing manufacturers to streamline operations and reduce labor costs. This evolution has continued into the 21st century, with the integration of digital technologies transforming how processing equipment is designed, manufactured, and maintained.
Today, the sector is characterized by a strong emphasis on sustainability, efficiency, and ethical sourcing. This ongoing evolution reflects the industry’s responsiveness to changing market dynamics and the growing importance of corporate responsibility in the global business landscape. For B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions that align with current trends and future developments in the processing equipment market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of Processing Equipment Manufacturers
-
How do I evaluate the reliability of a processing equipment manufacturer?
To assess a processing equipment manufacturer’s reliability, consider their industry experience, customer testimonials, and case studies. Research their compliance with international quality standards (e.g., ISO certifications) and inquire about their history of product performance. Additionally, engage with existing clients to gather insights into their satisfaction levels and the manufacturer’s support and service capabilities. A manufacturer with a solid track record, transparent practices, and positive feedback is often a dependable choice. -
What are the key factors to consider when selecting processing equipment for my industry?
When selecting processing equipment, evaluate factors such as the specific requirements of your production process, equipment capacity, energy efficiency, and adaptability to future needs. Assess the technology used and whether it aligns with your operational goals. Also, consider the manufacturer’s ability to provide customization options, technical support, and training for your staff. A thorough understanding of these elements will help ensure you choose the right equipment for your business. -
What is the typical lead time for processing equipment orders?
Lead times for processing equipment can vary significantly based on the manufacturer’s production capacity, the complexity of the equipment, and customization requirements. Generally, standard equipment may take 4-12 weeks, while custom solutions can extend to several months. It’s crucial to communicate your timelines upfront and establish a clear understanding with the manufacturer regarding expected delivery dates, potential delays, and logistics planning. -
How can I ensure the quality of processing equipment from international suppliers?
To ensure quality from international suppliers, request detailed product specifications, certifications, and compliance documents. Consider visiting the manufacturing facility or using third-party inspection services to verify quality standards. Establish clear quality assurance processes, including pre-shipment inspections and testing protocols. Building a strong relationship with your supplier can also enhance transparency and accountability in quality management. -
What are the common payment terms when sourcing processing equipment internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely among manufacturers but typically include options such as advance payment, payment upon delivery, or a letter of credit. It’s essential to negotiate terms that balance risk and cash flow for both parties. Ensure that you understand any additional costs involved, such as shipping, customs duties, and taxes. Clear communication and documented agreements can help prevent misunderstandings regarding payment expectations. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for processing equipment?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) depend on the manufacturer and the type of equipment. Some manufacturers may offer flexible MOQs for standard products, while custom equipment often comes with higher MOQs due to the specialized nature of production. Discussing your needs with the supplier can lead to more favorable terms, especially if you are willing to establish a long-term partnership or explore bulk purchasing options. -
How do I navigate logistics for importing processing equipment?
Navigating logistics for importing processing equipment involves understanding shipping options, customs regulations, and local import duties. Collaborate with freight forwarders who specialize in industrial equipment to ensure smooth transportation and compliance with local laws. Prepare all necessary documentation, including invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin, to facilitate customs clearance. It’s also wise to plan for potential delays and have contingency strategies in place. -
What should I know about equipment customization options from manufacturers?
Customization options vary significantly among manufacturers, depending on their capabilities and expertise. When discussing your project, be clear about your specific needs, such as size, functionality, and integration with existing systems. Ask about the manufacturer’s design and engineering process and their ability to accommodate modifications. A proactive approach in collaboration can lead to tailored solutions that enhance operational efficiency and meet your unique production requirements.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for Processing Equipment Manufacturers
In the ever-evolving landscape of processing equipment manufacturing, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical driver of efficiency and competitiveness. By leveraging partnerships with reputable manufacturers, buyers can access advanced technologies and innovative solutions that enhance product quality and operational performance. The diverse range of processing equipment available—from food and beverage machinery to complex chemical processing systems—underscores the importance of selecting suppliers that align with specific industry needs and regulatory standards.
As international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it is vital to prioritize relationships with manufacturers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability, technological advancement, and customer support. Engaging with trade associations, such as the Process Equipment Manufacturers’ Association (PEMA), can facilitate valuable connections and insights into best practices and emerging trends.
Looking ahead, the processing equipment sector is poised for growth, driven by increasing demands for efficiency and sustainability. Now is the time to act—evaluate your sourcing strategies, engage with trusted suppliers, and position your business for success in this dynamic market. Empower your operations through informed sourcing decisions and capitalize on the opportunities that lie ahead.